Deep Dyna-Q for Rapid Learning and Improved Formation Achievement in Cooperative Transportation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
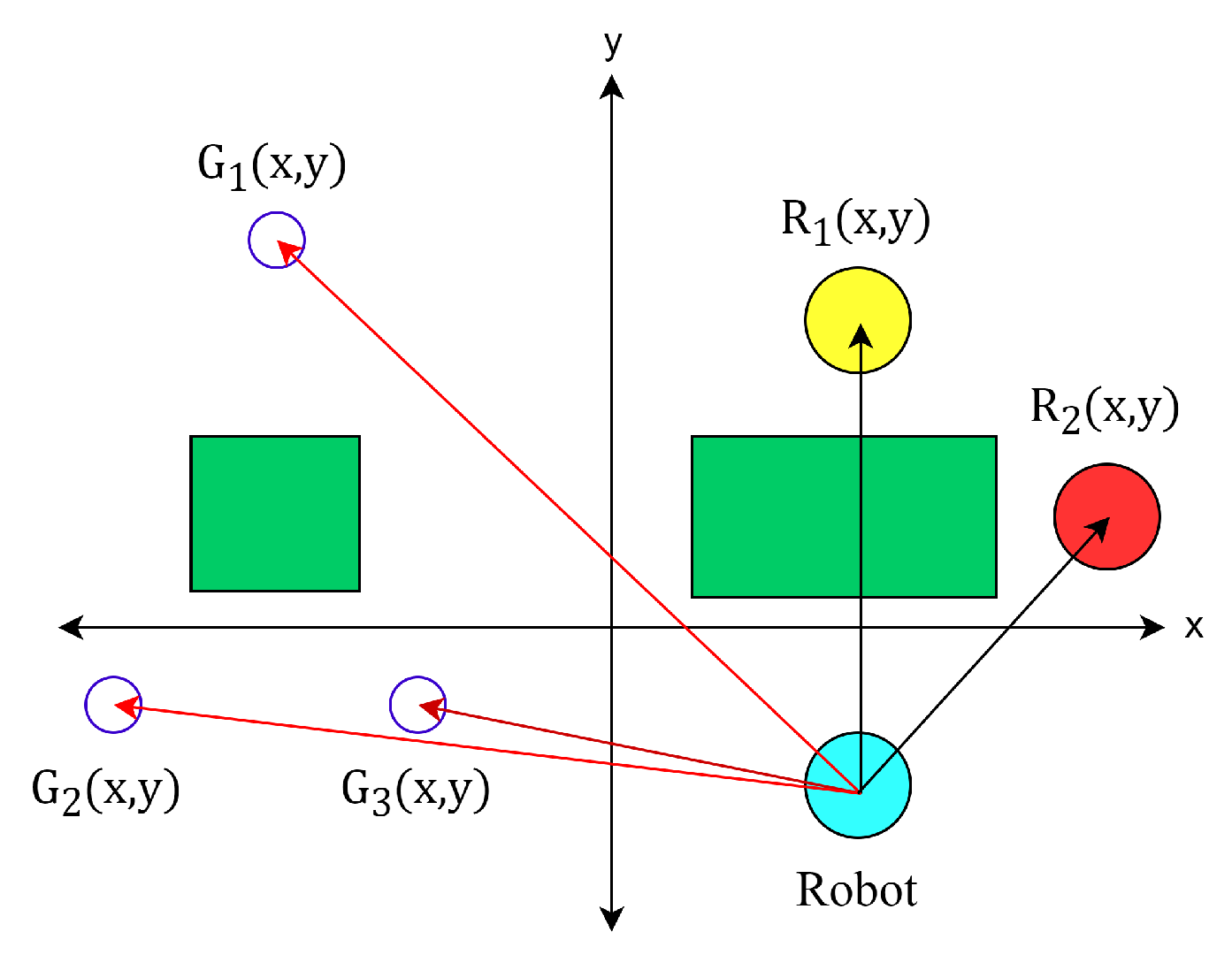
2. OpenAI Gym for a Simulated System
3. Configuration of Deep Dyna-Q for Formation Change
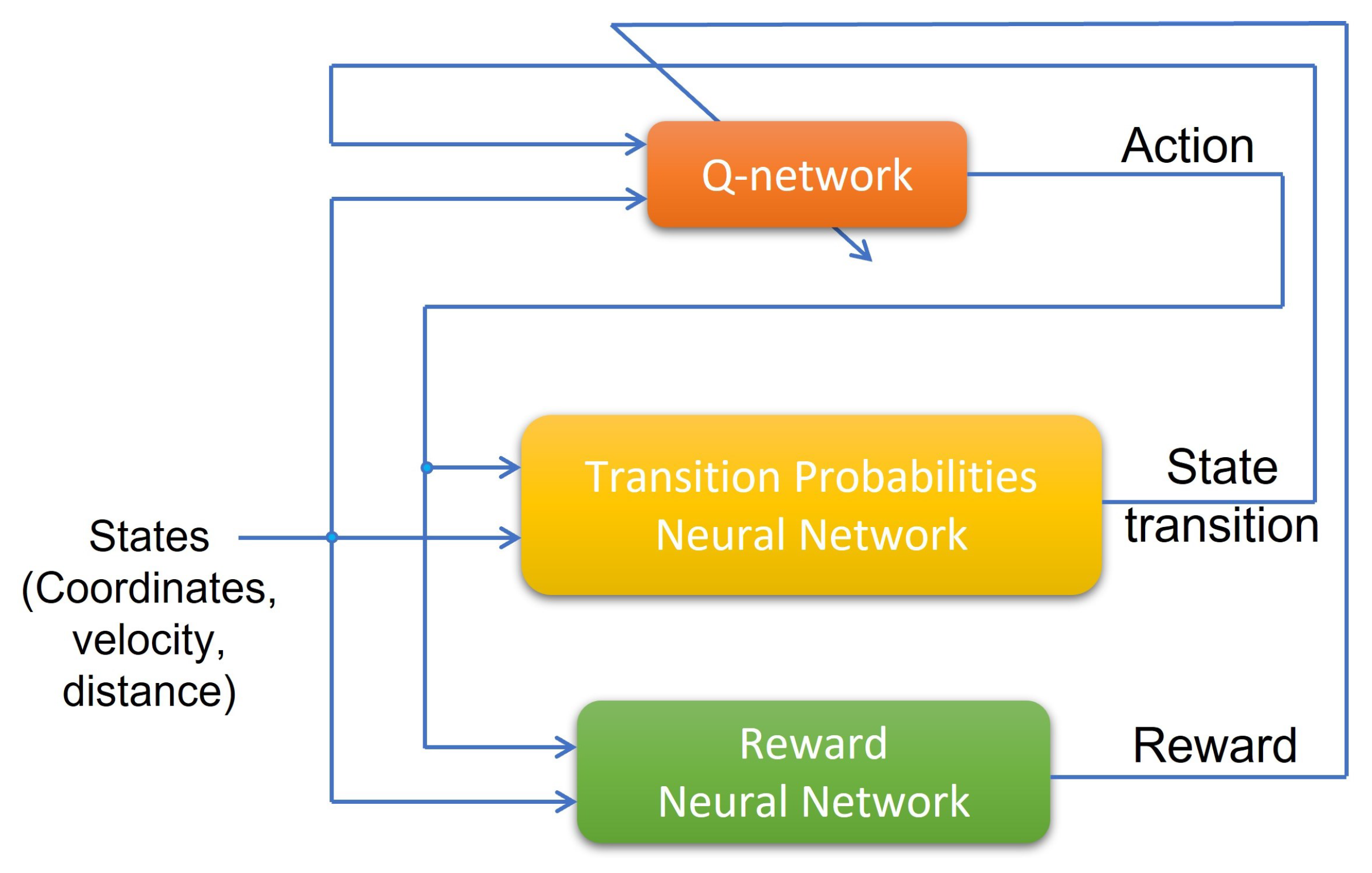
3.1. Deep Dyna-Q
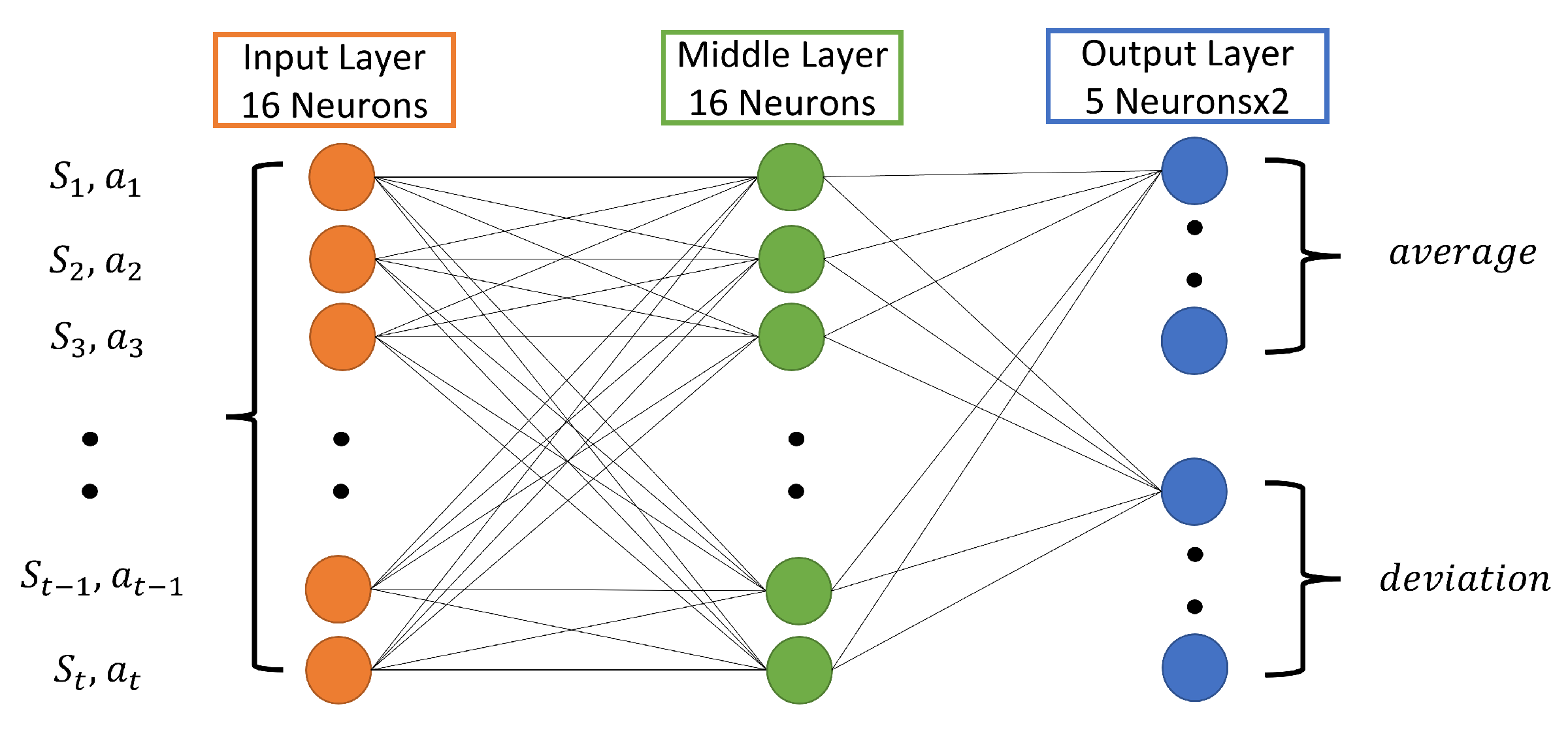
3.2. Learning Method and Neural Network Construction
4. Simulation Results
4.1. Transition of Rewards
4.2. Discount Rate Tuning
4.3. Learning Rate Tuning
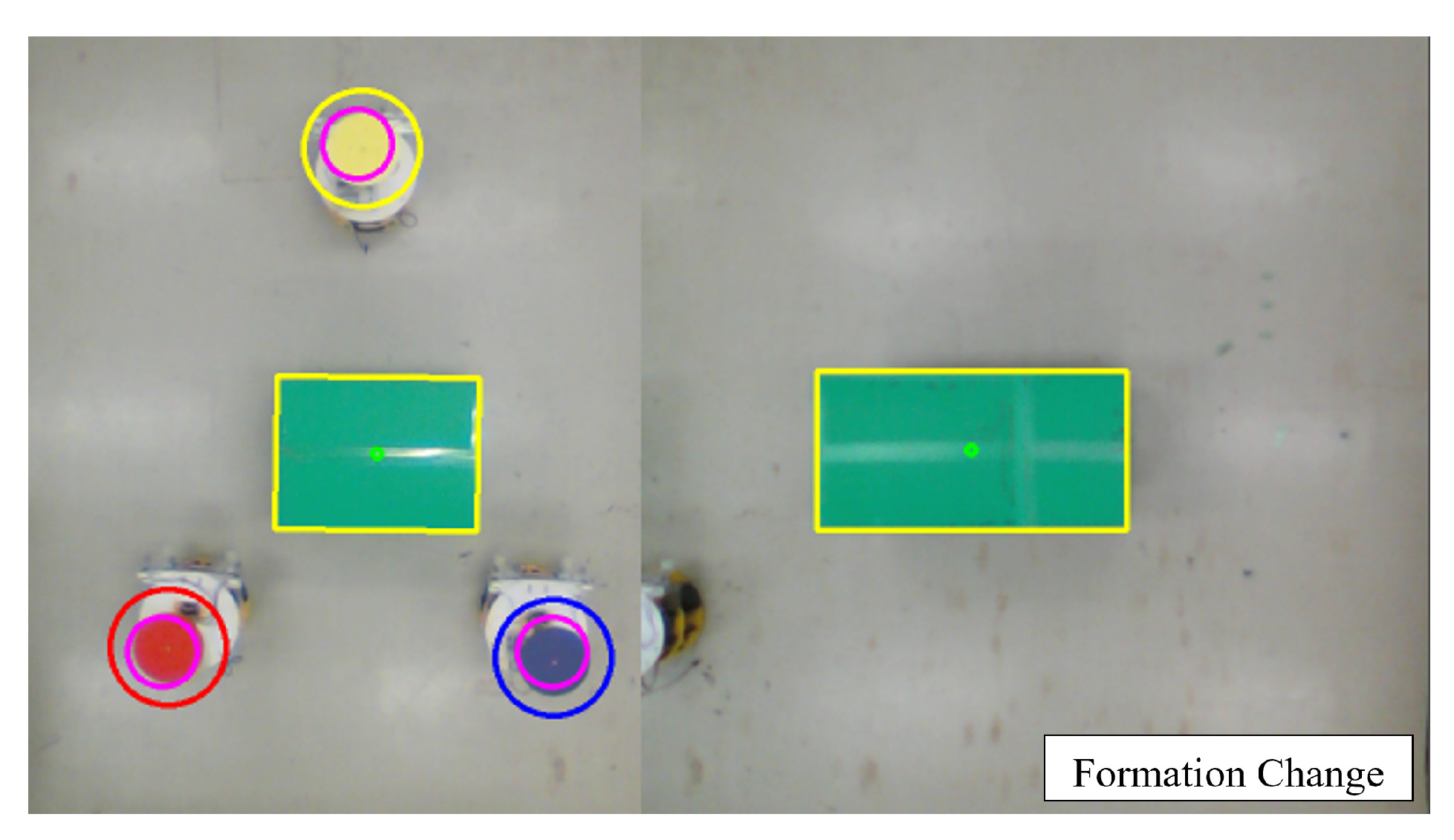
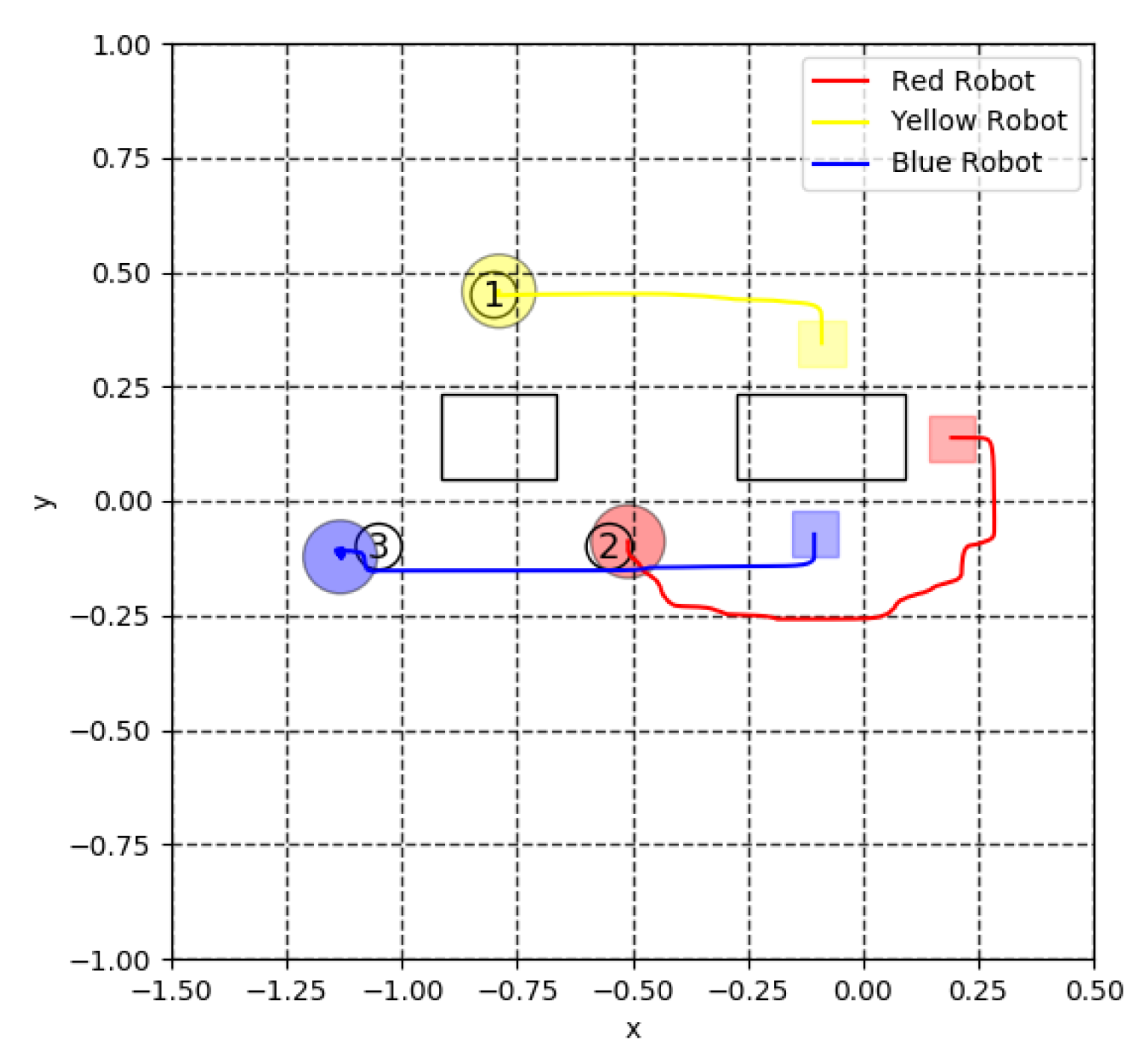
5. Experiment for Cooperative Transportation
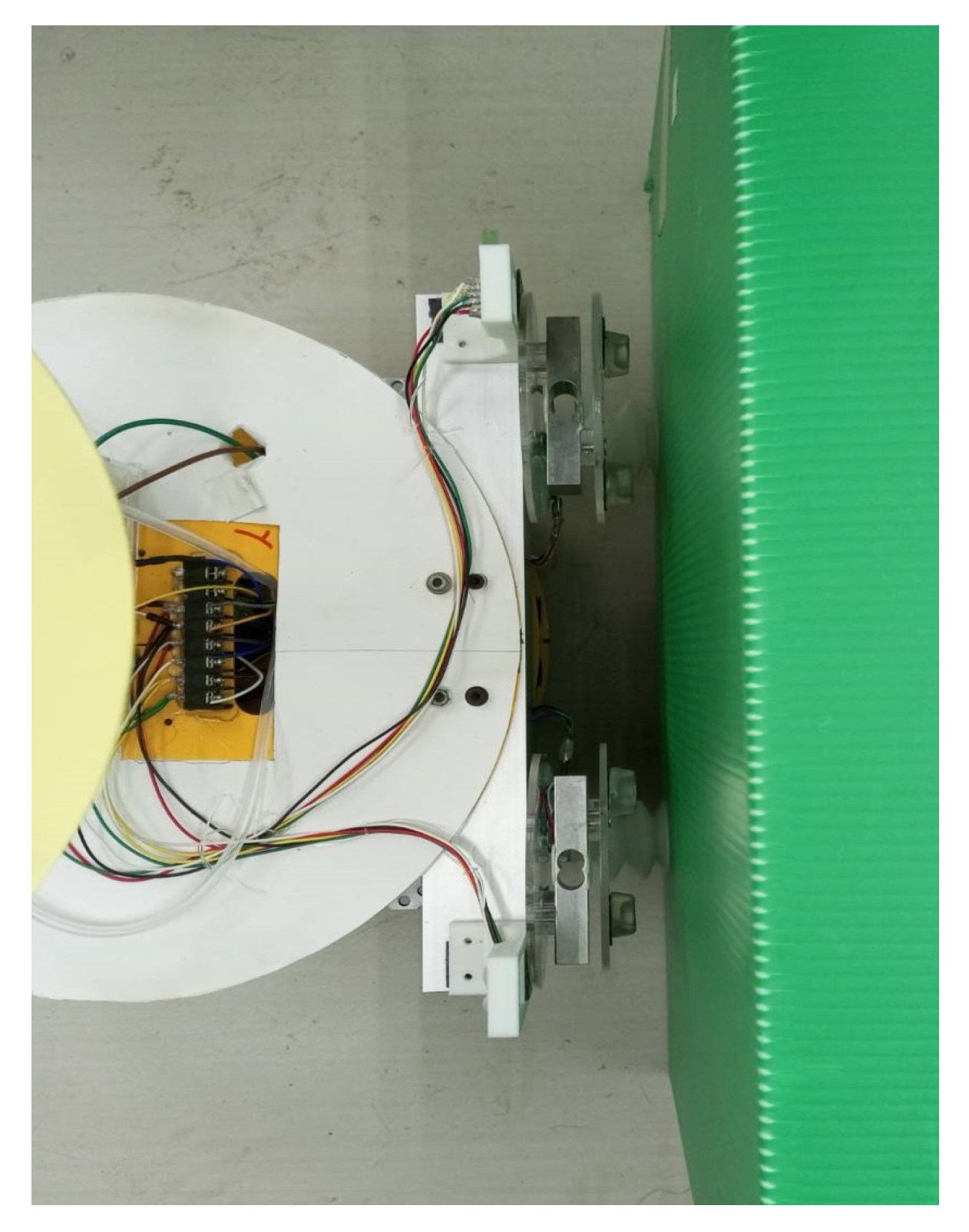
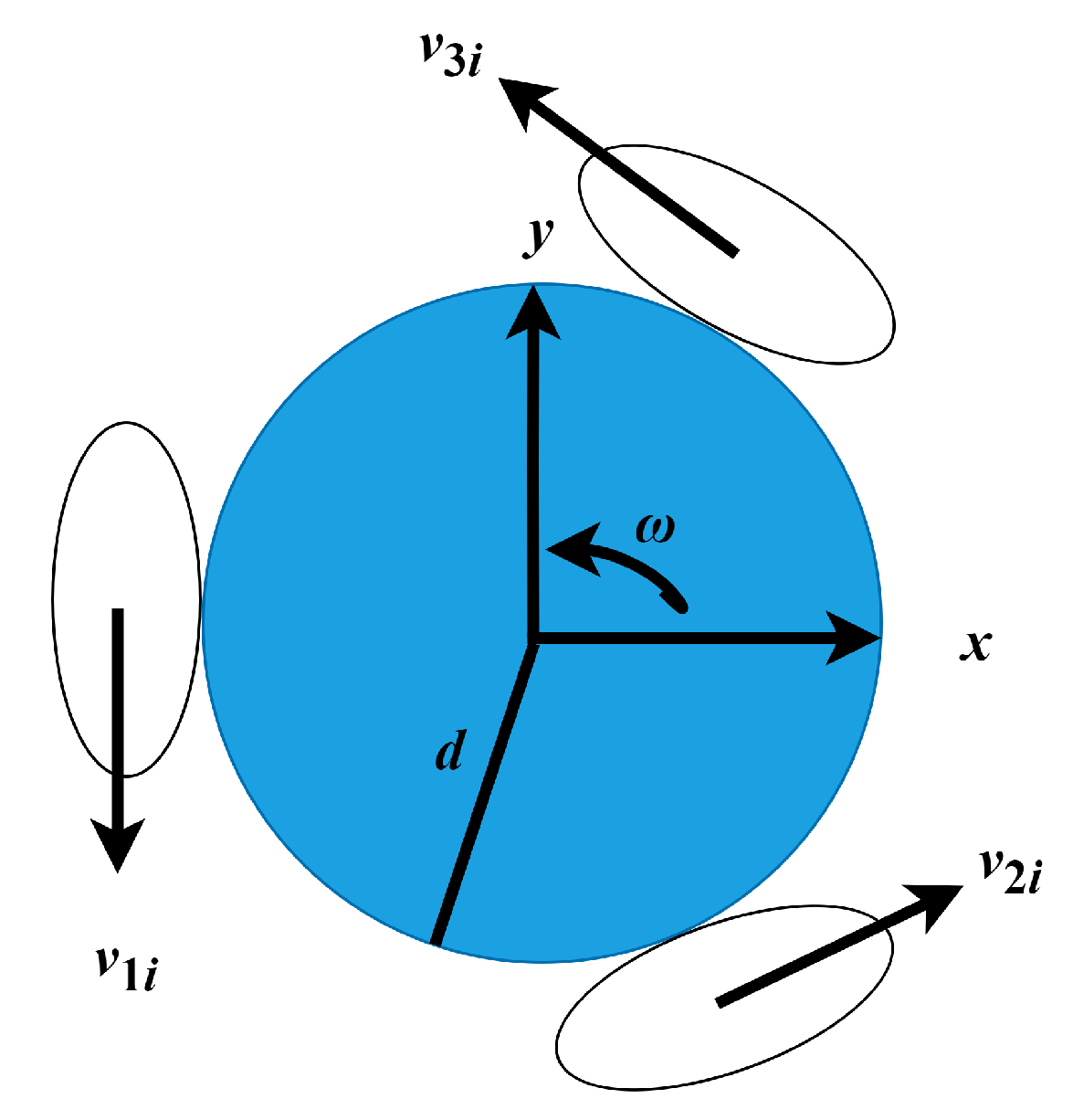
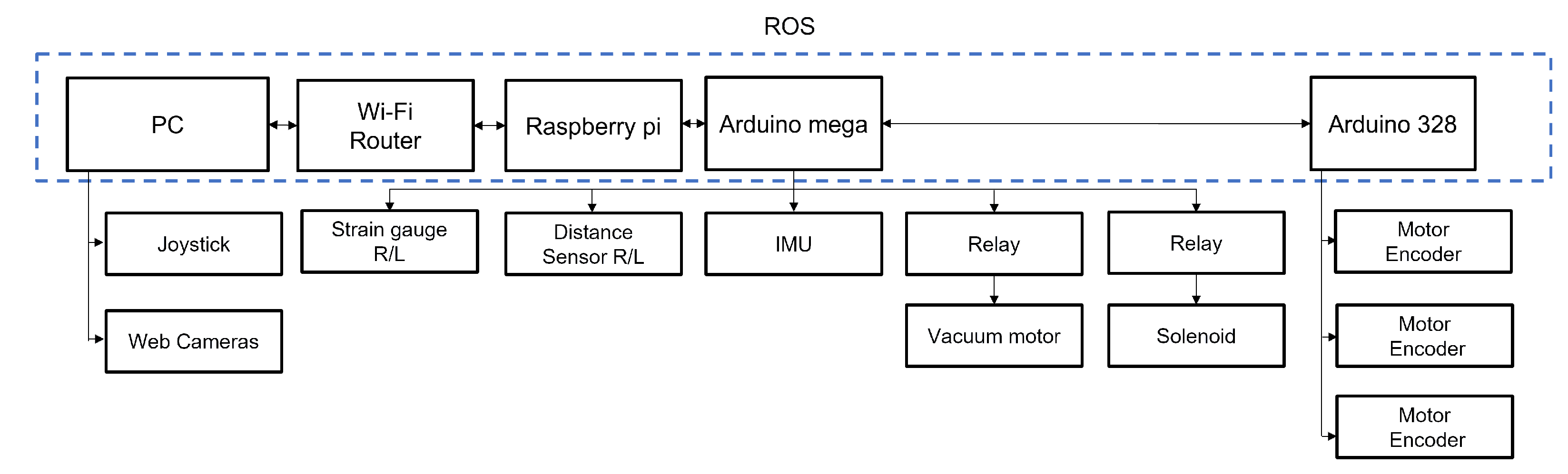
5.1. Robot Mechanism
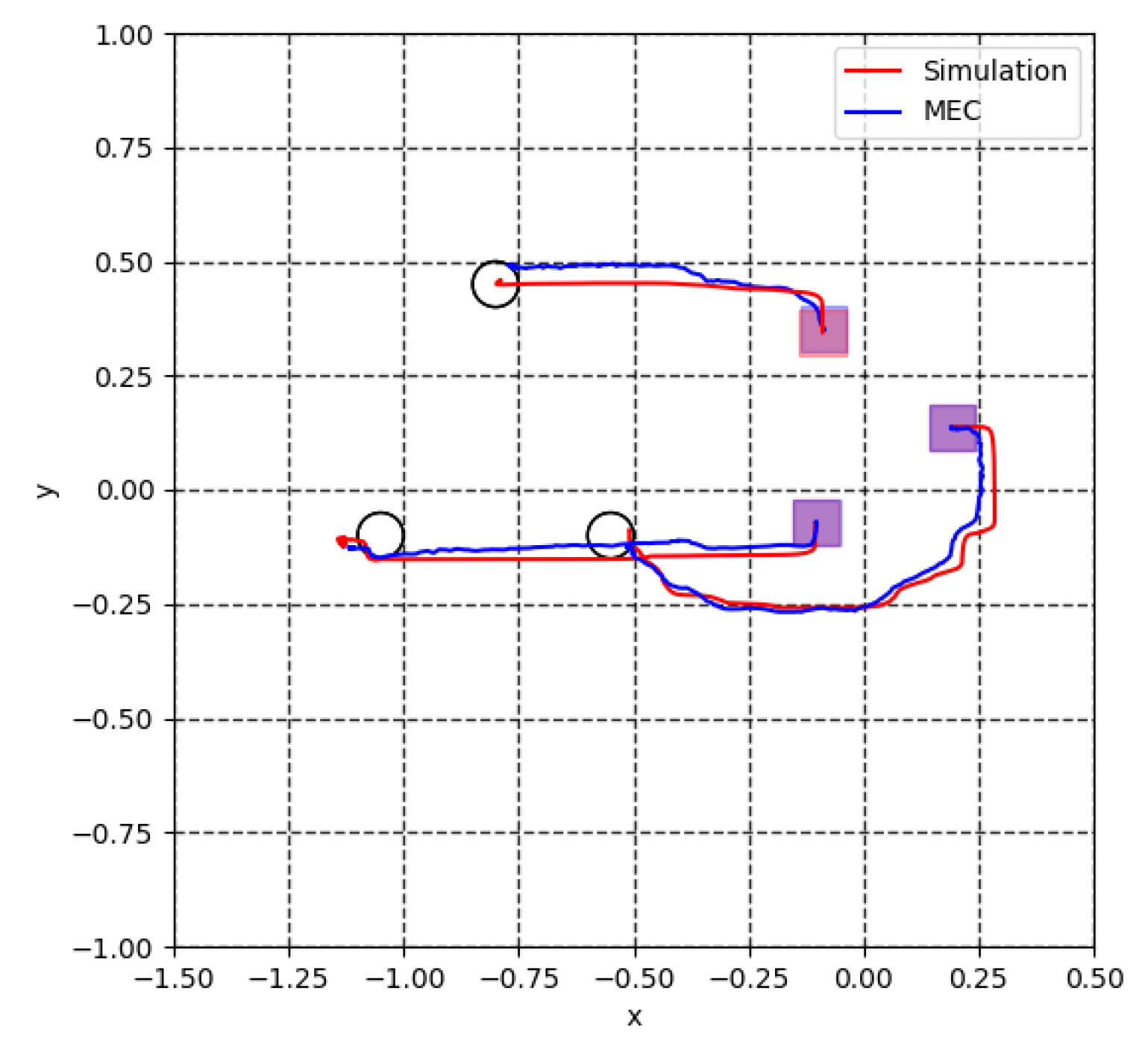
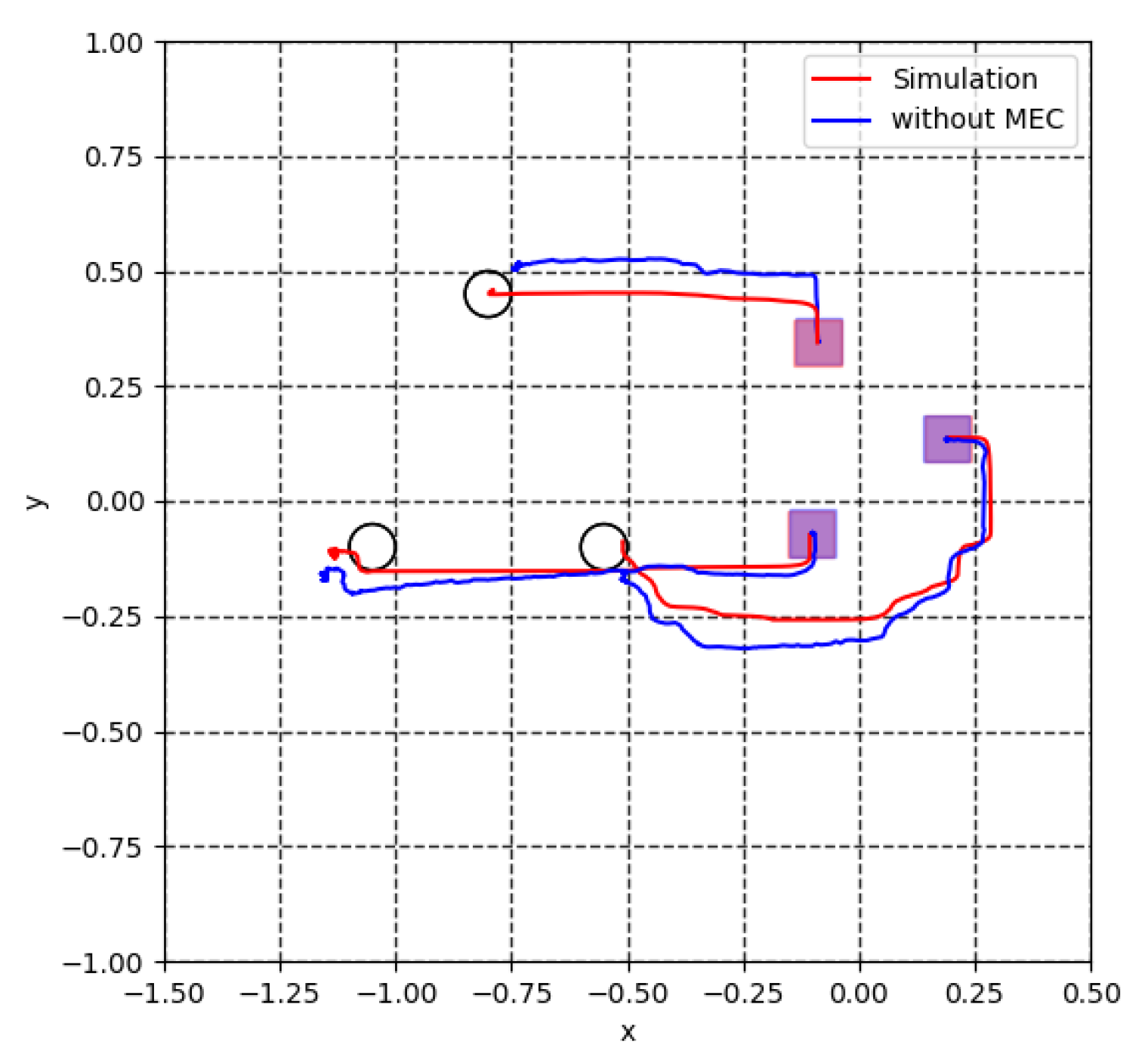
5.2. Model Error Compensator (MEC)
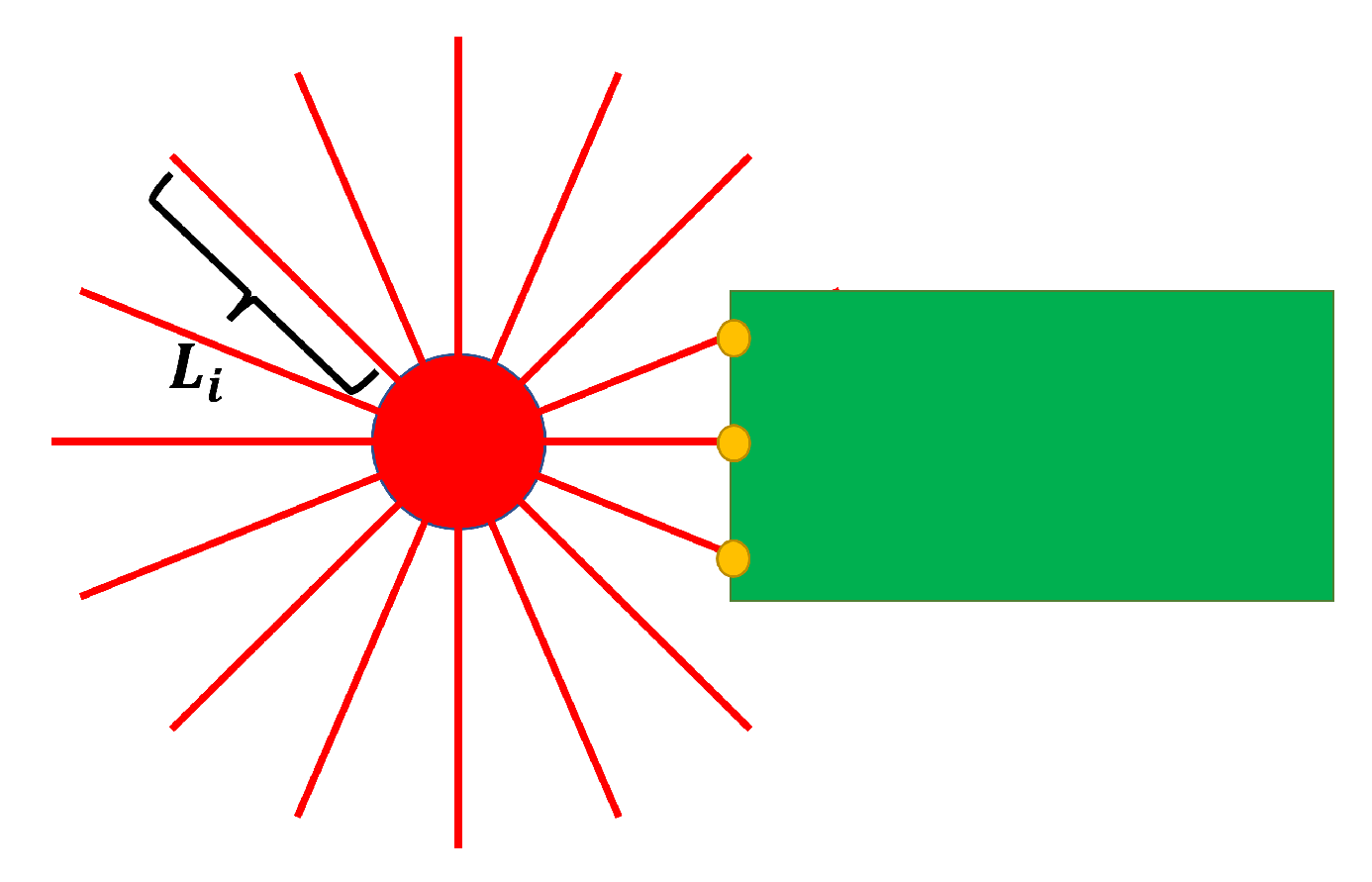
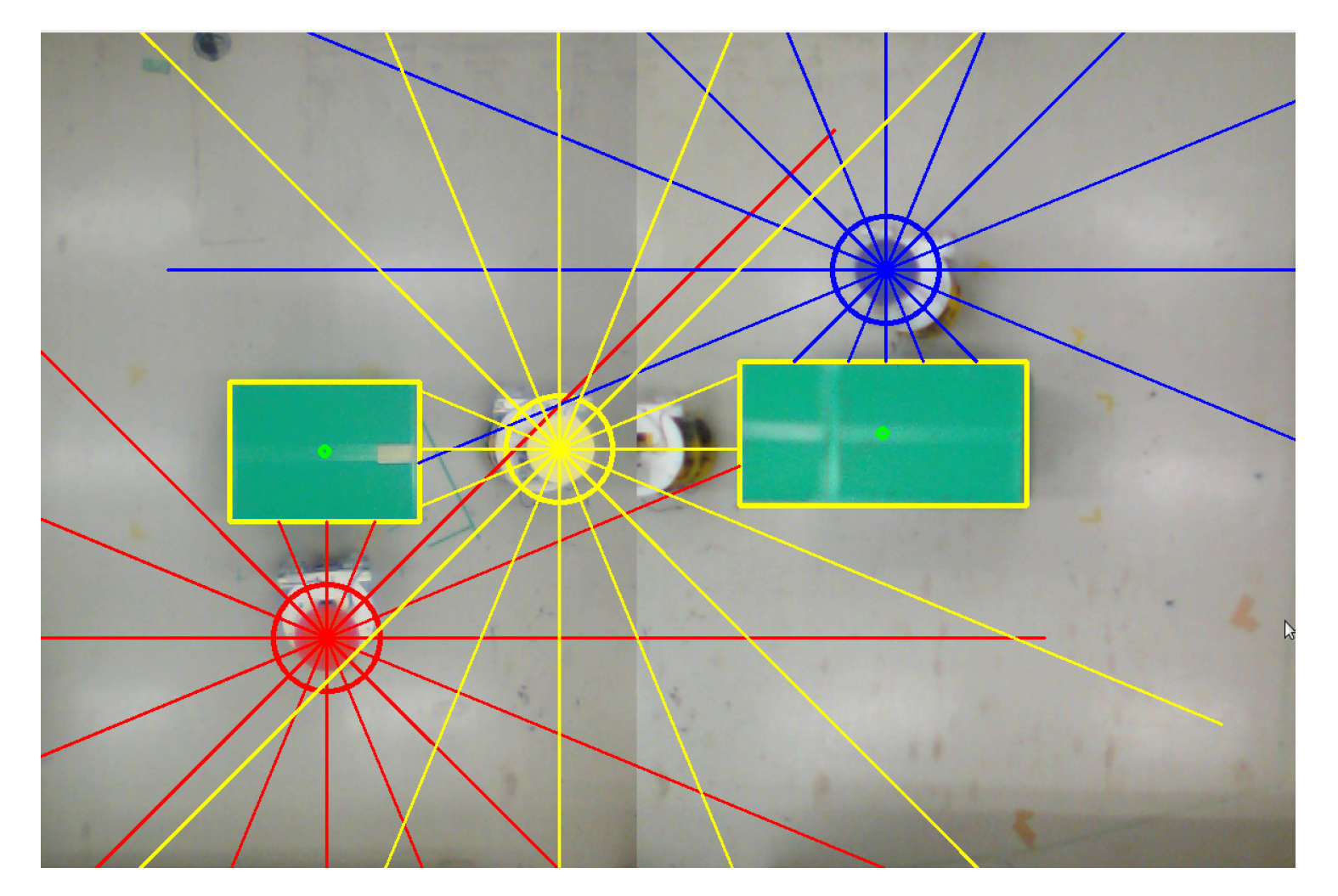
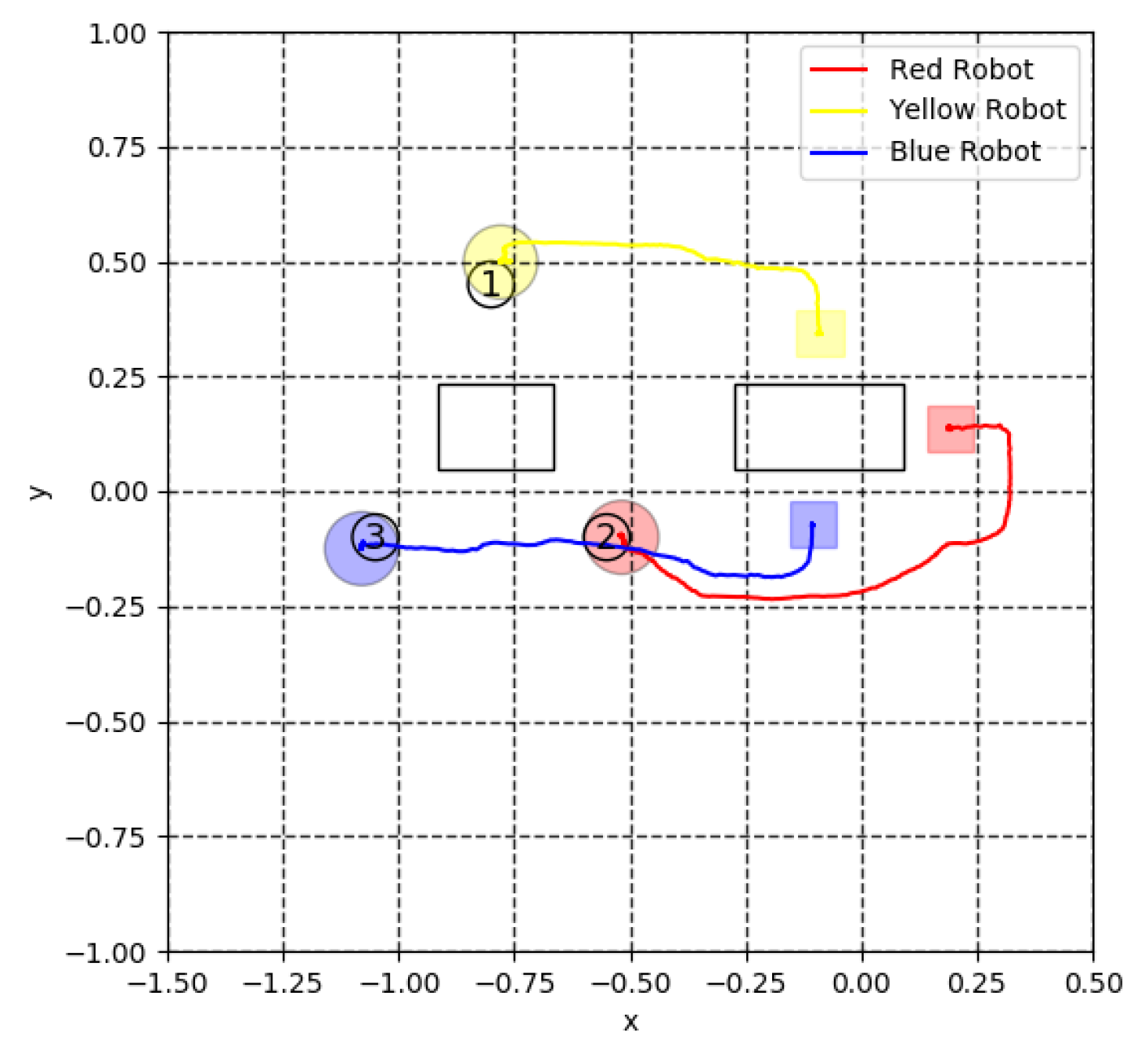
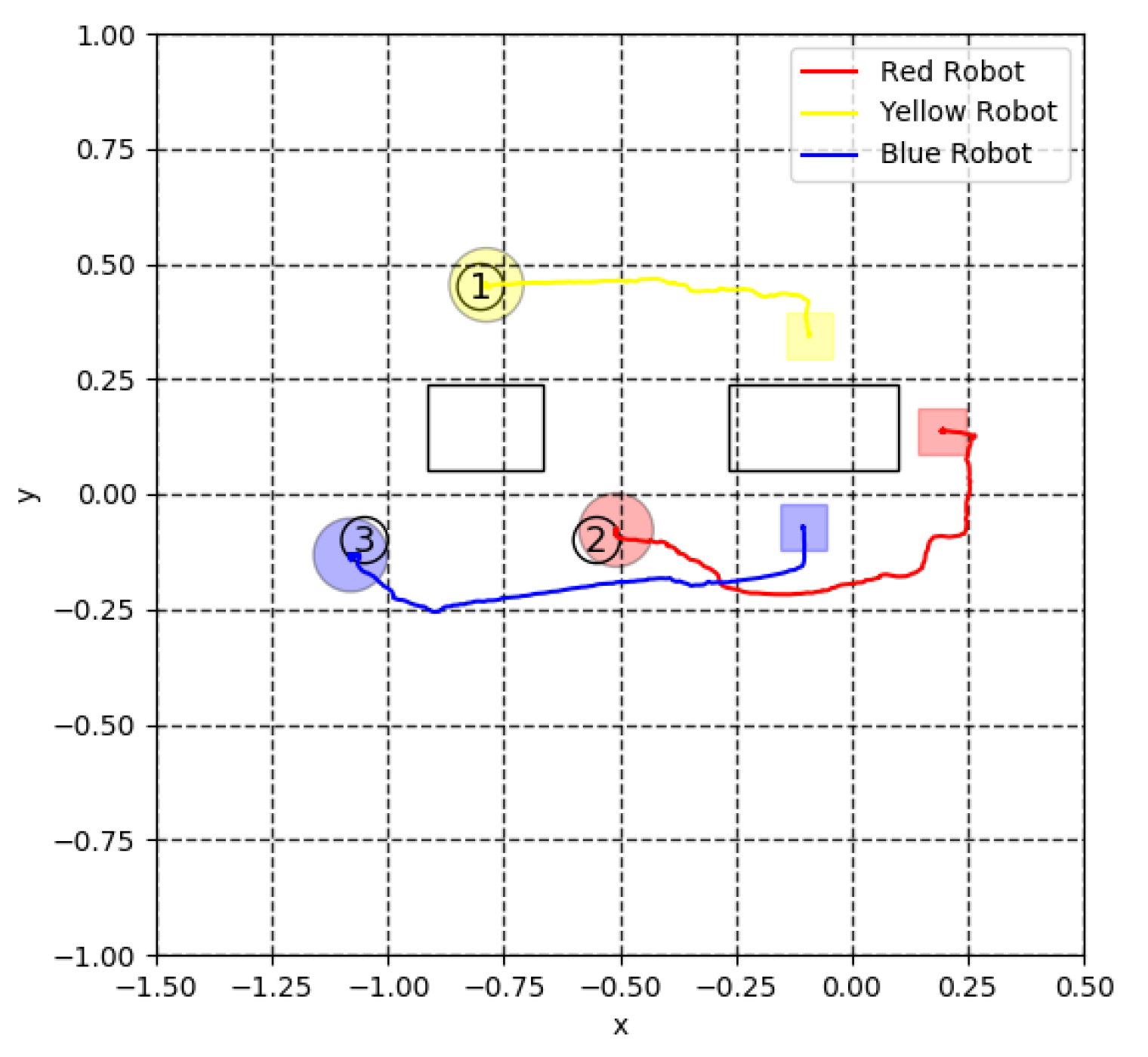
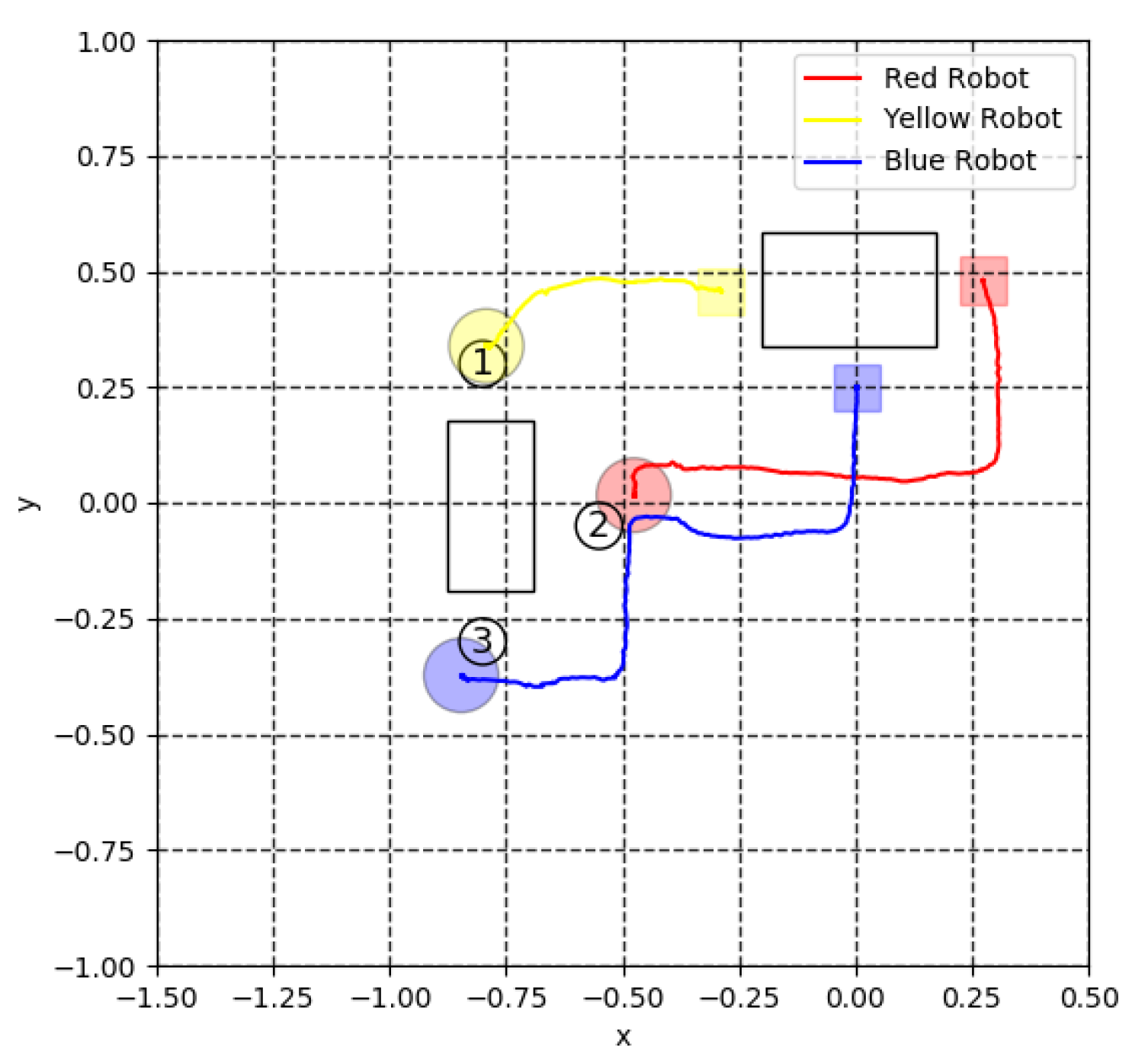
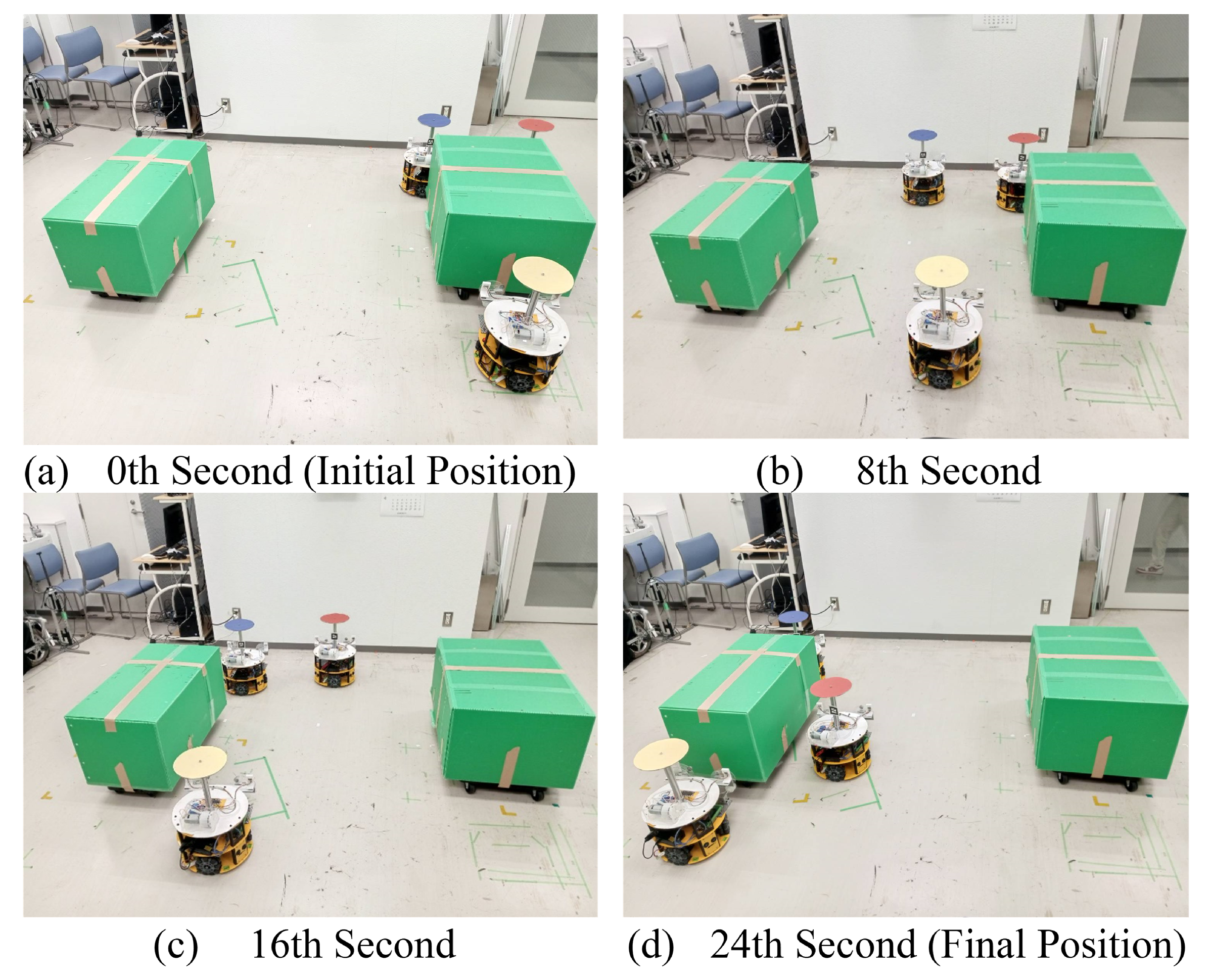
