Incorporation of Human Recombinant Tropoelastin into Silk Fibroin Membranes with the View to Repairing Bruch’s Membrane
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Properties of Fibroin and Tropoelastin Solutions

2.2. Effect of Tropoelastin on RPE Cell Attachment to Fibroin

2.3. Gross Morphology of the Freestanding Membranes

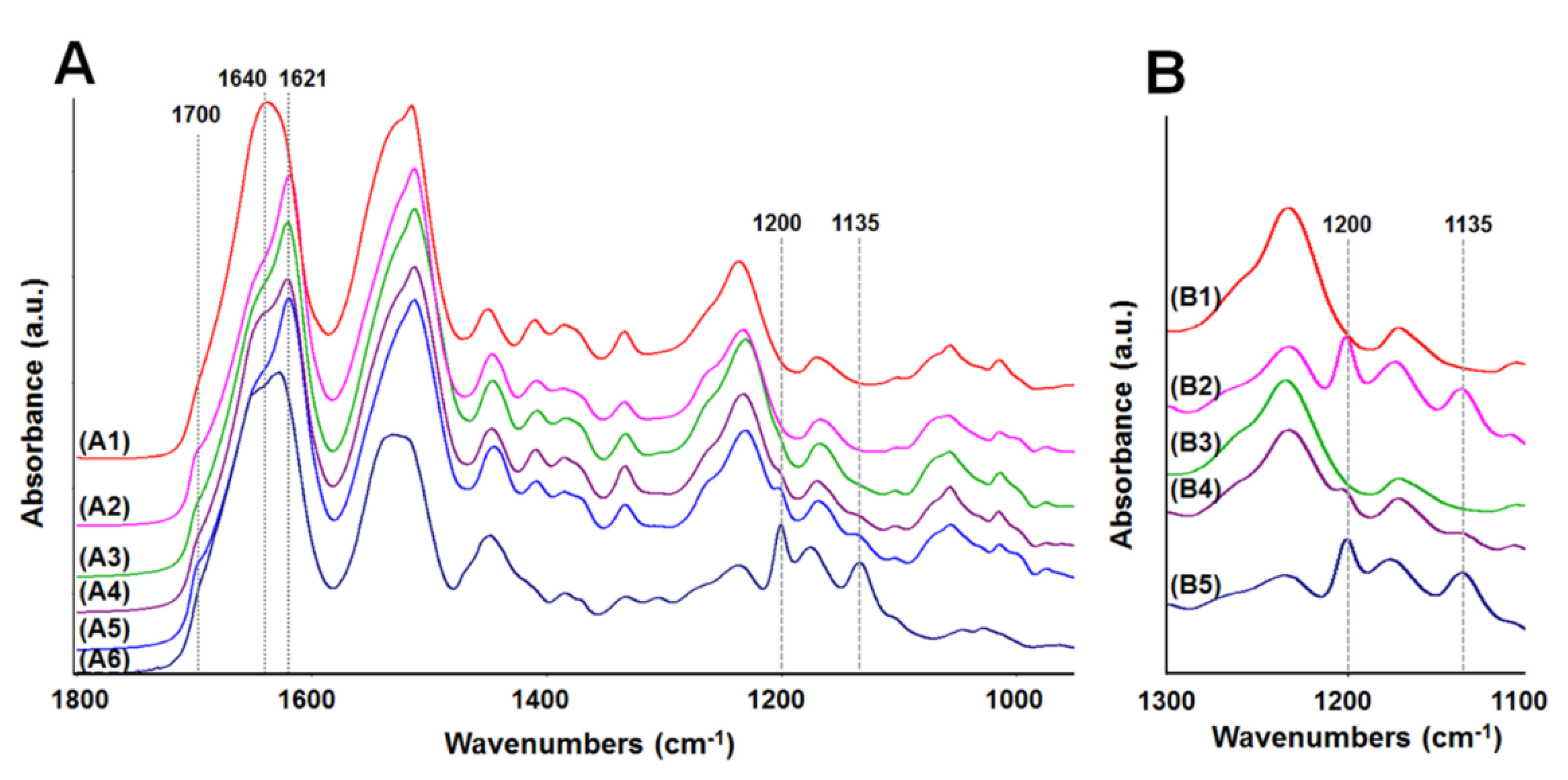
2.4. Analysis of Membrane Structure by Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy-Attenuated Total Reflectance, “FTIR-ATR”

