Study of the Lubricating Ability of Protic Ionic Liquid on an Aluminum–Steel Contact
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. NMR Characterization, and Viscosity and Thermagravimetric Analysis of DCi
3.2. Effect of Sliding Velocity
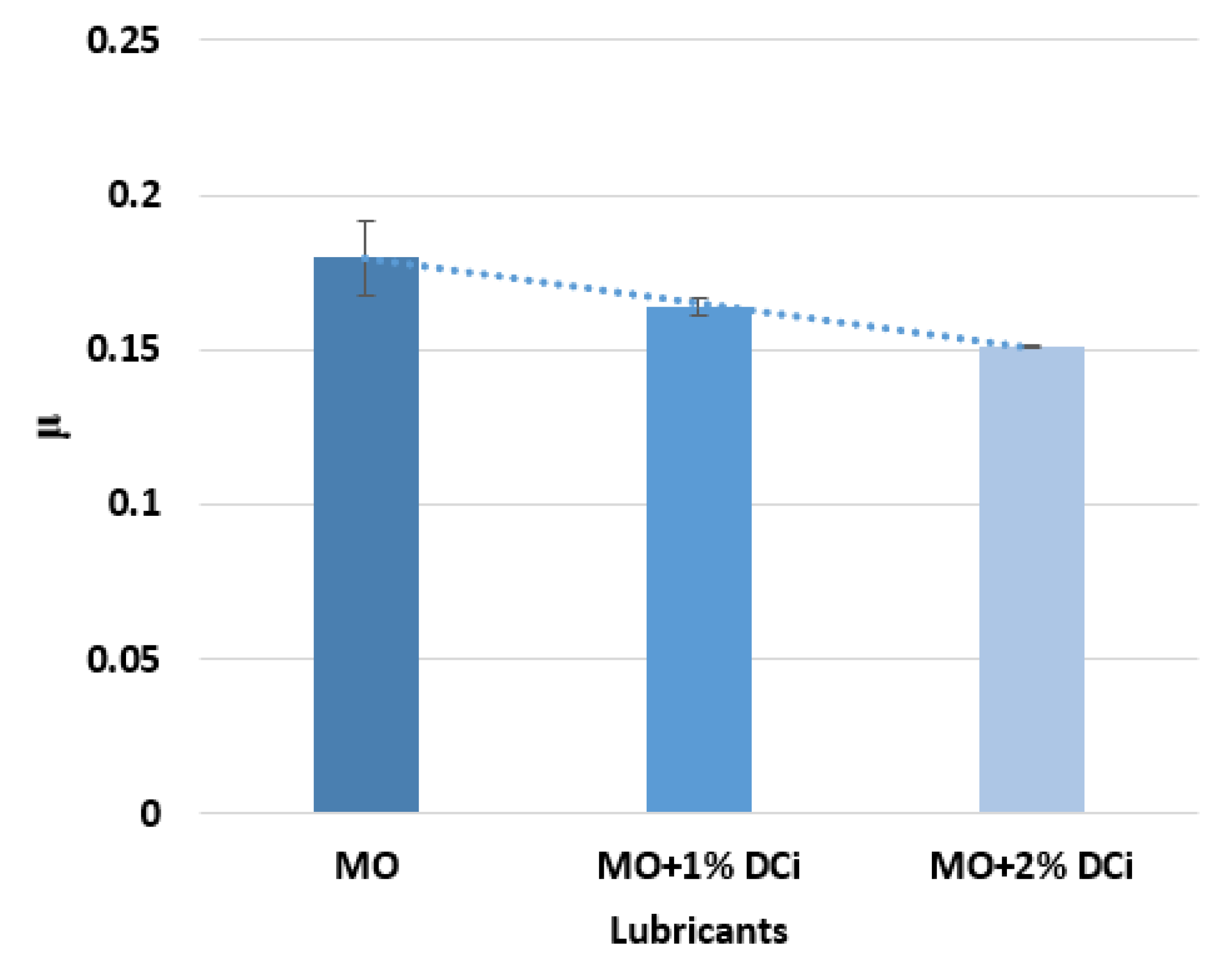
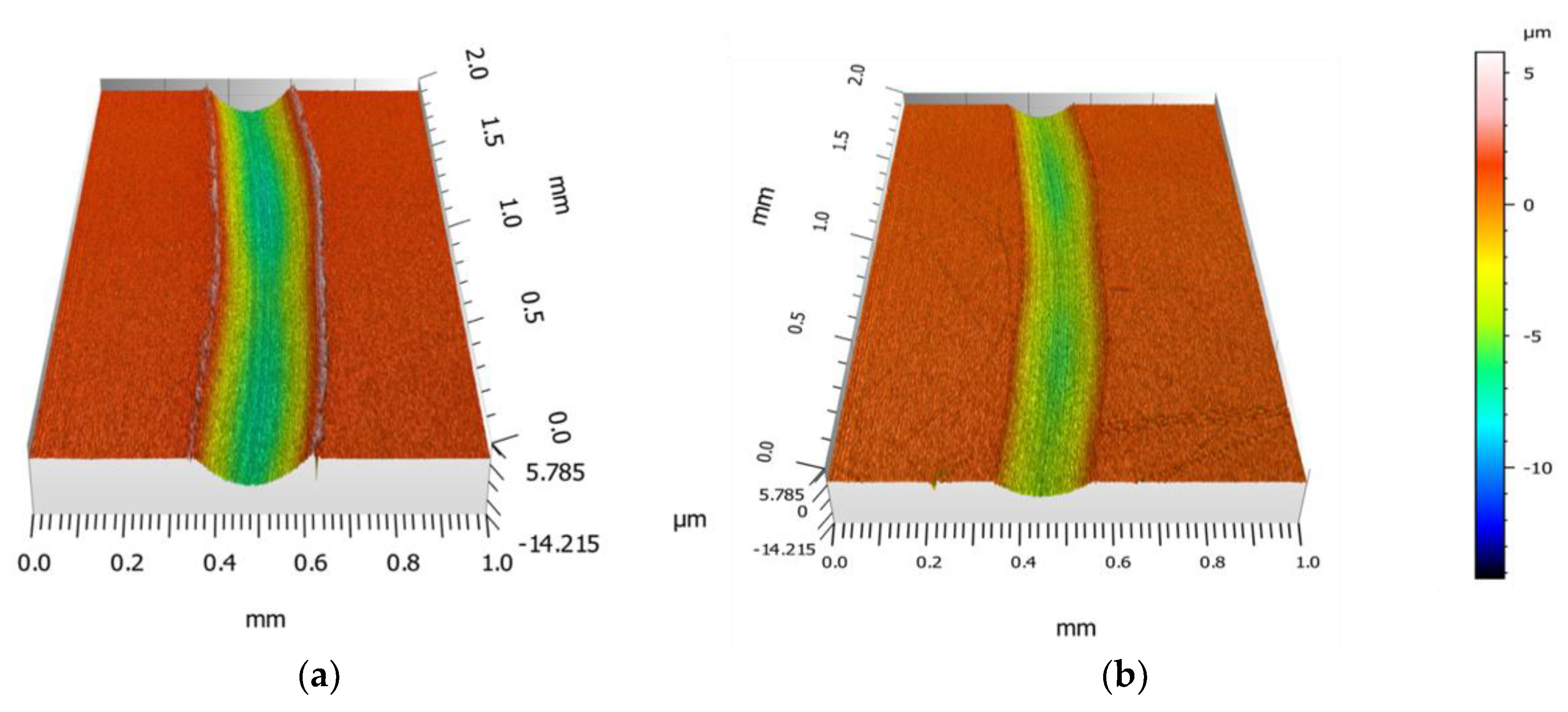
3.3. Effect of Ionic Liquid
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qu, J.; Blau, P.J.; Dai, S.; Luo, H.; Meyer, H.M.; Truhan, J.J. Tribological characteristics of aluminum alloys sliding against steel lubricated by ammonium and imidazolium ionic liquids. Wear 2009, 267, 1226–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.K.; Singh, S.; Shrivastava, A.K. Study of Tribological Behavior of Silicon Carbide Based Aluminum Metal Matrix Composites under Dry and Lubricated Environment. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 3813412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Z.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, S.; Liang, Y.; Liu, W. Effect of the functional groups in ionic liquid molecules on the friction and wear behavior of aluminum alloy in lubricated aluminum-on-steel contact. Tribol. Int. 2005, 38, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, P.; Bermúdez, M.D.; Carrión, F.J.; Martínez-Nicolás, G. Friction and wear of aluminium-steel contacts lubricated with ordered fluids-neutral and ionic liquid crystals as oil additives. Wear 2004, 256, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.; Inamuddin, D. (Eds.) Green Solvents II: Properties and Applications of Ionic Liquids; Springer Science & Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; ISBN 9789400728912. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls, M.A.; Do, T.; Norton, P.R.; Kasrai, M.; Bancroft, G.M. Review of the lubrication of metallic surfaces by zinc dialkyl-dithiophosphates. Tribol. Int. 2005, 38, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Truhan, J.J.; Dai, S.; Luo, H.; Blau, P.J. Ionic liquids with ammonium cations as lubricants or additives. Tribol. Lett. 2006, 22, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, M.; Haselkorn, M.; Iglesias, P. The lubrication ability of ionic liquids as additives for wind turbine gearboxes oils. Lubricants 2016, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gren, P. Feasibility of using digital speckle correlation in the study of seal contacts. Lubr. Sci. 2009, 21, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, A.E.; Khemchandani, B.; Howlett, P.C.; Sun, J.; Macfarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M. Ionic liquids as antiwear additives in base oils: Influence of structure on miscibility and antiwear performance for steel on aluminum. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 11544–11553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, L.J.; Liu, X.Q.; Liang, Y.M.; Xue, Q.J. Effect of tetraalkylphosphonium based ionic liquids as lubricants on the tribological performance of a steel-on-steel system. Tribol. Lett. 2007, 26, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, A.E.; Bermúdez, M.D. Ionic liquids as lubricants of titanium-steel contact. Part 3. Ti6Al4V lubricated with imidazolium ionic liquids with different alkyl chain lengths. Tribol. Lett. 2010, 40, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, M.R.O.; Parise, K.; Ramos, L.B.; Boff, U.; Mattedi, S.; Schaeffer, L.; Malfatti, C.F. Protic ionic liquids used as metal-forming green lubricants for aluminum: Effect of anion chain length. Mater. Res. 2017, 20, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, A.E.; Bermúdez, M.D.; Iglesias, P.; Carrión, F.J.; Martínez-Nicolás, G. 1-N-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium ionic liquids as neat lubricants and lubricant additives in steel-aluminium contacts. Wear 2006, 260, 766–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, A.E.; Bermúdez, M.D. Ionic liquids as lubricants of titanium-steel contact. Tribol. Lett. 2009, 33, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Qiao, D.; Zhang, L.; Feng, D. Study of tribological performance and mechanism of phosphonate ionic liquids for steel/aluminum contact. Tribol. Int. 2015, 84, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, A.E.; Howlett, P.C.; Sun, J.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M. Phosphonium ionic liquids as lubricants for aluminium-steel. WIT Trans. Eng. Sci. 2010, 66, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menne, S.; Anouti, M.; Balducci, A. Aprotic and protic ionic liquids in lithium ion batteries: A comparative study. In ECS Meeting Abstract; The Electrochemical Society: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, H. Protic Ionic Liquids with Ammonium Salts as Lubricants for Magnetic Thin Film Media. Tribol. Lett. 2008, 31, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angell, C.A.; Byrne, N.; Belieres, J. Parallel Developments in Aprotic and Protic Ionic Liquids: Physical Chemistry and Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greaves, T.L.; Drummond, C.J. Protic Ionic Liquids: Properties and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 206–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, M. Tribological