Feature Papers in Plant‒Soil Interactions
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Dr. Adriano Sofo
Dr. Adriano Sofo
 Dr. Adriano Sofo
Dr. Adriano Sofo
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Agricultural, Forestry, Food and Environmental Sciences (DAFE), Università degli Studi della Basilicata, Viale dell'Ateneo Lucano 20, 85100 Potenza, Italy
Interests: agricultural and environmental chemistry; environmental botany; soil ecology
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
This Topical Collection, entitled “Feature Papers in Plant–Soil Interactions”, aims to present a collection of high-quality original research articles, short communications, and review articles on the phenotypic, anatomical, morphological, physiological, cytological, histological, genetic, biochemical, molecular, and chemical aspects of and processes occurring at the interfaces between plants, roots, soil organisms (micro-organisms, fungi, and fauna), and organic and inorganic soil components.
Topics of interest include, but are not limited to:
- plant mineral nutrition and hydrology;
- absorption and accumulation of chemical species in plants;
- anatomy, morphology, and architecture of root systems;
- growth, development, and functioning of root systems;
- interactions between roots and physicochemical soil properties;
- root–soil organism crosstalk and symbiotic associations;
- root–rhizosphere processes and communication;
- plant/root–water relations;
- root endophytes and soil microbiota;
- ecological aspects of the soil–water–plant–atmosphere system;
- genetic control of root system properties;
- roots as a management tool in natural and cultivated soils;
- improvement and restoration of soil fertility aimed at sustainable development;
- soil bio-remediation;
- global climate change mitigation and adaptation
Prof. Dr. Adriano Sofo
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Plants is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- plant–microbe interactions
- plant and soil ecology
- plant and soil microbiota
- plant nutrition
- rhizosphere processes
- root growth and development
- soil bioremediation
- water relations
Published Papers (18 papers)
Open AccessArticle
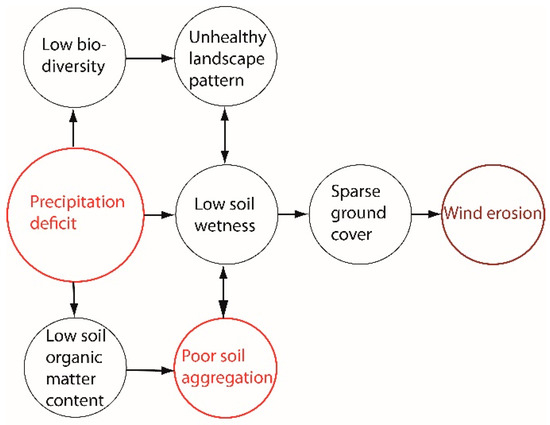
Soil Moisture Conservation through Crop Diversification and Related Ecosystem Services in a Blown-Sand Area with High Drought Hazard
by
Dénes Lóczy, József Dezső, Tamás Weidinger, László Horváth, Ervin Pirkhoffer and Szabolcs Czigány
Viewed by 1388
Abstract
Soil moisture reserves are a key factor in maintaining soil fertility and all other related ecosystem services (including carbon sequestration, soil biodiversity, and soil erosion control). In semiarid blown-sand areas under aridification, water preservation is a particularly crucial task for agriculture. The international
[...] Read more.
Soil moisture reserves are a key factor in maintaining soil fertility and all other related ecosystem services (including carbon sequestration, soil biodiversity, and soil erosion control). In semiarid blown-sand areas under aridification, water preservation is a particularly crucial task for agriculture. The international Diverfarming project (2017–2022), within the EU Horizon 2020 Program, focused on the impacts of crop diversification and low-input practices in all pedoclimatic regions of Europe. In this three-year experiment conducted in the Pannonian region, the impact of intercropping asparagus with different herbs on some provisioning and regulating ecosystem services was evaluated in the Kiskunság sand regions. Relying on findings based on a range of measured physical and chemical soil parameters and on crop yields and qualitative properties, advice was formulated for farmers. The message drawn from the experiment is somewhat ambiguous. The local farmers agree that crop diversification improves soil quality, but deny that it would directly influence farm competitiveness, which primarily depends on cultivation costs (such as fertilization, plant protection, and labour). Further analyses are needed to prove the long-term benefits of diversification through enriching soil microbial life and through the possible reduction of fertilizer use, while water demand is kept at a low level and the same crop-quality is ensured.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
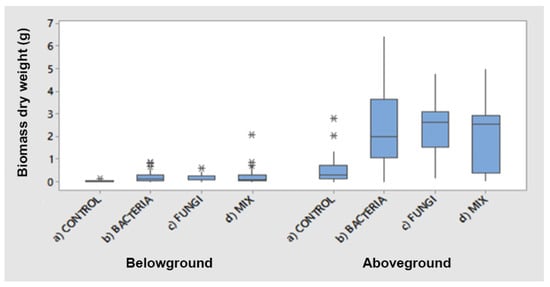
Effects of Bacterial and Fungal Inocula on Biomass, Ecophysiology, and Uptake of Metals of Alyssoides utriculata (L.) Medik.
by
Silvia Priarone, Sara Romeo, Simone Di Piazza, Stefano Rosatto, Mirca Zotti, Mauro Mariotti and Enrica Roccotiello
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1844
Abstract
The inoculation of plants with plant-growth-promoting microorganisms (PGPM) (i.e., bacterial and fungal strains) is an emerging approach that helps plants cope with abiotic and biotic stresses. However, knowledge regarding their synergic effects on plants growing in metal-rich soils is limited. Consequently, the aim
[...] Read more.
