Evolution of Transient Liquid-Phase Sintered Cu–Sn Skeleton Microstructure During Thermal Aging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- In the as-bonded state, the Cu–Sn skeleton microstructure was identified as comprising Cu particles connected with Cu6Sn5 and Cu3Sn IMCs partially filled with polyimide resin. In addition, submicron voids were observed at the interface between the Cu3Sn phase and Cu particles.
- After aging at 150–200 °C for 1000 h, the Cu6Sn5 phase fully transformed into Cu3Sn except for the small amount of (Cu,Ni)6Sn5 phase at the chip side interface. The phase transformation from Cu6Sn5 into Cu3Sn could have a positive impact on the shear strengths owing to the better mechanical properties of the Cu3Sn. Furthermore, the number of submicron voids at the interface between Cu3Sn and Cu particles appeared to increase after aging, which should be because of the Kirkendall effects between them. The formation of submicron voids could have a negative impact on the shear strengths, suggesting a good agreement with the factography after aging.
- The averaged shear strengths were found to be 22.1 (reference), 22.8 (+3%), 24.0 (+9%), and 19.0 MPa (−14%) for the as-bonded state and the specimens aged at 150, 175, and 200 °C for 1000 h, respectively. The TLPS joints maintained a shear strength over 19 MPa after the thermal aging at 200 °C for 1000 h because of both the positive and negative impacts of the thermal aging, as mentioned above. These results indicate an excellent thermal reliability of the TLPS Cu–Sn skeleton microstructure.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McNutt, T.; Passmore, B.; Fraley, J.; McPherson, B.; Shaw, R.; Olejniczak, K.; Lostetter, A. High-Performance, Wide-Bandgap Power Electronics. J. Electron. Mater. 2014, 43, 4552–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drevin-Bazin, A.; Lacroix, F.; Barbot, J.F. SiC die attach for high-temperature applications. J. Electron. Mater. 2014, 43, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, A.; Tatsumi, H.; Takeda, N.; Akada, Y.; Ogura, T.; Ide, E.; Morita, T. A novel metal-to-metal bonding process through in-situ formation of Ag nanoparticles using Ag2O microparticles. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2009, 165, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsumi, H.; Kumada, S.; Fukuda, A.; Yamaguchi, H.; Kashiba, Y. Impact of Metallurgical and Mechanical Properties of Sintered Silver Nanoparticles on Die-attach Reliability of High-temperature Power Modules. J. Microelectron. Electron. Packag. 2016, 13, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarifi, H.; Hu, A.; Yavuz, M.; Zhou, Y.N. Silver nanoparticle paste for low-temperature bonding of copper. J. Electron. Mater. 2011, 40, 1394–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Hu, A.; Gerlich, A.P.; Zou, G.; Liu, L.; Zhou, Y.N. Joining of Silver Nanomaterials at Low Temperatures: Processes, Properties, and Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 12597–12618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustain, H.A.; Brown, W.D.; Ang, S.S. Transient liquid phase die attach for high-temperature silicon carbide power devices. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 2010, 33, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajwa, A.A.; Qin, Y.; Reiner, R.; Quay, R.; Wilde, J. Assembly and Packaging Technologies for Higherature and High-Power GaN Devices. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 5, 1402–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.W.; Glover, M.D.; Shiozaki, K. Nickel-tin transient liquid phase bonding toward high-temperature operational power electronics in electrified vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 2448–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.S.; Yoon, J.W. Cu-Sn Intermetallic Compound Joints for High-Temperature Power Electronics Applications. J. Electron. Mater. 2018, 47, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, C.; Shearer, B.; Matijasevic, G.; Gandhi, P. Transient liquid phase sintering composites: Polymer adhesives with metallurgical bonds. J. Electron. Mater. 1999, 28, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Huang, J.; Yang, J.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, R.; Chen, S. A Transient Liquid Phase Sintering Bonding Process Using Nickel-Tin Mixed Powder for the New Generation of High-Temperature Power Devices. J. Electron. Mater. 