Dimples for Skin-Friction Drag Reduction: Status and Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
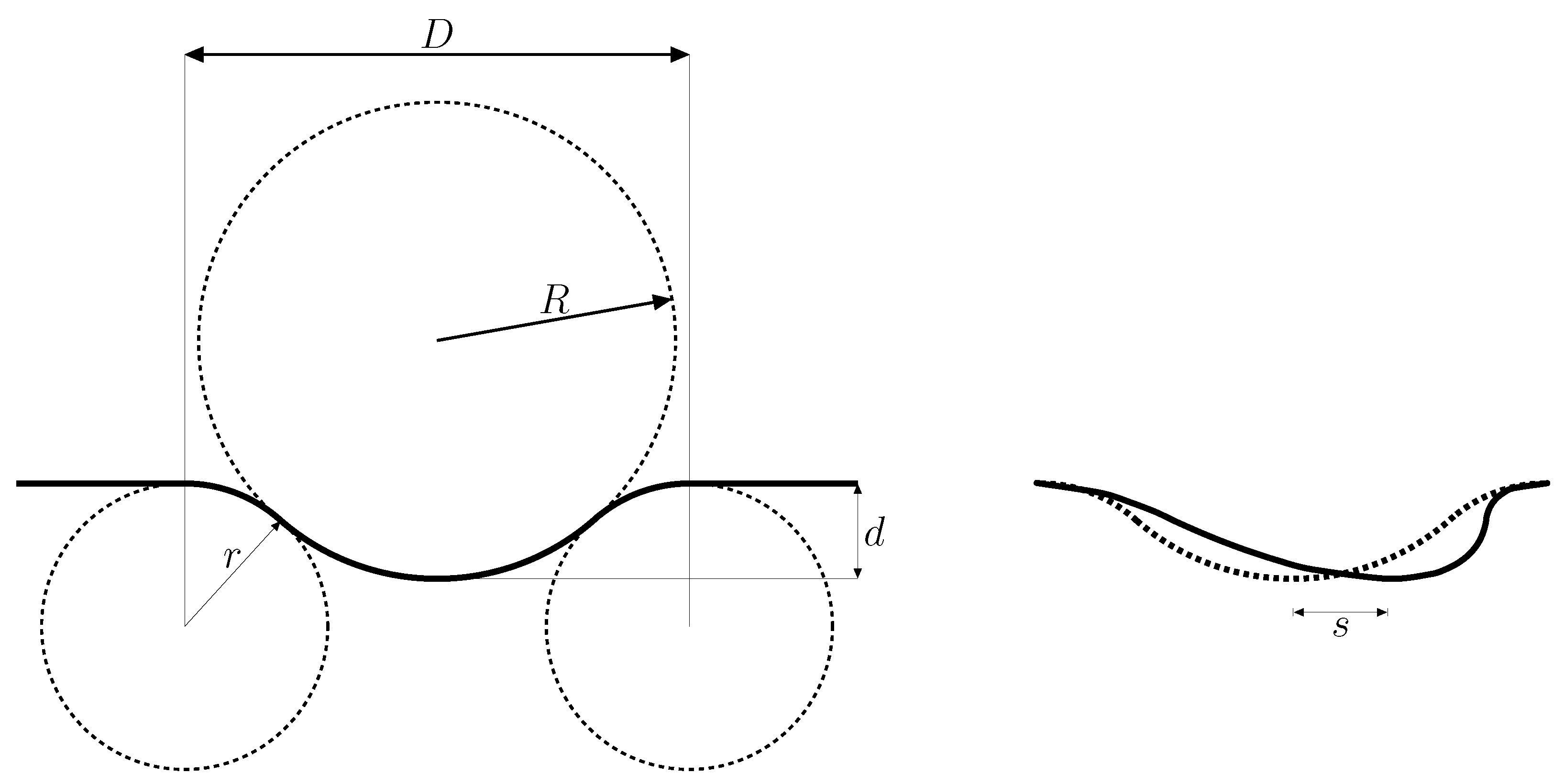
Characterization of a Dimpled Surface
2. Do Dimples Work?
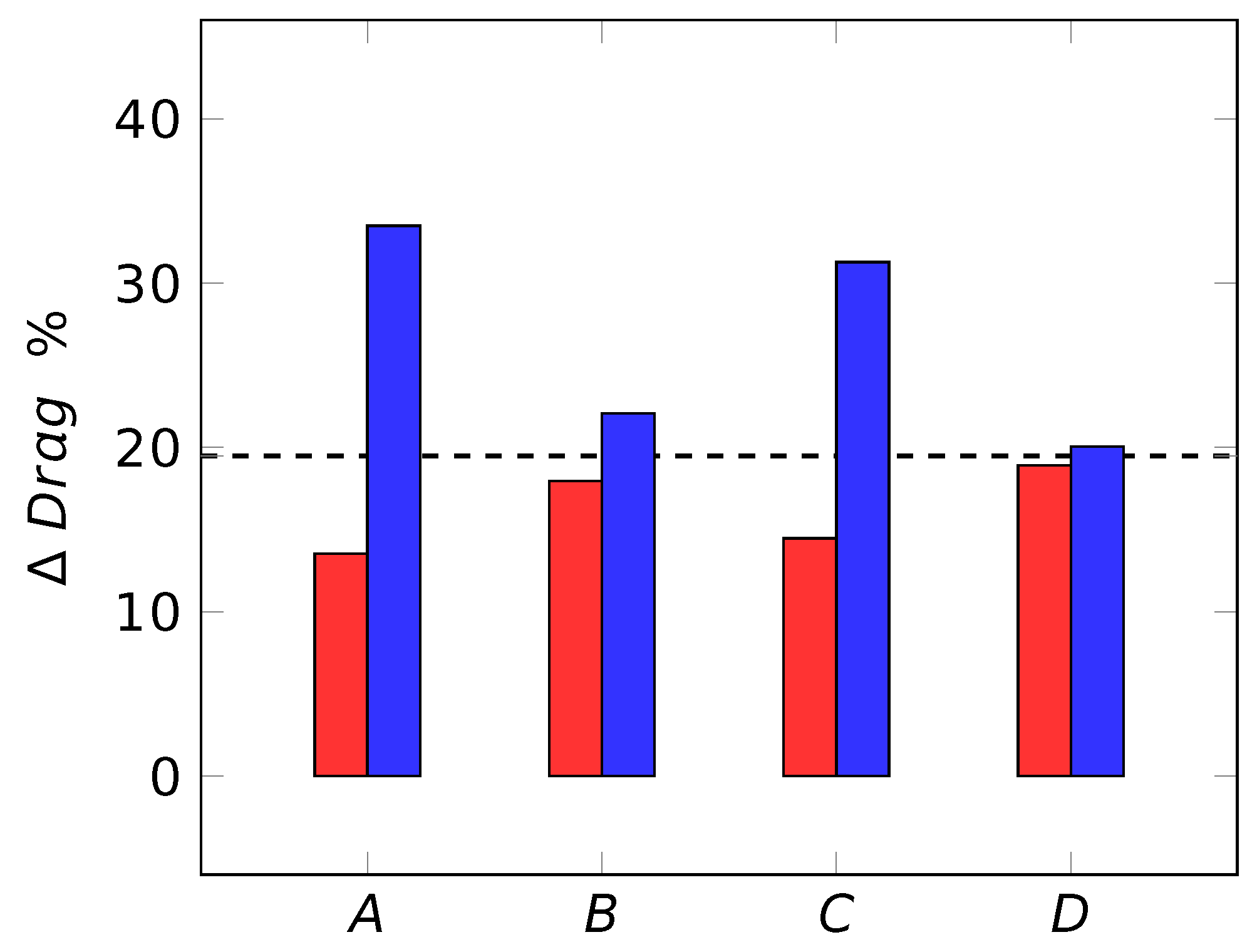
2.1. Experimental Studies
2.2. Numerical Simulations
3. How to Design Dimples?
3.1. The Shape of the Dimple
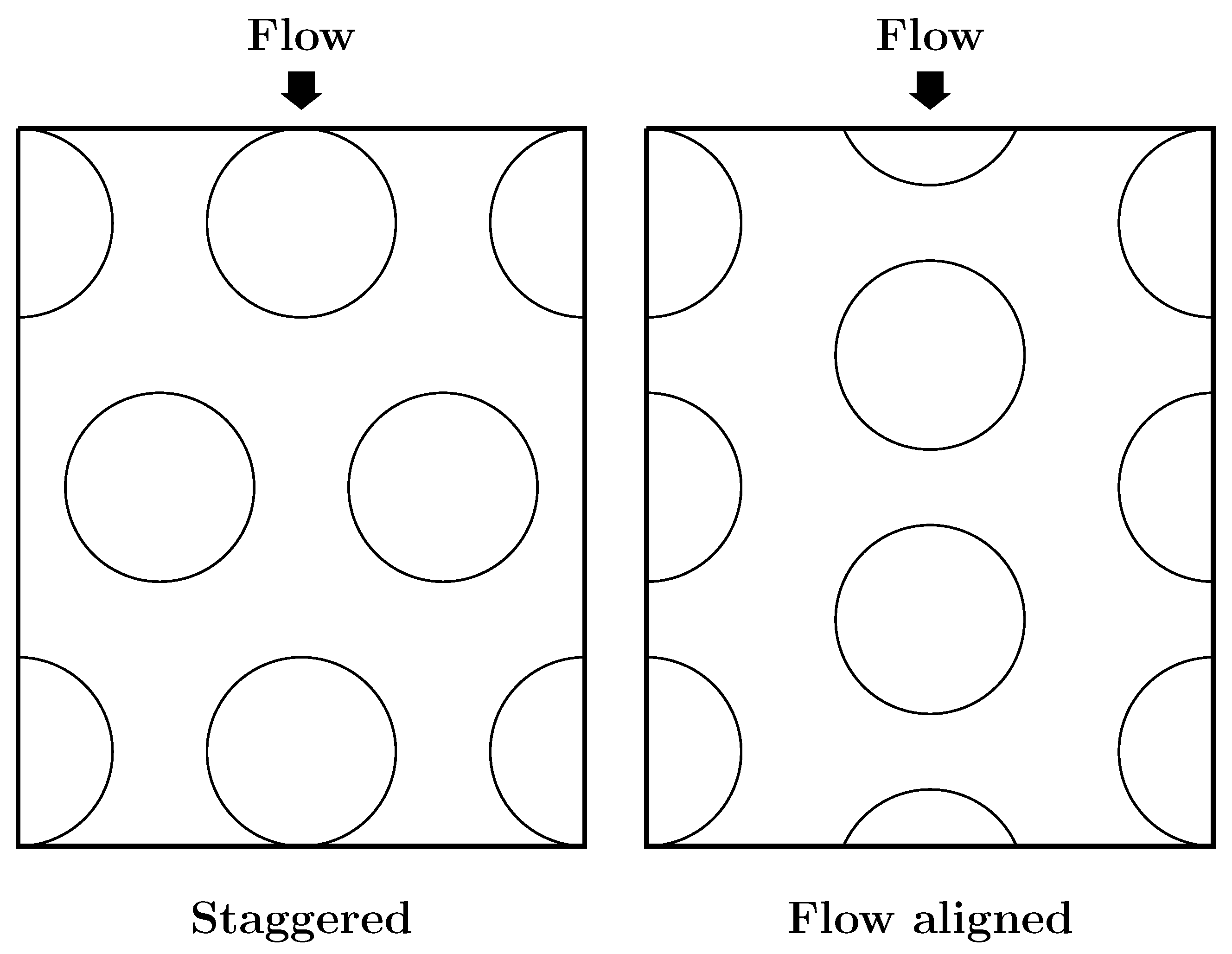
3.2. The Arrangement of the Dimples
4. How Do Dimples Work?
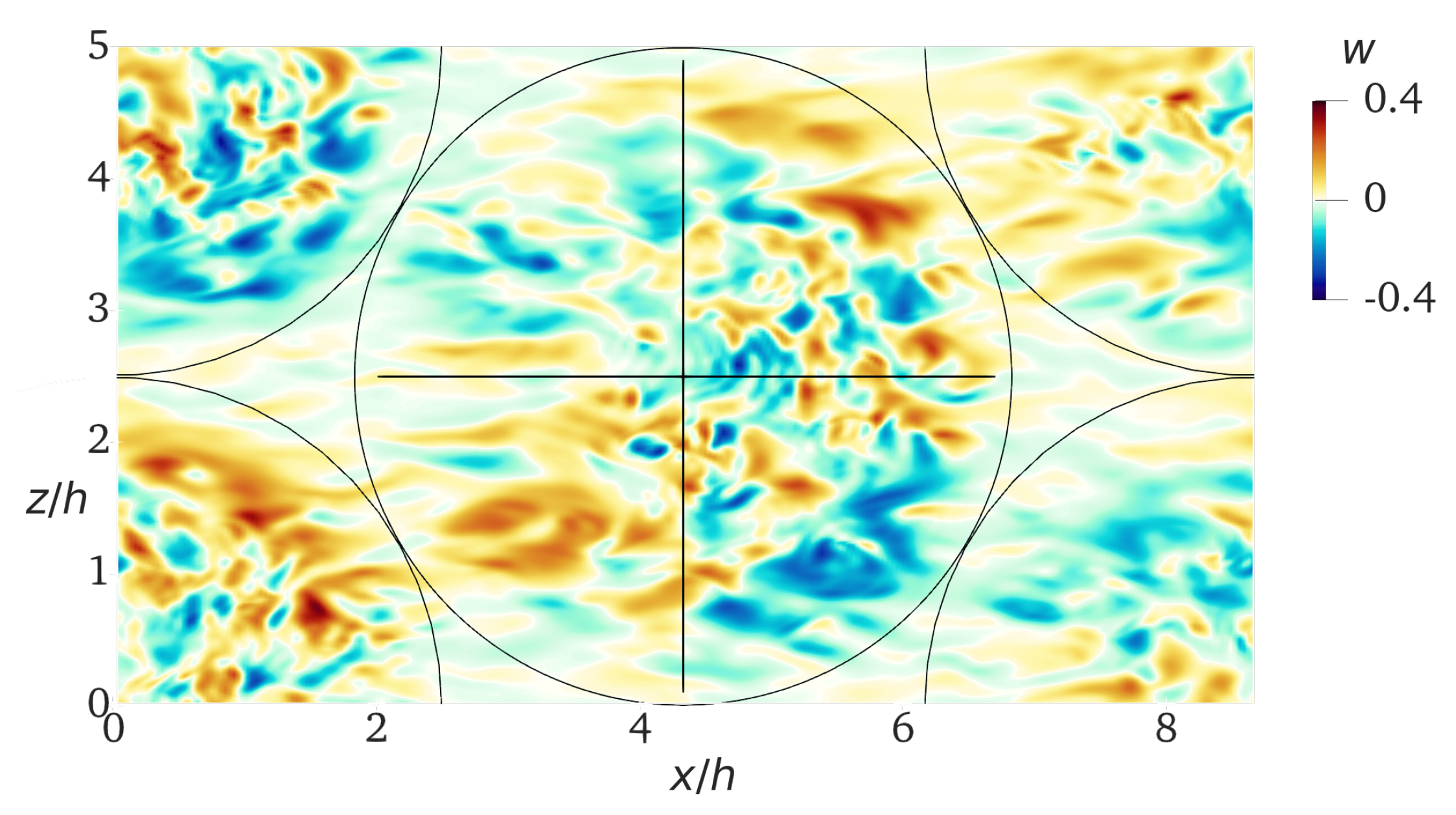
4.1. Self-Organized Secondary Tornado-like Jets
4.2. Spanwise Forcing
5. How to Set Up a Proper Comparison
5.1. Measurement of the Drag (Difference)
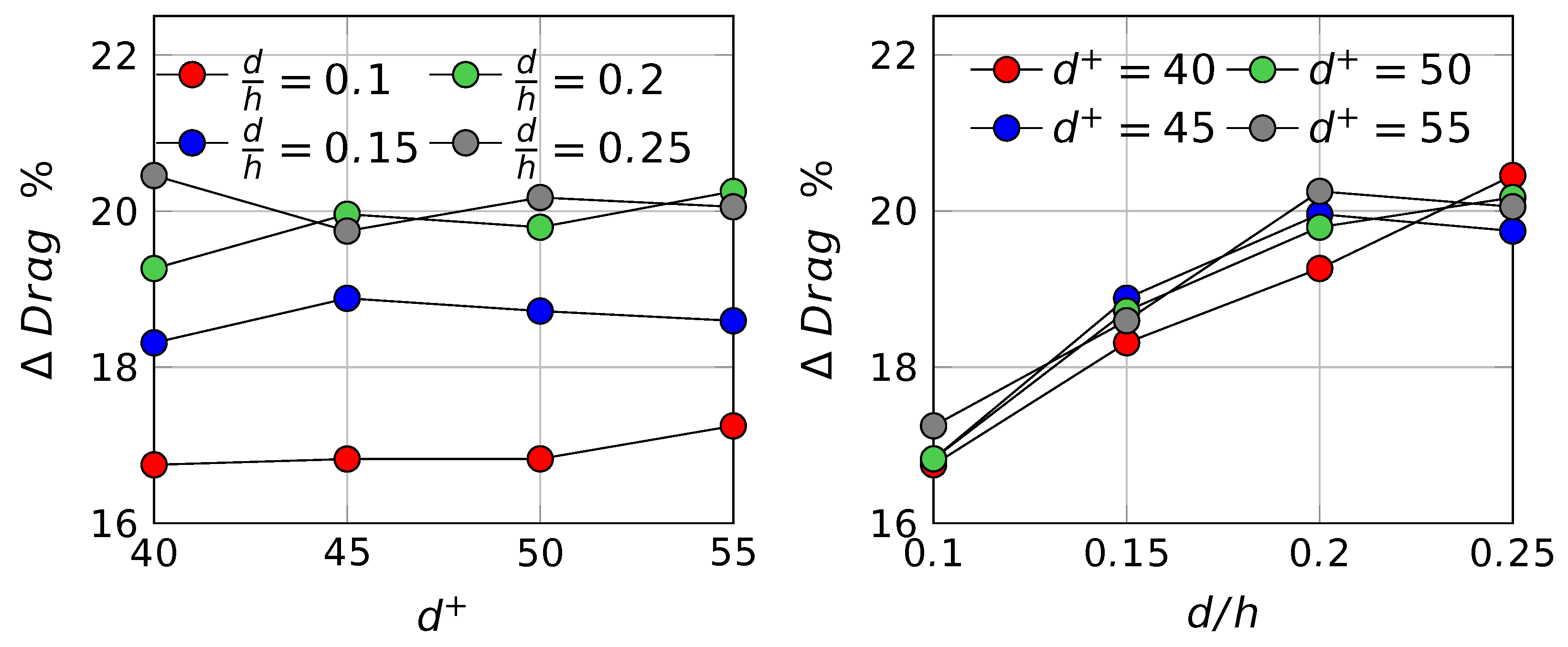
5.2. The Reynolds Number
5.3. The Equivalent Flat Wall
5.4. The Drag Reduction Metrics
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Computational Details
References
- García-Mayoral, R.; Jiménez, J. Drag Reduction by Riblets. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2011, 369, 1412–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quadrio, M.; Chiarini, A.; Banchetti, J.; Gatti, D.; Memmolo, A.; Pirozzoli, S. Drag Reduction on a Transonic Airfoil. J. Fluid. Mech. 2022, 942, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciatori, L.; Brignoli, C.; Mele, B.; Gattere, F.; Monti, C.; Quadrio, M. Drag Reduction by Riblets on a Commercial UAV. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, J.; George-Falvy, D.; Sullivan, P. Flight Test of Turbulent Skin-Friction Reduction by Riblets. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Turbulent Drag Reduction by Passive Means, London, UK, 15–17 September 1987; Volume RAeS 2, pp. 408–424. [Google Scholar]
