On Physical Aeroacoustics with Some Implications for Low-Noise Aircraft Design and Airport Operations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Noise Generation and Propagation
2.1. Open Rotor Noise
2.1.1. Airplane Propeller Noise
2.1.2. Helicopter Rotor Noise
2.1.3. Noise of Contra-Rotating Propulsors

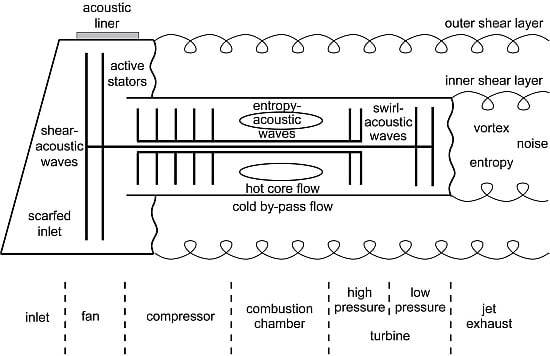
2.2. Ducted Engine Noise
2.2.1. Fan and Inlet Noise


2.2.2. Turbine Exhaust Noise

2.2.3. Combustion Stability and Noise
2.3. Installation and Flight Effects
2.3.1. Reflection, Shielding and Diffraction
2.3.2. Aerodynamic Noise Sources

2.3.3. Jet Noise and Scattering


3. Airport Noise Environment
3.1. Atmospheric and Ground Effects
3.1.1. Stratification and Wind Effects
3.1.2. Spectral Broadening by Turbulence


3.1.3. Absorption and Interference due to Ground and Buildings


3.2. Noise Annoyance to the Near Airport Resident
3.2.1. Outdoor-to-Indoor Noise Transmission
3.2.2. Variability of Circumstances and Individuals
3.2.3. Psychoacoustics: Is There a Less Annoying Noise?
3.3. Certification, Regulations and Limitations
3.3.1. International Noise Certification Standards
3.3.2. Local Regulations, Restrictions and Limitations
3.3.3. Community Action and Pressure Groups
4. Noise Reduction Measures
4.1. Retrofittable Acoustic Silencing Devices
4.1.1. Non Uniform Duct Acoustic Liner
4.1.2. Lobed and Chevron Nozzles



4.1.3. Aerodynamic fairings and tailoring

4.2. Noise Mitigation Technologies
4.2.1. Passive Attenuation or Absorption
4.2.2. Active Noise and Vibration Control
4.2.3. Noise Reduction at the Source


4.3. Noise Abatement Procedures
4.3.1. Approach with Engine at Idle
4.3.2. Thrust Cut-Back at Take-Off
4.3.3. Steep and Curved Flight Paths
5. Novel Aircraft Configurations
5.1. Radical New Designs
5.1.1. Flying Wing with Engine Nacelles

5.1.2. Flush or Buried Engines
5.1.3. Distributed Propulsion System
5.2. Evolutions of the Conventional Configuration
5.2.1. Engines between a U-Tail
5.2.2. Nacelle Joining Wing to Tailplane
5.2.3. Variable-Cycle Engines
5.3. Low-Noise Cruise-Efficient Aircraft
5.3.1. Design Requirements and Constraints
5.3.2. Configuration I: For a Ducted Turbofan

5.3.3. Configuration II: For Open Rotors


6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lighthill, M.J. On sound generated aerodynamically: I. General theory. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1952, A211, 564–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lighthill, M.J. On sound generated aerodynamically: II. Turbulence as source of sound. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1954, A222, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Lighthill, M.J. On sound generated aerodynamically. Bakerian Lecture. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1961, A267, 147–182. [Google Scholar]
- Lighthill, M.J. Waves in Fluids; Cambridge Univerysity Press: Cambridge, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. Modern trends in research on waves in fluids. Part I: Generation and scattering by turbulent and inhomogeneous flows. Portug. Phys. 1983, 14, 121–143. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. On waves in gases. Part I: Acoustics of jets, turbulence and ducts. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1986, 58, 117–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curle, N. The influence of solid boundaries upon aerodynamic sound. Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. 1955, A231, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ffowcs-Williams, J.E.; Hawkins, D.L. Sound generation by turbulence and surfaces in arbitrary motion. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. Lond. 1968, A264, 321–383. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Lau, F.J.P. On sound generation by moving surfaces and convected sources in a flow. Int. J. Aeroacoustics 2009, 11, 103–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayleigh, J.W.S. The Theory of Sound, 2nd ed.; Dover: Mineola, NY, USA, 1945; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Lamb, H. Dynamical Theory of Sound; Dover: Mineola, NY, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Morse, P.M.; Ingard, K.U. Theoretical Acoustics; McGraw-Hill: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Pierce, A.D. Acoustics; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Dowling, A.P.; Ffowcs-Williams, J.E. Sound and Sources of Sound; Ellis Harwood: London, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, M.E. Aeroacoustics; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Howe, M.S. Hydrodynamics and Sound; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Crighton, D.G.; Flowcs-Williams, J.E. Sound generation by turbulent two-phase flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1969, 36, 585–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glauert, H. Airfoil and Airscrew Theory; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1936. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, W.K. Mechanics of Flow-Induced Sound and Vibration I/II; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard, H.H. Aeroacoustics of Flight Vehices; Acoustical Society of America: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Hernandez, J.M. Advances in Acoustic Technology; Wiley: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. On some recent advances in aeroacoustics. Int. J. Acoust. Vib. 2004, 11, 27–45. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. On waves in fluids: Some mathematical, physical and engineering aspects. In Progress in Industrial Mathematics ECMI; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 73–105. [Google Scholar]
- Gutin, L. On the Sound Field of a Rotating Propeller; National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA): Washington, DC, USA, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard, H.H. Sound from Dual-Rotating and Multiple Single Rotating Propellers; National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA): Washington, DC, USA, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, D.B. Helicoidal surface theory for harmonic noise of propellers in the far field. AIAA J. 1980, 18, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, D.B. Influence of propeller design parameters on far-field harmonic noise in forward flight. AIAA J. 1980, 18, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahan, C.; Avezard, L.; Guillien, G.; Malarmey, C.; Chombard, J. Propeller light aircraft noise at discrete frequencies. AIAA J. Aircr. 1981, 18, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, D.B. Compressible helicoidal surface theory for propeller aerodynamics and noise. AIAA J. 1983, 21, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, D.B. Near-field frequency-domain theory for propeller noise. AIAA J. 1985, 23, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farassat, F. Prediction of advanced propeller noise in the time domain. AIAA J. 1986, 24, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.K.W.; Salikuddin, M. Weakly non-linear acoustic and shock wave theory of the noise of advanced high-speed turbo propellers. J. Fluid Mech. 1986, 164, 127–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farassat, F.; Dunn, M.H. Advanced turboprop noise prediction based in recent theoretical results. J. Sound Vib. 1987, 59, 53–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounet, H.; Lewy, S. Prediction of prop-fan noise by a frequency domain scheme. AIAA J. 1988, 25, 428–435. [Google Scholar]
- Tam, C.K.W.; Salikuddin, M.; Hanson, D.B. Acoustic interference of counter-rotation propellers. J. Sound Vib. 1988, 124, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuff, R. Noise field of a propeller with angular inflow. AIAA J. 1988, 26, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jou, W.H. Supersonic propeller noise in a uniform flow. AIAA J. 1989, 62, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, R. The radiation of sound from a propeller at angle of attack. Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. 1990, 431, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Envia, E. Asymptotic theory of supersonic propeller noise. AIAA J. 1994, 32, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. On the influence of angle-of-attack on far-field propeller noise. ASME J. Acoust. 1999, 121, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowson, M.V. Basic mechanism of noise generation by helicopters, V/STOL aircraft and ground effect machines. J. Sound Vib. 1966, 3, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leverton, J.W.; Taylor, F.W. Helicopter blade slap. J. Sound Vib. 1966, 4, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowson, M.V.; Ollerhead, J.B. A theoretical study of helicopter rotor noise. J. Sound Vib. 1969, 9, 197–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkings, D.L.; Lowson, M.V. Theory of open supersonic rotor noise. J. Sound Vib. 1974, 36, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravamudan, K.S.; Lee, A.; Harris, W.L. A simplified Mach number scaling law for helicopter rotor noise. J. Sound Vib. 1978, 57, 555–570, Erratum in 1979, 62, 595–597. [Google Scholar]
- Farassat, F. Linear acoustic formulas for calculation of rotating blade noise. AIAA J. 1981, 19, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farassat, F.; Martin, R.M. A note on the tip noise of rotating blades. J. Sound Vib. 1983, 86, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, T.F.; Marcolini, M.A. Airfoil tip vortex formation noise. AIAA J. 1986, 24, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, F.H.; Yu, Y.H. Helicopter impulsive noise: Theoretical and experimental status. J. Sound Vib. 1986, 109, 361–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, F.T.; Marcolini, M.A.; Pope, D.S. A directional array approach for the measurement of rotor noise source distributions with controlled spatial resolution. J. Sound Vib. 1987, 112, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.R.; Lyrintzis, A.S. Acoustics of transonic blade-vortex interactions. AIAA J. 1988, 26, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, A.; Tung, C. Two generalized fields and their governing equations applied to helicopter acoustics. Acustica 1989, 69, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lowson, M.V. Progress towards quiter civil helicopters. Aeron. J. 1991, 2, 209–223. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Macedo, C.M. On the predidiction of the broadband noise of helicopter from the impulse component. J. Acoust. 1992, 5, 531–542. [Google Scholar]
