Cysteine Proteinase C1A Paralog Profiles Correspond with Phylogenetic Lineages of Pathogenic Piroplasmids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
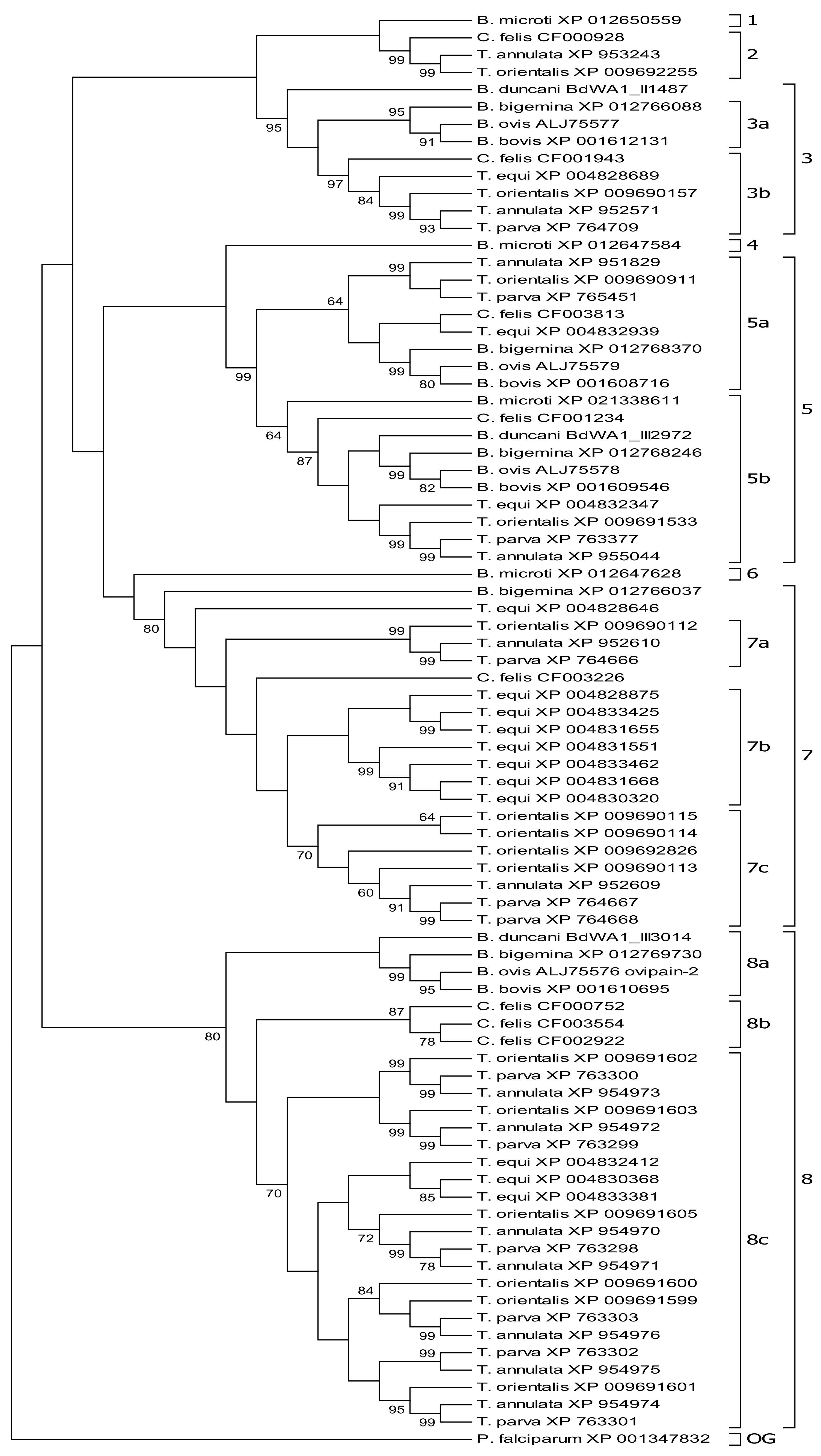
3.1. Molecular Phylogeny Allows Subgrouping of Piroplasmid C1A Cysteine Proteinases
3.2. Molecular Phylogeny Provides Evidence for Independent Duplication Events of C1A-Cp in Different Piroplasmid Lineages
3.3. C1A Cysteine Proteinase Profiles Characterize Piroplasmid Lineages
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodriguez, A.E.; Schnittger, L.; Tomazic, M.L.; Florin-Christensen, M. Current and prospective tools for the control of cattle-infecting Babesia parasites. In Protozoa: Biology, Classification and Role in Disease; Castillo, V., Harris, R., Eds.; Nova Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–44. ISBN 9781624170720. [Google Scholar]
- Schnittger, L.; Rodriguez, A.E.; Florin-Christensen, M.; Morrison, D.A. Babesia: A world emerging. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 1788–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florin-Christensen, M.; Suarez, C.E.; Rodriguez, A.E.; Flores, D.A.; Schnittger, L. Vaccines against bovine babesiosis: Where we are now and possible roads ahead. Parasitology 2014, 28, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, G.; Friedhoff, K. Lichtmikroskopische Untersuchungen ueber die Entwicklung yon Babesia ovis (Piroplasmidea) in Rhipicephalus bursa (Ixodoidea). Z. Parasitenk 1971, 35, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bock, R.; Jackson, L.; De Vos, A.; Jorgensen, W. Babesiosis of cattle. Parasitology 2004, 129, S247–S269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mans, B.J.; Pienaar, R.; Latif, A.A. A Review of Theileria diagnostics and epidemiology. Int. J. Parasitol. 2014, 4, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganzinelli, S.; Rodriguez, A.; Schnittger, L.; Florin-Christensen, M. Babesia in Domestic Ruminants. In Parasitic Protozoa of Farm Animals and Pets, 1st ed.; Florin-Christensen, M., Schnittger, L., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; ISBN 3319701312. [Google Scholar]
- Kiara, H.; Steinaa, L.; Vishvanath, N.; Svitek, N. Theileria in ruminants. In Parasitic Protozoa of Farm Animals and Pets, 1st ed.; Florin-Christensen, M., Schnittger, L., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; ISBN 3319701312. [Google Scholar]
- Mehlhorn, H.; Schein, E. Redescription of Babesia equi Laveran, 1901 as Theileria equi Mehlhorn, Schein 1998. Parasitol. Res. 1998, 84, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nietfeld, J.C.; Pollock, C. Fatal cytauxzoonosis in a free-ranging Bobcat (Lynx rufus). J. Wildl. Dis. 2002, 38, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.L.; Li, T.T.; Liu, G.H.; Zhu, X.Q.; Yao, C. Two tales of Cytauxzoon felis infections in domestic cats. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 861–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueti, M.W.; Knowles, D.P. Equine Piroplasmids. In Parasitic Protozoa of Farm Animals and Pets, 1st ed.; Florin-Christensen, M., Schnittger, L., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; ISBN 3319701312. [Google Scholar]