5.3. Virtual Lidar and Actual Experiment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kamel, M.A.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y. Formation Control and Coordination of Multiple Unmanned Ground Vehicles in Normal and Faulty Situations: A Review. Annu. Rev. Control 2020, 49, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, L.; Bai, X.; Yang, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, S. A Low-Cost Solution for Leader-Follower Formation Control of Multi-UAV System Based on Pixhawk. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1754, 012081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Huang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, S.; Nie, Y.; Tang, J.; Zhu, S. A Novel Virtual-Structure Formation Control Design for Mobile Robots with Obstacle Avoidance. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Chwa, D. Decentralized Behavior-Based Formation Control of Multiple Robots Considering Obstacle Avoidance. Intell. Serv. Robot. 2018, 11, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade, P.; Cunha, R.; Batista, P. Distributed Formation Control of Double-Integrator Vehicles with Disturbance Rejection. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2020, 53, 3118–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Liu, Z.; Bhamara, R. Collaborative Multi-Robot Formation Control and Global Path Optimization. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najm, A.A.; Ibraheem, I.K.; Azar, A.T.; Humaidi, A.J. Genetic Optimization-Based Consensus Control of Multi-Agent 6-Dof Uav System. Sensors 2020, 20, 3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorge, D.R.; Daniel, R.-R.; Jesus, H.-B.; Marco, P.-C.; Alma, Y.A. Formation Control of Mobile Robots Based on Pin Control of Complex Networks. Automation 2022, 10, 898. [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Resendiz, J.F.; Avilés, D.; Aranda-Bricaire, E. Formation Control for Second-Order Multi-Agent Systems with Collision Avoidance. Machines 2023, 11, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, S.; Uchibe, E.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Nakanishi, K.; Yasui, Y.; Ishii, S. Constrained Deep Q-Learning Gradually Approaching Ordinary Q-Learning. Front. Neurorobot. 2019, 13, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ikemoto, J.; Ushio, T. Continuous Deep Q-Learning with a Simulator for Stabilization of Uncertain Discrete-Time Systems. Nonlinear Theory Appl. 2021, 12, 738–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ulmer, M.W.; Thomas, B.W. Deep Q-Learning for Same-Day Delivery with Vehicles and Drones. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2022, 298, 939–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hester, T.; Deepmind, G.; Pietquin, O.; Lanctot, M.; Schaul, T.; Horgan, D.; Quan, J.; Sendonaris, A.; Dulac-Arnold, G.; Agapiou, J.; et al. Deep Q-Learning from Demonstrations. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; pp. 3223–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yin, K.; Zhang, R.; Huang, Z.; Wang, P. Dynamic Reward-Based Dueling Deep Dyna-Q: Robust Policy Learning in Noisy Environments. In Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2020), New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 9676–9684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, K.; Matsunaga, N.; Murata, K. Formation Path Learning for Cooperative Transportation of Multiple Robots Using MADDPG. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems, Jeju, Republic of Korea, 12–15 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Pitis, S. Rethinking the Discount Factor in Reinforcement Learning: A Decision Theoretic Approach. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Third AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Thirty-First Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence Conference and Ninth AAAI Symposium on Educational Advances In Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fedus, W.; Gelada, C.; Bengio, Y.; Bellemare, M.G.; Larochelle, H. Hyperbolic Discounting and Learning over Multiple Horizons. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.06865. [Google Scholar]
- Amit, R.; Meir, R.; Ciosek, K. Discount Factor as a Regularizer in Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Online, 13–18 July 2020; pp. 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, A.B.; Lin, C.-Y.; Tseng, Y.-C.; Van, L.-D.; Hu, W.-H.; Yu, C.-H. Accuracy-Time Efficient Hyperparameter Optimization Using Actor-Critic-based Reinforcement Learning and Early Stopping in OpenAI Gym Environment. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Internet of Things and Intelligence Systems (IoTaIS), Bali, Indonesia, 24–26 November 2022; pp. 230–234. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, R.; Wu, Y.; Tamar, A.; Harb, J.; Abbeel, P.; Mordatch, I. Multi-Agent Actor-Critic for Mixed Cooperative-Competitive Environments. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 6380–6391. [Google Scholar]