- Dunne, R.C.; Howe, M.S. Wall-bounded blade-tip vortex interaction noise. J. Sound Vib. 1997, 202, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doak, P.E. Acoustic radiation from a turbulent fluid containing foreign bodies. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1960, A254, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowson, M.V. The sound field for singularities in motion. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1965, 286, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowson, M.V. Theoretical analysis of compressor noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1968, 47, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ffowcs-Williams, J.E.; Hawkings, D.L. Theory relating to the noise of rotating machinery. J. Sound Vib. 1969, 10, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, M.E. Unified approach to aerodynamic sound generation in the presence of solid boundaries. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1974, 56, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farassat, F. Discontinuities in aerodynamics and aeroacoustics: The concept and applications of generalized derivatives. J. Sound Vib. 1977, 2, 165–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, A. Theory of vortex sound. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1964, 36, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candel, S.M. Analytical Studies of Some Acoustic Problems of Jet Engines. Ph.D. Thesis, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Morfey, C.L. Amplification of aerodynamic noise by convected flow inhomogeneities. J. Sound Vib. 1973, 31, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ffowcs-Williams, J.E.; Howe, M.S. The generation of sound by density inhomogeneities in low Mach number nozzle flows. J. Fluid Mech. 1975, 70, 605–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, M.S. On generation of sound by aerodynamic sources in inhomogeneous steady flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1975, 67, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, M.S. Contribution to the theory of aerodynamic sound with application to excess jet noise and the theory of the flute. J. Fluid Mech. 1975, 72, 625–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. On the emission of sound by an ionized inhomogeneity. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1978, A351, 65–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. On the fundamental acoustic mode in variable area, low Mach number nozzles. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 1985, 22, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. On linear and non-linear wave equations for the acoustics of high-speed potential flows. J. Sound. Vib. 1986, 110, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. On 36 forms of the acoustic wave equation in potential flows and inhomogeneous media. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2007, 60, 149–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. Complex Functions with Application to Flows and Fields; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lamb, H. Hydrodynamics, 6th ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1932. [Google Scholar]
- Milne-Thomson, L.M. Theoretical Aerodynamics; Dover: Mineola, NY, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. Transcendental Representations with Applications to Solids and Fluids; CRC Press: Mineola, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bassett, A.B. A Treatise on Hydrodynamics; Dover: Mineola, NY, USA, 1961; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Prandtl, L.; Tietjens, O.G. Fundamentals of Hydro and Aeromechanics; Dover: Mineola, NY, USA, 1957; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Landau, L.D.; Lifshitz, E.F. Fluid Mechanics; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Bateman, H.; Dryden, H.L.; Murnaghan, F.P. Hydrodynamics; Dover: Mineola, NY, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford, D.E. Fluid Dynamics; Oliver & Boyd: London, UK, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, W.J.; Thom, A.S.; Young, A.D. Mechanics of Fluids; Arnold: New York, NY, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Loitsyanski, L.G. Mechanics of Fluids and Gases; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Truesdell, C.A. Mechanical Foundations of Elasticity and Fluid Mechanics; Gordon & Breach: London, UK, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor, G.K. Fluid Dynamics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Curle, N.; Davies, H.J. Modern Fluid Dynamics; Van Nostrand: New York, NY, USA, 1968; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, R.E. Introduction to Mathematical Fluid Dynamics; Dover: Mineola, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Fediaevski, C.; Voitkounski, I. Hydromécanique; Editions Mir: Moscow, Russia, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke, M. An Album of Fluid Motion; Parabolic Press: Stanford, CA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Lighthill, M.J. An Informal Introduction to Fluid Mechanics; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Lighthill, M.J. Group velocity. J. Inst. Math. Appl. 1964, 1, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. On generalizations of the Doppler factor, local frequency, wave invariant and group velocity. Wave Motion 1988, 10, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernoulli, J., II. Euleri Opera Omnia; Series II; Academic Helvetica: Basel, Switherland, 1753; Volume 11, p. 301. [Google Scholar]
- Euler, L. Supplement aux et continuation des recherches sur la propagation due son. Mem. Acad. Sci. Berl. 1766, 15, 210–264. [Google Scholar]
- Euler, L. De motu vibratorio cordarum inequalter crassarum. Novi Comm. Acad. Sci. Petrop. 1764, 9, 246–304. [Google Scholar]
- Langrange, J.L. Nouvelles recherches sur la nature et la propagation du son. Misc. Turinesia 1760, 2, 11–171. [Google Scholar]
- Bernoulli, D. Mémoire sur les vibrations dês cordes d’une épaisseur inégale. Hist. Acad. Sci. Ber. 1767, 21, 281–366. [Google Scholar]
- Euler, L. Recherches sur le mouvement dês cordes inégualement grosses. Misc. Turinesia 1766, 3, 27–59. [Google Scholar]
- Euler, L. De motu aeris in tubis. Novi Comm. Acad. Sci. Petrop. 1772, 16, 281–421. [Google Scholar]
- Euler, L. Commentationes mechanicae ad theoriam corporum fluidorum pertinentes. Opera Omnia 1775, 2, 1–374. [Google Scholar]
- Poisson, S.D. Sur le mouvement des fluides elastiques dans les tuyaux cylindriques et sur la theorie des instruments à vent. Mem. Acad. Sci. Paris 1817, 2, 305–402. [Google Scholar]
- Euler, L. Testamen Novae Theoriae Musicae, Ex Typographia Academiae Scientiarum: St. Petersburg, Russia, 1818.
- Truesdell, C.A. Theory of aeial sound 1687–1788. In Euleri Opera Omnia; Series II; Academic Helvetica: Basel, Switherland, 1955; Volume 13b, pp. XIX–LXX. [Google Scholar]
- Truesdell, C.A. The rational mechanics of flexible or elastic bodies 1638–1788. In Euleri Opera Omnia; Series II; Academic Helvetica: Basel, Switherland, 1960; Volume 11b, pp. 15–405. [Google Scholar]
- Green, G. On the motion of waves in a canal of small depth and width. Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc. 1837, 6, 457–462. [Google Scholar]
- Duhamel, J.M.C. Sur les vibrations des gas dans les tuyaux cylindriques, coniques, etc. J. Math. Pures Appl. 1839, 14, 49–110. [Google Scholar]
- Pochhammer, L. Ueber die Fortpflanzungsgeschwindigkeiten der Schwingungen in einem ubegrentzen isotropen Kreiscylinder. Crelle 1876, 81, 324–336. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, E.H. On spherical radiation and vibrations in conical pipes. Phil. Mag. 1908, 15, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, G.W. The performance of conical horns. Phys. Rev. 1920, 16, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, A.G. Acoustical impedance and the theory of horns and the phonograph. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1919, 5, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoersch, V.A. Non-radial harmonic vibrations within a conical horn. Phys. Rev. 1925, 25, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, C.R.; Slepian, J. The function and design of horns of loudspeakers. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1924, 6, 275–278. [Google Scholar]
- Ballantine, S. On the propagation of sound in the general Bessel horn of infinite length. J. Frankl. Inst. 1927, 203, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, C.R. A discussion on the propagation of sound in the general Bessel horn of infinite length. J. Frankl. Inst. 1927, 203, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crandall, I.B. Theory of Vibrating Systems and Sound; Macmillan: London, UK, 1927. [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan, N.W. Loudspeakers: Theory, Performance, Testing and Design; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1934. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, H.F.; Massa, F. Applied Acoustics; P. Blakiston’s Sons & Co.,Inc.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1934. [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan, N.W. Elements of Loudspeaker Practice; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1935. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, S.; McLachlan, N.W. Sound waves of finite amplitude in an exponential horn. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1935, 6, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLachlan, N.W.; McKay, A.T. Transient oscillations in a loudspeaker horn. Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc. 1936, 32, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLachlan, N.W. The New Acoustics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1936. [Google Scholar]
- Freehafer, J.E. Acoustical impedance of an infinite hyperbolic horn. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1940, 11, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, H.F. Elements of Acoustical Engineering; Van Nostrand: New York, NY, USA, 1940. [Google Scholar]
- Parodi, M. Propagation sur une ligne electrique sans pertes dont les parameters lineiques sont des fontions exponentielles du carré de l’espace. J. Phys. 1945, 6, 331–332. [Google Scholar]
- Salmon, V. A new family of horns. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1946, 17, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, V. Generalized plane wave horn theory. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1946, 17, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, P.G. The wave equation in a medium with a variable index of refraction. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1946, 17, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawardi, O.K. Generalized solutions of Webster horn theory. J. Acoust. Soci. Am. 1949, 21, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiessen, G.J. Resonance characteristics of a finite catenoidal horn. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1950, 22, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, A.F. Exact and approximate solutions for wave propagation in acoustic horns. J. Appl. Phys. 1951, 22, 1461–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, A.F. General theory of electromagnetic horns. J. Appl. Phys. 1951, 22, 1447–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibel, E.S. On Webster’s horn equation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1955, 27, 726–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkulov, L.G. Design of ultrasonic concentrators. Sov. Phys. Acoust. 1957, 3, 246–255. [Google Scholar]
- Merkulov, L.G.; Kharitonov, A.V. Theory and analysis of sectional concentrators. Sov. Phys. Acoust. 1959, 5, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Moir, J. High-Quality Sound Reproduction; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Kinsler, L.E.; Frey, A. Fundamentals of Acoustics; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Bies, D.A. Tapering bar of uniform stress in longitudinal oscillation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1962, 34, 1567–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, E.J. Loudspeakers; Focal Press: London, UK, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Eisner, E. Design of sonic amplitude transformers for high magnification. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1963, 35, 1367–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkney, H.F.L.; Basso, G. On the Classification of Families of Shapes for Rods of Axially Varying Cross-Section in Longitudinal Vibration; National Research Council of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, R.F. Transformations in the analysis of non-uniform transmission lines. J. Frankl. Inst. 1964, 278, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyle, R.W. Duality principle for horns. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1965, 37, 1178A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisner, E. Complete solutions of Webster horn equation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1966, 41, 1126–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermelstein, P. Determination of the vocal tract shape from measured formant frequencies. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1966, 40, 1283–1294. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, H.F. Music, Physics and Engineering; Dover: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Nagarkar, B.N.; Finch, R.D. Sinusoidal horns. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1971, 50, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, M.R. Determination of the geometry of the human vocal tract by acoustic measurements. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1967, 41, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morse, P.M.; Ingard, K. Theoretical Acoustics; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Brekhovskikh, L.M. Waves in Layered Media, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, E.A.G. Acoustic horns with spatially varying density or elasticity. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1970, 50, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benade, A.H.; Jansson, E.V. On plane and spherical waves in horns with non-uniform flare. I: Theory of radiation, resonance, frequencies and mode conversion. Acustica 1974, 31, 79–98. [Google Scholar]
