Compound Formation and Microstructure of As-Cast High Entropy Aluminums
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Equilibrium Phase Diagram of the Alloys
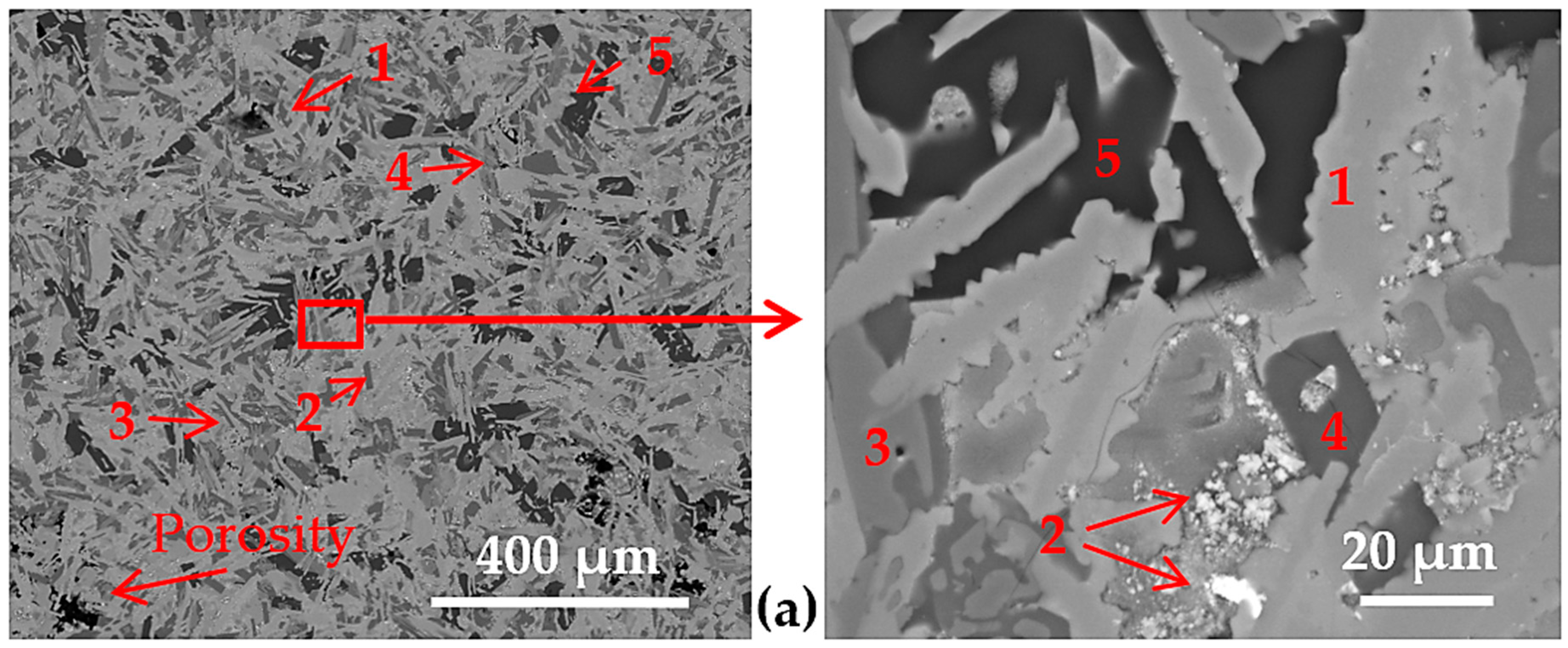
