Confounders of Ultrasound Attenuation Imaging in a Linear Probe Using the Canon Aplio i800 System: A Phantom Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ultrasound
2.2. Liver Tissue Phantoms and Experimental Set Up
2.3. Experimental Protocol
2.4. Measurements
2.5. Statistics
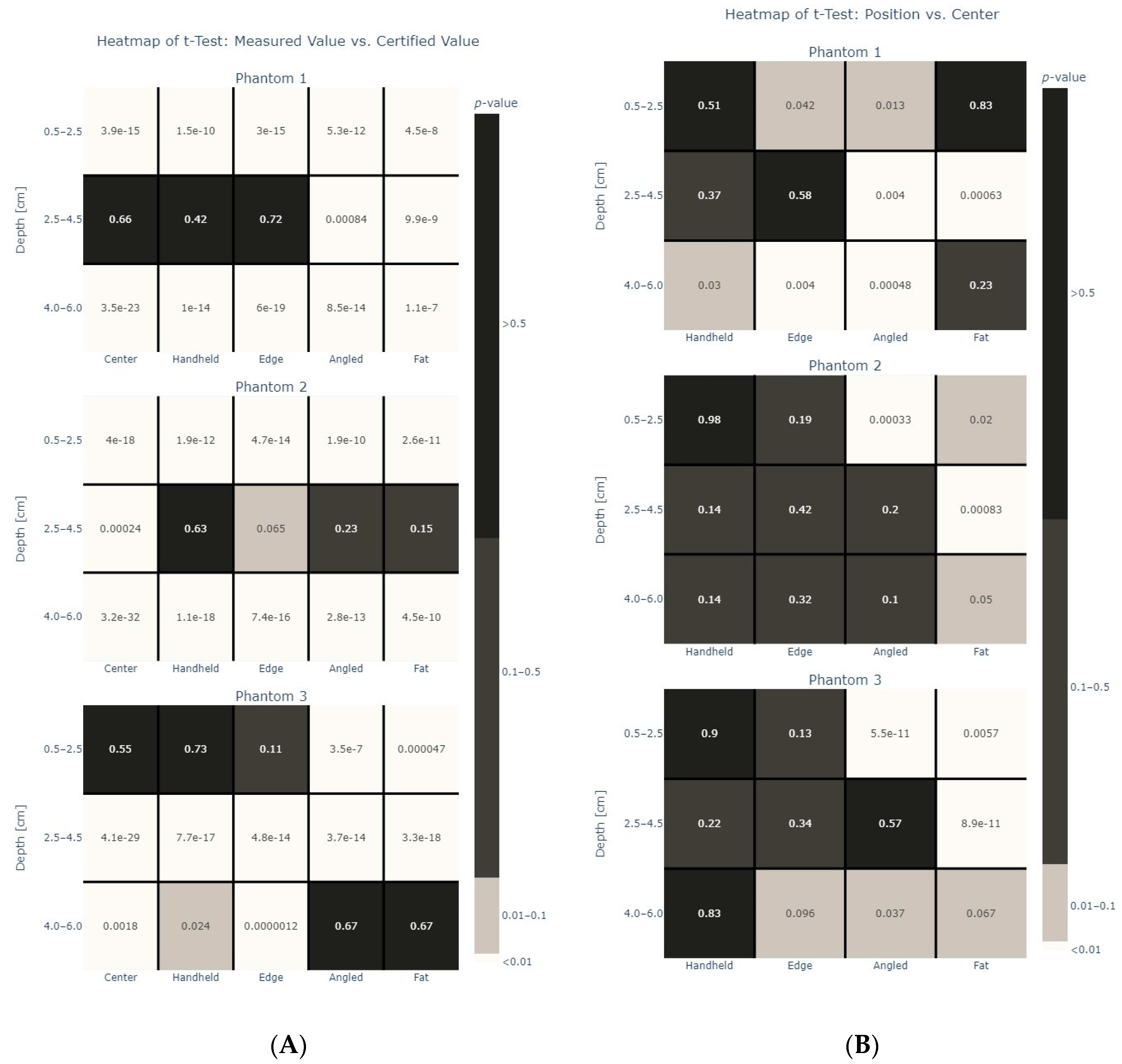
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nassir, F.; Rector, R.S.; Hammoud, G.M.; Ibdah, J.A. Pathogenesis and Prevention of Hepatic Steatosis. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 11, 167. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, S.R.; Thomas, E.L.; Bell, J.D.; Johnston, D.G.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D. Non-invasive means of measuring hepatic fat content. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 3476–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. NAFLD: A multisystem disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62 (Suppl. S1), S47–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraioli, G.; Monteiro, L.B.S. Ultrasound-based techniques for the diagnosis of liver steatosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 6053–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, K.; Moriyasu, F.; Oshiro, H.; Takeuchi, H.; Abe, M.; Yoshimasu, Y.; Kasai, Y.; Sakamaki, K.; Hara, T.; Itoi, T. The Role of Multiparametric US of the Liver for the Evaluation of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Radiology 2020, 296, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Cho, E.J.; Bae, J.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Yu, S.J.; Kim, H.; Lee, K.B.; Han, J.K.; Choi, B.I. Accuracy of Two-Dimensional Shear Wave Elastography and Attenuation Imaging for Evaluation of Patients With Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 797–805.