-
 Ferroptosis in Human Diseases: Fundamental Roles and Emerging Therapeutic Perspectives
Ferroptosis in Human Diseases: Fundamental Roles and Emerging Therapeutic Perspectives -
 Quantifying the Antioxidant Capacity of Inorganic Nanoparticles
Quantifying the Antioxidant Capacity of Inorganic Nanoparticles -
 Redox Signalling in Cardiovascular Disease: Links to Inflammation, Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Autophagy
Redox Signalling in Cardiovascular Disease: Links to Inflammation, Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Autophagy -
 Polyphenol-Rich Extracts from Avocado Residues via Ultrasound RSM: Antioxidant Potential and Valorization
Polyphenol-Rich Extracts from Avocado Residues via Ultrasound RSM: Antioxidant Potential and Valorization -
 Natural Products for Redox-Metabolic Control Targeting GLP-1-TXNIP-Thioredoxn Signaling in Metabolic Syndrome
Natural Products for Redox-Metabolic Control Targeting GLP-1-TXNIP-Thioredoxn Signaling in Metabolic Syndrome
Journal Description
Antioxidants
Antioxidants
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal related to the science and technology of antioxidants, published monthly online by MDPI. The International Coenzyme Q10 Association (ICQ10A), Israel Society for Oxygen and Free Radical Research (ISOFRR) and European Academy for Molecular Hydrogen Research (EAMHR) are affiliated with Antioxidants and their members receive discounts on the article processing charge.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, FSTA, PubAg, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Chemistry, Medicinal) / CiteScore - Q1 (Food Science)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 18.7 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Antioxidants.
- Companion journal: Oxygen.
Impact Factor:
6.6 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
7.3 (2024)
Latest Articles
Next-Generation Antioxidants in Cardiovascular Disease: Mechanistic Insights and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies
Antioxidants 2026, 15(2), 164; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15020164 (registering DOI) - 25 Jan 2026
Abstract
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) remain the leading cause of mortality worldwide. CVDs are associated with multiple factors, including oxidative stress, mediated endothelial dysfunction, vascular inflammation, and atherothrombosis. Although traditional antioxidant supplementation (such as vitamins C, E, and β-carotene) has shown promising results in rigorous
[...] Read more.
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) remain the leading cause of mortality worldwide. CVDs are associated with multiple factors, including oxidative stress, mediated endothelial dysfunction, vascular inflammation, and atherothrombosis. Although traditional antioxidant supplementation (such as vitamins C, E, and β-carotene) has shown promising results in rigorous animal model studies, it has consistently failed to demonstrate clinical benefit in most human trials. Consequently, there is a substantial unmet need for novel paradigms involving mechanistically and biologically relevant pharmaceutical-grade antioxidant therapies (“next-generation antioxidants”). Rapid advancements in redox biology, nanotechnology, genetic modulation of redox processes, and metabolic regulation have enabled the development of new antioxidant therapeutics, including mitochondrial-targeted agents, NADPH oxidase (NOX) inhibitors, selenoprotein and Nrf2 activators, engineered nanoparticles, catalytic antioxidants, and RNA-based and gene-editing strategies. These interventions have the potential to modulate specific oxidative pathways that contribute to CVD pathogenesis. This review provides a comprehensive assessment of current oxidative stress–modulating modalities and their potential to inform personalized cardiovascular prevention and treatment strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Harnessing Antioxidants: Pioneering Approaches in Cardiovascular Disease Prevention and Therapy)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Protective Effect of Resolvin D1, D2, and Their Methyl Esters on Oxidative Stress and Hyaluronidase—Induced Hyaluronic Acid Degradation
by
Zahra Kariminezhad, Mahdi Rahimi, Julio Fernandes, Hassan Fahmi and Mohamed Benderdour
Antioxidants 2026, 15(2), 163; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15020163 (registering DOI) - 25 Jan 2026
Abstract
Hyaluronic acid (HA) injections are commonly employed in the management of osteoarthritis (OA), yet their therapeutic benefits are often limited by oxidative degradation and enzymatic breakdown within the joint. This study investigates whether Resolvin D1, Resolvin D2, and their methyl ester derivatives can
[...] Read more.
Hyaluronic acid (HA) injections are commonly employed in the management of osteoarthritis (OA), yet their therapeutic benefits are often limited by oxidative degradation and enzymatic breakdown within the joint. This study investigates whether Resolvin D1, Resolvin D2, and their methyl ester derivatives can enhance the efficacy of HA injections by acting as dual-function agents with both antioxidant and enzyme inhibitory properties. A comprehensive series of in vitro assays—including ORAC, FRAP, DPPH, ABTS, HRS, and SOD—were performed to evaluate antioxidant capacity, using Trolox, Ascorbic acid, β-Carotene, and Quercetin as reference standards. The potential to inhibit HA degradation was assessed through ROS-induced HA fragmentation and hyaluronidase inhibition assay, with epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) serving as a positive control. The results indicate that Resolvin derivatives, particularly the methyl ester form of Resolvin D1, display mechanism-dependent antioxidant activity, showing pronounced effects in hydrogen atom transfer-based assays (e.g., ORAC and HRS), as well as in ABTS•+ and superoxide-related systems, along with protection against ROS and enzyme-induced HA degradation. These findings suggest that incorporating Resolvin derivatives may represent a promising strategy to improve HA-based viscosupplementation by enhancing stability and therapeutic persistence in osteoarthritic joints.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Natural and Synthetic Antioxidants)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Prenatal Melatonin Modulates Cardiovascular Function and Oxidative Stress in Guinea Pig Neonates Under Normoxic and Hypoxic Gestation
by
Adolfo A. Paz, Tamara A. Jiménez, Pedro Herrera, Josefa Carreño, Damaris Cornejo, Julieta Ibarra-González, Javiera N. Ponce, Felipe A. Beñaldo, Mario Salamanca, Rodrigo Jeria, Esteban G. Figueroa, Alejandro González-Candia and Emilio A. Herrera
Antioxidants 2026, 15(2), 162; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15020162 (registering DOI) - 25 Jan 2026
Abstract
Introduction: Gestational hypoxia (GH) increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases by inducing oxidative stress and vascular dysfunction. This study investigates whether prenatal melatonin can mitigate these effects in guinea pigs. Methods: Pregnant guinea pigs were exposed to normoxia or hypoxia and