- Jansson, E.V.; Bernade, A.H. On plane and spherical waves in horns with non-uniform flare. II: Predictions and measurements of resonance frequencies and radiation losses. Acustica 1974, 31, 185–203. [Google Scholar]
- Molloy, C. N-parameter ducts. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1975, 7, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benade, A.H. Fundamentals of Musical Instruments; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, K.; Matsudaira, M.; Kaneko, T. Input acoustic impedance measurement of the subglottal system. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1976, 60, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, H. Unidirectional Wave Motion; North-Holland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Benade, A.H. Horns, Strings and Harmony; Doubleday: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, Y.C. Rigorous solution for sound radiation from circular ducts with hyperbolic horn or infinite plane baffle. J. Sound Vib. 1980, 69, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabelli, A. Acoustic characteristics of duct bends. J. Sound Vib. 1980, 68, 369–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kergomard, J. Ondes quasi-stationares dans les pavillons avec pertes visco-thermiques aux parois. Acustica 1981, 48, 31–43. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, M. Sound wave propagation in ducts whose walls are lined a porous layer backed by cellular cavities. J. Sound Vib. 1981, 74, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamorski, T.; Wyrzykowski, R. Approximate methods for the solution of the equation of acoustic wave propagation in horns. Arch. Acoust. 1981, 6, 237–285. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, R.E.; Storck, D.G. The Physics of Sound; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Kergomard, J. Propagation des ondes dans les lignes finies: Discussion des notons d’onde évanescente et de fréquence de coupure. Rev. Phys. Appl. 1982, 17, 307–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostrom, A. Acoustic waves in a cylindrical duct with periodically-varying cross-section. Waves Motion 1983, 5, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. Some general properties of the exact acoustic fields in horns and baffles. J. Sound Vib. 1984, 95, 177–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Santos, A.J.P. On the propagation and damping of longitudinal oscillations in tapered visco-elastic bars. J. Sound Vib. 1988, 126, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohring, W. Energy flux in duct flow. J. Sound Vib. 1971, 18, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morfey, C.L. Sound transmission and generation in ducts with flow. J. Sound Vib. 1971, 14, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohring, W. On energy, group velocity and small damping of sound waves in ducts with shear flow. J. Sound Vib. 1973, 29, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumblee, H.E.; Dean, P.D.; Wynne, G.A.; Burrin, R.H. Sound Propagation in and Radiation from Acoustically Lined Flow Ducts: A Comparison of Experiment and Theory; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Nayfeh, A.H.; Kaiser, J.E.; Telionis, D.P. Transmission of sound through annular ducts of varing cross-section. AIAA J. 1975, 13, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohring, W.; Rahman, S. The influence of perturbations of the velocity and speed of sound on the propagation of sound waves in ducts. In Proceedings of the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics,Aero-Acoustics Conference, 3rd, Palo Alto, CA, USA, 20–23 July 1976; pp. 76–493.
- Kaiser, J.E.; Nayfeh, A.H. A wave envelope technique for wave propagation in non-uniform ducts. AIAA J. 1977, 15, 433–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayfeh, A.H.; Kaiser, J.E.; Marshall, R.L.; Hurst, C.J. A comparison of experiment and theory for sound propagation in variable area ducts. J. Sound Vib. 1980, 71, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, R. Low frequency sound propagation in quasi one-dimensional flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1981, 81, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, P.O.A.L. Flow-acoustic coupling in ducts. J. Sound Vib. 1981, 77, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinai, Y.I. Two-dimensional acoustic wave propagation in elastic ducts. J. Sound Vib. 1981, 74, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, R.J.; Lester, H.C. Sound propagation through a variable area duct: Experiment and theory. AIAA J. 1982, 20, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, M.S. The attenuation of sound in a randomly lined duct. J. Sound Vib. 1983, 87, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. On the propagation of sound in nozzles of variable cross-section containing a low Mach number mean flow. Zeits. Flugwiss. Weltaraumf. 1984, 8, 97–109. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. On longitudinal acoustic propagation in convergent and divergent nozzle flows. J. Sound Vib. 1987, 117, 131–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Lau, F.J.P. On sound in an inverse sinusoidal nozzle with low Mach number mean flow. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1996, 100, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Lau, F.J.P. On the acoustics of low Mach number bulged, throated and baffled nozzles. J. Sound Vib. 1996, 196, 611–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Lau, F.J.P. On the convection of sound in inverse catenoidal nozzles. J. Sound Vib. 2001, 244, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, F.J.P.; Campos, L.M.B.C. On the effect of wall undulations on the acoustics of ducts with flow. J. Sound Vib. 2003, 270, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haurwitz, B. Zur Theorie der Wellenbewegungen in Luft und Wasser. Veroff. Geophys. Inst. Leipz. 1931, 6, 324–364. [Google Scholar]
- Kucheman, D. Storungsbewegungen in einer Gasstromung mit Grenzschit. Zeits. Ang. Math. Mech. 1938, 18, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilley, G.M. On noise from jets. In Proceedings of the AGARD Conference on Noise Mechanisms; Advisory Group for Aerospace Research and Develepment (AGARD): Paris, France, 1973. AGARD-CP-131. pp. 13.1–13.12. [Google Scholar]
- Pridmore-brown, D.C. Sound propagation in a fluid flowing through an attenuating duct. J. Fluid Mech. 1958, 4, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohring, W.; Muller, E.A.; Obermeier, F. Problems in flow acoustics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1983, 55, 707–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalke, A. On the inviscid instability of the hyperbolic tangent velocity profile. J. Fluid Mech. 1964, 19, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, M.; Rice, E. Effect of shear on duct wall impedance. J. Sound Vib. 1973, 30, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.S. The scattering of sound by a simple shear layer. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1977, A284, 287–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.S. Acoustics of a splitter plate. J. Inst. Math. Appl. 1978, 21, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.N. Propagation of sound waves through a linear shear layer. Am. Inst. Aeron. Astron. J. 1979, 17, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoyannis, S.P. Characterization of acoustic disturbance in linearly sheared flows. J. Sound Vib. 1980, 68, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoyannis, S.P.; Karamchti, K.; Galant, D.C. Acoustic resonances and sound scattering by a shear layer. AIAA J. 1980, 18, 1446–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Oliveira, J.M.G.S.; Kobayashi, M.H. On sound propagation in a linear flow. J. Sound Vib. 1999, 95, 739–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Serrâo, P.G.T.A. On the acoustics of the exponential boundary layer. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1999, A356, 2335–2378. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Kobayashi, M.H. On the reflection and transmission of sound in a thick shear. J. Fluid Mech. 2000, 420, 303–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Kobayashi, M.H. On sound propagation in a high-speed non-isothermal shear flow. Int. J. Aeroacoustics 2007, 6, 93–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Kobayashi, M.H. On sound transmission from a source outside a non-isothermal boundary-layer. AIAA J. 2010, 48, 878–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Oliveira, J.M.G.S. Acoustic modes in a duct containing a parabolic shear flow. J. Sound Vib. 2011, 330, 1166–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Kobayashi, M.H. On an acoustic oscillation energy for shear flows. Int. J. Aeroacoustics 2013, 12, 125–170. [Google Scholar]
- Swinbanks, M.A. The sound field generated by a source distribution in a long duct carrying a mean shear flow. J. Sound Vib. 1975, 40, 51–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, M.; Liu, J. The generation of sound by vorticity waves in swirling flows. J. Fluid Mech. 1977, 81, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, M.E. Unsteady, vortical and entropic distortions of potential flows round arbitrary obstacles. J. Fluid Mech. 1978, 89, 433–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobulev, V.; Atassi, H. Sound propagation in an annular duct with mean potential swirling flow. J. Sound Vib. 1996, 198, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobulev, V.; Atassi, H. Acoustic-vorticity waves in swirling flows. J. Sound Vib. 1998, 209, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.; Auriault, L. The wave modes in ducted swirling flows. J. Fluid Mech. 1998, 419, 151–175. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, A.; Peake, N. Trapped acoustic modes in aeroengine intakes with swirling flow. J. Fluid Mech. 2000, 419, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaton, C.J.; Peake, N. Acoustic scattering in a duct with mean swirling flow. J. Fluid Mech. 2005, 540, 1353–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaton, C.J.; Peake, N. Algebraic and exponential instability of inviscid swirling flow. J. Fluid Mech. 2010, 565, 279–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. On 24 forms of the accoustic wave equation in vortical flows and dissipative media. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2007, 60, 291–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Serrão, P.G.T.A. On the discrete and continuous spectrum of acoustic-vortical waves. Int. J. Aeroacoustics 2013, 12, 743–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tack, D.H.; Lambert, R.F. Influence of shear flow on sound attenuation in lined ducts. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1965, 38, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungur, P.; Plumblee, H.E. Propagation and attenuation of sound in a soft walled annular duct containing a sheared flow. NASA Spec. Publ. 1969, 207, 305–327. [Google Scholar]
