Unveiling the Impact: Human Exposure to Non-Ionizing Radiation in the Millimeter-Wave Band of Sixth-Generation Wireless Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Exposure Regulations at mmWave Frequencies
3. The mmWave Band
| Sub-6 GHz Band [4,45] | Centimeter- and Millimeter-Wave Band [4,45,46,47] | Complementary Sub THz Band [41,42] | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency in (GHz) | 1.8 | 2.1 | 2.6 | 3.3 | 5 | 6.425–7.125 | 7–24 | 26 | 28 | 40 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 102–109 | 151.5–164 | 167–174.8 | 209–226 | 252–275 |
| Network Generation | Other technologies/4G/5G | 5G/6G | 6G only | ||||||||||||||||
3.1. The mmWave Path Loss
3.2. Foliage Loss
4. Radiation Metrics
4.1. Specific Absorption Rate (SAR)
4.2. Power Density
4.3. Steady-State Temperature (ssT)
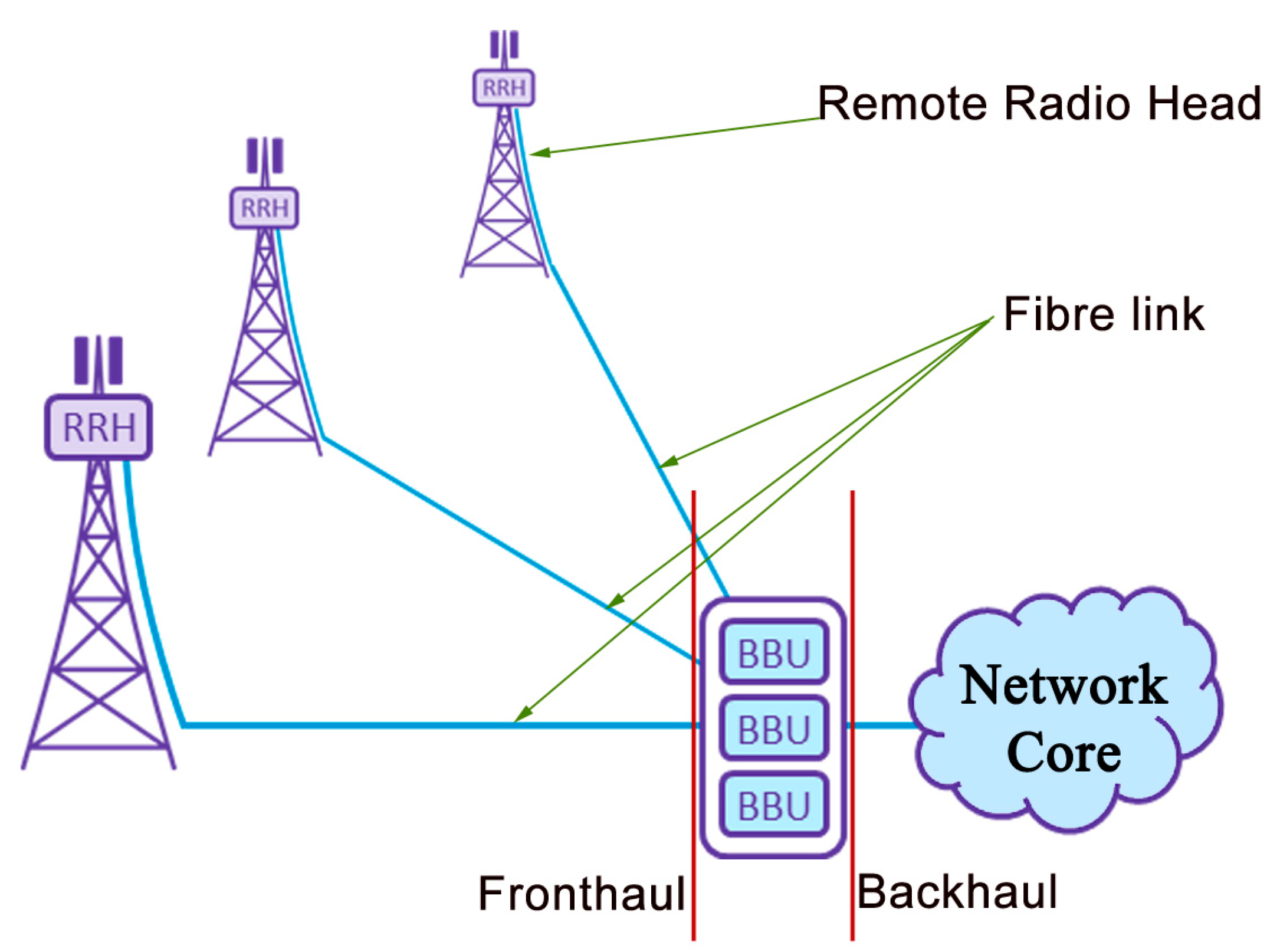
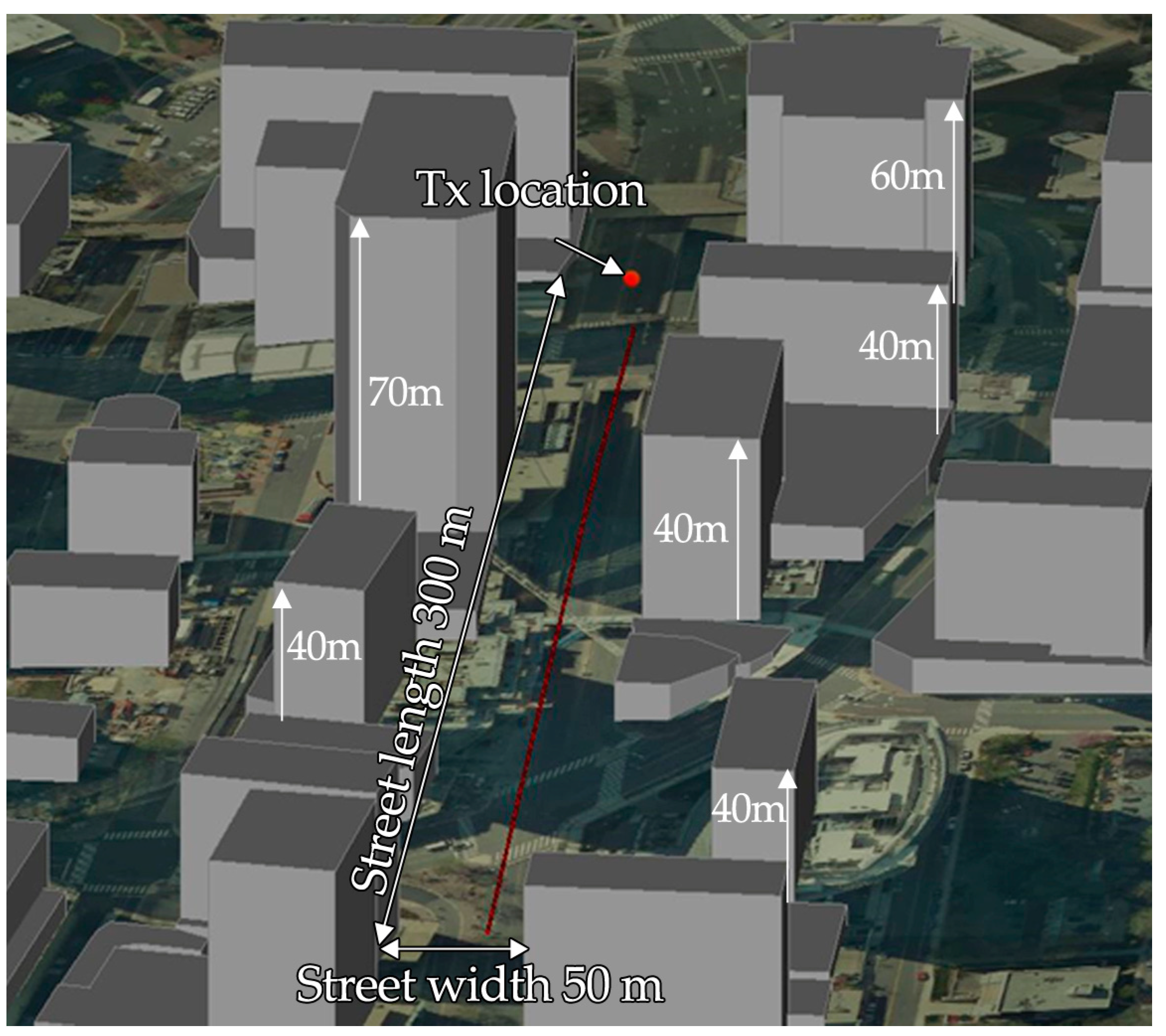
5. Network Model
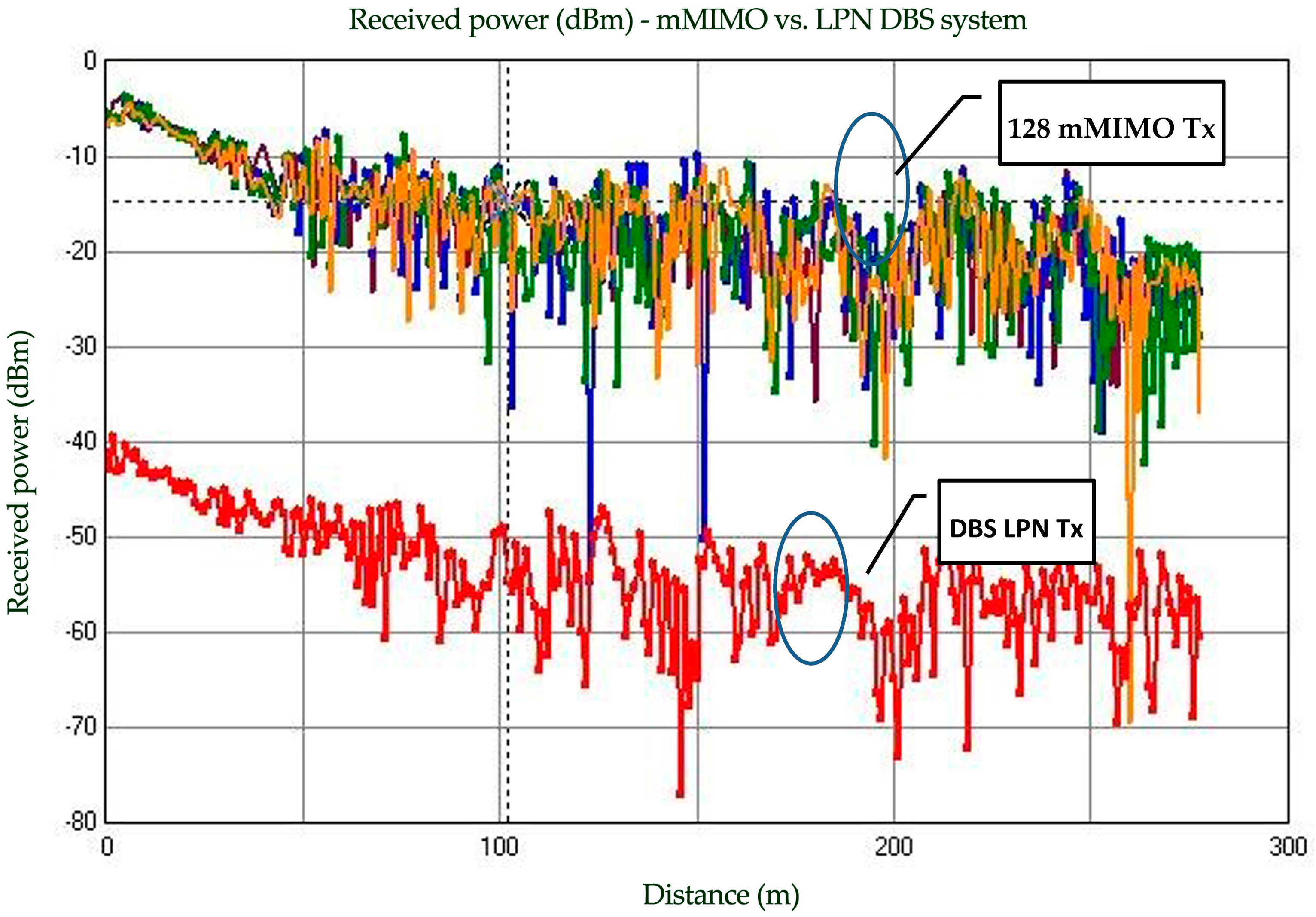
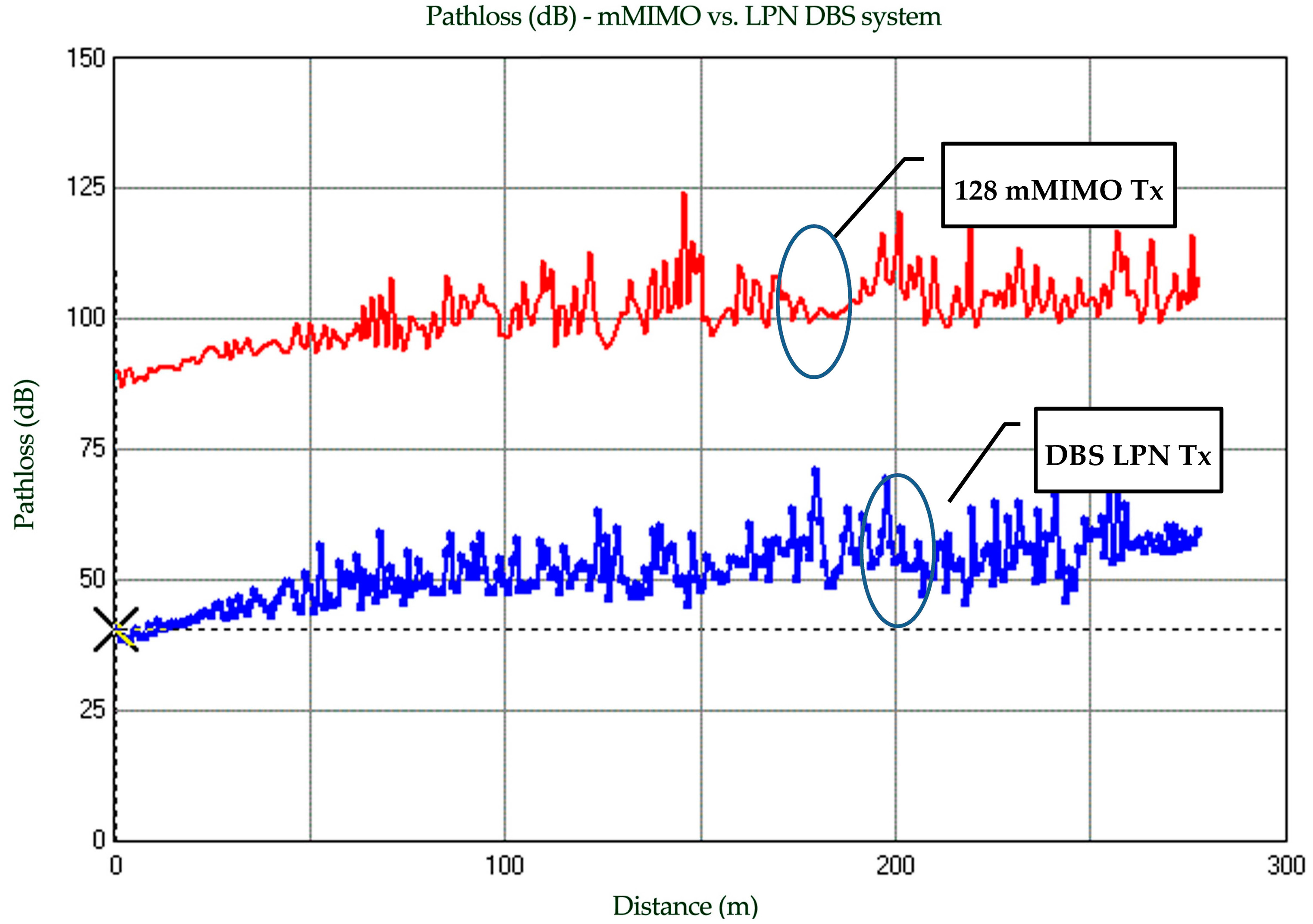
6. Results and Discussion
6.1. HPN with CBS Architecture
6.2. LPN with DBS Architecture
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ericsson. Mobile Data Traffic. Ericsson Mobility Visualizer. 2023. Available online: https://www.ericsson.com/en/reports-and-papers/mobility-report (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- ITU. Minimum Requirements Related to Technical Performance for IMT-2020 Radio Interface(s). Work. Party 5D, vol. November, no. 5D/TEMP/300(Rev.1). 2017, pp. 1–148. Available online: https://www.itu.int/pub/R-REP-M.2410-2017 (accessed on 3 January 2024).