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, T.; Iijima, H.; Kobayashi, N.; Yoshida, M.; Nishimura, T.; Kumada, T.; Kondo, R.; Yano, H.; Kage, M.; Nakano, C.; et al. Usefulness of Attenuation Imaging with an Ultrasound Scanner for the Evaluation of Hepatic Steatosis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 2679–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogino, Y.; Wakui, N.; Nagai, H.; Igarashi, Y. The ultrasound-guided attenuation parameter is useful in quantification of hepatic steatosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. JGH Open 2021, 5, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraioli, G.; Maiocchi, L.; Raciti, M.V.; Tinelli, C.; De Silvestri, A.; Nichetti, M.; De Cata, P.; Rondanelli, M.; Chiovato, L.; Calliada, F.; et al. Detection of Liver Steatosis With a Novel Ultrasound-Based Technique: A Pilot Study Using MRI-Derived Proton Density Fat Fraction as the Gold Standard. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesper, D.; Klett, D.; Schellhaas, B.; Pfeifer, L.; Leppkes, M.; Waldner, M.; Neurath, M.F.; Strobel, D. Ultrasound-Based Attenuation Imaging for the Non-Invasive Quantification of Liver Fat—A Pilot Study on Feasibility and Inter-Observer Variability. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2020, 8, 1800409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli, G.; Maiocchi, L.; Savietto, G.; Tinelli, C.; Nichetti, M.; Rondanelli, M.; Calliada, F.; Preda, L.; Filice, C. Performance of the Attenuation Imaging Technology in the Detection of Liver Steatosis. J. Ultrasound Med. 2021, 40, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Kuroda, H.; Abe, T.; Ishida, K.; Oguri, T.; Noguchi, S.; Sugai, T.; Kamiyama, N.; Takikawa, Y. The B-Mode Image-Guided Ultrasound Attenuation Parameter Accurately Detects Hepatic Steatosis in Chronic Liver Disease. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 2223–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasso, M.; Beaugrand, M.; de Ledinghen, V.; Douvin, C.; Marcellin, P.; Poupon, R.; Sandrin, L.; Miette, V. Controlled attenuation parameter (CAP): A novel VCTETM guided ultrasonic attenuation measurement for the evaluation of hepatic steatosis: Preliminary study and validation in a cohort of patients with chronic liver disease from various causes. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2010, 36, 1825–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, T.; Kumada, T.; Toyoda, H.; Nakamura, S.; Shibata, Y.; Yasuda, S.; Watanuki, Y.; Tsujii, K.; Fukuda, N.; Fujioka, M.; et al. Attenuation imaging based on ultrasound technology for assessment of hepatic steatosis: A comparison with magnetic resonance imaging-determined proton density fat fraction. Hepatol. Res. 2020, 50, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paige, J.S.; Bernstein, G.S.; Heba, E.; Costa, E.A.C.; Fereirra, M.; Wolfson, T.; Gamst, A.C.; Valasek, M.A.; Lin, G.Y.; Han, A.; et al. A Pilot Comparative Study of Quantitative Ultrasound, Conventional Ultrasound, and MRI for Predicting Histology-Determined Steatosis Grade in Adult Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 208, W168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.S.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, H.; Yu, S.J.; Lee, J.-H.; Cho, E.J.; Lee, Y.B.; Han, J.K.; Choi, B.I. Assessment of hepatic steatosis by using attenuation imaging: A quantitative, easy-to-perform ultrasound technique. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 6499–6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, K.J.; Riely, C.A.; Hammers, L.; Flax, S.; Weltin, G.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Conn, H.O.; Kuc, R.; Barwick, K.W. Quantitative US attenuation in normal liver and in patients with diffuse liver disease: Importance of fat. Radiology 1986, 160, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.N.; Fowler, K.J.; Hamilton, G.; Cui, J.Y.; Sy, E.Z.; Balanay, M.; Hooker, J.C.; Szeverenyi, N.; Sirlin, C.B. Liver fat imaging—A clinical overview of ultrasound, CT, and MR imaging. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91, 20170959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, K.J. Ultrasonic attenuation and absorption in liver tissue. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1983, 9, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.C.; Liao, Y.-Y.; Tsui, P.-H.; Yeh, C.-K. Ultrasound imaging in nonalcoholic liver disease: Current applications and future developments. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2019, 9, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, A.; Grajo, J.R.; Gee, M.S.; Benjamin, A.; Zubajlo, R.E.; Thomenius, K.E.; Anthony, B.W.; Samir, A.E.; Dhyani, M. Quantitative Hepatic Fat Quantification in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Using Ultrasound-Based Techniques: A Review of Literature and Their Diagnostic Performance. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 2461–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.-Y.; Yang, K.-C.; Lee, M.-J.; Huang, K.-C.; Chen, J.-D.; Yeh, C.-K. Multifeature analysis of an ultrasound quantitative diagnostic index for classifying nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.-K.; Wu, L.-S.; Su, W.-W.; Su, P.-Y.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Yen, H.-H.; Wu, C.-L. Comparing the controlled attenuation parameter using FibroScan and attenuation imaging with ultrasound as a novel measurement for liver steatosis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steyaert, L. Doppler sonography in breast pathology. JBR-BTR 2000, 83, 121–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balius, R.; Pedret, C.; Iriarte, I.; Sáiz, R.; Cerezal, L. Sonographic landmarks in hamstring muscles. Skelet. Radiol. 2019, 48, 1675–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegedüs, L. Thyroid ultrasound. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2001, 30, 339–360, viii–ix. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.-Y.; Cheng, W.-J.; Yu, J.-L.; Zhang, W.-J.; Jiang, Q.-L.; Wang, Y.-M.; Wen, Y.-L.; Liu, G.-J. Clinical Application of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Using High-Frequency Linear Probe in the Detection of Small Colorectal Liver Metastases. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 2765–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, H. Assessment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with Attenuation Imaging (ATI). Canon. Med. Syst. Corp. 2020, ULWP13175U, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, S.K.; Lee, J.M.; Joo, I.; Yoon, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Han, J.K. Prospective Evaluation of Hepatic Steatosis Using Ultrasound Attenuation Imaging in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease with Magnetic Resonance Imaging Proton Density Fat Fraction as the Reference Standard. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Kim, J.; Lim, H.J.; Kamiyama, N.; Oguri, T.; Koh, H.; Lee, M.-J. Attenuation Coefficient Measurement Using a High-Frequency (2–9 MHz) Convex Transducer for Children Including Fatty Liver. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2022, 48, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahir, A. Clinical Ultrasound Third. In Clinical Ultrasound; Allan, P.L., Baxter, G.M., Weston, M.J., Eds.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; p. 301. [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto, Y.; Taniguchi, M.; Hirono, T.; Yagi, M.; Yamagata, M.; Nakai, R.; Asai, T.; Yamada, Y.; Kimura, M.; Ichihashi, N. Influence of ultrasound focus depth on the association between echo intensity and intramuscular adipose tissue. Muscle Nerve 2022, 66, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dankel, S.J.; Abe, T.; Bell, Z.W.; Jessee, M.B.; Buckner, S.L.; Mattocks, K.T.; Mouser, J.G.; Loenneke, J.P. The Impact of Ultrasound Probe Tilt on Muscle Thickness and Echo-Intensity: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Clin. Densitom. 