Cutaneous Lymphoma Molecular Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management
A topical collection in Cells (ISSN 2073-4409).
Viewed by 57601Editors
2. President-Elect, Skin Research Group of Canada, Montreal, QC, Canada
Interests: cutaneous lymphoma; melanoma; basal cell carcinoma; carcinoma; squamous cell carcinoma
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: cutaneous lymphoma; psoriasis; genomics
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
2. Professor, LEO Foundation Skin Immunology Research Center; University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark
Interests: cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
Interests: cutaneous T-cell lymphoma; mycosis fungoides; Sézary Syndrome
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
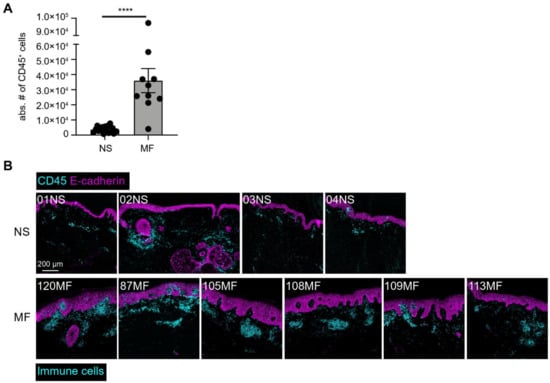
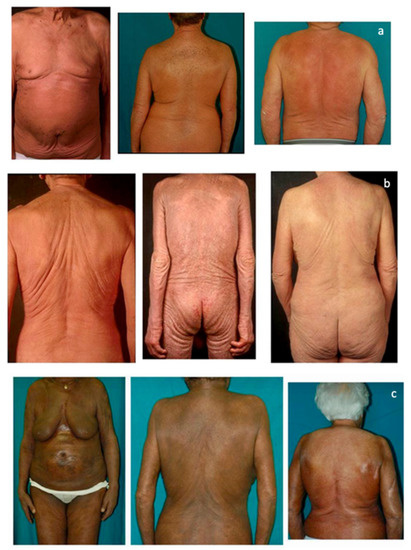
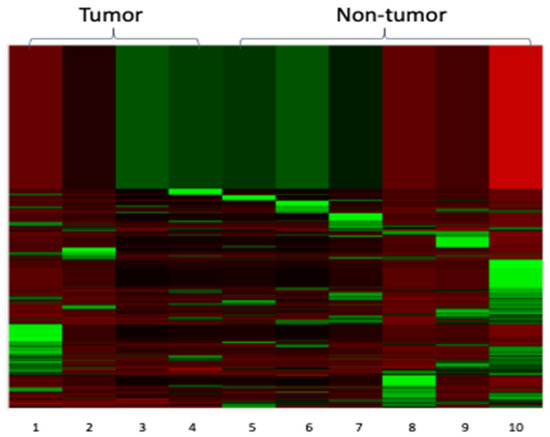
Primary cutaneous lymphomas are classified based on the type of malignant cells driving the disease process: primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas (PCBCLs) or primary cutaneous T-cell lymphomas (CTCL). CTCLs are a heterogeneous group of lymphoid malignancies derived from skin-homing T-cells. CTCLs account for 75% of all cutaneous lymphomas. While, Mycosis fungoides (MF), primary cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (and other CD30+ lymphoproliferative malignancies), and Sézary Syndrome represent the commonly recognized forms of the disease, other variants as defined by the WHO-EORTC classification are becoming increasingly prevalent (e.g., primary cutaneous CD4+ small/medium T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder and others). CTCL can be difficult to diagnose as it often mimics other dermatoses such as chronic eczema, psoriasis, drug eruptions, or skin infections. Skin biopsy and the detection of T-cell receptor (TCR) clonality are often not diagnostic for this malignancy. As a result, it takes on average ~6 years to establish the diagnosis of CTCL. Currently, there are no validated molecular markers to help identify this cancer and shorten the time to diagnosis. Furthermore, while >70% of patients present with stage I disease, only 20%–30% of them progress to higher stages. Currently, it is difficult to predict which patients will progress and which ones will experience an indolent disease course. Despite the available new treatments, the survival of patients with advanced CTCL remains poor (2–4 years).
PCBCL is a group of extranodal B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas that involve the skin. They account for approximately 25% of all cutaneous lymphomas and are classified as primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma (PCMZL), primary cutaneous follicle-center cell lymphoma (PCFCL), and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type (PCDLBCL, LT). Recently, Epstein–Barr virus positive (EBV+) mucocutaneous ulcer (EB-MCU) was added as a new provisional distinct entity. PCBCLs conventionally present as violaceous plaques, or nodules. Diagnosis requires skin biopsy and histological examination with appropriate immunohistochemical staining.
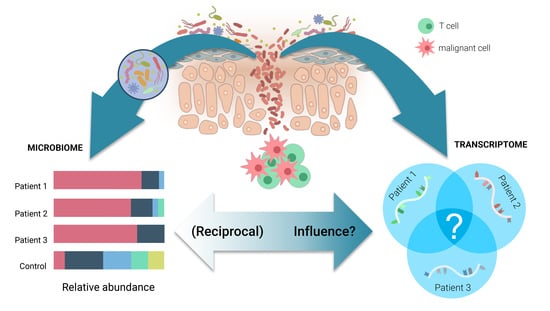
While certain external triggers/promoters (e.g., Borrelia burgdorferi for PCMZL, S. Aureus for CTCL or Human T-Cell Lymphotropic virus (HTLV-1) for Adult T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma) have been identified or suspected, the pathogenesis of both PCBCL and CTCL remains elusive. The field lacks reliable diagnostic markers for CTCL, or prognostic markers for both CTCL and PCBCL as well as novel therapeutic targets.
This Topical Collection is dedicated to research that can enhance our understanding of the molecular pathogenesis and evolution of cutaneous lymphomas, the genetics/genomic components of the disease, the diagnostic/prognostic markers, the role of the microbiome, as well as novel avenues for treating these challenging diseases.
Dr. Ivan V. Litvinov
Dr. Robert Gniadecki
Dr. Niels Ødum
Dr. Madeleine Duvic
Dr. Oleg Akilov
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cells is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- cutaneous lymphoma
- cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL)
- primary cutaneous B-cell lymphoma (PCBCL)
- pagetoid reticulosis
- folliculotropic mycosis fungoides
- granulomatous slack skin
- hypopigmented mycosis fungoides
- poikilodermatous mycosis fungoides
- erythodermic mycosis fungoides
- primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphomas
- primary cutaneous follicle center cell lymphomas
- primary cutaneous large B-cell lymphomas
- intravascular large B-cell lymphomas
- Sezary syndrome
- subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma
- lymphomatoid papulosis
- CD30-positive anaplastic large-cell lymphoma
- primary CD30-positive lymphoproliferative disorders
- extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma; nasal type
- adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma
- human T-cell lymphotropic virus (HTLV)
- thymocyte selection-associated HMG bOX (TOX)