A Study on the Microstructural Evolution of a Low Alloy Steel by Different Shot Peening Treatments
Abstract
:- Conventional and severe shot peening was performed on a low-alloy varying the surface coverage and keeping Almen intensity constant.
- The surface state was examined and analyzed in terms of microstructure, roughness, hardness, residual stresses, and surface work hardening.
- The surface state is strongly influenced by the coverage, even if saturation is noted, when coverage exceeds 5000%
- It is possible to develop severe shot peening treatments targeted to particular applications.
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Material and Samples
2.2. Shot Peening Treatment
2.3. Surface Roughness
2.4. Microstructure
2.5. Microhardness
2.6. Residual Stresses and Full Width at Half Maximum
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Roughness
3.2. Microstructure
3.2.1. Optical Analysis
3.2.2. FEGSEM Analysis
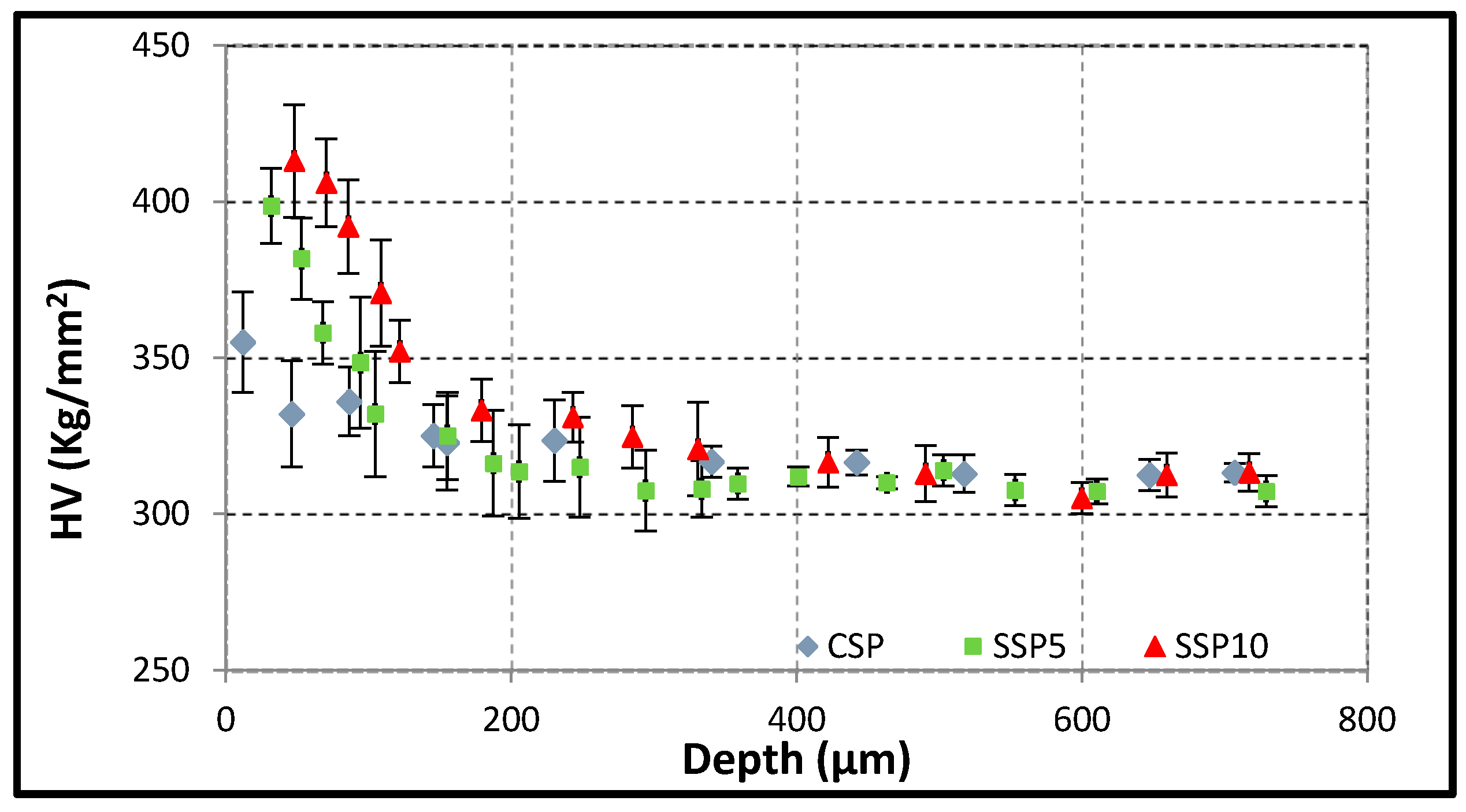
3.3. Microhardness Measurements
3.4. XRD Measurements
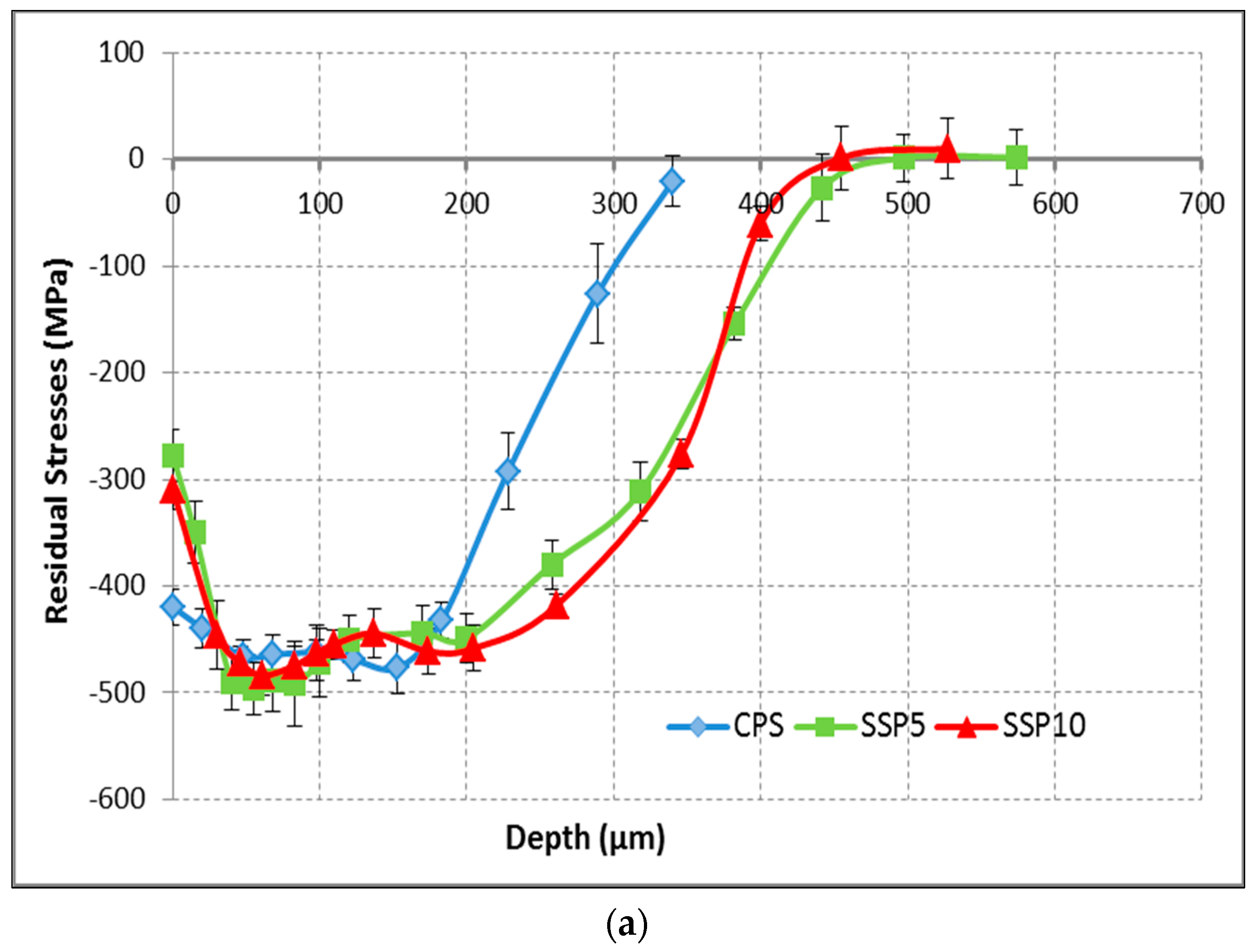
3.4.1. Residual Stresses
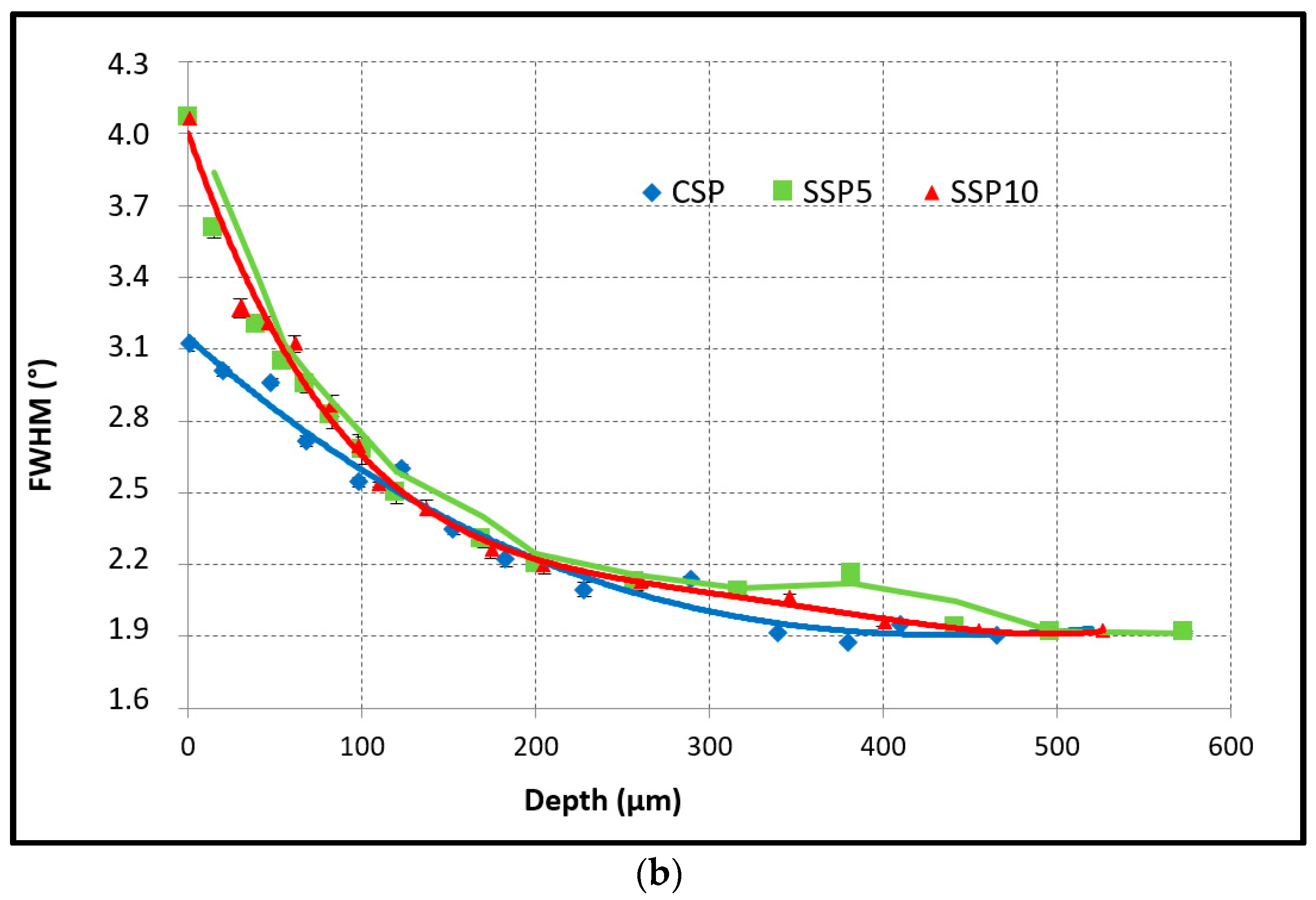
3.4.2. Full Width Half Maximum Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yinsheng, H.; Keun-Bong, Y.; Houyu, M.; Keesam, S. Study of the austenitic stainless steel with gradient structured surface fabricated via shot peening. Mater. Lett. 2018, 215, 187–190. [Google Scholar]
- Bandar, A.; Jenn-Ming, Y. Improving the surface quality and mechanical properties by shot-peening of 17-4 stainless steel fabricated by additive manufacturing. Mater. Des. 2016, 110, 914–924. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin, G.; Etienne, P.; Franck, M.; Catherine, V. A non-local approach to model the combined effects of forging defects and shot-peening on the fatigue strength of a pearlitic steel. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2018, 93, 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Bandar, A.; Jenn-Ming, Y. Integration of heat treatment with shot peening of 17-4 stainless steel fabricated by direct metal laser sintering. JOM 2017, 11, 2309–2313. [Google Scholar]
