Wastewater Management Efficiency and Determinant Factors in the Chinese Industrial Sector from 2004 to 2014
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Water Problems in China
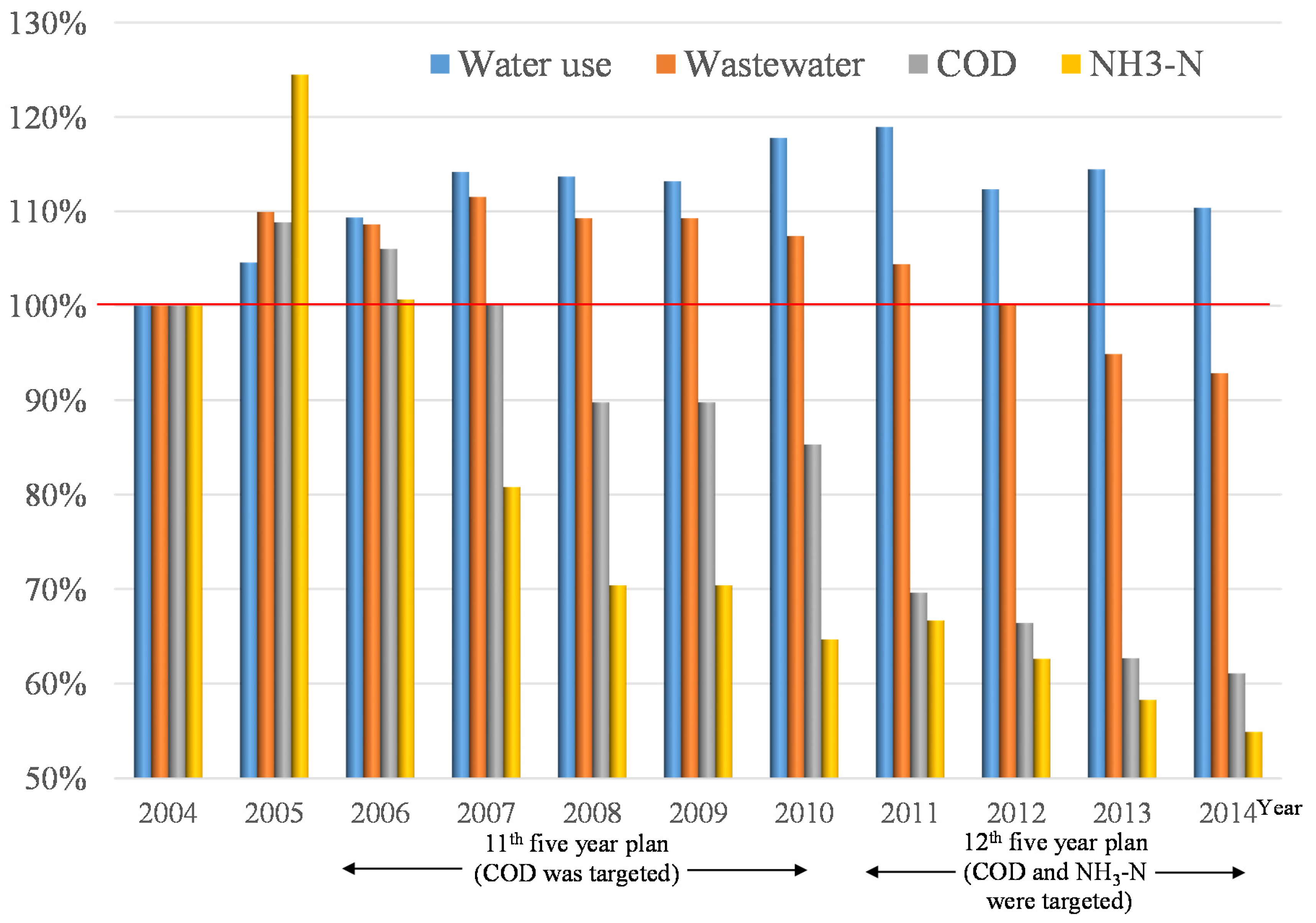
1.2. Industrial Wastewater Management Policies and Trends in China
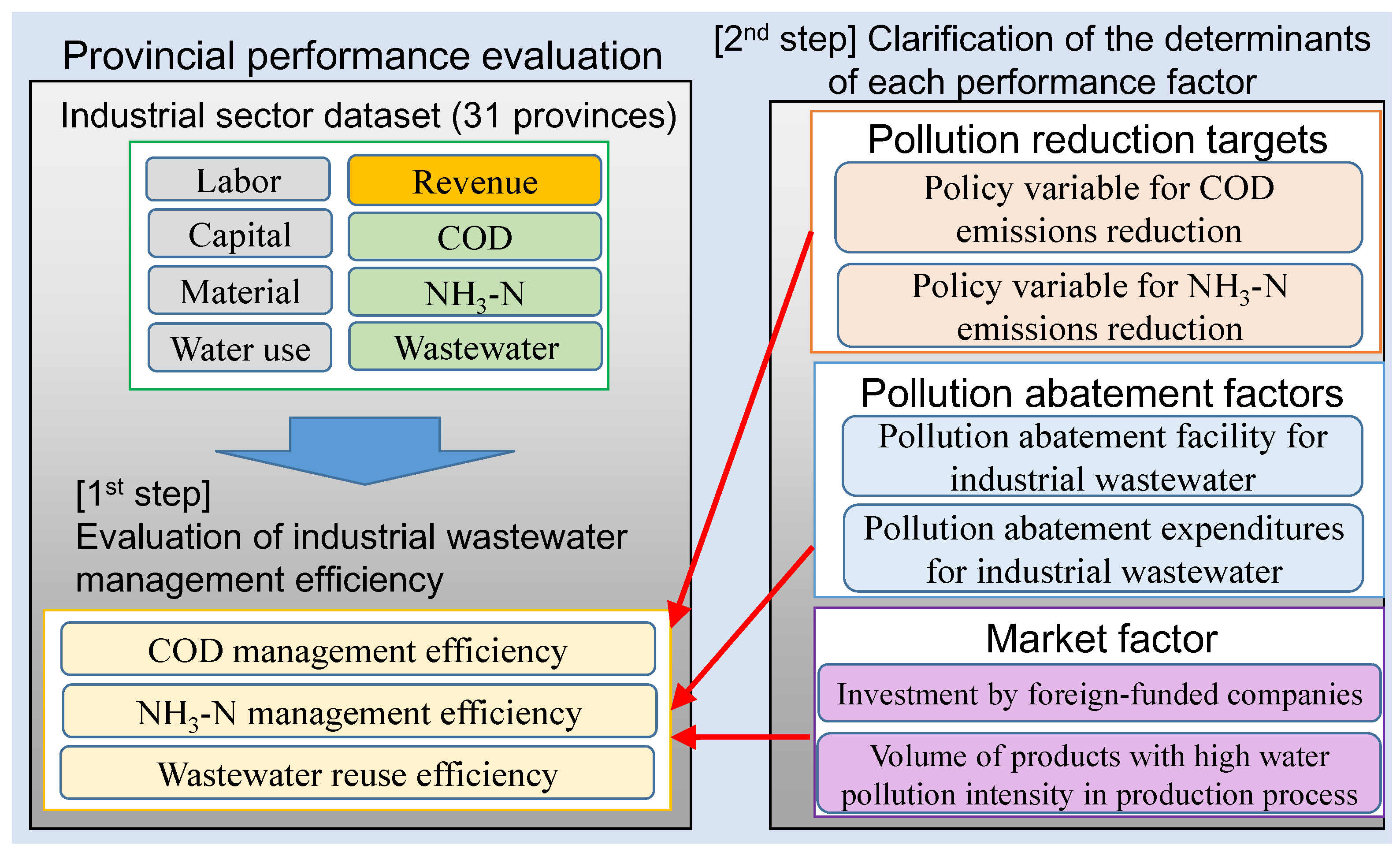
1.3. Objective and Research Framework
2. Methodology
2.1. Weighted Russell Directional Distance Model (WRDDM)