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Gestational hypoxia (GH) increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases by inducing oxidative stress and vascular dysfunction. This study investigates whether prenatal melatonin can mitigate these effects in guinea pigs. Methods: Pregnant guinea pigs were exposed to normoxia or hypoxia and treated with melatonin (1 mg/kg/day). Echocardiography, vascular reactivity, and molecular assays were used to assess cardiovascular structure, function, and redox balance in neonates. Results: GH reduced neonatal birth weight and altered left ventricular (LV) development, resulting in increased LV systolic function and aortic blood flow velocity. Melatonin treatment reversed these effects, restoring endothelial-dependent vasodilation and decreasing oxidative stress in the LV and thoracic aorta. Catalase antioxidant enzyme activity was elevated in melatonin-treated hypoxic neonates. Unexpectedly, melatonin treatment altered cardiac structure in normoxic pregnancies, increasing LV length and decreasing LV myocardial nuclei density. Conclusions: Prenatal melatonin partially modulates GH-induced endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress, offering potential therapeutic value. However, its effects under normoxic conditions deserve caution, emphasizing the need for targeted use only in pregnancies with evident hypoxic and oxidative stress conditions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Developmental Origins of Health and Disease: Antioxidants as Strategy for Prevention and Treatment)
Open AccessArticle
Traffic-Related Emissions Induce Angiotensin II-Dependent Oxidative Stress in the Hippocampus of ApoE-Null Male Mice
by
Tyler D. Armstrong, Usa Suwannasual, Analana Stanley, Bailee Johnson, Victoria L. Youngblood, Isabella Santiago, Mickaela Cook, Sophia M. Giasolli and Amie K. Lund
Antioxidants 2026, 15(2), 161; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15020161 (registering DOI) - 25 Jan 2026
Abstract
Traffic-related air pollution (TRAP) is known to contribute to oxidative stress in the central nervous system (CNS) and has been linked to increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Alterations in the renin–angiotensin system (RAS), specifically increased angiotensin II (Ang II) signaling via the
[...] Read more.
Traffic-related air pollution (TRAP) is known to contribute to oxidative stress in the central nervous system (CNS) and has been linked to increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Alterations in the renin–angiotensin system (RAS), specifically increased angiotensin II (Ang II) signaling via the angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor, are implicated in increased oxidative stress in the CNS via activation of NADPH oxidase (NOX). As exposure to TRAP may further elevate AD risk, we investigated whether exposure to inhaled mixed gasoline and diesel vehicle emissions (MVE) promotes RAS-dependent expression of factors that contribute to AD pathophysiology in an apolipoprotein E-deficient (ApoE−/−) mouse model. Male ApoE−/− mice (6–8 weeks old) on a high-fat diet were treated with either an ACE inhibitor (captopril, 4 mg/kg/day) or water and exposed to filtered air (FA) or MVE (200 µg PM/m3) for 30 days. MVE exposure elevated plasma Ang II, inflammation, and oxidative stress in the hippocampus, associated with increased levels of Aph-1 homolog B (APH1B), a gamma-secretase subunit, and beta-secretase 1 (BACE1), involved in Aβ production. Each of these endpoints was normalized with ACEi treatment. These findings indicate that TRAP exposure in ApoE−/− mice drives a RAS- and NOX-dependent oxidative and inflammatory response and shifts Aβ processing towards an amyloidogenic profile before overt Aβ deposition, suggesting a potential therapeutic approach for air pollution-induced AD risk.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Oxidative Stress Induced by Air Pollution, 3rd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Biosacetalin (1,1-Diethoxyethane) Improves Healthy Lifespan in C. elegans and Rats
by
Vu Hoang Trinh, Geun-Haeng Lee, Eun-Jong Kim, Jooyeon Sohn, Jin-Myung Choi, Thang Nguyen Huu, Dhiraj Kumar Sah, Sang-Chul Park, Min-Keun Song and Seung-Rock Lee
Antioxidants 2026, 15(2), 160; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15020160 (registering DOI) - 24 Jan 2026
Abstract
Recent evidence has highlighted the pivotal roles of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the SIRT1, AMPK, and mTOR signaling pathways in aging and longevity, making them attractive targets for studies of lifespan-extending interventions. We previously demonstrated that 1,1-diethoxyethane (1,1-DEE) could interact with mitochondrial
[...] Read more.
Recent evidence has highlighted the pivotal roles of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the SIRT1, AMPK, and mTOR signaling pathways in aging and longevity, making them attractive targets for studies of lifespan-extending interventions. We previously demonstrated that 1,1-diethoxyethane (1,1-DEE) could interact with mitochondrial complex I (NADH–ubiquinone oxidoreductase), leading to transient mitochondrial ROS (mtROS) production and activation of the AMPK pathway. This study further examined the effects of 1,1-DEE on longevity in model organisms. Treatment with 1,1-DEE decreased senescence in endothelial cell EA.hy926. In Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans), 1,1-DEE induced a hormetic response and extended the lifespan, whereas its structural isoform, 1,2-diethoxyethane (1,2-DEE), showed no such effect. In rat models, administration of 1,1-DEE markedly improved survival rate, mortality risk, restricted mean survival time (RMST), and median lifespan, associated with an accelerated body weight reduction. Additionally, 1,1-DEE could also enhance learning and memory, as assessed by the Morris water maze test in rats. These findings suggest that 1,1-DEE may serve as a novel small-molecule modulator of mitochondrial function and redox signaling, with potentials for promoting anti-aging and longevity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Oxidoreductases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Oxidative Stress Mediated by Macrophages Promotes Angiogenesis and Early Development of Endometriosis
by
Gene Chi Wai Man, Astrid Borchert, Tao Zhang, Sze Wan Hung, Hartmut Kühn and Chi Chiu Wang
Antioxidants 2026, 15(2), 159; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15020159 - 23 Jan 2026
Abstract
Endometriosis is a hormone-dependent gynecological disease manifested by cyclic pelvic pain and female infertility. Although many studies have shown that neoangiogenesis plays an essential role in the development of early endometriosis, the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms remain unclear. Recent evidence suggests that macrophages play
[...] Read more.