- Kurita, M.; Iijima, H.; Koga, S.; Nishizawa, A.; Kwak, D.; Iijima, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Abe, H. Flight Test for Paint Riblets. In AIAA Scitech 2020 Forum; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Leontiev, A.; Kiselev, N.; Vinogradov, Y.; Strongin, M.; Zditovets, A.; Burtsev, S. Experimental Investigation of Heat Transfer and Drag on Surfaces Coated with Dimples of Different Shape. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2017, 118, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Jeon, W.P.; Choi, H. Mechanism of Drag Reduction by Dimples on a Sphere. Phys. Fluids 2006, 18, 41702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allarton, R.; Yao, J.; Clifford, T.; Hitchborn, B.; Parker, L.; Shaw, J. Surface Flow Modification of Aerofoils for Automotive Racing Car Applications. Int. J. Mod. Phys. 2020, 34, 2040096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.W.; Fang, L.; Liu, Y.Q. Drag Reduction of Wall Bounded Incompressible Turbulent Flow Based on Active Dimples/Pimples. J. Hydrodyn. 2017, 29, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiknadze, G.I.; Krasnov, Y.K.; Chushkin, Y.V. Investigation of the Enhancement of Heat Transfer Due to Self-Organization of Ordered Dynamic Twisted Heat-Carrier Structures on a Heat-Transfer Surface; Technical Report 50.05/59; I. V. Kurchatov Institute of Atomic Energy: Moscow, Russia, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Alekseev, V.V.; Gachechiladze, I.A.; Kiknadze, G.I.; Oleinikov, V. Tornado-like Energy Transfer on Three-Dimensional Concavities of Reliefs-Structures of Self Organizing Flow, Their Visualisation, and Surface Streamlining Mechanism. Heat Transf. Intensif. Radiat. Complex Heat Transf. 