- Jaensch, F.; Klingel, L.; Verl, A. Virtual Commissioning Simulation as OpenAI Gym—A Reinforcement Learning Environment for Control Systems. In Proceedings of the 2022 5th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Industries (AI4I), Laguna Hills, CA, USA, 19–21 September 2022; pp. 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Budiyanto, A.; Azetsu, K.; Miyazaki, K.; Matsunaga, N. On Fast Learning of Cooperative Transport by Multi-Robots Using DeepDyna-Q. In Proceedings of the SICE Annual Conference, Kumamoto, Japan, 6–9 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, R.S.; Barto, A.G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction, 2nd ed.; MIT Press: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bergstra, G.; Bengio, Y. Random search for hyper-parameter optimization. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2012, 13, 281–305. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, B.; Li, X.; Gao, J.; Liu, J.; Wong, K.-F. Deep Dyna-Q: Integrating Planning for Task-Completion Dialogue Policy Learning. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Long Papers), Melbourne, Australia, 15–20 July 2018; pp. 2182–2192. [Google Scholar]
- Su, S.-Y.; Li, X.; Gao, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.-N. Discriminative Deep Dyna-Q: Robust Planning for Dialogue Policy Learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Almasri, E.; Uyguroğlu, M.K. Modeling and Trajectory Planning Optimization for the Symmetrical Multiwheeled Omnidirectional Mobile Robot. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, R.; Tanigawa, Y.; Okajima, H.; Matsunaga, N. A design method of model error compensator for systems with polytopic-type uncertainty and disturbances. SICE J. Control Meas. Syst. Integr. 2021, 14, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







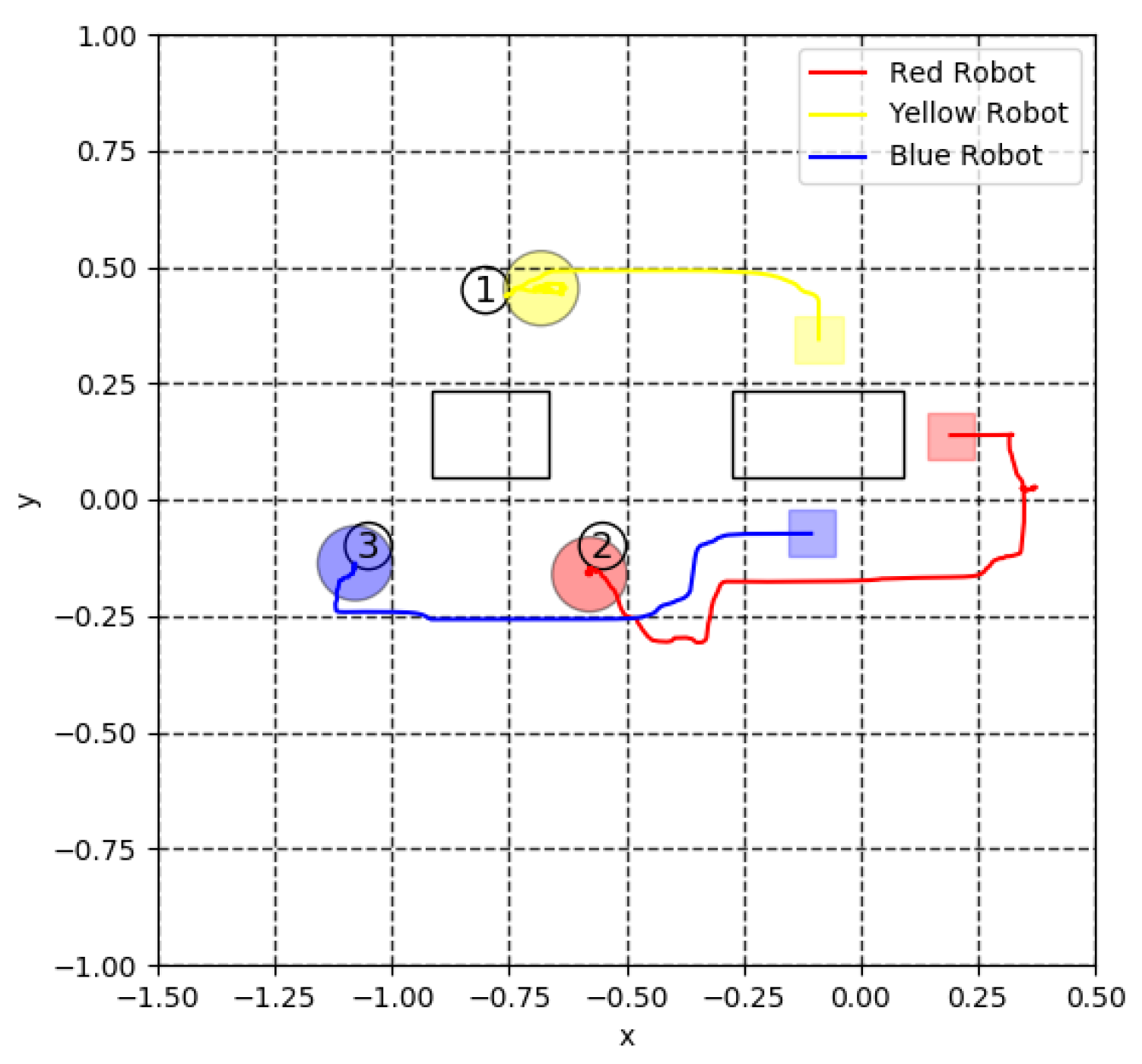


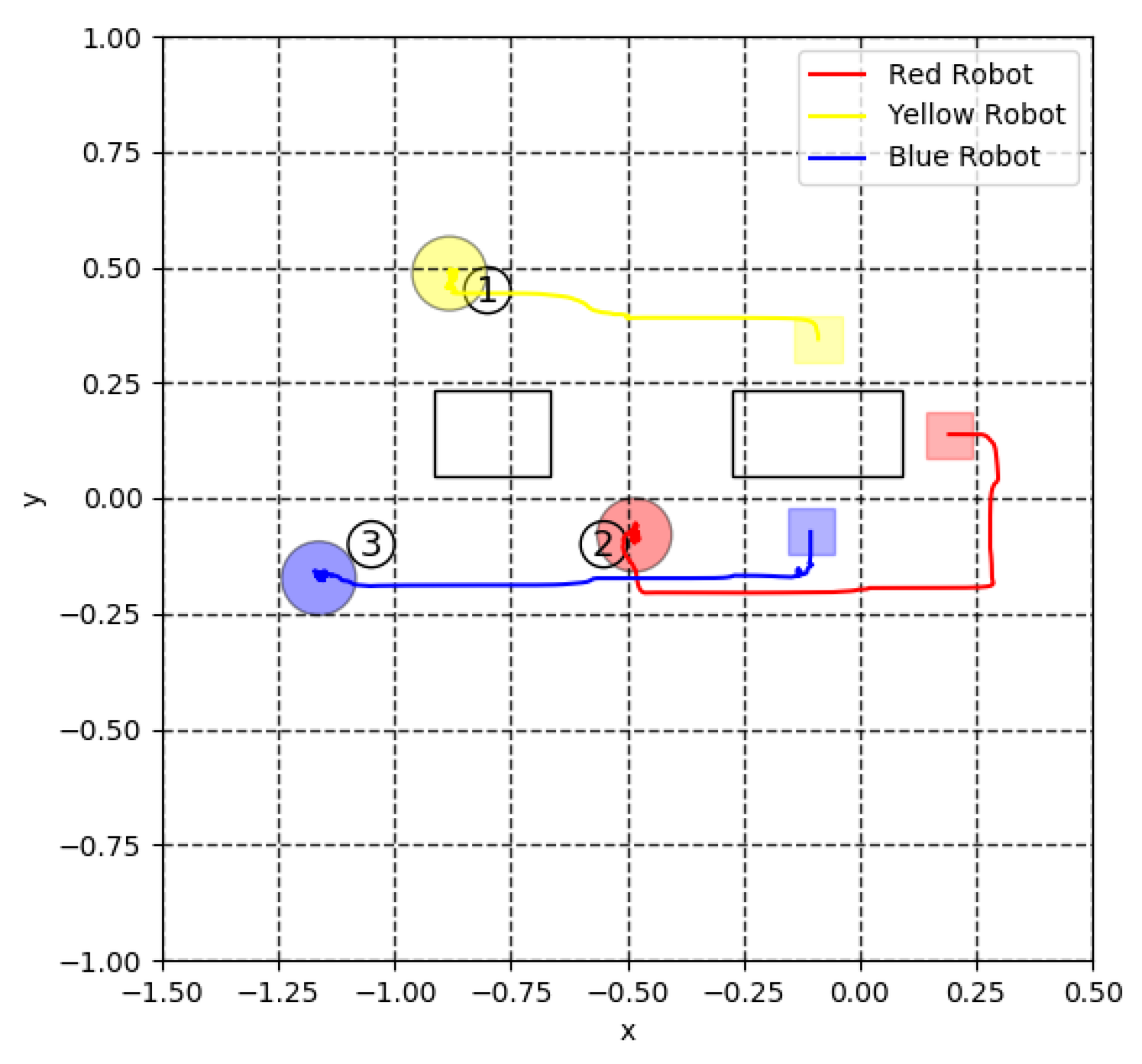
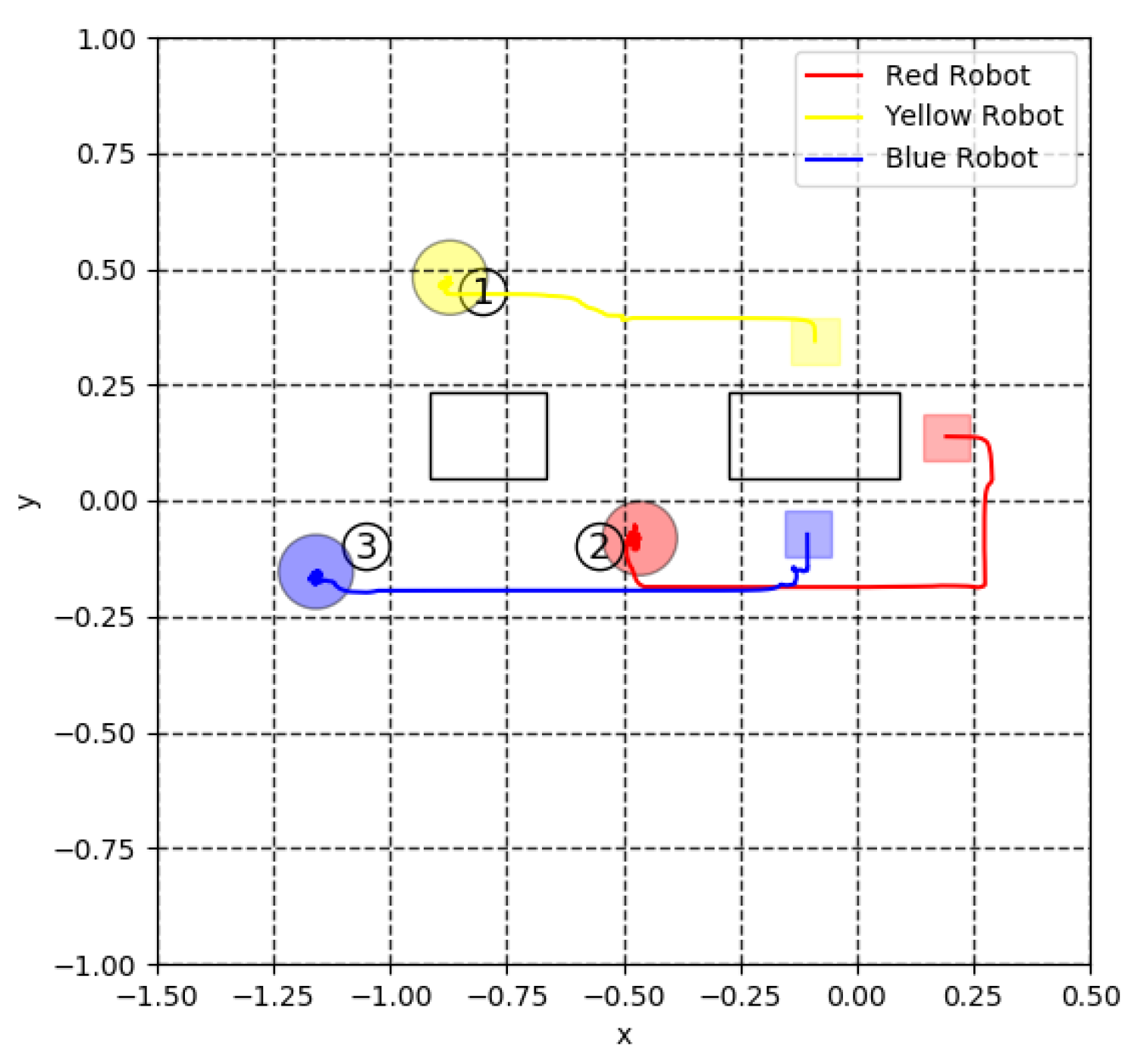



| Evaluation | 0.85 | 0.9 | 0.95 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Formation change achievement rate | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Collision number among agents | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Collision number between agents and transport objects | 1.35 | 1.01 | 1.23 |
| Evaluation | DDQ (0.001) | DDQ (0.01) | DDQ (0.04) | DDQ (0.08) | DQN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formation change achievement rate | 94% | 100% | 72% | 10% | 91% |
| Collision number among agents | 0 | 0 | 0.76 | 0.92 | 0.06 |
| Collision number between agents and transport objects | 2.15 | 1.01 | 1.75 | 3.01 | 3.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Budiyanto, A.; Matsunaga, N. Deep Dyna-Q for Rapid Learning and Improved Formation Achievement in Cooperative Transportation. Automation 2023, 4, 210-231. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation4030013
Budiyanto A, Matsunaga N. Deep Dyna-Q for Rapid Learning and Improved Formation Achievement in Cooperative Transportation. Automation. 2023; 4(3):210-231. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation4030013
Chicago/Turabian StyleBudiyanto, Almira, and Nobutomo Matsunaga. 2023. "Deep Dyna-Q for Rapid Learning and Improved Formation Achievement in Cooperative Transportation" Automation 4, no. 3: 210-231. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation4030013
APA StyleBudiyanto, A., & Matsunaga, N. (2023). Deep Dyna-Q for Rapid Learning and Improved Formation Achievement in Cooperative Transportation. Automation, 4(3), 210-231. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation4030013