Endometriosis is a hormone-dependent gynecological disease manifested by cyclic pelvic pain and female infertility. Although many studies have shown that neoangiogenesis plays an essential role in the development of early endometriosis, the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms remain unclear. Recent evidence suggests that macrophages play an important role in the pathogenesis of endometriosis and that the hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1α) may be involved, but when and how are largely unknown. Herein, we explore the role of macrophages in the early development of endometriosis using an in vivo subcutaneous implantation murine model. Upon depletion of macrophages, the subcutaneous injection of syngeneic endometrial material resulted in significant reduction in oxidative stress, endometriotic lesion size, and neovascularization. Likewise, inactivation of the lipid peroxidative gene Alox15 induced similar reduction in oxidative stress, lesion growth, and angiogenesis. Since HIF-1α is an important trigger of neoangiogenesis, we further administered a HIF-1α-specific inhibitor (PX-478) to our endometriotic model and further confirmed the same effects on the lesions. Taken together, these data suggest that an intact Alox15 pathway and HIF-1α signaling may play important roles in the macrophage-mediated oxidative stress and neovascularization of endometriosis in the early stages, suggesting anti-inflammation and antioxidation as potential therapeutic targets for the development of endometriosis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Oxidative Stress in Fertility and Infertility)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Formulation and Biological Evaluation of Glycyrrhiza glabra L. Methanolic Extract: An Exploratory Study in the Context of Rosacea
by
Iulia Semenescu, Larisa Bora, Adina Octavia Dușe, Claudia Geanina Watz, Ștefana Avram, Szilvia Berkó, Gheorghe Emilian Olteanu, Adina Căta, Zorița Diaconeasa, Daliana Ionela Minda, Cristina Adriana Dehelean, Delia Muntean and Corina Danciu
Antioxidants 2026, 15(2), 158; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15020158 - 23 Jan 2026
Abstract
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder characterized by oxidative stress, innate immune dysregulation, vascular instability, and microbiome-related triggers. Glycyrrhiza glabra (Gg, licorice) root contains phenolics and triterpenoids with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and anti-angiogenic properties that may benefit rosacea-prone skin. Xanthan-gum hydrogels containing
[...] Read more.
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder characterized by oxidative stress, innate immune dysregulation, vascular instability, and microbiome-related triggers. Glycyrrhiza glabra (Gg, licorice) root contains phenolics and triterpenoids with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and anti-angiogenic properties that may benefit rosacea-prone skin. Xanthan-gum hydrogels containing 2% methanolic Gg extract (S1, S2) were prepared and characterized. Rheology, in vitro release, and in vitro permeation were evaluated, with the aim of assessing their suitability as topical formulations for rosacea-prone skin. Antioxidant activity was assessed using DPPH, ABTS, and FRAP assays. Antimicrobial effects were tested against S. pyogenes, S. aureus, and C. acnes. Safety and bioactivity were examined through HaCaT keratinocyte assays (MTT, Neutral Red, LDH), the HET-CAM irritation test, and the CAM angiogenesis assay. Immunocytochemistry was performed on rosacea-related inflammatory markers. Both hydrogels showed suitable rheology, sustained release, and preserved strong antioxidant activity. Moderate antimicrobial effects were observed, particularly against S. pyogenes and C. acnes. HaCaT cell viability remained above 84% for the S2 formulation at the highest concentration (200 µg/mL), indicating improved cytocompatibility compared with formulation S1. The hydrogels were non-irritant in the HET-CAM model and reduced neovascularization in the CAM assay, with a more sustained effect observed for formulation S2. Immunohistochemistry supported potential modulation of inflammatory pathways relevant to rosacea, evidencing suppressed VEGF expression and preserved CD44-mediated integrity, particularly in the Labrasol-based formulation (S2), while Caspase-3 staining indicated a controlled apoptotic profile. Overall, Gg hydrogels are safe, biocompatible, non-irritant, and exhibit antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-angiogenic activities, supporting their potential as biocompatible topical formulations with antioxidant and pathway-modulating properties relevant to the biological features associated with rosacea, while underscoring the importance of formulation design.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Natural Antioxidants in Pharmaceuticals and Dermatocosmetology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Danthron Attenuates Intestinal Inflammation by Modulating Oxidative Stress via the EGFR-PI3K-AKT and Nrf2-HO-1 Pathways
by
Chujun Ni, Haiqing Liu, Haiyang Jiang, Zexing Lin, Kangjian Wu, Runnan Wang, Huan Yang, Weijie Li, Chaogang Fan and Yun Zhao
Antioxidants 2026, 15(2), 157; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15020157 - 23 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is characterized by excessive oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and persistent activation of pro-inflammatory signaling pathways. Danthron, a natural anthraquinone derivative from rhubarb, has been reported to possess anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, yet its regulatory mechanisms in intestinal inflammation remain
[...] Read more.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is characterized by excessive oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and persistent activation of pro-inflammatory signaling pathways. Danthron, a natural anthraquinone derivative from rhubarb, has been reported to possess anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, yet its regulatory mechanisms in intestinal inflammation remain unclear. In this study, we combined network pharmacology, transcriptomic profiling, cell-based assays, intestinal organoids, and a dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis model to determine the protective effects of Danthron against oxidative injury. Integrated target prediction and RNA-seq analysis identified EGFR–PI3K–AKT and Nrf2–HO-1 as key signaling axes modulated by Danthron. In macrophages and intestinal epithelial cells, Danthron markedly suppressed LPS- or H2O2-induced ROS accumulation, lipid peroxidation, and mitochondrial membrane potential collapse, while restoring superoxide dismutase activity and reducing malondialdehyde levels. Danthron also inhibited M1 macrophage polarization, preserved epithelial tight-junction proteins, and maintained transepithelial electrical resistance. CETSA, DARTS, and molecular docking confirmed direct engagement of Danthron with components of both the EGFR–PI3K–AKT and Nrf2–HO-1 pathways. In vivo, Danthron significantly ameliorated DSS-induced colitis, reducing inflammatory cytokines, epithelial apoptosis, oxidative stress, and myeloid cell infiltration while improving mucosal architecture and enhancing organoid regenerative capacity. These findings demonstrate that Danthron exerts potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects through coordinated inhibition of EGFR–PI3K–AKT signaling and activation of the Nrf2–HO-1 axis, suggesting its promise as a multi-target therapeutic candidate for IBD.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Ginseng Peptide Improves the Cryopreservation Efficiency and Fertilization Potential of Yak Semen via FOXO1/PI3K/AKT Axis
by
Xupeng Li, Jun Yu, Yuan Li, Zhuo Chen, Ruilan Zeng, Ying Cen, Yufan Wang, Chunhai Zhang, Deyi Zhang, Shi Yin, Yan Xiong, Xianrong Xiong and Jian Li
Antioxidants 2026, 15(2), 156; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15020156 - 23 Jan 2026
Abstract
Semen cryopreservation is a critical biotechnological approach for preserving superior genetic resources in livestock. Spermatozoa are particularly vulnerable to cryogenic stress during the freeze–thaw process, resulting in impaired structure and function. Therefore, the development of effective cryoprotective additives is essential for improving yak
[...] Read more.