The inoculation of plants with plant-growth-promoting microorganisms (PGPM) (i.e., bacterial and fungal strains) is an emerging approach that helps plants cope with abiotic and biotic stresses. However, knowledge regarding their synergic effects on plants growing in metal-rich soils is limited. Consequently, the aim of this study was to investigate the biomass, ecophysiology, and metal accumulation of the facultative Ni-hyperaccumulator
Alyssoides utriculata (L.) Medik. inoculated with single or mixed plant-growth-promoting (PGP) bacterial strain
Pseudomonas fluorescens Migula 1895 (SERP1) and PGP fungal strain
Penicillium ochrochloron Biourge (SERP03 S) on native serpentine soil (
n = 20 for each treatment). Photosynthetic efficiency (Fv/Fm) and performance indicators (PI) had the same trends with no significant differences among groups, with Fv/Fms > 1 and PI up to 12. However, the aboveground biomass increased 4–5-fold for single and mixed inoculated plants. The aboveground/belowground dry biomass ratio was higher for plants inoculated with fungi (30), mixed (21), and bacteria (17). The ICP-MS highlighted that single and mixed inocula were able to double the aboveground biomass’ P content. Mn metal accumulation significantly increased with both single and mixed PGP inocula, and Zn accumulation increased only with single PGP inocula, whereas Cu accumulation increased twofold only with mixed PGP inocula, but with a low content. Only Ni metal accumulation approached the hyperaccumulation level (Ni > 1000 mg/kg DW) with all treatments. This study demonstrated the ability of selected single and combined PGP strains to significantly increase plant biomass and plant tolerance of metals present in the substrate, resulting in a higher capacity for Ni accumulation in shoots.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
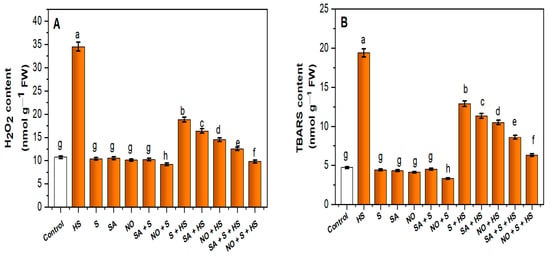
Nitric Oxide and Salicylic Acid Regulate Glutathione and Ethylene Production to Enhance Heat Stress Acclimation in Wheat Involving Sulfur Assimilation
by
Faisal Rasheed, Iqbal R. Mir, Zebus Sehar, Mehar Fatma, Harsha Gautam, Sheen Khan, Naser A. Anjum, Asim Masood, Adriano Sofo and Nafees A. Khan
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 1956
Abstract
Phytohormones have a role in stress adaptation. The major mechanism underlying the role of exogenously-sourced nitric oxide (NO; as sodium nitroprusside, SNP: 50.0 µM) and salicylic acid (SA; 0.5 mM) in the presence of 2.0 mM SO
4−2 was assessed in heat
[...] Read more.
Phytohormones have a role in stress adaptation. The major mechanism underlying the role of exogenously-sourced nitric oxide (NO; as sodium nitroprusside, SNP: 50.0 µM) and salicylic acid (SA; 0.5 mM) in the presence of 2.0 mM SO
4−2 was assessed in heat stress (HS; 40 °C for 6 h daily for 15 days) tolerance in wheat
(Triticum aestivum L. cv. HD-3226). The cultivar HD-3226 possessed high photosynthetic sulfur use efficiency (p-SUE) among the six cultivars screened. Plants grown under HS exhibited an increased content of reactive oxygen species (ROS; including superoxide radical and hydrogen peroxide) and extent of lipid peroxidation with a consequent reduction in photosynthesis and growth. However, both NO and SA were found to be protective against HS via enhanced S assimilation. Their application reduced oxidative stress and increased the activity of antioxidant enzymes. NO or SA supplementation along with S under HS recovered the losses and improved photosynthesis and growth. The use of SA inhibitor (2-aminoindane-2-phosphonic acid; AIP) and NO scavenger (cPTIO) confirmed that the mitigating effects of SA and NO involved induction in S assimilation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
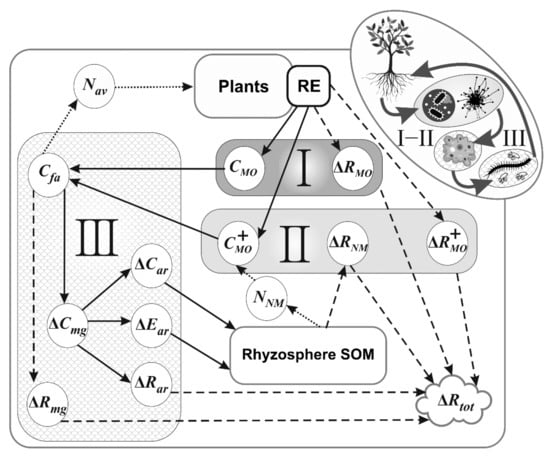
Modelling the Rhizosphere Priming Effect in Combination with Soil Food Webs to Quantify Interaction between Living Plant, Soil Biota and Soil Organic Matter
by
Oleg Chertov, Yakov Kuzyakov, Irina Priputina, Pavel Frolov, Vladimir Shanin and Pavel Grabarnik
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2112
Abstract
A model of rhizosphere priming effect under impact of root exudate input into rhizosphere soil was developed as an important process of the plant-soil interaction. The model was based on the concept of nitrogen (N) mining, compensating for the N scarcity in exudates
[...] Read more.
