Silencing of Mg-pat-10 and Mg-unc-87 in the Plant Parasitic Nematode Meloidogyne graminicola Using siRNAs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Oligonucleotides Design and siRNA Synthesis
| SiRNA | Oligonucleotides |
|---|---|
| unca | Antisense: 5′-AAGAAAAAATCCGTGCTAGTGCCTGTCTC-3′ Sense: 5′-AACACTAGCACGGATTTTTTCCCTGTCTC-3′ |
| uncb | Antisense: 5′-AAAAAGGAATGGTCAGCTTCGCCTGTCTC-3′ Sense: 5′-AACGAAGCTGACCATTCCTTTCCTGTCTC-3′ |
| uncbM | Antisense: 5′-AAAAAGGAATGGTCAGCTTCGCCTGTCTC-3′ Sense: 5′-AAGGAAGCTGACCATTCCTTTCCTGTCTC-3′ |
| uncc | Antisense: 5′-AATATCCAGAGGAGGCTGAAACCTGTCTC-3′ Sense: 5′-AATTTCAGCCTCCTCTGGATACCTGTCTC-3′ |
| pata | Antisense: 5′-AAATGGCCGAAAATATTGAAGCCTGTCTC-3′ Sense: 5′-AACTTCAATATTTTCGGCCATCCTGTCTC-3′ |
| patb | Antisense: 5′-AACCCTTCGAAAATTAATCCGCCTGTCTC -3′ Sense: 5′-AACGATTAATTTTCGAAGGGCCTGTCTC-3′ |
| patbM | Antisense: 5′-AAAAAGGAATGGTCAGCTTCGCCTGTCTC-3′ Sense:5′-AACCATTAATTTTCGAAGGGCCTGTCTC-3′ |
| patc | Antisense: 5′-AATTAATGGCTGGAGAGACTGCCTGTCTC-3′ Sense: 5′-AACAGTCTCTCCAGCCATTAACCTGTCTC-3′ |
| enga | Antisense: 5′-AACCCGCCTTATGGAAAATTACCTGTCTC-3′ Sense: 5′-AATAATTTTCCATAAGGCGGGCCTGTCTC-3′ |
| engb | Antisense: 5′-AATGGGAATGTTGTTCGTGCTCCTGTCTC-3′ Sense: 5′-AAAGCACGAACAACATTCCCACCTGTCTC-3′ |
| engbM | Antisense: 5′-AATGGGAATGTTGTTCGTGCTCCTGTCTC-3′ Sense: 5′-AATGCACGAACAACATTCCCACCTGTCTC-3′ |
| engc | Antisense: 5′-AACGCTGTTCTTACTCAAGTTCCTGTCTC-3′ Sense: 5′-AAAACTTGAGTAAGAACAGCGCCTGTCTC-3′ |
2.2. Nematode Culture, Collection and Soaking in siRNA
2.3. Migration Assay and Expression Analysis
| Gene | Fragment Length | Primer Name and Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Mg-pat-10 | 291-bp | Mg-pat-F 5′-CAACGTTTTCCTCTCTTAATTTTTC-3′ Mg-pat-R 5′-TTCGAAGGGTTTTCTCATCAA-3′ |
| Mg-unc-87 | 380-bp | Mg-unc-F 5′-GATTTGGAGCCTCTTCCAGA-3′ Mg-unc-R 5′-TATTCCGGATGGGCAGTATC-3′ |
