Research on the Fire Hazard of Different Cables Based on Cone Calorimetry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Experimental Equipment
2.2. Methods
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Time to Ignition
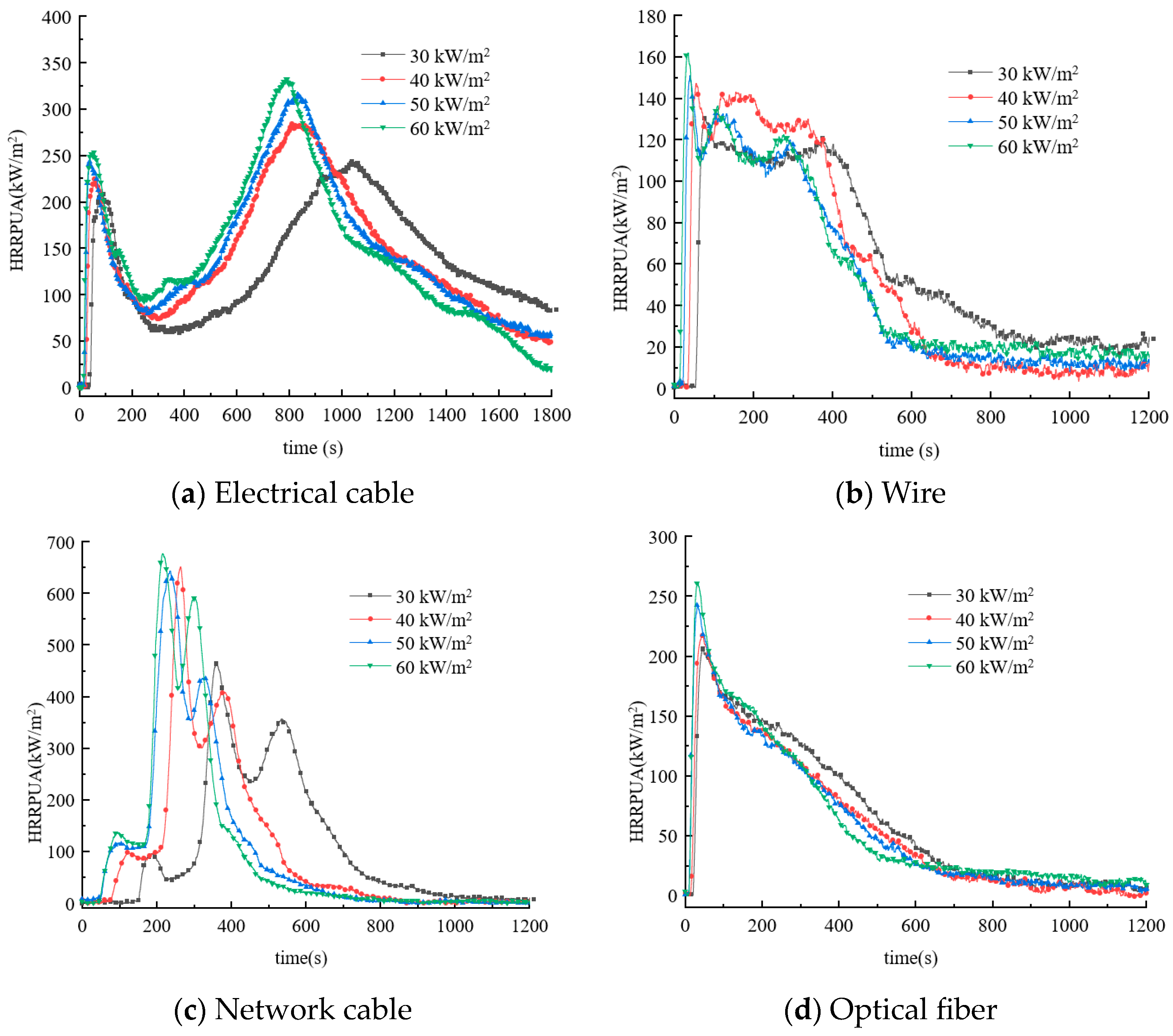
3.2. Heat Release Rate and Total Heat Release
3.2.1. Heat Release Rate
3.2.2. Total Heat Release
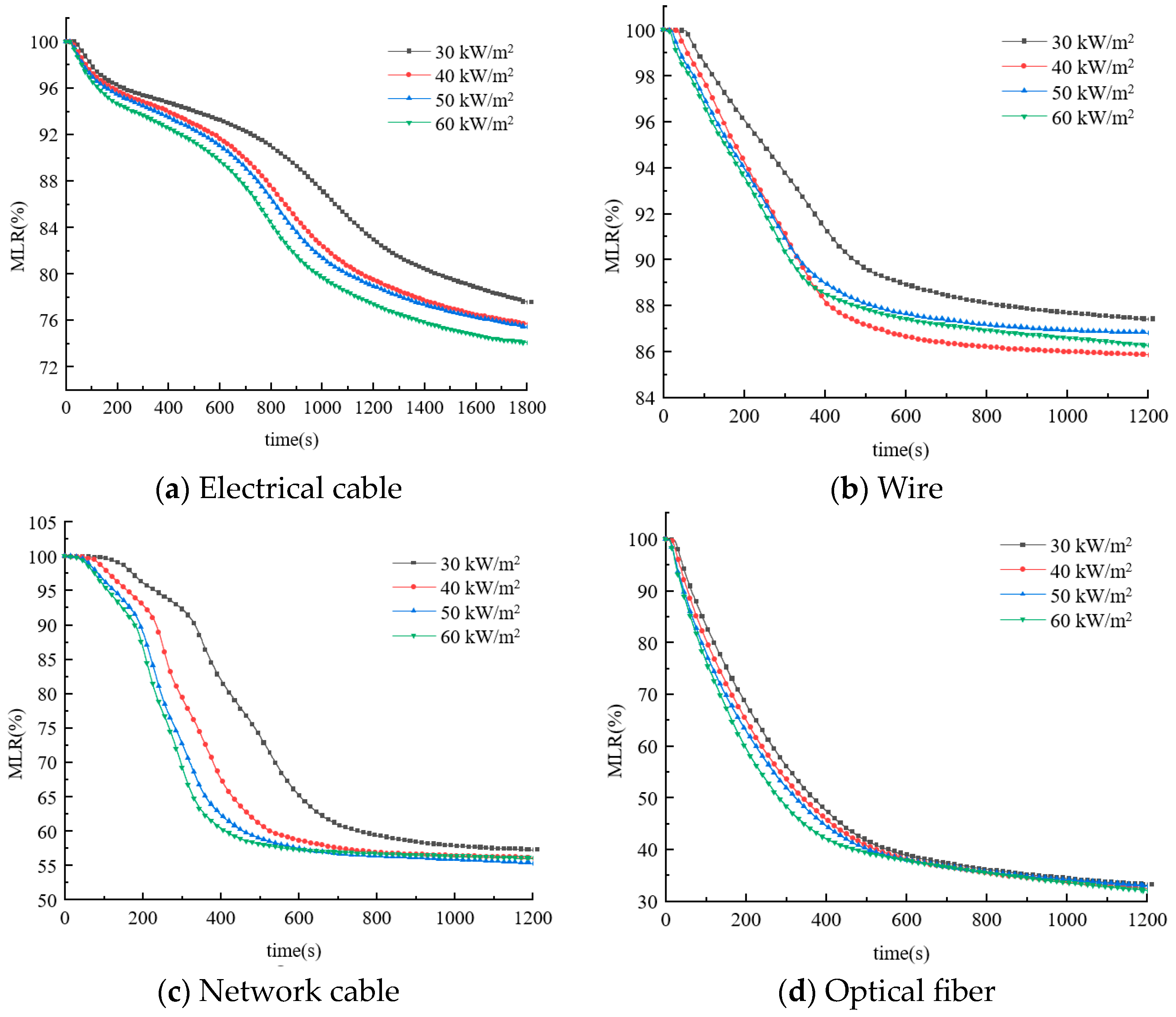
3.3. Mass Loss and Residual Mass
3.3.1. Mass Loss
3.3.2. Residual Mass
3.4. Comprehensive Fire Risk Analysis
3.4.1. Thermal Hazard Analysis
3.4.2. Smoke Toxicity Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TTI | time to ignition |
| HRRPUA | heat release rate per unit area |
| ave-HRR | average heat release rate |
| PHRR | peak heat release rate |
| THR | total heat release |
| MLR | mass loss rate |
| SPR | smoke production rate |
| SEA | smoke extinction area |
| FED | fractional effective dose |
References
- Xue, Y. Experimental Research on Fire Spread of PE and ETFE Conductors under Low-Pressure Conditions. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, K. Research on Horizontal and Inclined Fire Spread Behavior of Inner Core Wires with Different Thermal Conductivity under Low-Pressure Conditions. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Nakamura, Y. A Review of Fundamental Combustion Phenomena in Wire Fires. Fire Technol. 2020, 56, 315–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, G.; Ngohang, F.E.; Gay, L.; Bourbigot, S. Investigation of the Contribution to Fire of Electrical Cable by a Revisited Mass Loss Cone. In Fire Science and Technology 2015: The Proceedings of 10th Asia-Oceania Symposium on Fire Science and Technology; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 687–693. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Cai, G.; Guo, J.; Gao, W.; Huang, Y.; Tong, X. Combustion Characteristics and Thermal Decomposition Mechanism of the Flame-Retardant Cable in Urban Utility Tunnel. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 44, 102887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliot, P.; Whiteley, R. A Cone Calorimeter Test for the Measurement of Flammability Properties of Insulated Wire. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1999, 64, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.A.; Briggs, P.J.; Hirschler, M.M.; Matheson, A.F.; O’Neill, T.J. A Comparative Study of the Fire Performance of Halogenated and Non-Halogenated Materials for Cable Applications. Part I Tests on Materials and Insulated Wires. Fire Mater. 