1998, 6, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Chew, Y.T.; Khoo, B.C. Enhancement of Heat Transfer in Turbulent Channel Flow over Dimpled Surface. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 8100–8121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praß, J.; Wannmacher, H.; Franke, J.; Becker, S. The Influence of Different Arrangements of Shallow Dimples on the Resistance of Plates Subjected to Relative Fluid Motion. Tech. Mech. 2019, 39, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Tay, C.M.J.; Khoo, B.C.; Chew, Y.T. Use of DES in Mildly Separated Internal Flow: Dimples in a Turbulent Channel. J. Turbul. 2017, 18, 1180–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.; Jaiman, R.; Lim, T.; Tay, C.; Khoo, B. Geometric Effects of Shallow Dimples in Turbulent Channel Flows at Reτ≈ 180: A Vorticity Transport Perspective. Flow Turbul. Combust. 2020, 105, 83–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldhuis, L.; Vervoort, E. Drag Effect of a Dented Surface in a Turbulent Flow. In Proceedings of the 27th AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference, San Antonio, TX, USA, 22–25 June 2009; p. 3950. [Google Scholar]
- Tay, C. Determining the Effect of Dimples on Drag in a Turbulent Channel Flow. In Proceedings of the 49th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition, Orlando, FL, USA, 4–7 January 2011; p. 682. [Google Scholar]