2017, 46, 4152–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Chen, H.; Li, M.; Zhao, Z. Cu@Sn Core–Shell Structure Powder Preform for High-Temperature Applications Based on Transient Liquid Phase Bonding. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 32, 441–451. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, D.; Huang, H.; McDonald, S.D.; Nogita, K. Creep and mechanical properties of Cu6Sn5 and (Cu,Ni)6Sn5 at elevated temperatures. J. Electron. Mater. 2013, 42, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hu, X.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y. Interfacial reaction and microstructure between the Sn3Ag0.5Cu solder and Cu–Co dual-phase substrate. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2018, 124, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaku, Y.; Liu, X.J.; Ohnuma, I.; Kainuma, R.; Ishida, K. Interfacial Reaction and Morphology Between Molten Sn Base Solders and Cu Substrate. Mater. Trans. 2004, 45, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, P.L.; Chan, Y.C.; Lai, J.K.L. Effect of intermetallic compounds on the thermal fatigue of surface mount solder joints. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. Part B 1997, 20, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, R.; Sommer, P.; Fix, A.; Rzepka, S.; Michel, B. Reliability issues for high temperature interconnections based on transient liquid phase soldering. In Proceedings of the 2013 14th International Conference on Thermal, Mechanical and Multi-Physics Simulation and Experiments in Microelectronics and Microsystems (EuroSimE 2013), Wroclaw, Poland, 14–17 April 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Guth, K.; Oeschler, N.; Böwer, L.; Speckels, R.; Strotmann, G.; Heuck, N.; Krasel, S.; Ciliox, A. New assembly and interconnect technologies for power modules. In Proceedings of the 2012 7th International Conference on Integrated Power Electronics Systems (CIPS), Nuremberg, Germany, 6–8 March 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Guth, K.; Heuck, N.; Stahlhut, C.; Ciliox, A.; Oeschler, N.; Ag, I.T. End-of-life investigation on the XT interconnect technology. In Proceedings of the PCIM Europe 2015, Nuremberg, Germany, 19–20 May 2015; pp. 72–79. [Google Scholar]