A model of rhizosphere priming effect under impact of root exudate input into rhizosphere soil was developed as an important process of the plant-soil interaction. The model was based on the concept of nitrogen (N) mining, compensating for the N scarcity in exudates for microbial growth by accelerating SOM mineralisation. In the model, N deficiency for microbial growth is covered (“mined”) by the increased SOM mineralisation depending on the C:N ratio of the soil and exudates. The new aspect in the model is a food web procedure, which calculates soil fauna feeding on microorganisms, the return of faunal by-products to SOM and mineral N production for root uptake. The model verification demonstrated similar magnitude of the priming effect in simulations as in the published experimental data. Model testing revealed high sensitivity of the simulation results to N content in exudates. Simulated CO
2 emission from the priming can reach 10–40% of CO
2 emission from the whole Ah horizon of boreal forest soil depending on root exudation rates. This modeling approach with including food web activity allows quantifying wider aspects of the priming effect functioning including ecologically important available N production.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
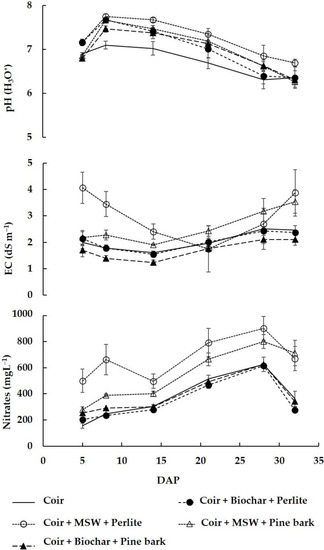
Effects of Coir-Based Growing Medium with Municipal Solid Waste Compost or Biochar on Plant Growth, Mineral Nutrition, and Accumulation of Phytochemicals in Spinach
by
Rui M. A. Machado, Isabel Alves-Pereira, Carolina Morais, André Alemão and Rui Ferreira
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 2513
Abstract
The use of municipal solid waste compost (MSW) and biochar, two renewable resources with a low carbon footprint as components of substrates, may be an alternative to reducing peat and coir usage. The aim of this study was to assess the suitability of
[...] Read more.
The use of municipal solid waste compost (MSW) and biochar, two renewable resources with a low carbon footprint as components of substrates, may be an alternative to reducing peat and coir usage. The aim of this study was to assess the suitability of selectively collected MSW and biochar as components of the coir-based substrate to spinach grown. An experiment was carried out to evaluate five substrates, coir and four coir-based blends (coir + biochar + perlite, coir + municipal waste compost + perlite, coir + biochar + pine bark, and coir + biochar + pine bark) with 12% (
v/v) MSW or biochar and 10% (
v/v) perlite or pine bark. Spinach seedlings were transplanted into Styrofoam planting boxes filled with the substrate. Each planting box was irrigated daily by drip with a complete nutrient solution. Plants grown with MSW had a higher content of calcium. Shoot Mn increased in the biochar-containing mixes. The shoot dry weight of the plants grown in the different blends was higher than those grown in coir. Fresh yield was higher in mixes with MSW and perlite (3 kg/m
2) or pine bark (2.87 kg/m
2). Total phenols and DPPH antioxidant activity were not affected by the substrates. However, shoot ascorbate (AsA) content was higher or equal to those plants grown in coir. MSW and biochar are alternatives to reduce the use of coir and peat.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
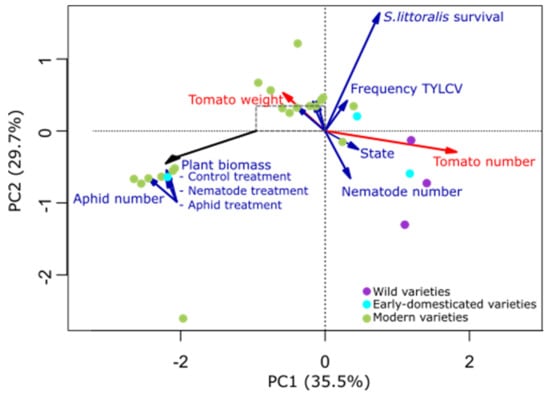
Resistance and Not Plant Fruit Traits Determine Root-Associated Bacterial Community Composition along a Domestication Gradient in Tomato
by
Lisanne Smulders, Victoria Ferrero, Eduardo de la Peña, María J. Pozo, Juan Antonio Díaz Pendón, Emilio Benítez and Álvaro López-García
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2942
Abstract
Soil bacterial communities are involved in multiple ecosystem services, key in determining plant productivity. Crop domestication and intensive agricultural practices often disrupt species interactions with unknown consequences for rhizosphere microbiomes. This study evaluates whether variation in plant traits along a domestication gradient determines
[...] Read more.
Soil bacterial communities are involved in multiple ecosystem services, key in determining plant productivity. Crop domestication and intensive agricultural practices often disrupt species interactions with unknown consequences for rhizosphere microbiomes. This study evaluates whether variation in plant traits along a domestication gradient determines the composition of root-associated bacterial communities; and whether these changes are related to targeted plant traits (e.g., fruit traits) or are side effects of less-often-targeted traits (e.g., resistance) during crop breeding. For this purpose, 18 tomato varieties (wild and modern species) differing in fruit and resistance traits were grown in a field experiment, and their root-associated bacterial communities were characterised. Root-associated bacterial community composition was influenced by plant resistance traits and genotype relatedness. When only considering domesticated tomatoes, the effect of resistance on bacterial OTU composition increases, while the effect due to phylogenetic relatedness decreases. Furthermore, bacterial diversity positively correlated with plant resistance traits. These results suggest that resistance traits not selected during domestication are related to the capacity of tomato varieties to associate with different bacterial groups. Taken together, these results evidence the relationship between plant traits and bacterial communities, pointing out the potential of breeding to affect plant microbiomes.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
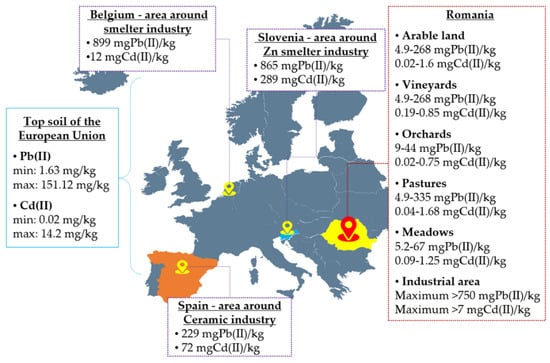
New Evidence of Model Crop Brassica napus L. in Soil Clean-Up: Comparison of Tolerance and Accumulation of Lead and Cadmium
by
Mihaela Rosca, Petronela Cozma, Mariana Minut, Raluca-Maria Hlihor, Camelia Bețianu, Mariana Diaconu and Maria Gavrilescu
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 3201
Abstract
The potential of the model crop
Brassica napus L. (rapeseed) for the phytoremediation of soils polluted with metals was investigated at laboratory scale. The first step consists in the evaluation of the seed germination and growth of the
Brassica napus L. plant in
[...] Read more.
