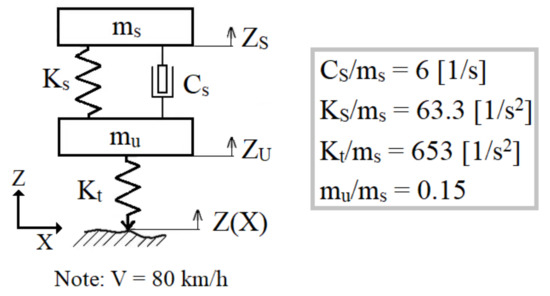
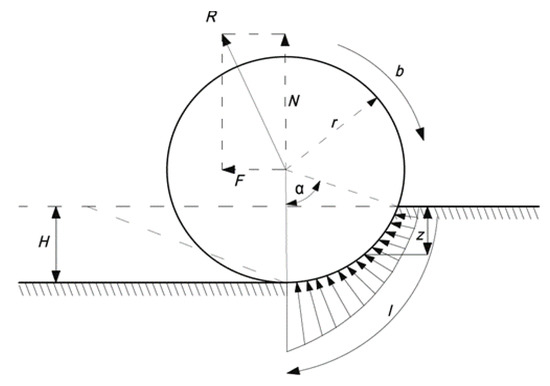
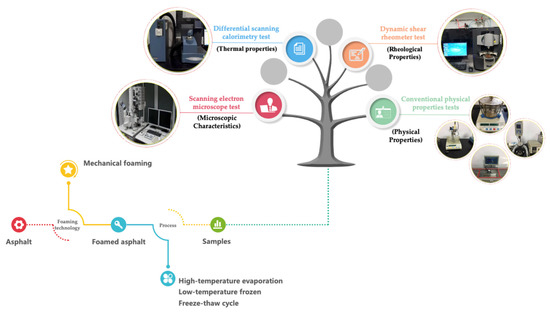
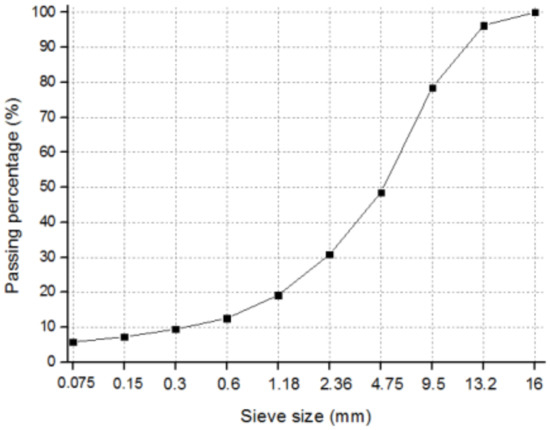
Pavement Surface Coatings (Closed)
A topical collection in Coatings (ISSN 2079-6412). This collection belongs to the section "Surface Characterization, Deposition and Modification".
Viewed by 110780Editors
Interests: design and construction of road, railways and airport infrastructure; active and passive road safety; road pavements; sustainable mobility; context sensitive design
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: road structure health monitoring
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Pavement surface characteristics are crucial for both safety and funtional quality of transportation infrastructure. The correct design of pavement coatings, together with adequate construction and maintenance processes, ensures good performances in terms of skid resistance, regularity, structural resistance, vehicle control and dynamics, drainage and prevention of aquaplaning, vehicle operational costs, and environmental sustainability.
Mechanical, thermal, chemical and/or physical properties and characteristics of bitumens, aggregates, asphalt or cement concrete, as well as rheological characteristics of these materials, can significantly influence road surface performance.
The availability of new natural and industrial resources and the opportunity to recycle materials or reuse by-products in road constructions have modified the approach to pavement manufacture. In addition, techniques and procedures for road pavements design and construction have been constantly improved in the last few decades.
Scope of the Special Issue is to present and discuss the most recent research advances in this field and to consider how these results allow to obtain better functional and structural performances of pavement surface coatings.
In particular, the topics of interest include, but are not limited to:
- Pavement surface characteristics and performances;
- Pavement design, construction, management, maintenance, and rehabilitation techniques;
- Pavement management systems;
- Pavement surface and subsurface drainage;
- Pavement mechanics and pavement design;
- Innovative design methods;
- Pavement materials;
- Pavement recycling;
- Environmental issues, low-noise and sustainable pavements;
- Pavement and surface testing;
- Functional and structural evaluation;
- Pavement-vehicle interaction and safety issues.
Prof. Dr. Giuseppe Cantisani
Prof. Dr. Giuseppe Loprencipe
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Coatings is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.