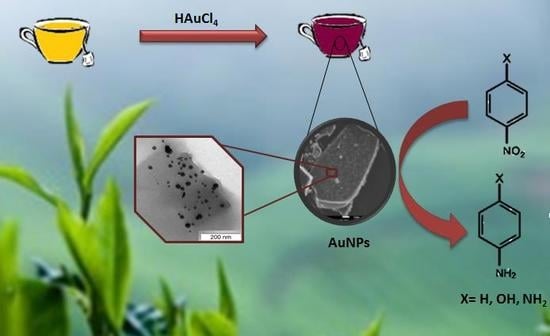
Effect of Phenolic Compounds on the Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles and its Catalytic Activity in the Reduction of Nitro Compounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Instrumentation
2.2. Preparation of Au Nanoparticles Using Tea Extracts
2.3. Determination of Total Polyphenol Content in Tea by the Folin–Ciocalteu Method
2.4. Reduction of Nitro Compounds in Aqueous Solution
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Au Nanoparticle Identification
3.2. Characterization of AuNPs
3.3. Determination of Total Polyphenol Content
3.4. Catalytic Studies
3.4.1. Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol in Aqueous Solution
3.4.2. Reduction of Other Nitro Compounds
3.4.3. Recycling Studies for AuNPs in 4-NP Reduction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iravani, S.; Korbekandi, H.; Mirmohammadi, S.V.; Zolfaghari, B. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Chemical, physical and biological methods. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 9, 385–406. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iravani, S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2638–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gu, J.W. Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using the bacteria Rhodopseudomonas capsulate. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 3984–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southam, G.; Beveridge, T.J. The occurrence of bacterially derived sulphur and phosphorus within pseudocrystalline and crystalline octahedral gold formed in vitro. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 4369–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Mukherjee, P.; Senapati, S.; Mandal, D.; Khan, M.I.; Kumar, R.; Sastry, M. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Fusarium oxysporum. Colloids Surf. B 2003, 28, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankamwar, B. Biosynthesis of Gold Nanoparticles (Green-gold) Using Leaf Extract of Terminalia catappa. J. Chem. 2010, 7, 1334–1339. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Weng, X.; Chen, Z.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles by various tea extracts: Comparative study of the reactivity. Spectrochim. Acta A 2014, 130, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, S.A.O.; Pinto, R.J.B.; Rocha, S.M.; Marques, P.A.A.P.; Neto, C.P.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Freire, C.S.R. Unveiling the chemistry behind the green synthesis of metal nanoparticles. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 2704–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharissova, O.V.; Dias, H.V.R.; Kharisov, B.I.; Pérez, B.O.; Pérez, V.M.J. The greener synthesis of nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadagouda, M.N.; Varma, R.S. Green synthesis of silver and palladium nanoparticles at room temperature using coffee and tea extract. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 859–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, Q.; Sun, D.; Lu, Y.; Su, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Shao, W.; He, N.; et al. Biosynthesis of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles by Novel Sundried Cinnamomum camphora Leaves. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 105104–105115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilchis-Nestor, A.R.; Sánchez-Mendieta, V.; Camacho-López, M.A.; Gómez-Espinosa, R.M.; Camacho-López, M.A.; Arenas-Alatorre, J.A. Solventless synthesis and optical properties of Au and Ag nanoparticles using Camellia sinensis extract. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 3103–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Mañas, M.; Pleixats, R. Formation of Carbon–Carbon Bonds under Catalysis by Transition-Metal Nanoparticles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2003, 36, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Meng, X.; Chen, D.; Tang, F.; Jiao, J. Using silver nanoparticle to enhance current response of biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 21, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhayalan, M.; Denison, M.I.J.; Jegadeeshwari, A.; Krishnan, K.; Gandhi, N. In vitro antioxidant, antimicrobial, cytotoxic potential of gold and silver nanoparticles prepared using Embelia ribes. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.K.; Gulati, S.; Mehta, S. Preparation of Gold Nanoparticles Using Tea: A Green Chemistry Experiment. J. Chem. Educ. 2012, 89, 1316–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, M.C.; Astruc, D. Gold Nanoparticles: Assembly, Supramolecular Chemistry, Quantum-Size-Related Properties, and Applications toward Biology, Catalysis, and Nanotechnology. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 293–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dykmana, L.; Khlebtsov, N. Gold nanoparticles in biomedical applications: Recent advances and perspectives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2256–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Lorenzo, L.; Rica, R.; Alvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Liz-Marzan, L.M.; Stevens, M.M. Plasmonic nanosensors with inverse sensitivity by means of enzyme-guided crystal growth. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thielecke, N.; Aytemir, M.; Pruesse, U. Selective oxidation of carbohydrates with gold catalysts: Continuous-flow reactor system for glucose oxidation. Catal. Today 2007, 121, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, R. Reactive Template Method to Synthesize Gold Nanoparticles with Controllable Size and Morphology Supported on Shells of Polymer Hollow Microspheres and Their Application for Aerobic Alcohol Oxidation in Water. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 1112–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalawade, P.; Mukherjee, T.; Kapoor, S. Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Glycerol as a Reducing Agent. Adv. Nanoparticles 2013, 2, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruta, M. When Gold Is Not Noble: Catalysis by Nanoparticles. Chem. Rec. 2003, 3, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Vemula, P.K.; Ajayan, P.M.; John, G. Silver-nanoparticle-embedded antimicrobial paints based on vegetable oil. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, K.O.; Elias, W.C.; Signori, A.M.; Giacomelli, F.C.; Yang, H.J.; Domingos, B. Synthesis and Catalytic Properties of Silver Nanoparticle-Linear Polyethylene Imine Colloidal Systems. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 4594–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, B.; Gabriel, G.J.; Akbashev, M.J.; Booher, M.E. Facile synthesis of silver nanoparticles stabilized by cationic polynorbornenes and their catalytic activity in 4-nitrophenol reduction. Langmuir 2013, 29, 4225–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, K.; Yoshimura, T.; Esumi, K. Preparation of Gold-Dendrimer Nanocomposites by Laser Irradiation and Their Catalytic Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol. Langmuir 2003, 19, 5517–5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, K.; Ishida, M.; Haruta, M. Reduction of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol over Au nanoparticles deposited on PMMA. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2009, 298, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Yashchenok, A.; Li, L.; Möhwald, H.; Bargheer, M. Mechanistic study on reduction reaction of nitro compounds catalyzed by gold nanoparticles using in situ SERS monitoring. Colloids Surf. A. 2015, 470, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.; Kaur, H. Resin-trapped gold nanoparticles: An efficient catalyst for reduction of nitro compounds and Suzuki-Miyaura coupling. J. Mol. Catal. A 2014, 381, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Wunder, S.; Lu, Y.; Ballauff, M. Kinetic analysis of the catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol by metallic nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 18618–18625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, N.; Pal, A.; Pal, T. Catalytic Reduction of Aromatic Nitro Compounds by Coinage Metal Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2001, 17, 1800–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.A.; Makis, J.J.; Marvin, K.A.; Rodenbusch, S.E.; Stevenson, K.J. Size-Dependent Hydrogenation of p-Nitrophenol with Pd Nanoparticles Synthesized with Poly(amido)amine Dendrimer Templates. