Multi-Criteria Assessment of Land Cover Dynamic Changes in Halgurd Sakran National Park (HSNP), Kurdistan Region of Iraq, Using Remote Sensing and GIS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
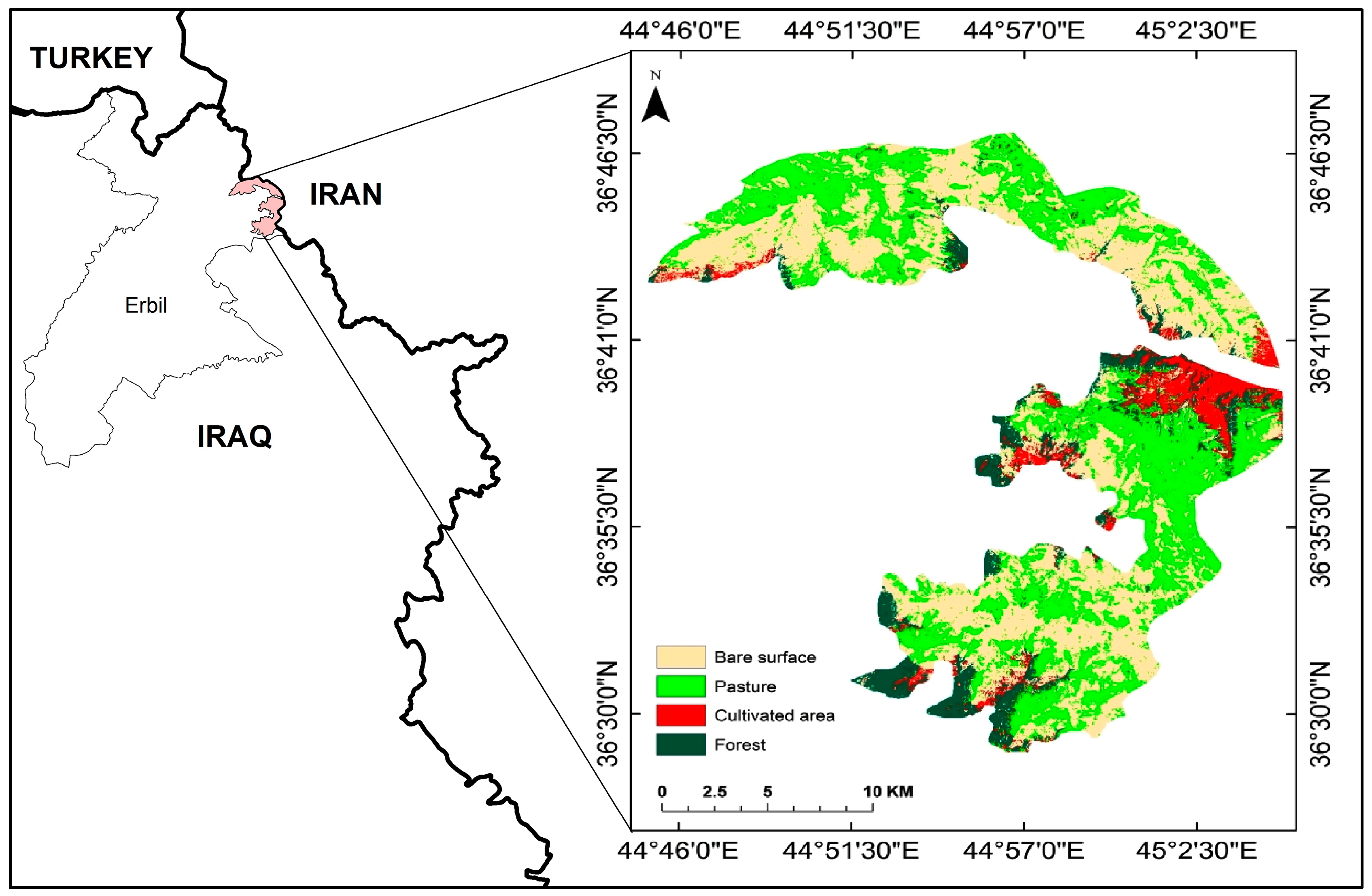
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Satellite Imagery and Data Processing
2.3. Land Use Change and Accuracy Assessment
2.4. Socioeconomic Changes
2.5. Quantifying Landscape Pattern
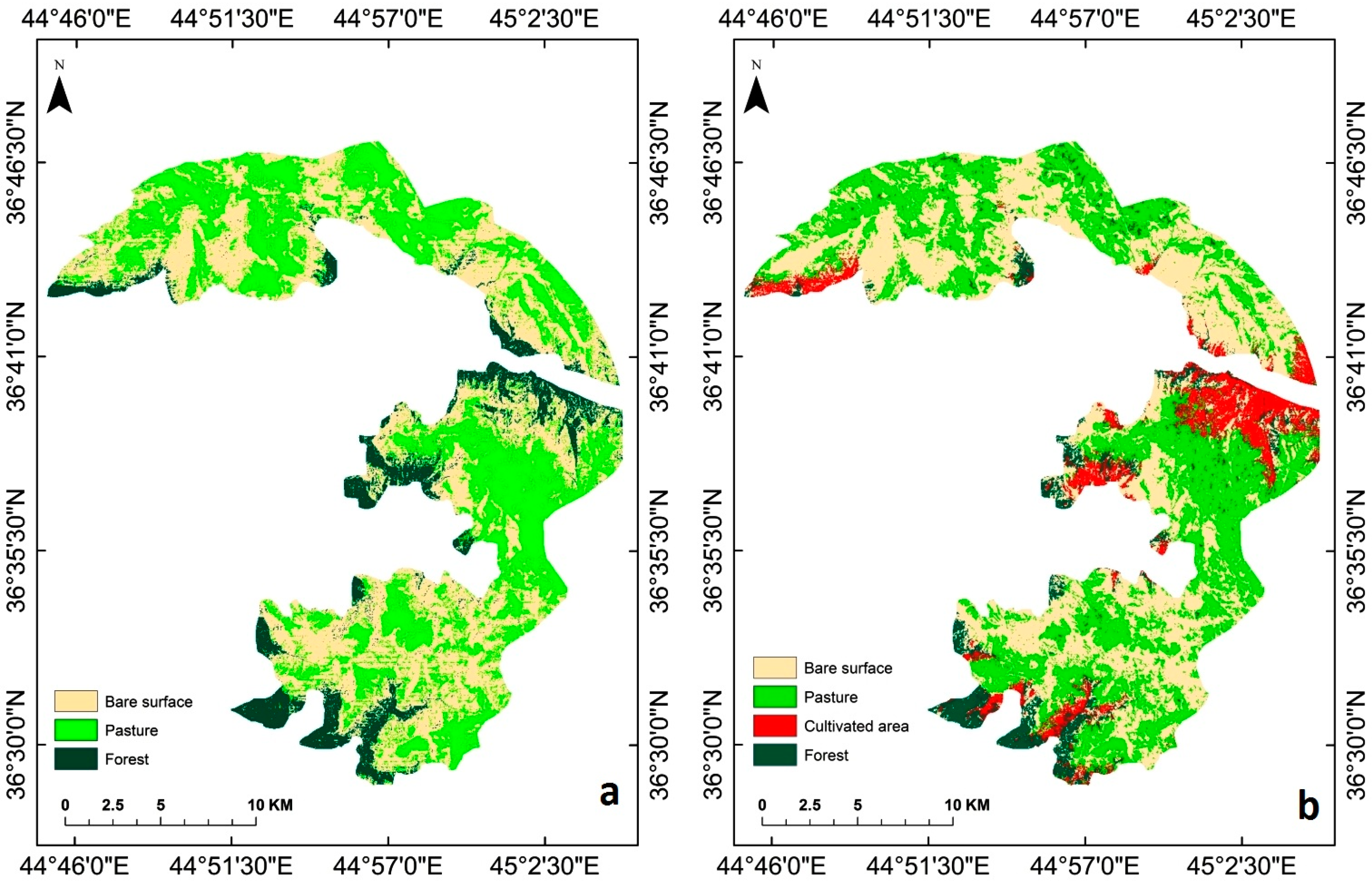
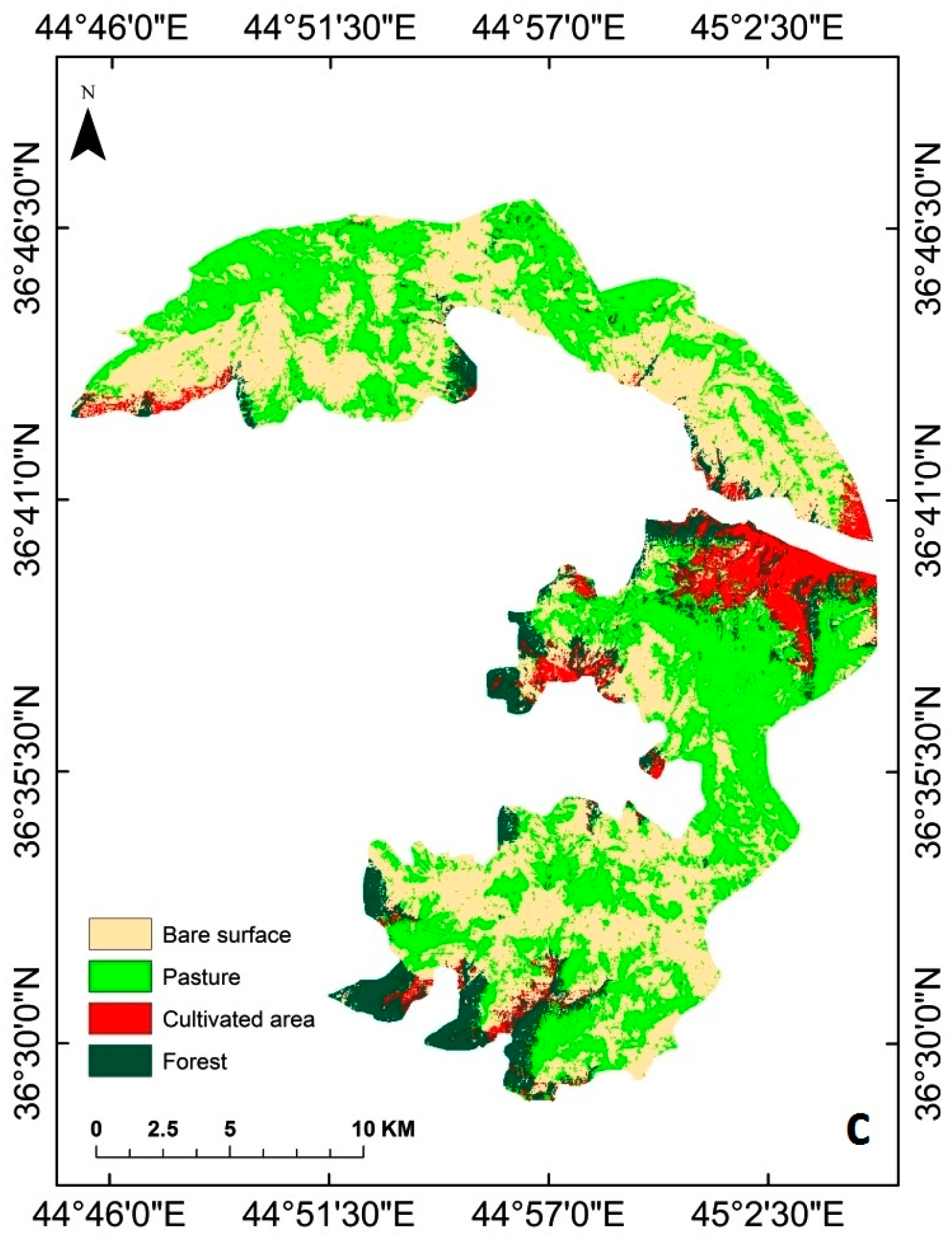
3. Results
3.1. Accuracy Assessment
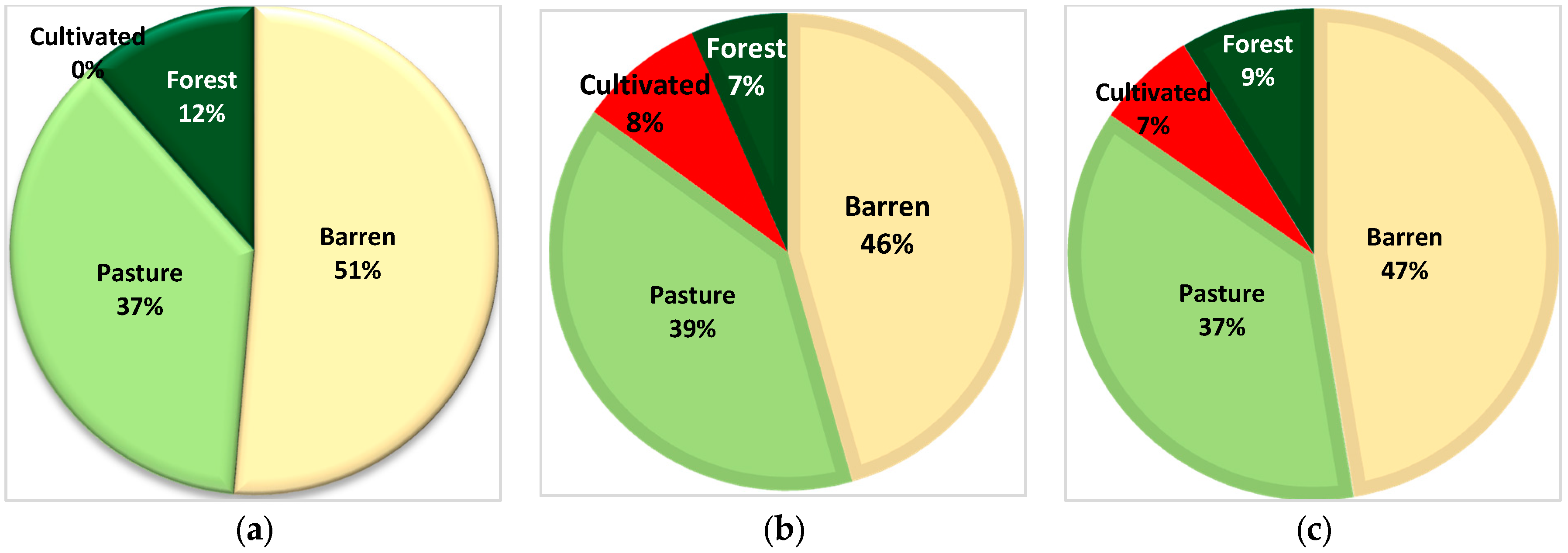
3.2. Landscape Structure and Dynamics
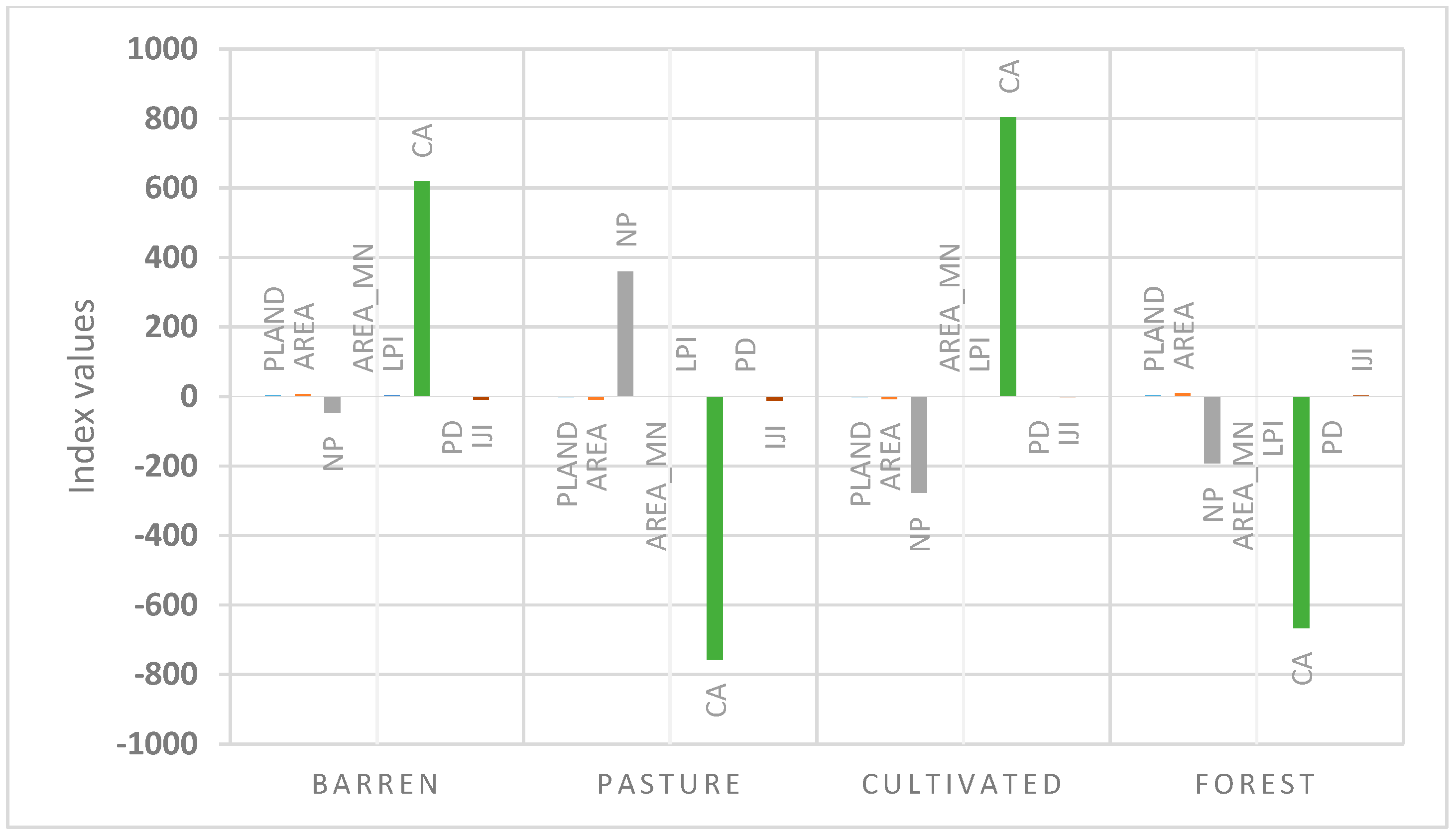
3.3. Analysis of Landscape Metrics at Class Level
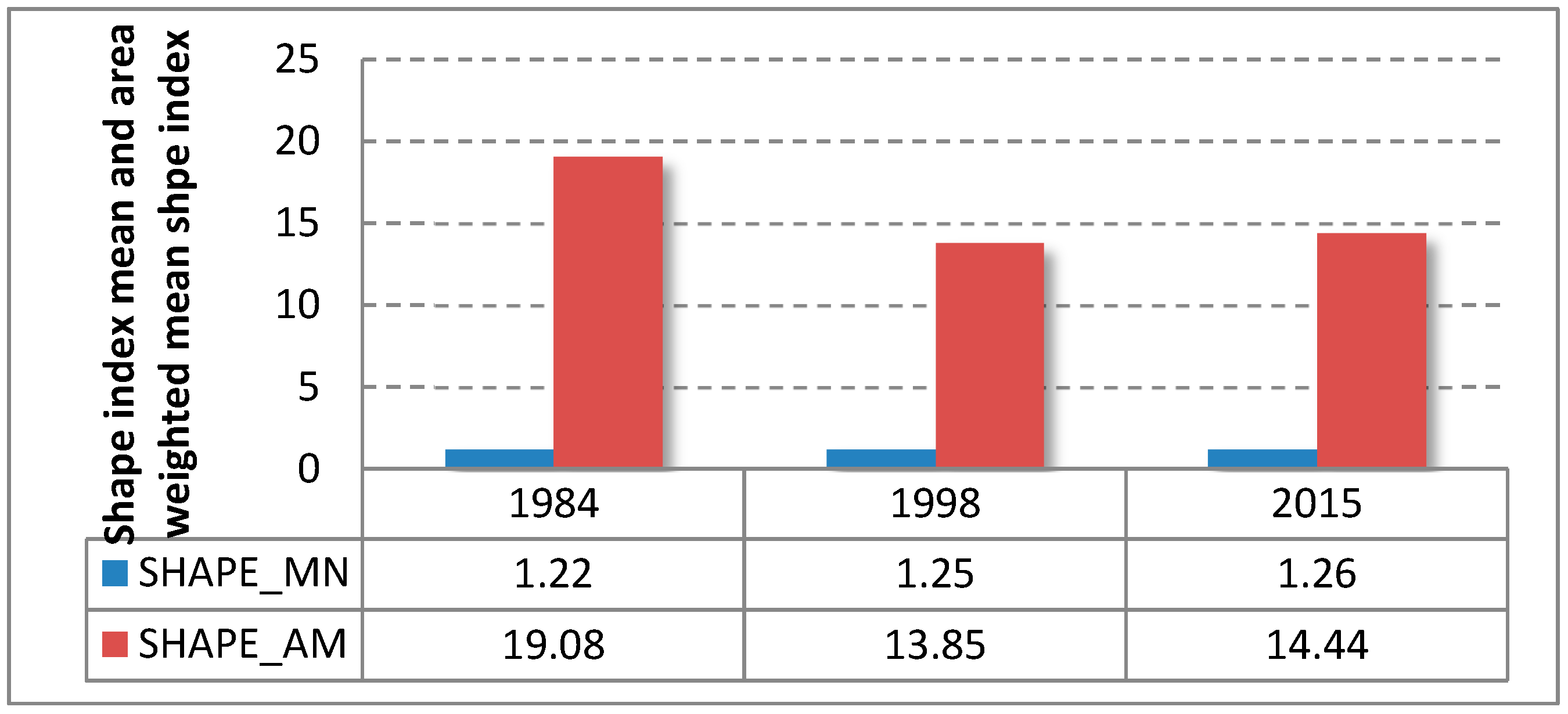
3.4. Analysis of Landscape Metrics at the Landscape Level
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eklund, L.; Seaquist, J. Meteorological, agricultural and socioeconomic drought in the Duhok Governorate, Iraqi Kurdistan. Nat. Hazards 2015, 76, 421–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.M. Emergence of Kurdistan Regional Government. In Iraqi Kurds and Nation-Building; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 7–28. [Google Scholar]