- Ferrag, M.A.-H.M.A.; Debbah, M. Generative AI for Cyber Threat-Hunting in 6G-enabled IoT Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM 23rd International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Internet Computing Workshops (CCGridW), Bangalore, India, 1–4 May 2023; pp. 16–25. [Google Scholar]
- Al-falahy, N.; Alani, O.Y.K. Millimetre Wave Frequency Band as a Candidate Spectrum for 5G Network Architecture: A Survey. Phys. Commun. 2019, 32, 120–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-falahy, N.; Alani, O.Y.K. Reducing the Exposure to Millimetre Wave Radiation Using Distributed Base Stations in C-RAN Architecture. In Proceedings of the 10th Computer Science & Electronic Engineering Conference (CEEC), Colchester, UK, 19–21 September 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- LEXNET. LEXNET Project: Low EMF Exposure Networks. 2018. Available online: http://www.lexnet.fr (accessed on 15 March 2018).
- Wu, T.; Rappaport, T.S.; Collins, C.M. The Human Body and Millimeter-Wave Wireless Communication Systems: Interactions and Implications. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications, London, UK, 8–12 June 2015; pp. 2423–2429. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE Std C95.1-2005; IEEE Standard for Safety Levels with Respect to Human Exposure to Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Fields, 3 kHz to 300 GHz. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 1–238. [CrossRef]
- International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP). Guidelines for limiting exposure to time-varying electric, magnetic, and electromagnetic fields (up to 300 GHz). Health Phys. 1998, 74, 494–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Falahy, N.; Alani, O. Technologies for 5G Networks: Challenges and Opportunities. IEEE IT Prof. 2017, 19, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modenese, A.; Gobba, F. Occupational Exposure to Non-Ionizing radiation. Main effects and criteria for health surveillance of workers according to the European Directives. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering (EEEIC), Madrid, Spain, 9–12 June 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport, T.S.; Sun, S.; Mayzus, R.; Zhao, H.; Azar, Y.; Wang, K.; Wong, G.N.; Schulz, J.K.; Samimi, M.; Gutierrez, F. Millimeter Wave Mobile Communications for 5G Cellular: It Will Work ! IEEE Access 2013, 1, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-falahy, N.; Alani, O. The Impact of Base Station Antennas Configuration on the Performance of Millimetre Wave 5G Networks. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks (ICUFN), Milan, Italy, 4–7 July 2017; pp. 636–641. [Google Scholar]
- G-PPP. 5G Infrastructure Public Private Partnership. 2018. Available online: https://5g-ppp.eu/ (accessed on 20 March 2018).
- Siegel, P.; Pikov, V. Impact of Low Intensity Millimeter-Waves on Cell Membrane Permeability. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves, IRMMW-THz, Busan, Republic of Korea, 21–25 September 2009; p. 978. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, K.; Colombi, D. Thermal response of tissue to RF exposure from canonical dipoles at frequencies for future mobile communication systems. Electron. Lett. 2017, 53, 360–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guraliuc, A.R.; Zhadobov, M.; Sauleau, R.; Marnat, L.; Dussopt, L. Near-Field User Exposure in Forthcoming 5G Scenarios in the 60 GHz Band. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 6606–6615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basikolo, T.; Yoshida, T.; Sakurai, M. Electromagnetic field exposure evaluation for 5G in millimeter wave frequency band. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and USNC-URSI Radio Science Meeting, APSURSI 2019, Atlanta, GA, USA, 7–12 July 2019; pp. 1523–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Sasaki, K.; Watanabe, S. EMF Exposure from 5G Equipment at Millimeter Wave Frequencies. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Electromagnetics: Applications and Student Innovation Competition, iWEM 2018, Nagoya, Japan, 29–31 August 2018; p. 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombi, D.; Thors, B.; Tornevik, C.; Balzano, Q. RF Energy Absorption by Biological Tissues in Close Proximity to Millimeter-Wave 5G Wireless Equipment. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 4974–4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirkel, A.Z.; Lai, J.C.S.; Evans, T.A.; Rankin, G.A. Effects of millimeter wave exposure on termite behavior. In Proceedings of the Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium, Marrakesh, Morocco, 20–23 March 2011; pp. 1581–1585. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H. A Unified Quantitative Index to Assess Non-ionizing Radiation Safety. IEEE Consum. Electron. Mag. 2022, 12, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; An, K.