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 22644–22651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervés, P.; Peréz-Lorenzo, M.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Dzubiella, J.; Lu, Y.; Ballauff, M. Catalysis by metallic nanoparticles in aqueous solution: Model reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 5577–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, N.; Pal, A.; Pal, T. Silver nanoparticle catalyzed reduction of aromatic nitro compounds. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2002, 196, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esumi, K.; Isono, R.; Yoshimura, T. Preparation of PAMAM- and PPI-Metal (Silver, Platinum, and Palladium) Nanocomposites and Their Catalytic Activities for Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol. Langmuir 2004, 20, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Errokh, A.; Ferraria, A.M.; Conceição, D.S.; Vieira Ferreira, L.F.; Botelho do Rego, A.M.; Rei Vilar, M.; Boufi, S. Controlled growth of Cu2O nanoparticles bound to cotton fibres. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 141, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenger, R.; Fertitta, E.; Kirmse, H.; Thünemann, A.F.; Rademann, K. Size dependent catalysis with CTAB-stabilized gold nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 9343–9349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panigrahi, S.; Basu, S.; Praharaj, S.; Pande, S.; Jana, S.; Pal, A.; Ghosh, S.K.; Pal, T. Synthesis and Size-Selective Catalysis by Supported Gold Nanoparticles: Study on Heterogeneous and Homogeneous Catalytic Process. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 4596–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, P.J.; Sharma, P.; Saranya, S.; Tamuli, R.; Bora, U. Green Synthesis and Characterization of Biocompatible Gold Nanoparticles Using Solanum indicum Fruits. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2013, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of folin-ciocalteu reagent. Method Enzymol. 1999, 299, 152–178. [Google Scholar]
- Link, S.; El-Sayed, M.A. Size and Temperature Dependence of the Plasmon Absorption of Colloidal Gold Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 4212–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sareen, S.; Mutreja, V.; Pal, B.; Singh, S. Homogeneous dispersion of Au nanoparticles into mesoporous SBA-15 exhibiting improved catalytic activity for nitroaromatic reduction. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 202, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Fan, W.; Shimojima, A.; Okubo, T. Microwave-induced synthesis of highly dispersed gold nanoparticles within the pore channels of mesoporous silica. J. Solid State Chem. 2008, 181, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carapeto, A.P.; Ferraria, A.M.; Boufi, S.; Rei Vilar, M.; Botelho do Rego, A.M. Ion reduction in metallic nanoparticles nucleation and growth on cellulose films: Does substrate play a role? Cellulose 2015, 22, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seah, M.P. Summary of ISO/TC 201 Standard: VII ISO 15472: 2001—Surface chemical analysis—X-ray photoelectron spectrometers—Calibration of energy scales. Surf. Interface Anal. 2001, 31, 721–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boufi, S.; Ferraria, A.M.; Botelho do Rego, A.M.; Battaglini, N.; Herbst, F.; Rei Vilar, M. Surface functionalisation of cellulose with noble metals nanoparticles through a selective nucleation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1586–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mystrioti, C.; Xanthopoulou, T.D.; Tsakiridis, P.E.; Papassiopi, N.; Xenidis, A. Comparative evaluation of five plant extracts and juices for nanoiron synthesis and application for hexavalent chromium reduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çekiç, S.D.; Filik, H.; Apak, R. Simultaneous Spectrophotometric Determination of Paracetamol and p-Aminophenol in Pharmaceutical Products with Tiron Using Dissolved Oxygen as Oxidant. J. Anal. Chem. 2005, 60, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, R.Y.G.; Schwarze, M.; Schomäcker, R.; Stubenrauch, C. Catalytic