2020, 23, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rominger, M.B.; Kälin, P.; Mastalerz, M.; Martini, K.; Klingmüller, V.; Sanabria, S.; Frauenfelder, T. Influencing Factors of 2D Shear Wave Elastography of the Muscle—An Ex Vivo Animal Study. Ultrasound Int. Open 2018, 4, E54–E60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.; Zagzebski, J.A.; Hall, T.J. Quantitative Assessment of In Vivo Breast Masses Using Ultrasound Attenuation and Backscatter. Ultrason. Imaging 2013, 35, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, C.; Vilkomerson, D.; Mezrich, R.; Etzold, K.F.; Kingsley, B.; Haskin, M. Differences in the attenuation of ultrasound by normal, benign, and malignant breast tissue. J. Clin. Ultrasound 1976, 4, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, K.; Rosado-Mendez, I.M.; Wirtzfeld, L.A.; Ghoshal, G.; Pawlicki, A.D.; Madsen, E.L.; Lavarello, R.J.; Oelze, M.L.; Zagzebski, J.A.; O’brien, W.D.; et al. Comparison of Ultrasound Attenuation and Backscatter Estimates in Layered Tissue-Mimicking Phantoms among Three Clinical Scanners. Ultrason. Imaging 2012, 34, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Zidan, F.M.; Hefny, A.F.; Corr, P. Clinical ultrasound physics. J. Emerg. Trauma. Shock. 2011, 4, 501–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, W.D. Ultrasound-biophysics mechanisms. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2007, 93, 212–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.K.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, K.W. Accuracy of the ultrasound attenuation coefficient for the evaluation of hepatic steatosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Ultrasonography 2022, 41, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hida, T.; Ando, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Ito, K.; Tsushima, M.; Kobayakawa, T.; Morozumi, M.; Tanaka, S.; Machino, M.; Ota, K.; et al. Ultrasound measurement of thigh muscle thicknessfor assessment of sarcopenia. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2018, 80, 519. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, C.; Zabal, J.; Hernandez, H.J.; Woletz, P.; Manning, H.; Teixeira, C.; DiPietro, L.; Blackman, M.R.; Harris-Love, M.O. Diagnostic ultrasound estimates of muscle mass and muscle quality discriminate between women with and without sarcopenia. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zçakar, L.O.; Merve Ata, A.; Kaymak, B.; Kara, M.; Kumbhare, D. Ultrasound imaging for sarcopenia, spasticity and painful muscle syndromes. Curr. Opin. Support. Palliat. Care 2018, 12, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
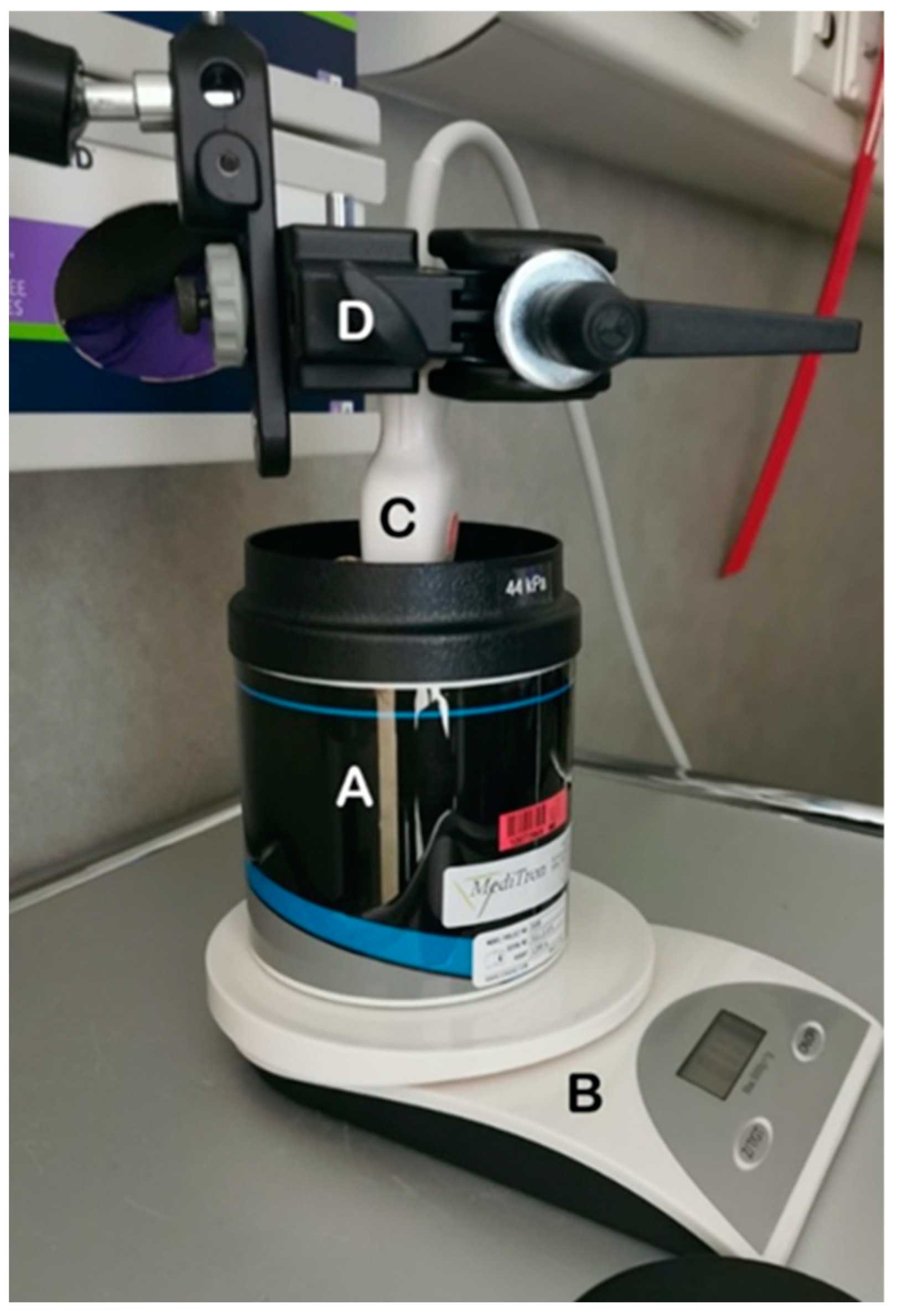


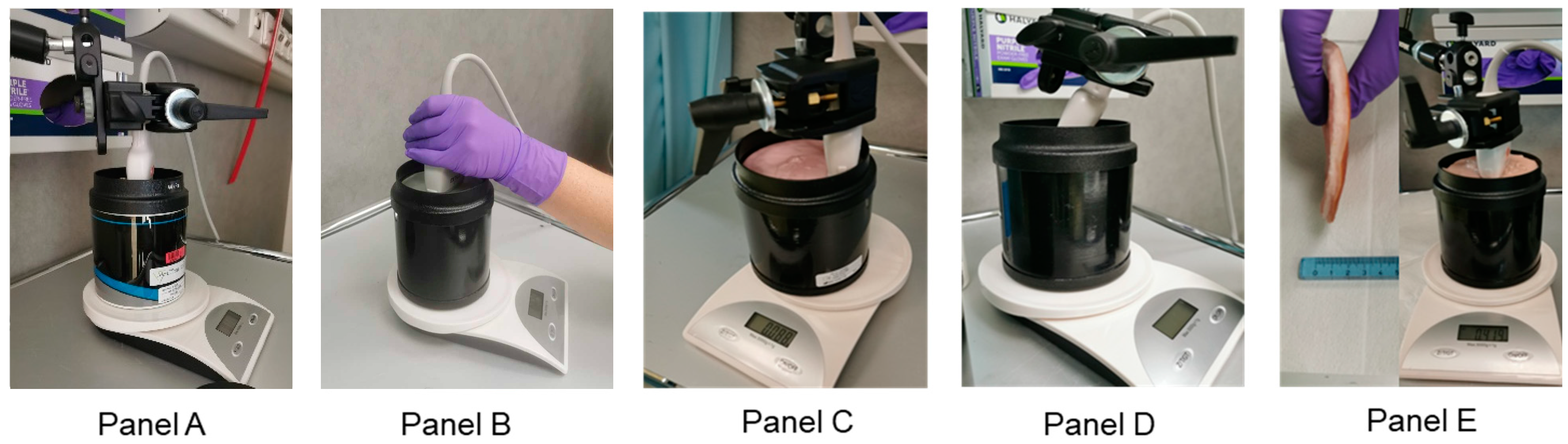

| Phantom | Certified Attenuation Value (dB/cm/MHz) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0.35 |
| 2 | 0.42 |
| 3 | 0.51 |
| Setting | ROI | Depth |
|---|---|---|
| A | 4 cm × 2 cm = 8 cm2 | 0.5–2.5 cm, 2.5–4.5 cm, 4–6 cm |
| B | 2 cm × 2 cm = 4 cm2 | 0.5–2.5 cm, 2.5–4.5 cm, 4–6 cm |
| C | 3 cm × 2 cm = 6 cm2 | 0.5–2.5 cm, 2.5–4.5 cm, 4–6 cm |
| D | 2 cm × 2 cm = 4 cm2 | 0.5–2.5 cm, 2.5–4.5 cm, 4–6 cm |
| E | 4 cm × 2 cm = 8 cm2 | 0.5–2.5 cm, 2.5–4.5 cm, 4–6 cm, 6–8 cm, 8–10 cm |
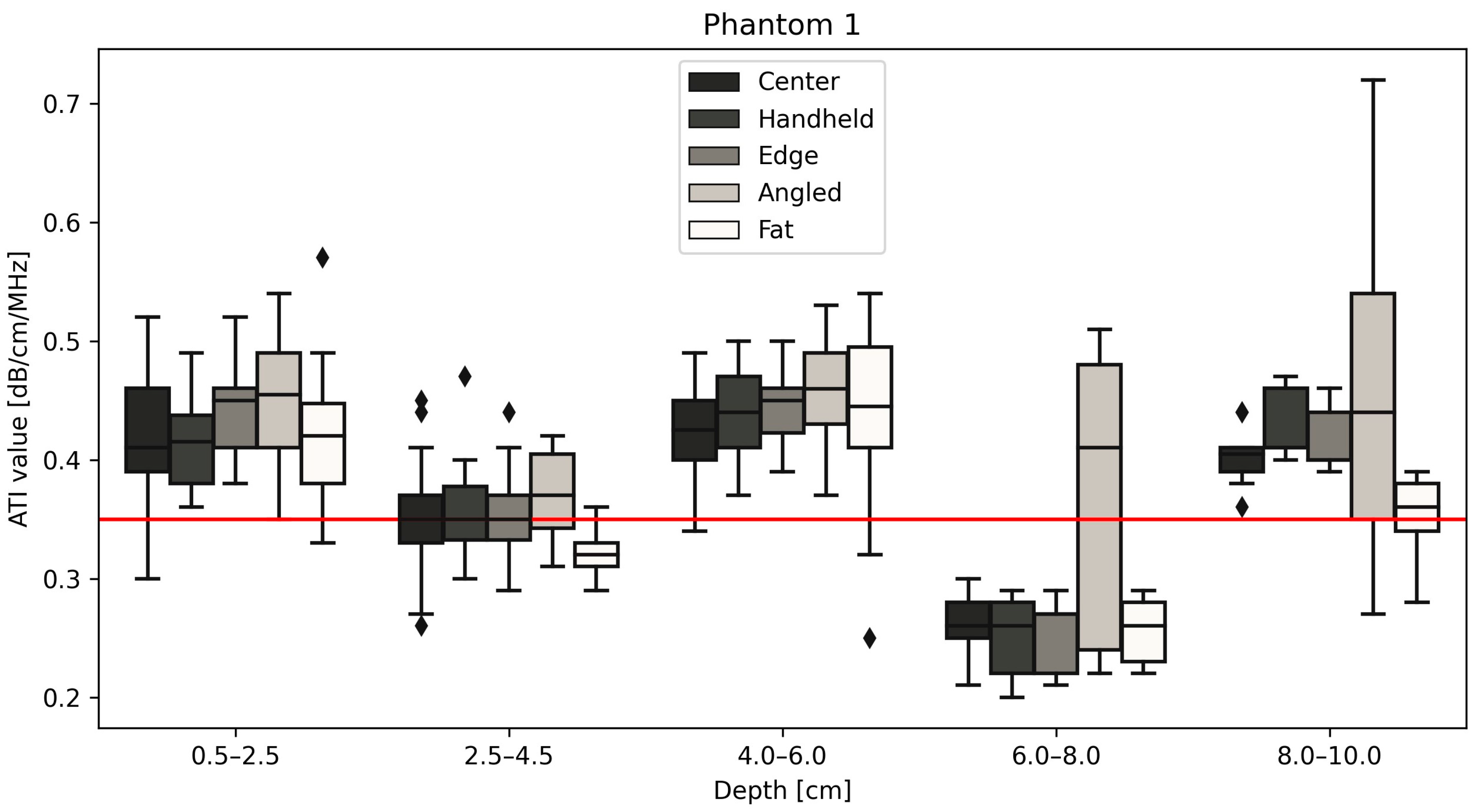
| Phantom 1 Median ATI values | Depth | |||||
| 0.5–2.5 cm | 2.5–4.5 cm | 4–6 cm | 6–8 cm | 8–10 cm | ||
| Position | Center | 0.410 | 0.350 | 0.425 | 0.260 | 0.405 |
| Handheld | 0.415 | 0.350 | 0.440 | 0.260 | 0.410 | |
| Edge | 0.450 | 0.350 | 0.450 | 0.270 | 0.400 | |
| Angled | 0.455 | 0.370 | 0.460 | 0.410 | 0.440 | |
| Fat | 0.420 | 0.320 | 0.445 | 0.260 | 0.360 | |
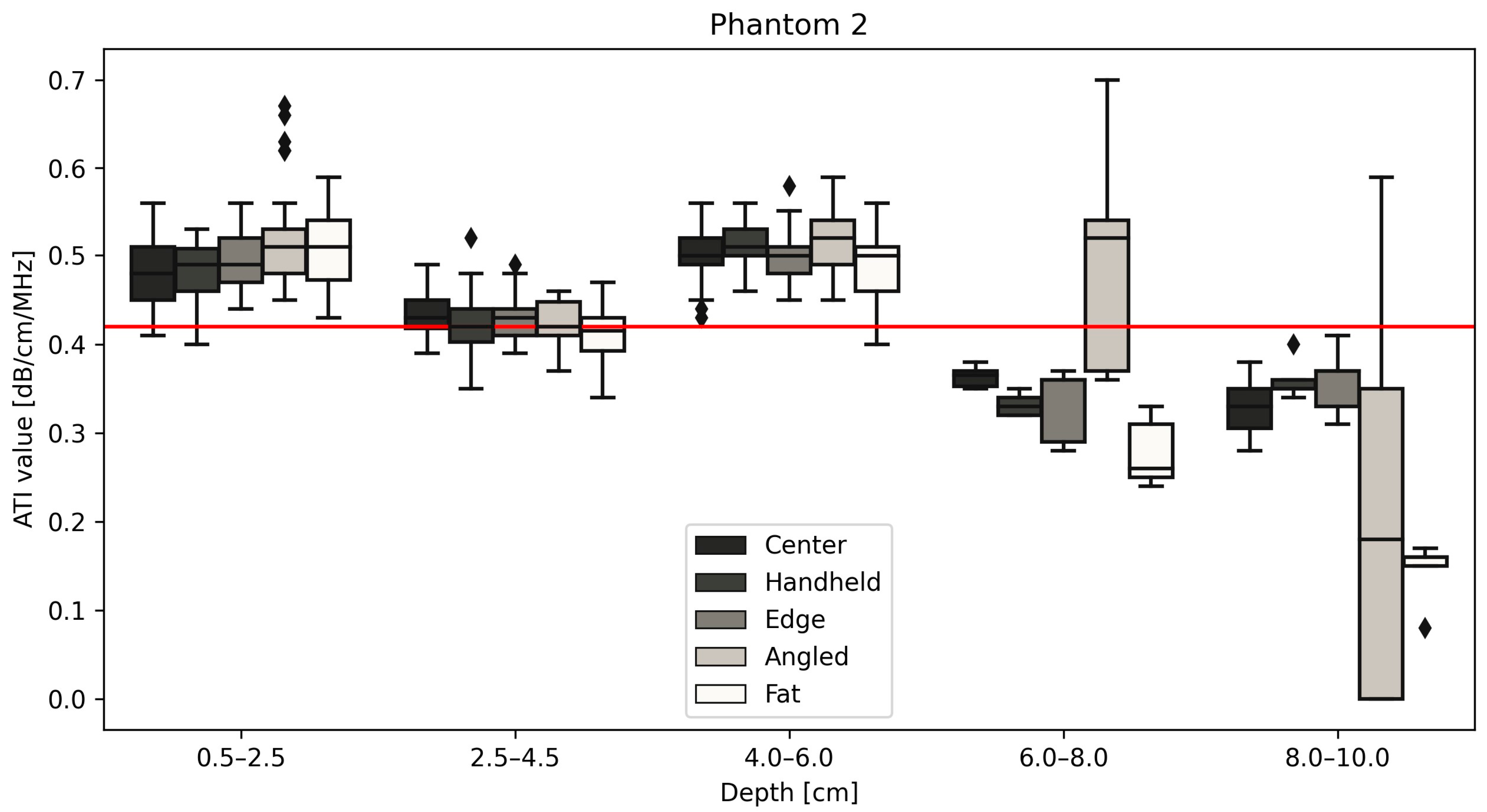
| Phantom 2 Median ATI values | Depth | |||||
| 0.5–2.5 cm | 2.5–4.5 cm | 4–6 cm | 6–8 cm | 8–10 cm | ||
| Position | Center | 0.480 | 0.430 | 0.500 | 0.365 | 0.330 |
| Handheld | 0.490 | 0.420 | 0.510 | 0.330 | 0.350 | |
| Edge | 0.490 | 0.430 | 0.500 | 0.360 | 0.370 | |
| Angled | 0.510 | 0.420 | 0.520 | 0.520 | 0.180 | |
| Fat | 0.510 | 0.415 | 0.500 | 0.260 | 0.160 | |
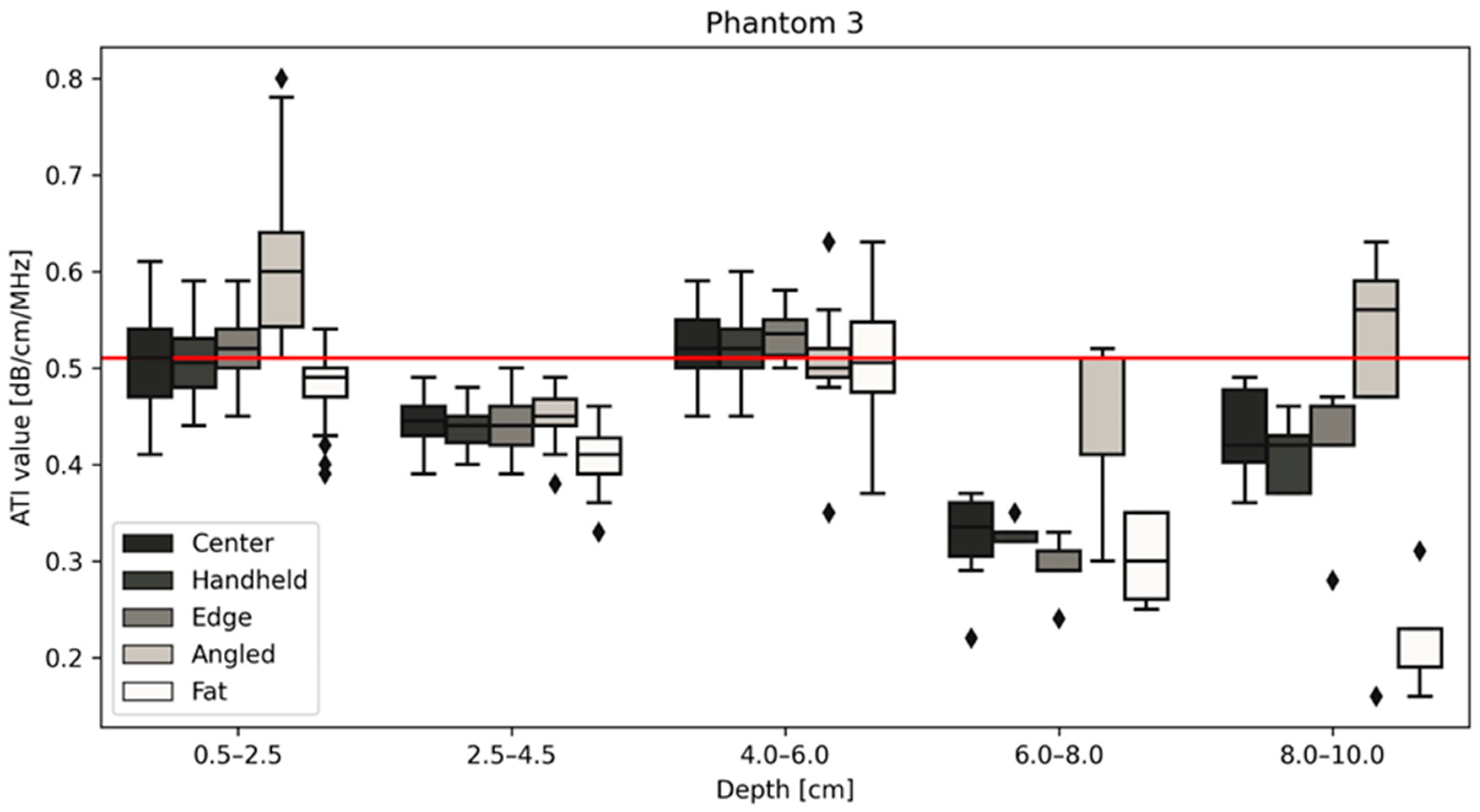
| Phantom 3 Median ATI values | Depth | |||||
| 0.5–2.5 cm | 2.5–4.5 cm | 4–6 cm | 6–8 cm | 8–10 cm | ||
| Position | Center | 0.510 | 0.445 | 0.520 | 0.335 | 0.420 |
