Changes in SOD and NF-κB Levels in Substantia Nigra and the Intestine through Oxidative Stress Effects in a Wistar Rat Model of Ozone Pollution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Exposure to Ozone
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Western Blot
2.5. Superoxide Dismutase Activity
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
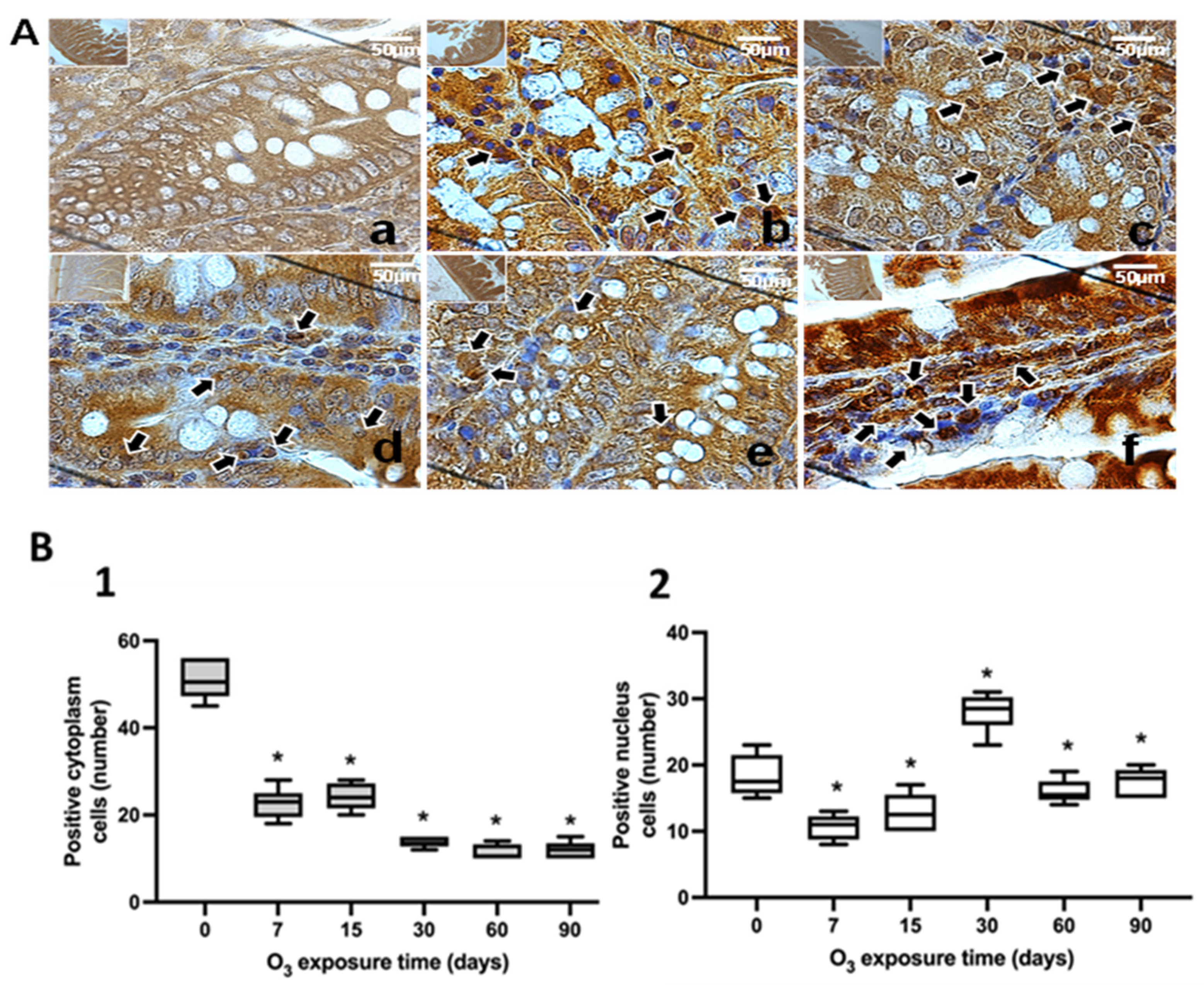
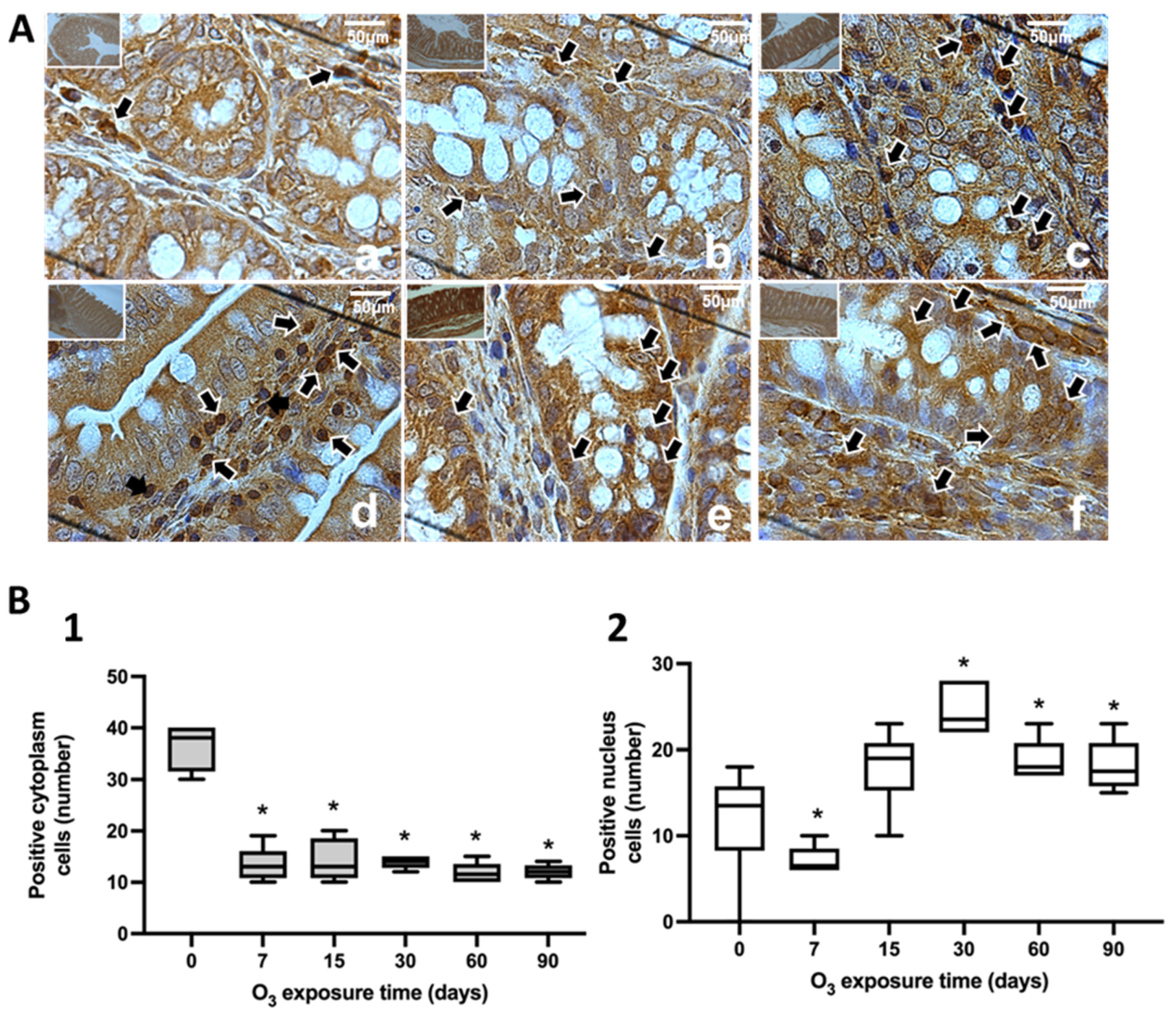
3.1. Immunohistochemical Tests against NFκB
3.2. Lipid Oxidation: 4-Hydroxynonenal
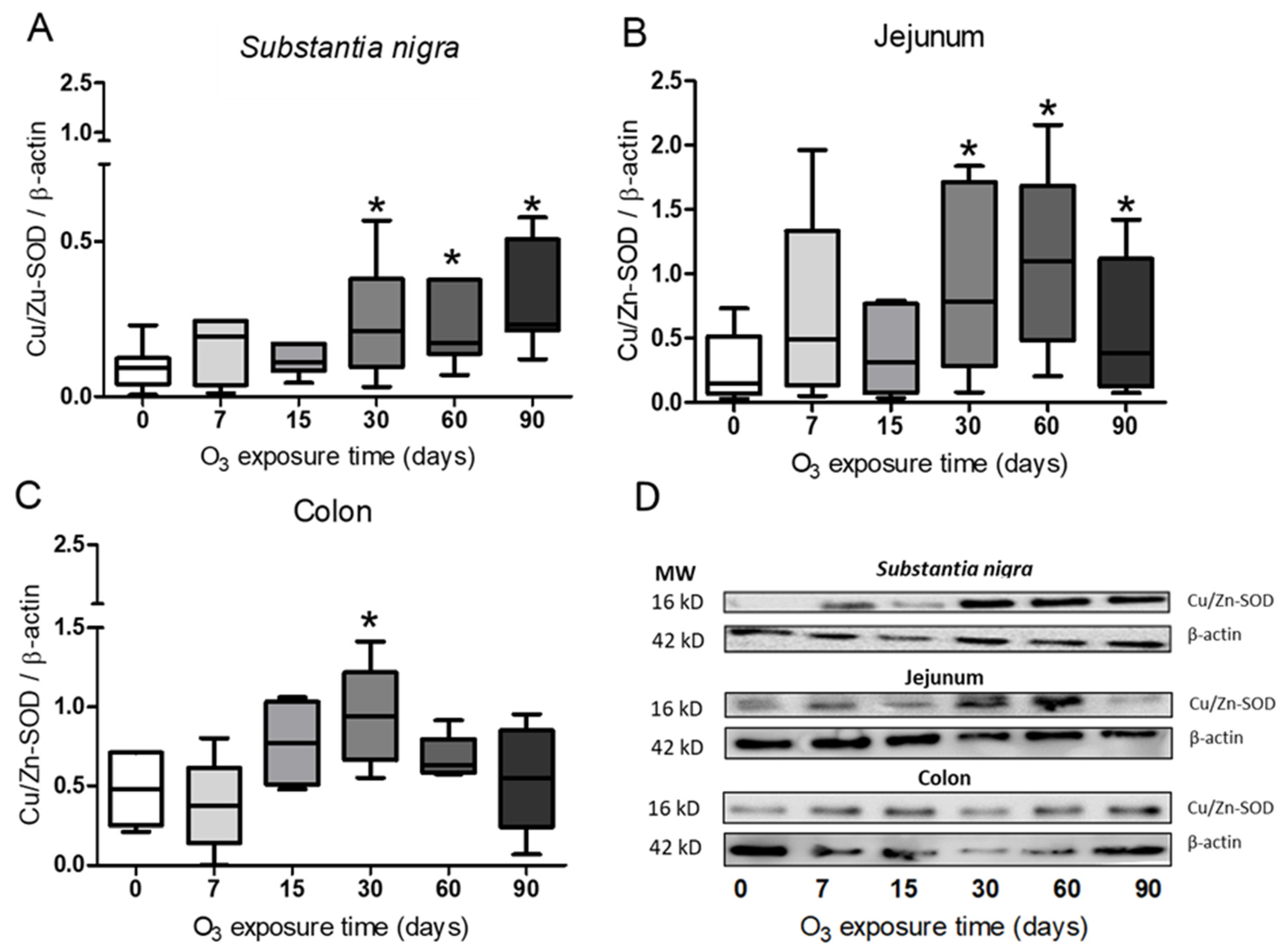
3.3. Determination of Cu/Zn-SOD in Substantia Nigra, Jejunum, and Colon
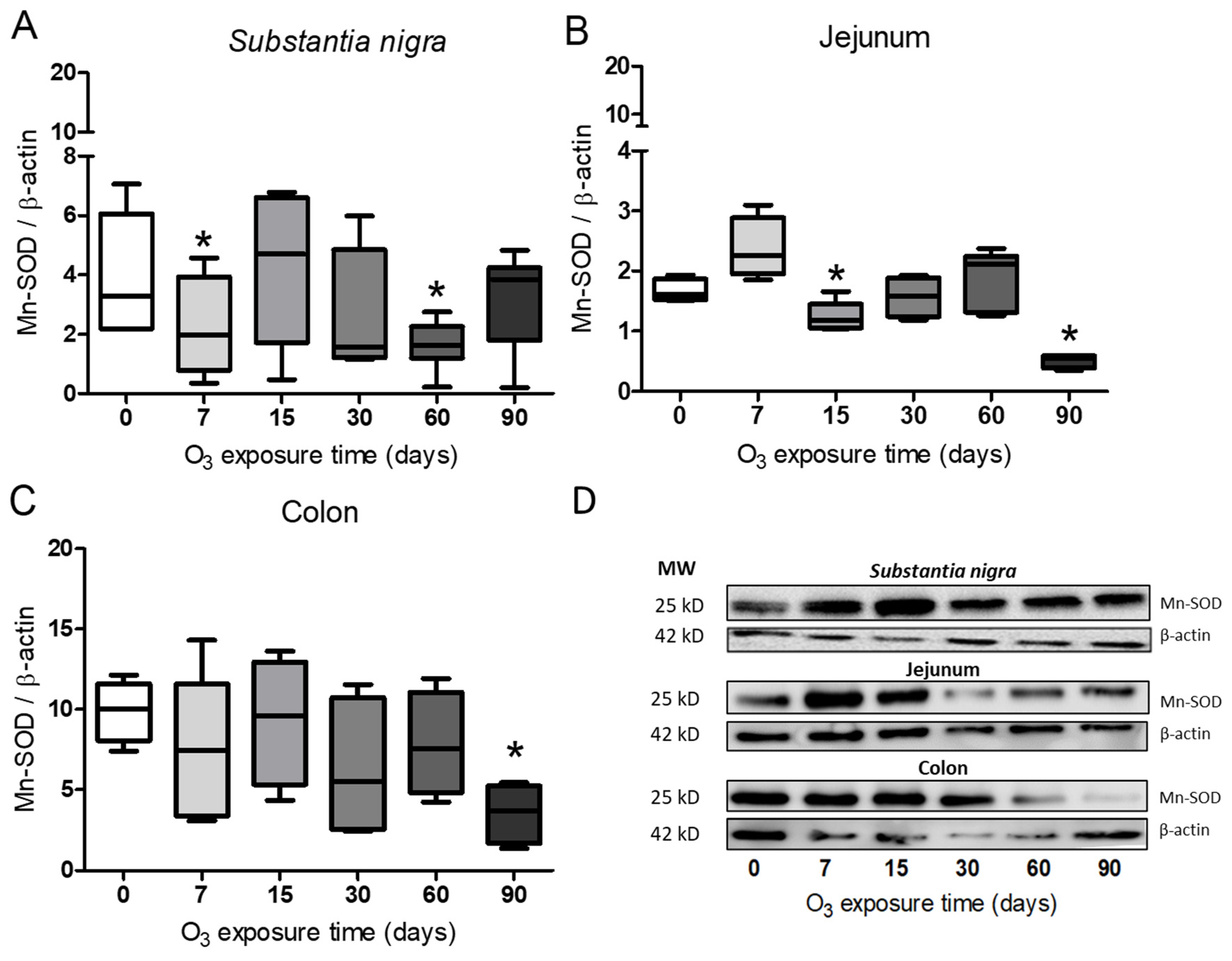
3.4. Determination of Mn-SOD in Substantia Nigra, Jejunum, and Colon
3.5. SOD Activity in Substantia Nigra, Jejunum, and Colon
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manisalidis, I.; Stavropoulou, E.; Stavropoulos, A.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Environmental and Health Impacts of Air Pollution: A Review. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 505570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-Arancibia, S.; Miranda-Martínez, A.; Rodríguez-Martínez, E.; Hernández-Orozco, E.; Valdés-Fuentes, M.; De la Rosa-Sierra, R. Ozone Environmental Pollution: Relationship between the Intestine and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, E.; Martínez, F.; Espinosa-García, M.T.; Maldonado, P.; Rivas-Arancibia, S. Mitochondrial dysfunction in the hippocampus of rats caused by chronic oxidative stress. Neuroscience 2013, 252, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereyra-Muñoz, N.; Rugerio-Vargas, C.; Angoa-Pérez, M.; Borgonio-Pérez, G.; Rivas-Arancibia, S. Oxidative damage in substantia nigra and striatum of rats chronically exposed to ozone. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2006, 31, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poljsak, B.; Milisav, I. The neglected significance of “antioxidative stress”. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 480895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solleiro-Villavicencio, H.; Hernández-Orozco, E.; Rivas-Arancibia, S. Effect of exposure to low doses of ozone on interleukin 17A expression during progressive neurodegeneration in the rat hippocampus. Neurologia Engl. Ed. 2021, 36, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younan, D.; Petkus, A.J.; Widaman, K.F.; Wang, X.; Casanova, R.; Espeland, M.A.; Gatz, M.; Henderson, V.W.; Manson, J.E.; Rapp, S.R.; et al. Particulate matter and episodic memory decline mediated by early neuroanatomic biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2020, 143, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwak, M.G.; Chang, S.Y. Gut-Brain Connection: Microbiome, Gut Barrier, and Environmental Sensors. Immune Netw. 2021, 21, e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvo Romero, E.; Alonso Cotoner, C.; Pardo Camacho, C.; Casado Bedmar, M.; Vicario, M. The intestinal barrier function and its involvement in digestive disease. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2015, 107, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, A.; Jijon, H.; Chan, R.; Ford, K.; Hirota, C.; Kaplan, G.G.; Beck, P.L.; Iacucci, M.; Fort Gasia, M.; Barkema, H.W.; et al. Increased prevalence of circulating novel IL-17 secreting Foxp3 expressing CD4+ T cells and defective suppressive function of circulating Foxp3+ regulatory cells support plasticity between Th17 and regulatory T cells in inflammatory bowel disease patients. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2013, 19, 2522–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.; Kim, S.; Yang, D.H.; Lee, J.; Park, K.W.; Go, J.; Hyun, C.L.; Jee, Y.; Kang, K.S. Mucosal Immunity Related to FOXP3(+) Regulatory T Cells, Th17 Cells and Cytokines in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2018, 