Activity of Mono- and Bi-Metallic Nanoparticles Synthesized via Microemulsions. Catalysts 2014, 4, 256–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonels, N.A.; Meijboom, R. Preparation of well-defined dendrimer encapsulated ruthenium nanoparticles and their evaluation in the reduction of 4-nitrophenol according to the Langmuir-Hinshelwood approach. Langmuir 2013, 29, 13433–13442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Tao, K.; Hua, D.; Ma, Z.; Zhou, S. Size Effect of Gold Nanoparticles in Catalytic Reduction of p-Nitrophenol with NaBH4. Molecules 2013, 18, 12609–12620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekhar, M.; Wang, J.; Lee, W.-S.; Williams, W.D.; Kim, S.M.; Stach, E.A.; Miller, J.T.; Delgass, W.N.; Riberio, F.H. Size and support effects for the water-gas shift catalysis over gold nanoparticles supported on model Al2O3 and TiO2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 4700–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, K.; Miyamoto, Y.; Kawasaki, T.; Tanji, T.; Tai, Y.; Satsuma, A. Chemoselective Hydrogenation of Nitroaromatics by Supported Gold Catalysts: Mechanistic Reasons of Size- and Support-Dependent Activity and Selectivity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 17803–17810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valden, M.; Pak, S.; Lai, X.; Goodman, D.W. Structure sensitivity of CO oxidation over model Au/TiO22 catalysts. Catal. Lett. 1998, 56, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laoufi, I.; Saint-Lager, M.-C.; Lazzari, R.; Jupille, J.; Robach, O.; Garaudée, S.; Cabailh, G.; Dolle, P.; Cruguel, H.; Bailly, A. Size and Catalytic Activity of Supported Gold Nanoparticles: An in Operando Study during CO Oxidation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 4673–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangula, A.; Podila, R.; Ramakrishna, M.; Karanam, L.; Janardhana, C.; Rao, A.M. Catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol using biogenic gold and silver nanoparticles derived from Breynia rhamnoides. Langmuir 2011, 27, 15268–15274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.D.; Day, M.T.; MacPherson, V.J.; Pikramenou, Z. Luminescent nanobeads: Attachment of surface reactive Eu(III) complexes to gold nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2006, 17, 1433–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiro, M. Heterogeneous Catalysis of Solution Reactions. In Essays in Chemistry; Bradley, J.N., Gillard, R.D., Hudson, R.F., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1973; Volume 5, p. 63. [Google Scholar]
- Gallezot, P.; Laurain, N.; Isnard, P. Catalytic wet-air oxidation of carboxylic acids on carbon-supported platinum catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 1996, 9, L11–L17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintar, A.; Levec, J. Catalytic oxidation of aqueous p-chlorophenol and p-nitrophenol solutions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1994, 49, 4391–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, T.; Schwan-Jonczyk, A.; Lang, G.; Schuh, W.; Liebscher, K.D.; Springob, C.; Franzke, M.; Balzer, W.; Imhoff, S.; Maresch, G.; et al. Hair Preparations; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Engels, H.; Weidenhaupt, H.; Pieroth, M.; Hofmann, W.; Menting, K.; Mergenhagen, T.; Schmoll, R.; Uhrlandt, S. Chemicals and Additives; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Smiley, R.A. Phenylene- and Toluenediamines; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Liang, S.; Chen, Y.; Shen, L.; Zheng, H.; Wu, L. High efficient photocatalytic reduction of 4-nitroaniline to p-phenylenediamine over microcrystalline SrBi2Nb2O9. Catal. Commun. 2012, 17, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, F.Z. Gradual electrolytic reduction of nitrobenzene with limited cathode potential. Elektrochem. Angew. Phys. Chem. 1898, 22, 506–514. [Google Scholar]
