Experimental Assessment of an Electrofilter and a Tandem Positive-Negative Corona Charger for the Measurement of Charged Nanoparticles formed in Selective Catalytic Reduction Systems
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The use of an electrofilter (hereinafter EF) upstream of a corona charger to remove all charged particles below the lowest detection size required by the regulation before entering the sensor. The concept is similar to the use of an elevated ion trap to adjust the cut-off size of DC-based instruments [26]. However, by applying the electric field upstream of the corona, the EF only tackles the charged fraction of the sampled aerosol, thus selectively targeting the particles formed in the SCR.
- The use of a negative and a positive corona charger in tandem to condition (neutralize) the sample aerosol by exposing it to a bipolar ion-environment (hereinafter referred to as TC = Tandem Negative-Positive Corona). Similar approaches have been previously successfully established in other commercial instruments [27].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Setup and Measurement Protocol
2.1.1. Characterization of Technical Solutions
2.1.2. Exhaust Measurements
2.2. Calculations
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Technical Solutions
3.1.1. Unipolar Corona of Light-Duty (LD) System
3.1.2. Tandem Negative Positive Corona (TC)
3.1.3. Electrofilter (EF)
3.2. Exhaust Aerosol Measurements
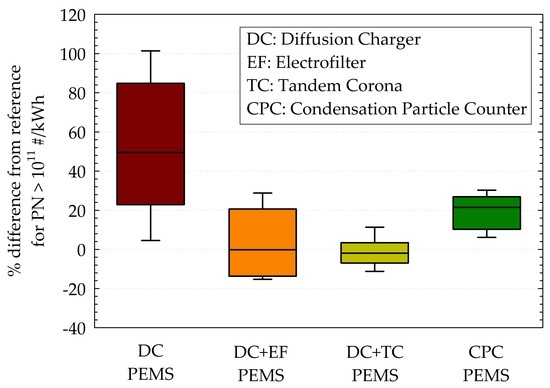
3.2.1. Cycle-Average Emissions
3.2.2. Real-Time Emission Traces
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer
Appendix A

References
- European Environmental Agency. Air Quality in Europe 2018; EEA Report, No. 123/2018; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Health Effects Institute. State of Global Air 2018: A Special Report on Global Exposure to Air Pollution and Its Disease Burden; HEI: Boston, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Mamakos, A.; Andersson, J.; Dilara, P.; Martini, G.; Schindler, W.; Bergmann, A. Measurement of automotive nonvolatile particle number emissions within the European legislative framework: A review. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 719–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Lähde, T.; Suarez-Bertoa, R.; Clairotte, M.; Grigoratos, T.; Zardini, A.; Perujo, A.; Martini, G. Particle number measurements in the European legislation and future JRC activities. Combust. Eng. 2018, 174, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Bergmann, A. Validation of 14 used, re-calibrated and new TSI 3790 condensation particle counters according to the UN-ECE Regulation 83. J. Aerosol Sci. 2011, 42, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaniyala, S.; Fierz, M.; Keskinen, J.; Marjamäki, M. Instruments based on electrical detection of aerosols. In Aerosol Measurement: Principles, Techniques, and Applications, 3rd ed.; Kulkarni, P., Baron, P., Willeke, K., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Commission Regulation (EU). Commission Regulation (EU) 2017/1154 of 7 June 2017 amending Regulation (EU) 2017/1151 supplementing Regulation (EC) No 715/2007 of the European Parliament and of the Council on type-approval of motor vehicles with respect to emissions from light passenger and commercial vehicles (Euro 5 and Euro 6) and on access to vehicle repair and maintenance information, amending Directive 2007/46/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, Commission Regulation (EC) No 692/2008 and Commission Regulation (EU) No 1230/2012 and repealing Regulation (EC) No 692/2008 and Directive 2007/46/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards real-driving emissions from light passenger and commercial vehicles (Euro 6). Off. J. Eur. Un. 2017, L175, 708–732. [Google Scholar]
- Schriefl, M.; Bergmann, A.; Fierz, M. Design principles for sensing particle number concentration and mean particle size with unipolar diffusion charging. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierz, M.; Houle, C.; Steigmeier, P.; Burtscher, H. Design, calibration, and field performance of a miniature diffusion size classifier. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Riccobono, F.; Bonnel, P. Feasibility Study on the Extension of the Real Driving Emissions (RDE) Procedure to Particle Number (PN): Chassis Dynamometer Evaluation of Portable Emission Measurement Systems (PEMS) to Measure Particle Number (PN) Concentration: Phase II; Ispra: EU Report 27451; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Maricq, M.; Ntziachristos, L.; Dardiotis, C.; Wang, X.; Axmann, H.; Bergmann, A.; Schindler, W. Review of motor vehicle particulate emissions sampling and measurement: From smoke and filter mass to particle number. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2014, 67, 48–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwelberger, M.; Giechaskiel, B. Evaluation of Portable Number Emission Systems for Heavy-Duty Applications under Steady State and Transient Vehicle Operation conditions on a Chassis Dynamometer; SAE Technical Paper, 2018-01-0348; Society of Automotive Engineers, Inc.: Detroit, MI, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Schwelberger, M.; Delacroix, C.; Marchetti, M.; Feijen, M.; Prieger, K.; Andersson, S.; Karlsson, H. Experimental assessment of solid particle number portable emissions measurement systems (PEMS) for heavy-duty vehicles applications. J. Aerosol Sci. 2018, 123, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamakos, A.; Schwelberger, M.; Fierz, M.; Giechaskiel, B. Effect of selective catalytic reduction on exhaust non-volatile particle emissions of Euro VI heavy-duty compression ignition vehicles. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Schaber, P.M.; Colson, J.; Higgins, S.; Thielen, D.; Anspach, B.; Brauer, J. Thermal decomposition (pyrolysis) of urea in an open reaction vessel. Thermochim. Acta 2004, 424, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanatidis, A.; Ntziachristos, L.; Giechaskiel, B.; Bergmann, A.; Samaras, Z. Impact of selective catalytic reduction on exhaust particle formation over excess ammonia events. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11527–11534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittelson, D. Engines and nanoparticles: A review. J. Aerosol Sci. 1998, 29, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maricq, M. On the electrical charge of motor vehicle exhaust particles. J. Aerosol Sci. 2006, 37, 858–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biskos, G.; Mastorakos, E.; Collings, N. Monte-Carlo simulation of unipolar diffusion charging for spherical and non-spherical particles. J. Aerosol Sci. 2004, 35, 707–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogak, S.; Flagan, R. Bipolar diffusion charging of spheres and agglomerate aerosol particles. J. Aerosol Sci. 1992, 23, 693–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Kittelson, D. Characterization of aerosol surface instruments in transition regime. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, H.; Kuhlbusch, T.; Rath, S.; Götz, U.; Sprenger, M.; Wels, D.; Polloczek, J.; Bachmann, V.; Dziurowitz, N.; Kiesling, H.; Schwiegelshohn, A.; Monz, C.; et al. Comparability of mobility particle sizers and diffusion chargers. J. Aerosol Sci. 2013, 57, 156–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabile, L.; Cauda, E.; Marini, S.; Buonanno, G. Metrological assessment of a portable analyzer for monitoring the particle size distribution of ultrafine particles. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2014, 58, 860–876. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maricq, M. Monitoring motor vehicle PM emissions: An evaluation of three portable low-cost aerosol instruments. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Asbach, C.; Shin, W.; Fissan, H.; Pui, D. The effect of particle pre-existing charge on unipolar charging and its implication on electrical aerosol measurements. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanatidis, S.; Maricq, M.; Ntziachristos, L.; Samaras, Z. Measuring number, mass, and size of exhaust particles with diffusion chargers: The dual Pegasor particle sensor. J. Aerosol Sci. 2016, 92, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.; Caldow, R.; Pöcher, A.; Mirme, A.; Kittelson, D. A New Electrical Mobility Particle Size Spectrometer for Engine Exhaust Particle Measurements; SAE Technical Paper, 2004-01-1341; Society of Automotive Engineers, Inc.: Detroit, MI, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, C.; Ferron, G.; Karg, E.; Lentner, B.; Schumann, G.; Takenaka, S.; Heyder, J. Generation of ultrafine particles by spark discharging. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanatidis, S.; Ntziachristos, L.; Giechaskiel, B.; Katsaounis, D.; Samaras, Z.; Bergmann, A. Evaluation of an oxidation catalyst (catalytic stripper) in eliminating volatile material from combustion aerosol. J. Aerosol Sci. 2013, 57, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 27891:2015. Aerosol Particle Number Concentration—Calibration of Condensation Particle Counters; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Marjamäki, M.; Keskinen, J.; Chen, D.; Pui, D. Performance evaluation of the electrical low-pressure impactor (ELPI). J. Aerosol Sci. 2000, 31, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Cresnoverh, M.; Jörgl, H.; Bergmann, A. Calibration and accuracy of a particle number measurement system. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierz, M.; Meier, D.; Steigmeier, P.; Burtscher, H. Aerosol measurement by induced currents. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kondo, K.; Otsuki, Y.; Haruta, K. A New On-Board PN Analyzer for Monitoring the Real-Driving Condition; SAE Technical Paper, 2017-01-1001; Society of Automotive Engineers, Inc.: Detroit, MI, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Casadei, S.; Mazzini, M.; Sammarco, M.; Montabone, G.; Tonelli, R.; Deana, M.; Costi, G.; Di Tanno, F.; Prati, M.V.; et al. Inter-laboratory correlation exercise with portable emissions measurement systems (PEMS) on chassis dynamometers. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B. Solid particle number emission factors of Euro VI heavy-duty vehicles on the road and in the laboratory. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, N. On the stationary charge distribution on aerosol particles in a bipolar ionic atmosphere. Geofis. Pura E Appl. 1963, 56, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppel, W.; Frick, G. Ion-aerosol attachment coefficients and the steady-state charge distribution on aerosols in a bipolar environment. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1986, 5, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reischl, G.; Mäkelä, J.; Karch, R.; Necid, J. Bipolar charging of ultrafine particles in the size range below 10 nm. J. Aerosol Sci. 1996, 27, 931–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntziachristos, L.; Giechaskiel, B.; Ristimäki, J.; Keskinen, J. Use of a corona charger for the characterisation of automotive exhaust aerosol. J. Aerosol Sci. 2004, 35, 943–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinds, W. Aerosol Technology: Properties, Behavior, and Measurement of Airborne Particles, 2nd ed.; Willey Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wiedensohler, A. An approximation of the bipolar charge distribution for particles in the submicron size range. J. Aerosol Sci. 1988, 19, 387–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.; Backhaus, J.; Foley, R.; Liu, Z. The Effect of Diesel Exhaust Fluid Dosing on Tailpipe Particle Number Emissions; SAE Technical Paper, 2016-01-0995; Society of Automotive Engineers, Inc.: Detroit, MI, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Czerwinski, J.; Zimmerli, Y.; Mayer, A.; D’Urbano, G.; Zürcher, D. Emission reduction with diesel particle filter with SCR coating (SDPF). Emiss. Control. Sci. Technol. 2015, 1, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutson, E.; Whitby, K. Aerosol classification by electric mobility: Apparatus, theory, and applications. J. Aerosol Sci. 1975, 6, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.; Baron, P.; Willeke, K. (Eds.) Aerosol Measurement: Principles, Techniques, and Applications, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Flagan, R. Scanning electrical mobility spectrometer. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1990, 13, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamakos, A. Methodology to quantify the ratio of multiple-to single-charged fractions acquired in aerosol neutralizers. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Diameter (nm) | Experimental | Fuchs 2 × 1012 m−3s | Fuchs 3 × 1012 m−3s | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| +1 | +2 | +1 | +2 | +1 | +2 | |
| 23 | 27%(±7%) | noise 1 | 18% | 26% | 4% | 5% |
| 30 | 8%(±2%) | 23%(±17%) | 12% | 18% | 3% | 4% |
| 41 | 8%(±2%) | 19%(±13%) | 7% | 11% | 2% | 3% |
| 50 | 3%(±2%) | 10%(±14%) | 5% | 8% | 1% | 2% |
| 70 | 5%(±4%) | 3%(±25%) | 3% | 5% | 1% | 1% |
| 100 | −2%(±9%) | noise 1 | 2% | 3% | 0% | 1% |
| 200 | 4%(±57%) | noise 1 | 1% | 1% | 0% | 0% |
| d (nm) | 23 | 30 | 41 | 50 | 70 | 100 | 200 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| +1 | −32% | 14% | 27% | 24% | 17% | 13% | 6% |
| +2 | −100% | −99% | 19% | 41% | 41% | 30% | 13% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schwelberger, M.; Mamakos, A.; Fierz, M.; Giechaskiel, B. Experimental Assessment of an Electrofilter and a Tandem Positive-Negative Corona Charger for the Measurement of Charged Nanoparticles formed in Selective Catalytic Reduction Systems. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9061051
Schwelberger M, Mamakos A, Fierz M, Giechaskiel B. Experimental Assessment of an Electrofilter and a Tandem Positive-Negative Corona Charger for the Measurement of Charged Nanoparticles formed in Selective Catalytic Reduction Systems. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(6):1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9061051
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchwelberger, Matthias, Athanasios Mamakos, Martin Fierz, and Barouch Giechaskiel. 2019. "Experimental Assessment of an Electrofilter and a Tandem Positive-Negative Corona Charger for the Measurement of Charged Nanoparticles formed in Selective Catalytic Reduction Systems" Applied Sciences 9, no. 6: 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9061051
APA StyleSchwelberger, M., Mamakos, A., Fierz, M., & Giechaskiel, B. (2019). Experimental Assessment of an Electrofilter and a Tandem Positive-Negative Corona Charger for the Measurement of Charged Nanoparticles formed in Selective Catalytic Reduction Systems. Applied Sciences, 9(6), 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9061051