Behavior of Protic Ionic Liquids with Dodecylamine Salts of Dialkyldithiocarbamate as Additives in Lithium Complex Grease. Tribol. Lett. 2012, 48, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society for Testing and Materials. ASTM G99-05 Standard Test Method for Wear Testing with a Pin-On-Disk Apparatus1; West Conshohocken: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bermúdez, M.-D.; Carrión, F.-J.; Iglesias, P.; Jiménez, A.-E.; Martínez-Nicolás, G.; Sanes, J. Ionic Liquids Interactions with Materials Surfaces Applications in Tribology and Nanotechnology. In Proceedings of the Materials Research Society (MRS) Spring Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–28 March 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cigno, E.; Magagnoli, C.; Pierce, M.; Iglesias, P. Lubricating ability of two phosphonium-based ionic liquids as additives of a bio-oil for use in wind turbines gearboxes. Wear 2017, 376, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, T.; Jimenez, M.; Sanes, J.; Jimenez, A.E.; Iglesias, M.; Bermudez, M.D. Ultra-low friction with a protic ionic liquid boundary film at the water-lubricated sapphire-stainless steel interface. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

















| Molecular Structure | Empirical Formula | |
|---|---|---|
| Cation | Anion | |
 | 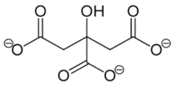 | C18H41O13N3 |
| Material | Modulus of Elasticity (GPa) | Poisson’s Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | 68,900 | 0.33 |
| Steel | 210 | 0.28 |
| Lubricant | Onset Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|
| MO | 291.2 |
| DCi | 191.2 |
| MO + 1% DCi | 300.4 |
| MO + 2% DCi | 300.2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patel, A.; Guo, H.; Iglesias, P. Study of the Lubricating Ability of Protic Ionic Liquid on an Aluminum–Steel Contact. Lubricants 2018, 6, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6030066
Patel A, Guo H, Iglesias P. Study of the Lubricating Ability of Protic Ionic Liquid on an Aluminum–Steel Contact. Lubricants. 2018; 6(3):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6030066
Chicago/Turabian StylePatel, Akshar, Hong Guo, and Patricia Iglesias. 2018. "Study of the Lubricating Ability of Protic Ionic Liquid on an Aluminum–Steel Contact" Lubricants 6, no. 3: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6030066
APA StylePatel, A., Guo, H., & Iglesias, P. (2018). Study of the Lubricating Ability of Protic Ionic Liquid on an Aluminum–Steel Contact. Lubricants, 6(3), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6030066