- Mariano, S. Effect of wall shear layers on the sound attenuation in acoustically lined rectangular ducts. J. Sound Vib. 1971, 19, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersh, A.S.; Catton, I. Effects of shear flow on sound propagation in rectangular ducts. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1971, 50, 992–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eversman, W. Effect of boundary layer on the transmission and attenuation of sound in an acoustically treated circular duct. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1971, 39, 1372–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eversman, W.; Beckenmeyer, R.J. Transmission of sound in ducts with thin shear layers: Convergence to the uniform flow case. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1972, 52, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, P.N. Acoustic refraction by duct shear layers. J. Fluid Mech. 1971, 47, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, P.N. Acoustic refraction and attenuation in cylindrical and annular ducts. J. Sound Vib. 1972, 22, 233–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.H. Sound attenuation in acoustically lined circular ducts in the presence of uniform flow and shear flow. J. Sound. Vib. 1972, 22, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, M.K.; Chuang, S.L. Uniform asymptotic approximations for duct acoustic modes in a thin boundary-layer flow. AIAA. J. 1983, 22, 1234–1241. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, D.B. Shielding of propfan cabin noise by the fuselage boundary layer. J. Sound Vib. 1984, 92, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almgren, M. Acoustic boundary layer influence in scale model simulation of sound propagation: Theory and numerical examples. J. Sound Vib. 1986, 105, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, S.; Kakutani, T. Acoustic waves in parallel shear flows in a duct. J. Sound Vib. 1987, 113, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Legendre, C.; Sambuc, C. Acoustic of an impedance liner with shear and cross-flows. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 2014, A470, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.C. Hydrodynamic Stability; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekhar, S. Hydrodynamic and Hydromagnetic Stability; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, D.D. Stability of Fluid Motions; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1976; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Drazin, P.G.; Reid, W.H. Hydrodynamic Stability; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Sommerfeld, A. Mathematische Theorie der Diffraction. Math. Ann. 1896, 67, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, B. The Wiener-Hopf Technique; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, H.; Schwinger, J. On the radiation of sound from an unflanged circular pipe. Phys. Rev. 1948, 73, 383–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajnstein, L.A. The theory of sound waves in open tubes. Inst. Math. Sci. 1954, EM-63, 88–116. [Google Scholar]
- Ando, Y. On sound radiation from semi-infinite circular pipe of certain wall thickness. Acoustica 1970, 22, 219–225. [Google Scholar]
- Savkar, S.D. Radiation of cylindrical duct acoustic modes with flow mismatch. J. Sound Vib. 1975, 42, 363–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingard, U.; Singhal, V.K. Effect of flow on the acoustic resonances of an open-ended duct. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1975, 58, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, M.S.; Zukovski, E.E. Effect of flow on the acoustic radiation coefficient at a duct inlet. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1976, 59, 1497–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, C.J. Sound radiation from a cylindrical duct. Part 1. Ray structure of the duct modes and of the external field. J. Fluid Mech. 1994, 281, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, H.D. Effect of inlet reflections on fan noise radiation. AIAA J. 1996, 34, 1771–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snakowska, A.; Idczak, H.; Borgusz, B. Modal analysis of the acoustic field radiated from an unflanged cylindrical duct: Theory and measurement. Acustica 1996, 82, 201–206. [Google Scholar]
- Snakowska, A.; Idczak, H. Prediction of multitone sound radiation from a circular duct. Acustica 1997, 83, 955–962. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, P.; Morfey, C.L. Multimode radiation from an unflanged, semi-infinite circular duct. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1999, 105, 2590–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, C.J. Caustics in cylindrical ducts. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1999, A455, 2529–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocter, S.T. Exact and approximate directivity patterns of the sound radiated from cylindrical duct. J. Sound Vib. 1999, 227, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocter, S.T. Sound reflection into a cylindrical duct. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 2000, A456, 2707–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocter, S.T. Sound radiated from a cylindrical duct with Keller’s geometrical theory. J. Sound. Vib. 2000, 231, 1243–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, M.S. Acoustics of Fluid-Stucture Interaction; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Howe, M.S. Theory of Vortex Sound; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Munt, R.M. On the interaction of sound with a subsonic jet issuing from a semi-infinite pipe. J. Fluid. Mach. 1977, 83, 609–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rienstra, S.W. Acoustic and vibration from a semi-infinite duct in a uniform subsonic mean flow. J. Sound. Vib. 1984, 94, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. Sur la propagation du son dans les écoulements non-uniformes et non-stationaires. Revue Acoust. 1983, 67, 217–233. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Serrão, P.G.T.A. On the directivity and spectra of noise from unheated and heated jets. Int. J. Aeroacoustics 2007, 6, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. On the spectra of aerodynamic noise and aeroacoustic fatigue. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 1997, 33, 353–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. The spectral broadening of sound by turbulent shear layers. Part I: The scattering by turbulence and random interfaces. J. Fluid Mech. 1978, 89, 723–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. The spectral broadening of sound by turbulent shear layers. Part II: The application to experimental and aircraft noise. J. Fluid Mech. 1978, 89, 751–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candel, A.M.; Guédel, A.; Julienne, A. Refraction and scattering of sound in an open wind tunnel flow. In Proceedings of the International Congress on Instrumentation in Aerospace Simulation Facilities, 6th, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 22–24 September 1975; pp. 288–300.
- Candel, S.M.; Julienne, A.; Julliand, M. Etude de L’effet de masque produit par un ecran fluide. Fiche Tech. 1975. YKA869SNECMA. [Google Scholar]
- Breuhovskikh, L.M. Waves in Layered Media, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Piercy, J.E.; Embleton, T.F.W.; Sutherland, L.C. Review of sound propagation in the atmosphere. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1977, 61, 1403–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delany, M.E. Sound propagation in the atmosphere: A historial review. Proc. Inst. Acoust. 1978, 1, 32–72. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, E.; Hall, F.F., Jr. Advances in atmospheric acoustics. Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 1978, 16, 47–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Červený, V.; Popov, M.M.; Pšenčík, I. Computation of wave fields in inhomogeneous media-gaussian beam approach. Geophys. J. R. Astron. Soc. 1982, 70, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, L.C.; Gaigle, G.A. Atmospheric sound propagation. In Handbook of Acoustics; Crocker, M.J., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998; Volume 28, pp. 305–329. [Google Scholar]
- Raspet, R.; Lee, S.W.; Kuester, E.; Chang, D.C.; Richards, W.F.; Gilbert, R.; Bong, N. A fast-field program for sound propagation in a layered atmosphere above an impedance ground. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1985, 77, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, T.L.; Attenborough, K. Accurate FFT-Based Hankel transforms for predictions of outdoor sound propagation. J. Sound Vib. 1986, 109, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.M. A high-frequency approximation of sound propagation in a stratified moving atmosphere above a porous ground surface. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1994, 95, 1840–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Esperance, A.; Herzog, P.; Daigle, G.A.; Nicolas, J. Heuristic model for outdoor sound propagation based on an extension of the geometrical ray theory in the case of a linear sound field profile. Appl. Acoust. 1992, 37, 111–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspet, R.; Baird, G.; Wu, W. Normal mode solution for low frequency sound propagation in a downward refracting atmosphere above a complex impedance plane. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1992, 91, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabillet, Y.; Schroeder, H.; Daigle, G.A.; L’Esperance, A. Aplication of the Gaussian beam approach to sound propagation in the atmosphere. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1993, 93, 3105–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, H.E.; Sutherland, L.C.; Zuckerwar, A.J.; Blackstock, D.T.; Heste, D.M. Atmospheric absorption of sound: Further developments. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1995, 97, 680–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attenborough, K.; Taherzaden, S.; Bass, H.E.; Di, X.; Raspet, R.; Becker, G.R.; Güdesen, A.; Chrestman, A.; Daigle, G.A.; L’Espérance, A.; et al. Benchmark cases for outdor sound propagation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1995, 97, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostashev, V.E. Acoustics in Moving Inhomogeneous Media; Spon: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Salomons, E.M. Computational Atmospheric Acoustics; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Nertherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, D.W.; Tilmann, P.M. Experimental study of sound phase fluctuations caused by turbulent wakes. J. Acoust. Am. 1970, 47, 1310–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.M.; Kovasznay, L.S.G. Propagation of a coherent acoustic wave through a turbulent shear flow. J. Acoustic. Soc. Am. 1976, 60, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.M.; Kovasznay, L.S.G. Acoustical shadowgraph. Phys. Fluids 1976, 19, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. Effects on acoustic fatique loads of multiple reflections between a plate and a turbulent wake. Acoustica 1998, 76, 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. On the correlation of acoustic pressures induced by a turbulent wake on a nearby wall. Acta Acust. Acust. 1996, 82, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Bourgine, A.; Bonomi, B. Comparison of theory and experiment on aeroacoustic loads and deflections. J. Fluids Struct. 1999, 13, 3–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernov, L.A. Wave Propagation in a Random Medium; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Tatarski, V.I. Wave Propagation in a Turbulent Medium; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Uscinski, J.A. Wave Propagation in a Random Media; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Ishimaru, A. Wave Propagation and Scattering in Random Media; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvy, J.A. Wave Scattering from Random Rough Surfaces; American Institute of Physics: Melville, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Kolmogorov, A.N. Foundations of the Theory of Probability; Chelsea: New York, NY, USA, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor, G.K. Homogeneous Turbulence; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Hinze, J.O. Turbulence; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Monin, A.S.; Yaglom, A.M. Statistical Fluid Mechanics: Mechanics of Turbulence; Massachusetts Institute of Technology Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1971; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Townsend, A.A. Structure of Turbulent Shear Flow; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Doppler, C. Ueber das farbige Licht der Doppelsterne und einiger anderer Gestirne des Himmels. Abh. Bohm. Ges. Wiss. 1893, 2, 467. [Google Scholar]
