Supplementation of Saponins from Leaves of Panax quinquefolius Mitigates Cisplatin-Evoked Cardiotoxicity via Inhibiting Oxidative Stress-Associated Inflammation and Apoptosis in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
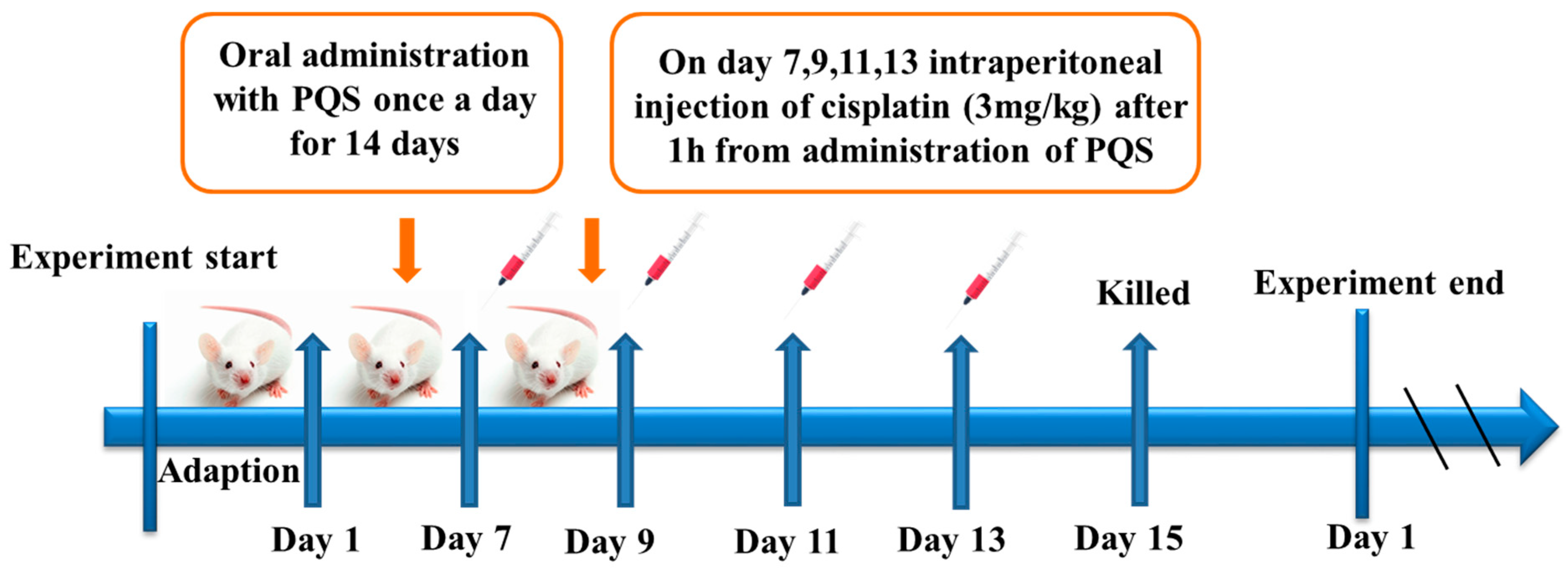
2.2. Animal and Experiments Design
2.3. Biochemical Parameters Determination
2.3.1. Cardiac Biomarkers
2.3.2. Assessment of Cardiac Oxidative Stress
2.3.3. Assessment of Proinflammatory Cytokine
2.4. H&E Staining
2.5. Immunohistochemistry
2.6. Immunofluorescence and Hoechst 33258 Staining
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
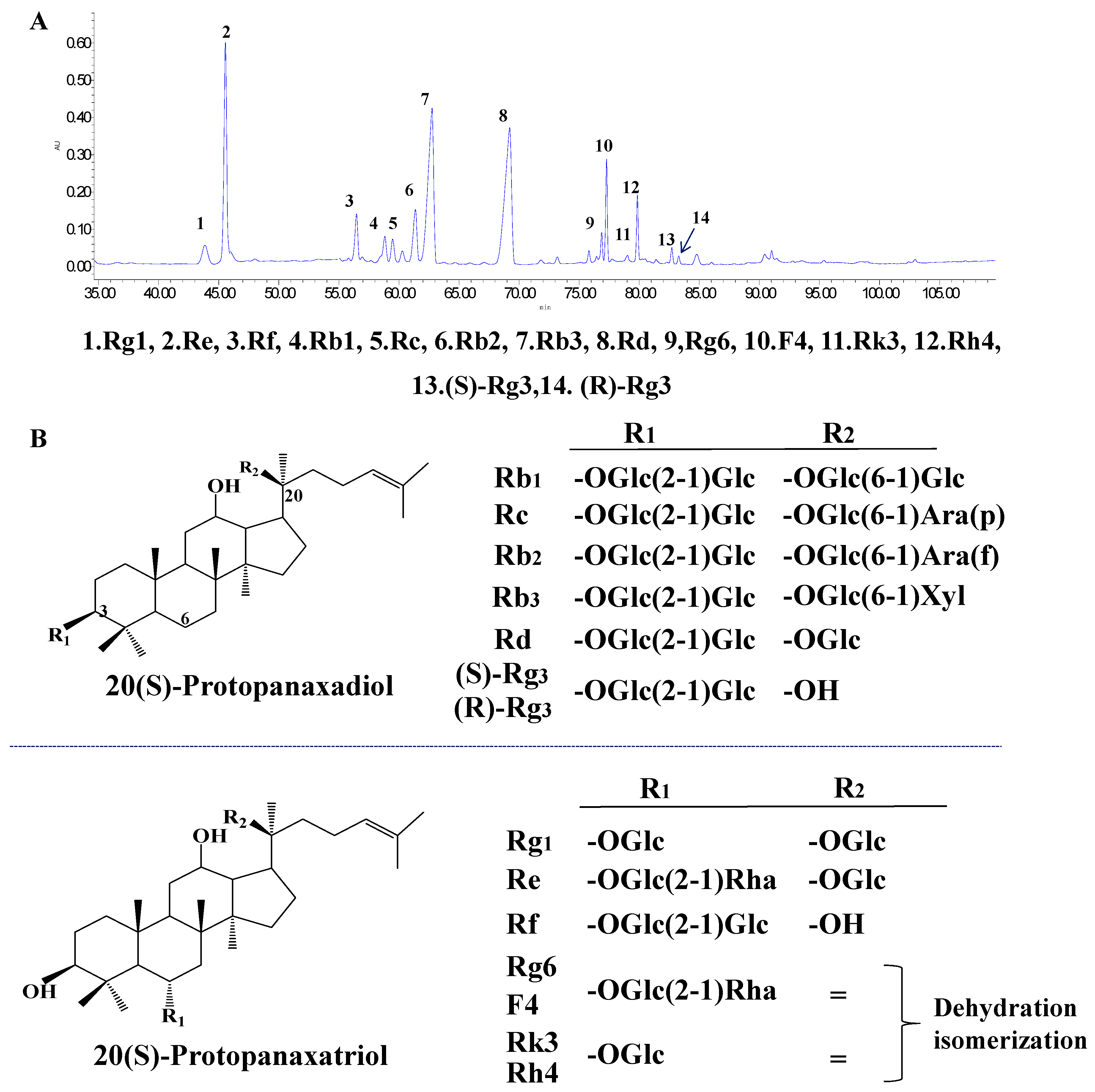
3.1. Typical HPLC Chromatogram of PQS
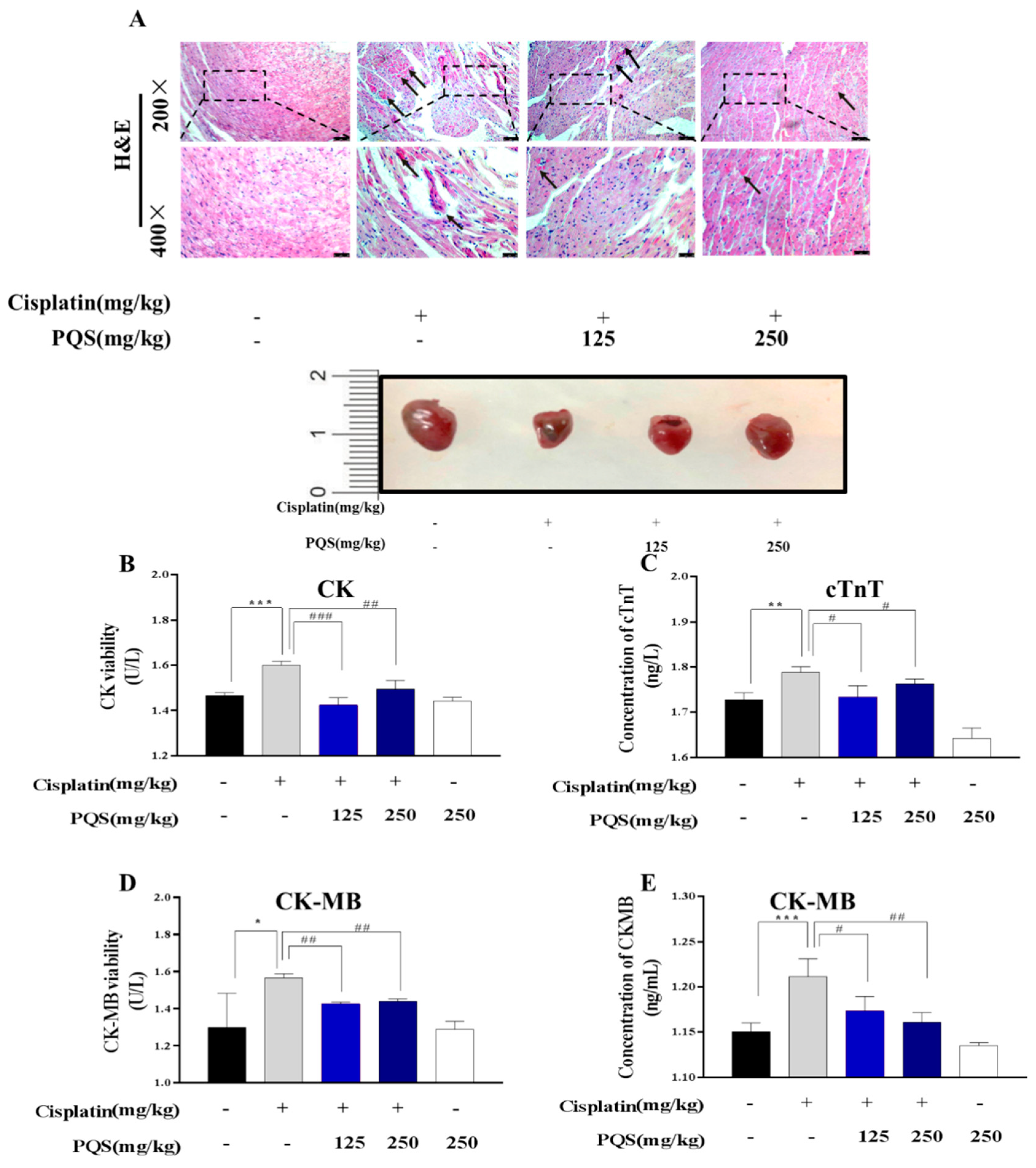
3.2. PQS Protects Against Cisplatin-Induced Cardiotoxicity
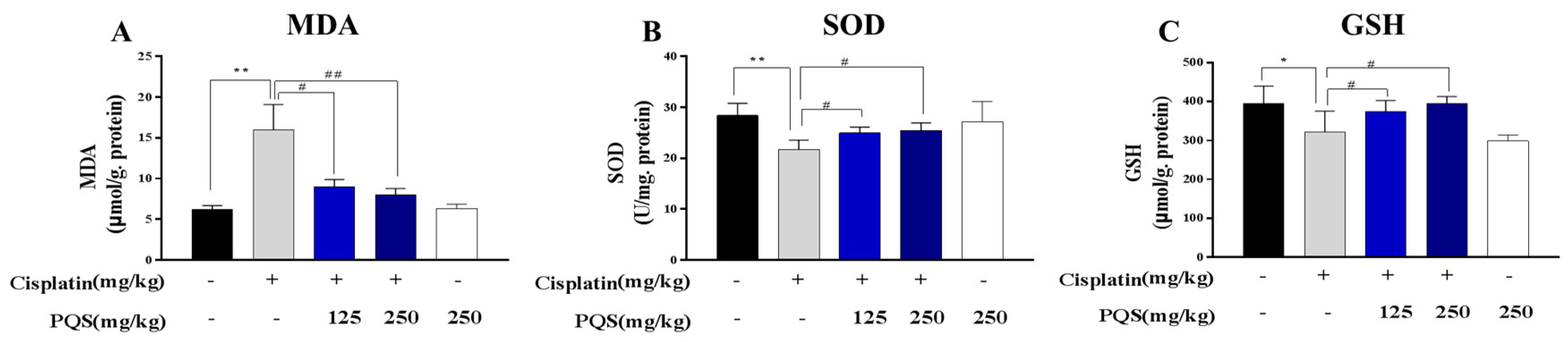
3.3. PQS Inhibits Oxidative Stress Induced by Cisplatin Treatment
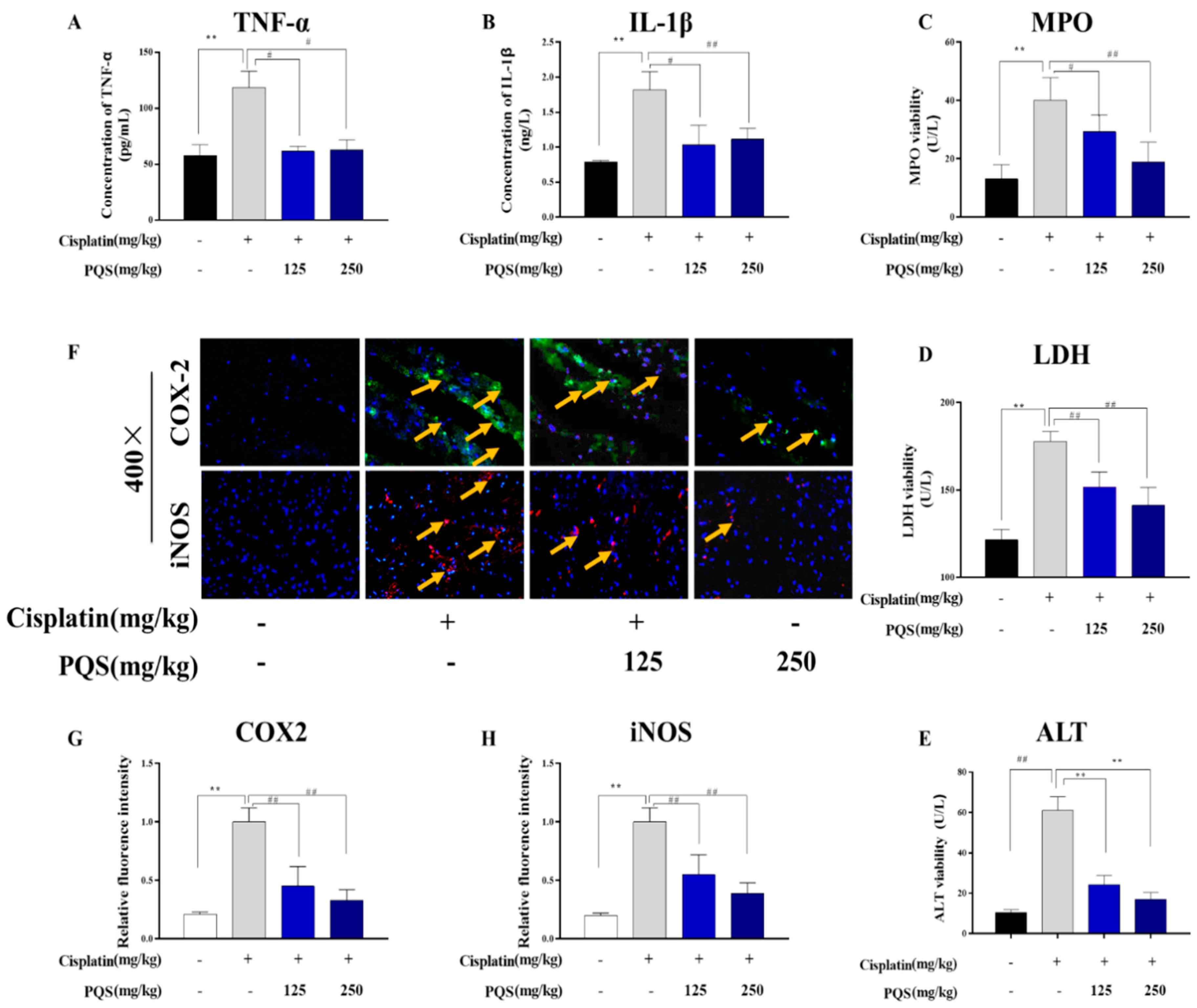
3.4. Effect of PQS on Cardiac Inflammation
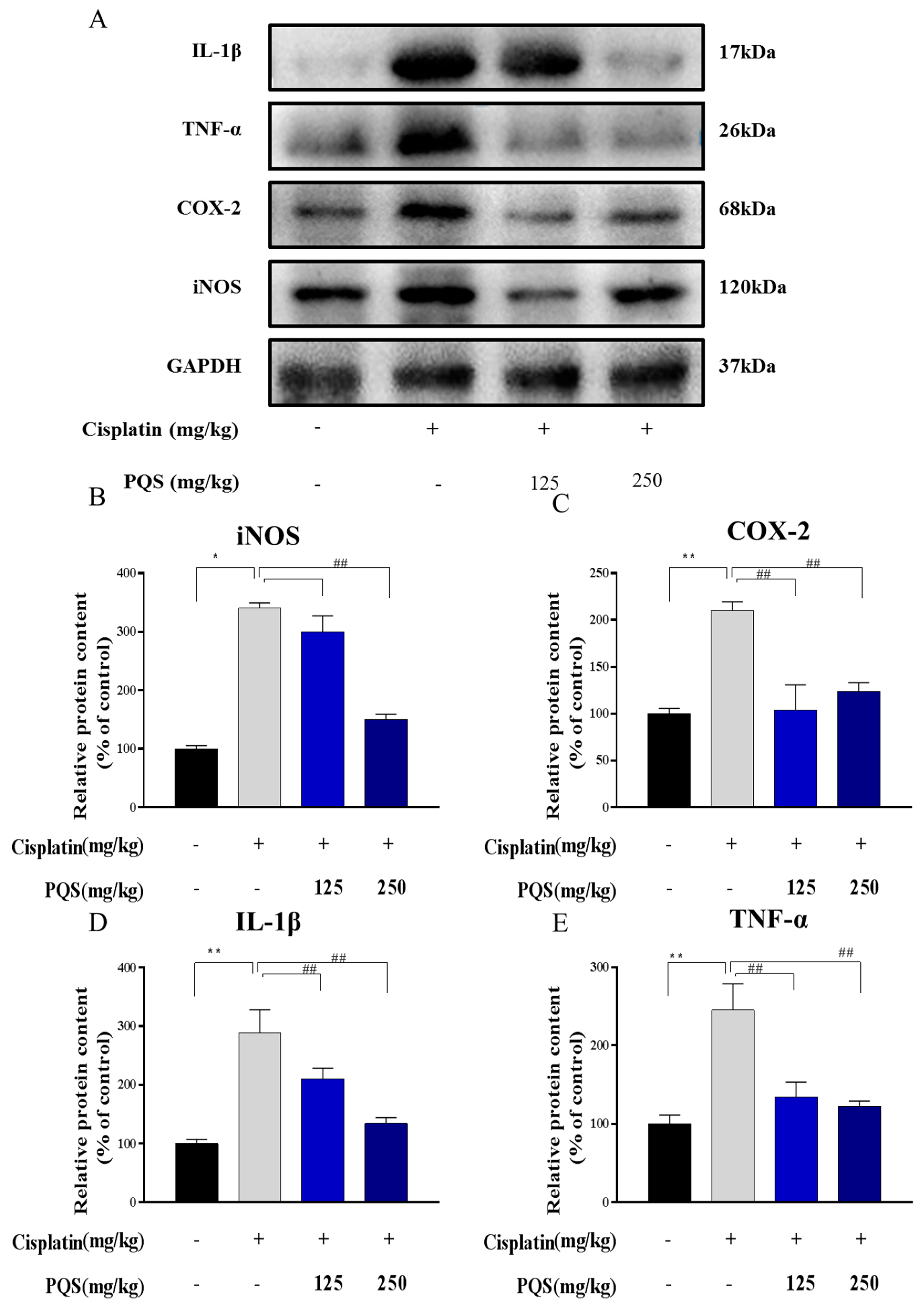
3.5. Effects of PQS Treatment on Cisplatin-Induced Inflammatory Markers
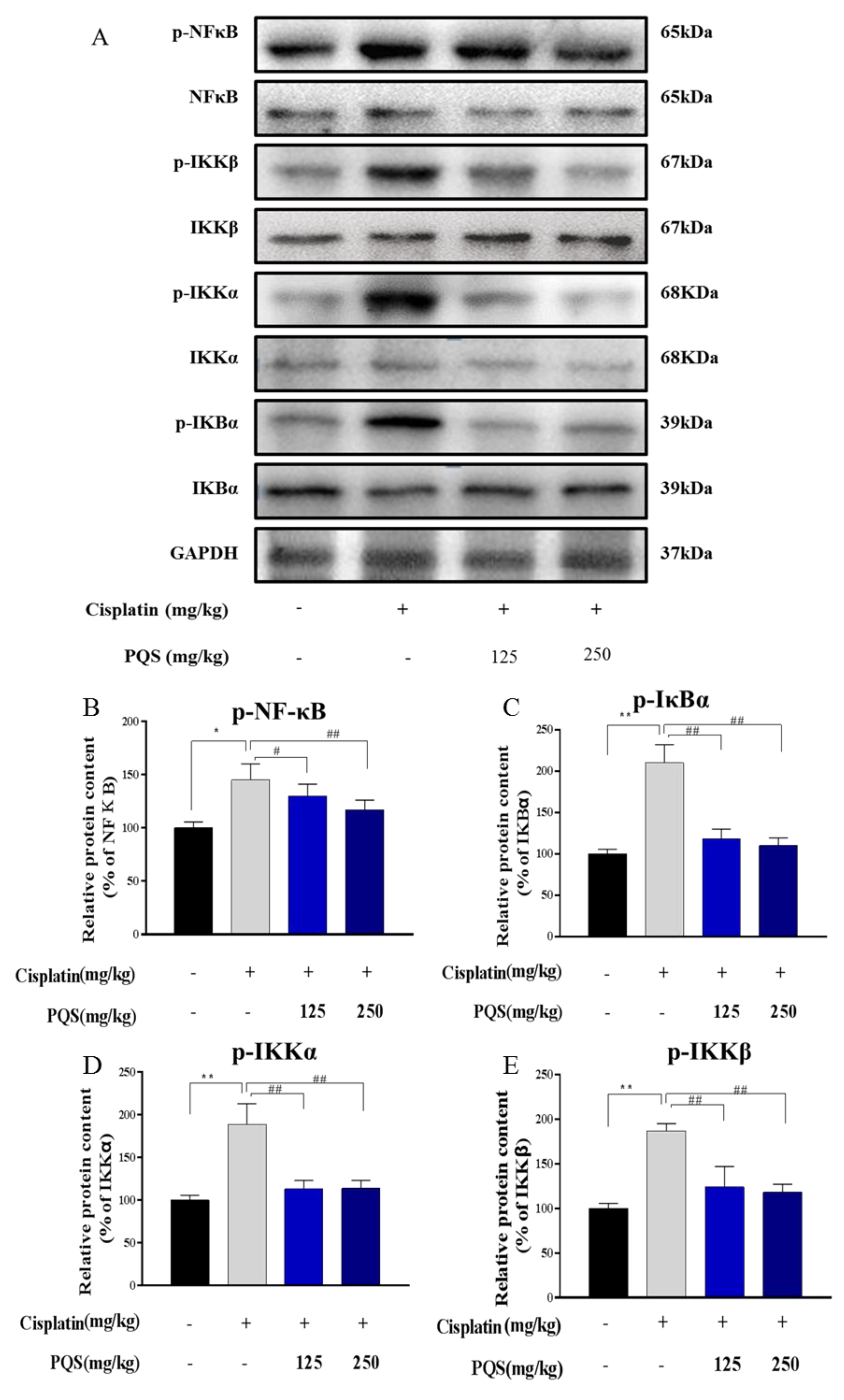
3.6. Effects of PQS on the NF-κB Signaling Pathway
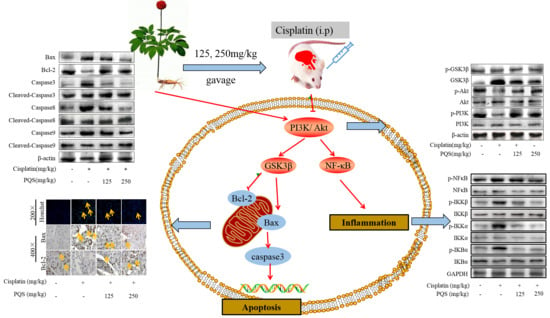
3.7. PQS Attenuates the Intrinsic Mitochondrial Apoptotic Pathway In Vivo
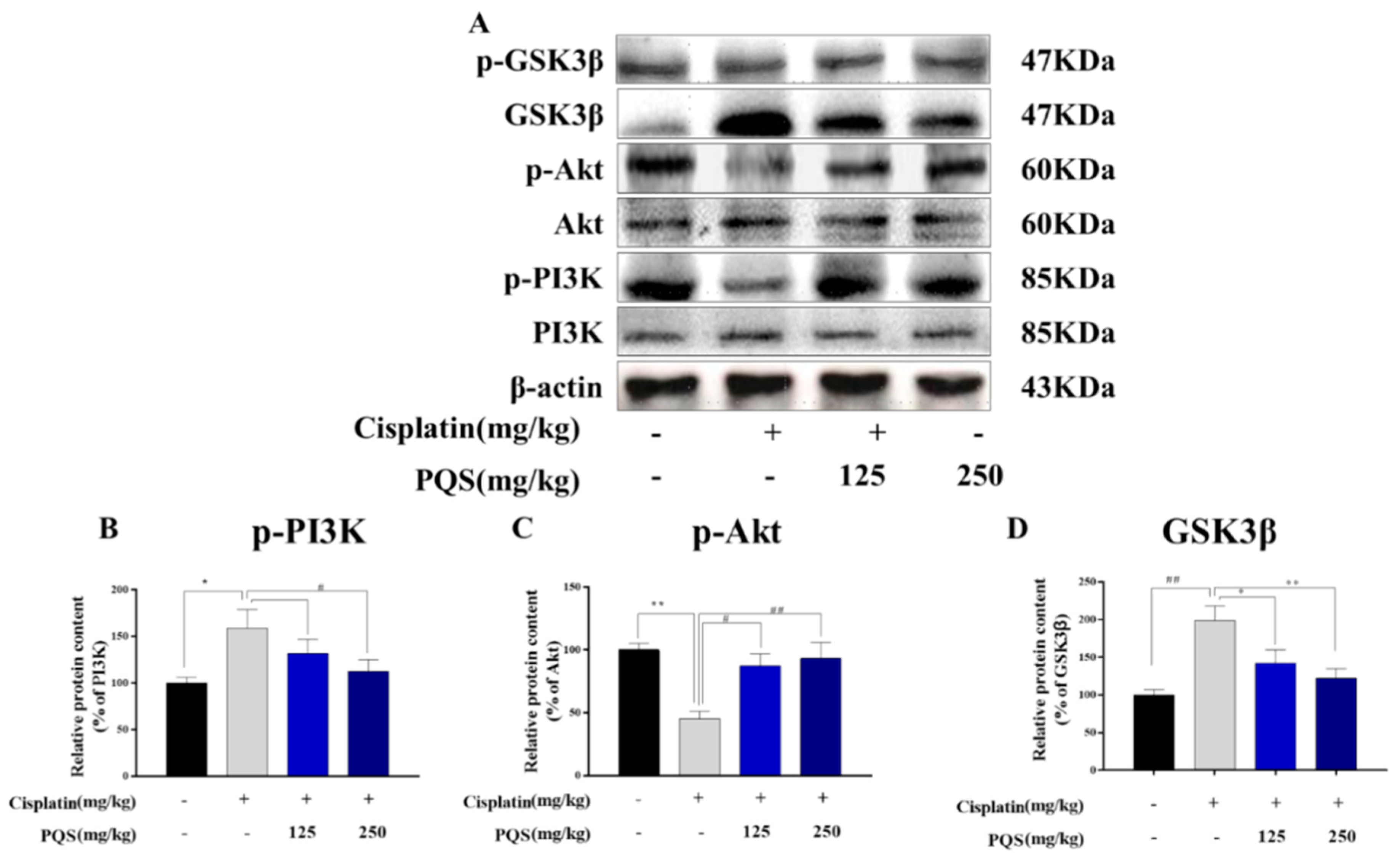
3.8. PQS Attenuates Cisplatin-Induced through PI3K/ Akt/ GSK-3β Signal Pathway
3.9. Mechanism of PQS Improving Cardiac Toxicity Induced by Cisplatin
3.10. PQS Attenuates Cisplatin-Induced through PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β Signal Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CK | Creatine kinase |
| MPO | Myeloperoxidase |
| CK-MB | Creatine kinase isoenzyme MB |
| CTnT | Plasma cardiac troponin T Glutathione |