Semen cryopreservation is a critical biotechnological approach for preserving superior genetic resources in livestock. Spermatozoa are particularly vulnerable to cryogenic stress during the freeze–thaw process, resulting in impaired structure and function. Therefore, the development of effective cryoprotective additives is essential for improving yak semen cryopreservation. In this study, ginseng peptide (GFREH) was incorporated into the freezing extender at different concentrations (0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, and 1.0 mg/mL) to evaluate its effects on post-thaw sperm quality, in vitro fertilization (IVF) capacity, and the underlying regulatory mechanisms. Semen samples treated with 0 and 0.75 mg/mL GFREH were further subjected to proteomic analysis to elucidate the molecular basis of its cryoprotective action. The results demonstrated that GFREH significantly increased total motility (TM), progressive motility (PM), straight-line velocity (VSL), curvilinear velocity (VCL), average path velocity (VAP), as well as plasma membrane and acrosome integrity of frozen–thawed yak spermatozoa (p < 0.05). GFREH also significantly reduced malondialdehyde (MDA) levels while enhancing antioxidant enzyme activities, mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), and ATP content (p < 0.05). Moreover, GFREH at concentrations of 0.5, 0.75, and 1.0 mg/mL significantly improved IVF and blastocyst formation rates compared with the control (p < 0.05), with the 0.75 mg/mL group exhibiting the highest fertilization and blastocyst rates. Proteomic analysis further revealed that GFREH modulated the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and downregulated FOXO1 expression. Collectively, these findings indicate that ginseng peptides enhance yak sperm cryotolerance by coordinating oxidative balance, mitochondrial energy metabolism, and survival-related signaling, with 0.75 mg/mL representing an optimal effective concentration within the functional dose range tested.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Advances in Applications of Antioxidants in Livestock Health and Reproduction)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Heme as a Pro-Inflammatory Stimulus in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
by
Yuchao Ding, László Potor, Péter Sótonyi, Ágnes Szappanos, Gergő Péter Gyurok, Szilárd Póliska, Andreas Patsalos, Gábor Méhes, Lívia Beke, Katalin Éva Sikura, Erzsébet Zavaczki, Tamás Gáll, Dávid Pethő, Attila Fintha, Beáta Nagy, Béla Juhász, László Nagy, György Balla and József Balla
Antioxidants 2026, 15(2), 155; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15020155 - 23 Jan 2026
Abstract
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a lethal vascular disease characterized by intramural hemorrhage. This study delineates the signatures of heme and its metabolic imbalance related to progression and inflammation in AAA. Clinical analyses of patients undergoing open AAA surgery show that AAA patients
[...] Read more.
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a lethal vascular disease characterized by intramural hemorrhage. This study delineates the signatures of heme and its metabolic imbalance related to progression and inflammation in AAA. Clinical analyses of patients undergoing open AAA surgery show that AAA patients exhibit vascular inflammation, with elevated serum CRP, IL-6, and heme levels correlating with the expression of heme-regulated gene Hmox1/HO-1 (heme oxygenase-1) in the affected aortic wall. Oxidation of hemoglobin to ferri state leading to accumulation of methemoglobin readily releasing heme occurs in human AAA and in angiotensin II (AngII)-induced AAA in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Transcriptomic analysis for AngII-induced AAA identifies upregulated genes predominantly enriched in inflammatory signaling, extracellular matrix degradation, oxidative stress pathways, and altered expression of genes related to heme metabolism including Hmox1. Immunohistochemistry for IL1β and TNFα confirms inflammatory activation within AAA tissues. The signatures of heme-responsive gene inductions, enhanced expression of HO-1 and H-ferritin, are detected. Mechanistic studies employing endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells reveal that heme exposure of resident cells markedly enhances the expression of IL1β and ICAM1, as well as the inflammasome component NLRP3, and such inflammatory response is controlled by HO-1. Intervention with Normosang (heme arginate), an HO-1 inducer, attenuates aneurysm progression, whereas HO-1 inhibition by Tin protoporphyrin IX abolishes this protection. Induction of HO-1 accompanied by elevated H-ferritin level also mitigated aortic wall inflammation as reflected by lowering IL1β and TNFα. These findings highlight the heme-HO-1-H-ferritin axis as an element of AAA pathogenesis and a potential therapeutic target.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Insight into Redox Homeostasis and Oxidative Stress in Health and Disease: Focus on Cardiac and Vascular Function)
►▼
Show Figures
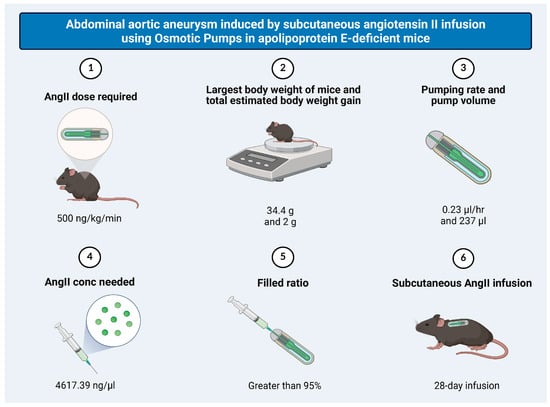
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Natural Products as Potentiators of β-Lactam Antibiotics: A Review of Mechanisms, Advances, and Future Directions
by
Wenjie Yang, Shuocheng Fan, Jie Luo, Yichu Zhou, Xingyang Dai, Jinhu Huang, Liping Wang and Xiaoming Wang
Antioxidants 2026, 15(2), 154; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15020154 - 23 Jan 2026
Abstract
This review focuses on the research progress on natural products as β-lactam antibiotic adjuvants, aiming to address the escalating challenge of antibiotic resistance, particularly the inactivation of antibiotics caused by β-lactamases. The article provides an in-depth analysis of the mechanisms by which plant-derived
[...] Read more.