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, G.; Wong, K.K.; Chatzinotas, S.; Ng, D.W.K.; Guan, D. Energy-Efficient Hybrid Beamforming for Multilayer RIS-Assisted Secure Integrated Terrestrial-Aerial Networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2022, 70, 4189–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Niu, H.; An, K.; Hu, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; Al-Dhahir, N. Pain without Gain: Destructive Beamforming from a Malicious RIS Perspective in IoT Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023. early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; An, K.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, G.; Wong, K.K.; Chatzinotas, S.; Yin, H.; Liu, P. RIS-Assisted Robust Hybrid Beamforming against Simultaneous Jamming and Eavesdropping Attacks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 9212–9231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansal, K.A.; Jose, D.S.; Rajan, R.K. Review on Biological Effect of Electromagnetic Radiation. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Circuits and Systems in Digital Enterprise Technology, ICCSDET 2018, Kottayam, India, 21–22 December 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kour, H.; Jha, R.K. EM Radiation Reduction in WCN: Towards Safe Generations. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Communication Systems and Networks, Comsnets 2020, Bangalore, India, 7–11 January 2020; pp. 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Amrani, L.; Mazri, T.; Hmina, N. The Specific Absorption Rate induced in human organs due Ionizing and Non Ionizing Radiations exposure. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Wireless Networks and Mobile Communications (WINCOM), Marrakesh, Morocco, 16–19 October 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kour, H.; Jha, R.K. Electromagnetic Radiation Reduction in 5G Networks and beyond Using Thermal Radiation Mode. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 11841–11856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajibare, A.T.; Ramotsoela, D.; Akinyemi, L.F.; Oladejo, S.O. RF EMF Radiation Exposure Assessment of 5G Networks: Analysis, Computation and Mitigation Methods. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE AFRICON, Arusha, Tanzania, 13–15 September 2021; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, V.; Suárez, S.D.; Marina, P.; Febles, V.M.; Rabassa, L.E.; Hernández, J. Survey of RF Electromagnetic Field Exposure in a Public Health Research Environment. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility—EMC Europe, Kraków, Poland, 4–8 September 2023; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharel, B.; Lopez, O.L.A.; Mahmood, N.H.; Alves, H.; Latva-Aho, M. Fog-RAN Enabled Multi-Connectivity and Multi-Cell Scheduling Framework for Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 7059–7072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinini, R.I.; Batista, D.M.E.; Figueiredo, G.B.; Tornatore, M.; Mukherjee, B. Energy-Efficient vBBU Migration and Wavelength Reassignment in Cloud-Fog RAN. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2021, 5, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, J.R.F.; Sylvar, D.M.; Ulcek, J.L. Evaluating Compliance with FCC Guidelines for Human Exposure to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields. OET Bull. 1997, 65, 1–84. [Google Scholar]
- Federal Communications Commission (FCC). Radio Spectrum Allocation. 2018. Available online: www.fcc.gov/engineering-technology/policy-and-rules-division/general/radio-spectrum-allocation (accessed on 6 April 2018).
- International Telecommunication Union (ITU). World Radiocommunication Conferences (WRC). 2018. Available online: https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-R/conferences/wrc (accessed on 6 April 2018).
- Federal Communications Commission (FCC). Use of Spectrum Bands Above 24 GHz for Mobile Radio Services; Technical Report, no. GN Docket No. 14-177; Federal Communications Commission (FCC): Washington, DC, USA, 2017; pp. 1–137.
- Roh, W.; Seol, J.-Y.; Park, J.; Lee, B.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.; Cho, J.; Cheun, K.; Aryanfar, F. Millimeter-Wave Beamforming as an Enabling Technology for 5G Cellular Communications: Theoretical Feasibility and Prototype Results. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccardi, F.; Heath, R.W., Jr.; Lozano, A.; Marzetta, T.L.; Popovski, P. Five Disruptive Technology Directions for 5G. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofcom. Update on 5G Spectrum in the UK; Ofcom: London, UK, 2017; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Nokia. Spectrum for 6G Explained. 2023. Available online: https://www.nokia.com/about-us/newsroom/articles/spectrum-for-6G-explained/ (accessed on 15 December 2023).
- Rappaport, T.S.; Xing, Y.; Kanhere, O.; Ju, S.; Madanayake, A.; Mandal, S.; Alkhateeb, A.; Trichopoulos, G.C. Wireless communications and applications above 100 GHz: Opportunities and challenges for 6g and beyond. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 78729–78757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ITU. World Radiocommunication Conference. 2023. Available online: https://www.itu.int/wrc-23/ (accessed on 18 December 2023).