- Lighthill, M.J. On the energy scattered by the interaction of turbulence with sound and shock waves. Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc. 1953, 44, 531–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Cunha, F.S.R.P. On the power spectrum of sound transmitted through turbulence. Int. J. Aeroacoustics 2012, 11, 475–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, A.J.; Hicks, B.B. Flux gradient relationship in a constant flux layer. Quart. J. R. Met. Soc. 1978, 96, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, K.E.; Di, X. A fast Green’s function method for one-way sound propagation in the atmosphere. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1993, 94, 2343–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomons, E.M. Improved Green’s function parabolic equation method for atmospheric sound propagation. J. Acoustic. Soc. Am. 1998, 104, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attenborough, K.; Li, K.M.; Horoshenkov, K. Prediction of Outdoor Sound Propagation; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Heimann, D.; Bakermans, M.; Defrance, J.; Kuhner, D. Vertical sound speed profiles determined from metereological measurements near the ground. Acustica 2007, 93, 228–240. [Google Scholar]
- Vecherin, S.N.; Wilson, K. Incorporating source directionality into outdoor sound propagation calculations. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 130, 3608–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wunderli, J.M.; Pierren, R.; Heutschi, K. The Swiss shooting sound calculation model son ARMS. Noise Contr. Eng. J. 2012, 60, 224–235. [Google Scholar]
- Binder, U.; Isermann, U.; Schmid, R. Influence of real atmospheric conditions on free propagation of aircraft noise. Acustica 2013, 99, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arntzen, M.; Hordijk, M.; Simons, D.G. Including atmospheric propagation effects in aircraft take-off noise modelling. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Arntzen, M.; Rizzi, S.A.; Visser, H.G.; Simons, D.G. Framework for simulating aircraft fleg-over noise through non-standart atmospheres. AIAA J. Aircr. 2014, 51, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Takanashi, T.; Yokoyama, S.; Ishii, H. Field experiment on sound propagation from an elevated directional source. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Wall, M.; Liljergren, M.; Heed, C.; Tasi, A. Angular and distance dependence of the standard deviation of maximum sound level for aircraft noise. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Yokota, T.; Makino, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Ishii, H. Experimental study of metereological and ground effects on outdoor propagation for developing aircraft noise prediction model. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Zellman, C.; Wunderli, S.M. Influence of the atmospheric stratification on the sound propagation in single flights. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Bolt, R.H. On the design of perforated facing for acoustic materials. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1947, 19, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.J.; Swearingen, M.E. Influence of scattering, atmospheric reffraction and ground effect on sound propagation through a pine forest. J. Acoustic. Soc. Am. 2007, 122, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koussa, F.; Defrance, J.; Jean, J.; Blanc-Benon, P. Acoustical effiency of a sonic crystal assisted noise barrier. Acoustica 2013, 99, 399–409. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, C.W.; Law, R.P.; Chien, S.C.; Yels, P.H. Development and sound absorption of interior adjustable acoustical panels. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Hao, Y.; Kang, J. Influence of mesoscale urban morphology on spatial noise attenuation of flyover aircraft. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 84, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamies, T.; Romeu, J.; Genescá, M.; Arcos, R. Active control of aircraft fly-over sound transmission through an open window. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 84, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probst, W. Calculation of sound propagation with highly reflective environments. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Shin, H.-C.; Taherzadeh, S.; Attenborough, K. Ground effect due to periodic and resonant roughness structures. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Simões, G.; Patrício, J.; Faria, P. Preliminary study of the acoustic behaviour concerning an innovative prototype for indoor modular partitioning. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Trimpop, M.; Mann, T. Determination of noise damping by forests. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Yamada, I. Practical method of considering the effects of terrain and building structures on sound propagation. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Miller, L.N.; Beranek, L.L.; Kryter, K.D. Airports and jet noise. Noise Control 1959, 5, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryter, K.D. Scaling human reactions to the sound from aircraft. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1959, 31, 1415–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomer, P.D.; Suzuki, Y.; Saito, F. Evaluation of loudness level weightings for assessing the annoyance of environmental noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2001, 110, 2390–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasberg, B.F.; Moore, B.C.J. A model of loudness applicable to time-varying sounds. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2002, 50, 331–342. [Google Scholar]
- Miedema, H.M.E. Relationship between exposure to multiple noise sources and noise annoyance. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2004, 116, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kryter, K.D. Acoustical model and theory for predicting the effects of environmental noise on people. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 125, 3707–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booker, P. Do people react more strongly to aircraft noise today than in the past? Appl. Acoust. 2009, 70, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, K. New insights into perception of aircraft and community noise events. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Axelsson, O.; Nilsson, M.E.; Berglund, B. A principal components model of soundscape perception. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 128, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidell, S.; Mestre, V.; Schomer, P.; Berry, B.; Gjestland, M.; Vallet, M.; Field, T. A first principles model for estimating the prevalence of annoyance with aircraft noise exposure. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 130, 791–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, S.A.; Conten, M.R.; Vog, H.; van Kamp, I. The effect of the number of aircraft noise events on sleep quality. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 84, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez, M.M.; Fernandez, L.P.S.; Guerra, S.S.; Perez, L.A.S. Aircraft take-off noise classification based on human auditor’s matched feature extraction. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 84, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlittenlacher, J.; Hashimoto, T.; Kuwano, S.; Namba, S. Overall loudness of short time-varying sounds. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Skoda, S.; Steffens, J.; Schweitzer, J.B. Contribution of single sounds to sound quality assessments of multi-source environments. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Tarabini, M.; Muschioni, G.; Asensio, C.; Bionchi, D.; Saggin, B. Unattended acoustic events classification at the vicinity of airports. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 84, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignaccolo, M. Environmental capacity: Noise pollution at Catania-Fontanarossa international airport. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2000, 6, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafa, M.H.; Osman, T.A.; Latif, I.A.A. Noise assessment and mitigation schemes for Hurghada airport. Appl. Acoust. 2007, 68, 1373–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, D.; Ekstrand, H.; Prats, X.; Gronstedt, T. An environmental assessment of air traffie speed constraints in the departure phase of flight: A case study at Gothenburg Landvelter airport, Sweden. Transp. Res. 2012, D17, 610–618. [Google Scholar]
- Asensio, C.; Recuero, M.; Pavon, I. Citizen’s perception of the efficacy of airport noise insulation programmes in Spain. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 84, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licitra, G.; Gagliardi, P.; Fredianelli, L.; Simonetti, D. Noise mitigation action plan of Pisa civil and military airport and its effects on people exposure. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 84, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkurt, N.; Sari, D.; Akdag, A.; Kutukoglu, M.; Gurarslass, A. Modelling of noise pollution and estimated human expossure around Istanbul Ataturk airport in turkey. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 482–483, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taff, D.; Neuman, P.; Lawson, S.R.; Bright, A.; Marin, L.; Gidson, A.; Archie, T. The role of messaging on acceptability of military aircraft sound in Sequoia National Park. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 84, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogiatzis, K. Assessment of environmental noise due to aircraft operation at the Athens International Airport according to the 2002/49/EC directive and the new greek national legislation. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 84, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Li, H.; Kang, J. The characteristics and control strategies of aircraft noise in China. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 84, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurocontrol: Aircraft Noise and Performance Data Base. Available online: http://www.aircraftnoisemodel.org/ (accessed on 30 January 2015).
- Method of Predicting Lateral Attenuation of Airplane Noise; SAE Air 5662; Society of Automotive Engineers: Warrendale, MI, USA, 2012.
- Acoustics-Method for Calculating Loudness Level; ISO 532–1975 (E); International Standards Organization: Geneva, Switherland, 1975.
- Acoustics-Procedure for Describing Aircraft Noise Heard on the Ground; ISO 3891–1978 (E); International Standards Organization: Geneva, Switherland, 1978.
- Acoustics-Software for the Calculation of Sound Outdoors; ISO 17534; International Standards Organization: Geneva, Switherland, 1992.
- Acoustics-Attenuation of Sound during Propagation Outdoors—Part 2: General Method of Calculation; ISO 9613-2; International Standards Organization: Geneva, Switherland, 1996.
- Acoustics-Attenuation of Sound during Propagation Outdoors. Part 1: Calculation of the Absorption of Sound by the Atmosphere; ISO 9613-1; International Standards Organization: Geneva, Switherland, 1993.