This review focuses on the research progress on natural products as β-lactam antibiotic adjuvants, aiming to address the escalating challenge of antibiotic resistance, particularly the inactivation of antibiotics caused by β-lactamases. The article provides an in-depth analysis of the mechanisms by which plant-derived (e.g., flavonoids, tannins, phenolics, terpenoids, and alkaloids) and microbial-derived (e.g., clavulanic acid, fungal metabolites, bacteriophages) natural products enhance antimicrobial efficacy. Key potentiation strategies discussed include efflux pump inhibition, membrane permeability alteration, biofilm disruption, PBP2a inhibition, and direct β-lactamase inhibition. Additionally, the review outlines in vitro methods (e.g., dilution and checkerboard assays) and in vivo models (e.g., mouse infection models) used to assess synergistic effects. It also addresses major challenges in identifying active compounds, elucidating mechanisms of action, and pharmacokinetic characterization. Looking forward, the article highlights the potential of multi-omics approaches, artificial intelligence, and nanotechnology to overcome existing bottlenecks, providing novel strategies for the development of effective and safe antibiotic adjuvants. These advances are expected to provide both theoretical insights and practical guidance for combating antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Recent Advances in Veterinary Pharmacology and Toxicology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Hypoxia, ROS, and HIF Signaling in I/R Injury: Implications and Future Prospects
by
Manish Kumar Singh, Hyeong Rok Yun, Jyotsna S. Ranbhise, Sunhee Han, Sung Soo Kim and Insug Kang
Antioxidants 2026, 15(2), 153; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15020153 - 23 Jan 2026
Abstract
Ischemic heart disease (IHD) remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury (MIRI) is a significant contributor to cardiac tissue damage, resulting from an abrupt reduction in blood flow that leads to a reduction in the supply of oxygen
[...] Read more.
Ischemic heart disease (IHD) remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury (MIRI) is a significant contributor to cardiac tissue damage, resulting from an abrupt reduction in blood flow that leads to a reduction in the supply of oxygen and nutrients. The resulting hypoxia triggers severe cellular injury and impairs organ function. Hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) play a central role in maintaining oxygen homeostasis in mammalian tissues. As primary oxygen sensors, HIFs trigger the transcriptional activation of a wide range of genes that facilitate cellular adaptation to reduced oxygen availability and assist in minimizing ischemic damage. Mitochondria are particularly vulnerable to hypoxic stress and are a major source of reactive oxygen species (ROS) during I/R injury. Stabilization of HIFs has been shown to reduce loss of cardiomyocytes under these conditions, highlighting the importance of HIF-dependent pathways in preserving mitochondrial integrity and promoting cell survival. Collectively, these observations suggest that hypoxia, HIF signaling, and mitochondrial dysfunction are tightly interconnected processes in the pathogenesis of IHD. This review, therefore, focuses on the interaction between hypoxia-driven HIF responses and mitochondrial regulation, emphasizing their implications for therapeutic strategies in managing IHD.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs))
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Temporal Exercise Conditioning Confers Dual-Phase Cardioprotection Against Isoproterenol-Induced Injury in a Rat Model
by
Krisztina Kupai, Zsolt Murlasits, Hsu Lin Kang, Eszter Regős, Ákos Várkonyi, Csaba Lengyel, Imre Pávó, Zsolt Radák, Béla Juhász, Dániel Priksz and Anikó Pósa
Antioxidants 2026, 15(2), 152; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15020152 - 23 Jan 2026
Abstract
Exercise training has demonstrated potential benefits in addressing the adverse effects of cardiovascular diseases, particularly myocardial infarction (MI). This study analyzed the cardioprotective effects of moderate exercise before and after MI in rats subjected to isoproterenol (ISO)-induced heart damage. Wistar rats were assigned
[...] Read more.
Exercise training has demonstrated potential benefits in addressing the adverse effects of cardiovascular diseases, particularly myocardial infarction (MI). This study analyzed the cardioprotective effects of moderate exercise before and after MI in rats subjected to isoproterenol (ISO)-induced heart damage. Wistar rats were assigned to five groups: controls (CTRL), isoproterenol-treated (ISO), swimming before ISO (PRE + ISO), swimming after ISO (ISO + POST), and swimming both before and after ISO (PRE + ISO + POST). Cardiac function was assessed through echocardiography, while oxidative stress markers, Heme Oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and Myeloperoxidase (MPO), were quantified using biochemical assays and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Statistical analyses were conducted by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), accompanied by Tukey’s post hoc test. Exercise performed post-MI and both pre- and post-MI significantly reduced ISO-induced infarct size and improved left ventricular function (stroke volume (SV), ejection fraction (EF), and Tei index). HO-1 protein concentration and HO enzyme activity were restored, while swim training reduced the activity of MPO compared to the ISO group. Moderate exercise training, when appropriately timed, provides cardioprotection against ISO-induced myocardial damage by reducing oxidative stress and cardiac dysfunction.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Insight into Redox Homeostasis and Oxidative Stress in Health and Disease: Focus on Cardiac and Vascular Function)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impact of a Longer-Term Physical Activity Intervention on Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Older People with Metabolic Syndrome
by
Maria Magdalena Quetglas-Llabrés, Margalida Monserrat-Mesquida, Silvia García, Marina Ródenas-Munar, David Mateos, Lucía Ugarriza, Cristina Gómez, Antoni Sureda, Cristina Bouzas and Josep A. Tur
Antioxidants 2026, 15(2), 151; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15020151 - 23 Jan 2026
Abstract
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is characterised by cardiometabolic risk factors and is closely associated with increased oxidative stress and chronic low-grade inflammation. MetS is largely driven by adverse lifestyle behaviours, particularly physical inactivity, and regular physical activity is recognised as a central strategy for
[...] Read more.