- Švajda, J.; Fenichel, E.P. Evaluation of integrated protected area management in Slovakian National Parks. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2011, 20, 1053. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, G.; King, L. First Nations values in protected area governance: Tla-o-qui-aht tribal parks and Pacific Rim National Park Reserve. Hum. Ecol. 2012, 40, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, C.J.; Boutin, S.; Boonstra, R. Ecosystem Dynamics of the Boreal Forest; New York7 The Kluane Project; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, F. Handbook of Ecosystem Theories and Management; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ezebilo, E.E.; Mattsson, L. Socio-economic benefits of protected areas as perceived by local people around Cross River National Park, Nigeria. For. Policy Econ. 2010, 12, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFries, R.; Hansen, A.; Turner, B.L.; Reid, R.; Liu, J. Land use change around protected areas: Management to balance human needs and ecological function. Ecol. Appl. 2007, 17, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forman, R.T. Land Mosaics: The Ecology of Landscapes and Regions (1995); Island Press: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vorovencii, I. Quantifying landscape pattern and assessing the land cover changes in Piatra Craiului National Park and Bucegi Natural Park, Romania, using satellite imagery and landscape metrics. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrig, L. Effects of habitat fragmentation on biodiversity. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2003, 34, 487–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henareh Khalyani, A.; Mayer, A.L.; Falkowski, M.J.; Muralidharan, D. Deforestation and landscape structure changes related to socioeconomic dynamics and climate change in Zagros forests. J. Land Use Sci. 2013, 8, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, A.; Sefidi, K.; Feghhi, J. Structure and spatial pattern of land uses patches in the Zagros Mountains region in the west of Iran. Biodivers. J. 2014, 15, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.G.; Gardner, R.H.; O’neill, R.V. Landscape Ecology in Theory and Practice; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 401. [Google Scholar]
- Paliwal, A.; Mathur, V.B. Spatial pattern analysis for quantification of landscape structure of Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve, Central India. J. For. Res. 2014, 25, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linh, N.; Erasmi, S.; Kappas, M. Quantifying land use/cover change and landscape fragmentation in Danang City, Vietnam: 1979–2009. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2012, 1, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Castillo, E.M.; García-Martin, A.; Aladrén, L.A.L.; de Luis, M. Evaluation of forest cover change using remote sensing techniques and landscape metrics in Moncayo Natural Park (Spain). Appl. Geogr. 2015, 62, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halgurd Sakran National Park. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Halgurd_Sakran_National_Park (accessed on 25 January 2017).
- District of Choman. 2012. Available online: http://hawlergov.org/en/region.php?id=1330758915 (accessed on 25 January 2017).
- Sisakian, V.K. The Geology of Erbil and Mahabad Quadrangle; Iraq Geological Survey: Baghdad, Iraq, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Brenneman, R.L. As Strong as the Mountains: A Kurdish Cultural Journey; Waveland Press: Long Grove, IL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lortz, M.G. Willing to Face Death: A History of Kurdish Military Forces—The Peshmerga—From the Ottoman Empire to Present-Day Iraq; Florida State University: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Eklund, L.; Persson, A.; Pilesjö, P. Cropland changes in times of conflict, reconstruction, and economic development in Iraqi Kurdistan. Ambio 2016, 45, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDowall, D. Modern History of the Kurds; IB Tauris: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, L. Masters of Chaos: The Secret History of the Special Forces; PublicAffairs: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Iraqi kurdistan. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iraqi_Kurdistan (accessed on 3 March 2017).