The potential of the model crop
Brassica napus L. (rapeseed) for the phytoremediation of soils polluted with metals was investigated at laboratory scale. The first step consists in the evaluation of the seed germination and growth of the
Brassica napus L. plant in a controlled environment, followed by the determination of the photosynthetic pigments content represented by chlorophyll a and b and carotenoids. The degree of metal accumulation in rapeseed has been evaluated by the bioaccumulation factor (BAC), the bioconcentration factor (BCF) and the translocation factor (TF). Phytotoxicity tests were performed in Petri dishes with filter papers moistened with metal solutions in the range of 0 to 300 mg/L Pb(II) or Cd(II). At the highest concentration of the lead and cadmium treatments (300 mg/L),
B. napus L. showed the lowest germination degree (56.67% and 43.33%, respectively). According to Tukey test results, Pb(II) concentrations of up to 300 mg/L do not significantly affect the length of the hypocotyls, whereas, in the case of Cd(II), the mean of the radicle and hypocotyl lengths of the seedlings are significantly affected compared to the mean of the control. In soil pot experiments, important changes have been obtained in the pigment content, especially in the case of cadmium. For both metals and for each treatment (100 to 1500 mg/kg Pb(II) and 1 to 30 mg/kg Cd(II)), a TF < 1 indicates an ineffective metal transfer from root to shoot. Finally, rapeseed can be considered a tolerant plant and a suitable candidate for Pb(II) and Cd(II) accumulation and for the phytostabilization of contaminated soil under the experimental conditions adopted in the present study.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
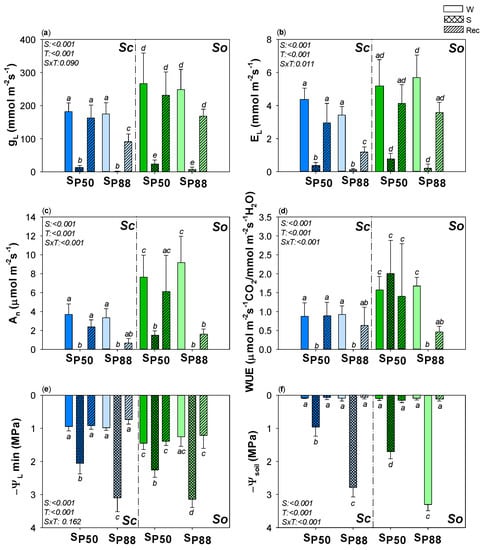
When Water Availability Is Low, Two Mediterranean Salvia Species Rely on Root Hydraulics
by
Elisa Abate, Maria Azzarà and Patrizia Trifilò
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 2090
Abstract
Increase in severity and frequency of drought events is altering plant community composition, exposing biomes to a higher risk of biodiversity losses. This is exacerbated in the most fragile areas as Mediterranean biome. Thus, identifying plant traits for forecasting species with a high
[...] Read more.
Increase in severity and frequency of drought events is altering plant community composition, exposing biomes to a higher risk of biodiversity losses. This is exacerbated in the most fragile areas as Mediterranean biome. Thus, identifying plant traits for forecasting species with a high risk of drought-driven mortality is particularly urgent. In the present study, we investigated the drought resistance strategy of two Mediterranean native species:
Salvia ceratophylloides Ard. (
Sc) and
Salvia officinalis L. (
So) by considering the impact of drought-driven water content decline on plant hydraulics. Well-watered samples of
Sc displayed higher leaf and stemsaturated water content and lower shoot biomass than
So samples, but similar root biomass. In response to drought,
Sc showed a conservative water use strategy, as the prompt stomatal closure and leaves shedding suggested. A drought-tolerant mechanism was confirmed in
So samples. Nevertheless,
Sc and
So showed similar drought-driven plant hydraulic conductance (K
plant) recover ability. Root hydraulic traits played a key role to reach this goal. Relative water content as well as loss of cell rehydration capability and membrane damages, especially of stem and root, were good proxies of drought-driven K
plant decline.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
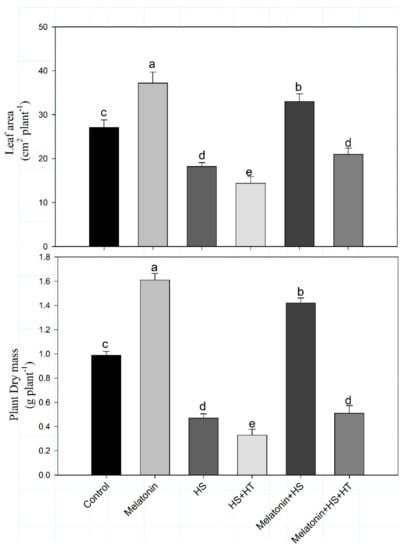
The Crosstalk of Melatonin and Hydrogen Sulfide Determines Photosynthetic Performance by Regulation of Carbohydrate Metabolism in Wheat under Heat Stress
by
Noushina Iqbal, Mehar Fatma, Harsha Gautam, Shahid Umar, Adriano Sofo, Ilaria D’ippolito and Nafees A. Khan
Cited by 98 | Viewed by 4764
Abstract
Photosynthesis is a pivotal process that determines the synthesis of carbohydrates required for sustaining growth under normal or stress situation. Stress exposure reduces the photosynthetic potential owing to the excess synthesis of reactive oxygen species that disturb the proper functioning of photosynthetic apparatus.
[...] Read more.