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is characterised by cardiometabolic risk factors and is closely associated with increased oxidative stress and chronic low-grade inflammation. MetS is largely driven by adverse lifestyle behaviours, particularly physical inactivity, and regular physical activity is recognised as a central strategy for its prevention and management. This study aimed to assess the long-term impact of a five-year follow-up period of physical activity on oxidative stress, inflammatory biomarkers, and cardiometabolic health in adults with MetS. Forty participants diagnosed with MetS (50% men, aged 55–75 years) were selected and stratified into two groups: those who increased their physical activity and those who reduced it during the intervention. Physical activity was assessed using metabolic equivalent task minutes per week (MET·min/week), and evaluations were performed at baseline, 3 years, and 5 years. Participants who increased physical activity showed a progressive reduction in reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), together with a decrease in plasma malondialdehyde (MDA). Antioxidant enzyme activities, including catalase and superoxide dismutase, exhibited a favourable long-term profile, with recovery or maintenance of higher activity levels by the end of follow-up, reflecting enhanced endogenous antioxidant defence. Inflammatory status improved and was characterised by a reduction in myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity and a sustained increase in plasma interleukin-15 (IL-15). These participants also showed reductions in body weight, body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, fasting glucose, and glycosylated haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), consistent with improved insulin sensitivity and metabolic control. Participants who reduced physical activity tended to show unfavourable trajectories in several biomarkers. Increasing physical activity over time is associated with substantial improvements in redox balance, inflammatory status, and cardiometabolic health in adults with MetS. These findings reinforce the central role of physical activity as a fundamental therapeutic component within lifestyle interventions aimed at mitigating metabolic dysfunction and preventing MetS progression.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Oxidative Stress During Physical Activity)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Plasma EV miR-186-5p as an Early Biomarker and Regulator of IFN-α-Mediated Oxidative and β-Cell Dysfunction in Prediabetes
by
Jae-Hyung Park, Thi Nhi Nguyen, Hye Min Shim, Yun-Ui Bae, Gyeong Im Yu, Junho Kang, Eun Yeong Ha and Hochan Cho
Antioxidants 2026, 15(2), 150; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15020150 - 23 Jan 2026
Abstract
Prediabetes is accompanied by early β-cell stress and oxidative imbalance before overt hyperglycemia. Circulating extracellular vesicle (EV) microRNAs (miRNAs) may capture early metabolic disturbances, but their mechanistic relevance remains unclear. Plasma EV miRNA profiles were analyzed across normoglycemia, prediabetes, and newly diagnosed type
[...] Read more.
Prediabetes is accompanied by early β-cell stress and oxidative imbalance before overt hyperglycemia. Circulating extracellular vesicle (EV) microRNAs (miRNAs) may capture early metabolic disturbances, but their mechanistic relevance remains unclear. Plasma EV miRNA profiles were analyzed across normoglycemia, prediabetes, and newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes, with validation in an independent cohort (n = 150). Functional studies were performed in pancreatic β-cells exposed to glucolipotoxic stress to examine miRNA regulation, IFN-α signaling, mitochondrial redox status, and insulin secretion. Six EV miRNAs, including miR-186-5p, were consistently reduced in prediabetes and correlated with glycemic and insulin resistance indices. In β-cells, glucolipotoxic stress selectively suppressed miR-186-5p, leading to derepression of IFNA2, activation of IFN-α–JAK/STAT signaling, increased mitochondrial ROS, impaired ATP/ADP dynamics, and reduced glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Restoration of miR-186-5p or pharmacologic JAK inhibition mitigated these defects, and luciferase assays confirmed IFNA2 as a direct target of miR-186-5p. EV-associated miR-186-5p represents an early marker of metabolic stress in prediabetes and provides mechanistic insight into IFN-α–driven oxidative and secretory dysfunction in β-cells.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mitochondria, Redox and Pancreatic β-Cells: Maturation, Function and Inflammatory Stress)
►▼
Show Figures
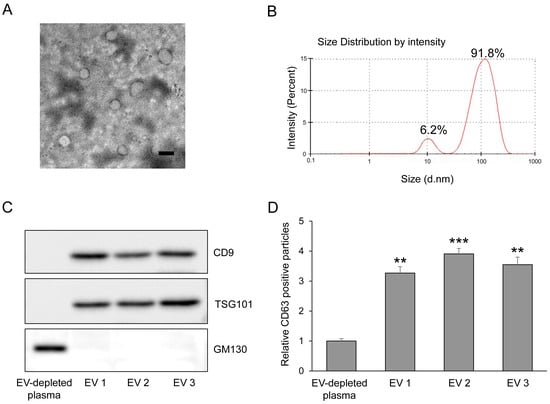
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Targeting Skin Aging Hallmarks In Vitro: Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Senescence Effects of Phenolic-Rich Extracts from Cistus L. Species
by
Mário Pedro Marques, Euclides Landim, Carla Varela, Ricardo M. F. da Costa, Joana Marques, Luís A. E. Batista de Carvalho, Ana Silva, Maria Teresa Cruz, Rebeca André, Patrícia Rijo, Maria Inês Dias, Aida Carvalho, Paulo J. Oliveira and Célia Cabral
Antioxidants 2026, 15(1), 149; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15010149 - 22 Jan 2026
Abstract
Plant-based extracts are rich sources of phenolic compounds, which may act as skin antiaging mediators. Herein, Cistus albidus L. (Ca), Cistus ladanifer L. subsp. ladanifer (Cl) and Cistus salviifolius L. (Cs) were selected to test whether their phytochemical profile and bioactive potential align
[...] Read more.