- Lillesand, T.; Kiefer, R.W.; Chipman, J. Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Millard, K.; Richardson, M. On the importance of training data sample selection in random forest image classification: A case study in peatland ecosystem mapping. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8489–8515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and regression by randomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Horning, N. Random Forests: An algorithm for image classification and generation of continuous fields data sets. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Geoinformatics for Spatial Infrastructure Development in Earth and Allied Sciences 2010, Hanoi, Vietnam, 9–11 December 2010.
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM). Available online: https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/missions/shuttle-radar-topography-mission-srtm/ (accessed on 3 March 2017).
- Lu, D.; Hetrick, S.; Moran, E. Impervious surface mapping with Quickbird imagery. Int. J. Remote sens. 2011, 32, 2519–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiumnoh, A.; Shrestha, R.P. Application of DEM data to Landsat image classification: Evaluation in a tropical wet-dry landscape of Thailand. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2000, 66, 297–304. [Google Scholar]
- Baldi, G.; Guerschman, J.P.; Paruelo, J.M. Characterizing fragmentation in temperate South America grasslands. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 116, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, K.J.; SivaSathya, S. SVM and random forest classification of satellite image with NDVI as an additional attribute to the dataset. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Soft Computing for Problem Solving; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Varshney, P.K.; Arora, M.K. Advanced Image Processing Techniques for Remotely Sensed Hyperspectral Data; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Natya, S.; Rehna, V. Land Cover Classification Schemes Using Remote Sensing Images: A Recent Survey. Br. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) Global 1 Arc Second Data. Available online: https://eros.usgs.gov/views-news/SRTM-30m-90m-data (accessed on 14 Apirl 2014).
- Franklin, S.; Wulder, M. Remote sensing methods in medium spatial resolution satellite data land cover classification of large areas. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2002, 26, 173–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M. Status of land cover classification accuracy assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, J. An improved method for producing high spatial-resolution NDVI time series datasets with multi-temporal MODIS NDVI data and Landsat TM/ETM+ images. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 7865–7891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Planning 2016. Kurdistan Regional Statistics Office-KRSO. Available online: http://www.mop.gov.krd (accessed on 25 January 2017).