| Mg-tubulin | 158-bp | Mg-Tub-F 5′-TCTGGCATAAATAAAATAAGCGAGT-3′ Mg-Tub-R 5′-TCAAGATGCAACTGTTGAGGA-3′ |
| Mg-eng | 160-bp | Mg-eng F 5′-TAGCAGCTAACCCGCCTTATG-3′ Mg-eng R 5′-TAGTGCCTCAGGGAAATTGC-3′ |
3. Results
3.1. Mg-pat-10 and Mg-unc-87 Genes Can Be Silenced Using siRNA
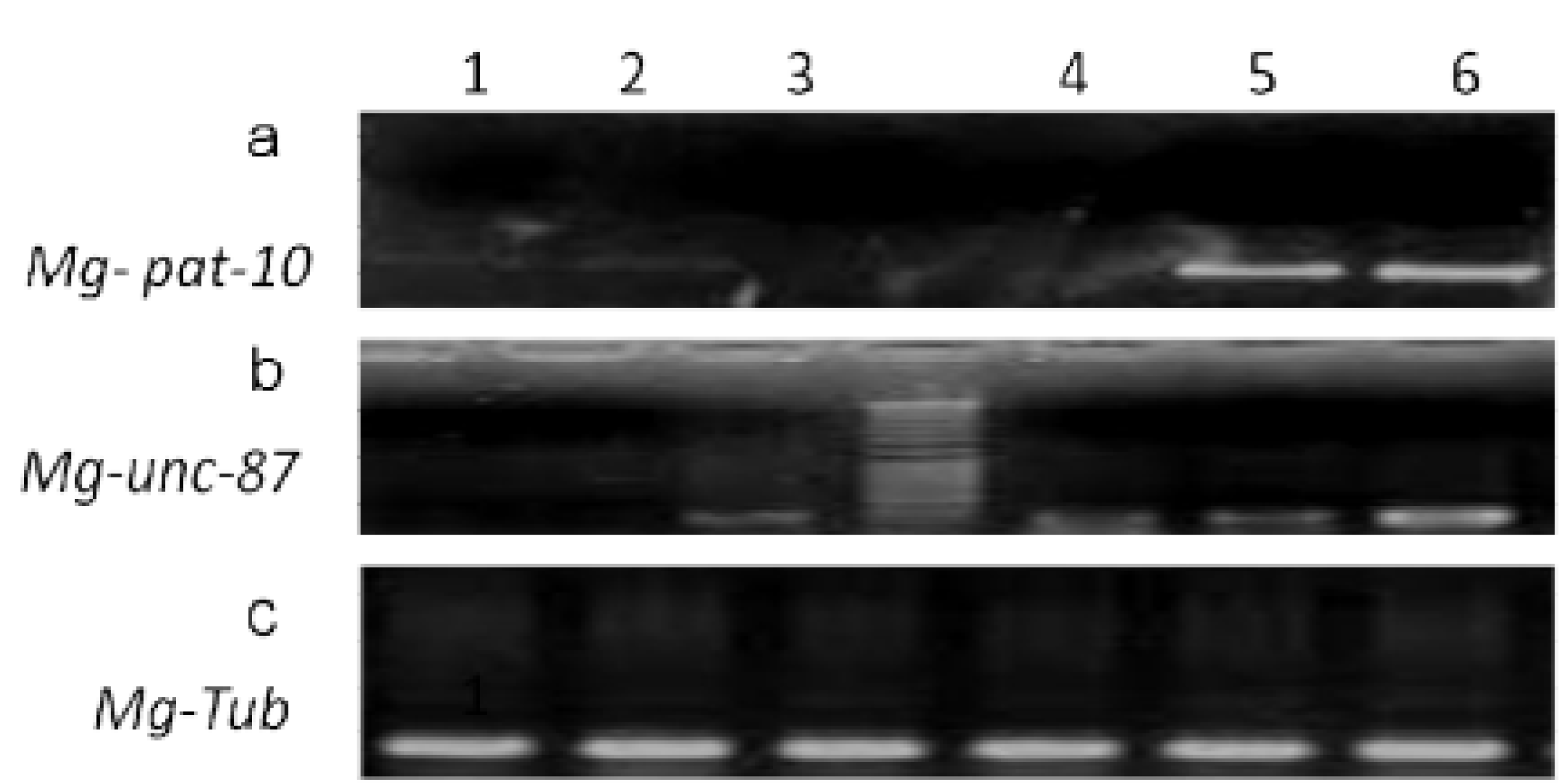
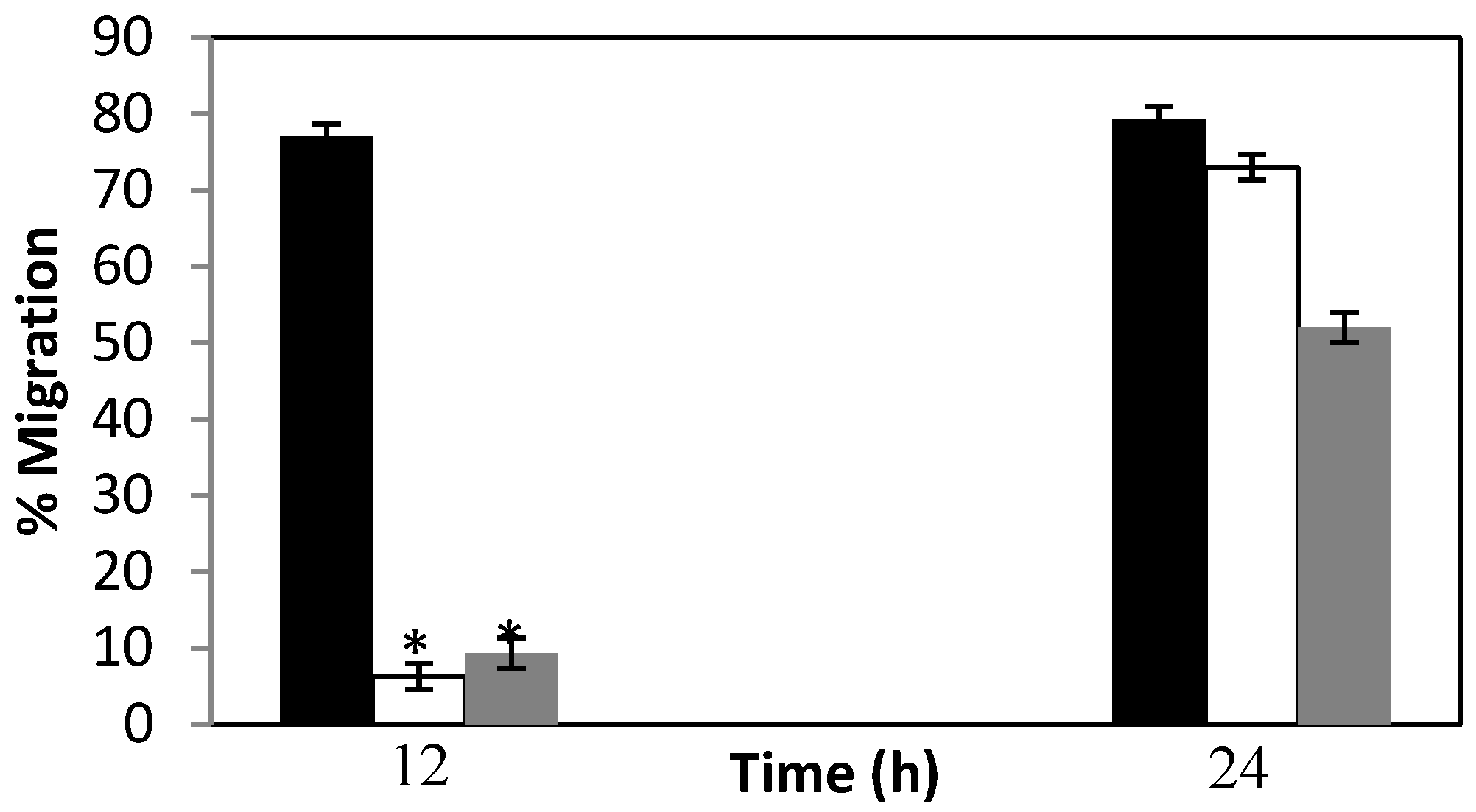
3.2. Silencing of Mg-pat-10 and Mg-unc-87 Impairs Migration Capacity of M. graminicola
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nicol, J.M.; Turner, S.J.; Coyne, D.L.; den Nijs, L.; Hockland, S.; Maafi, Z.T. Current nematode treaths to world agriculture. Genomics Mol. Genet. Plant Nematode Interact 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, R.K.; Kumar, D.; Singh, K.P. Relationship between growth of rice seedlings and time of infection with Meloidogynegraminicola. Libyan Agric. Res. Center J. Int. 2012, 3, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, R.; Gowen, S. Studies on the infection of Meloidogyne spp. with isolates of Pasteuria penetrans. Nematol. Mediterr. 1991, 19, 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Arguel, M.J.; Jaouannet, M.; Magliano, M.; Abad, P.; Rosso, M.N. siRNAs trigger efficient silencing of a parasitism gene in plant parasitic root-knot nematodes. Genes 2012, 3, 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbashir, S.M.; Harborth, J.; Lendeckel, W.; Yalcin, A.; Weber, K.; Tuschl, T. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature 2001, 411, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fire, A.; Xu, S.; Montgomery, M.K.; Kostas, S.A.; Driver, S.E.; Mello, C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998, 391, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, M.N.; Jones, J.T.; Abad, P. RNAi and functional genomics in plant parasitic nematodes. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2009, 47, 207–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimber, J.K.; McKinney, S.; McMaster, S.; Day, A.T.; Fleming, C.C.; Maule, G.A. Flp gene disruption in parasitic nematode reveals motor dysfunction and unusual neuronal sensitivity to RNA interference. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, B.; Warner, A.; Wong, K.; Dube, N.; Lorch, A.; McKay, S.J.; Khattra, J.; Rogalski, T.; Somasiri, A.; Chaudhry, I.; et al. An integrated strategy to study muscle development and myofilament structure in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranewitter, W.J.; Ylann, E.J.; Gimona, M. UNC-87 is an actin-bundling protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 6306–6312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashiro, S.; Gimona, M.; Ono, S. UNC-87, a calponin-related protein in C. elegans, antagonizes ADF/cofilin-mediated actin filament dynamics. J. CellSci. 2007, 120, 3022–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmer, F.; Moorman, C.; van der Linden, A.M.; Kuijk, E.; van den Berghe, P.V.E.; Kamath, R.S.; Fraser, A.G.; Ahringer, J.; Plasterk, R.H.A. Genome-wide RNAi of C. elegans using the hypersensitive rrf-3 strain reveals novel gene functions. PLoS Biol. 2003, 1, e12. [Google Scholar]
- Haegeman, A.; Bauters, L.; Kyndt, T.; Rahman, M.; Gheysen, G. Identification of candidate effector genes in the transcriptome of the rice root knot nematode Meloidogyne graminicola. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 14, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Translate a DNA Sequence. Available online: http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/molkit/translate/ (accessed on 10 July 2010).