Photosynthesis is a pivotal process that determines the synthesis of carbohydrates required for sustaining growth under normal or stress situation. Stress exposure reduces the photosynthetic potential owing to the excess synthesis of reactive oxygen species that disturb the proper functioning of photosynthetic apparatus. This decreased photosynthesis is associated with disturbances in carbohydrate metabolism resulting in reduced growth under stress. We evaluated the importance of melatonin in reducing heat stress-induced severity in wheat (
Triticum aestivum L.) plants. The plants were subjected to 25 °C (optimum temperature) or 40 °C (heat stress) for 15 days at 6 h time duration and then developed the plants for 30 days. Heat stress led to oxidative stress with increased production of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) and hydrogen peroxide (H
2O
2) content and reduced accrual of total soluble sugars, starch and carbohydrate metabolism enzymes which were reflected in reduced photosynthesis. Application of melatonin not only reduced oxidative stress through lowering TBARS and H
2O
2 content, augmenting the activity of antioxidative enzymes but also increased the photosynthesis in plant and carbohydrate metabolism that was needed to provide energy and carbon skeleton to the developing plant under stress. However, the increase in these parameters with melatonin was mediated via hydrogen sulfide (H
2S), as the inhibition of H
2S by hypotaurine (HT; H
2S scavenger) reversed the ameliorative effect of melatonin. This suggests a crosstalk of melatonin and H
2S in protecting heat stress-induced photosynthetic inhibition via regulation of carbohydrate metabolism.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
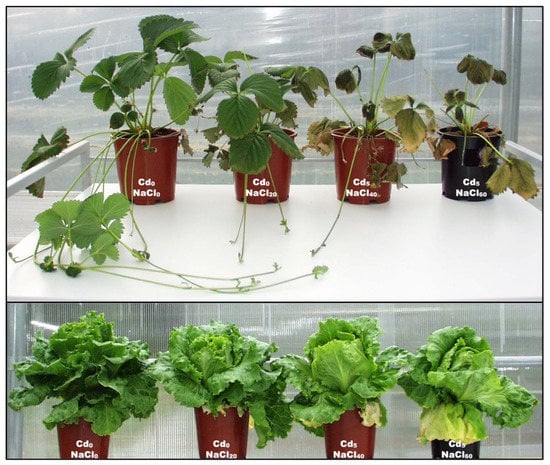
Growth and Element Uptake by Salt-Sensitive Crops under Combined NaCl and Cd Stresses
by
Gabrijel Ondrasek, Zed Rengel, Nada Maurović, Nada Kondres, Vilim Filipović, Radovan Savić, Boško Blagojević, Vjekoslav Tanaskovik, Cristian Meriño Gergichevich and Davor Romić
Cited by 23 | Viewed by 3236
Abstract
To test an assumption that organic soil can ameliorate nutritional disorders associated with metal and salinity stresses, we exposed salt-sensitive strawberry and lettuce to four salinity (0–60 mM NaCl) and three contamination (0.3–5 mg Cd/kg) rates in peat (pH
H2O = 5.5). The
[...] Read more.
To test an assumption that organic soil can ameliorate nutritional disorders associated with metal and salinity stresses, we exposed salt-sensitive strawberry and lettuce to four salinity (0–60 mM NaCl) and three contamination (0.3–5 mg Cd/kg) rates in peat (pH
H2O = 5.5). The results showed that, even at 20 mM NaCl, salinity stress exerted a dominant effect on rhizosphere biogeochemistry and physiological processes, inducing leaf-edge burns, chlorosis/necrosis, reducing vegetative growth in crops; at ≥40 mM, NaCl mortality was induced in strawberry. Signifiacntly decreased K/Na, Ca/Na and Mg/Na concentration ratios with raising salinity were confirmed in all tissues. The combined CdxNaCl stresses (vs. control) increased leaf Cd accumulation (up to 42-fold in lettuce and 23-fold in strawberry), whereas NaCl salinity increased the accumulation of Zn (>1.5-fold) and Cu (up to 1.2-fold) in leaves. Lettuce accumulated the toxic Cd concentration (up to 12.6 mg/kg) in leaves, suggesting the strong root-to-shoot transport of Cd. In strawberry Cd, concentration was similar (and sub-toxic) in fruits and leaves, 2.28 and 1.86 mg/kg, respectively, suggesting lower Cd root-to-shoot translocation, and similar Cd mobility in the xylem and phloem. Additionally, the accumulation of Cd in strawberry fruits was exacerbated at high NaCl exposure (60 mM) compared with lower NaCl concentrations. Thus, in salinized, slightly acidic and organically rich rhizosphere, pronounced organo- and/or chloro-complexation likely shifted metal biogeochemistry toward increased mobility and phytoavailability (with metal adsorption restricted due to Na
+ oversaturation of the caton exchange complex in the substrate), confirming the importance of quality water and soils in avoiding abiotic stresses and producing non-contaminated food.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
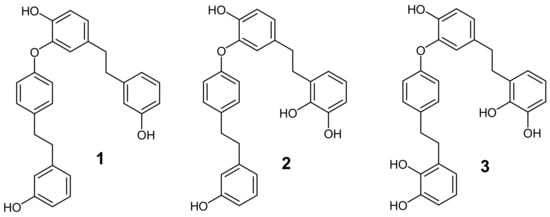
Bis-Bibenzyls from the Liverwort Pellia endiviifolia and Their Biological Activity
by
Ivana Ivković, Miroslav Novaković, Milan Veljić, Marija Mojsin, Milena Stevanović, Petar D. Marin and Danka Bukvički
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 3266
Abstract
Based on previous investigations where bis-bibenzyls isolated from liverworts showed various biological activities (cytotoxic, antimicrobial, and antiviral), we investigated their cytotoxic activity in several human cancer cell lines. From the methylene-chloride/methanol extract of the liverwort
Pellia endiviifolia, three bis-bibenzyls of the perrottetin
[...] Read more.