- Gökyer, E. Understanding landscape structure using landscape metrics. In Advances in Landscape Architecture; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kadioğullari, A.I.; Başkent, E.Z. Spatial and temporal dynamics of land use pattern in Eastern Turkey: A case study in Gümüşhane. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 138, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGarigal, K.; Marks, B.J. FRAGSTATS: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Quantifying Landscape Structure; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Research Station: Portland, OR, USA, 1995.
- McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.A.; Neel, M.C.; Ene, E. FRAGSTATS: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Categorical Maps; University of Massachusetts: Amherst, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, M.G. Spatial and temporal analysis of landscape patterns. Landsc. Ecolo. 1990, 4, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FRAGSTATS Software Package. 23 January 2015. Available online: http://www.umass.edu/landeco/research/Fragstats/documents/fragstats.help.4.2.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2017).
- O’neill, R.; Hunsaker, C.T.; Timmins, S.P.; Jackson, B.L.; Jones, K.B.; Riitters, K.H.; Wickham, J.D. Scale problems in reporting landscape pattern at the regional scale. Landsc. Ecol. 1996, 11, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.R. A Land Use and Land Cover Classification System for Use with Remote Sensor Data; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1976; vol. 964.
- Salas, E.A.L.; Boykin, K.G.; Valdez, R. Multispectral and texture feature application in image-object analysis of summer vegetation in Eastern Tajikistan Pamirs. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.G.; Gergel, S.E. Learning Landscape Ecology: A Practical Guide to Concepts and Techniques; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jaafari, S.; Shabani, A.A.; Danehkar, A.; Nazarisamani, A. Spatial Pattern Analysis for Monitoring of National Parks: Sorkhe Hesar National Park, Iran. Res. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, M.; Schnabel, S.; Lavado Contador, J.F.; Lozano-Parra, J.; González, F. The impact of heavy grazing on soil quality and pasture production in rangelands of SW Spain. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Noronha Vaz, E.; Vaz, M.T.d.; Nijkamp, P. An Exploratory Landscape Metrics Approach to Agricultural Changes: Applications of Spatial Economic Consequences for the Algarve, Portugal; Tinbergen Institute: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Forman, R.T. Road Ecology: Science and Solutions; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Vannette, R.L.; Leopold, D.R.; Fukami, T. Forest area and connectivity influence root-associated fungal communities in a fragmented landscape. Ecology 2016, 97, 2374–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Satellite Sensors | Path/Row | Acquisition Date | Resolution | Band Nos. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat 5 TM | 169/035 | 18 August 1984 | 30 m | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7 |