- Tay, C.; Khoo, B.; Chew, Y. Mechanics of Drag Reduction by Shallow Dimples in Channel Flow. Phys. Fluids 2015, 27, 035109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nesselrooij, M.; Veldhuis, L.; Van Oudheusden, B.; Schrijer, F. Drag Reduction by Means of Dimpled Surfaces in Turbulent Boundary Layers. Exp. Fluids 2016, 57, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, C.; Lim, T.; Khoo, B.; Jaiman, R. Effectiveness of Triangular Depressions and Asymmetric Circular Dimples for Drag Reduction. In Proceedings of the 20th Australasian Fluid Mechanics Conference, Perth, Australia, 5–8 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tay, J.; Lim, T.T. Drag Reduction with Non-Axisymmetric Dimples. In Proceedings of the 35th AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 5–9 June 2017; p. 3569. [Google Scholar]
- Tay, J.; Lim, T.T. Drag Reduction with Teardrop-Shaped Dimples. In Proceedings of the 2018 Flow Control Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 25–29 June 2018; p. 3528. [Google Scholar]
- Spalart, P.; Shur, M.; Strelets, M.; Travin, A.; Paschal, K.; Wilkinson, S. Experimental and Numerical Study of the Turbulent Boundary Layer over Shallow Dimples. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2019, 78, 108438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Campenhout, O.; Van Nesselrooij, M.; Veldhuis, L.L.; Van Oudheusden, B.; Schrijer, F. An Experimental Investigation into the Flow Mechanics of Dimpled Surfaces in Turbulent Boundary Layers. In Proceedings of the 2018 AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Kissimmee, FL, USA, 8–12 January 2018; p. 2062. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, R. Reynolds Number Dependence of Skin Friction and Other Bulk Flow Variables in Two-Dimensional Rectangular Duct Flow. Trans. ASME J. Fluids Eng. 1978, 100, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lienhart, H.; Breuer, M.; Köksoy, C. Drag Reduction by Dimples?