Surface Roughness Investigation and Stress Modeling by Finite Element on Orthogonal Cutting of Copper
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Work
2.1. Materials and Methods
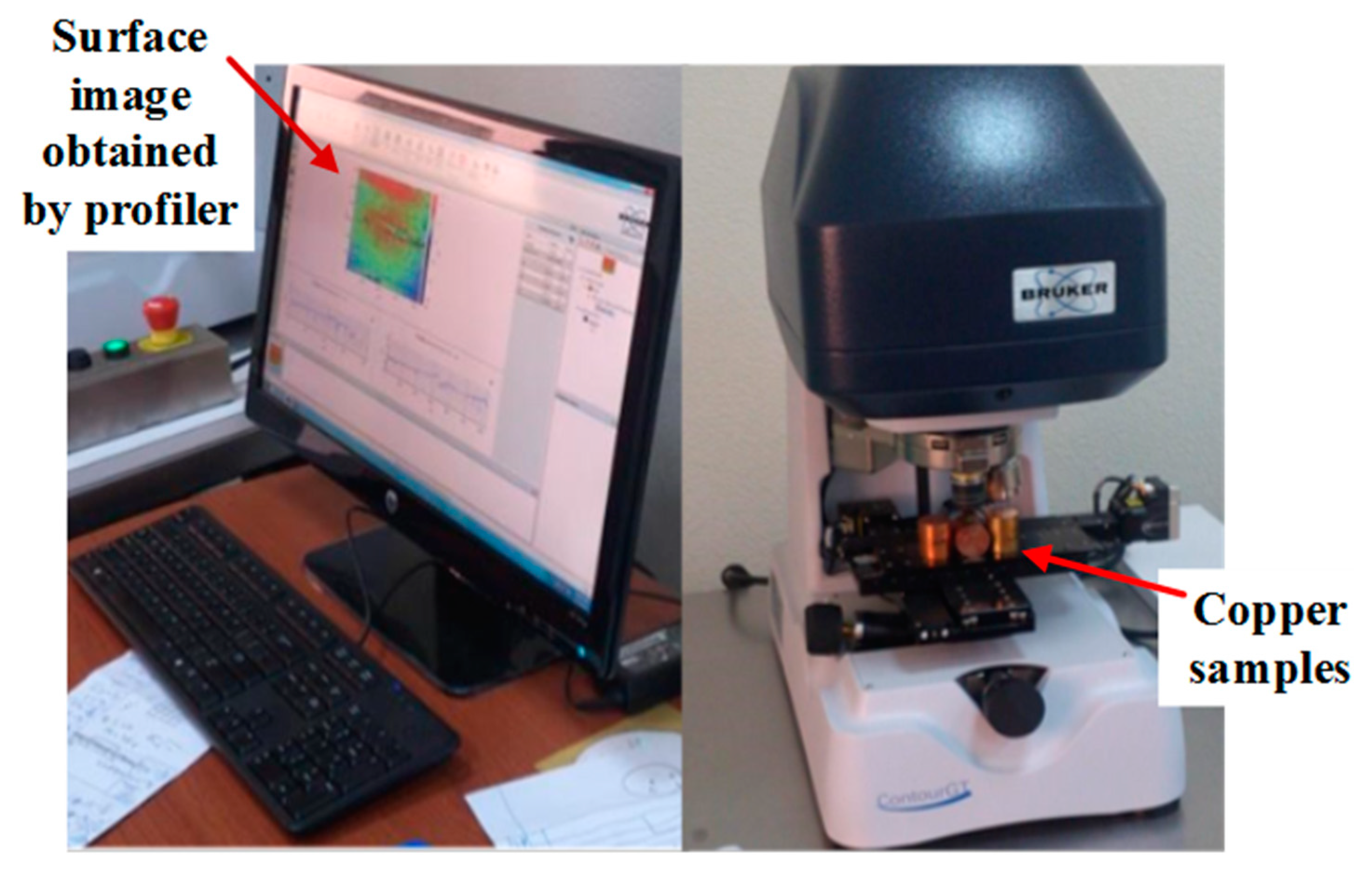
2.2. Surface Roughness Measurement
3. Simulation Model
3.1. Finite Element Model
3.2. Material Properties for Modeling
3.3. Material Modeling
3.4. Von-Mises Stress Criterion
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Microscopic Observations and Surface Roughness Results
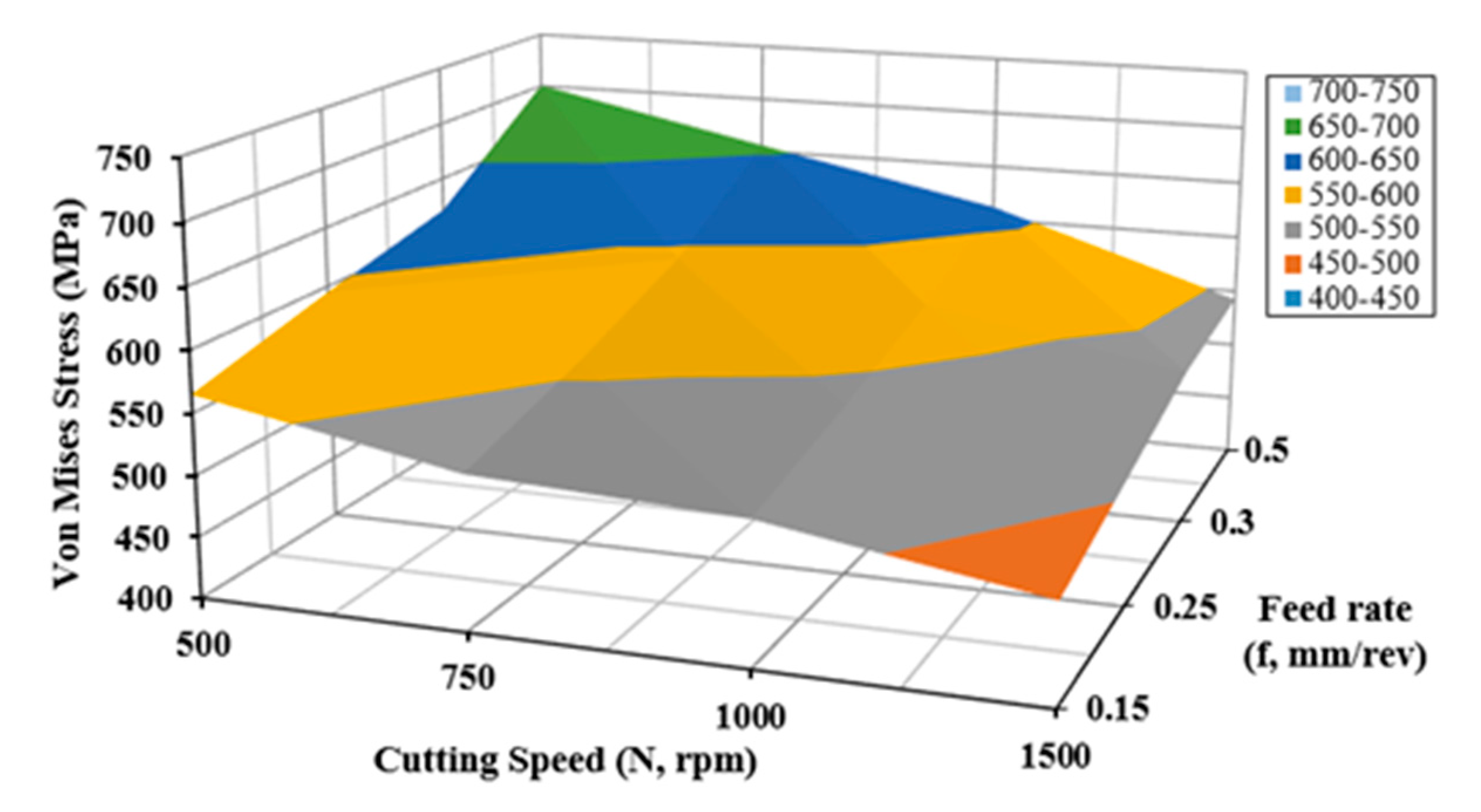
4.2. Results of Simulation Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hatem, H. Study the Effect of Cutting Conditions for turning process on the Machined Surface. Nahrain Univ. Coll. Eng. J. 2011, 14, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Ashvin, J.; Nanavati, J.I. Optimization of machining parameters for turning operations based on response surface methodology. Measurement 2013, 46, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar]
- Sarosh, M.; Jahanzaib, M.; Mumtaz, J.; Sarfraz, S. Investigation of Electric Discharge Machining Parameters to Minimize Surface Roughness. Pak. J. Sci. 2016, 68, 315–325. [Google Scholar]
- Charles, S.; Arunachalam, V.P. Property Analysis and Mathematical modeling of machining properties of Aluminum alloy hybrid composites produced by liquid metallurgy techniques. Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci. 2004, 11, 473–480. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, Y.C.; Coker, S.A. Surface Roughness Measure by Ultrasonic Sensing for in Process Monitoring. J. Eng. Ind. 1995, 117, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoba, C.; Ramanaiah, N.; Rao, D.N. Optimizing the Machining Parameters for Minimum Surface Roughness in Turning Al/6% SiC/6% RHA Hybrid Composites. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2015, 10, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, P.V.S.; Rao, P.V.; Deshmukh, S.G. A genetic algorithmic approach for optimization of surface roughness prediction model. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2002, 42, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davim, J.P. A note on the determination of optimal cutting conditions for surface finish obtained in turning using design of experiments. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2001, 116, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, R.M.; Silva, F.J.G.; Reis, P.; Baptista, A.P.M. Machining Duplex Stainless Steel: Comparative Study Regarding End Mill Coated Tools. Coatings 2016, 6, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gallab, M.; Sklad, M. Machining of Al/SiCp metal matrix composites, part 1. Tool performance. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1998, 83, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyha, I.; Gariani, S.; El-Sayed, M.A.; Huo, D. Analysis of Microstructure and Chip Formation When Machining Ti-6Al-4V. Metals 2018, 8, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, R.K.; Kumar, S.; Das, S. Effect of machining parameters on surface roughness and tool wear for 7075 Al alloy SiC composite. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 50, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozben, T.; Kilickap, E.; Cakir, O. Investigation of mechanical and machinability properties of SiC particle reinforced Al-MMC. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 198, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, J.; Melkote, S. Effect of innovative geometry and workpiece hardness on surface generation in the finish hard turning of AISI 52100 Steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1999, 94, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouici, H.; Yallese, M.A.; Fnides, B.; Mabrouki, T. Machinability investigation in hard turning of AISI H11 hot work steel with CBN tool. Mechanika 2010, 6, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Shashi Kiran, G.; Prasanna, N.D. Machinability Studies on Copper Based Alloy Optimization of Control Parameters in Turning Operation Using Taguchi Method. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2013, 2, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Papanikolaou, M.; Frank, M.; Drikakis, D. Effects of surface roughness on shear viscosity. Phys. Rev. 2017, 95, 33108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fnides, B.; Aouici, H.; Yallese, M.A. Cutting forces and surface roughness in hard turning of hot work steel X38CrMoV5-1 using mixed ceramic. J. Mech. 2008, 2, 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Sundara Murthy, K.; Rajendran, I. A study on optimization of cutting parameters and prediction of surface roughness in end milling of aluminum under MQL machining. Int. J. Mach. Mach. Mater. 2010, 7, 112–128. [Google Scholar]
- Bacaria, J.L.; Dalverny, O.; Pantale, O.; Rakotomalala, R.; Caperaa, S. 2D and 3D Numerical Models of Metal Cutting with Damage Effects. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2004, 193, 4383–4399. [Google Scholar]
- Sivararnakrishnaiah, M.; Nanda, K.P. Effect of Cutting Speed in Turning Process using Finite Element Modeling. Int. J. Latest Trends Eng. Technol. 2016, 7, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Xuebin, L.; Xibin, W.; Chongning, L.; Sanpeng, D. Finite Element Simulation of the Orthogonal Cutting Based on Abaqus. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 821–822, 1410–1413. [Google Scholar]
- Kun, H.; Wenyu, Y.; Qilin, C. Analytical model of stress field in workpiece machined surface layer in orthogonal cutting. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2015, 103, 127–140. [Google Scholar]
- Irfan, O.M.; Mukras, S.M.S.; Al-Mufadi, F.A.; Djavanroodi, F. Surface Modelling of Nanostructured Copper Subjected to Erosion-Corrosion. Metals 2017, 7, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, K.A.; Sadaiah, M.; Gawande, S.H. Experimental Investigations of Surface Roughness on OFHC Copper by Diamond Turning Machine. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2010, 2, 5215–5220. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: http://www.circuitinsight.com/pdf/measuring_copper_surface_roughness_ipc.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2018).