- Segurado, E.; Belzunce, F.J.; Fernández-Pariente, I. Effects of low intensity shot peening treatments applied with different types of shots on the fatigue performance of a high-strength steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 340, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Estrin, Y.; Horita, Z.; Langdon, T.G.; Zechetbauer, M.J.; Zhu, Y.T. Producing bulk ultra-fine-grained materials by severe plastic deformation. JOM 2006, 58, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.Y.; Lian, J.S.; Jiang, Q. Effect of grain size on corrosion behavior of electrodeposited bulk nanocrystalline Ni. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, K.M.S.; Koch, C.C.; Fedkiw, P.S. Improved corrosion behavior of nanocrystalline zinc produced by pulse-current electrodeposition. Corros. Sci. 2004, 46, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Bush, M.B. The effects of grain size and porosity on the elastic modulus of nanocrystalline materials. Nanostruct. Mater. 1999, 11, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C. The structure and properties of nanocrystalline materials: Issues and concerns. JOM 2002, 54, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.B.; Tao, N.R.; Li, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, G.; Luc, J.; Lua, K. Effect of surface nanocrystallization on friction and wear properties in low carbon steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2003, 352, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasheghani Farahani, M.; Emadoddin, E.; Emamyb, M.; Honarbakhsh Raouf, A. Effect of grain refinement on mechanical properties and sliding wear resistance of extruded Sc-free 7042 aluminum alloy. Mater. Des. 2014, 54, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Chen, J.; Guan, D. Friction and wear behaviors of nanocrystalline surface layer of medium carbon steel. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 2216–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, M.; Bagherifard, S.; Guagliano, M.; Fernández Pariente, I. Influence of severe shot peening on wear behaviour of an aluminium alloy. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2014, 37, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherifard, S.; Guagliano, M. Fatigue behavior of a low-alloy steel with nanostructured surface obtained by severe shot peening. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2012, 81, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherifard, S.; Fernández Pariente, I.; Ghelichi, R.; Guagliano, M. Fatigue properties of nanocrystallized surfaces obtained by high energy shot peening. Procedia Eng. 2010, 2, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherifard, S.; Fernandez Pariente, I.; Ghelichi, R.; Guagliano, M. Effect of severe shot peening on microstructure and fatigue strength of cast iron. Int. J. Fatigue 2014, 65, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.W.; Villegas, J.C.; Yuan, W.; Fielden, D.; Shaw, L.; Liaw, P.K.; Klarstrom, D.L. A study of the effect of nanostructured surface layers on the fatigue behaviors of a C-2000 superalloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 468, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lin, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, W.; Xue, Q.; Hu, L.; Zhang, J. Electrochemical corrosion behavior of nanocrystalline Co coatings explained by higher grain boundary density. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 4342–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Xue, Q.; Hua, L.; Xu, T. Grain size effect in corrosion behavior of electrodeposited nanocrystalline Ni coatings in alkaline solution. Scr. Mater. 