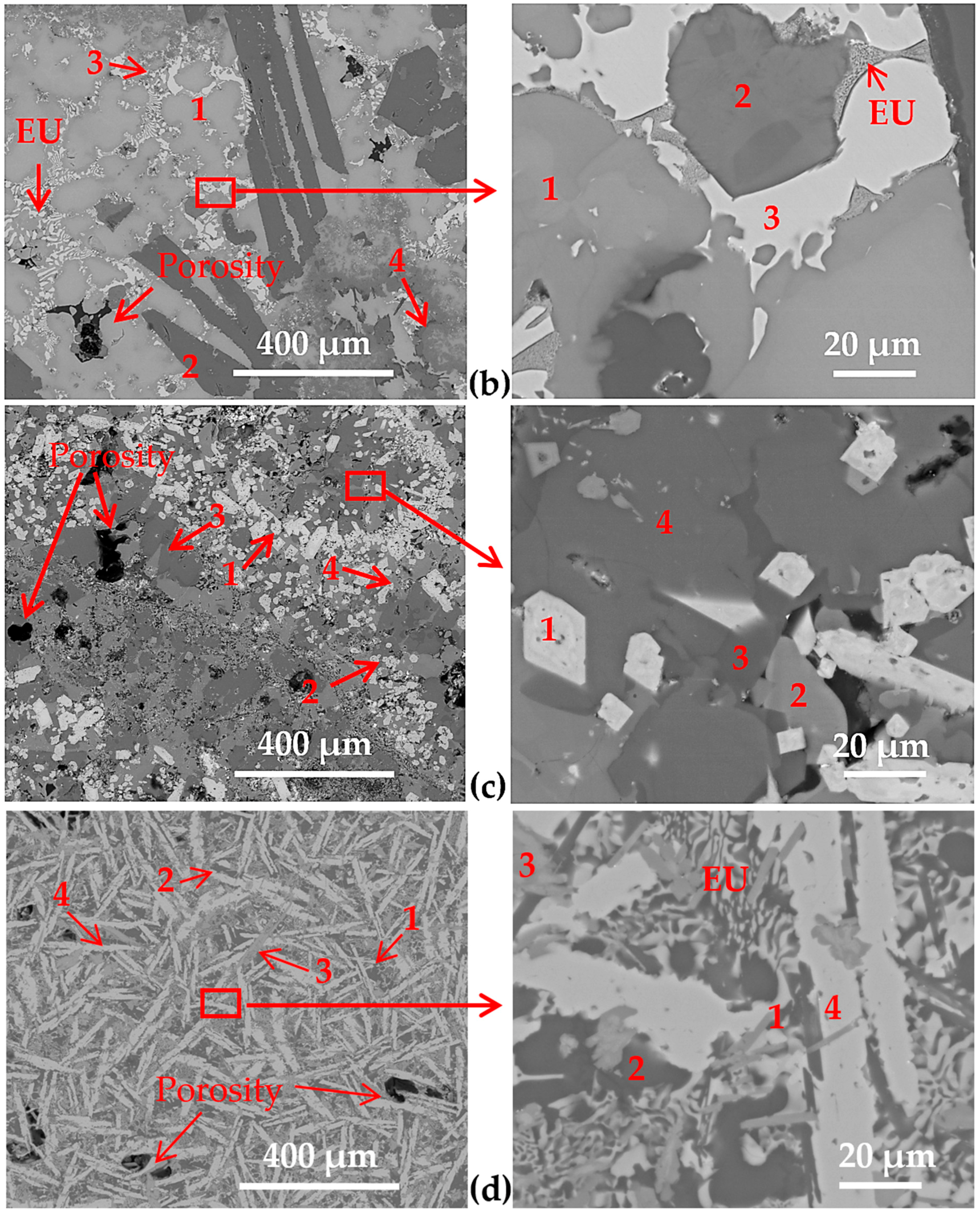
3.2. Microstructure of the Cast Samples
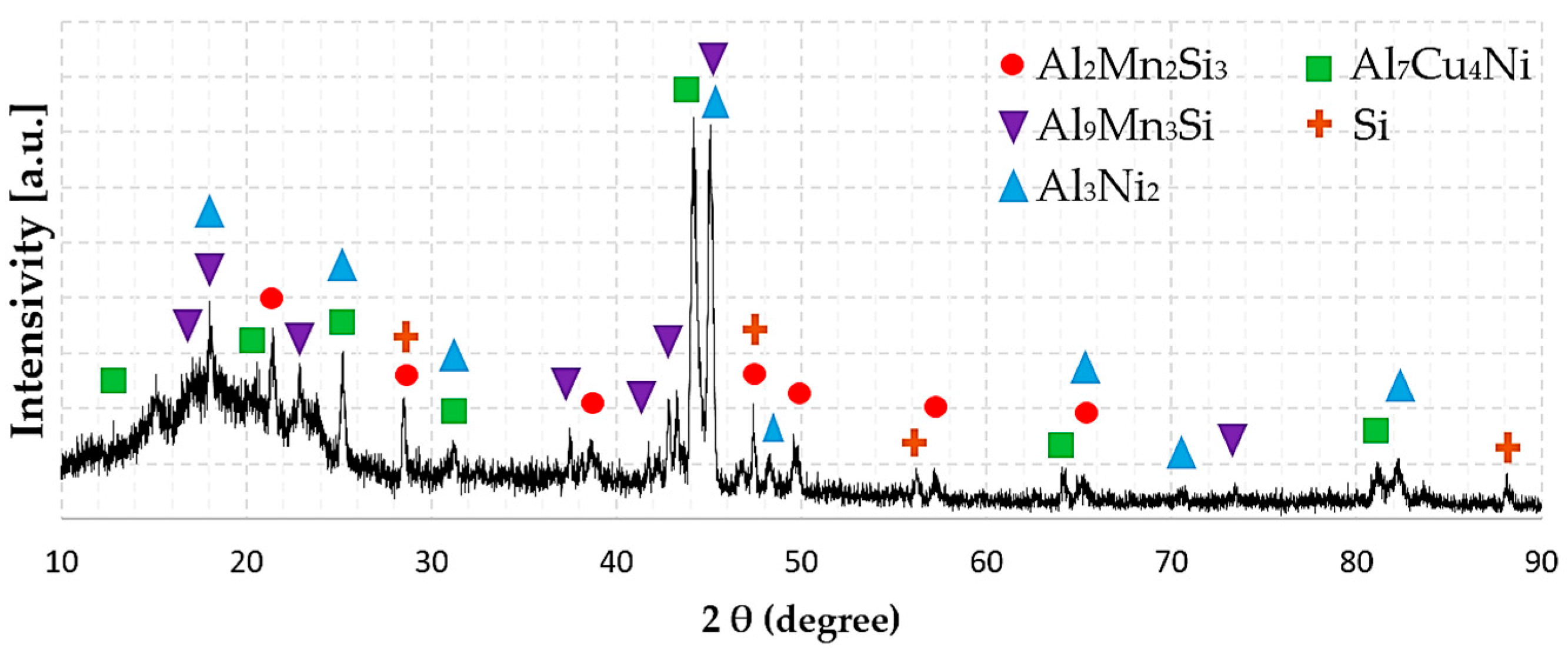
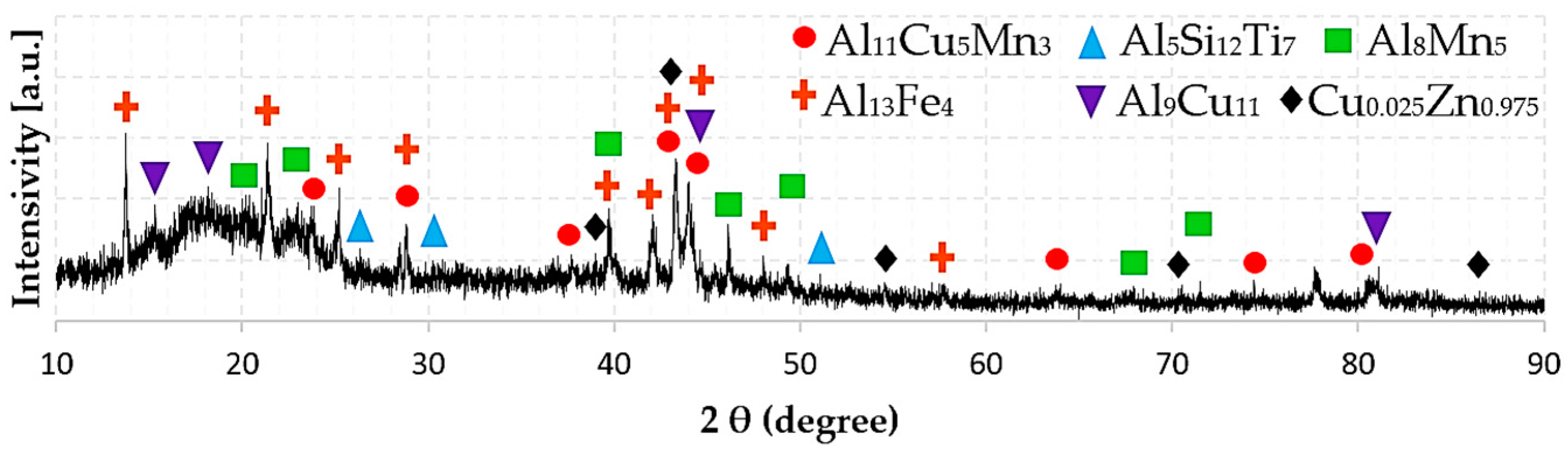
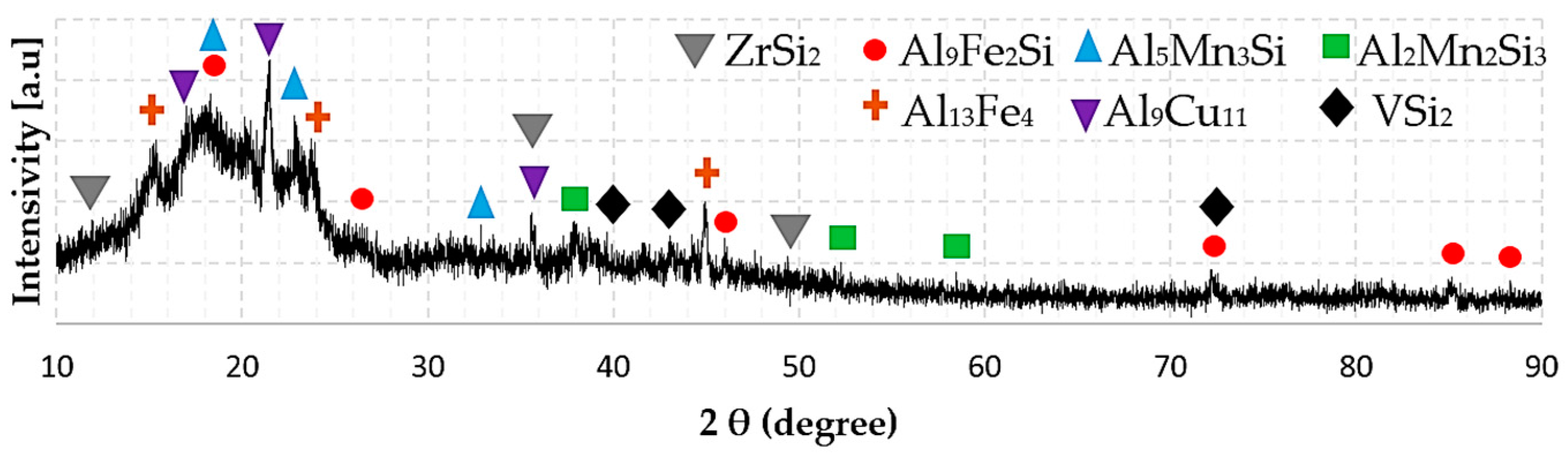
3.3. Phase Composition
3.4. Microhardness of the Samples
4. Conclusions
- The LWHEAs have been made by traditional casting on a scale never done before (~4 kg). Our results suggested that LWHEAs with high strength and high hardness, as well as good liquidity and castability, can be adapted to large-scale industrial production. The non-equimolar character of alloys with a high Al composition has allowed it.
