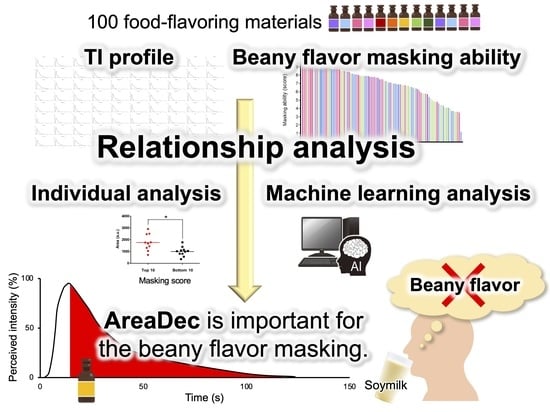
Time-Series Sensory Analysis Provided Important TI Parameters for Masking the Beany Flavor of Soymilk
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Food-Flavoring Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation for Sensory Evaluation
2.3. Panelists and Training
2.4. TI Analysis of the 100 Food-Flavoring Materials
2.5. Evaluation of the Masking Ability of the Food-Flavoring Materials against the Beany Flavor of Soymilk
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. In Silico Analysis of the Time-Series Sensory Data for the Classification of the Food-Flavoring Materials
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. TI Analysis of the 100 Food-Flavoring Materials
3.2. Analysis of the Relationship between TI Profile and Beany Flavor Masking Ability of the Food-Flavoring Materials
3.3. Classification of the Food-Flavoring Materials by Unsupervised Machine Learning Based on Time-Series Sensory Data
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Quan, D. An Overview of Taste-Masking Technologies: Approaches, Application, and Assessment Methods. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tuccillo, F.; Lampi, A.M.; Knaapila, A.; Pulkkinen, M.; Kariluoto, S.; Coda, R.; Edelmann, M.; Jouppila, K.; Sandell, M.; et al. Flavor challenges in extruded plant-based meat alternatives: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 2898–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, J. The Flavor of Plant-Based Meat Analogues. Cereal Foods World 2020, 65, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Burseg, K.; de Jong, C. Application of the Olfactoscan method to study the ability of saturated aldehydes in masking the odor of methional. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9086–9090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ni, H.; Qiu, X.J.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.Z.; Li, L.J.; Jiang, Z.D.; Li, Q.B.; Chen, F.; Zheng, F.P. Suppressive Interaction Approach for Masking Stale Note of Instant Ripened Pu-Erh Tea Products. Molecules 2019, 24, 4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montero-Fernandez, I.; Marcia-Fuentes, J.A.; Cascos, G.; Saravia-Maldonado, S.A.; Lozano, J.; Martin-Vertedor, D. Masking Effect of Cassia grandis Sensory Defect with Flavoured Stuffed Olives. Foods 2022, 11, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentini, M.; Kinchla, A.J.; Nolden, A.A. Role of Sensory Evaluation in Consumer Acceptance of Plant-Based Meat Analogs and Meat Extenders: A Scoping Review. Foods 2020, 9, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempere, S.; Schaaper, M.H.; Cuzange, E.; de Lescar, R.; de Revel, G.; Sicard, G. The olfactory masking effect of ethylphenols: Characterization and elucidation of its origin. Food Qual. Prefer. 2016, 50, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.; Correia, E.; Dinis, L.T.; Vilela, A. An Overview of Sensory Characterization Techniques: From Classical Descriptive Analysis to the Emergence of Novel Profiling Methods. Foods 2022, 11, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visalli, M.; Galmarini, M.V. Multi-attribute temporal descriptive methods in sensory analysis applied in food science: Protocol for a scoping review. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawless, H.T.; Heymann, H. Time-Intensity Methods. In Sensory Evaluation of Food: Principles and Practices; Lawless, H.T., Heymann, H., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1999; pp. 265–300. [Google Scholar]