—A Complementary Experimental/Numerical Investigation. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2008, 29, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, J.; Lim, T.T.; Khoo, B.C. Drag Reduction with Diamond-Shaped Dimples. In Proceedings of the AIAA Aviation 2019 Forum, Dallas, TX, USA, 17–21 June 2019; p. 3296. [Google Scholar]
- Kovalenko, G.; Terekhov, V.; Khalatov, A. Flow Regimes in a Single Dimple on the Channel Surface. J. Appl. Mech. Tech. Phys. 2010, 51, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, C.; Chew, Y.; Khoo, B.; Zhao, J. Development of Flow Structures over Dimples. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2014, 52, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.; Jaiman, R.; Lim, T. A Numerical Study for Passive Turbulent Drag Reduction via Shallow Dimples. In Proceedings of the 21st Australasian Fluid Mechanics Conference, Adelaide, Australia, 10–13 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lashkov, Y.A.; Samoilova, N. On the Viscous Drag of a Plate with Spherical Recesses. Fluid Dyn. 2002, 37, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiknadze, G.; Gachechiladze, I.; Barnaveli, T. The Mechanisms of the Phenomenon of Tornado-Like Jets Self-Organization in the Flow Along the Dimples on the Initially Flat Surface. In Proceedings of the ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Houston, TX, USA, 9–15 November 2012; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, W.; Mangiavacchi, N.; Akhavan, R. Suppression of Turbulence in Wall-Bounded Flows by High-Frequency Spanwise Oscillations. Phys. Fluids A 1992, 4, 