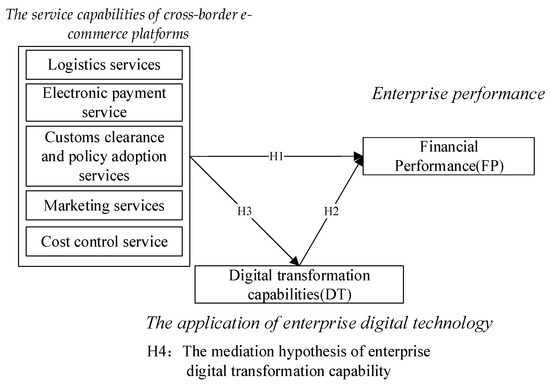
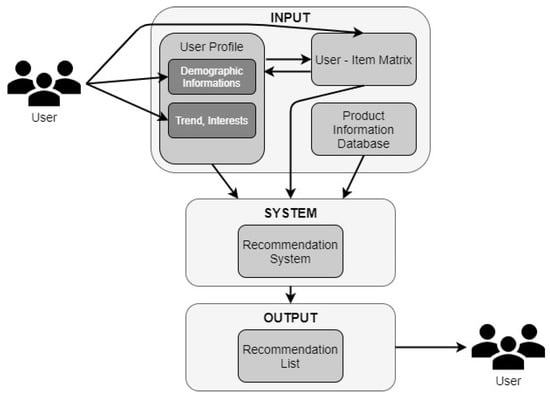
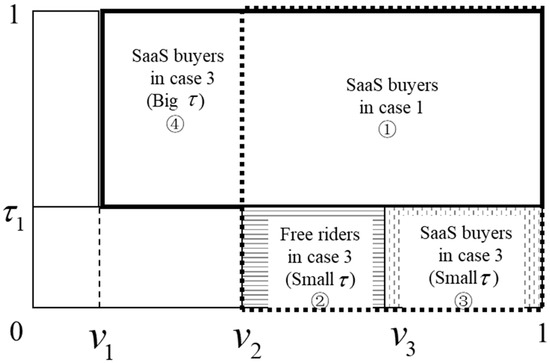
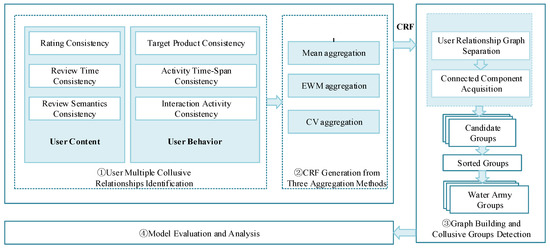
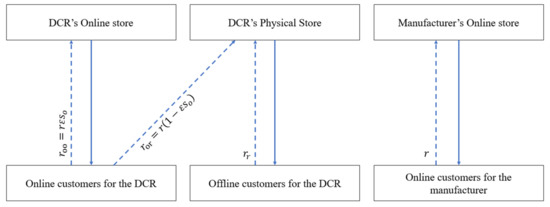
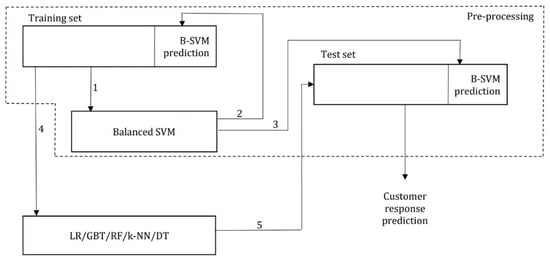
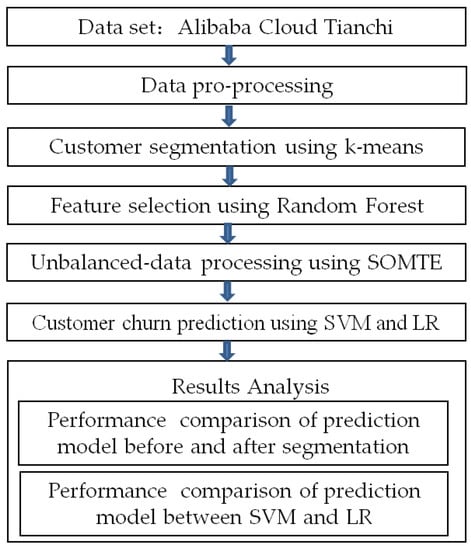
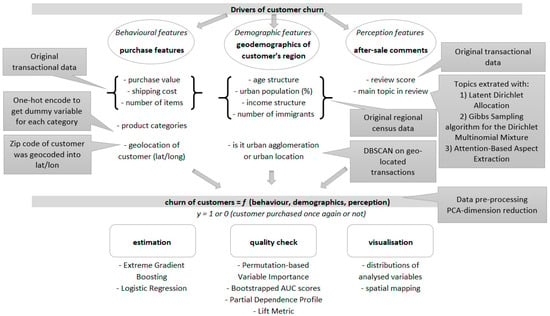
Utilizing Models for e-Business Decision-Making: From Data to Wisdom
A topical collection in Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research (ISSN 0718-1876). This collection belongs to the section "e-Commerce Analytics".