- Lin, Z.; Lin, M.; Champagne, B.; Zhu, W.P.; Al-Dhahir, N. Secrecy-Energy Efficient Hybrid Beamforming for Satellite-Terrestrial Integrated Networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2021, 69, 6345–6360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabu, R.T.; Benisha, M.; Bai, V.T.; Yokesh, V. Millimeter Wave for 5G Mobile Communication Application. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Information, Communication and Bio-Informatics (AEEICB16), Chennai, India, 27–28 February 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.; Zhang, P.; Pollin, S. 6G Wireless Communications in 7–24 GHz Band: Opportunities, Techniques, and Challenges. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.06425. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Cao, Y.; Raimundo, X.; Cheema, A.; Salous, S. Rain Statistics Investigation and Rain Attenuation Modeling for Millimeter Wave Short-Range Fixed Links. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 156110–156120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, S.; Abu-Surra, S.; Malmirchegini, M. Channel Feasibility for Outdoor Non-Line-of-Sight mmWave Mobile Communication. In Proceedings of the IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Fall) 2012, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 3–6 September 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport, T.S.; Gutierrez, F.; Ben-dor, E.; Murdock, J.N.; Qiao, Y.; Tamir, J.I. Broadband Millimeter-Wave Propagation Measurements and Models Using Adaptive-Beam Antennas for Outdoor Urban Cellular Communications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 1850–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3GPP Technical Report 38.901. Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network; Study on channel model for frequencies from 0.5 to 100 GHz. 2017. Available online: https://www.3gpp.org/dynareport/38901.htm (accessed on 3 January 2024).