- The comparison between the experimental and Thermo-Calc results, demonstrates the applicability of TCAL5 database in simulating the microstructure of Al-based LWHEAs. Whereas the formation of phases in HEAl-1, HEAl-2, and HEAl-3 alloys correspond to the phases predicted by Thermo-Calc, the formation of phases in HEAl-4 corresponds only partially to the predicted ones.
- Although Al is the major element, none of the microstructures present the typical dendritic microstructure of as-cast traditional Al alloys, consisting on α-Al phase matrix with eutectics or precipitates. Al is well-distributed over the whole alloy, forming different microstructures with the rest of elements.
- In the context of current developments in LWHEAs, the obtained results provide an approach to the development of new alloys. New LWHEAs can provide a combination of low density and microstructures reinforced with ICs that could increase wear, strength, and performance at high temperatures. The obtained results in terms of hardness and density reflect the advantage of these new alloys over traditional lightweight alloys.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375–377, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-H.; Yeh, J.-W. High-Entropy Alloys: A Critical Review. Mater. Res. Lett. 2014, 23, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miracle, D.B.; Senkov, O.N. A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Mater. 2017, 122, 448–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorsse, S.; Miracle, D.B.; Senkov, O.N. Mapping the world of complex concentrated alloys. Acta Mater. 2017, 135, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Y. Prediction of high-entropy stabilized solid-solution in multi-component alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 132, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.J.; Lin, J.P.; Chen, G.L.; Liaw, P.K. Solid-solution phase formation rules for multi-component alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S. Phase selection rules for cast high entropy alloys: An overview. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Ng, C.; Lu, J.; Liu, C.T. Effect of valence electron concentration on stability of fcc or bcc phase in high entropy alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.C.; Zhang, C.; Gao, P.; Zhang, F.; Ouyang, L.Z.; Widom, M.; Hawk, J.A. Thermodynamics of concentrated solid solution alloys. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2017, 21, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, C.; Chen, S.L.; Zhu, J.; Cao, W.S.; Kattner, U.R. An understanding of high entropy alloys from phase diagram calculations. Calphad Comput. Coupling Phase Diagr. Thermochem. 2014, 45, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Varga, L.K.; Chen, N.; Delczeg, L.; Vitos, L. Ab initio investigation of high-entropy alloys of 3D elements. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2013, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lei, Y.; Gray, C.; Wang, G. Examination of Solid-Solution Phase Formation Rules for High Entropy Alloys from Atomistic Monte Carlo Simulations. JOM 2015, 67, 2364–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.C.; Liaw, P.K.; Yeh, J.-W.; Zhang, Y. High-Entropy Alloys: Fundamentals and Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 9783319270135. [Google Scholar]