| PQS | Panax quinquefolius saponins |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and Eosin |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-kappa B |
| Akt | Protein kinase B |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
References
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karasawa, T.; Steyger, P.S. An integrated view of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 237, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topal, I.; Özbek Bilgin, A.; Çimen, F.K.; Kurt, N.; Süleyman, Z.; Bilgin, Y.; Özçiçek, A.; Altuner, D. The effect of rutin on cisplatin-induced oxidative cardiac damage in rats. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2018, 20, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.-M.; Kim, H.-K.; Shim, W.; Anwar, M.A.; Kwon, J.-W.; Kwon, H.-K.; Kim, H.J.; Jeong, H.; Kim, H.M.; Hwang, D.; et al. Mechanism of Cisplatin-Induced Cytotoxicity Is Correlated to Impaired Metabolism Due to Mitochondrial ROS Generation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, Z.V.; Ferdinandy, P.; Liaudet, L.; Pacher, P. Drug-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and cardiotoxicity. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2015, 309, H1453–H1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugbartey, G.J.; Peppone, L.J.; De Graaf, I.A. An integrative view of cisplatin-induced renal and cardiac toxicities: Molecular mechanisms, current treatment challenges and potential protective measures. Toxicology 2016, 371, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Chen, Z.; Qi, J.; Duan, S.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wu, L.