| Landsat7 ETM+ | 169/035 | 13 September1998 | 30 m | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7 |
| Landsat 8 LDCM | 169/035 | 24 August 2015 | 30 m | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9 |
| SRTM (1 arc) | N36_E044/N36_E045 | September 2014 | 30 m | GDEM |
| Acronym | Metric | Description | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class Level | |||
| PLAND | Percentage of landscape | Proportion of the landscape occupied by certain LULC class | McCarigal & Marks (1995) [46] |
| AREA | Area | Area of patches (ha) | McCarigal & Marks (1995) [46] |
| NP | Number of patches | Number of patches in the landscape of the same LULC class | McCarigal & Marks (1995) [46] |
| LPI | Large patch index | Percentage of the landscape comprised by the largest patch of the corresponding LULC class | Forman (1995) [9] |
| CA | Class area | Class area (ha) Dominance index | McCarigal & Marks (1995) [46] |
| PD | Patch density | Calculation of the density of patches for each class within the landscape | McCarigal & Marks (1995) [46] |
| AREA_MN | Mean patch size (MPS) | Mean area of patches of the same LULC class (m2) | McCarigal et al. (2002) [47] |
| IJI | Interspersion and Juxtaposition index | Measure of evenness of patch adjacencies, equals 100 for even, and approaches 0 for uneven adjacencies | McCarigal & Marks (1995) [46] |
| Landscape Level | |||
| SHAPE_AM | Area-weighted mean shape index | Measures the complexity of patch shape of a particular class compared to a standard shape (square), by weighting patches according to their size. It equals 1 when all patches are square and increases with the complexity of patch shapes | McCarigal & Marks (1995) [46] |
| SHAPE_MN | Shape index mean | Computes an area-adjusted measure (to a square) of the average shape complexity for each class | McCarigal & Marks (1995) [46] |
| IJI | Interspersion/juxtaposition index | Measure of evenness of patch adjacencies, equals 100 for even and approaches 0 for uneven adjacencies | McCarigal & Marks (1995) [46] |
| CONTAG | Contag index | Measure of configuration that degree of spatial aggregation of land cover type | O’Neill, Krummel et al. (1996) [50] |
| SIEI | Simpson’s evenness index | A measure of configuration that quantifies the distribution of area among patch types | Simpson (1949) [46] |
| Land Use/Cover | 1984 | 1998 | 2015 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P * | U * | P | U | P | U | |
| Bare surface | 96 | 93 | 97 | 98 | 99 | 98 |
| Pasture | 93 | 97 | 97 | 98 | 98 | 97 |
| Cultivated area | 0 | 0 | 93 | 96 | 88 | 96 |
| Forest | 87 | 98 | 99 | 96 | 98 | 96 |
| Overall accuracy | 96 | 97 | 97 | |||
| Overall Kappa Statistic | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.96 | |||