Based on previous investigations where bis-bibenzyls isolated from liverworts showed various biological activities (cytotoxic, antimicrobial, and antiviral), we investigated their cytotoxic activity in several human cancer cell lines. From the methylene-chloride/methanol extract of the liverwort
Pellia endiviifolia, three bis-bibenzyls of the perrottetin type were isolated, namely perrottetin E, 10′-hydroxyperrottetin E, and 10,10′-dihydroxyperrottetin E. The last two were found for the first time in this species. Their structures were resolved using 1D and 2D NMR, as well as by comparison with data in the literature. Cytotoxic activity of the isolated compounds was tested on three human leukemia cell lines, HL-60 (acute promyelocytic leukemia cells), U-937 (acute monocytic leukemia cells), and K-562 (human chronic myelogenous leukemia cells), as well as on human embryonal teratocarcinoma cell line (NT2/D1) and human glioblastoma cell lines A-172 and U-251, and compared to the previously isolated bis-bibenzyls (perrottetins) of similar structure. The isolated compounds exhibited modest activity against leukemia cells and significant activity against NT2/D1 and A-172. Overall, the most active cytotoxic compounds in this investigation were perrottetin E (1), isolated in this work from
Pellia endiviifolia, and perrottetin F phenanthrene derivative (7), previously isolated from
Lunularia cruciata and added for a comparison of their cytotoxic activity.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
The Interplay between Light Quality and Biostimulant Application Affects the Antioxidant Capacity and Photosynthetic Traits of Soybean (Glycine max L. Merrill)
by
Ermenegilda Vitale, Violeta Velikova, Tsonko Tsonev, Ida Ferrandino, Teresa Capriello and Carmen Arena
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 3140
Abstract
This paper evaluates the combined effect of biostimulant and light quality on bioactive compound production and seedling growth of soybean (
Glycine max L. Merrill) plants. Germinated seeds pre-treated with different concentrations (0.01%, 0.05%, 0.5%) of an amino acid-based biostimulant were grown for
[...] Read more.
This paper evaluates the combined effect of biostimulant and light quality on bioactive compound production and seedling growth of soybean (
Glycine max L. Merrill) plants. Germinated seeds pre-treated with different concentrations (0.01%, 0.05%, 0.5%) of an amino acid-based biostimulant were grown for 4 days at the dark (D), white fluorescent light (FL), full-spectrum LED (FS), and red-blue (RB) light. Potential changes in the antioxidant content of sprouts were evaluated. Part of the sprouts was left to grow at FL, FS, and RB light regimes for 24 days to assess modifications in plants’ anatomical and physiological traits during the early developmental plant stage. The seed pre-treatment with all biostimulant concentrations significantly increased sprout antioxidant compounds, sugar, and protein content compared to the control (seeds treated with H
2O). The positive effect on bioactive compounds was improved under FS and RB compared to D and FL light regimes. At the seedling stage, 0.05% was the only concentration of biostimulant effective in increasing the specific leaf area (SLA) and photosynthetic efficiency. Compared to FL, the growth under FS and RB light regimes significantly enhanced the beneficial effect of 0.05% on SLA and photosynthesis. This concentration led to leaf thickness increase and shoot/root ratio reduction. Our findings demonstrated that seed pre-treatment with proper biostimulant concentration in combination with specific light regimes during plant development may represent a useful means to modify the bioactive compound amount and leaf structural and photosynthetic traits.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
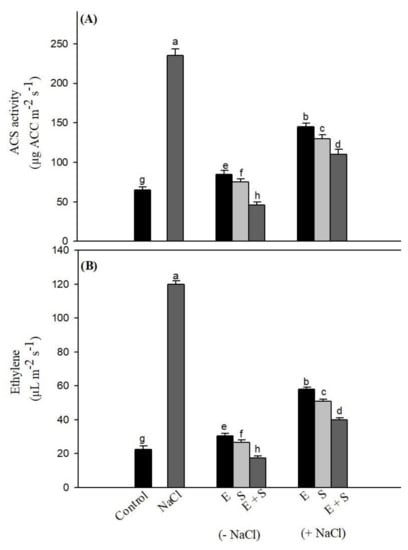
Ethylene and Sulfur Coordinately Modulate the Antioxidant System and ABA Accumulation in Mustard Plants under Salt Stress
by
Mehar Fatma, Noushina Iqbal, Harsha Gautam, Zebus Sehar, Adriano Sofo, Ilaria D’Ippolito and Nafees A. Khan
Cited by 58 | Viewed by 5330
Abstract
This study explored the interactive effect of ethephon (2-chloroethyl phosphonic acid; an ethylene source) and sulfur (S) in regulating the antioxidant system and ABA content and in maintaining stomatal responses, chloroplast structure, and photosynthetic performance of mustard plants (
Brassica juncea L. Czern.)
[...] Read more.
This study explored the interactive effect of ethephon (2-chloroethyl phosphonic acid; an ethylene source) and sulfur (S) in regulating the antioxidant system and ABA content and in maintaining stomatal responses, chloroplast structure, and photosynthetic performance of mustard plants (
Brassica juncea L. Czern.) grown under 100 mM NaCl stress. The treatment of ethephon (200 µL L
−1) and S (200 mg S kg
−1 soil) together markedly improved the activity of enzymatic and non-enzymatic components of the ascorbate-glutathione (AsA-GSH) cycle, resulting in declined oxidative stress through lesser content of sodium (Na
+) ion and hydrogen peroxide (H
2O
2) in salt-stressed plants
. These changes promoted the development of chloroplast thylakoids and photosynthetic performance under salt stress. Ethephon + S also reduced abscisic acid (ABA) accumulation in guard cell, leading to maximal stomatal conductance under salt stress. The inhibition of ethylene action by norbornadiene (NBD) in salt- plus non-stressed treated plants increased ABA and H
2O
2 contents, and reduced stomatal opening, suggesting the involvement of ethephon and S in regulating stomatal conductance. These findings suggest that ethephon and S modulate antioxidant system and ABA accumulation in guard cells, controlling stomatal conductance, and the structure and efficiency of the photosynthetic apparatus in plants under salt stress.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
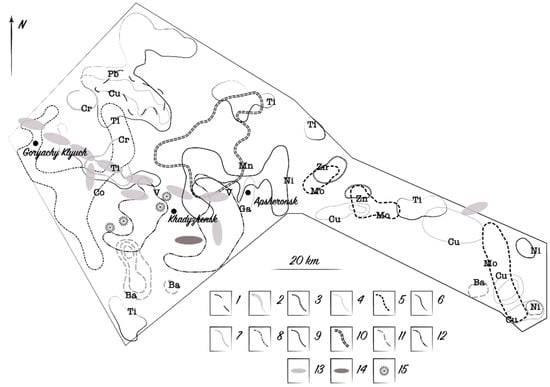
Element Accumulation Patterns of Native Plant Species under the Natural Geochemical Stress
by
Vladimir A. Alekseenko, Natalya V. Shvydkaya, Alexey V. Alekseenko, Maria M. Machevariani, Jaume Bech, Mariya A. Pashkevich, Alexander V. Puzanov, Aleksey V. Nastavkin and Núria Roca
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 3498
Abstract
A biogeochemical study of more than 20,000 soil and plant samples from the North Caucasus, Dzungarian Alatau, Kazakh Uplands, and Karatau Mountains revealed features of the chemical element uptake by the local flora. Adaptation of ore prospecting techniques alongside environmental approaches allowed the
[...] Read more.