2.5. Cytocompatibility of the Membranes

2.6. Mechanical Properties of the Membranes

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Production of Aqueous Solutions of Fibroin
3.2. Preparation of Films Cast in TCP Wells: Fibroin and Tropoelastin Solutions Blended in Different Ratios
3.3. Cell Culture of the Human RPE Cell Line ARPE-19
3.4. Testing the Attachment of RPE Cells on Films of Fibroin and Tropoelastin Blended in Different Ratios
3.5. Preparation of Fibroin Membranes
3.6. Preparation of Freestanding Membranes of Fibroin and Tropoelastin, Proteins Blended in 90:10 Solution Ratio
3.7. Preparation of Freestanding Layered (Fibroin-Tropoelastin-Fibroin) Membranes
3.8. Suspension of the Membranes in Custom-Made Teflon® Chambers
3.9. Visualization of Tropoelastin within the Membranes Using Immunofluorescence
3.10. Testing Cell Growth of RPE Cells on the Membranes
3.11. Extended Culture of RPE Cells on the Membranes
3.12. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy of the Membranes
3.13. Mechanical Testing of the Membranes
3.14. Statistical Analyses
4. General Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Binder, S.; Stanzel, B.V.; Krebs, I.; Glittenberg, C. Transplantation of the RPE in AMD. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2007, 26, 516–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Cruz, L.; Chen, F.K.; Ahmado, A.; Greenwood, J.; Coffey, P. RPE transplantation and its role in retinal disease. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2007, 26, 598–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Maclaren, R.E. Sources of retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) for replacement therapy. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 95, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, B.S.; Bharti, K. Regenerating retinal pigment epithelial cells to cure blindness: a road towards personalized artificial tissue. Curr. Stem Cell Rep. 2015, 1, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hynes, S.R.; Lavik, E.B. A tissue-engineered approach towards retinal repair: Scaffolds for cell transplantation to the subretinal space. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2010, 248, 763–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, S. Scaffolds for retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) replacement therapy. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 95, 441–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harkin, D.G.; George, K.A.; Madden, P.W.; Schwab, I.R.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Chirila, T.V. Silk fibroin in ocular tissue reconstruction. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 2445–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadforth, A.M.A.; George, K.A.; Kwan, A.S.; Chirila, T.V.; Harkin, D.G. The cultivation of human retinal pigment epithelial cells on Bombyx mori silk fibroin. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 4110–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shadforth, A.M.A.; Suzuki, S.; Theodoropoulos, C.; Richardson, N.A.; Chirila, T.V.; Harkin, D.G. A Bruch’s membrane substitute fabricated from silk fibroin supports the function of retinal pigment epithelial cells in vitro. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2015, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Wise, S.G.; Mithieux, S.M.; Weiss, A.S. Engineered tropoelastin and elastin-based biomaterials. In Advances in Protein Chemistry and Structural Biology; McPherson, A., Ed.; Elsevier Science: Oxford, UK, 2009; Volume 78, pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Booij, J.C.; Baas, D.C.; Beisekeeva, J.; Gorgels, T.G.; Bergen, A.A. The dynamic nature of Bruch’s membrane. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2010, 29, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leure-duPree, A. Ultrastructure of the retinal pigment epithelium in domestic sheep. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1968, 65, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutto, I.; Lutty, G. Understanding age-related macular degeneration (AMD): Relationships between the photoreceptor/retinal pigment epithelium/Bruch’s membrane/choriocapillaris complex. Mol. Aspects Med. 2012, 33, 295–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tezel, T.H.; Del Priore, L.V. Reattachment to a substrate prevents apoptosis of human retinal pigment epithelium. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 1997, 235, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tezel, T.H.; Kaplan, H.J.; Del Priore, L.V. Fate of human retinal pigment epithelial cells seeded onto layers of human Bruch’s membrane. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1999, 40, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tezel, T.H.; Del Priore, L.V. Repopulation of different layers of host human Bruch’s membrane by retinal pigment epithelial cell grafts. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1999, 40, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sugino, I.K.; Sun, Q.; Wang, J.; Nunes, C.F.; Cheewatrakoolpong, N.; Rapista, A.; Johnson, A.C.; Malcuit, C.; Klimanskaya, I.; Lanza, R.; et al. Comparison of fRPE and human embryonic stem cell-derived RPE behavior on aged human Bruch’s membrane. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 4979–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachi, H.; Sato, F.; Murata, H.; Nakazawa, J.; Starcher, B.C.; Seyama, Y. Development of a new in vitro model of elastic fiber assembly in human pigmented epithelial cells. Clin. Biochem. 2005, 38, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wray, L.S.; Hu, X.; Gallego, J.; Georgakoudi, I.; Omenetto, F.G.; Schmidt, D.; Kaplan, D.L. Effect of processing on silk-based biomaterials: Reproducibility and biocompatibility. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2011, 99, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.L.; Vrhovski, B.; Weiss, A.S. Total synthesis and expression in Escherichia coli of a gene encoding human tropoelastin. Gene 1995, 154, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Park, S.-H.; Gil, E.S.; Xia, X.-X.; Weiss, A.S.; Kaplan, D.L. The influence of elasticity and surface roughness on myogenic and osteogenic-differentiation of cells on silk-elastin biomaterials. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 8979–8989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Rnjak, J.; Weiss, A.S.; Kaplan, D.L. Biomaterials derived from silk-tropoelastin protein systems. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 8121–8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, L.J.; George, K.A.; Suzuki, S.; Chirila, T.V.; Harkin, D.G. Fabrication of a corneal-limbal tissue substitute using silk fibroin. In Corneal Regenerative Medicine: Methods and Protocols; Wright, B., Connon, C.J., Eds.; Springer Science+Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 1014, pp. 131–139. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Kaplan, D.; Cebe, P. Determining beta-sheet crystallinity in fibrous proteins by thermal analysis and infrared spectroscopy. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 6161–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, L.J.; George, K.A.; Ainscough, S.L.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Chirila, T.V.; Harkin, D.G. Human corneal epithelial equivalents constructed on Bombyx mori silk fibroin membranes. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 5086–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeffer, B.A.; Philp, N.J. Cell culture of retinal pigment epithelium: Special Issue. Exp. Eye Res. 2014, 126, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curcio, C.A.; Johnson, M. Structure, function, and pathology of Bruch’s membrane. In Retina; Ryan, S.J., Schachat, A.P., Wilkinson, C.P., Hinton, D.R., Sadda, S., Wiedemann, P., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 465–481. [Google Scholar]
- Chirila, T.V.; Barnard, Z.; Harkin, D.G.; Schwab, I.R.; Hirst, L.W. Bombyx mori silk fibroin membranes as potential substrata for epithelial constructs used in the management of ocular surface disorders. Tissue Eng. A 2008, 14, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maminishkis, A.; Chen, S.; Jalickee, S.; Banzon, T.; Shi, G.; Wang, F.E.; Ehalt, T.; Hammer, J.A.; Miller, S.S. Confluent monolayers of cultured human fetal retinal pigment epithelium exhibit morphology and physiology of native tissue. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 3612–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shadforth, A.M.A.; Suzuki, S.; Alzonne, R.; Edwards, G.A.; Richardson, N.A.; Chirila, T.V.; Harkin, D.G. Incorporation of Human Recombinant Tropoelastin into Silk Fibroin Membranes with the View to Repairing Bruch’s Membrane. J. Funct. Biomater. 2015, 6, 946-962. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb6030946
Shadforth AMA, Suzuki S, Alzonne R, Edwards GA, Richardson NA, Chirila TV, Harkin DG. Incorporation of Human Recombinant Tropoelastin into Silk Fibroin Membranes with the View to Repairing Bruch’s Membrane. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2015; 6(3):946-962. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb6030946
Chicago/Turabian StyleShadforth, Audra M. A., Shuko Suzuki, Raphaelle Alzonne, Grant A. Edwards, Neil A. Richardson, Traian V. Chirila, and Damien G. Harkin. 2015. "Incorporation of Human Recombinant Tropoelastin into Silk Fibroin Membranes with the View to Repairing Bruch’s Membrane" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 6, no. 3: 946-962. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb6030946
APA StyleShadforth, A. M. A., Suzuki, S., Alzonne, R., Edwards, G. A., Richardson, N. A., Chirila, T. V., & Harkin, D. G. (2015). Incorporation of Human Recombinant Tropoelastin into Silk Fibroin Membranes with the View to Repairing Bruch’s Membrane. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 6(3), 946-962. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb6030946