2.2. Determinant Analysis Using a Panel Tobit Regression Model
3. Data and Model
4. Results
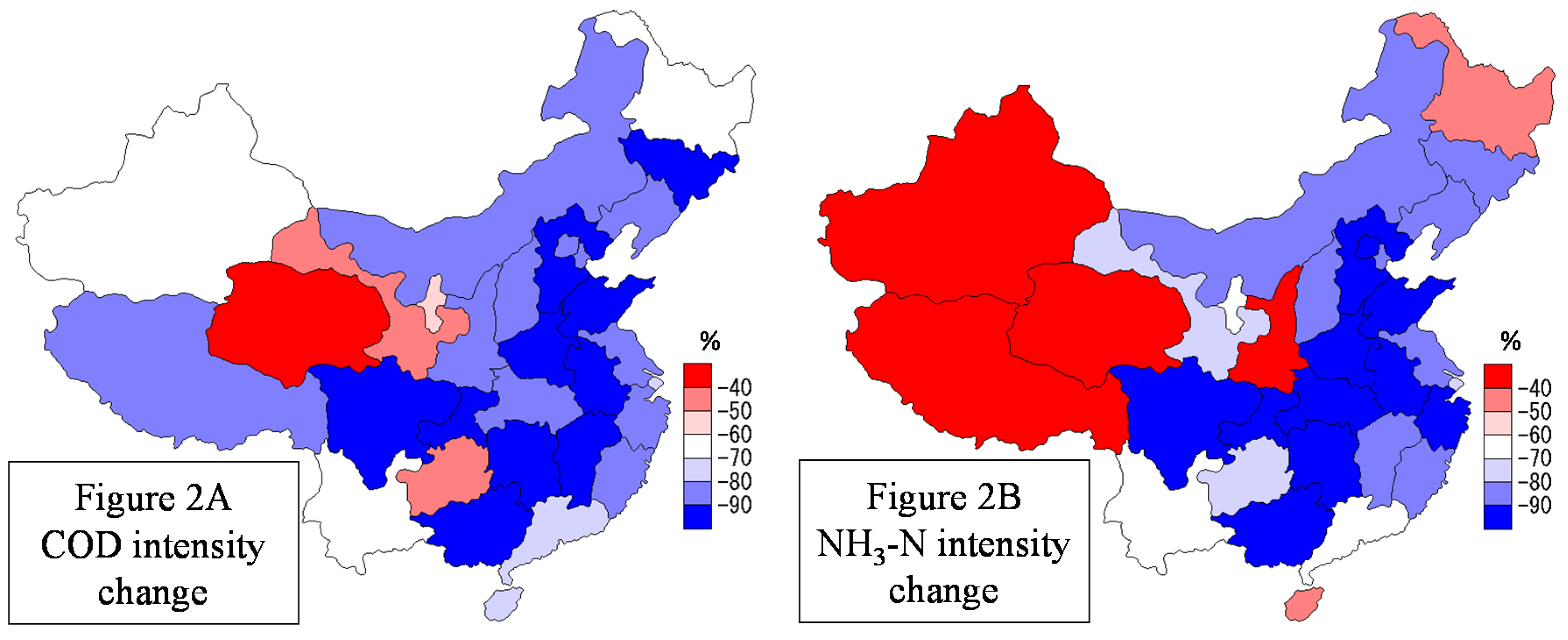
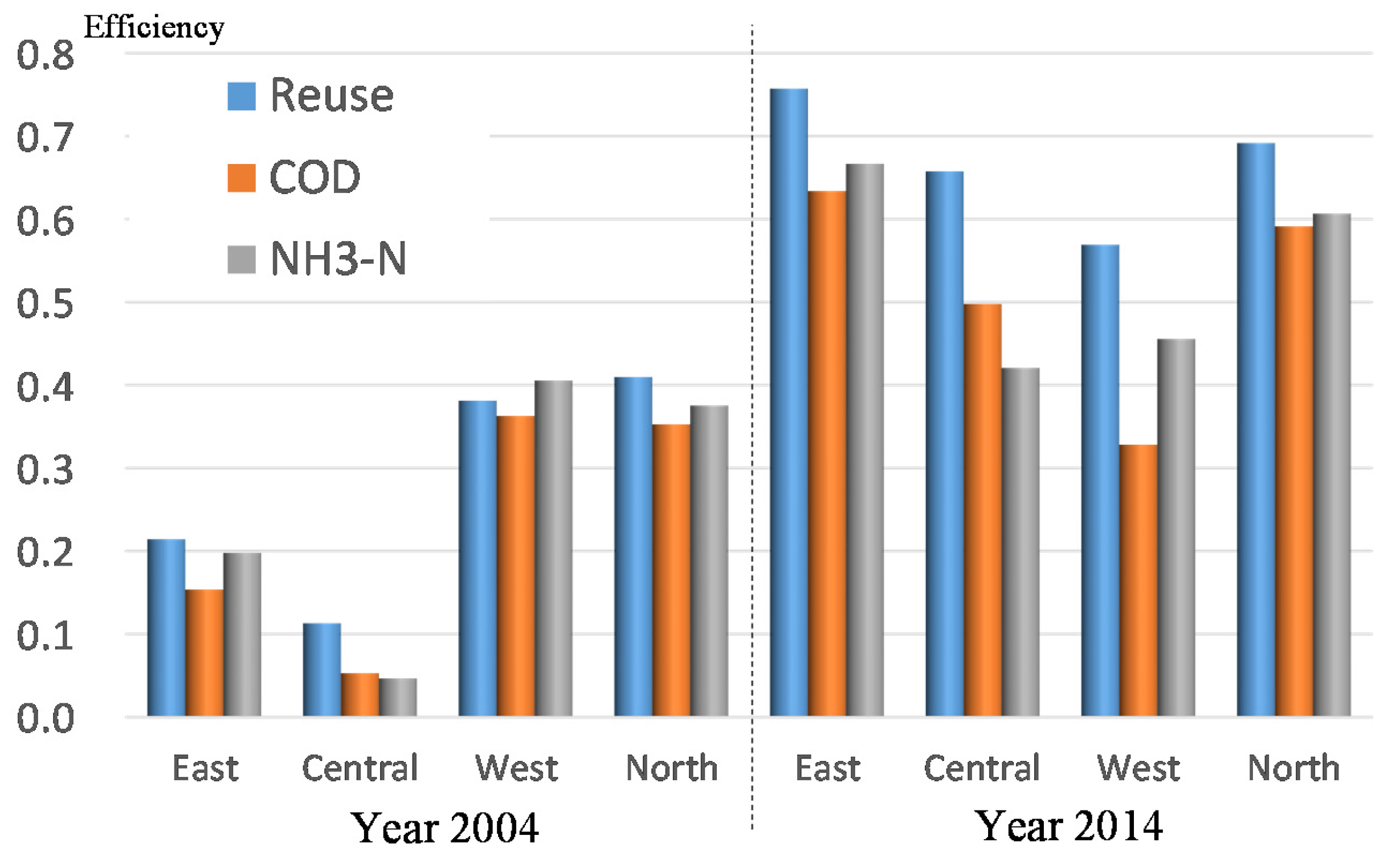
4.1. Efficiency Scores for Industrial Wastewater Management
4.2. Determinants of Industrial Wastewater Management Efficiency
5. Conclusions and Policy Implications
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Policy Implications
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shang, Y.; Wang, J.; Ye, Y.; Lei, X.; Gong, J.; Shi, H. An analysis of the factors that influence industrial water use in Tianjin, China. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2017, 33, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Managi, S.; Kaneko, S. A water resource efficiency analysis of the Chinese industrial sector. Environ. Econ. 2012, 3, 82–92. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Varis, O.; Yin, H. China’s water resources vulnerability: A spatio-temporal analysis during 2003–2013. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 2901–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardian. Four-Fifths of China’s Water from Wells ‘Unsafe Because of Pollution’, 2016. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2016/apr/12/four-fifths-of-chinas-water-from-wells-unsafe-because-of-pollution (accessed on 17 May 2017).