| Handheld | 0.505 | 0.440 | 0.520 | 0.330 | 0.420 | |
| Edge | 0.520 | 0.440 | 0.535 | 0.290 | 0.460 | |
| Angled | 0.600 | 0.450 | 0.500 | 0.410 | 0.560 | |
| Fat | 0.490 | 0.410 | 0.505 | 0.300 | 0.190 | |
| Phantom 1 | Phantom 2 | Phantom 3 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Standard Deviation | Certified Value | Mean | Standard Deviation | Certified Value | Mean | Standard Deviation | Certified Value | |
| Center | 0.397 | 0.054 | 0.35 | 0.473 | 0.043 | 0.42 | 0.492 | 0.048 | 0.51 |
| Handheld | 0.403 | 0.050 | 0.473 | 0.048 | 0.491 | 0.049 | |||
| Edge | 0.413 | 0.053 | 0.473 | 0.042 | 0.499 | 0.051 | |||
| Angled | 0.425 | 0.056 | 0.488 | 0.062 | 0.520 | 0.084 | |||
| Fat | 0.392 | 0.071 | 0.469 | 0.056 | 0.463 | 0.062 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hänni, O.; Ruby, L.; Paverd, C.; Frauenfelder, T.; Rominger, M.B.; Martin, A. Confounders of Ultrasound Attenuation Imaging in a Linear Probe Using the Canon Aplio i800 System: A Phantom Study. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14030271
Hänni O, Ruby L, Paverd C, Frauenfelder T, Rominger MB, Martin A. Confounders of Ultrasound Attenuation Imaging in a Linear Probe Using the Canon Aplio i800 System: A Phantom Study. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(3):271. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14030271
Chicago/Turabian StyleHänni, Olivia, Lisa Ruby, Catherine Paverd, Thomas Frauenfelder, Marga B. Rominger, and Alexander Martin. 2024. "Confounders of Ultrasound Attenuation Imaging in a Linear Probe Using the Canon Aplio i800 System: A Phantom Study" Diagnostics 14, no. 3: 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14030271
APA StyleHänni, O., Ruby, L., Paverd, C., Frauenfelder, T., Rominger, M. B., & Martin, A. (2024). Confounders of Ultrasound Attenuation Imaging in a Linear Probe Using the Canon Aplio i800 System: A Phantom Study. Diagnostics, 14(3), 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14030271