33, e336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpellini, E.; Balsiger, L.M.; Broeders, B.; Houte, K.V.D.; Routhiaux, K.; Raymenants, K.; Carbone, F.; Tack, J. Nutrition and Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction. Nutrients 2024, 16, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Wang, L.; Dong, S.; Ge, S.; Zhu, T. Immune regulation of the gut-brain axis and lung-brain axis involved in ischemic stroke. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 19, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Rodriguez, A.B.; Hennessy, E.; Murray, C.L.; Nazmi, A.; Delaney, H.J.; Healy, D.; Fagan, S.G.; Rooney, M.; Stewart, E.; Lewis, A.; et al. Acute systemic inflammation exacerbates neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: IL-1β drives amplified responses in primed astrocytes and neuronal network dysfunction. Alzheimers Dement. 2021, 17, 1735–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poma, P. NF-κB and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serasanambati, M.; Chilakapati, S.R. Function of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kB) in human diseases—A review. S. Indian J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 2, 368–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kensche, T.; Tokunaga, F.; Ikeda, F.; Goto, E.; Iwai, K.; Dikic, I. Analysis of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) essential modulator (NEMO) binding to linear and lysine-linked ubiquitin chains and its role in the activation of NF-κB. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 23626–23634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.; Gevezova, M.; Sarafian, V.; Maes, M. Redox regulation of the immune response. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 1079–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priya Dharshini, L.C.; Vishnupriya, S.; Sakthivel, K.M.; Rasmi, R.R. Oxidative stress responsive transcription factors in cellular signalling transduction mechanisms. Cell. Signal. 