- Al-Falahy, N.; Alani, O. Improved Capacity and Fairness of Massive Machine Type Communications in Millimetre Wave 5G Network. Computers 2018, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozuomba, S.; Johnson, E.H.; Udoiwod, E.N. Application of Weissberger Model for Characterizing the Propagation Loss in a Gliricidia sepium Arboretum. Univ. J. Commun. Netw. 2018, 6, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, M.; Pattan, B. Millimeter Wave Propagation: Spectrum Management Implications. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2005, 6, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, T.S.; Dowdey, J.E.; Murry, R.C. Christensen’s Physics of Diagnostic Radiology, 4th ed.; Lea & Febiger, U.S.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Zhadobov, M.; Chahat, N.; Sauleau, R.; Le Quement, C.; Le Drean, Y. Millimeter-wave interactions with the human body: State of knowledge and recent advances. Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol. 2011, 3, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Falahy, N.; Alani, O. Supporting Massive M2M Traffic in the Internet of Things Using Millimetre Wave 5G Network. In Proceedings of the 9th Computer Science & Electronic Engineering Conference (CEEC), Colchester, UK, 27–29 September 2017; pp. 83–88. [Google Scholar]







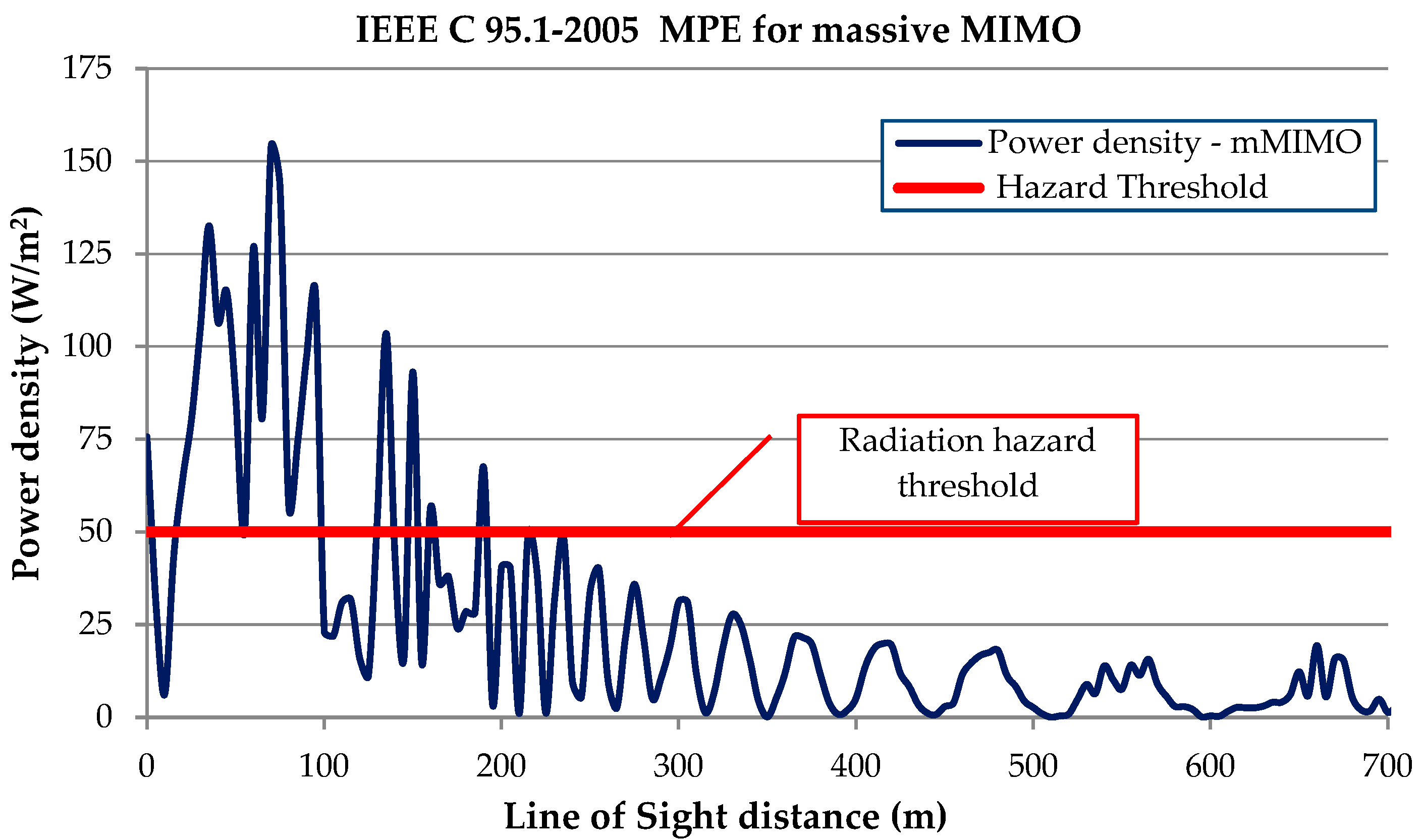

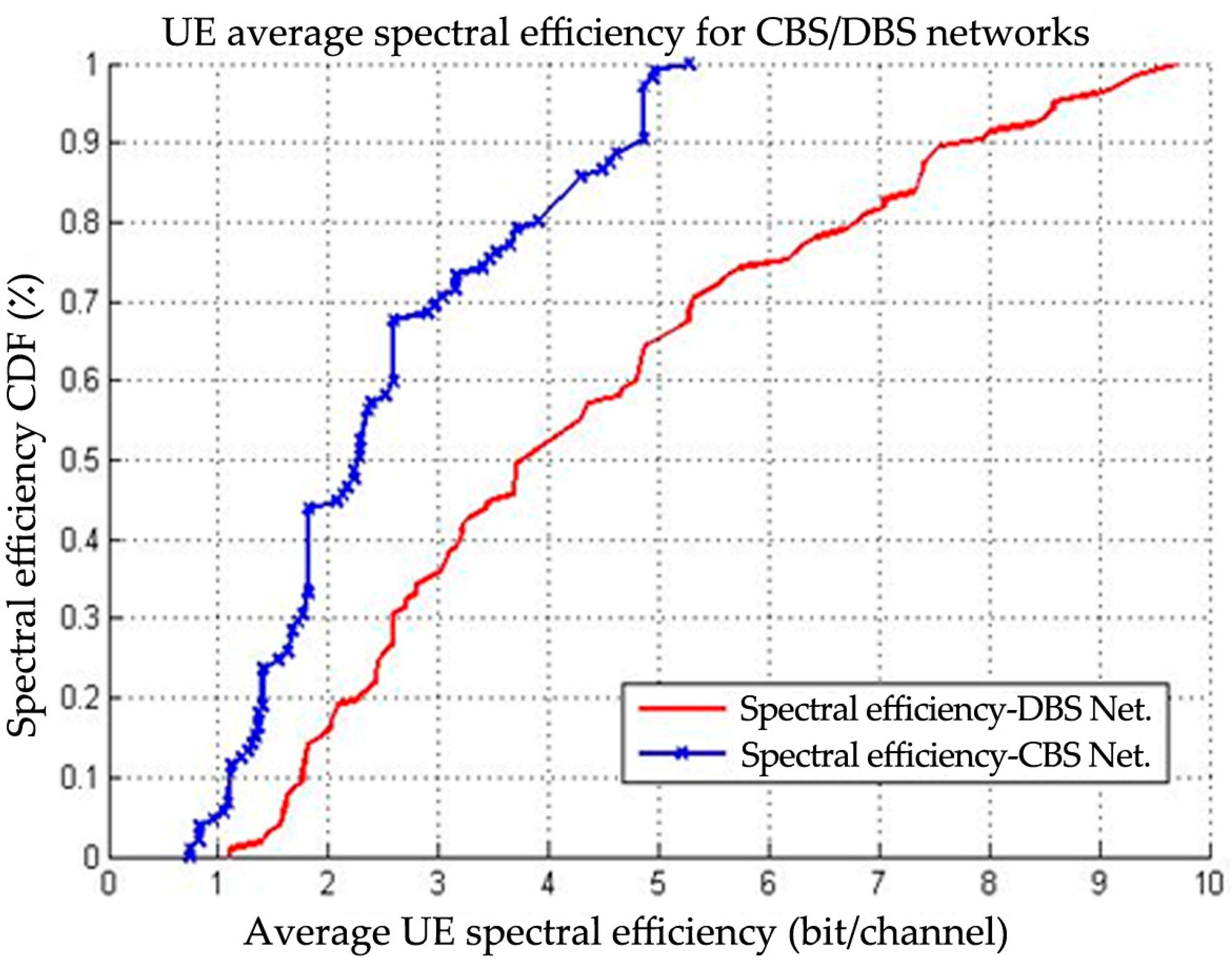
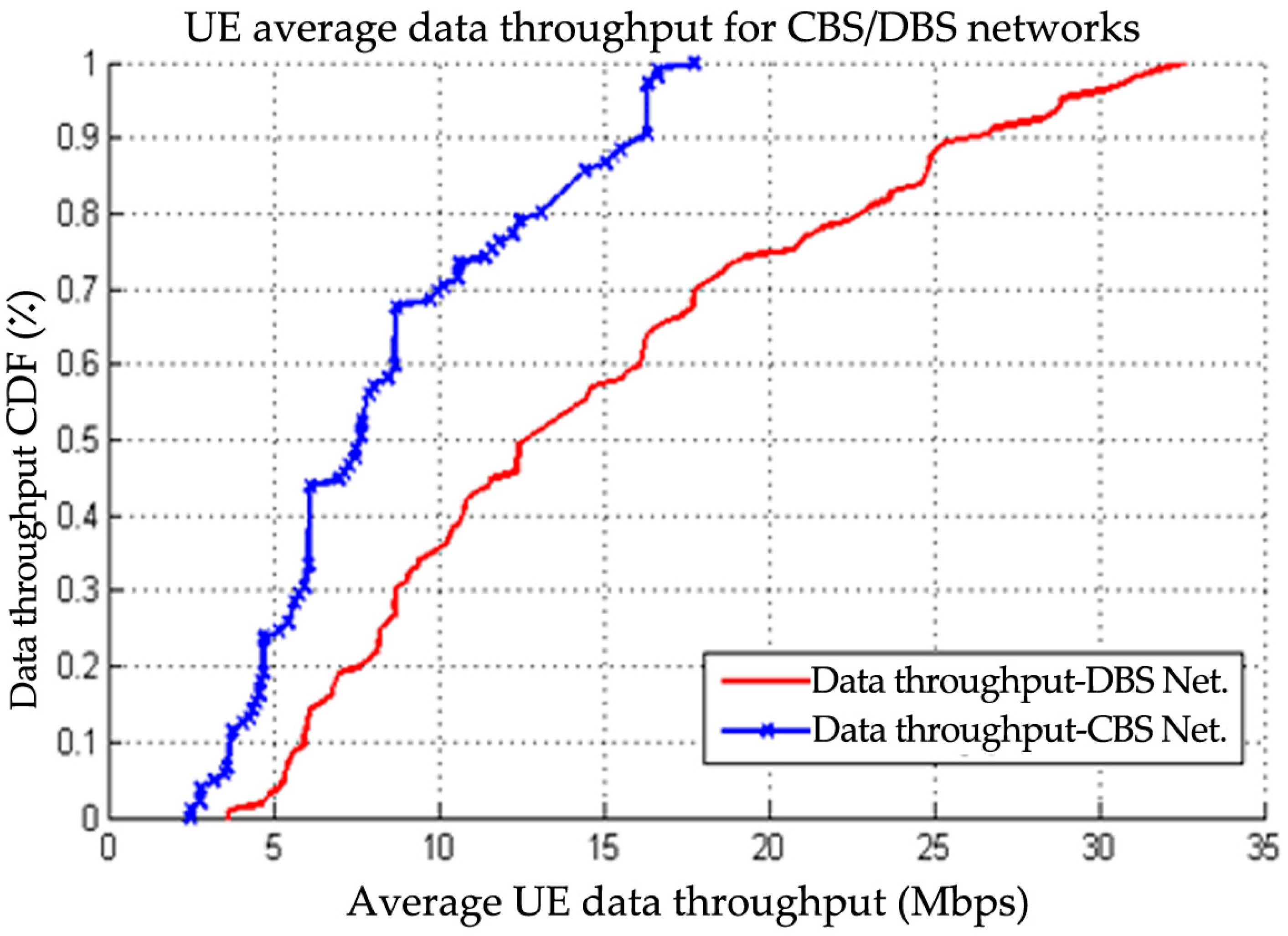
| Frequency (GHz) | Power Density (Controlled Envir.) “Upper Tier” in W/m2 | Power Density (Uncontrolled Envir.) “Lower Tier” in W/m2 |
|---|---|---|
| 3 to 30 | 100 in avg. time = 19.63/f1.079 min | 10 in avg. time = 150/f min |