1996, 20, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Li, C.; Ma, C.; Liu, G.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, B. A Comparative Study on Fire Hazards of Cables Used in Nuclear Power Plants Based on Small- and Large-Scale Experiments. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 14659–14671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheson, A.F.; Charge, R.; Corneliussen, T. Properties of PVC Compounds with Improved Fire Performance for Electrical Cables. Fire Saf. J. 1992, 19, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschler, M.M. Survey of Fire Testing of Electrical Cables. Fire Mater. 1992, 16, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczorek-Chrobak, K.; Fangrat, J.; Papis, B.K. Calorimetric Behavior of Electric Cables. Energies. 2021, 14, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, S.Y.; Hwang, C.H. Experimental and Numerical Studies on Major Pyrolysis Properties of Flame Retardant PVC Cables Composed of Multiple Materials. Materials 2020, 13, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Qian, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jing, J.; Ren, F.; Li, J. Research on the Combustion Characteristics of ZR-YJLV Cables Based on Flame Propagation Calorimetry. China Saf. Prod. Sci. Technol. 2020, 16, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, Y.; Feng, R.; Li, K.; Huang, Y.; Shang, F. Characteristics and Reaction Mechanism of Pyrolysis Solid Gas Products of Typical Substation Flame-Retardant Low-Voltage Cable Outer Sheath Materials under Fire Conditions. J. Tsinghua Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 62, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z. Experimental Analysis and Numerical Simulation of Radiation Ignition Behavior of Subway Cables; Capital University of Economics and Business: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 5660-1; Reaction-to-Fire Tests-Heat Release, Smoke Production and Mass Loss Rate-Part1 Release Rate (Cone Calorimeter Method) and Smoke Production Rate (Dynamic Measurement). International Organization for Standardization (IOS): Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- Meinier, R.; Sonnier, R.; Zavaleta, P.; Suard, S.; Ferry, L. Fire Behavior of Halogen-Free Flame Retardant Electrical Cables with the Cone Calorimeter. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 342, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R. Research on Pyrolysis and Combustion Characteristics of Typical Interior Materials of Subway Trains; University of Science and Technology of China: Hefei, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q. Comparison of Experimental Methods for Fire Response of Materials. Fire Sci. Technol. 2007, 2007, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, Z.; Xu, X.; Li, X. Fire Combustion Performance Evaluation of Polymer Materials: Cone Calorimeter Test Method; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Petrella, R. The Assessment of Full-Scale Fire Hazards from Cone Calorimeter Data. J. Fire Sci. 1994, 12, 14–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y. Research on Fire Protection Development System of Passenger Cars Based on Fire Risk Analysis; University of Science and Technology of China: Hefei, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]




| Type | Manufacturer | Size |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical cable | Kangpu Technology Co., Ltd. (Suzhou, China) | 100 mm |
| Wire | Henggong Technology Co., Ltd. (Taizhou, China) | 100 mm |
| Network cable | Kangpu Technology Co., Ltd. (Suzhou, China) | 100 mm |
| Optical fiber | Youpuguang Technology Co., Ltd.(Shenzhen, China) | 100 mm |
| NO. | Cable Type | Outer Sheath | Insulating Layer | Intensity of External Heat Radiation (kW/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-1 | Electrical cable | Flame-retardant PVC | XLPE | 30 |
| T-2 | 40 | |||
| T-3 | 50 | |||
| T-4 | 60 | |||
| T-5 | Wire | Flame-retardant PVC | None | 30 |
| T-6 | 40 | |||
| T-7 | 50 | |||
| T-8 | 60 | |||
| T-9 | Network cable | LSZH | HDPE | 30 |
| T10 | 40 | |||
| T-11 | 50 | |||
| T-12 | 60 | |||
| T-13 | Optical fiber | PVC | None | 30 |
| T-14 | 40 | |||
| T-15 | 50 | |||
| T-16 | 60 |
| TTI(s) | Intensity of External Heat Radiation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 kW/m2 | 40 kW/m2 | 50 kW/m2 | 60 kW/m2 | |
| Electrical cable | 37 | 25 | 18 | 15 |
| Wire | 54 | 33 | 20 | 13 |
| Network cable | 151 | 77 | 49 | 46 |
| Optical fiber | 19 | 12 | 8 | 8 |