2020, 72, 109670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, S. Nuclear initiated NF-κB signaling: NEMO and ATM take center stage. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konturek, S.J.; Konturek, J.W.; Pawlik, T.; Brzozowski, T. Brain-gut axis and its role in the control of food intake. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2004, 55 Pt 2, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Socała, K.; Doboszewska, U.; Szopa, A.; Serefko, A.; Włodarczyk, M.; Zielińska, A.; Poleszak, E.; Fichna, J.; Wlaź, P. The role of microbiota-gut-brain axis in neuropsychiatric and neurological disorders. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 172, 105840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marogianni, C.; Sokratous, M.; Dardiotis, E.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.M.; Bogdanos, D.; Xiromerisiou, G. Neurodegeneration and Inflammation-An Interesting Interplay in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albus, U. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed.; SAGE Publications Sage UK: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- NOM-062-ZOO-1999; Especificaciones técnicas para la producción, cuidado y uso de los animales de laboratorio. Diario Oficial de la Federación-SEGOB: Mexico City, Mexico, 2001.
- CICUAL: Comité Interno para el Cuidado y Uso de Animales de Laboratorio; División de Investigación, Facultad de Medicina: Mexico City, México, 2018.
- Rivas-Arancibia, S.; Guevara-Guzmán, R.; López-Vidal, Y.; Rodríguez-Martínez, E.; Zanardo-Gomes, M.; Angoa-Pérez, M.; Raisman-Vozari, R. Oxidative stress caused by ozone exposure induces loss of brain repair in the hippocampus of adult rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 113, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOM-033-SAG/ZOO-2014; Métodos para dar Muerte a los Animales Domésticos y Silvestres. Diario Oficial de la Federación-SEGOB: Mexico City, Mexico, 2015.