2006, 55, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleiter, H. Nanocrystalline materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 1989, 33, 223–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, K.; Dillon, S.J. Scaling effects on grain boundary diffusivity; Au in Cu. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 1851–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Sui, M.L. Thermal expansion behaviors in nanocrystalline materials with a wide grain size range. Acta Metall. Mater. 1995, 43, 3325–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.S.C.; Koch, C.C. The hall-petch relationship in nanocrystalline iron produced by ball milling. Scr. Metall. Mater. 1990, 24, 1599–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fecht, H.J.; Hellstern, E.; Fu, Z.; Johnson, W.L. Nanocrystalline metals prepared by high-energy ball milling. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1990, 21, 2333–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moelle, C.H.; Fecht, H.J. Thermal stability of nanocrystalline iron prepared by mechanical attrition. Nanostruct. Mater. 1995, 6, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Umemoto, M.; Liu, Z.G.; Tsuchiya, K. Formation mechanism and annealing behavior of nanocrystalline ferrite in pure Fe fabricated by ball milling. ISIJ Int. 2001, 41, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilmann, P.; Clark, W.A.T.; Rigney, D.A. Orientation determination of subsurface cells generated by sliding. Acta Metall. 1983, 31, 1293–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D.A.; Dawson, D.B.; Korellis, J.S.; Weingarten, L.I. A microstructurally based method for stress estimates. Wear 1995, 181, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.P.