- Corma, A.; Concepcion, P.; Serna, P. A Different Reaction Pathway for the Reduction of Aromatic Nitro Compounds on Gold Catalysts. Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 7404–7407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; Serna, A. Chemoselective hydrogenation of nitro compounds with supported gold catalysts. Science 2006, 313, 332–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wunder, S.; Polzer, F.; Lu, Y.; Mei, Y.; Ballauff, M. Kinetic Analysis of Catalytic Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol by Metallic Nanoparticles Immobilized in Spherical Polyelectrolyte Brushes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 8814–8820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Carroll, D.; Sleep, B.; Krol, M.; Boparai, H.; Kocur, C. Nanoscale zero valent iron and bimetallic particles for contaminated site remediation. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 104–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fattah, T.A.; Wixtrom, A. Catalytic Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol Using Gold Nanoparticles Supported on Carbon Nanotubes. ECS J. Solid State Sci. 2014, 3, M18–M20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











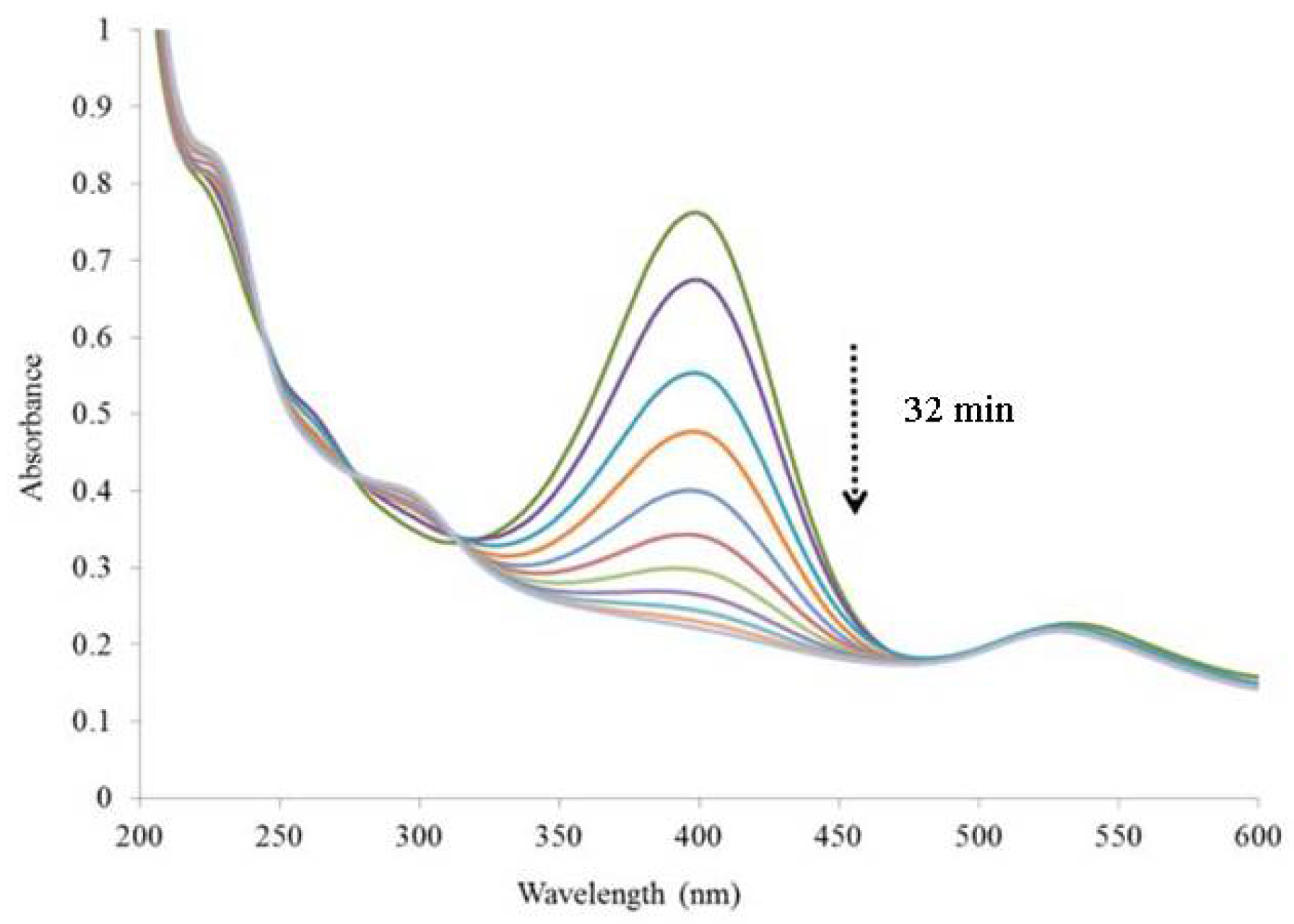
| Entry | [AuNPs] (M) | kapp × 103 (min−1) | Conversion b (%) | TOF b,c (h−1) | Time d (min) | Conversion (%) | TOF c (h−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.0 × 10−7 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 40 | 0.4 | 5.1 |
| 2 | 2.8 × 10−6 | 22.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 20 | 9.3 | 25.8 |
| 3 | 8.0 × 10−6 | 82.8 | 22.7 | 72.8 | 18 | 72.1 | 77.1 |
| 4 | 2.3 × 10−5 | 325 | 64.3 | 71.8 | 14 | 93.1 | 45.2 |
| 5 | 3.2 × 10−5 | 464 | 94.0 | 75.4 | 6 | 94.0 | 75.4 |
| Entry | [NaBH4] (M) | k’app × 103 (min−1) | Conversion b (6 min) (%) | Time d (min) | Conversion (%) | TOF c (h−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.0 × 10−4 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 40 | 2.4 | 8.5 |
| 2 | 5.0 × 10−4 | 38.1 | 2.4 | 40 | 18.5 | 43.9 |
| 3 | 8.0 × 10−4 | 168 | 22.8 | 40 | 30.2 | 130 |
| 4 | 1.2 × 10−3 | 315 | 55.9 | 14 | 88.2 | 76.3 |
| 5 | 1.6 × 10−3 | 464 | 94.0 | 6 | 94.0 | 127 |
| Entry | Substrate | Product | kapp × 102 (min−1) | Time (min) | Conversion (%) | TOF b (h−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 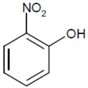 |  | 23.9 | 8 | 80 | 61.1 |
| (2-NP) | (2-AP) | |||||
| 2 |  |  | 17.3 | 8 | 40 | 30.5 |
| (2-NA) | (2-PD) | |||||
| 3 | 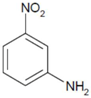 | 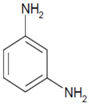 | 2.5 | 8 | 15 | 11.4 |
| (3-NA) | (3-PD) | |||||
| 4 | 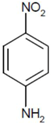 |  | 37.8 | 8 | 77 | 58.7 |
| (4-NA) | (4-PD) | |||||
| 5 | 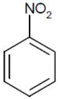 |  | 4.6 | 8 | 61 | 46.5 |
| (NB) | (NA) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alegria, E.C.B.A.; Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Mendes, M.; Ferraria, A.M.; Do Rego, A.M.B.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Effect of Phenolic Compounds on the Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles and its Catalytic Activity in the Reduction of Nitro Compounds. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8050320
Alegria ECBA, Ribeiro APC, Mendes M, Ferraria AM, Do Rego AMB, Pombeiro AJL. Effect of Phenolic Compounds on the Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles and its Catalytic Activity in the Reduction of Nitro Compounds. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(5):320. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8050320
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlegria, Elisabete C. B. A., Ana P. C. Ribeiro, Marta Mendes, Ana M. Ferraria, Ana M. Botelho Do Rego, and Armando J. L. Pombeiro. 2018. "Effect of Phenolic Compounds on the Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles and its Catalytic Activity in the Reduction of Nitro Compounds" Nanomaterials 8, no. 5: 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8050320
APA StyleAlegria, E. C. B. A., Ribeiro, A. P. C., Mendes, M., Ferraria, A. M., Do Rego, A. M. B., & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2018). Effect of Phenolic Compounds on the Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles and its Catalytic Activity in the Reduction of Nitro Compounds. Nanomaterials, 8(5), 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8050320