1605–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quadrio, M.; Ricco, P. Critical Assessment of Turbulent Drag Reduction through Spanwise Wall Oscillation. J. Fluid Mech. 2004, 521, 251–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quadrio, M.; Sibilla, S. Numerical Simulation of Turbulent Flow in a Pipe Oscillating around Its Axis. J. Fluid Mech. 2000, 424, 217–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viotti, C.; Quadrio, M.; Luchini, P. Streamwise Oscillation of Spanwise Velocity at the Wall of a Channel for Turbulent Drag Reduction. Phys. Fluids 2009, 21, 115109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nesselrooij, M.; Van Campenhout, O.; Van Oudheusden, B.; Schrijer, F.; Veldhuis, L. Development of an Experimental Apparatus for Flat Plate Drag Measurements and Considerations for Such Measurements. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2022, 33, 055303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, D.; Güttler, A.; Frohnapfel, B.; Tropea, C. Experimental Assessment of Spanwise-Oscillating Dielectric Electroactive Surfaces for Turbulent Drag Reduction in an Air Channel Flow. Exp. Fluids 2015, 56, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechert, D.W.; Hoppe, G.; Van Der Hoeven, J.G.T.; Makris, R. The Berlin Oil Channel for Drag Reduction Research. Exp. Fluids 1992, 12, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Quadrio, M.; Frohnapfel, B. Numerical Simulation of Turbulent Duct Flows at Constant Power Input. J. Fluid Mech. 2014, 750, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiménez, J. Turbulent Flows Over Rough Wall. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech 2004, 36, 173–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchini, P. Reducing the Turbulent Skin Friction. In Computational Methods in Applied Sciences 1996; Knoerzer, D., Periaux, J., Tuovinen, T., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Spalart, P.; McLean, J. Drag Reduction: Enticing Turbulence, and Then an Industry. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2011, 369, 1556–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gatti, D.; Quadrio, M. Reynolds-Number Dependence of Turbulent Skin-Friction Drag Reduction Induced by Spanwise Forcing. J. Fluid Mech. 2016, 802, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luchini, P. Immersed-Boundary Simulation of Turbulent Flow Past a Sinusoidally Undulated River Bottom. Eur. J. Mech. B/Fluids 2016, 55, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchini, P. Linearized No-Slip Boundary Conditions at a Rough Surface. J. Fluid Mech. 2013, 737, 349–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiménez, J.; Moin, P. The Minimal Flow Unit in Near-Wall Turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 1991, 225, 213–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Article | Num/Exp | Flow | Re | Shape | Cov% | Layout | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LBK-08 [26] | Exp | CF | ≈10,000 | Circ | 5 | - | - | 0 | A | 0 | ||
| DNS (FVM) | CF | Circ | 5 | - | - | 0 | A | |||||
| VV-09 [16] | Exp | BL | - | Circ | - | 5 | - | - | 0 | 60 | S | |
| T-11 [17] | Exp | CF | ≈17,500 | Circ | 5 | 5 | 0 | 90 | S | |||
| TKC-15 [18] | Exp | CF | ≈32,100 | Circ | 5 | 5 | 0 | 90 | S | |||
| VVVS-16 [19] | Exp | BL | ≈1500 | Circ | 0 | S | ||||||
| TLKJ-16 [20] | Exp | CF | ≈5625 | Triang Up | 5 | - | - | - | S | |||