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, J.X.; Li, D.Y.; Manc, C.S.; Shepard, M.J.; Zhai, T. Enhancement of fatigue and corrosion properties of pure Ti by sandblasting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 429, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Li, D. Mechanical and electrochemical behavior of nanocrystalline surface of 304 stainless steel. Electrochim. Acta 2002, 47, 3939–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, N.R.; Sui, M.L.; Lu, J.; Lua, K. Surface nanocrystallization of iron induced by ultrasonic shot peening. Nanostruct. Mater. 1999, 11, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Lu, J.; Lu, K. Surface nanocrystallization of 316L stainless steel induced by ultrasonic shot peening. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 286, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Tao, N.; Hong, Y.; Xu, B.; Lu, J.; Lu, K. Microstructure and evolution of mechanically-induced ultrafine grain in surface layer of AL-alloy subjected to USSP. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 2075–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherifard, S.; Fernandez Pariente, I.; Ghelichi, R.; Guagliano, M. Fatigue behavior of notched steel specimens with nanocrystallized surface obtained by severe shot peening. Mater. Des. 2013, 45, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherifard, S.; Slawik, S.; Fernandez Pariente, I.; Pauly, C.; Mücklich, F.; Guagliano, M. Nanoscale surface modification of AISI 316L stainless steel by severe shot peening. Mater. Des. 2016, 102, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guagliano, M.; Vergani, L. An approach for prediction of fatigue strength of shot peened components. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2004, 71, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, C.; Guagliano, M.; Vergani, L. Fatigue crack growth behaviour of nitrided and shot peened specimens. SID 2005, 1, 253–265. [Google Scholar]
- J443: Procedures for Using Standard Shot Peening Almen test Strip; SAE Interational: New York, NY, USA, 2010.