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, B.; Wang, N.; et al. Drp1-dependent mitophagy protects against cisplatin-induced apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells by improving mitochondrial function. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 20988–21000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubera, I.; Duranton, C.; Melis, N.; Cougnon, M.; Mograbi, B.; Tauc, M. Role of CFTR in oxidative stress and suicidal death of renal cells during cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhoshani, A.R.; Hafez, M.M.; Husain, S.; Al-Sheikh, A.M.; Alotaibi, M.R.; Al Rejaie, S.S.; Alshammari, M.A.; Almutairi, M.M.; Al-Shabanah, O.A. Protective effect of rutin supplementation against cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity in rats. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, P.; Horváth, B.; Kechrid, M.; Tanchian, G.; Rajesh, M.; Naura, A.S.; Boulares, A.H.; Pacher, P. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 is a key mediator of cisplatin-induced kidney inflammation and injury. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 1774–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Jiang, X.; Li, A.; Zhao, Z.; Li, S. S-Allylmercaptocysteine Attenuates Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity through Suppression of Apoptosis, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation. Nutrients 2017, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marullo, R.; Werner, E.; Degtyareva, N.; Moore, B.; Altavilla, G.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Doetsch, P.W. Cisplatin Induces a Mitochondrial-ROS Response That Contributes to Cytotoxicity Depending on Mitochondrial Redox Status and Bioenergetic Functions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, D.; Bai, H.; Yin, S. Renoprotective effects of emodin against diabetic nephropathy in rat models are mediated via PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β and Bax/caspase-3 signaling pathways. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 5163–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hao, Y.; Alway, S.E. Suppression of GSK-3β activation by M-cadherin protects myoblasts against mitochondria-associated apoptosis during myogenic differentiation. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 3835–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Jiang, X.; Wei, F.; Zhu, H. Leonurine protects cardiac function following acute myocardial infarction through anti-apoptosis by the PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 1582–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Qiao, X.; Wu, S. Carbamylated erythropoietin attenuates cardiomyopathy via PI3K/Akt activation in rats with diabetic cardiomyopathy. Exp. Ther. Med. 2013, 6, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hang, P.; Zhao, J.; Sun, L.; Li, M.; Han, Y.; Du, Z.; Li, Y. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiac dysfunction through activating Akt signalling in rats. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobasher, M.A.; González-Rodriguez, A.; Santamaría, B.; Ramos, S.; Martín, M.Á.; Goya, L.; Rada, P.; Letzig, L.; James, L.P.; Cuadrado, A.; et al. Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B modulates GSK3β/Nrf2 and IGFIR signaling pathways in acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.-N.; Li, Y.-Z.; Li, W.; Yan, X.-T.; Yang, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, L.-C.; Yang, L.-M. Nephroprotective Effects of Saponins from Leaves of Panax quinquefolius against Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.Y.; Zhang, W.Z.; Yan, X.T.; Hou, J.G.; Wang, Z.; Ding, C.B.; Liu, W.C.; Zheng, Y.N.