- Wang, Q.; Yang, Z.-M. Industrial water pollution, water environment treatment, and health risks in China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Song, S.; Wang, R.; Liu, Z.; Meng, J.; Sweetman, A.J.; Jenkins, A.; Ferrier, R.C.; Li, H.; Luo, W.; et al. Impacts of soil and water pollution on food safety and health risks in China. Environ. Int. 2015, 77, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, T.; Xin, K. Public health: A sustainable plan for China’s drinking water. Nature 2014, 511, 527–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortajada, C. Policy dimensions of development and financing of water infrastructure: The cases of China and India. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 64, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Araral, E. The effects of migration on collective action in the commons: Evidence from rural China. World Dev. 2016, 88, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W. Effectiveness of water protection policy in China: A case study of Jiaxing. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; Jian, H.; Xie, D.; Gu, Z.; Chen, C. Multi-perspectives’ comparisons and mitigating implications for the COD and NH3-N discharges into the wastewater from the industrial sector of China. Water 2017, 9, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics, China Statistical Yearbook on Environment, Ministry of Environmental Protection. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/ztjc/ztsj/hjtjzl/ (accessed on 18 June 2017). (In Chinese)
- Li, T.; Han, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, P. Urgency, development stage and coordination degree analysis to support differentiation management of water pollution emission control and economic development in the eastern coastal area of China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 71, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Currell, M.J.; Cao, G. Deep challenges for China’s war on water pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 1222–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; He, C.; Liu, Y. Going green or going away: Environmental regulation, economic geography and firms’ strategies in China’s pollution-intensive industries. Geoforum 2014, 55, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ching, L. Institutional legitimacy: An exegesis of normative incentives. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2013, 29, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Managi, S.; Kaneko, S. Wastewater pollution abatement in China: A comparative study of fifteen industrial sectors from 1998 to 2010. J. Environ. Protect. 2013, 4, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, C.P.; Managi, S.; Matousek, R. The technical efficiency of the Japanese banks: Non-radial directional performance measurement with undesirable output. Omega 2012, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.C.; Yu, M.M.; Chang, C.C.; Hsu, S.H.; Managi, S. Non-radial directional performance measurement with undesirable outputs: An application to OECD and non-OECD countries. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Dec. Mak. 2015, 14, 481–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Cao, J.; Managi, S. Decomposition of productivity considering multi-environmental pollutants in Chinese industrial sector. Rev. Dev. Econ. 2015, 19, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics, China Statistical Yearbook, China Statistics Press, Beijing, China. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/english/Statisticaldata/AnnualData/ (accessed on 18 June 2017).
- Managi, S.; Kaneko, S. Environmental performance and returns to pollution abatement in China. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, S.; Fujii, H.; Sawazu, N.; Fujikura, R. Financial allocation strategy for the regional pollution abatement cost of reducing sulfur dioxide emissions in the thermal power sector in China. Energ. Policy 2010, 38, 2131–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Guo, H.; Zhang, B.; Bu, M. Westward movement of new polluting firms in China: Pollution reduction mandates and location choice. J. Comp. Econ. 2017, 45, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, D.; Chen, X.; Cheng, R.; Min, S.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, J. Overview of membrane technology applications for industrial wastewater treatment in China to increase water supply. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2015, 105, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asia Development Bank. Addressing Water Security in the People’s Republic of China: The 13th Five-Year Plan (2016–2020) and Beyond; Asia Publishing Development Bank: Manila, Philippines, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.; Lu, Y.; Wu, M.; Yu, L. Does environmental regulation drive away inbound foreign direct investment? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. J. Dev. Econ. 2016, 123, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Input Variables | Desirable Output Variable | Undesirable Output Variables | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wages of labor | Capital assets | Cost of sales | Industrial water use | Revenue | Industrial wastewater | COD emissions | NH3-N emissions | |