Plant-based extracts are rich sources of phenolic compounds, which may act as skin antiaging mediators. Herein, Cistus albidus L. (Ca), Cistus ladanifer L. subsp. ladanifer (Cl) and Cistus salviifolius L. (Cs) were selected to test whether their phytochemical profile and bioactive potential align to target human skin aging. Hydroethanolic extracts (HEs) were prepared and characterized using infrared vibrational spectroscopy (FTIR-ATR) and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS). Non-toxic concentrations were screened, and cytoprotective and antioxidant effects were studied in tert-butyl hydroperoxide-stimulated normal human dermal fibroblasts (NHDFs). Lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages were used to assess anti-inflammatory activity, the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Test Guideline No. 439 was used to assess irritant effects, and the anti-senescence potential was assessed in etoposide-stimulated NHDFs. A series of enzymatic inhibition assays was performed. All extracts comprised ellagic acid derivatives, as well as myricetin and quercetin derivatives in Cs and Ca. The HE of Cs was also markedly composed of ligstroside. At non-toxic concentrations, cytoprotective effects were observed in NHDFs. However, only Cs and Cl exhibited significant antioxidant activity in these cells (p < 0.001 and p < 0.0001, respectively). In addition to that, Cl demonstrated highly significant anti-inflammatory (p < 0.0001) and anti-senescence (p < 0.0001) effects. Cs and Cl showed a remarkable potential to inhibit elastase; in addition, Cs also showed anti-hyaluronidase and anti-tyrosinase activities. Meaningfully, Cs and Cl extracts did not exhibit skin irritant effects. The unveiled potential of Cl in skin aging offset highlights the need to elucidate the detailed mechanisms of action, paving the way for the development of skin anti-aging formulations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Natural Antioxidants for Cosmetic Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Role of Glutathione in Alleviating Chilling Injury in Bovine Blastocysts: Mitochondrial Restoration and Apoptosis Inhibition
by
Jingyu Ren, Fuhan Liu, Gang Liu, Biao Wang, Jie Zhu, Yongbin Liu and Yanfeng Dai
Antioxidants 2026, 15(1), 148; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15010148 - 22 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Short-term hypothermic storage at 4 °C represents a promising non-freezing alternative for transporting bovine embryos and synchronizing assisted reproductive procedures. However, chilling induces oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and apoptosis, which markedly impair post-preservation embryonic viability. Glutathione (GSH), a key intracellular antioxidant, may mitigate
[...] Read more.
Short-term hypothermic storage at 4 °C represents a promising non-freezing alternative for transporting bovine embryos and synchronizing assisted reproductive procedures. However, chilling induces oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and apoptosis, which markedly impair post-preservation embryonic viability. Glutathione (GSH), a key intracellular antioxidant, may mitigate these damaging effects, yet its protective mechanisms during bovine blastocyst hypothermic preservation remain unclear. Here, we investigated the impact of exogenous GSH supplementation on the survival, hatching ability, cellular integrity, mitochondrial function, and developmental potential of bovine blastocysts preserved at 4 °C for seven days. Optimization experiments revealed that 4 mM GSH provided the highest post-chilling survival and hatching rates. Using DCFH-DA, TUNEL, and γ-H2AX staining, we demonstrated that 4 °C preservation significantly increased intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS), DNA fragmentation, and apoptosis. GSH supplementation markedly alleviated oxidative injury, reduced apoptotic cell ratio, and decreased DNA double-strand breaks. MitoTracker and JC-1 staining indicated severe chilling-induced mitochondrial suppression, including decreased mitochondrial activity and membrane potential (ΔΨm), which were largely restored by GSH. Gene expression analyses further revealed that chilling downregulated antioxidant genes (SOD2, GPX1, TFAM, NRF2), pluripotency markers (POU5F1, NANOG), and IFNT, while upregulating apoptotic genes (BAX, CASP3). GSH effectively reversed these alterations and normalized the BAX/BCL2 ratio. Moreover, SOX2/CDX2 immunostaining, total cell number, and ICM/TE ratio confirmed improved embryonic structural integrity and developmental competence. Collectively, our findings demonstrate that exogenous GSH protects bovine blastocysts from chilling injury by suppressing ROS accumulation, stabilizing mitochondrial function, reducing apoptosis, and restoring developmental potential. This study provides a mechanistic foundation for improving 4 °C embryo storage strategies in bovine reproductive biotechnology.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Integrative Transcriptomic and Network Analysis of Hemocyte Volume Plasticity and Redox Regulation Under Osmotic Stress in Penaeus monodon
by
Sheng Huang, Falin Zhou, Qibin Yang, Song Jiang, Jilin Chen, Jie Xiong, Erchao Li and Yundong Li
Antioxidants 2026, 15(1), 147; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15010147 - 22 Jan 2026
Abstract
Osmotic stress affects ion transport and cell hydration, potentially disrupting redox homeostasis through altered proteostasis and mitochondrial metabolism. However, how immune hemocytes coordinate volume regulation with these stress-linked processes, particularly oxidative stress and antioxidant responses, remains unclear in crustaceans. This study integrated quantitative
[...] Read more.
Osmotic stress affects ion transport and cell hydration, potentially disrupting redox homeostasis through altered proteostasis and mitochondrial metabolism. However, how immune hemocytes coordinate volume regulation with these stress-linked processes, particularly oxidative stress and antioxidant responses, remains unclear in crustaceans. This study integrated quantitative cytology, RNA sequencing, and network analysis to profile hemocyte volume plasticity in the euryhaline shrimp Penaeus monodon across a salinity gradient. Hemocytes were incubated for 24 h in hypoosmotic, isosmotic, and hyperosmotic media, with significant volume shifts observed while maintaining membrane integrity and morphology. The permeability of solutes (urea and sorbitol) suggested that volume adjustment is coupled with solute transport. Transcriptomic analyses identified key salinity-responsive pathways, including oxidative phosphorylation, MAPK signaling, ribosome biogenesis, and antioxidant defense mechanisms, underscoring the activation of redox-regulatory systems under osmotic stress. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis highlighted ribosomal proteins as central hubs in a salinity-responsive module, with qRT-PCR confirming the co-regulation of these hubs alongside representative osmoregulatory and antioxidant genes (AQP4, Na+/K+-ATPase, HSP70, CHOP, and antioxidant enzymes). These findings reveal how hemocyte volume dynamics are coupled to redox regulation, providing a mechanistic framework for understanding osmotic stress–redox coupling in crustacean immune cells.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antioxidant Defenses Against Stress Caused by Physical or Chemical Environmental Changes)
Open AccessArticle
Olive Leaf Extract Added to Losartan Treatment Improved Klotho/Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Hypertensive Rats with Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
by
Danijela Karanović, Nevena Mihailović-Stanojević, Milan Ivanov, Una-Jovana Vujačić, Jelica Grujić-Milanović, Maja Životić, Dragana Dekanski, Djurdjica Jovović and Zoran Miloradović
Antioxidants 2026, 15(1), 146; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15010146 - 22 Jan 2026
Abstract
The downregulation of Klotho in renal injury predicts the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Klotho acts as an antagonist of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, which is involved in the pathogenesis of proteinuria, glomerulosclerosis and tubulointerstitial fibrosis. We investigated whether losartan (L, angiotensin II
[...] Read more.