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.R.; et al. Arginyl-fructosyl-glucose, a Major Maillard Reaction Product of Red Ginseng, Attenuates Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Regulating Nuclear Factor kappaB and Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B Signaling Pathways. J Agric Food Chem 2019, 67, 5754–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, X.J.; Hou, J.G.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Z.; Tang, S.; Liu, X.X.; Wang, Y.P.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, W. Maltol Mitigates Thioacetamide-induced Liver Fibrosis through TGF-beta1-mediated Activation of PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 1392–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, J.J.; Hou, J.G.; Ma, Z.N.; Wang, Z.; Ren, S.; Wang, Y.P.; Liu, W.C.; Chen, C.; Li, W. Ginsenoside Rb3 provides protective effects against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity via regulation of AMPK-/mTOR-mediated autophagy and inhibition of apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Cell Prolif. 2019, 52, e12627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahadır, A.; Ceyhan, A.; Öz Gergin, Ö.; Yalçın, B.; Ülger, M.; Özyazgan, T.M.; Yay, A.; Bahadir, A. Protective effects of curcumin and beta-carotene on cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity: An experimental rat model. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2018, 19, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Hong, M.; Tan, H.-Y.; Wang, N.; Feng, Y. Insights into the Role and Interdependence of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Liver Diseases. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 4234061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Grijalva, A.; Skowronski, A.; Van Eijk, M.; Serlie, M.J.; Ferrante, A.W. Obesity Activates a Program of Lysosomal-Dependent Lipid Metabolism in Adipose Tissue Macrophages Independently of Classic Activation. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 816–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.Y.; Hu, J.N.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, R.; He, Y.F.; Hou, W.; Wang, Z.Q.; Yang, G.; Li, W. Saponins (Ginsenosides) from the Leaves of Panax quinquefolius Ameliorated Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3684–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, C.E.R.; Nie, W.; Sinnett-Smith, J.; Rozengurt, E.; Yoo, J. TNF-α potentiates lysophosphatidic acid-induced COX-2 expression via PKD in human colonic myofibroblasts. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2011, 300, G637–G646. [Google Scholar]
- Decean, H.; Fischer-Fodor, E.; Tatomir, C.; Perde-Schrepler, M.; Somfelean, L.; Burz, C.; Hodor, T.; Orasan, R.; Virag, P. Vitis vinifera seeds extract for the modulation of cytosolic factors BAX-α and NF-kB involved in UVB-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis of human skin cells. Clujul Med. 2016, 89, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Saad, A.; Rjeibi, I.; Ncib, S.; Zouari, N.; Zourgui, L. Ameliorative Effect of Cactus (Opuntia ficus indica) Extract on Lithium-Induced Nephrocardiotoxicity: A Biochemical and Histopathological Study. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 8215392. [Google Scholar]