A biogeochemical study of more than 20,000 soil and plant samples from the North Caucasus, Dzungarian Alatau, Kazakh Uplands, and Karatau Mountains revealed features of the chemical element uptake by the local flora. Adaptation of ore prospecting techniques alongside environmental approaches allowed the detection of geochemical changes in ecosystems, and the lessons learned can be embraced for soil phytoremediation. The data on the influence of phytogeochemical stress on the accumulation of more than 20 chemical elements by plants are considered in geochemical provinces, secondary fields of deposits, halos surrounding ore and nonmetallic deposits, zones of regional faults and schist formation, and over lithological contact lines of chemically contrasting rocks overlain by 5–20 m thick soils and unconsolidated cover. We have corroborated the postulate that the element accumulation patterns of native plants under the natural geochemical stress depend not only on the element content in soils and the characteristics of a particular species but also on the values of ionic radii and valences; with an increase in the energy coefficients of a chemical element, its plant accumulation decreases sharply. The contribution of internal factors to element uptake from solutions gives the way to soil phytoremediation over vast contaminated areas. The use of hyperaccumulating species for mining site soil treatment depends on several external factors that can strengthen or weaken the stressful situation, viz., the amount of bedrock exposure and thickness of unconsolidated rocks over ores, the chemical composition of ores and primary halos in ore-containing strata, the landscape and geochemical features of sites, and chemical element migration patterns in the supergene zone.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Single and Combined Abiotic Stress in Maize Root Morphology
by
Rosa Vescio, Maria Rosa Abenavoli and Agostino Sorgonà
Cited by 22 | Viewed by 3946
Abstract
Plants are continually exposed to multiple stresses, which co-occur in nature, and the net effects are frequently more nonadditive (i.e., synergistic or antagonistic), suggesting “unique” responses with respect to that of the individual stress. Further, plant stress responses are not uniform, showing a
[...] Read more.
Plants are continually exposed to multiple stresses, which co-occur in nature, and the net effects are frequently more nonadditive (i.e., synergistic or antagonistic), suggesting “unique” responses with respect to that of the individual stress. Further, plant stress responses are not uniform, showing a high spatial and temporal variability among and along the different organs. In this respect, the present work investigated the morphological responses of different root types (seminal, seminal lateral, primary and primary lateral) of maize plants exposed to single (drought and heat) and combined stress (drought + heat). Data were evaluated by a specific root image analysis system (WinRHIZO) and analyzed by uni- and multivariate statistical analyses. The results indicated that primary roots and their laterals were the types more sensitive to the single and combined stresses, while the seminal laterals specifically responded to the combined only. Further, antagonistic and synergistic effects were observed for the specific traits in the primary and their laterals and in the seminal lateral roots in response to the combined stress. These results suggested that the maize root system modified specific root types and traits to deal with different stressful environmental conditions, highlighting that the adaptation strategy to the combined stress may be different from that of the individual ones. The knowledge of “unique or shared” responses of plants to multiple stress can be utilized to develop varieties with broad-spectrum stress tolerance.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
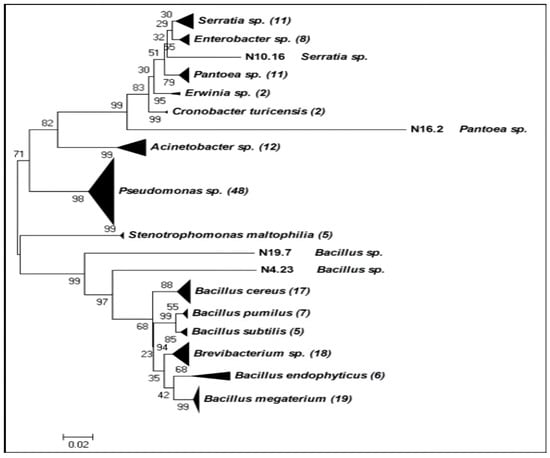
Bioeffectors as Biotechnological Tools to Boost Plant Innate Immunity: Signal Transduction Pathways Involved
by
Helena Martin-Rivilla, Ana Garcia-Villaraco, Beatriz Ramos-Solano, Francisco Javier Gutierrez-Mañero and Jose Antonio Lucas
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 3130
Abstract
The use of beneficial rhizobacteria (bioeffectors) and their derived metabolic elicitors are efficient biotechnological alternatives in plant immune system elicitation. This work aimed to check the ability of 25 bacterial strains isolated from the rhizosphere of
Nicotiana glauca, and selected for their
[...] Read more.