- Life Technologies Website. Available online: http://www.ambion.com/techlib/misc/siRNA_tools.html (accessed on 21 May 2010).
- Biolegio Home Page. Available online: www.biolegio.com (accessed on 2 June 2010).
- De Ahmed, F.; Raghava, G.P.S. Designing of highly effective complementary and mismatch siRNAs for silencing a gene. PLoS One 2011, 6, e23443. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, D.J.; Hallmann, J.; Subbotin, S. Methods for Extraction, Processing and Detection of Plant and Soil Nematodes. In Plant Parasitic Nematodes in Subtropical and Tropical Agriculture; Luc, M., Sikora, R.A., Bridge, J., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2005; pp. 53–86. [Google Scholar]
- WormBase Website. Available online: www.wormbase.org/db/searches/blast-blast (accessed on 24 March 2010).
- Dalzell, J.J.; McMaster, S.; Fleming, C.C.; Maule, G.A. Short interfering RNA-mediated gene silencing in Globodera pallida and Meloidogyne incognita infective stage juveniles. Int. J. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, M.N.; Favery, B.; Piotte, C.; Arthaud, L.; de Boer, J.M.; Hussey, R.S.; Bakker, J.; Baum, T.J.; Abad, P. Isolation of a cDNA encoding a β-1,4-endoglucanase in the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita and expression analysis during plant parasitism. MPMI 1999, 12, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.D.; Waterston, R.H. Genes critical for muscle development and function in Caenorhabditis elegans identified through lethal mutations. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 124, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terami, H.; Williams, B.D.; Kitamura, S.; Sakube, Y.; Matsumoto, S.; Doi, S.; Obinata, T.; Kagawa, H. Genomic organization, expression, and analysis of the troponin C gene pat-10 of Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 146, 193–202. [Google Scholar]
- Goetinck, S.; Waterston, R.H. The Caenorhabditis elegans UNC-87 protein is essential for maintenance, but not assembly, of body wall muscle. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 127, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.; Gheysen, G.; Subramaniam, K. RNA interference in Pratylenchus coffeae: Knock down of Pc-pat-10 and Pc-unc-87 impedes migration. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2012, 186, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.C.H.; Jones, M.G.K.; Fuso-Nyarko, J. Gene silencing in root lesion nematodes (Pratylenchus. spp.) significantly reduces reproduction in a plant host. Exp. Parasitol. 2013, 133, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, M.N.; Dubrana, M.P.; Cimbolini, N.; Jaubert, S.; Abad, P. Application of RNA interference to root-knot nematode genes encoding esophageal gland proteins. Mol. PlantMicrobe Interact. 2005, 18, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalzell, J.J.; Warnock, N.D.; Stevenson, M.A.; Mousley, A.; Fleming, C.C.; Maule, G.A. Short interfering RNA-mediated knockdown of drosha and pasha in undifferentiated Meloidogyne incognita eggs leads to irregular growth and embryonic lethality. Inter. J. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Appendix
A1. >Mg_pat-10
A2. >Mg_unc-87
A3. >Mg-eng
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Nsengimana, J.; Bauters, L.; Haegeman, A.; Gheysen, G. Silencing of Mg-pat-10 and Mg-unc-87 in the Plant Parasitic Nematode Meloidogyne graminicola Using siRNAs. Agriculture 2013, 3, 567-578. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture3030567
Nsengimana J, Bauters L, Haegeman A, Gheysen G. Silencing of Mg-pat-10 and Mg-unc-87 in the Plant Parasitic Nematode Meloidogyne graminicola Using siRNAs. Agriculture. 2013; 3(3):567-578. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture3030567
Chicago/Turabian StyleNsengimana, Joseph, Lander Bauters, Annelies Haegeman, and Godelieve Gheysen. 2013. "Silencing of Mg-pat-10 and Mg-unc-87 in the Plant Parasitic Nematode Meloidogyne graminicola Using siRNAs" Agriculture 3, no. 3: 567-578. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture3030567
APA StyleNsengimana, J., Bauters, L., Haegeman, A., & Gheysen, G. (2013). Silencing of Mg-pat-10 and Mg-unc-87 in the Plant Parasitic Nematode Meloidogyne graminicola Using siRNAs. Agriculture, 3(3), 567-578. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture3030567