- Kou, N.; Xue, M.; Yang, L.; Zang, M.-X.; Qu, H.; Wang, M.-M.; Miao, Y.; Yang, B.; Shi, D.-Z. Panax quinquefolius saponins combined with dual antiplatelet drug therapy alleviate gastric mucosal injury and thrombogenesis through the COX/PG pathway in a rat model of acute myocardial infarction. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.-N.; Xu, X.-Y.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.-M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.-P. Ginsenoside Rk1 ameliorates paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity in mice through inhibition of inflammation, oxidative stress, nitrative stress and apoptosis. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.-C. The non-canonical NF-κB pathway in immunity and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, Y.; Goto, Y.; Kondo, T.; Kurata, M.; Nishio, K.; Kawai, S.; Osafune, T.; Naito, M.; Hamajima, N. Eradication rate of Helicobacter pylori according to genotypes of CYP2C19, IL-1B, and TNF-A. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2006, 3, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, M.M.; Alanazi, W.A.; Alshammari, M.A.; Alotaibi, M.R.; Alhoshani, A.R.; Al-Rejaie, S.S.; Hafez, M.M.; Al-Shabanah, O.A. Neuro-protective effect of rutin against Cisplatin-induced neurotoxic rat model. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, X.-J.; Hou, J.-G.; Wang, Z.; Han, Y.; Ren, S.; Hu, J.-N.; Chen, C.; Li, W. The protective effects of maltol on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity through the AMPK-mediated PI3K/Akt and p53 signaling pathways. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, B.; Ray, P. Cisplatin triggers cancer stem cell enrichment in platinum-resistant cells through NF-κB-TNFα-PIK3CA loop. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.-R.; Wu, J.; Sun, H.; Chi, L.-Q.; Wang, J.-H. PAK4 confers the malignance of cervical cancers and contributes to the cisplatin-resistance in cervical cancer cells via PI3K/AKT pathway. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 10, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, J.-J.; Hou, J.-G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.-B.; Jiang, S.; Ren, S.; Wang, Y.-P.; Shen, Q.; Li, W.; Li, X.-D.; et al. Supplementation of Saponins from Leaves of Panax quinquefolius Mitigates Cisplatin-Evoked Cardiotoxicity via Inhibiting Oxidative Stress-Associated Inflammation and Apoptosis in Mice. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8090347
Xing J-J, Hou J-G, Liu Y, Zhang R-B, Jiang S, Ren S, Wang Y-P, Shen Q, Li W, Li X-D, et al. Supplementation of Saponins from Leaves of Panax quinquefolius Mitigates Cisplatin-Evoked Cardiotoxicity via Inhibiting Oxidative Stress-Associated Inflammation and Apoptosis in Mice. Antioxidants. 2019; 8(9):347. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8090347
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Jing-Jing, Jin-Gang Hou, Ying Liu, Ruo-Bing Zhang, Shuang Jiang, Shen Ren, Ying-Ping Wang, Qiong Shen, Wei Li, Xin-Dian Li, and et al. 2019. "Supplementation of Saponins from Leaves of Panax quinquefolius Mitigates Cisplatin-Evoked Cardiotoxicity via Inhibiting Oxidative Stress-Associated Inflammation and Apoptosis in Mice" Antioxidants 8, no. 9: 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8090347
APA StyleXing, J.-J., Hou, J.-G., Liu, Y., Zhang, R.-B., Jiang, S., Ren, S., Wang, Y.-P., Shen, Q., Li, W., Li, X.-D., & Wang, Z. (2019). Supplementation of Saponins from Leaves of Panax quinquefolius Mitigates Cisplatin-Evoked Cardiotoxicity via Inhibiting Oxidative Stress-Associated Inflammation and Apoptosis in Mice. Antioxidants, 8(9), 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8090347