- Report on the Standard Method of Computing Noise Contours around Civil Airports, 3rd ed.; ECAC. CEAC; European Civil Aviation Conference: Paris, France, 2005; Doc. 29; Volume 2.
- Beeker, E.R.; Dingers, E.; He, B.; Fleming, G.; Roof, C.J.; Gerbi, P.J. Integrated Noise Model (INM), Version 7.0; US Department of Transportation: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Unattended Monitoring of Aircraft Sound in the Vicinity of Airports; ISO 20906; International Standards Organization: Geneva, Switherland, 2009.
- Acoustics-Noise from Shooting Ranges—Part 3: Guidelines for Sound Propagation Calculations; DIN EN ISO 17201-3; Deutsches Institut fur Normung: Berlin, Germany, 2010.
- Notario, A. Assessing all noise sources in one model. Implementation of INM and ECAC 3rd Edition in noise mapping software. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Heidmann, M. Interim Prediction Method for Fan and Compressor Source Noise; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1975; CR-198-300. [Google Scholar]
- Fink, A.R. Approximate prection of airframe noise. AIAA J. Aircr. 1976, 13, 833–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, M.R. Airframe Noise Prediction; United States Federal Aviation Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, L.V.; Burley, C.L. (Eds.) Design of the Mext Generation Noise Prediction Program: ANNOPP 22011; ANNOPP: Porland, OR, USA, 2010.
- Prats, X.; Puig, V.; Quevedo, J.; Nejjari, F. Multi-objective optimization for aircraft departure trajectories minimizing noise annoyance. Transp. Res. 2010, C18, 975–989. [Google Scholar]
- Prats, X.; Puig, V.; Quevedo, J. A multi-objective optimization strategy for designing aircraft noise abatement procedures. Case study at Gerona airport. Transp. Res. 2011, D16, 31–41. [Google Scholar]
- Diez, M.; Iemma, U. Multidisciplinary conceptual design optimization of aircraft using a sound-matching-based objective function. Eng. Optim. 2012, 44, 591–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iemma, U.; Burghignoli, L.; Contracchio, F.; Valuzzi, V. Multi-objective optimization of take-off and landing procedures: Level abatement as quality improvement for aircraft noise. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Roselund, M.; Berglind, N.; Pershagen, G.; Jarup, L.; Bluhm, G. Increased prevalence of hypertension in a population exposed to aircraft noise. Occup. Environ. Med. 2001, 58, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, C.; Roselund, M.; Peshagen, G.; Hilding, A.; Ustenson, C.G.; Bluhm, G. Aircraft noise and incidence of hypertension. Epidemology 2007, 18, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarup, L.; Babisch, W.; Houthuijs, D.; Pershagen, G.; Katsouyanni, K.; Cadum, E.; Dudley, M.-L.; Savigny, P.; Seiffert, I.; Swart, W.; et al. Hypertension and exposure to noise near airports. Environ. Heaths Perspect. 2007, 116, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralabidis, A.S.; Dimakopoulou, K.; Taglianti, F.V.; Giampaolo, M.; Borgini, A.; Dudley, M.L.; Pershagen, G.; Bluhm, G.; Houthuijs, D.; Babisch, W.; et al. Acute effects of night-time noise exposure on blood pressure in populations living near airports. Eur. Heart J. 2008, 29, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babisch, W.; van Kamp, I. Exposure-response relationship of the association between aircraft noise and the risk of hypertension. Noise Heaths 2009, 11, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enksson, C.; Blahm, G.; Hilding, A.; Osterson, C.G.; Pershagem, G. Aircraft noise and the incidence of hypertension-gender specific effects. Environ. Res. 2010, 110, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, A.; Petters, J.; Levy, J.; Melly, S.; Dominici, F. Residential exposure to aircraft noise and hospital admissions for cardiovascular diseases: Multi-airport retrospective study. Br. Med. J. 2013, 347, f5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansell, A.L.; Blangiardo, M.; Fortunato, L.; Floud, S.; de Hoogh, K.; Fecht, D.; Ghosh, R.E.; Laszlo, H.E.; Pearson, C.; Beale, L.; et al. Daytime and night-time aircraft noise and cardiovascular disease near Heathrow airport in London. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Lijeesen, M.; Straten, W.V.D.; Dekkers, J.; Elk, R.V.; Blokdijk, J. How much noise reduction at airports? Transp. Res. 2010, D15, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Mahashabde, A.; Wolfe, P.; Ashok, A.; Dorbian, C.; He, Q.; Fan, A.; Lukachko, S.; Mozdzanowska, A.; Wollersheim, C.; Barrett, S.R.H.; et al. Assessing the environmental impacts of aircraft noise and emissions. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2011, 47, 15–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netjasov, F. Contemporary measures for noise reduction at airport surroundings. Appl. Acoust. 2012, 73, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, C.; Bolin, K. Continuous judgment by category-ratio scaling of aircraft noise. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 84, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, W.G.; Hall, C.A.; Morales, V.M. The potential of future aircraft technology for noise and pollutant emissions reduction. Transp. Policy 2014, 34, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C. Combining a theoretical approach and practical considerations for establishing aircraft noise change schemes. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 84, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, B.; Pluss, S.; Thomann, G. Estimating the model-specific uncertainty of aircraft noise calculations. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 84, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrel, P.; Lu, C.H.Y. Aircraft noise social cost and change mechanisms-a case study at Amsterdam Schiphol airport. Transp. Res. 2000, D5, 305–320. [Google Scholar]
- Harding, A.; Frost, G.; Tan, E.; Tsuchiya, A.; Mason, H. The cost of hypertension-environmental noise. Noise Health 2013, 15, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, D.; Berry, B.; Knoeles, A. The economic value of aircraft noise effects. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Job, R.F.S. Community response to noise: A review of the factors influencies the relationship between noise exposure and reaction. J. Acoustic. Soc. Am. 1988, 83, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjonkman, M.; Ahrlin, U.; Rylander, R. Aircraft noise annoyance and average versus maximum noise levels. Arch. Environ. Heal. 1992, 47, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, J.M. Effect of personal and situation variables on noise annoyance in residential areas. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1993, 93, 2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjestland, T.; Liasjo, K.H.; Granoien, I.L.N. Community response to noise from short-term military aircraft exercise. J. Sound Vib. 1995, 182, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rylander, R.; Bjorkman, M. Annoyance by aircraft noise around airports. J. Sound Vib. 1997, 205, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miedema, H.M.E.; Vos, H. Demographic and attitudinal factors that modify annoyance. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1999, 105, 3336–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miedema, H.M.E.; Vos, H.; de Jong, R.G. Community reaction to aircraft noise: Time-of-day penalty and trade-off between levels of over flights. J. Acoustic. Soc. Am. 2000, 107, 3245–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, J.M.; de Jong, R.G.; Flindell, I.M.; Job, R.F.S.; Kurra, S.; Lercher, P.; Vallet, M.; Yano, T.; Guski, R.; Felscher-Suhr, U.; et al. Standardized general-purpose noise reaction questions for community noise surveys: Research and a recommendation. J. Sound Vib. 2001, 242, 641–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miedema, H.M.E.; Oudshoorn, C.O. Annoyance from transportation noise: Relationships with exposure metrics DNL and DENL and their confidence intervals. Environ. Heath Perspect. 2001, 109, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miedema, H.M.E.; Fields, J.M.; Vos, H. Effect of season and meteorological conditions on community noise annoyance. J. Acoustic Soc. Am. 2005, 117, 2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babisch, W.; Houthuijs, D.; Perhagem, G.; Cadum, E.; Katsouyanni, K.; Velomakis, M.; Dudley, M.-L.; Marohn, H.-D.; Swart, W.; Breugelmans, O.; et al. Annoyance due to aircraft noise has increased over the years-results from the Hyena studies. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooker, P. Aircraft noise annoyance estimation: UK time-pattern effects. Appl. Acoust. 2010, 71, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Screckenberg, D.; Meiss, M.; Kahl, C.; Peschel, C.; Eikmann, T. Aircraft noise and the quality of life around Frankfurt airport. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 3382–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelderblom, F.; Gjestland, T.T.; Granein, I.L.N.; Taraldsen, G. The impact of civil versus military aircraft noise on noise annoyance. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Weinandy, R.; Myck, T.; Thierbachs, R. Land-use planning at airports in Germany. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Zeisler, A. Public participation at measures to reduce noise in Germany. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Candel, S. Acoustic radiation from the end of a two-dimensional duct, effects of uniform duct and duct lining. J. Sound Vib. 1973, 28, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, W. Attenuation of sound in multi-element acoustically lined rectangular ducts in the absence of mean flow. J. Sound Vib. 1977, 52, 459–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlins, A.D. Radiation of sound from an unflanged rigid cylindrical duct with an acoustically absorbing internal surface. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1978, A361, 65–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogimoto, K.G.; Johnston, W. Modal radiation impedances for semi-infinite unflanged circular ducts including flow effects. J. Sound. Vib. 1979, 62, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namba, M.; Fukushige, K. Application of the equivalent surface source method to the acoustics of duct systems with non-uniform wall impedance. J. Sound Vib. 1980, 73, 125–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, W.; Mohring, W. Eigensolutions for liners in uniform mean flow ducts. AIAA J. 1981, 21, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, M.S. The attenuation of sound in a randomly lined duct. J. Sound Vib. 1983, 87, 83–103. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, W.R. An acoustic evaluation of circumferentially segmented duct liners. AIAA J. 1984, 22, 1229–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, C.R. Propagation and radiation of sound from flanged circular ducts with circumferentially varying wall admittances. Part I: Semi-infinite ducts. J. Sound Vib. 1984, 93, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, C.R. Propagation and radiation of sound from flanged circular ducts with circumferentially varying wall admittances. Part II finite ducts with sources. J. Sound Vib. 1984, 93, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, P.G. The propagation of sound in ducts lined with circumferentially non-uniform admittance of the form ηo + ηqexp(iqθ). J. Sound Vib. 1985, 100, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rienstra, S.W. Contributions to the theory of sound propagation in ducts with bulk-reacting lining. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1985, 77, 1681–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernyhough, M.; Evans, D.V. Comparison of a step approximation to an exact solution of acoustic scattering in a uniform-width pipe with non-uniform wall impedance. Quart. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 1996, 49, 419–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regan, B.; Eaton, J. Modelling the influence of acoustic linear non-uniformities on duct modes. J. Sound Vib. 1999, 219, 859–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Oliveira, J.M.G.S. On the optimization of non-uniformacoustic liners on anular nozzles. J. Sound Vib. 2004, 275, 557–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Oliveira, J.M.G.S. On the acoustic modes in a cylindrical nozzle with an arbitrary impedance distribution. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2004, 116, 3336–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Oliveira, J.M.G.S. On the sound generation in cylindrical flow ducts with non-uniform wall impedance. Int. J. Aeroacoustics 2014, 12, 189–227. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. An Active Noise Reducing Nozzle. U.S. Patent 6705547, 7 August 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Fuller, C.R.; Jones, J.D. Experiments on reduction of propeller-induced interior noise by active control of cylinder vibration. J. Sound Vib. 1987, 112, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorling, C.M.; Eatwell, G.P.; Hutchins, D.M.; Ross, C.F.; Sutcliffe, S.G.C. A demonstration of active noise reduction in an aircraft cabin. J. Sound Vib. 1989, 128, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullmore, A.J.; Nelson, A.P.; Elliott, S.J. Theoretical studies of active control of propeller-induced cabin noise. J. Sound Vib. 1990, 140, 191–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salikuddin, M.; Tarna, H.K.; Burrin, R.H.; Khan, M.M.S. Aplication of active noise control to model propeller noise. J. Sound Vib. 1990, 137, 9–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullmore, A.J.; Nelson, A.P.; Curtiss, A.R.D.; Elliott, S.J. Active minimization of harmonic enclosed sound fields. Part II: A computer simulation. J. Sound Vib. 1987, 117, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Snyder, S.D.; Hansen, C.H.; Fuller, C.R. Active control of far-field sound radiated by a rectangular panel: A general analysis. J. Acoustic. Soc. Am. 1992, 91, 2056–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, S.D.; Hansen, C.H. The design of systems to systems to control actively period sound transfmission into enclosed spaces. Part I: Analytical models. J. Sound Vib. 1994, 170, 433–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.R.; Nelson, P.; Elliott, S.J. Active control of the transmission of sound through a thin cylindrical shell. Part I: The minimization of vibration energy. J. Sound Vib. 1993, 167, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloxidge, G.J.; Dowling, A.P.; Hooper, N.; Langhorne, P.J. Active control of reheat buzz. AIAA J. 1988, 26, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepperd, I.C.; la Fontaine, R.F.; Cabelli, A. The influence of turbulent pressure fluctuations on an active attenator in a flow duct. J. Sound Vib. 1989, 130, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, P.A.; Elliott, S.J. Active Control of Sound; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Lau, F.J.P. On active noise reduction in a cylindrical duct with flow. Int. J. Acoust. Vib. 2009, 14, 150–162. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, S.D.; Hansen, C.H. The design of systems to systems to control actively period sound transfmission into enclosed spaces. Part II: Mechanisms and trends. J. Sound Vib. 1994, 170, 451–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.R.; Nelson, P.; Elliott, S.J. Active control of the transmission of sound through a thin cylindrical shell. Part II: The minimization of acoustic potential energy. J. Sound Vib. 1993, 167, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaporozhets, O.I.; Tokarev, V.I. Predicted flight procedures for minimum noise impact. Appl. Acoust. 1998, 55, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, J.P. The role of advanced air traffic management in reducing the impact of aircraft noise and enabling aviation growth. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2003, 9, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijnen, R.A.A.; Visser, H.G. Optimal departure trajectories with respect to sleep disturbance. Aerosp. Sci. Tech. 2003, 7, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, H.G. Generic and site-specific criteria in the optimization of noise abatement trajectories. Transp. Res. 2005, D10, 405–419. [Google Scholar]
- Girvin, R. Aircraft noise-abatement and mitigation strategies. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2009, 15, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arntzen, M.; Simons, D.G. Modelling and synthesis of aircraft flyover noise. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 84, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepworth, P.; Shilton, S.; Jones, N.; Burdett, M. Lessons form round 2 noise mapping in England. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Ishii, H.; Yokoto, T.; Makino, K.; Shinohara, N.; Sugawara, M. Measurement of noise exposure plan or distribution in aircraft approach vicinity. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Perez, L.A.S.; Fernandez, L.P.S.; Guerra, S.G.; Molina, M.M. Geo-referenced flight path estimation based on spatial-temporal information extracted from aircraft take-off noise. Digit. Signal Proc. 2014, 30, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, N.; Knowles, A.; Fisher, N.; Southgate, D. The next generation of supplementary aviation noise metrics and their use in imaging aviation noise. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Shinohara, N.; Yamada, I. Reliability of aircraft noise evaluation by measurement for comparison with prediction. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- White, K.; Arntzen, M.; Bronkhorst, A.; Meeter, M. Continuous descent Approachs (CDA) compared with regular descent produres; less annoying? In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Iversen, J.D.; Berstein, S. Trailing vortex effects on following aircraft. J. Aircr. 1974, 11, 60–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R.C. Dynamic behaviour of an aircraft encountering wake turbulence. J. Aircr. 1976, 13, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, O.J.; Nelsen, J.N.; Suhwind, R.G.; Delenius, M.F.E. Rolling moments in a trailing-vortex flow field. J. Aircr. 1978, 15, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossow, V.J.; Tinling, B.E. Research on aircraft vortex-wave interactions to determine acceptable level of wave intensity. J. Aircr. 1988, 25, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Marques, J.M.G. On wake vortex response for all combinations of five classes of aircraft. Aeron. J. 2004, 108, 295–310. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Marques, J.M.G. On aircraft response and control during a wave encouenter. In Progress in Industrial Mathematics at ECMI 2008; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 747–752. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Marques, J.M.G. On the compensation and damping of roll induced by wave vortices. Aeron. J. 2014, 118, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Bochis, V. Dynamics of an aircraft in a windshear of arbitrary direction. AIAA J. Guid. 1971, 7, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, W.; Cosby, B.; Camp, D.W. Flight through thunderstom outflow. AIAA J. Aircr. 1979, 16, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. On the influence of atmospheric disturbances on aircraft aerodynamics. Aeron. J. 1984, 88, 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. On aircraft flight performance in a perturbed atmosphere. Aeron. J. 1986, 90, 301–312. [Google Scholar]
- Ashley, H. Engineering Analysis of Flight Vehicles; Addison-Wesley: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Torenbeek, E. Synthesis of Subsonic Airplane Design; Martinus Nijhoff: Amsterdam, The Nertherlands, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Huenecke, K. Modern Combat Aircraft Design; Airlife Publishing Limited: London, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. Aircraft Design Integration and Affordability; Agardograph AGARD-R-826; AGARD: Paris, France, 1998; p. 103. [Google Scholar]
- Whitford, R. Design for Air Combat; Jane’s: London, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Roskam, J. Airplane Design, 2nd ed.; DAR Corporation: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2002; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Fielding, J.P. Aircraft Design; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.D. Aircraft Performance and Design; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Environmentally Responsible Aircraft (ERA), National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), USA. Available online: http://www.aeronautics.nasa.gov/isrp/era/ (accessed on 16 January 2015).
- Horizon 2020 (H2020). Transportation Research, European Union. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/programmes/horizon2020/en/h2020-sections (accessed on 16 January 2015).
- Advisory Council for Aviation Research in Europe (ACARE). Available online: http://www.acare4europe.com/ (accessed on 16 January 2015).
- Strategic Research and Innovation Agenda (SRIA). Available online: http://www.acare4europe.org/sites/acare4europe.org/files/attachment/SRIA%20Volume%201.pdf (accessed on 16 January 2015).
- Clean Sky Joint Undertaking. Available online: http://www.cleansky.eu/ (accessed on 16 January 2015).
- Single European Sky ATM Research (SESAR) Joint Undertaking. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/research/transport/pdf/morten_jensen_sesar_en.pdf (accessed on 16 January 2015).
- Sixth Framework Research Programme (FP6), European Union. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/research/fp6/pdf/fp6-in-brief_en.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- Schwela, D.H.; Finegold, L.S.; Gjestland, T. Progress on environmental noise policies from 2008–2013 in Asia and the world. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Bauer, M.; Collin, D.; Iemma, U.; Janssens, K.; Marki, F.; Miiller, O. Cosma-A European approach to aircraft noise annoyance research. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Bauer, M.; Buscher, A.; Pott-Pollensker, M. AfloNext-A European contribution to airframe noise control. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Oosten, N.V.; Collin, D. NINHA-Noise Impact from aircraft with novel engine configurations in mid-to high-altitude operations. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Kors, E. Optimization for low Environmental Noise Impact Aircraft-OPENAIR. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Collin, D. European aviation noise research network. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014.