| Land Use/Land Cover Class | Metric | Years | Changes 1984–1998 | Changes 1998–2015 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1984 | 1998 | 2015 | ||||
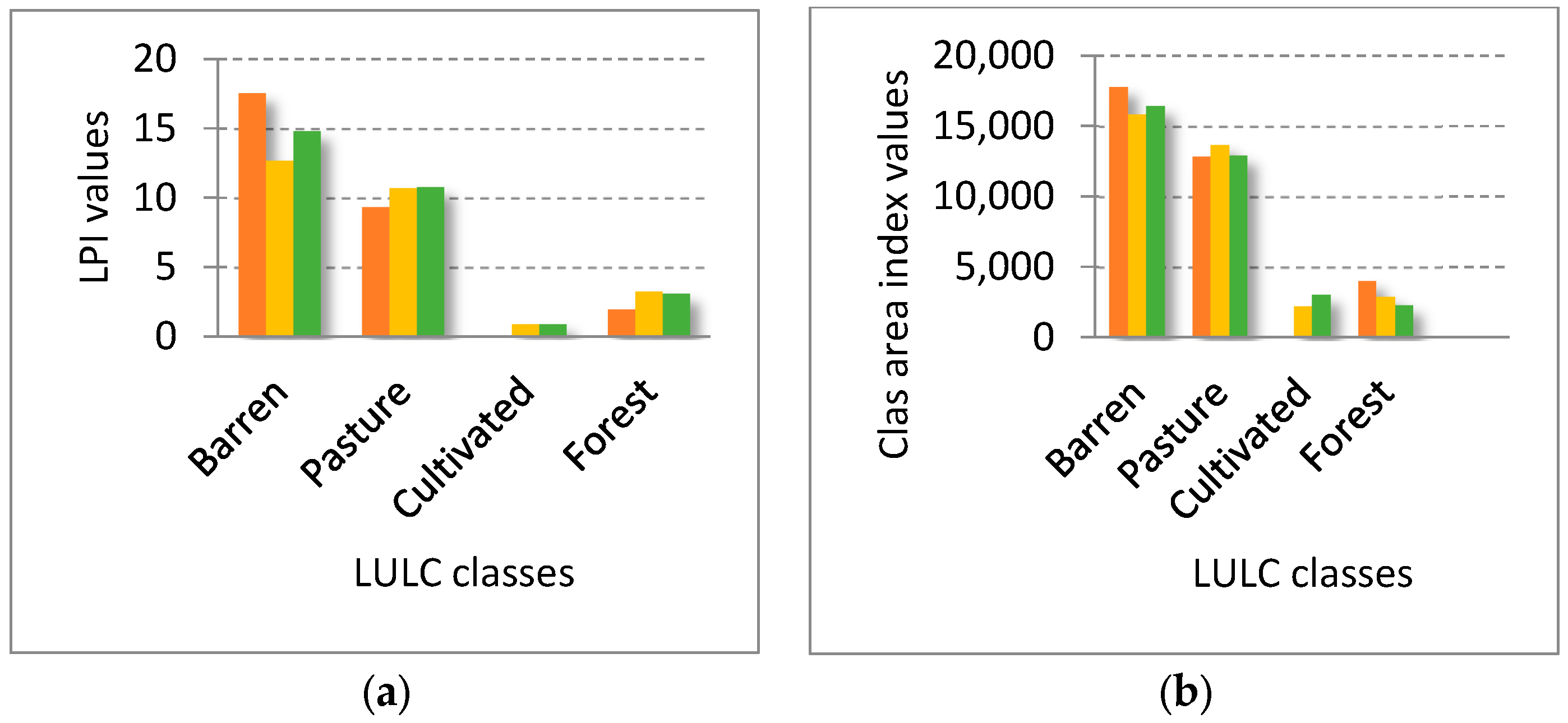
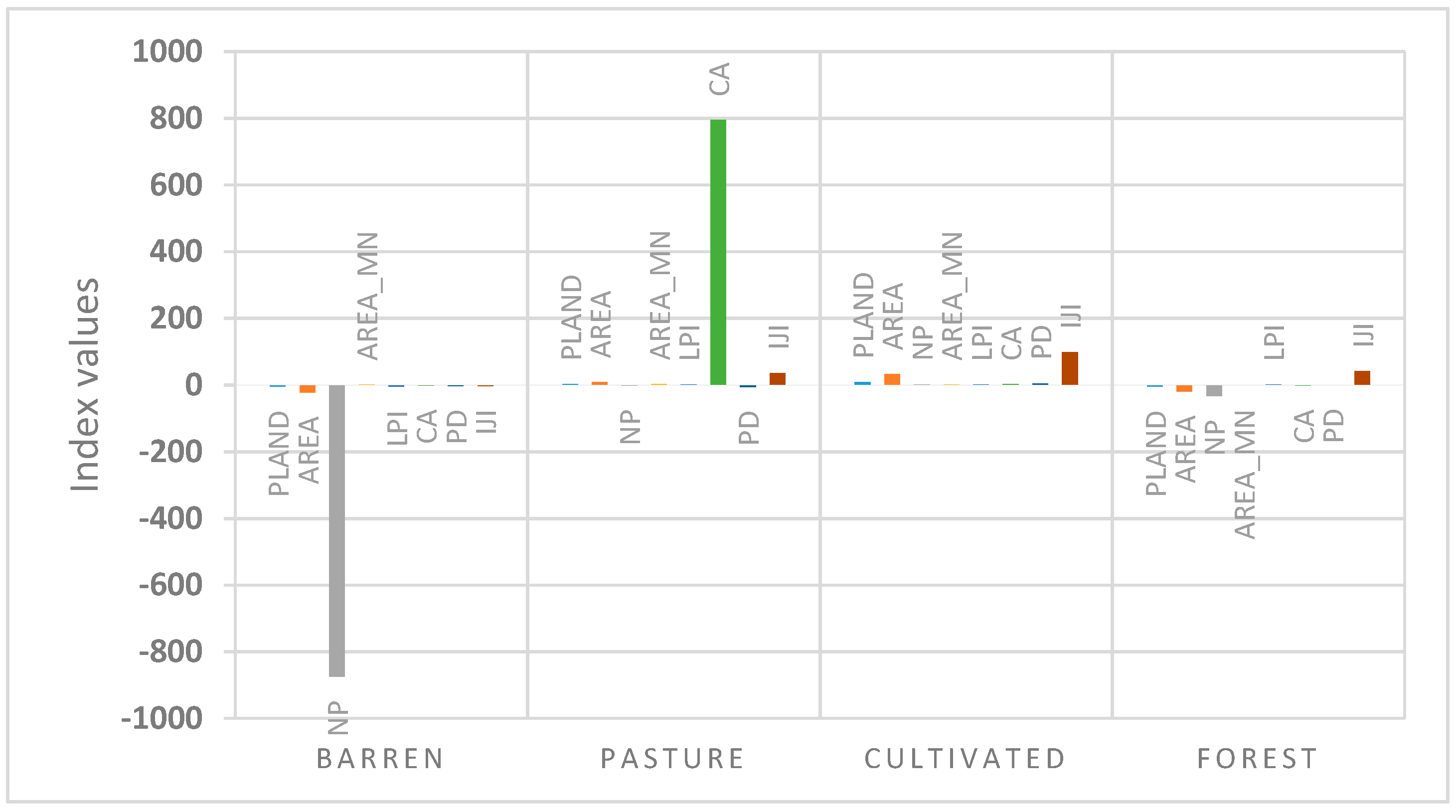
| Barren | PLAND | 51.34 | 45.60 | 47.38 | −5.74 | 1.78 |
| AREA | 198,383 | 176,209 | 183,093 | −22.174 | 6.884 | |
| NP | 3438 | 2563 | 2517 | −875 | −46 | |
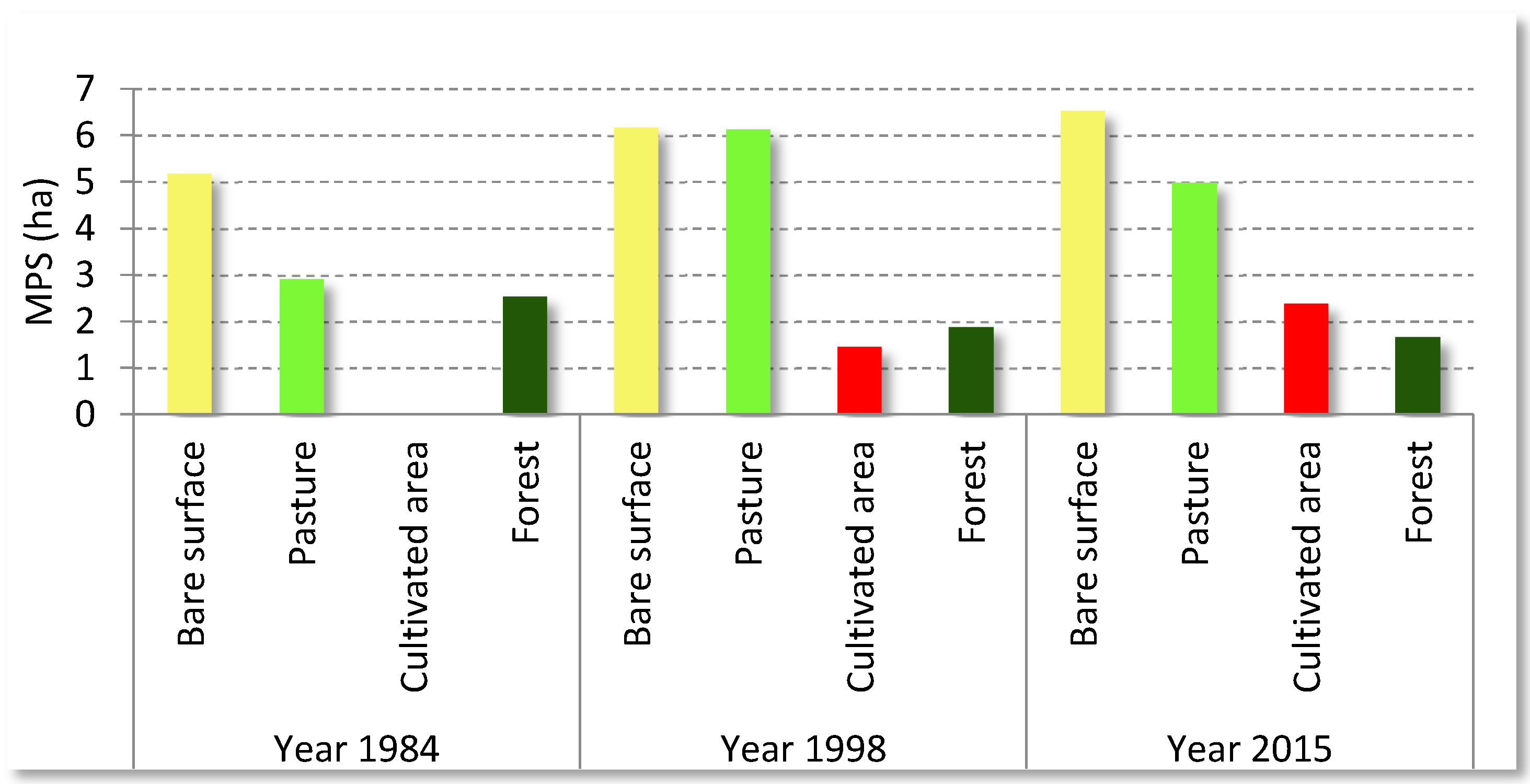
| AREA_MN | 5.19 | 6.18 | 6.54 | 0.99 | 0.36 | |
| LPI | 17.6 | 12.7 | 14.8 | −4.9 | 1.9 | |
| CA | 17,854 | 15,859 | 16,478 | −1.995 | 619 | |
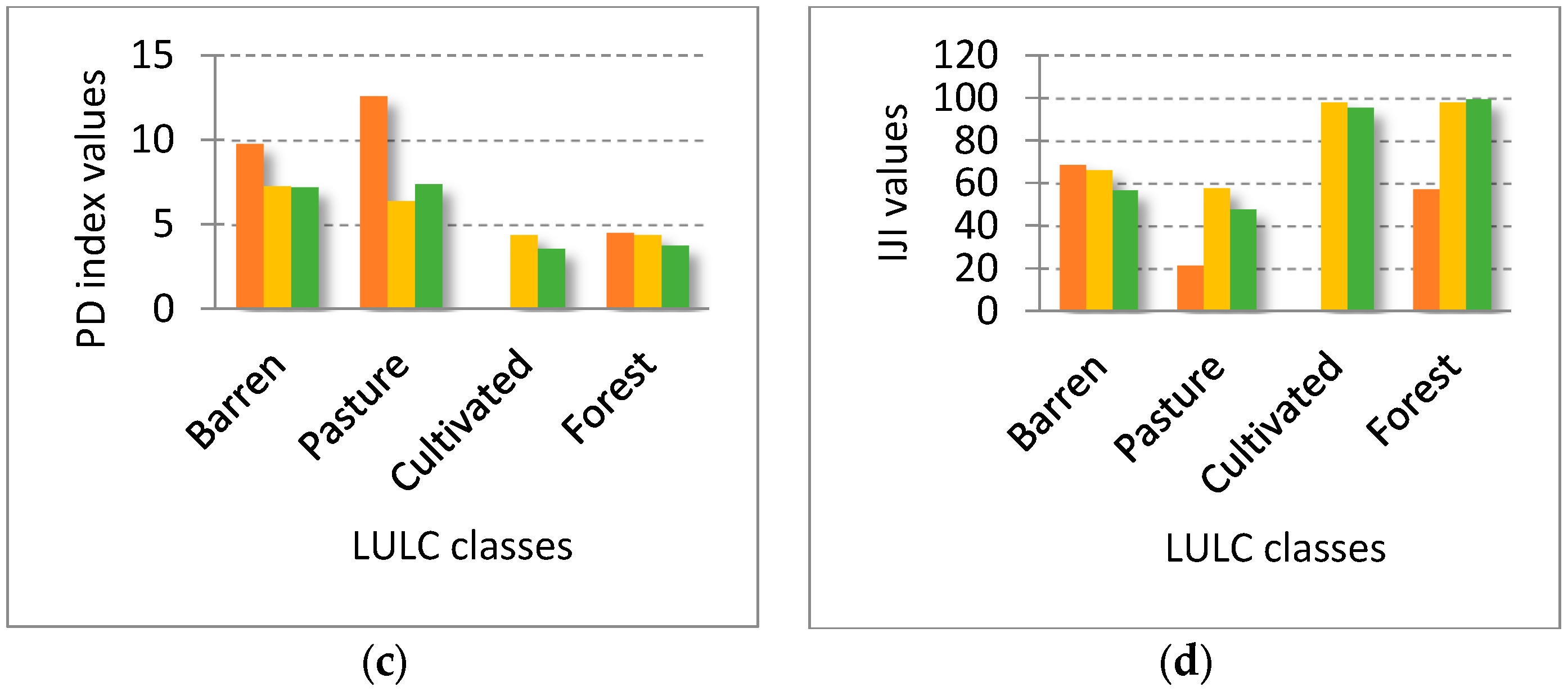
| PD | 9.8 | 7.3 | 7.2 | −2.5 | −0.1 | |
| IJI | 69.04 | 66.21 | 56.72 | −2.83 | −9.49 | |
| Pasture | PLAND | 37.07 | 39.35 | 37.18 | 2.28 | −2.17 |
| AREA | 143,240 | 152,083 | 143,673 | 8.843 | −8.410 | |
| NP | 4391 | 2226 | 2586 | −2.165 | 360 | |
| AREA_MN | 2.39 | 6.14 | 5.00 | 3.21 | −1.14 | |
| LPI | 9.4 | 10.7 | 10.8 | 1.3 | 0.1 | |
| CA | 12,892 | 13,687 | 12,930 | 795 | −757 | |
| PD | 12.6 | 6.4 | 7.4 | −6.2 | 1 | |
| IJI | 21.65 | 57.63 | 48.09 | 35.98 | −12.11 | |
| Cultivated | PLAND | 0 | 8.48 | 6.57 | 8.48 | −1.91 |
| AREA | 0 | 32,806 | 25,398 | 32.806 | −7.408 | |
| NP | 0 | 1559 | 1282 | 1.559 | −277 | |
| AREA_MN | 0 | 1.46 | 2.40 | 1.46 | 0.94 | |
| LPI | 0 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0 | |
| CA | 0 | 2279 | 3083 | 2.279 | 804 | |
| PD | 0 | 4.4 | 3.6 | 4.4 | −0.8 | |
| IJI | 0 | 98.08 | 95.74 | 98.08 | −2.34 | |
| Forest | PLAND | 11.58 | 6.55 | 8.86 | −5.03 | 2.31 |
| AREA | 44,750 | 25,321 | 34,255 | −19.429 | 8.934 | |
| NP | 1579 | 1546 | 1354 | −33 | −192 | |
| AREA_MN | 2.55 | 1.90 | 1.68 | −0.65 | −0.22 | |
| LPI | 2.0 | 3.3 | 3.1 | 1.3 | −0.2 | |
| CA | 4027 | 2952 | 2286 | −1.075 | −666 | |
| PD | 4.5 | 4.4 | 3.8 | −0.1 | −0.6 | |
| IJI | 57.43 | 98.12 | 99.81 | 40.69 | 1.69 | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamad, R.; Balzter, H.; Kolo, K. Multi-Criteria Assessment of Land Cover Dynamic Changes in Halgurd Sakran National Park (HSNP), Kurdistan Region of Iraq, Using Remote Sensing and GIS. Land 2017, 6, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/land6010018
Hamad R, Balzter H, Kolo K. Multi-Criteria Assessment of Land Cover Dynamic Changes in Halgurd Sakran National Park (HSNP), Kurdistan Region of Iraq, Using Remote Sensing and GIS. Land. 2017; 6(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/land6010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamad, Rahel, Heiko Balzter, and Kamal Kolo. 2017. "Multi-Criteria Assessment of Land Cover Dynamic Changes in Halgurd Sakran National Park (HSNP), Kurdistan Region of Iraq, Using Remote Sensing and GIS" Land 6, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/land6010018
APA StyleHamad, R., Balzter, H., & Kolo, K. (2017). Multi-Criteria Assessment of Land Cover Dynamic Changes in Halgurd Sakran National Park (HSNP), Kurdistan Region of Iraq, Using Remote Sensing and GIS. Land, 6(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/land6010018