- Tatsumi, H.; Lis, A.; Monodane, T.; Yamaguchi, H.; Kashiba, Y.; Hirose, A. Transient Liquid Phase Sintering Using Copper-Solder-Resin Composite for High- temperature Power Modules. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 68th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), San Diego, CA, USA, 29 May–1 June 2018; pp. 564–567. [Google Scholar]
- Tatsumi, H.; Lis, A.; Yamaguchi, H.; Kashiba, Y.; Hirose, A. Stiffness Reduction Approach of Transient Liquid-Phase Sintered Joints for SiC Die-Attach Applications. 2018; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Y.; Wu, A.; Shao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, L.; Zou, G. Microstructural evolution and mechanical reliability of transient liquid phase sintered joint during thermal aging. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 54, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Yu, C.F.; Cheng, H.C.; Lu, S.T. Crystal size and direction dependence of the elastic properties of Cu3Sn through molecular dynamics simulation and nanoindentation testing. Microelectron. Reliab. 2012, 52, 1699–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Feng, Y.; Hu, C.; Dai, H.; Song, M.; Yang, W.; Liu, H.; Wei, X. First-principles calculations of structural and mechanical properties of Cu6Sn5. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. Rapid Commun. 2016, 10, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subrahmanvan, B. Elastic Moduli of some complicated binary alloys systems. Mater. Trans. 1971, 13, 93–95. [Google Scholar]
- Rhee, H.; Lucas, J.P.; Subramanian, K.N. Micromechanical characterization of thermomechanically fatigued lead-free solder joints. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2002, 13, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, F.X.; Pang, J.H.L. Characterization of IMC layer and its effect on thermomechanical fatigue life of Sn-3.8Ag-0.7Cu solder joints. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 541, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Chawla, N.; Chawla, K.K.; Koopman, M. Deformation behavior of (Cu, Ag)-Sn intermetallics by nanoindentation. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 4291–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Pang, J.H.L. Nanoindentation on SnAgCu lead-free solder joints and analysis. J. Electron. Mater. 2006, 35, 2107–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.-F.; Lai, Y.-S.; Jian, S.-R.; Chen, J.; Chen, R.-S. Nanoindentation identifications of mechanical properties of Cu6Sn5, Cu3Sn, and Ni3Sn4 intermetallic compounds derived by diffusion couples. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 485, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Wu, Y.; An, B. Micro-mechanical and fracture characteristics of Cu6Sn5 and Cu3Sn intermetallic compounds under micro-cantilever bending. Intermetallics 2016, 76, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, L.; Chen, Z.; Wu, F.; Liu, C. Microstructural and mechanical analysis on Cu-Sn intermetallic micro-joints under isothermal condition. Intermetallics 2015, 66, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; He, S.; Nishikawa, H. Low temperature solid-state bonding using Sn-coated Cu particles for high temperature die attach. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 695, 2165–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Huang, J.; Peng, X.; Lv, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, S.; Zhao, X. Microstructural Evolution of Ni-Sn Transient Liquid Phase Sintering Bond during High-Temperature Aging. J. Electron. Mater. 2018, 47, 4642–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Kim, J.Y. Effects of residual S on Kirkendall void formation at Cu/Sn-3.5Ag solder joints. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 5514–5523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurila, T.; Vuorinen, V.; Kivilahti, J.K. Interfacial reactions between lead-free solders and common base materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2005, 49, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Messler, R.W.; Felton, L.E. Microstructure Evolution of Eutectic Sn-Ag Solder Joints.pdf. J. Electron. Mater. 1994, 23, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

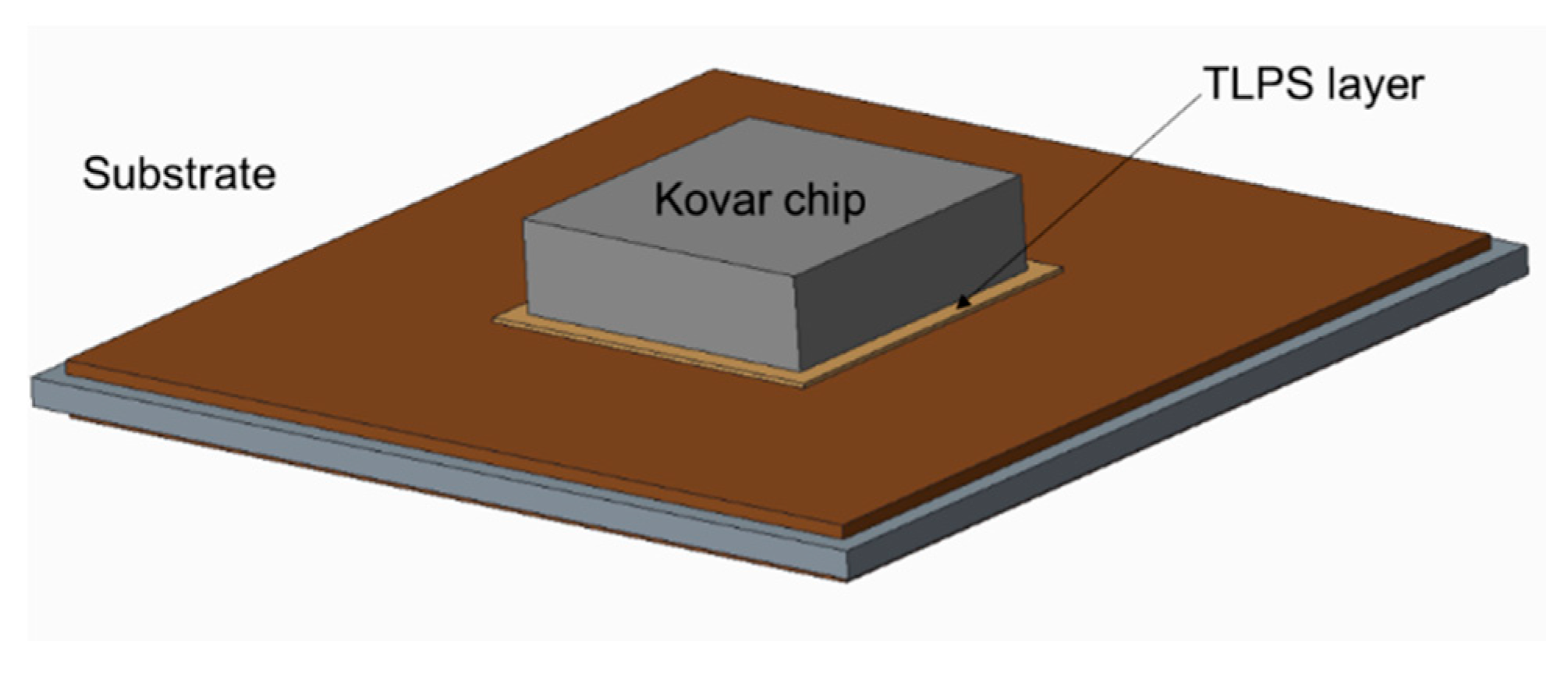


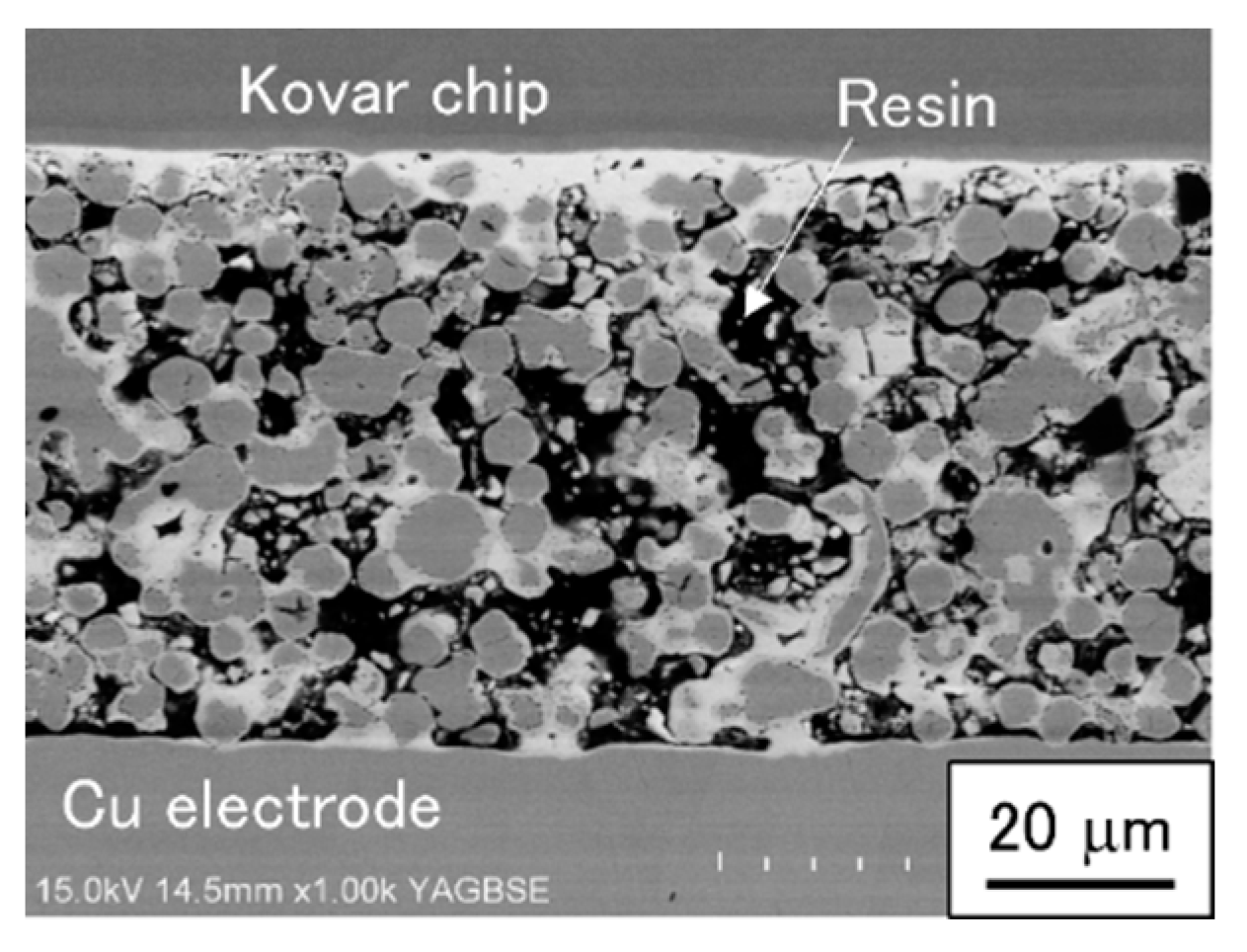






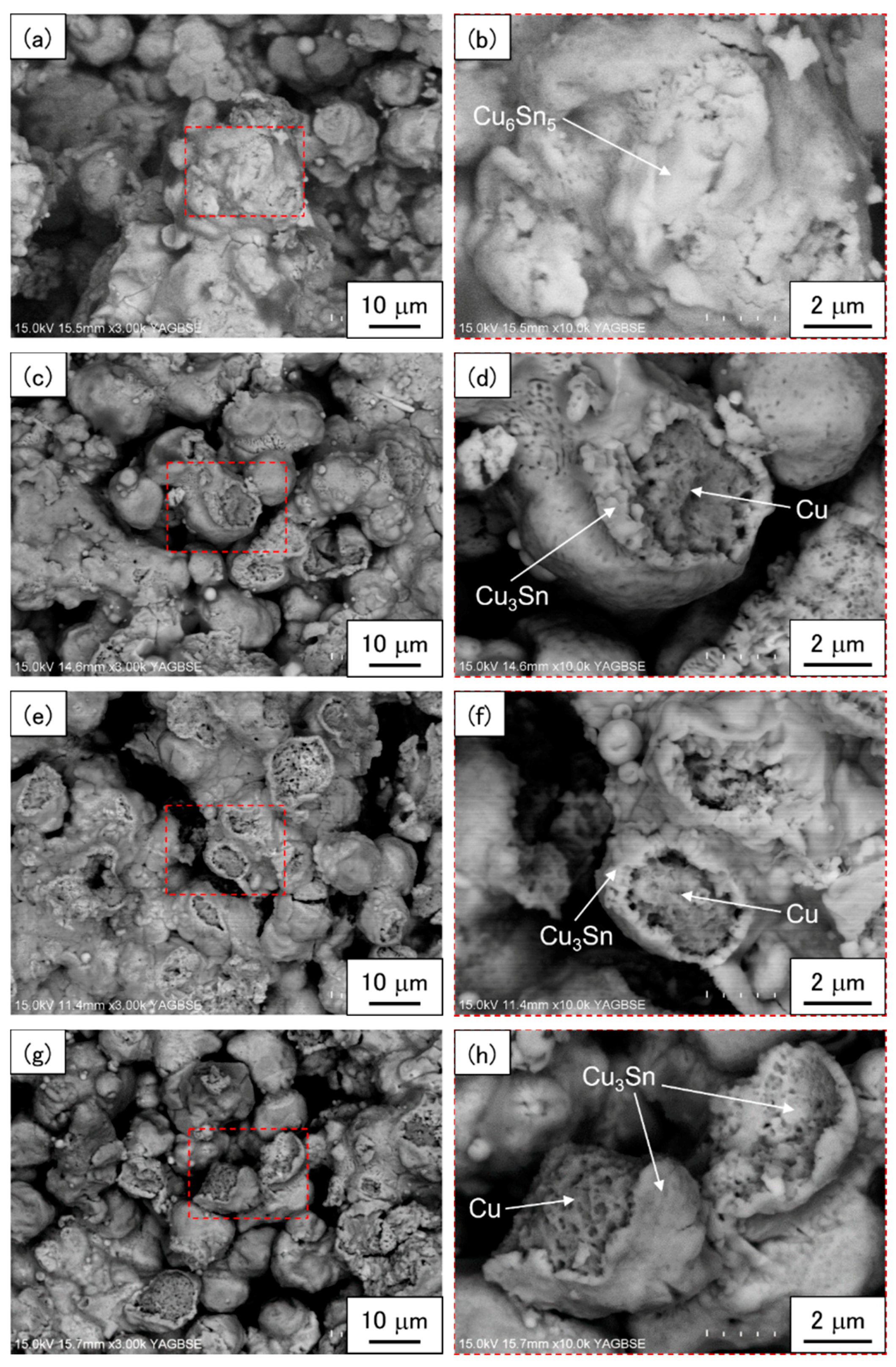