- Dammin, G.J.; Spielman, A. The rising incidence of clinical Babesia microti infection. Hum. Pathol. 1981, 12, 1979–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, P.A.; Kjemtrup, A.M.; Carreno, R.A.; Thomford, J.; Wainwright, K.; Eberhard, M.; Quick, R.; Telford, S.R.; Herwaldt, B.L. Description of Babesia duncani sp. nov. (Apicomplexa: Babesiidae) from humans and its differentiation from other piroplasms. Int. J. Parasitol. 2006, 36, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabsley, M.J.; Shock, B.C. Natural history of zoonotic Babesia: Role of wildlife reservoirs. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2013, 2, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baneth, G.; Florin-Christensen, M.; Cardoso, L.; Schnittger, L. Reclassification of Theileria annae as Babesia vulpes sp. nov. Parasite Vector 2015, 8, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehlhorn, H.; Schein, E.; Ahmed, J.S. Theileria. In Parasitic Protozoa; Kreier, J.P., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1994; pp. 217–304. ISBN 0123960339. [Google Scholar]
- Reichard, M.V.; Van Den Bussche, R.A.; Meinkoth, J.H.; Hoover, J.P.; Kocan, A.A. A New species of Cytauxzoon from Pallas’ Cats caught in Mongolia and comments on the systematics and taxonomy of piroplasmids. J. Parasitol. 2005, 91, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uilenberg, G. Babesia-a historical overview. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 138, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lack, J.B.; Reichard, M.V.; Van Den Bussche, R.A. Phylogeny and evolution of the piroplasmida as inferred from 18S rRNA sequences. Int. J. Parasitol. 2012, 42, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kappmeyer, L.S.; Thiagarajan, M.; Herndon, D.R.; Ramsay, J.D.; Caler, E.; Djikeng, A.; Gillespie, J.J.; Lau, A.O.; Roalson, E.H.; Silva, J.C.; et al. Comparative genomic analysis and phylogenetic position of Theileria equi. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreeg, M.E.; Marr, H.S.; Tarigo, J.L.; Cohn, L.A.; Bird, D.M.; Scholl, E.H.; Levy, M.G.; Wiegmann, B.M.; Birkenheuer, A.J. Mitochondrial genome sequences and structures aid in the resolution of piroplasmida phylogeny. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paparini, A.; Macgregor, J.; Ryan, U.M.; Irwin, P.J. First molecular characterization of Theileria ornithorhynchi Mackerras, 1959: Yet another challenge to the systematics of the piroplasms. Protist 2015, 166, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabsley, M.J.; Vanstreels, R.E.T.; Shock, B.C.; Purdee, M.; Horne, E.C.; Peirce, M.A.; Parsons, N.J. Molecular characterization of Babesia peircei and Babesia ugwidiensis provides insight into the evolution and host specificity of avian piroplasmids. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2017, 24, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemba, M.; Goldberg, D.E. Biological roles of proteases in parasitic protozoa. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002, 71, 275–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K. Role of proteases in host cell invasion by Toxoplasma gondii and other Apicomplexa. Acta Trop. 2004, 91, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowman, A.F.; Crabb, B.S. Invasion of red blood cells by malaria parasites. Cell 2006, 124, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanspal, M.; Dua, M.; Takakuwa, Y.; Chishti, A.H.; Mizuno, A. Plasmodium falciparum cysteine protease falcipain-2 cleaves erythrocyte membrane skeletal proteins at late dtages of parasite fevelopment. Blood 2002, 100, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sijwali, P.S.; Rosenthal, P.J. Gene disruption confirms a critical role for the cysteine protease falcipain-2 in hemoglobin hydrolysis by Plasmodium falciparum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4384–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Child, M.A.; Bogyo, M. Proteases as regulators of pathogenesis: Examples from the Apicomplexa. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Proteins Proteom. 2012, 1824, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesplet, M.; Echaide, I.; Dominguez, M.; Mosqueda, J.J.; Suarez, C.E.; Schnittger, L.; Florin-Christensen, M. Bovipain-2, the falcipain-2 ortholog, is expressed in intraerythrocytic stages of the tick-transmitted hemoparasite Babesia bovis. Parasite Vector 2010, 3, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carletti, T.; Barreto, C.; Mesplet, M.; Mira, A.; Weir, W.; Shiels, B.; Gonzalez Oliva, A.; Schnittger, L.; Florin-Christensen, M. Characterization of a papain-like cysteine protease essential for the survival of Babesia ovis merozoites. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, T.M.; Gonçalves, L.M.; Capela, R.; Moreira, R.; do Rosário, V.E.; Domingos, A. Effect of synthesized inhibitors on babesipain-1, a new cysteine protease from the bovine piroplasm Babesia bigemina. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2010, 57, 68–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, T.M.; do Rosário, V.E.; Domingos, A. Expression and characterization of the Babesia bigemina cysteine protease BbiCPL1. Acta Trop. 2012, 121, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajid, M.; Blackman, M.J.; Doyle, P.; He, C.; Land, K.M.; Lobo, C.; Mackey, Z.; Ndao, M.; Reed, S.L.; Shiels, B.; et al. Proteases of Parasitic Protozoa–Current Status and Validation. In Antiparasitic and Antibacterial Drug Discovery: From Molecular Targets to Drug Candidates, 1st ed.; Selzer, P.M., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2009; pp. 190–197. ISBN 3527323279. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, T.M.; do Rosário, V.E.; Domingos, A. Identification of papain-like cysteine proteases from the bovine piroplasm Babesia bigemina and evolutionary relationship of piroplasms C1 family of cysteine proteases. Exp. Parasitol. 2011, 127, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnittger, L.; Mesplet, M.; Florin-Christensen, M. Proteinases of piroplasmid bovine pathogens: Comparative genomic analysis of Babesia bovis and Theileria annulata. In Proceedings of the International Conference of International Congress of Parasitology (ICOPA), Mexico City, Mexico, 10–15 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Poklepovich, T.J.; Mesplet, M.; Florin-Christensen, M.; Schnittger, L. Comparative degradome analysis of the bovine piroplasmid pathogens Babesia bovis and Theileria annulata. 2018; (unpublished data). [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, A.P.; Otto, T.D.; Darby, A.; Ramaprasad, A.; Xia, D.; Echaide, I.E.; Farber, M.; Gahlot, S.; Gamble, J.; Gupta, D.; et al. The evolutionary dynamics of variant antigen genes in Babesia reveal a history of genomic innovation underlying host-parasite interaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 7113–7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brayton, K.A.; Lau, A.O.; Herndon, D.R.; Hannick, L.; Kappmeyer, L.S.; Berens, S.J.; Bidwell, S.L.; Brown, W.C.; Crabtree, J.; Fadrosh, D.; et al. Genome sequence of Babesia bovis and comparative analysis of apicomplexan hemoprotozoa. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, 1401–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.C.; Cornillot, E.; McCracken, C.; Usmani-Brown, S.; Dwivedi, A.; Ifeonu, O.O.; Crabtree, J.; Gotia, H.T.; Virji, A.Z.; Reynes, C.; et al. Genome-wide diversity and gene expression profiling of Babesia microti isolates identify polymorphic genes that mediate host-pathogen interactions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 352–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pain, A.; Renauld, H.; Berriman, M.; Murphy, L.; Yeats, C.A.; Weir, W.; Kerhornou, A.; Aslett, M.; Bishop, R.; Bouchier, C.; et al. Genome of the host-cell transforming parasite Theileria annulata compared with T. parva. Science 2005, 309, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashida, K.; Hara, Y.; Abe, T.; Yamasaki, C.; Toyoda, A.; Kosuge, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, S.; Katayama, T.; et al. Comparative genome analysis of three eukaryotic parasites with differing abilities to transform leukocytes reveals key mediators of Theileria-induced leukocyte transformation. MBio 2012, 3, e00204-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, M.J.; Bishop, R.; Shah, T.; de Villiers, E.P.; Carlton, J.M.; Hall, N.; Ren, Q.; Paulsen, I.T.; Pain, A.; Berriman, M.; et al. Genome sequence of Theileria parva, a bovine pathogen that transforms lymphocytes. Science 2005, 309, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarigo, J.L.; Scholl, E.H.; McK Bird, D.; Brown, C.C.; Cohn, L.A.; Dean, G.A.; Levy, M.G.; Doolan, D.L.; Trieu, A.; Nordone, S.K.; et al. A novel candidate vaccine for cytauxzoonosis inferred from comparative apicomplexan genomics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, S.Q.; Gascuel, O. An Improved General Amino Acid Replacement Matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1307–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajer, A.; Alsarraf, M.; Bednarska, M.; Mohallal, E.M.; Mierzejewska, E.J.; Behnke-Borowczyk, J.; Zalat, S.; Gilbert, F.; Welc-Falęciak, R. Babesia behnkei sp. nov.; a novel Babesia species infecting isolated populations of Wagner’s gerbil, Dipodillus dasyurus, from the Sinai Mountains, Egypt. Parasite Vector 2014, 7, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criado-Fornelio, A.; Martinez-Marcos, A.; Buling-Saraña, A.; Barba-Carretero, J.C. Molecular Studies on Babesia, Theileria and Hepatozoon in Southern Europe: Part II. Phylogenetic Analysis and Evolutionary History. Vet. Parasitol. 2003, 114, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodder, A.N.; Drew, D.R.; Epa, V.C.; Delorenzi, M.; Bourgon, R.; Miller, S.K.; Moritz, R.L.; Frecklington, D.F.; Simpson, R.J.; Speed, T.P.; et al. Enzymic, phylogenetic, and structural characterization of the unusual papain-like protease domain of Plasmodium falciparum SERA5. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 48169–48177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnittger, L.; Yin, H.; Gubbels, M.J.; Beyer, D.; Niemann, S.; Jongejan, F.; Ahmed, J.S. Phylogeny of sheep and goat Theileria and Babesia parasites. Parasitol. Res. 2003, 91, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Species | Classic Taxonomy | 3 Phylogenetic Clade | Common Designation | Diseases | Geographic Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. microti | Babesia s.l. | I | B. microti-group | human babesiosis | USA, Europe, Japan, |
| B. duncani | II | 4 western clade | human babesiosis | USA | |
| 1T. bicornis | IIIa | Theileria s.l. | n.d. | Africa | |