| NO. | Type | Intensity of External Heat Radiation (kW/m2) | PHRR (kW/m2) | TP (s) | ave-HRR1 | ave-HRR3 | ave-HRR5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-1 | Electrical cable | 30 | 243.98 ± 1.28 | 1038 | 166.55 | 145.47 | 114.84 |
| T-2 | 40 | 284.14 ± 1.31 | 826 | 198.10 | 153.93 | 124.98 | |
| T-3 | 50 | 316.08 ± 2.73 | 837 | 204.67 | 156.97 | 128.88 | |
| T-4 | 60 | 333.74 ± 2.63 | 792 | 216.71 | 177.71 | 146.89 | |
| T-5 | Wire | 30 | 130.67 ± 1.52 | 76 | 110.62 | 112.49 | 112.12 |
| T-6 | 40 | 147.33 ± 1.33 | 55 | 117.50 | 130.83 | 129.35 | |
| T-7 | 50 | 151.83 ± 3.29 | 39 | 114.35 | 121.06 | 117.01 | |
| T-8 | 60 | 162.73 ± 2.73 | 33 | 120.52 | 121.06 | 118.46 | |
| T-9 | Network cable | 30 | 463.59 ± 3.46 | 360 | 53.03 | 75.07 | 180.10 |
| T10 | 40 | 653.03 ± 5.17 | 264 | 69.48 | 144.08 | 247.42 | |
| T-11 | 50 | 644.63 ± 2.89 | 235 | 90.65 | 190.67 | 296.59 | |
| T-12 | 60 | 676.31 ± 3.68 | 213 | 95.29 | 213.88 | 325.40 | |
| T-13 | Optical fiber | 30 | 206.51 ± 1.89 | 46 | 165.90 | 161.01 | 150.87 |
| T-14 | 40 | 217.36 ± 1.74 | 44 | 170.56 | 159.79 | 145.38 | |
| T-15 | 50 | 242.87 ± 2.65 | 31 | 192.27 | 167.41 | 148.99 | |
| T-16 | 60 | 261.72 ± 2.56 | 32 | 202.46 | 179.65 | 158.29 |
| THR (MJ/m2) | Intensity of External Heat Radiation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 kW/m2 | 40 kW/m2 | 50 kW/m2 | 60 kW/m2 | |
| Electrical cable | 245.47 | 259.33 | 266.89 | 262.26 |
| Wire | 71.88 | 65.07 | 59.63 | 63.49 |
| Network cable | 127.21 | 120.33 | 121.77 | 122.31 |
| Optical fiber | 77.13 | 69.41 | 70.74 | 73.71 |
| Value | Total Heat Release (THR) | X0 Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| 0.1–1 | Ultra-low risk | Low risk |
| 1–10 | Low risk | Medium risk |
| 10–100 | Medium risk | High risk |
| 100–1000 | High risk | -- |
| NO. | Type | Intensity of External Heat Radiation (kW/m2) | TTI (s) | THR (MJ/m2) | X0 Parameter | Overview |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-1 | Electrical cable | 30 | 37 | 245.47 ± 1.26 high risk | 6.59 medium risk | Medium to high risk |
| T-2 | 40 | 25 | 259.33 ± 1.28 high risk | 11.37 high risk | high risk | |
| T-3 | 50 | 18 | 266.89 ± 2.11 high risk | 17.56 high risk | high risk | |
| T-4 | 60 | 15 | 262.26 ± 2.34 high risk | 22.25 high risk | high risk | |
| T-5 | Wire | 30 | 54 | 71.88 ± 0.57 medium risk | 2.42 medium risk | medium risk |
| T-6 | 40 | 33 | 65.07 ± 0.82 medium risk | 4.46 medium risk | medium risk | |