- Umemoto, M.; Todaka, Y.; Tsuchiya, K. Formation of nanocrystalline structure in steels by air blast shot peening. Mater. Trans. 2003, 44, 1488–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherifard, S.; Guagliano, M. Review of shot peening processes to obtain nanocrystalline surfaces in metal alloys. Surf. Eng. 2009, 25, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemoto, M. Nanocrystallization of steels by severe plastic deformation. Mater. Trans. 2003, 44, 1900–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Shaw, L. Comparison between shot peening and surface nanocrystallization and hardening processes. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 463, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, D.; Abyaneh, M.Y. Theoretical basis of shot peening coverage control. Shot Peener 1999, 9, 28–30. [Google Scholar]
- Bagherifard, S.; Ghelichi, R.; Guagliano, M. On the shot peening surface coverage and its assessment by means of finite element simulation: A critical review and some original developments. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 259, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, O.; Varol, R. Almen intensity effect on microstructure and mechanical properties of low carbon steel subjected to severe shot peening. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 290, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyan, I.C.; Cohen, J.B. Residual Stress Measurement by Diffraction and Interpretation; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Sadegh, P.A.; Ali-Reza, K.R.; Abolfazl, B. Surface nanocrystallization and gradient microstructural evolutions in the surface layers of 321 stainless steel alloy treated via severe shot peening. Vacuum 2017, 144, 152–159. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Pariente, I.; Bagherifard, S.; Guagliano, M.; Ghelichi, R. Fatigue behavior of nitrided and shot peened steel with artificial small surface defects. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2013, 103, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
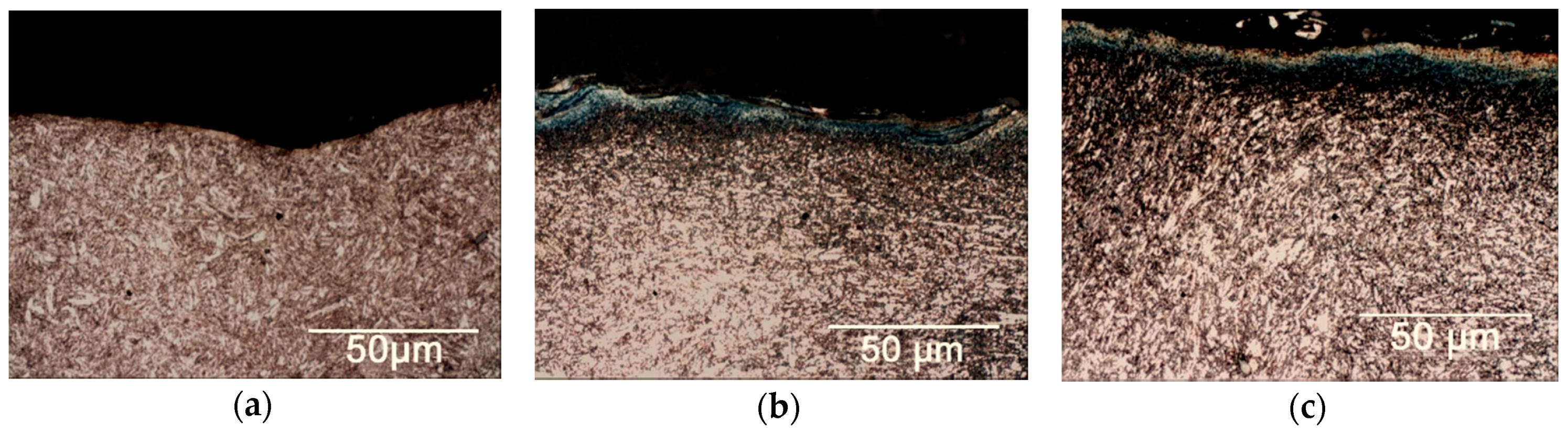
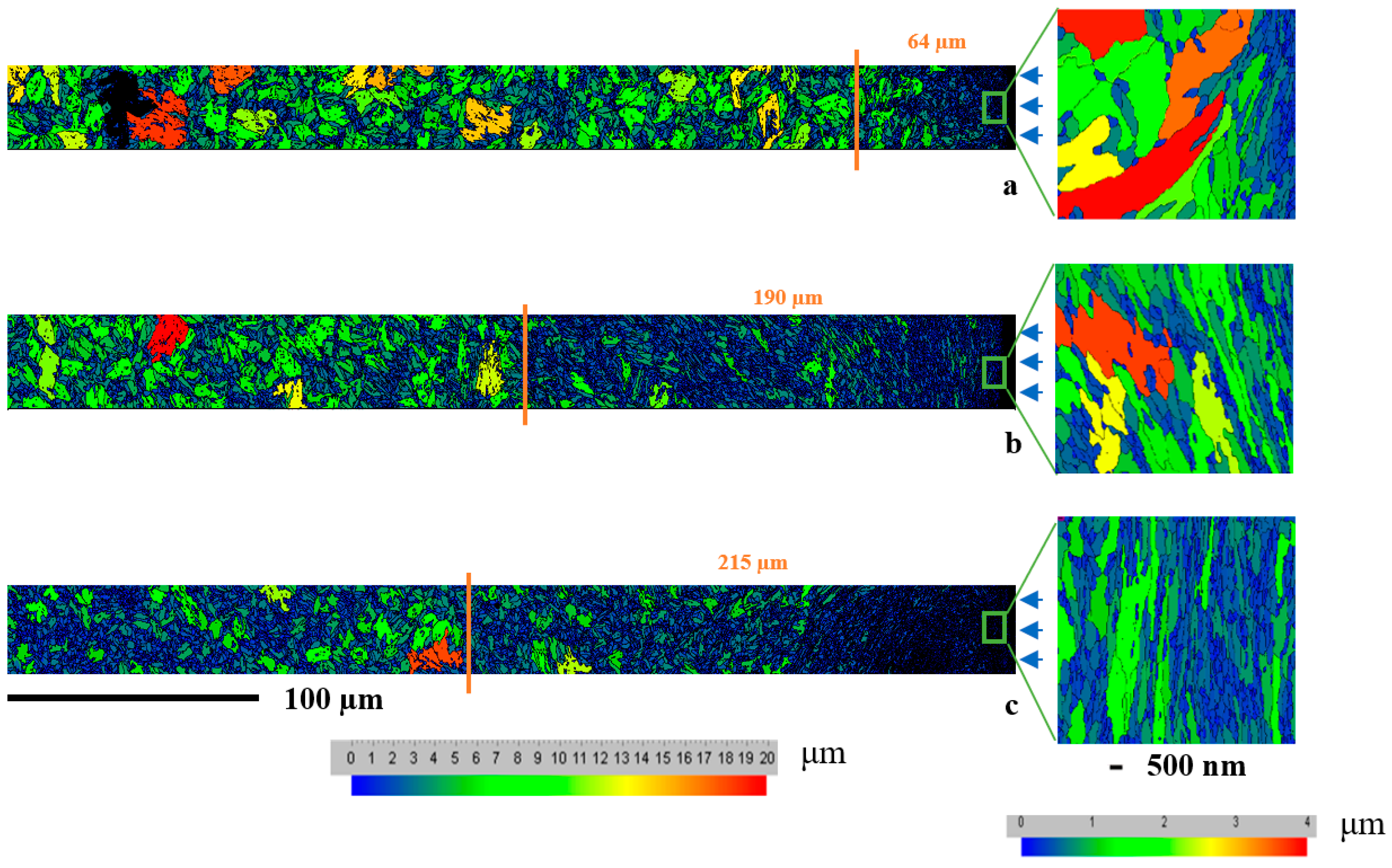
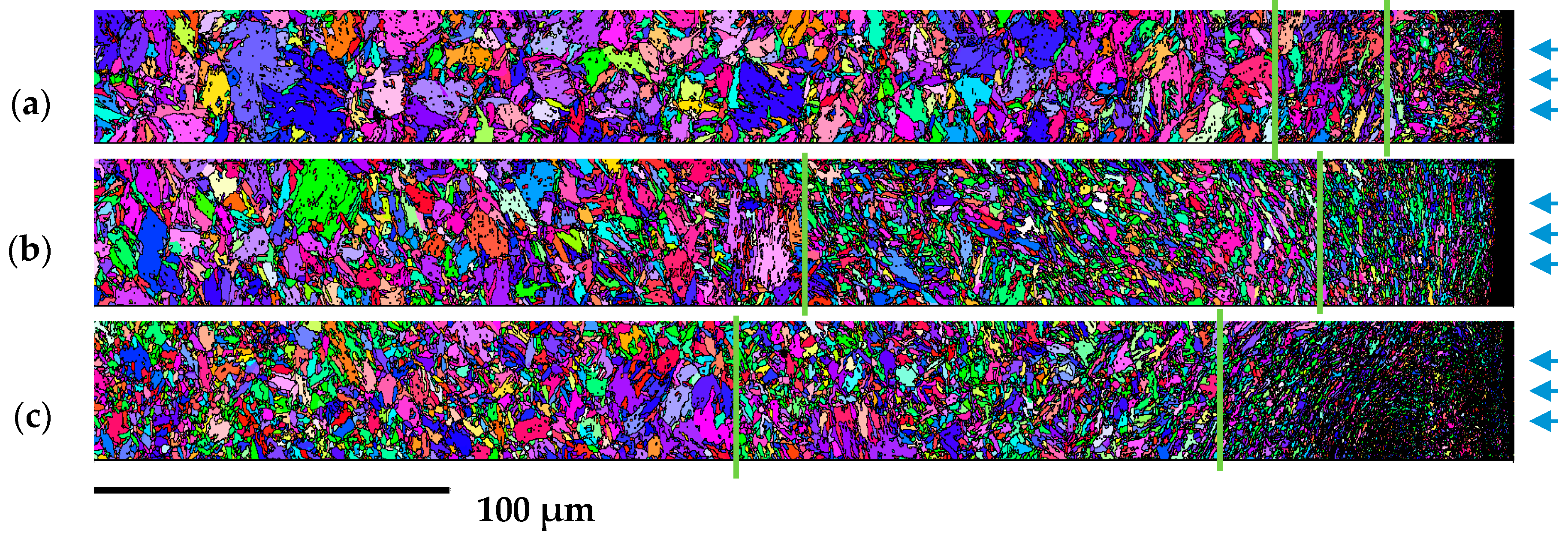
| C | Mn | P | S | Cr | Si | Mo | Ni | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min | max | min | Max | Max | Max | min | Max | max | min | max | min | max |
| 0.35 | 0.43 | 0.50 | 0.80 | 0.025 | 0.035 | 0.60 | 1.00 | 0.4 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.70 | 1.00 |
| Series | Coverage (%) | Ra (μm) | Rz (μm) | Rmax (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSP | 100 | 5.84 ± 0.50 | 27.94 ± 2.62 | 34.30 ± 4.01 |
| SSP5 | 5000 | 7.05 ± 0.89 | 33.75 ± 3.31 | 44.37 ± 5.81 |
| SSP10 | 10,000 | 6.58 ± 0.51 | 31.71 ± 2.47 | 44.83 ± 8.41 |