| C. felis | Cytauxzoon | IIIb | Cytauxzoon | feline cytauxzoonosis | USA |
| T. equi | 2Theileria s.s. | IV | 5T. equi | 6 equine piroplasmosis | tropical and subtropical regions worldwide |
| T. annulata T. parva T. orientalis | Theileria s.s. | V | true Theileria | tropical theileriosis East Coast Fever oriental theileriosis | tropical and subtropical regions of the old world East Africa Asia |
| B. bovis B. bigemina B. ovis | Babesia s.s. | VI | true Babesia | 7 bovine babesiosis ovine babesiosis | tropical and subtropical regions worldwide |
| 2 C1A-Cp Group | 1 Piroplasmid Clade | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | IIIb | IV | V | VI | |||||
| B. microti | B. duncani | C. felis | T. equi | T. annulata | T. parva | T. orientalis | B. ovis | B. bovis | B. bigemina | |
| 1 | XP_012650559 | |||||||||
| 2 | CF000928 | XP_953243 | 3 XP_764233 | XP_009692255 | ||||||
| 3 | BdWA1_II1487 | CF001943 | XP_004828689 | XP_952571 | XP_764709 | XP_009690157 | ALJ75577 | XP_001612131 | XP_012766088 | |
| 4 | XP_012647584 | |||||||||
| 5 | XP_021338611 | BdWA1_III2972 | CF001234 | XP_004832347 | XP_955044 | XP_763377 | XP_009691533 | ALJ75578 | XP_001609546 | XP_012768370 |
| CF003813 | XP_004832939 | XP_951829 | XP_765451 | XP_009690911 | ALJ75579 | XP_001608716 | XP_012768246 | |||
| 6 | XP_012647628 | |||||||||
| 7 | CF003226 | XP_004828646 | XP_952610 | XP_764666 | XP_009690112 | |||||
| XP_004828875 | XP_952609 | XP_764667 | XP_009690113 | XP_012766037 | ||||||
| XP_004830320 | XP_764668 | XP_009690114 | ||||||||
| XP_004831551 | XP_009690115 | |||||||||
| XP_004831655 | XP_009692826 | |||||||||
| XP_004831668 | ||||||||||
| XP_004833425 | ||||||||||
| XP_004833462 | ||||||||||
| 8 | BdWA1_III3014 | CF002922 | XP_004830368 | XP_954970 | XP_763298 | XP_009691605 | ALJ75576 | XP_001610695 | XP_012769730 | |
| CF003554 | XP_004832412 | XP_954972 | XP_763299 | XP_009691603 | ||||||
| CF000752 | XP_004833381 | XP_954973 | XP_763300 | XP_009691602 | ||||||
| XP_954974 | XP_763301 | XP_009691601 | ||||||||
| XP_954976 | XP_763303 | XP_009691599 | ||||||||
| XP_954975 | XP 763302 | XP_009691600 | ||||||||
| XP_954971 | ||||||||||
| ∑ 83 | 4 | 3 | 8 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 15 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ascencio, M.E.; Florin-Christensen, M.; Mamoun, C.B.; Weir, W.; Shiels, B.; Schnittger, L. Cysteine Proteinase C1A Paralog Profiles Correspond with Phylogenetic Lineages of Pathogenic Piroplasmids. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci5020041
Ascencio ME, Florin-Christensen M, Mamoun CB, Weir W, Shiels B, Schnittger L. Cysteine Proteinase C1A Paralog Profiles Correspond with Phylogenetic Lineages of Pathogenic Piroplasmids. Veterinary Sciences. 2018; 5(2):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci5020041
Chicago/Turabian StyleAscencio, Mariano E., Monica Florin-Christensen, Choukri B. Mamoun, William Weir, Brian Shiels, and Leonhard Schnittger. 2018. "Cysteine Proteinase C1A Paralog Profiles Correspond with Phylogenetic Lineages of Pathogenic Piroplasmids" Veterinary Sciences 5, no. 2: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci5020041
APA StyleAscencio, M. E., Florin-Christensen, M., Mamoun, C. B., Weir, W., Shiels, B., & Schnittger, L. (2018). Cysteine Proteinase C1A Paralog Profiles Correspond with Phylogenetic Lineages of Pathogenic Piroplasmids. Veterinary Sciences, 5(2), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci5020041