- Miracle, D.B.; Miller, J.D.; Senkov, O.N.; Woodward, C.; Uchic, M.D.; Tiley, J. Exploration and development of high entropy alloys for structural applications. Entropy 2014, 16, 494–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.C.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K.; Lu, Z.P. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 61, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Jensen, J.K.; Pilchak, A.L.; Miracle, D.B.; Fraser, H.L. Compositional variation effects on the microstructure and properties of a refractory high-entropy superalloy AlMo0.5NbTa0.5TiZr. Mater. Des. 2018, 139, 498–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Senkova, S.V.; Woodward, C.; Miracle, D.B. Low-density, refractory multi-principal element alloys of the Cr-Nb-Ti-V-Zr system: Microstructure and phase analysis. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 1545–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Grosso, M.F.; Bozzolo, G.; Mosca, H.O. Determination of the transition to the high entropy regime for alloys of refractory elements. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 534, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Dong, T. An ab initio and experimental studies of the structure, mechanical parameters and state density on the refractory high-entropy alloy systems. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 714, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanov, N.D.; Shaysultanov, D.G.; Salishchev, G.A.; Tikhonovsky, M.A. Structure and mechanical properties of a light-weight AlNbTiV high entropy alloy. Mater. Lett. 2015, 142, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Huang, X.; Luo, A.A. Phase formations in low density high entropy alloys. Calphad Comput. Coupling Phase Diagr. Thermochem. 2017, 56, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, S.Y.; Cotton, J.D.; Zhang, Y. Phase Stability of Low-Density, Multiprincipal Component Alloys Containing Aluminum, Magnesium, and Lithium. JOM 2014, 66, 2009–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Gao, M.; Lee, C.; Mathes, M.; Zuo, T.; Chen, S.; Hawk, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liaw, P. Design of Light-Weight High-Entropy Alloys. Entropy 2016, 18, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Gupta, M. An Insight into Evolution of Light Weight High Entropy Alloys: A Review. Metals 2016, 6, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, K.M.; Zaddach, A.J.; Niu, C.; Irving, D.L.; Koch, C.C. A Novel Low-Density, High-Hardness, High-entropy Alloy with Close-packed Single-phase Nanocrystalline Structures. Mater. Res. Lett. 2015, 3, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Gao, J.C.; Fan, K. Study to Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Mg Containing High Entropy Alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum 2010, 650, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Gao, J.-C.; Fan, K. Microstructure and mechanical properties of MgMnAlZnCu high entropy alloy cooling in three conditions. Mater. Sci. Forum 2011, 686, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, K.; Yang, Y.; Juan, C.; Chin, T.; Tsai, C.; Yeh, J. A light-weight high-entropy alloy Al20Be20Fe10Si15Ti35. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2017, 841, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.O.; Helander, T.; Höglund, L.; Shi, P.; Sundman, B. Thermo-Calc & DICTRA, computational tools for materials science. Calphad Comput. Coupling Phase Diagr. Thermochem. 