The downregulation of Klotho in renal injury predicts the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Klotho acts as an antagonist of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, which is involved in the pathogenesis of proteinuria, glomerulosclerosis and tubulointerstitial fibrosis. We investigated whether losartan (L, angiotensin II type-1 receptor blocker) alone or combined with synthetic (tempol, T) or natural antioxidants (olive leaf extract, O) could alter Klotho/Wnt4/β-catenin signaling, thus reducing fibrosis and slowing the progression of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). The rats were divided into five groups. The control rats received a vehicle. The other groups received adriamycin (2 mg/kg, i.v., twice in a 3-week interval) for FSGS induction. Treatments with L, L+T and L+O (10, 10 + 100 and 10 + 80 mg/kg/day, respectively) were administered by gavage during six weeks. In the kidneys of model rats, Klotho and Wnt4 were downregulated, whereas β-catenin and fibronectin levels were increased compared with the control group. L+T did not alter Klotho, Wnt4 or fibronectin levels, while it further increased β-catenin. In contrast, L+O improved Klotho, and reduced β-catenin and fibronectin levels, although it increased PAI-1. The L+O combination reduced proteinuria more efficiently than L and decreased renal injury close to control levels. Although these findings indicate that combined treatment of losartan and olive leaf extract is promising in slowing the progression of the experimental FSGS, further clinical studies are needed to confirm its favorable outcomes and safety in CKD patients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Natural and Synthetic Antioxidants)
►▼
Show Figures
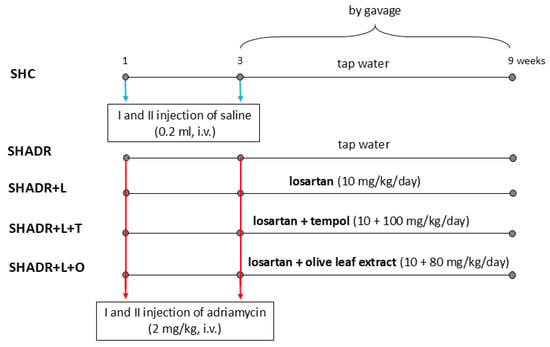
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Metal-Chelating Macroalgal Extract as a Marine Antioxidant for Stabilizing DHA Nanoemulsions
by
Sakhi Ghelichi, Behdad Shokrollahi Yancheshmeh, Mona Hajfathalian, Seyed Hossein Helalat, Arpan Shrestha, Saroj Katwal and Charlotte Jacobsen
Antioxidants 2026, 15(1), 145; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15010145 - 22 Jan 2026
Abstract
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), an omega-3 fatty acid essential for human health, is highly prone to oxidation in nanoemulsions due to their large interfacial area and presence of transition metal ions. This study investigated macroalgal chelators for stabilizing DHA-rich nanoemulsions. Sequential enzymatic–alkaline extraction using
[...] Read more.
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), an omega-3 fatty acid essential for human health, is highly prone to oxidation in nanoemulsions due to their large interfacial area and presence of transition metal ions. This study investigated macroalgal chelators for stabilizing DHA-rich nanoemulsions. Sequential enzymatic–alkaline extraction using Alcalase® produced an extract with the strongest Fe2+-chelating activity (IC50 = 1.22 mg/mL), protein content of 10.11 ± 0.15%, and total phenolics ≈ 17 µg GAE/mL. This extract was incorporated into nanoemulsions (5 wt% DHA oil, 1 wt% Tween® 20) at 0.61, 1.22, and 2.44 mg/mL and compared with controls containing EDTA (0.025 mg/mL) or no antioxidant. Droplet size remained stable (D3,2 ≈ 77–80 nm; D4,3 ≈ 199–215 nm) and zeta potential averaged −17 to −19 mV, confirming physical stability. Confocal microscopy revealed concentration-dependent interfacial adsorption of extract components. During iron-accelerated storage, extract-treated nanoemulsions slowed hydroperoxide formation and delayed tocopherol depletion compared to the control, while reducing volatile oxidation markers such as 1-penten-3-ol by up to 40%. However, EDTA consistently provided superior protection against oxidation. These findings highlight the potential of macroalgal extracts as clean-label, natural chelators for mitigating metal-driven oxidation in DHA nanoemulsions, though synthetic chelators remain more effective under severe prooxidant conditions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antioxidants from the Sea and Their Application)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Antioxidants Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Antioxidants, Cancers, Gastroenterology Insights, Life, Nutrients
Oxidative Stress and Diet: The Health Implications of Advanced Glycation and Lipid Oxidation End-Products
Topic Editors: Joseph Kanner, Ron KohenDeadline: 31 March 2026
Topic in
Antioxidants, Molecules, Nutraceuticals, Nutrients, Plants
Memory-Enhancing Activity of Bioactive Compounds: From Natural Sources to Brain, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Lucian Hritcu, Simone CarradoriDeadline: 30 April 2026
Topic in
Antioxidants, Dietetics, Foods, Nutrients, Plants
Exploring Nutritional, Antioxidant and Functional Potential of Plant-Based Food and Plant Bioactive Compounds in Human Health
Topic Editors: Gianluca Rizzo, Andrea ArmaniDeadline: 31 May 2026
Topic in
Molecules, Plants, Toxins, Antioxidants
Exploring the Cytotoxic and Antioxidant Potential of Plant Extracts
Topic Editors: Claudio Frezza, Manuela CipolettiDeadline: 30 June 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Antioxidants
Redox Balance and Autophagy in Neuroinflammation
Guest Editors: Anna Colell, Vicente Roca-AgujetasDeadline: 26 January 2026
Special Issue in
Antioxidants
Environmental Risk Factors and Oxidative Stress in the Retina
Guest Editor: Adrian GerickeDeadline: 30 January 2026
Special Issue in
Antioxidants
Redox Signaling in Chronic Diseases
Guest Editor: Emma BorrelliDeadline: 30 January 2026
Special Issue in
Antioxidants
Oxidative Stress and Diabetic Retinopathy
Guest Editor: Tatsuya MimuraDeadline: 30 January 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Antioxidants
Advances in Antioxidant Ingredients from Natural Products
Collection Editors: Carla Susana Correia Pereira, Lillian Barros