| 30 to 100 | 100 in avg. time = 2.524/f0.476 min | 10 in avg. time = 25.24/f0.476 min |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Link | Downlink |
| Designated frequency | 28 GHz |
| Path loss model | As per 3GPP Report 38.901 [50] |
| Foliage loss model | Weissberger model [52] |
| Bandwidth | Up to 500 MHz |
| Tx Power | 30–46 dBm |
| RRH gain | 15 dB |
| MIMO array gain | 30 dB |
| RRH distribution | 3 per BBU |
| Antenna type | SISO and MIMO |
| Tx height | 10 m |
| Rx height | 1.5 m |
| MIMO | 128 elements |
| Polarization | −45/45 X-POL |
| RoI | 300 × 50 m Street Canyon |
| MPE model | IEEE C 95.1-2005 model |
| Network Type | HPN–CBS | LPN–DBS |
|---|---|---|
| All UEs | 1000 | 1000 |
| LOS + NLOS | 880 | 968 |
| Outage UEs | 120 | 32 |
| Prob. of Coverage | 88% | 96.8% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Falahy, N.; Alani, O.Y. Unveiling the Impact: Human Exposure to Non-Ionizing Radiation in the Millimeter-Wave Band of Sixth-Generation Wireless Networks. Electronics 2024, 13, 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13020246
Al-Falahy N, Alani OY. Unveiling the Impact: Human Exposure to Non-Ionizing Radiation in the Millimeter-Wave Band of Sixth-Generation Wireless Networks. Electronics. 2024; 13(2):246. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13020246
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Falahy, Naser, and Omar Y. Alani. 2024. "Unveiling the Impact: Human Exposure to Non-Ionizing Radiation in the Millimeter-Wave Band of Sixth-Generation Wireless Networks" Electronics 13, no. 2: 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13020246
APA StyleAl-Falahy, N., & Alani, O. Y. (2024). Unveiling the Impact: Human Exposure to Non-Ionizing Radiation in the Millimeter-Wave Band of Sixth-Generation Wireless Networks. Electronics, 13(2), 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13020246