2002, 26, 273–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, T.P.; Ding, M.; Ehler, D.S.; Foreman, T.M.; Kaszuba, J.P.; Sauer, N.N. Beryllium in the environment: A review. J. Environ. Sci. Heal. Part A Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2003, 38, 439–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnowski, M.; Gierlotka, S.; Kulik, T. Nanocrystalline Al3Ni2 alloy with high hardness produced by mechanical alloying and high-pressure hot-pressing consolidation. Intermetallics 2013, 42, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabor, D. The physical meaning of indentation and scratch hardness. Br. J. Appl. Phys. 1956, 7, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Alloy | Al | Cu | Si | Mn | Zn | Ni | Fe | Ti | Ca | Zr | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEAl-1 | 40 | 15 | 20 | 5 | 15 | 5 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| HEAl-2 | 45 | 15 | 5 | 5 | 20 | -- | 5 | 5 | -- | -- | -- |
| HEAl-3 | 35 | 5 | 30 | 5 | -- | -- | 5 | -- | -- | 10 | 10 |
| HEAl-4 | 50 | 5 | 20 | -- | -- | 10 | -- | 10 | 5 | -- | -- |
| Alloy | Phase | Phase Constitution |
|---|---|---|
| HEAl-1 | Al2Mn2Si3 | (Al)2 (Mn)2 (Si)3 |
| Al3Ni2 | (Al,Si,Zn)3 (Al,Cu,Ni)2 (Ni,VA)1 | |
| Al7Cu4Ni | (Al)1 (Cu,Ni,VA)1 | |
| τ8-AlMnSi | (Al)6 (Mn)3 (Al,Mn,Si)3 (Al,Si)1 | |
| Diamond (A4) | (Al,Si,Zn) | |
| Epsilon | (Cu,Mn,Zn)1 | |
| HEAl-2 | Al11Cu5Mn3 | (Al)11 (Mn)3 (Cu)5 |
| Al13Fe4 | (Al,Cu)0.63 (Fe,Mn,Zn)0.23 (Al,Si,VA,Zn)0.14 | |
| Al5Si12Ti7 | (Al,Si)0.21 (Si)0.5 (Ti)0.29 | |
| Al8Mn5 | (Al,Zn)12 (Mn)5 (Al,Cu,Mn,Si)9 | |
| θ-AlCu | (Al)9 (Cu,Fe)11 | |
| FeB (B27) | (Fe,Mn,Ti)1 (Al,Si,Zn)1 | |
| δ-FeZn | (Fe)0.06 (Al,Cu,Fe,Mn,Si,Zn)0.18 (Zn)0.53 (Zn)0.24 | |
| HEAl-3 | Al13Fe4 | (Al,Cu)0.63 (Fe,Mn)0.23 (Al,Si,VA)0.14 |
| Al2Mn2Si3 | (Al)2 (Mn)2 (Si)3 | |
| Al9Fe2Si2 | (Al)0.6 (Fe)0.15 (Si)0.1 (Al,Si)0.15 | |
| θ-AlCu | (Al)9 (Cu,Fe)11 | |
| τ8-AlMnSi | (Al)6 (Mn)3 (Al,Mn,Si)3 (Al,Si)1 | |
| CrSi2 (C40) | (Si,V)1 (Al,Si)2 | |
| SI2Zr (C49) | (Si)2 (Zr)1 | |
| HEAl-4 | Al2Cu (C16) | (Al,Ni)2 (Al,Cu,Ni,Si)1 |
| Al3Ni (D011) | (Al,Ni)0.75 (Ni)0.25 | |
| Al5Si12Ti7 | (Al,Si)0.21 (Si)0.5 (Ti)0.29 | |
| CaSi2 | (Ca)0.33 (Si)0.67 | |
| Diamond (A4) | (Al, Si, Zn) | |
| FCC (L12) | (Al,Ca,Cu,Ni,Si,Ti)0.75 (Al,Ca,Cu,Ni,Si,Ti)0.25 (VA)1 |
| Alloy | Region | Al | Cu | Si | Mn | Zn | Ni | Fe | Ti | Ca | Zr | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEAl-1 | 1 | 57 | 11 | 5 | -- | -- | 27 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| 2 | 48 | 6 | -- | -- | 46 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| 3 | 25 | -- | 42 | 33 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| 4 | 62 | 3 | 17 | 16 | 2 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| 5 | -- | 2 | 98 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| overall | 36 | 12 | 34 | 6 | 7 | 5 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| HEAl-2 | 1 | 42 | 42 | -- | -- | 15 | -- | 1 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| 2 | 52 | 3 | 16 | 7 | 3 | -- | 19 | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| 3 | 7 | 22 | -- | -- | 71 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| 4 | 5 | 2 | -- | -- | 2 | -- | -- | 91 | -- | -- | -- | |
| overall | 38 | 15 | 16 | 4 | 10 | -- | 6 | 11 | -- | -- | -- | |
| HEAl-3 | 1 | -- | -- | 51 | 3 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 21 | 25 |
| 2 | 26 | -- | 32 | 7 | -- | -- | 13 | -- | -- | 20 | 2 | |
| 3 | 66 | 3 | 15 | 8 | -- | -- | 8 | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| 4 | 62 | 26 | 7 | 3 | -- | -- | 1 | -- | -- | -- | 1 | |
