Aqueous Fe(II)-Induced Phase Transformation of Ferrihydrite Coupled Adsorption/Immobilization of Rare Earth Elements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ferrihydrite Preparation
2.2. Experiments of Fe(II)aq-Induced Transformation of Ferrihydrite
2.3. Analyses of Ln(III)
2.4. Characterization of Solid Phase
2.5. Isotope Tracer Experiments for Fe Atom Exchange
3. Results and Discussion
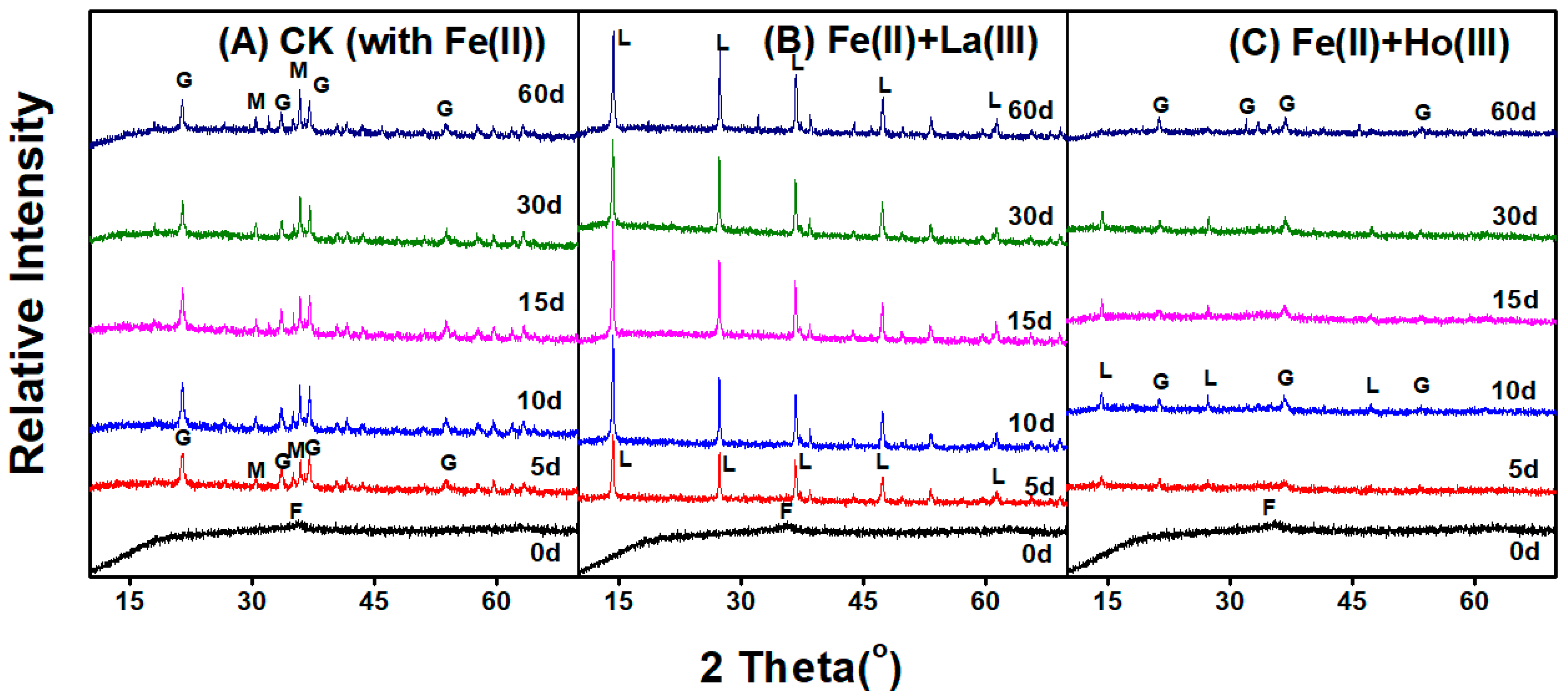
3.1. Phase Transformation of Ferrihydrite Induced by Fe(II)aq
3.2. Iron Atom Exchange between Fe(II)aq and Fe(III)oxide
3.3. Distribution of Ln(III) Species During Fe(II)aq-Induced Transformation of Ferrihydrite
3.4. The Mechanism of Fe(II)aq-Induced Ferrihydrite Transformation Coupled REE Immobilization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Latta, D.E.; Gorski, C.A.; Scherer, M.M. Influence of Fe2+-catalysed iron oxide recrystallization on metal cycling. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2012, 40, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suter, D.; Siffert, C.; Sulzberger, B.; Stumm, W. Catalytic dissoluion of iron(III)(hydr)oxides by oxalic acid in the presence of Fe(II). Naturwissenschaften 1988, 75, 571–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.G.; Scherer, M.M. Spectroscopic evidence for Fe(II)-Fe(III) electron transfer at the iron oxide—Water interface. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4782–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, H.D.; Postma, D.; Jakobsen, R.; Larsen, O. Fast transformation of iron oxyhydroxides by the catalytic action of aqueous Fe(II). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 3967–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, Z.; Li, F.; Liu, T.; Liao, C.; Lee, J.J.; Shih, K.; Tao, L.; Wu, Y. Fe(II)-induced phase transformation of ferrihydrite: The inhibition effects and stabilization of divalent metal cations. Chem. Geol. 2016, 444, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frierdich, A.J.; Scherer, M.M.; Bachman, J.E.; Engelhard, M.H.; Rapponotti, B.W.; Catalano, J.G. Inhibition of trace element release during Fe(II)-activated recrystallization of Al-, Cr-, and Sn-substituted goethite and hematite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10031–10039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrences and Uses, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinhein, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.S.; Li, F.B.; Chen, M.J.; Liao, C.Z.; Tong, H.; Hua, J. Adsorption and stabilization of lead during Fe(II)-catalyzed phase transformation of ferrihydrite. Acta Chim. Sin. 2017, 75, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Peacock, C.L.; Chen, W.; Huang, Q. Binding of Cd by ferrihydrite organo-mineral composites: Implications for Cd mobility and fate in natural and contaminated environments. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freslon, N.; Bayon, G.; Toucanne, S.; Bermell, S.; Bollinger, C.; Cheron, S.; Etoubleau, J.; Germain, Y.; Khripounoff, A.; Ponzevera, E.; et al. Rare earth elements and neodymium isotopes in sedimentary organic matter. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 140, 177–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Q.; Liang, T. Geochemical fractions of rare earth elements in soil around a mine tailing in Baotou, China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leybourne, M.I.; Johannesson, K.H. Rare earth elements (REE) and yttrium in stream waters, stream sediments, and Fe-Mn oxyhydroxides: Fractionation, speciation, and controls over REE plus Y patterns in the surface environment. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 5962–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y. A human health risk assessment of rare earth elements in soil and vegetables from a mining area in Fujian Province, Southeast China. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1240–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolanz, R.M.; Kiefer, S.; Göttlicher, J.; Steininger, R. Hematite (alpha-Fe2O3)—A potential Ce4+ carrier in red mud. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedel, S.; Nedel, K.; Dideriksen, B.C.; Christiansen, N.; Bovet, S.L.S.; Stipp, S.L. Uptake and Release of Cerium During Fe-Oxide Formation and Transformation in Fe(II) Solutions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 4493–4498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmann, M.; Stille, P. Controls on transport and fractionation of the rare earth elements in stream water of a mixed basaltic-granitic catchment basin (Massif Central, France). Chem. Geol. 2008, 254, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migaszewski, Z.M.; Galuszka, A. The Characteristics, Occurrence, and Geochemical Behavior of Rare Earth Elements in the Environment: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 429–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Hendry, M.J.; Essilfie-Dughan, J. Effects of Adsorbed Arsenate on the Rate of Transformation of 2-Line Ferrihydrite at pH 10. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5557–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boland, D.D.; Collins, R.N.; Miller, C.J.; Glover, C.J.; Waite, T.D. Effect of solution and solid-phase conditions on the Fe(II)-accelerated transformation of ferrihydrite to lepidocrocite and goethite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 5477–5485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.S.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.B.; Chen, M.J.; Zhai, G.; Tao, L.; Liu, C. Influence of geochemical properties and land-use types on the microbial reduction of Fe(III) in subtropical soils. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 1938–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, T.R.; Frierdich, A.J.; Beard, B.L.; Johnson, C.M. The effect of pH on stable iron isotope exchange and fractionation between aqueous Fe(II) and goethite. Chem. Geol. 2015, 397, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guelke, M.; Blanckenburg, F.; Schoenberg, R.; Staubwasser, M.; Stuetzel, H. Determining the stable Fe isotope signature of plant-available iron in soils. Chem. Geol. 2010, 277, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frierdich, A.J.; Beard, B.L.; Scherer, M.M.; Johnson, C.M. Determination of the Fe(II)aq–magnetite equilibrium iron isotope fractionation factor using the three-isotope method and a multi-direction approach to equilibrium. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2014, 391, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICDD. Powder Diffraction File (PDF 2), Release 2008; International Centre for Diffraction Data: Newtown Square, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Hendry, M.J.; Essilfie-Dughan, J. Transformation of Two-Line Ferrihydrite to Goethite and Hematite as a Function of pH and Temperature. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.W.; Shih, K.M.; Liu, C.S.; Wang, F. Extraction of Metallic Lead from Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) Funnel Glass by Thermal Reduction with Metallic Iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 9972–9978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Torre, A.G.; Bruque, S.; Aranda, M.A.G. Rietveld quantitative amorphous content analysis. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2001, 34, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernasconi, A.; Dapiaggi, M.; Gualtieri, A.F. Accuracy in quantitative phase analysis of mixtures with large amorphous contents. The case of zircon-rich sanitary-ware glazes. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2014, 47, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frierdich, A.J.; Helgeson, M.; Liu, C.; Wang, C.; Rosso, K.M.; Scherer, M.M. Iron atom exchange between hematite and aqueous Fe(II). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8479–8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Li, P.; Zhu, M.Y.; Wei, Y.; Sun, Y.H. Fe(II)-induced transformation from ferrihydrite to lepidocrocite and goethite. J. Solid State Chem. 2007, 180, 2121–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, M.S.; Lezama-Pacheco, J.S.; Michel, F.M.; Fendorf, S. Uranium incorporation into aluminum-substituted ferrihydrite during iron(II)-induced transformation. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 2137–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masue-Slowey, Y.; Loeppert, R.H.; Fendorf, S. Alteration of ferrihydrite reductive dissolution and transformation by adsorbed As and structural Al: Implications for As retention. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 870–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latta, D.E.; Bachman, J.E.; Scherer, M.M. Fe Electron Transfer and Atom Exchange in Goethite: Influence of Al-Substitution and Anion Sorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10614–10623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.M.; Collins, R.N.; Rose, J.; Waite, T.D. The effect of silica and natural organic matter on the Fe(II)-catalysed transformation and reactivity of Fe(III) minerals. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 4409–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, E.; Dutrizac, J.E. The behaviour of the rare earth elements during the precipitation of ferrihydrite from sulphate media. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 172, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, H.R.; Li, B. Comparative complexation behavior of the rare earths. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 4575–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppin, F.; Berger, G.; Bauer, A.; Castet, S.; Loubet, M. Sorption of lanthanides on smectite and kaolinite. Chem. Geol. 2002, 182, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, K.G.; Elliott, H.A.; Cannon, F.S. Adsorption and coprecipitation of copper with the hydrous oxides of iron and aluminum. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 2721–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Paige, C.R.; Snodgrass, W.J. The effect of cadmium on the transformation of ferrihydrite into crystalline products at pH 8. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1996, 91, 307–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, T.; Mitamura, H.; Nakayama, S.; Nakashima, S. Formation of goethite and hematite from neodymium-containing ferrihydrite suspensions. Clays Clay Miner. 1999, 47, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardenne, K.; Schäfer, T.; Lindqvist-Reis, P.; Denecke, M.A.; Plaschke, M.; Rothe, J.; Kim, J.I. Low temperature XAFS investigation on the lutetium binding changes during the 2-line ferrihydrite alteration process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 5092–5099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozau, E.; Gottlicher, J.; Stark, H.J. Rare earth element fractionation during the precipitation and crystallisation of hydrous ferric oxides from anoxic lake water. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 3473–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fei, Y.; Hua, J.; Liu, C.; Li, F.; Zhu, Z.; Xiao, T.; Chen, M.; Gao, T.; Wei, Z.; Hao, L. Aqueous Fe(II)-Induced Phase Transformation of Ferrihydrite Coupled Adsorption/Immobilization of Rare Earth Elements. Minerals 2018, 8, 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8080357
Fei Y, Hua J, Liu C, Li F, Zhu Z, Xiao T, Chen M, Gao T, Wei Z, Hao L. Aqueous Fe(II)-Induced Phase Transformation of Ferrihydrite Coupled Adsorption/Immobilization of Rare Earth Elements. Minerals. 2018; 8(8):357. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8080357
Chicago/Turabian StyleFei, Yingheng, Jian Hua, Chengshuai Liu, Fangbai Li, Zhenke Zhu, Tangfu Xiao, Manjia Chen, Ting Gao, Zhiqi Wei, and Likai Hao. 2018. "Aqueous Fe(II)-Induced Phase Transformation of Ferrihydrite Coupled Adsorption/Immobilization of Rare Earth Elements" Minerals 8, no. 8: 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8080357
APA StyleFei, Y., Hua, J., Liu, C., Li, F., Zhu, Z., Xiao, T., Chen, M., Gao, T., Wei, Z., & Hao, L. (2018). Aqueous Fe(II)-Induced Phase Transformation of Ferrihydrite Coupled Adsorption/Immobilization of Rare Earth Elements. Minerals, 8(8), 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8080357