- Cliff, M.; Heymann, H. Development and use of time-intensity methodology for sensory evaluation: A review. Food Res. Int. 1993, 26, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijksterhuis, G.B.; Piggott, J.R. Dynamic methods of sensory analysis. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2001, 11, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolini, H.M.A.; Lima, R.S.; Freitas, R.L.; Medeiros, A.C. Preference Drivers for Blackberry Nectar (Rubus spp., Rosaceae) with Different Sweeteners. Foods 2023, 12, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, A.; Tavares, E.; Bolini, H.M.A. Descriptive Sensory Profile and Consumer Study Impact of Different Nutritive and Non-Nutritive Sweeteners on the Descriptive, Temporal Profile, and Consumer Acceptance in a Peach Juice Matrix. Foods 2022, 11, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodstein, E.S.; Bohlscheid, J.C.; Evans, M.; Ross, C.F. Perception of flavor finish in model white wine: A time-intensity study. Food Qual. Prefer. 2014, 36, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Araújo, L.; Parker, D.; Woods, E. Temporal Sensory Methods for Beer. J. Sens. Stud. 2013, 28, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Medeiros, A.C.; Tavares Filho, E.R.; Bolini, H.M.A. Temporal profile of low calorie lactose-free ice cream chocolate flavor: Temporal dominance sensation and multiple time-intensity analysis. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 3164–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, R.; Atchley, A.; Ali, S.; Shingleton, J.; Luckett, C.R. Retronasal Habituation: Characterization and Impact on Flavor Perception Using Time-Intensity. Chemosens. Percept. 2018, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaoka, K.; Vallet, N.; Giampaoli, P.; Heyd, B.; MacLeod, P. Possible influence of breathing on detection frequency and intensity rating in gas chromatography-olfactometry. Food Chem. 2001, 72, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pionnier, E.; Chabanet, C.; Mioche, L.; Le Quere, J.L.; Salles, C. 1. In Vivo Aroma Release during Eating of a Model Cheese: Relationships with Oral Parameters. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippe, E.; Seuvre, A.M.; Colas, B.; Langendorff, V.; Schippa, C.; Voilley, A. Behavior of flavor compounds in model food systems: A thermodynamic study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 1393–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Kang, D.; Zhang, W.; Lorenzo, J.M. Recent advantage of interactions of protein-flavor in foods: Perspective of theoretical models, protein properties and extrinsic factors. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammari, A.; Schroen, K. Flavor Retention and Release from Beverages: A Kinetic and Thermodynamic Perspective. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9869–9881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffo, R. Persistence of aroma compounds in human breath after consuming an aqueous model aroma mixture. Food Chem. 2005, 89, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Hikida, A.; Kawai, S.; Lan, V.T.; Motoyama, T.; Kitagawa, S.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Kato, R.; Kawarasaki, Y. Analysing the substrate multispecificity of a proton-coupled oligopeptide transporter using a dipeptide library. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terada, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Matsuyama, M.; Fujitani, M.; Shibuya, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kato, R.; Ito, K. Collection of Data Variation Using a High-Throughput Image-Based Assay Platform Facilitates Data-Driven Understanding of TRPA1 Agonist Diversity. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.R.; Gawel, R.; Francis, I.L.; Waters, E.J. The influence of interactions between major white wine components on the aroma, flavour and texture of model white wine. Food Qual. Prefer. 2008, 19, 596–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesme, H.; Rannou, C.; Famelart, M.-H.; Bouhallab, S.; Prost, C. Yogurts enriched with milk proteins: Texture properties, aroma release and sensory perception. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 98, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premjit, Y.; Pandhi, S.; Kumar, A.; Rai, D.C.; Duary, R.K.; Mahato, D.K. Current trends in flavor encapsulation: A comprehensive review of emerging encapsulation techniques, flavour release, and mathematical modelling. Food Res. Int. 2022, 151, 110879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifullah, M.; Shishir, M.R.I.; Ferdowsi, R.; Tanver Rahman, M.R.; Van Vuong, Q. Micro and nano encapsulation, retention and controlled release of flavor and aroma compounds: A critical review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 230–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.G.; Carpinteiro, D.A.; Thomazini, M.; Rocha-Selmi, G.A.; da Cruz, A.G.; Rodrigues, C.E.C.; Favaro-Trindade, C.S. Coencapsulation of xylitol and menthol by double emulsion followed by complex coacervation and microcapsule application in chewing gum. Food Res. Int. 2014, 66, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Material Type | Notation | Main Solvents | Chemical Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Essence type | e | Alcohols | Water-soluble/High volatility |
| Oil type | o | Glycerol fatty acid esters/Vegetable oils | Oil-soluble/Low volatility |
| Flavor type | f | Propylene glycol/Glycerin | Intermediate polarity/High volatility |
| Ingredient | g |
|---|---|
| Almond milk | 34 |
| Soy protein RT-1 | 3.0 |
| Dextrin | 3.0 |
| Water | 60 |
| Top | AreaInc | Area (a.u.) | DurInc | Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Orange essential_o | 1016 | Satsuma mandarin essential_o | 21.3 |
| 2 | Satsuma mandarin essential_o | 919 | Yuzu essential_o | 18.3 |
| 3 | Coconut_o | 776 | Coconut_o | 18.0 |
| 4 | Orange_o | 765 | Orange essential_o | 18.0 |
| 5 | Cherry_o | 735 | Orange_o | 17.0 |
| 6 | Yuzu essential_o | 644 | Apple_o | 16.3 |
| 7 | Rose_o | 597 | Banana_o | 15.3 |
| 8 | Mango_o | 595 | Orange_e | 14.0 |
| 9 | Maple_f | 563 | Cherry_o | 13.7 |
| 10 | Apple_o | 558 | Rose_o | 13.3 |
| Bottom | AreaDec | Area (a.u.) | DurDec | Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | White peach_e | 352 | Pineapple_e | 18.7 |
| 2 | Pineapple_e | 380 | White peach_e | 19.7 |
| 3 | Honey_e | 414 | Cheese_e | 20.0 |
| 4 | Caramel_e | 484 | Caramel_e | 25.7 |
| 5 | White peach_f | 515 | Cranberry_e | 25.7 |
| 6 | Honey_f | 539 | Orange_e | 31.0 |
| 7 | Cheese_e | 552 | Pineapple_f | 31.3 |
| 8 | Raspberry_o | 554 | Cinnamon_e | 31.7 |
| 9 | Brown sugar_f | 565 | Honey_e | 33.0 |
| 10 | Orange_e | 594 | White peach_f | 33.3 |
| Top | Material Name | Masking Score | Bottom | Material Name | Masking Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cinnamon_o | 9.9 | 1 | Cocoa_e | 1.2 |
| 2 | Peppermint_o | 9.9 | 2 | Raspberry_o | 3.5 |
| 3 | Orange essential_o | 9.6 | 3 | Apple_o | 3.6 |
| 4 | Herb_f | 9.5 | 4 | Kabosu_f | 3.6 |
| 5 | Pineapple_o | 9.3 | 5 | Sudachi_f | 3.6 |
| 6 | Rose_o | 9.3 | 6 | White peach_e | 3.7 |
| 7 | Yuzu essential_o | 9.3 | 7 | Lemon_e | 3.7 |
| 8 | Coffee_f | 9.2 | 8 | Lemon_f | 4.0 |
| 9 | Rose_e | 9.2 | 9 | Apple_e | 4.1 |
| 10 | Cheese_o | 9.1 | 10 | Kyoho grape_f | 4.1 |
| 11 | Framboise_f | 4.1 |
| Material Name | Masking Score |
|---|---|
| Satsuma mandarin essential_o | 8.4 |
| Rose_o | 9.3 |
| Cherry_o | 9.0 |
| Maple_f | 7.0 |
| Herb_f | 9.5 |
| Plum_f | 8.8 |
| Custard_f | 4.8 |
| Banana_e | 9.0 |
| Average | 8.2 |
| Imax | Tstart | DurInc | DurDec | SIMInc | SIMDec | AreaInc | AreaDec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.015 | −6.00 × 10−5 | 0.0015 | 0.026 | 0 | 0 | 0.167 | 0.985 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masuda, M.; Terada, Y.; Tsuji, R.; Nakano, S.; Ito, K. Time-Series Sensory Analysis Provided Important TI Parameters for Masking the Beany Flavor of Soymilk. Foods 2023, 12, 2752. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142752
Masuda M, Terada Y, Tsuji R, Nakano S, Ito K. Time-Series Sensory Analysis Provided Important TI Parameters for Masking the Beany Flavor of Soymilk. Foods. 2023; 12(14):2752. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142752
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasuda, Miyu, Yuko Terada, Ryoki Tsuji, Shogo Nakano, and Keisuke Ito. 2023. "Time-Series Sensory Analysis Provided Important TI Parameters for Masking the Beany Flavor of Soymilk" Foods 12, no. 14: 2752. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142752