Trends and Advances in Tumor Immunology
A topical collection in Cells (ISSN 2073-4409). This collection belongs to the section "Cellular Immunology".
Viewed by 45573Editors
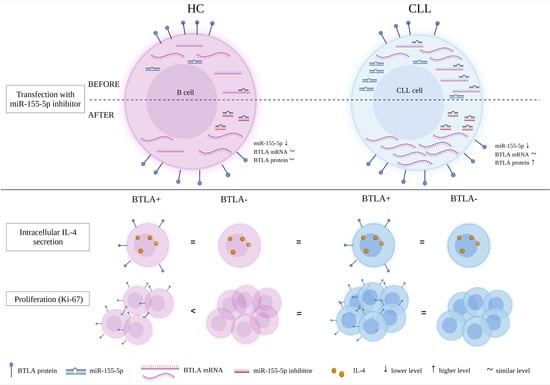
Interests: tumor microenvironment;cancer immunology;leukemia;flow cytometry
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: ovarian cancer microenvironment; immune checkpoints; tumor-infiltrating immune cells
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
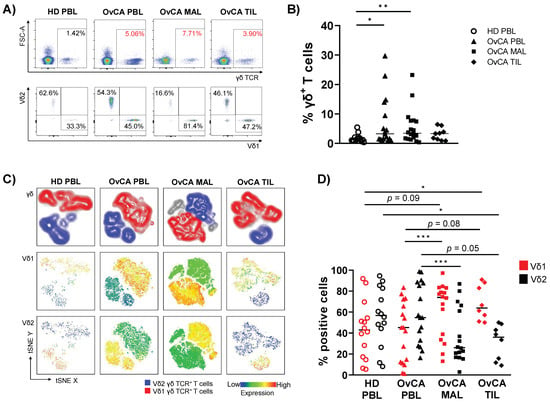
Interests: flow cytometry; tumour immunology; autoimmunity; γδ T cells
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
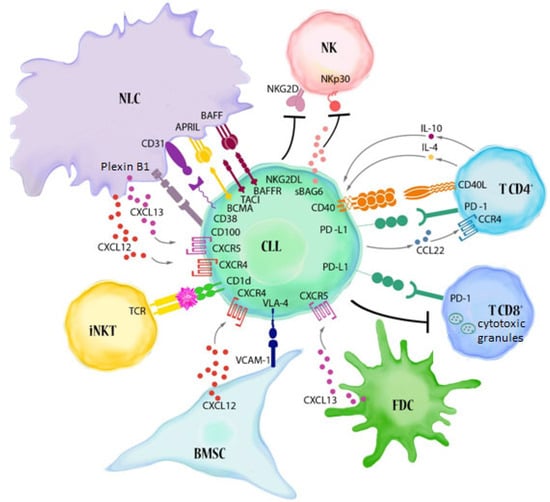
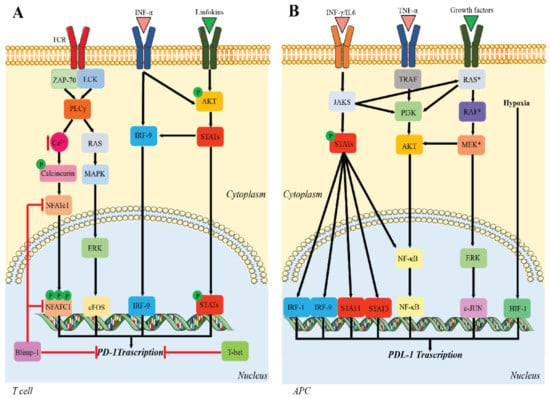
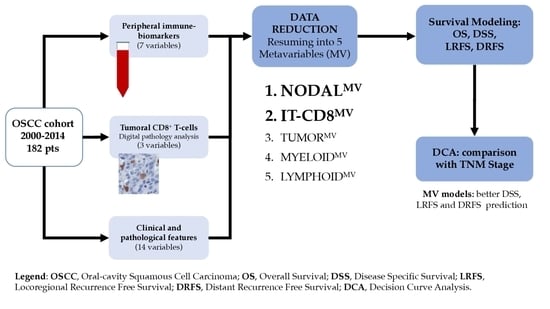
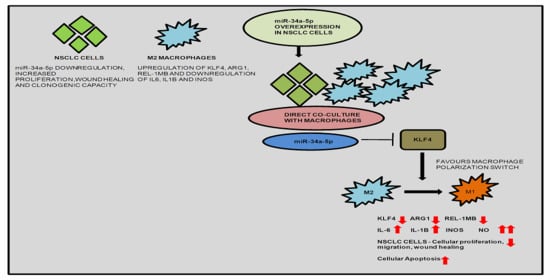
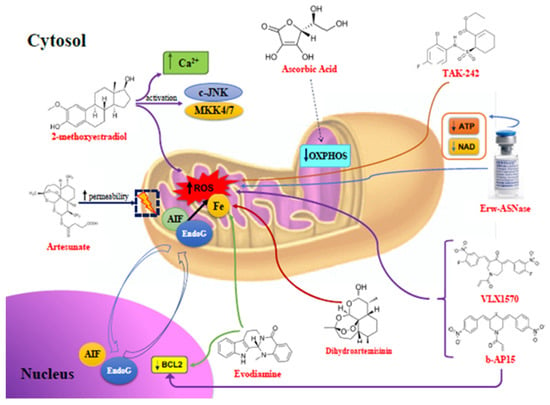
Many cellular and molecular mechanisms are important for the origin and growth of tumors as well as the body's immune defense against cancer. The tumor undergoes continuous remodeling at the genetic, epigenetic, and metabolic level to evade apoptosis. At the same time, it successfully changes all the components of the immune system so as to avoid its antitumor effects. The tumor cells can alter the balance of suppressive versus cytotoxic responses. This complex interaction between immune system and cancer cells can both inhibit and enhance tumor growth. The cellular and noncell components of the tumor immune microenvironment play essential roles in tumor