| overall | 38 | 6 | 32 | 5 | -- | -- | 5 | -- | -- | 8 | 6 | |
| HEAl-4 | 1 | 34 | 1 | 49 | -- | -- | 1 | -- | -- | 15 | -- | -- |
| 2 | 91 | 5 | 4 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| 3 | 13 | -- | 60 | -- | -- | -- | -- | 27 | -- | -- | -- | |
| 4 | 59 | 13 | 2 | -- | -- | 26 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| overall | 56 | 7 | 21 | -- | -- | 7 | -- | 4 | 5 | -- | -- |
| Alloy | Phase | Space Group | Lattice Parameter (Å) | Thermo-Calc |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEAl-1 | Al2Mn2Si3 | P6 (174) | a = b = 9.61, c = 3.56 | Al2Mn2Si3 |
| Al3Ni2 | Pm1 (164) | a = b = 4.06, c = 4.90 | Al3Ni2 | |
| Al7Cu4Ni | Rm (166) | a = b = 4.10, c = 4.00 | Al7Cu4Ni | |
| Al9Mn3Si | P63/mmc (194) | a = b = 7.51, c = 7.74 | τ8-AlMnSi | |
| Si | Fdm (227) | a = b = c = 5.43 | Diamond (A4) | |
| HEAl-2 | Al11Cu5Mn3 | P (0) | a = 12.10, b = 24.08, c = 19.20 | Al11Cu5Mn3 |
| Al13Fe4 | C2/m (12) | a = 15.49, b = 8.08, c = 12.47 | Al13Fe4 | |
| Al5Si12Ti7 | I41/amd (141) | a = b = 3.57, c = 27.15 | Al5Si12Ti7 | |
| Al8Mn5 | Rm (166) | a = b = 12.64, c =15.85 | Al8Mn5 | |
| Al9Cu11 | Imm2 (44) | a = 4.09, b = 7.03, c = 9.98 | θ-AlCu | |
| Cu0.025Zn0.975 | P63/mmc (194) | a = 12.1, b = 24.08, c = 19.20 | δ-FeZn | |
| HEAl-3 | Al13Fe4 | C2/m (12) | a = 15.49, b = 8.08, c = 12.47 | Al13Fe4 |
| Al2Mn2Si3 | P6 (174) | a = b = 9.61, c = 3.56 | Al2Mn2Si3 | |
| Al9Fe2Si | C2/c (15) | a = 20.80, b = 6.16, c = 6.15 | Al9Fe2Si | |
| Al9Cu11 | Imm2 (44) | a = 4.09, b = 7.03, c = 9.98 | θ-AlCu | |
| Al9Mn3Si | P63/mmc (194) | a = b = 7.51, c = 7.74 | τ8-AlMnSi | |
| VSi2 | P6222 (180) | a = b = 4.57, c = 6.37 | CrSi2 (C40) | |
| ZrSi2 | Cmcm (63) | a = 3.71, b = 14.73, c = 3.66 | Si2Zr (C49) | |
| HEAl-4 | CuAl2 | I4/mcm (140) | a = b = 6.07, c = 4.89 | Al2Cu (C16) |
| Al3Ni2 | Pm1 (164) | a = b = 4.06, c = 4.90 | Al3Ni (D011) | |
| Al5Si12Ti7 | I41/amd (141) | a = b = 3.57, c = 27.15 | Al5Si12Ti7 | |
| Al2CaSi2 | Pm1 (164) | a = b = 4.13, c = 7.14 | CaSi2 | |
| α-Al | Fmm (225) | a = b = c = 4.05 | FCC (L12) |
| Alloy | Hardness (Hv) | Density (g/cm3) | σy (Mpa) | σy/Density (MPa/g·cm−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEAl-1 | 887 ± 273 | 4.08 | 2900 | 711 |
| HEAl-2 | 744 ± 134 | 5.07 | 2432 | 480 |
| HEAl-3 | 751 ± 54 | 3.96 | 2455 | 620 |
| HEAl-4 | 437 ± 88 | 3.33 | 1429 | 429 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanchez, J.M.; Vicario, I.; Albizuri, J.; Guraya, T.; Koval, N.E.; Garcia, J.C. Compound Formation and Microstructure of As-Cast High Entropy Aluminums. Metals 2018, 8, 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8030167
Sanchez JM, Vicario I, Albizuri J, Guraya T, Koval NE, Garcia JC. Compound Formation and Microstructure of As-Cast High Entropy Aluminums. Metals. 2018; 8(3):167. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8030167
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanchez, Jon Mikel, Iban Vicario, Joseba Albizuri, Teresa Guraya, Natalia E. Koval, and Jose Carlos Garcia. 2018. "Compound Formation and Microstructure of As-Cast High Entropy Aluminums" Metals 8, no. 3: 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8030167
APA StyleSanchez, J. M., Vicario, I., Albizuri, J., Guraya, T., Koval, N. E., & Garcia, J. C. (2018). Compound Formation and Microstructure of As-Cast High Entropy Aluminums. Metals, 8(3), 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8030167