The use of beneficial rhizobacteria (bioeffectors) and their derived metabolic elicitors are efficient biotechnological alternatives in plant immune system elicitation. This work aimed to check the ability of 25 bacterial strains isolated from the rhizosphere of
Nicotiana glauca, and selected for their biochemical traits from a group of 175, to trigger the innate immune system of
Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings against the pathogen
Pseudomonas syringae pv.
tomato DC3000. The five strains more effective in preventing pathogen infection were used to elucidate signal transduction pathways involved in the plant immune response by studying the differential expression of Salicylic acid and Jasmonic acid/Ethylene pathway marker genes. Some strains stimulated both pathways, while others stimulated either one or the other. The metabolic elicitors of two strains, chosen for the differential expression results of the genes studied, were extracted using n-hexane, ethyl acetate, and n-butanol, and their capacity to mimic bacterial effect to trigger the plant immune system was studied. N-hexane and ethyl acetate were the most effective fractions against the pathogen in both strains, achieving similar protection rates although gene expression responses were different from that obtained by the bacteria. These results open an amount of biotechnological possibilities to develop biological products for agriculture.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
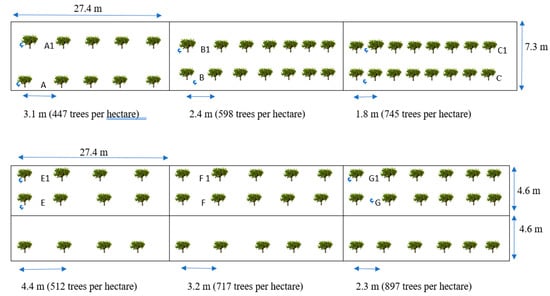
Effect of Various Irrigation Rates on Growth and Root Development of Young Citrus Trees in High-Density Planting
by
Said A. Hamido and Kelly T. Morgan
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 3433
Abstract
Citrus yields have declined by almost 56% since Huanglongbing (HLB) was first found in Florida (2005). That reduction forced citrus growers to replant trees at much higher densities to counter-balance tree loss. The current project aims to determine how much water is required
[...] Read more.
Citrus yields have declined by almost 56% since Huanglongbing (HLB) was first found in Florida (2005). That reduction forced citrus growers to replant trees at much higher densities to counter-balance tree loss. The current project aims to determine how much water is required to grow citrus trees at higher planting densities without reducing their productivity. The study was initiated in November 2017 on eight-month-old sweet orange (
Citrus sinensis) trees grafted on the ‘US-897′ (Cleopatra mandarin × Flying Dragon trifoliate orange) citrus rootstock planted in the University of Florida, Southwest Florida Research and Education Center (SWFREC) demonstration grove, in Immokalee, FL (lat. 26.42° N, long. 81.42° W). The soil in the grove is Immokalee fine sand (Sandy, siliceous, hyperthermic Arenic Alaquods). The demonstration grove included three densities on two rows of beds (447, 598, and 745 trees per ha) replicated four times each and three densities of three rows of beds (512, 717, 897 trees per ha) replicated six times. Each density treatment was irrigated at one of two irrigation rates (62% or 100%) during the first 15 months (2017–2019) then adjusted (2019–2020) to represent 26.5, 40.5, 53, and 81% based on recommended young citrus trees evapotranspiration (ETc). Tree growth measurements including trunk diameter, height, canopy volume, leaf area, and root development were evaluated. During the first year, reducing the irrigation rate from 100% to 62% ETc did not significantly reduce the young citrus tree growth. Conversely, the lower irrigation rate (62% ETc) had increased citrus tree’s leaf area, canopy volume and tree heights, root lifespan, and root length by 4, 9, 1, 2, and 24% compared with the higher irrigation rate (100%), respectively. Furthermore, the root lifespan was promoted by increasing planting density. For instance, the average root lifespan increased by 12% when planting density increased from 447 to 897 trees per ha, indicating that planting young trees much closer to each other enhanced the root’s longevity. However, when treatments were adjusted from April 2019 through June 2020, results changed. Increasing the irrigation rate from 26.5% to 81% ETc significantly enhanced the young citrus tree growth by increasing citrus tree’s canopy volume (four fold), tree heights (29%), root lifespan (86%), and root length (two fold), respectively. Thus, the application of 81% ET
c irrigation rate in commercial citrus groves is more efficient for trees from two to four years of age.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Structural and Functional Organization of the Root System: A Comparative Study on Five Plant Species
by
Adriano Sofo, Hazem S. Elshafie and Ippolito Camele
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 4263
Abstract
Plants are affected by soil environments to the same extent that they affect soil functioning through interactions between environmental and genetic factors. Here, five plant species (broad bean, pea, cabbage, fennel, and olive) grown under controlled pot conditions were tested for their ability
[...] Read more.
Plants are affected by soil environments to the same extent that they affect soil functioning through interactions between environmental and genetic factors. Here, five plant species (broad bean, pea, cabbage, fennel, and olive) grown under controlled pot conditions were tested for their ability to differently stimulate the degradation of standard litter. Litter, soil C and N contents were measured for evaluating chemical changes due to plant presence, while soil microbial abundance was evaluated to assess if it had a positive or negative catalyzing influence on litter decomposition. The architecture and morphological traits of roots systems were also evaluated by using specific open-source software (SmartRoot). Soil chemical and microbiological characteristics were significantly influenced by the plant species. Variations in soil C/N dynamics were correlated with the diversity of root traits among species. Early stage decomposition of the standard litter changed on the basis of the plant species. The results indicated that key soil processes are governed by interactions between plant roots, soil C and N, and the microbial metabolism that stimulate decomposition reactions. This, in turn, can have marked effects on soil chemical and microbiological fertility, both fundamental for sustaining crops, and can promote the development of new approaches for optimizing soil C and N cycling, managing nutrient transport, and sustaining and improving net primary production.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Planned Papers
The below list represents only planned manuscripts. Some of these
manuscripts have not been received by the Editorial Office yet. Papers
submitted to MDPI journals are subject to peer-review.
1. Title: Phytostimulatory influence of Comamonas testosteroni and Silver nanoparticles on Linum usitatissimum L. under salinity stress
Author: Hussein Migdadi