| Year | (million yuan) | (million yuan) | (million yuan) | (10,000 tons) | (million yuan) | (10,000 tons) | (tons) | (tons) |
| 2004 | 218 | 7540 | 5945 | 396,410 | 7133 | 71,336 | 164,419 | 13,607 |
| 2005 | 245 | 9026 | 7671 | 414,581 | 9108 | 78,423 | 178,946 | 16,938 |
| 2006 | 284 | 10,443 | 9441 | 433,471 | 11,203 | 77,482 | 174,326 | 13,697 |
| 2007 | 328 | 12,267 | 11,585 | 452,597 | 13,857 | 79,564 | 164,859 | 10,994 |
| 2008 | 360 | 13,974 | 13,710 | 450,674 | 16,199 | 77,952 | 147,608 | 9578 |
| 2009 | 437 | 17,004 | 15,734 | 448,684 | 18,663 | 77,952 | 147,608 | 9578 |
| 2010 | 486 | 19,125 | 18,879 | 466,877 | 22,508 | 76,604 | 140,247 | 8798 |
| 2011 | 608 | 20,543 | 21,530 | 471,484 | 25,589 | 74,476 | 114,452 | 9071 |
| 2012 | 682 | 23,762 | 24,264 | 445,323 | 28,730 | 71,479 | 109,179 | 8521 |
| 2013 | 984 | 26,882 | 27,667 | 453,710 | 32,441 | 67,690 | 103,054 | 7930 |
| 2014 | 1088 | 30,902 | 30,339 | 437,548 | 35,597 | 66,240 | 100,436 | 7471 |
| Variables (Code) | Units | Mean Value | Std. Dev. | Min. | Max. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COD emissions reduction target (COD target) | Dummy variable | 0.818 | 0.386 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| NH3-N emissions reduction target (NH3-N target) | Dummy variable | 0.364 | 0.481 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| Total investment by foreign-funded companies (Foreign) | Billion US$ | 7.910 | 12.233 | 0.030 | 71.810 |
| Production-scale change of high water pollution intensity products (Polluted) | Year 2004 = 1 | 2.311 | 4.259 | 0.364 | 36.342 |
| Capacity of industrial wastewater treatment facilities (Capacity) | Million tons per day | 7.441 | 7.323 | 0.008 | 63.912 |
| Pollution abatement cost of wastewater treatment (Abatement) | Billion yuan | 1.607 | 1.594 | 0.001 | 9.667 |
| Wastewater Reuse Efficiency | COD Management Efficiency | NH3-N Management Efficiency | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coef. | z-Value | Coef. | z-Value | Coef. | z-Value | ||||
| COD target | 0.114 | 2.6 | *** | ||||||
| NH3-N target | 0.091 | 2.36 | ** | ||||||
| Foreign | 0.019 | 5.13 | *** | 0.016 | 3.81 | *** | 0.012 | 3.01 | *** |
| Polluted | 0.002 | 0.42 | 0.001 | 0.14 | −0.002 | −0.48 | |||
| Capacity | 0.001 | 0.23 | −0.002 | −0.58 | −0.003 | −0.75 | |||
| Abatement | 0.086 | 3.74 | *** | 0.058 | 2.13 | ** | 0.076 | 2.78 | *** |
| West x Foreign | 0.109 | 4.50 | *** | 0.052 | 1.82 | * | 0.059 | 2.03 | ** |
| West x Polluted | −0.025 | −1.08 | −0.033 | −1.24 | −0.046 | −1.73 | * | ||
| West x Capacity | −0.01 | −0.66 | −0.015 | −0.93 | −0.011 | −0.71 | |||
| West x Abatement | −0.024 | −0.46 | 0.003 | 0.05 | 0.058 | 0.97 | |||
| Constant | 0.2 | 2.48 | ** | 0.137 | 1.77 | * | 0.245 | 3.15 | *** |
| Number of observations | 341 | 341 | 341 | ||||||
| chi-square | 143.4 | 82.7 | 92.76 | ||||||
| Prob > chi-square | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||||
| Log likelihood | −75.38 | −123.32 | −117.41 | ||||||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fujii, H.; Managi, S. Wastewater Management Efficiency and Determinant Factors in the Chinese Industrial Sector from 2004 to 2014. Water 2017, 9, 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080586
Fujii H, Managi S. Wastewater Management Efficiency and Determinant Factors in the Chinese Industrial Sector from 2004 to 2014. Water. 2017; 9(8):586. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080586
Chicago/Turabian StyleFujii, Hidemichi, and Shunsuke Managi. 2017. "Wastewater Management Efficiency and Determinant Factors in the Chinese Industrial Sector from 2004 to 2014" Water 9, no. 8: 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080586
APA StyleFujii, H., & Managi, S. (2017). Wastewater Management Efficiency and Determinant Factors in the Chinese Industrial Sector from 2004 to 2014. Water, 9(8), 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080586