initiation, progression, metastasis, and response to therapies. So far, multiple cellular targets have been examined for preventing or treating cancers including but not limited to transcription factors, epigenetic targeting of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes, kinase signaling pathways, and immune checkpoint inhibitors. Nevertheless, the clinical efficiency of these therapeutic strategies remains unsatisfactory.
This Topical Collection of Cells will present research articles and reviews that cover the scope of both cellular and molecular mechanisms of tumor immunology. Furthermore, this Topical Collection aims to promote the exchange of ideas, concepts, and findings in any area of cancer and related biomedical science studies, from a molecular point of view. All scientists working in these fields are cordially invited to submit their manuscripts.
Dr. Agnieszka Bojarska-Junak
Prof. Iwona Wertel
Dr. Michal Zarobkiewicz
Dr. Wioleta Kowalska
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cells is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- cancer immunology
- immune cells in cancer
- molecular pathways in cancer
- tumor microenvironment
- cytokines
- cytokine receptors
- exosomes and cancer
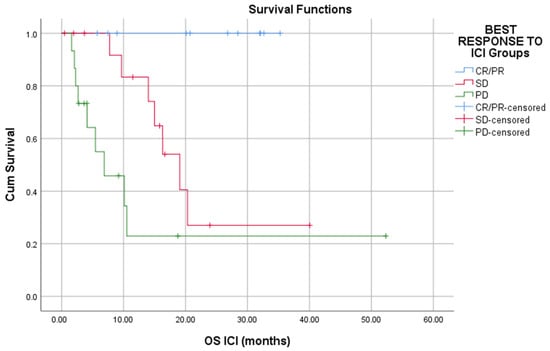
- immune checkpoints
- activating receptors
- inhibitory receptors
- inflammation and cancer
- signaling pathways
- immune response
- macrophage
- myeloid-derived suppressor cells
- tumor infiltration
- γδ T cells
- cytotoxic T cells
- NKT cells