| Serie | Coverage (%) | Average Grain Size in Surface Layer (μm) | Max. Diameter (μm) | Total Number of Grains |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSP | 100 | 0.292 ± 0.471 | 3.9398 | 346 |
| SSP5 | 5000 | 0.28 ± 0.363 | 3.6772 | 477 |
| SSP10 | 10,000 | 0.185 ± 0.182 | 1.9633 | 752 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González, J.; Peral, L.-B.; Colombo, C.; Fernández Pariente, I. A Study on the Microstructural Evolution of a Low Alloy Steel by Different Shot Peening Treatments. Metals 2018, 8, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8030187
González J, Peral L-B, Colombo C, Fernández Pariente I. A Study on the Microstructural Evolution of a Low Alloy Steel by Different Shot Peening Treatments. Metals. 2018; 8(3):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8030187
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález, Juan, Luis-Borja Peral, Chiara Colombo, and Ines Fernández Pariente. 2018. "A Study on the Microstructural Evolution of a Low Alloy Steel by Different Shot Peening Treatments" Metals 8, no. 3: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8030187
APA StyleGonzález, J., Peral, L.-B., Colombo, C., & Fernández Pariente, I. (2018). A Study on the Microstructural Evolution of a Low Alloy Steel by Different Shot Peening Treatments. Metals, 8(3), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8030187