| Area | Cu | Sn | Ni | Au | Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 73.8 | 25.0 | -- | 1.2 | Cu3Sn |
| 2 | 44.2 | 44.6 | 5.3 | 6.0 | (Cu,Ni)6Sn5 + Au |
| 3 | 75.6 | 24.4 | -- | -- | Cu3Sn |
| 4 | 56.0 | 44.0 | -- | -- | Cu6Sn5 |
| Aging Condition | Area | Cu | Sn | Ni | Au | Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150 °C 1000 h | 1 | 74.2 | 24.7 | -- | 1.0 | Cu3Sn |
| 2 | 46.9 | 42.0 | 4.1 | 7.1 | (Cu,Ni)6Sn5 + Au | |
| 175 °C 1000 h | 3 | 72.8 | 26.0 | -- | 1.2 | Cu3Sn |
| 4 | 47.8 | 36.3 | 4.4 | 11.5 | (Cu,Ni)6Sn5 + Au | |
| 200 °C 1000 h | 5 | 71.7 | 26.6 | -- | 1.7 | Cu3Sn |
| 6 | 47.6 | 38.4 | 5.8 | 8.1 | (Cu,Ni)6Sn5 + Au |
| Aging Condition | Area | Cu | Sn | Ni | Au | Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150 °C 1000 h | 1 | 75.7 | 24.3 | -- | -- | Cu3Sn |
| 2 | 73.1 | 26.9 | -- | -- | Cu3Sn | |
| 175 °C 1000 h | 3 | 73.6 | 26.4 | -- | -- | Cu3Sn |
| 4 | 78.7 | 21.3 | -- | -- | Cu3Sn | |
| 200 °C 1000 h | 5 | 75.5 | 24.5 | -- | -- | Cu3Sn |
| 6 | 76.1 | 23.9 | -- | -- | Cu3Sn |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tatsumi, H.; Lis, A.; Yamaguchi, H.; Matsuda, T.; Sano, T.; Kashiba, Y.; Hirose, A. Evolution of Transient Liquid-Phase Sintered Cu–Sn Skeleton Microstructure During Thermal Aging. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010157
Tatsumi H, Lis A, Yamaguchi H, Matsuda T, Sano T, Kashiba Y, Hirose A. Evolution of Transient Liquid-Phase Sintered Cu–Sn Skeleton Microstructure During Thermal Aging. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(1):157. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010157
Chicago/Turabian StyleTatsumi, Hiroaki, Adrian Lis, Hiroshi Yamaguchi, Tomoki Matsuda, Tomokazu Sano, Yoshihiro Kashiba, and Akio Hirose. 2019. "Evolution of Transient Liquid-Phase Sintered Cu–Sn Skeleton Microstructure During Thermal Aging" Applied Sciences 9, no. 1: 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010157
APA StyleTatsumi, H., Lis, A., Yamaguchi, H., Matsuda, T., Sano, T., Kashiba, Y., & Hirose, A. (2019). Evolution of Transient Liquid-Phase Sintered Cu–Sn Skeleton Microstructure During Thermal Aging. Applied Sciences, 9(1), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010157