- Study of Noise and Aerodynamics of Advanced Propellers (SNAAP). Available online: http://cordis.europa.eu/project/rcn/5577_en.html (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- Advanced Propulsion Integration of Aerodynamics and Noise (APIAN). Available online: http://www.2020-horizon.com/APIAN-Advanced-propulsion-integration-aerodynamics-and-noise%28APIAN%29-s17074.html (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- Helicopter Rotor Noise Reduction (HELINOISE). Available online: http://cordis.europa.eu/project/rcn/17191_en.html (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- Helicopter Aerodynamics and Aeroacoustics (HELISHAPE). Available online: http://cordis.europa.eu/project/rcn/5881_en.html (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- Advanced Study of Active Noise Control in Aircraft (ASANCA). Available online: http://cordis.europa.eu/project/rcn/17202_en.html (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- Active Noise and Vibration Reduction in Aircraft (ASANCA II). Available online: http://www.bth.se/fou/forskinfo.nsf/0/4c246ae6eb7bf99dc12569f10037a543/$FILE/PHDthesis_sjo.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- Jet Enhaust Aerodynamics and Noise (JEAN). Available online: http://cordis.europa.eu/project/rcn/54241_en.html (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- Environmental Noise Associated with Turbulent Boundary Layer Excitation (ENABLE). Available online: http://www.2020-horizon.com/ENABLE-Environmental-noise-associated-with-turbulent-boudary-layer-excitation%28ENABLE%29-s16448.html (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- Acoustic Fatigue of Composite Aircraft Structures (ACOUFAT). Available online: http://cordis.europa.eu/project/rcn/17199_en.html (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- Applications of Multi-Agent Knowledge-Based Systems (AMAKS). Available online: http://www.iaeng.org/publication/IMECS2010/IMECS2010_pp59-64.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- Assessment of Wave Vortex Safety (S-WAKE). Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/research/growth/aeronautics-days/pdf/posters/s-swake.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- New Empenage for Aircraft (NEFA). Available online: http://cordis.europa.eu/project/rcn/68738_en.html (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- Research on Silent Aircraft Concepts (ROSAS). Available online: http://cordis.europa.eu/project/rcn/61169_en.html (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- Very Efficient Large Aircraft (VELA). Available online: http://www.dlr.de/as/en/Desktopdefault.aspx/tabid-188/379_read-636/ (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- Sound Engineering for Aircraft (SEFA). Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/research/transport/projects/items/sefa_en.htm (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- Community Oriented Solutions to Minimize Aircraft Noise Annoyance (COSMA). Available online: http://www.fp7-cosma.eu/ (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- Significantly Lower Community Exposure to Noise (Reduction) (SILENCER). Available online: http://www.xnoise.eu/index.php?id=85 (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- Integration of Technologies in Support of a Passenger and Environmentally Friendly Helicopter (FRIENDCOPTER). Available online: http://cordis.europa.eu/project/rcn/72786_en.html (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- New Aircraft Concepts Research (NACRE). Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/research/transport/projects/items/nacre_en.htm (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- Aircraft External Noise Network 2002–2005 (X-NOISE). Available online: http://www.aerodays2006.org/sessions/A_Sessions/A3/A31.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2015).
- Aircraft Noise Network 2005–2007 (X2-NOISE). Available online: http://cordis.europa.eu/project/rcn/65130_en.html (accessed on 21 January 2015).
- Aircraft Noise Network 2008–2010 (X3-Noise). Available online: http://lema.epfl.ch/index.php/research/eu/37-fp7/439-x3-noise (accessed on 21 January 2015).
- Aircraft Noise Network Evolution 2011–2015 (X-Noise EV). Available online: http://cordis.europa.eu/result/rcn/149346_en.html (accessed on 21 January 2015).
- Silent Aircraft Initiative (SIA): MIT Joint Project. Available online: http://silentaircraft.org/ (accessed on 21 January 2015).
- Gallman, J.; Kroo, I. Structural optimization for joined wing synthesis. AIAA J. Aircr. 1994, 33, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroo, I.M. Novel aircraft concepts for the XXIst contury. In NATO Course; Instituto Superior Tecnico: Lisbon, Portugal, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Marques, J.M.G. On the minimization of cruise drag due to pitch trim in a flying-wing configuration. In Proceedings of the 2nd NACRE Workshop, Greenwich University, Greenwich, UK, 8–10 July 2008.
- Fidkowski, K.; Kroo, I.M.; Willcox, K. Multifidelity optimization methodology for incorporating advanced technologies in conceptual design. In Proceedings of the 12th AIAA/ISSMO Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization Conference, Victoria, BC, Canada, 10 September 2008.
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Marques, J.M.G. On the minimization of trim drag for aircraft with multiple control surfaces. In Proceedings of the 16th conference of the European Consortium for Mathematics in Industry, Wuppertal, Germany, 26–30 July 2010.
- McMasters, J.; Kroo, I.M. Advanced Configurations for very Large Transport Aeroplanes; AIAA 98-0439; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA): Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wakayama, S.; Kroo, I. The Challenge and Promise of Blended Wing-Body Optimization; AIAA 98-4736; Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Beniawski, S.; Kroo, I.M.; Walpert, D. Flight control with distributed effectors. In Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 15–17 August 2005.
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Marques, J.M.G. On lateral-longitudinal coupling and unsteady aerodynamics for airplane stability and control. In Proceedings of the 1st NACRE Workshop, Technishe Universitat Munchen, Garching, Germany, 6–8 October 2006.
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Marques, J.M.G. On the maximization of control power in low-speed flight for a flying wing configuration. In Proceedings of the 27th International Congress of Aeronautical Sciences, Nice, France, 19–24 September 2010.
- Kroo, I.M. Drag due to lift: Concepts for prediction and reduction. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2000, 33, 587–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. Acoustic fatigue of aircraft structures. In Proceedings of Noise-93, St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 10–12 May 1993; Volume 4, pp. 16–29.
- Kroo, I.M. Non-planar wing concepts for increased aircraft efficiency. In Proceedings of the VKI Lecture Series, Rhode St. Genese, Belgium, 6–10 June 2005.
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Marta, A.C. Analytical flutter frequencies of a tapered wing. In Proceedings of the 28th International Congress of Aeronautical Sciences, Brisbane, Australia, 23–28 September 2012.
- Antoine, I.; Kroo, I.M. Optimizing aircraft and operations for minimum noise. In Proceedings of the AIAA’s Aircraft Technology, Integration, and Operations (ATIO) 2002 Technical, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1–3 October 2002.
- Campos, L.M.B.C. Aeroacoustics modelling of aircraft noise. In Proceedings of Noise-93, St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 10–12 May 1993; Volume 4, pp. 2–15.
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Lau, F.J.P. On the shielding of engine noise by an aircraft wing. In Proceedings of the 10th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference, Manchester, UK, 10–12 May 2004.
- Campos, L.M.B.C. On three modelling methods for acoustic shielding and installation effects. In Proceedings of the 1st NACRE Workshop, Technische Universitat Munchen, Garching, Germany, 6–8 October 2006.
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Lau, F.J.P. Shielding of engine noise by aircraft structure. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2010, Lisbon, Portugal, 13–16 June 2010.
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Gil, P.J.S. On noise shielding by conical surfaces. In Proceedings of the 2nd NACRE Workshop, Greenwich University, London, UK, 8–10 July 2008.
- Antoine, I.; Kroo, I.M. Aircraft optimization for minimal environmental impact. AIAA J. Aircr. 2004, 41, 796–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, G.C.; Kroo, I.M. Multi-objective aircraft optimization for minimum cost and emissions over specific route networks. In Proceedings of the 26th Congress of International Council of the Aeronautical Sciences, Anchorage, AK, USA, 14–19 September 2008.
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Fonseca, A.A. Building effects on airport noise. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2010, Lisbon, Portugal, 13–16 June 2010.
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Oliveira, J.M.G. Ground effects on helicopter noise. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2010, Lisbon, Portugal, 13–16 June 2010.
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Serrão, P.G.T.A. Outdoor to indoor transmission of aircraft noise. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2010, Lisbon, Portugal, 13–16 June 2010.
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Fonseca, A.A.; Oliveira, J.M.C. Effect of buildings and rough ground on aircraft noise. In Proceedings of the 17th ASC-CEAS/X-NOISE EV Workshop, Seville, Spain, 24–25 September 2013.
- Filippone, A. Aircraft noise prediction. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2014, 68, 27–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingard, K.U. The influence of fluid motion past a plane boundary on sound reflection, absorption and transmission. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1959, 31, 1035–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, M.K. On the acoustic boundary condition in the presence of flow. J. Sound Vib. 1980, 71, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambly, E. Myers boundary condition. In Proceedings of the 16th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference, Stockholm, Sweden, 7–9 June 2010.
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campos, L.M.B.C. On Physical Aeroacoustics with Some Implications for Low-Noise Aircraft Design and Airport Operations. Aerospace 2015, 2, 17-90. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace2010017
Campos LMBC. On Physical Aeroacoustics with Some Implications for Low-Noise Aircraft Design and Airport Operations. Aerospace. 2015; 2(1):17-90. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace2010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampos, Luís M. B. C. 2015. "On Physical Aeroacoustics with Some Implications for Low-Noise Aircraft Design and Airport Operations" Aerospace 2, no. 1: 17-90. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace2010017
APA StyleCampos, L. M. B. C. (2015). On Physical Aeroacoustics with Some Implications for Low-Noise Aircraft Design and Airport Operations. Aerospace, 2(1), 17-90. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace2010017