Viewed by 71667Editors
Interests: data science; artificial networks; simulation modeling; decision trees; cluster analysis; association rules; supervised learning; unsupervised learning; system dynamics
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: electronic commerce; big data; data analytics; machine learning; public policies; customer behavior; digitalization
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Data has become omnipresent, as every aspect of personal and business activities is gradually being measured in numerous ways and turned into data, which is analyzed and used to form a value. In recent years, datafication has become a challenge, as processing all the data is nearly impossible due to its abundance, which is increasing exponentially year after year.
Nowadays, data is collected continuously both by humans and by machines, in both structured and non-structured manners. Relational databases, data warehouses, and data marts store the structured data that is often generated as the result of various interactions in e-businesses environments. Textual data is stored in the form of various business and other documents. Social media is also a rich source of textual data since our society has been transforming our communication platforms from analogic sources to digital, through online channels which are used both by persons and businesses for their communications. Moreover, human communication has been extended to the frequent online use of visual media, in the form of static pictures and video, which is also reflected in various e-business models. Soon, there will be more machines connected online than humans, and all of these machines, including mobile phones, the Internet-of-Things, and smart devices, among others, are collecting data.
What to do with all of these data? How to make the best use of it? Plenty of approaches have been adapted or invented to analyze these data, which are well known under various names such as data mining, knowledge discovery in databases, data science, data analytics, and others. All of them prescribe a certain process of data collection, data transformation, data analysis, model development and model deployment, combining machine learning, artificial intelligence and statistical analysis to understand it.
Because of the rich data sources and various methods that are nowadays easy to implement due to the availability of computed analytical tools, data analysis has become omnipresent. However, more data does not automatically lead to better decision making. On the contrary, plenty of data creates various problems that range from the issue of data selection to the misuse of data analysis that mixes correlation with causation. Besides, data analysis is often data-driven, and not decision-driven. In other words, decisions are often inspired by the available data, though data analysis should be driven by the decisions that are needed to improve performance. Finally, it is important to note that doing good analysis is not always a sign of improvement, as many organizations do not evolve to be real data-driven organizations and reject making decisions based on analysis, thus making them fail.
In the topic collection, we intend to focus on all of the stages in data analysis. First, we invite papers that discuss the availability, quality, and transformation of data used in e-business analysis. Second, the selection of existing, and invention of new data analysis approaches is a strong driver of improved e-business modes. Finally, the practical and theoretical implications of the data analysis in e-business are still not sufficiently explored. We invite you to participate in this topic collection with your case studies, original analysis, reviews, conceptual papers, and commentaries.
Prof. Dr. Mirjana Pejic-Bach
Dr. María Teresa Ballestar
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research is an international peer-reviewed open access quarterly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1000 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- decision-making
- datafication
- business performance
- data analysis
- data science
- data mining
- knowledge discovery in databases
- big data
- business intelligence
- artificial intelligence
- machine learning
- security
- privacy