| T-7 | 50 | 20 | 59.63 ± 1.58 medium risk | 7.59 medium risk | medium risk | |
| T-8 | 60 | 13 | 63.49 ± 2.10 medium risk | 12.52 high risk | Medium to high risk | |
| T-9 | Network cable | 30 | 151 | 127.20 ± 1.07 high risk | 3.07 medium risk | Medium to high risk |
| T10 | 40 | 77 | 120.33 ± 1.82 high risk | 8.48 medium risk | Medium to high risk | |
| T-11 | 50 | 49 | 121.77 ± 2.42 high risk | 13.16 high risk | high risk | |
| T-12 | 60 | 46 | 122.31 ± 2.26 high risk | 14.74 high risk | high risk | |
| T-13 | Optical fiber | 30 | 19 | 77.13 ± 1.52 medium risk | 10.87 high risk | Medium to high risk |
| T-14 | 40 | 12 | 69.41 ± 1.95 medium risk | 18.21 high risk | Medium to high risk | |
| T-15 | 50 | 8 | 70.74 ± 2.49 medium risk | 30.36 high risk | Medium to high risk | |
| T-16 | 60 | 8 | 73.70 ± 2.76 medium risk | 32.71 high risk | Medium to high risk |
| NO. | Type | Intensity of External Heat Radiation (kW/m2) | CO Peak (ppm) | FED = [CO]/5000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-1 | Electrical cable | 30 | 250.7 ± 1.50 | 0.0501 |
| T-2 | 40 | 256.5 ± 1.28 | 0.0513 | |
| T-3 | 50 | 269.3 ± 2.11 | 0.0539 | |
| T-4 | 60 | 308.3 ± 2.08 | 0.0617 | |
| T-5 | Wire | 30 | 208.4 ± 1.02 | 0.0417 |
| T-6 | 40 | 253.2 ± 1.54 | 0.0506 | |
| T-7 | 50 | 262.9 ± 2.17 | 0.0526 | |
| T-8 | 60 | 322.8 ± 3.01 | 0.0646 | |
| T-9 | Network cable | 30 | 101.5 ± 1.21 | 0.0203 |
| T10 | 40 | 133.4 ± 1.36 | 0.0267 | |
| T-11 | 50 | 168.4 ± 2.27 | 0.0337 | |
| T-12 | 60 | 217.3 ± 2.51 | 0.0435 | |
| T-13 | Optical fiber | 30 | 253.5 ± 1.23 | 0.0507 |
| T-14 | 40 | 302.8 ± 1.55 | 0.0606 | |
| T-15 | 50 | 328.0 ± 1.87 | 0.0656 | |
| T-16 | 60 | 346.9 ± 2.14 | 0.0694 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, B.; Yang, C.; Long, H. Research on the Fire Hazard of Different Cables Based on Cone Calorimetry. Fire 2023, 6, 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire6110431
Shi B, Yang C, Long H. Research on the Fire Hazard of Different Cables Based on Cone Calorimetry. Fire. 2023; 6(11):431. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire6110431
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Bobo, Chenyang Yang, and Haifan Long. 2023. "Research on the Fire Hazard of Different Cables Based on Cone Calorimetry" Fire 6, no. 11: 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire6110431