- Sun, Y.; Oberley, L.W.; Li, Y. A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin. Chem. 1988, 34, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Saredy, J.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, H. Innate-adaptive immunity interplay and redox regulation in immune response. Redox Biol. 2020, 37, 101759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlgren, C.; Karlsson, A. Respiratory burst in human neutrophils. J. Immunol. Methods 1999, 232, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forman, H.J.; Torres, M. Reactive oxygen species and cell signaling: Respiratory burst in macrophage signaling. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166 Pt 2, S4–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampson, T.R.; Debelius, J.W.; Thron, T.; Janssen, S.; Shastri, G.G.; Ilhan, Z.E.; Challis, C.; Schretter, C.E.; Rocha, S.; Gradinaru, V.; et al. Gut Microbiota Regulate Motor Deficits and Neuroinflammation in a Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Cell 2016, 167, 1469–1480.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, J.C.; Kertesy, S.; Jones, M.B.; Marinis, J.M.; Cobb, B.A.; Tigno-Aranjuez, J.T.; Abbott, D.W. Innate immune-directed NF-κB signaling requires site-specific NEMO ubiquitination. Cell Rep. 2013, 4, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonowal, H.; Ramana, K.V. 4-Hydroxy-Trans-2-Nonenal in the Regulation of Anti-Oxidative and Pro-Inflammatory Signaling Pathways. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 5937326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Zhong, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, M.; Yang, C. The role of gut microbiota in intestinal disease: From an oxidative stress perspective. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1328324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, H.; Shao, D.