- Simulia. Abaqus Analysis User’s Manual, Volume IV: Elements; Dassault Systèmes Simulia Corp.: Johnston, RI, USA, 2016; pp. 29.6.1–29.6.10. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, B. Effects of surface roughness on scratch resistance and stress-strain fields during scratch tests. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 35217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiener, D.; Motz, C.; Schoberl, T.; Jenko, M.; Dehm, G. Determination of Mechanical Properties of Copper at the Micron Scale. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2006, 8, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedberg, D.; Svoboda, A.; Lindgren, L.-E. Modelling high strain rate phenomena in metal cutting simulation. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2012, 20, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrazola, P.J.; Villar, A.; Ugarte, D.; Marya, S. Serrated chip prediction in Finite Element modeling of the chip formation process. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2007, 11, 367–390. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, G.R.; Cook, W.H. Fracture Characteristics of Three Metals Subjected to Various Strains, strain Rates, Temperature, and Pressures. Eng. Fract. Mech. J. 1985, 21, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agmell, M.; Ahadi, A.; Stahl, J.E. The Link between Plasticity Parameters and Process Parameters in Orthogonal Cutting. Procedia CIRP 2013, 8, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouhar, J.; Piska, M. Modelling the orthogonal machining process using cutting tools with different geometry. MM Sci. J. 2008, 48/49, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bai, Y.; Xu, C. Evaluation of ductile fracture models in finite element simulation of metal cutting processes. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2014, 136, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, Z. Shear localization sensitivity analysis for Johnson–Cook constitutive parameters on serrated chips in high speed machining of Ti6Al4V. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2015, 55, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K. Calibration of the Johnson-Cook Failure Parameters as the Chip Separation Criterion in the Modeling of the Orthogonal Metal Cutting Process. Master’s Thesis, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2016; pp. 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Bendarma, A.; Jankowiak, T.; Rusinek, A.; Klosak, M. Experimental and numerical analysis of aluminum alloy AW5005 behavior subjected to tension and perforation under dynamic loading. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 2017, 55, 1219–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABAQUS. Abaqus/Explicit User’s Manuals; Version 6.11; Dassault Systèmes Simulia Corp.: Providence, RI, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Barber, J.R. Intermediate Mechanics of Materials, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Irfan, O.M.; Al-Mufadi, F.; Al-Shataif, Y.; Djavanroodi, F. Effect of Equal Channel Angular Pressing (ECAP) on Erosion-Corrosion of Pure Copper. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biermann, D.; Hollmann, F. Thermal Effects in Complex Machining Processes; Springer International Publishing AG: Basel, Switzerland, 2018; p. 127. [Google Scholar]
- Biermann, D.; Liedschulte, M. Plasma-assisted turning of hard alloys on an iron base with PKB. Ind. Diam. Rundsch. 1994, 28, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Astakhov, V.P. Effects of the cutting feed, depth of cut, and work piece (bore) diameter on the tool wear rate. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2007, 34, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agmell, M.; Ahadi, A.; Gutnichenko, O.; Stahl, J. The influence of tool micro-geometry on stress distribution in turning operations of AISI 4140 by FE analysis. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 89, 3109–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