| Exp | CF | ≈5625 | Triang Do | 5 | - | - | - | S | ||||
| Exp | CF | ≈50,350 | Circ | 5 | 5 | - | - | 90 | S | |||
| TKC-17 [14] | DES (FVM) | CF | ≈2830 | Circ | 5 | 0 | 90 | S | ||||
| TL-17 [21] | Exp | CF | ≈28,600 | Circ | 5 | - | - | 90 | S | |||
| TL-18 [22] | Exp | CF | ≈42,850 | Circ | 5 | 5 | - | - | 0 | - | S | |
| Exp | CF | ≈30,140 | Tear Up | 5 | - | - | 84 | S | ||||
| Exp | CF | ≈22,270 | Tear Dp | 5 | - | - | 84 | S | ||||
| VVVVS-18 [24] | Exp | BL | - | Circ | - | - | 0 | - | S/A/H | |||
| SSSTPW-19 [23] | DNS (FVM) | BL | 30,000 | Circ | - | - | 0 | - | S | |||
| TLK-19 [27] | Exp | CF | ≈30,000 | Diam | 5 | - | - | 0 | 99 | S | ||
| PWFB-19 [13] | LES (FVM) | HCF | ≈6121 | Circ | 0 | - | S | |||||
| NJLTK-20 [15] | DNS (SEM) | CF | 2800 | Circ | 5 | 5 | S | |||||
| DNS (SEM) | CF | 2800 | Ell | 5 | 0 | S | ||||||
| DNS (SEM) | CF | 2800 | Tear Up | 5 | S | |||||||
| DNS (SEM) | CF | 2800 | Tear Dp | 5 | S | |||||||
| DNS (SEM) | CF | 2800 | Diam | 5 | 0 | S |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gattere, F.; Chiarini, A.; Quadrio, M. Dimples for Skin-Friction Drag Reduction: Status and Perspectives. Fluids 2022, 7, 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids7070240
Gattere F, Chiarini A, Quadrio M. Dimples for Skin-Friction Drag Reduction: Status and Perspectives. Fluids. 2022; 7(7):240. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids7070240
Chicago/Turabian StyleGattere, Federica, Alessandro Chiarini, and Maurizio Quadrio. 2022. "Dimples for Skin-Friction Drag Reduction: Status and Perspectives" Fluids 7, no. 7: 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids7070240