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, G. Intraperitoneal injection of 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE), a lipid peroxidation product, exacerbates colonic inflammation through activation of Toll-like receptor 4 signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 131, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lick, S.D.; Awasthi, Y.C.; Boor, P.J. Endothelial glutathione-S-transferase A4-4 protects against oxidative stress and modulates iNOS expression through NF-kappaB translocation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 230, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorado Martinez, C.R.-M.V.; Rugerio-Vargas, C.; Rodriguez-Martinez, E.; Pereyra-Munoz, N.; Gonzalez-Rivas, S.; Borgonio-Perez, G.; Rivas-Arancibia, S. Neural Response to Oxidative Stress Caused by Repeated Ozone Exposure in Rats. Is It Recovery? In Proceedings of the Society for Neuroscience Annual Meeting 2002, Orlando, FL, USA, 2–7 November 2002. [Google Scholar]
- AlAsmari, A.F.; Alharbi, M.; Alqahtani, F.; Alasmari, F.; AlSwayyed, M.; Alzarea, S.I.; Al-Alallah, I.A.; Alghamdi, A.; Hakami, H.M.; Alyousef, M.K.; et al. Diosmin Alleviates Doxorubicin-Induced Liver Injury via Modulation of Oxidative Stress-Mediated Hepatic Inflammation and Apoptosis via NfkB and MAPK Pathway: A Preclinical Study. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besong, E.E.; Akhigbe, T.M.; Obimma, J.N.; Obembe, O.O.; Akhigbe, R.E. Acetate Abates Arsenic-Induced Male Reproductive Toxicity by Suppressing HDAC and Uric Acid-Driven Oxido-inflammatory NFkB/iNOS/NO Response in Rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, A.; Wollman, R. Information transmission from NFkB signaling dynamics to gene expression. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1008011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaltschmidt, B.; Sparna, T.; Kaltschmidt, C. Activation of NF-kappa B by reactive oxygen intermediates in the nervous system. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 1999, 1, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Simone, V.; Franzè, E.; Ronchetti, G.; Colantoni, A.; Fantini, M.C.; Di Fusco, D.; Sica, G.S.; Sileri, P.; MacDonald, T.T.; Pallone, F.; et al. Th17-type cytokines, IL-6 and TNF-α synergistically activate STAT3 and NF-kB to promote colorectal cancer cell growth. Oncogene 2015, 34, 3493–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalla, D.K. Ozone-induced lung inflammation and mucosal barrier disruption: Toxicology, mechanisms, and implications. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 1999, 2, 31–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Cavallero, S.; Hsiai, T.; Li, R. Impact of air pollution on intestinal redox lipidome and microbiome. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 151, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rivas-Arancibia, S.; Rodríguez-Martínez, E.; Valdés-Fuentes, M.; Miranda-Martínez, A.; Hernández-Orozco, E.; Reséndiz-Ramos, C. Changes in SOD and NF-κB Levels in Substantia Nigra and the Intestine through Oxidative Stress Effects in a Wistar Rat Model of Ozone Pollution. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050536
Rivas-Arancibia S, Rodríguez-Martínez E, Valdés-Fuentes M, Miranda-Martínez A, Hernández-Orozco E, Reséndiz-Ramos C. Changes in SOD and NF-κB Levels in Substantia Nigra and the Intestine through Oxidative Stress Effects in a Wistar Rat Model of Ozone Pollution. Antioxidants. 2024; 13(5):536. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050536
Chicago/Turabian StyleRivas-Arancibia, Selva, Erika Rodríguez-Martínez, Marlen Valdés-Fuentes, Alfredo Miranda-Martínez, Eduardo Hernández-Orozco, and Citlali Reséndiz-Ramos. 2024. "Changes in SOD and NF-κB Levels in Substantia Nigra and the Intestine through Oxidative Stress Effects in a Wistar Rat Model of Ozone Pollution" Antioxidants 13, no. 5: 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050536