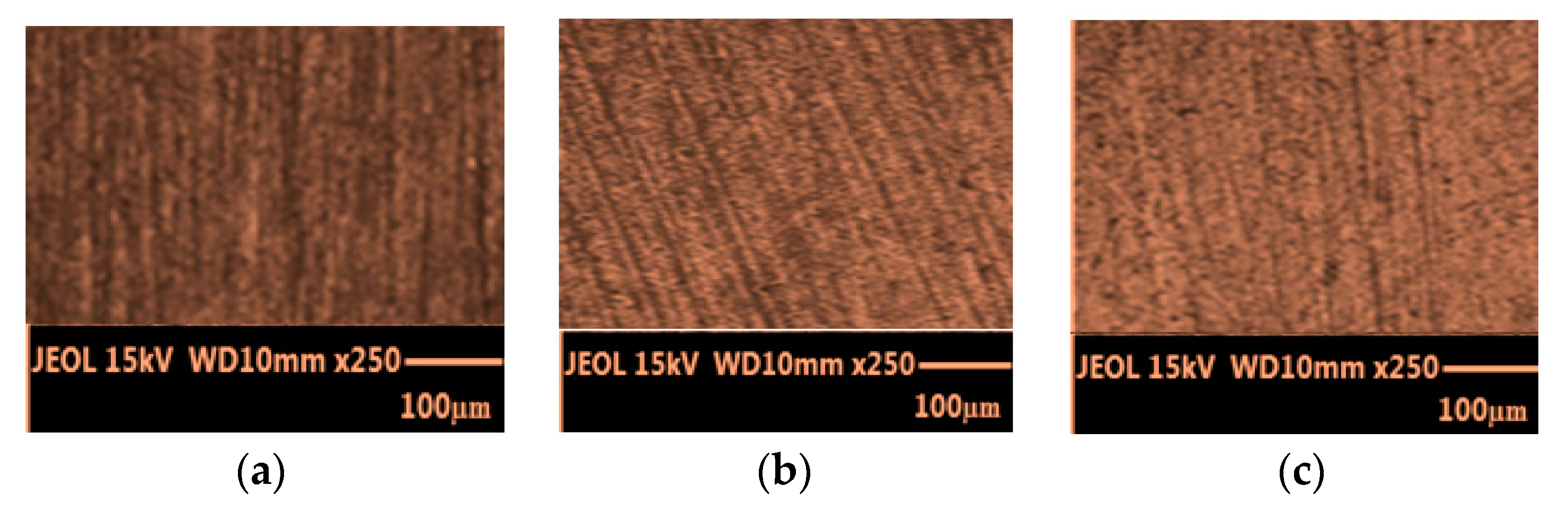
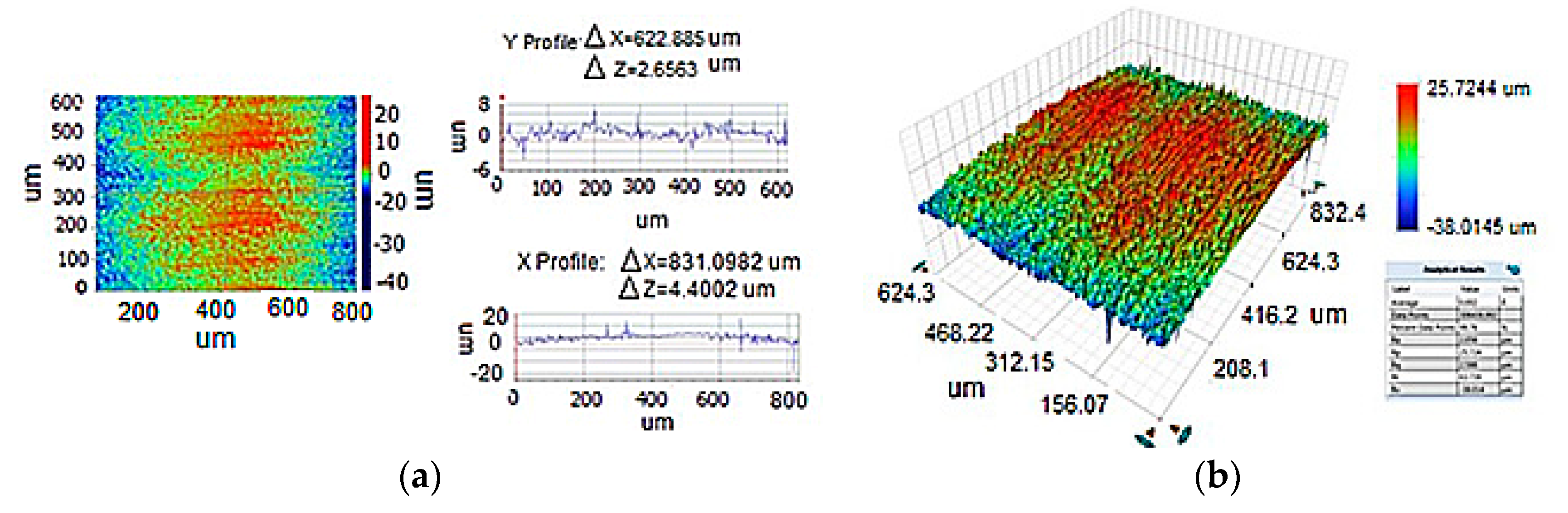




| Group | Constant Cutting Condition | Samples | Changed Cutting Condition | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample No. | |||||||
1  | 2  | 3  | 4  | 5  | |||
| A | N = 750, dc = 0.5 | f, (mm/rev) | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.35 |
| B | ƒ = 0.5, dc = 0.5 | N, (rpm) | 500 | 750 | 1000 | 1250 | 1500 |
| C | ƒ = 0.5, N = 750 | dc, (mm) | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Young’s modulus (E) | 117 GPa |
| Poisson’s ratio (ν) | 0.33 |
| Density (ρ) | 8950 Kg/m3 |
| Yield stress (σyo) | 112 MPa |
| A | B | C | n | m |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90 MPa | 292 MPa | 0.025 | 0.31 | 1.09 |
| D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.54 | 4.89 | −3.03 | 0.014 | 1.12 |
| Parameter | Objective | Optimum Cutting Conditions | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Von Mises (σV.M.) stress | Minimum | N, (rpm) | f, (mm/rev) | dc, (mm) |
| 1500 | 0.15 | 0.5 | ||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zein, H.; Irfan, O.M. Surface Roughness Investigation and Stress Modeling by Finite Element on Orthogonal Cutting of Copper. Metals 2018, 8, 418. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8060418
Zein H, Irfan OM. Surface Roughness Investigation and Stress Modeling by Finite Element on Orthogonal Cutting of Copper. Metals. 2018; 8(6):418. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8060418
Chicago/Turabian StyleZein, Hussein, and Osama M. Irfan. 2018. "Surface Roughness Investigation and Stress Modeling by Finite Element on Orthogonal Cutting of Copper" Metals 8, no. 6: 418. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8060418
APA StyleZein, H., & Irfan, O. M. (2018). Surface Roughness Investigation and Stress Modeling by Finite Element on Orthogonal Cutting of Copper. Metals, 8(6), 418. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8060418






