Abstract
As a novel decentralized computing paradigm, blockchain is expected to disrupt the existing e-commerce architecture and process. Secure smart contracts are the crucial foundation for e-commerce based on blockchain. However, vulnerabilities in smart contracts occur from time to time and cause significant financial losses in e-commerce. Some static verification methods have been developed to guarantee security for e-commerce smart contracts at design time, but they cannot support complex scenarios at runtime. As a lightweight verification method, runtime verification is a potential method for secure e-commerce smart contracts. The existing runtime verification methods are based on the manual instrument, which leads to additional overheads and gas consumption. To deal with this, we propose a passive learning-based runtime verification framework for e-commerce smart contracts. Firstly, by exploring the Genetic algorithm to evolve state merging and automaton reorganizing in order to simultaneously split time and gas behaviors, we propose a passive learning method to model runtime information for e-commerce smart contracts (PL4ESC). It directly learns P2TA (priced probabilistic timed automaton) from runtime traces without any prior knowledge. Then, we integrate PL4ESC with the open-source PAT (Process Analysis Toolkit) to automatically verify the security of runtime e-commerce smart contracts. The experiments show that PL4ESC is better at accuracy and precision than state-of-the-art passive learning methods. It improves accuracy by 1 to 4 percent compared to TAG and RTI+. As far as we know, it is not only the first learning method that can learn a P2TA from traces, but it is also the first automated runtime verification framework for e-commerce smart contracts. This will provide security guarantees for blockchain-based e-commerce.
1. Introduction
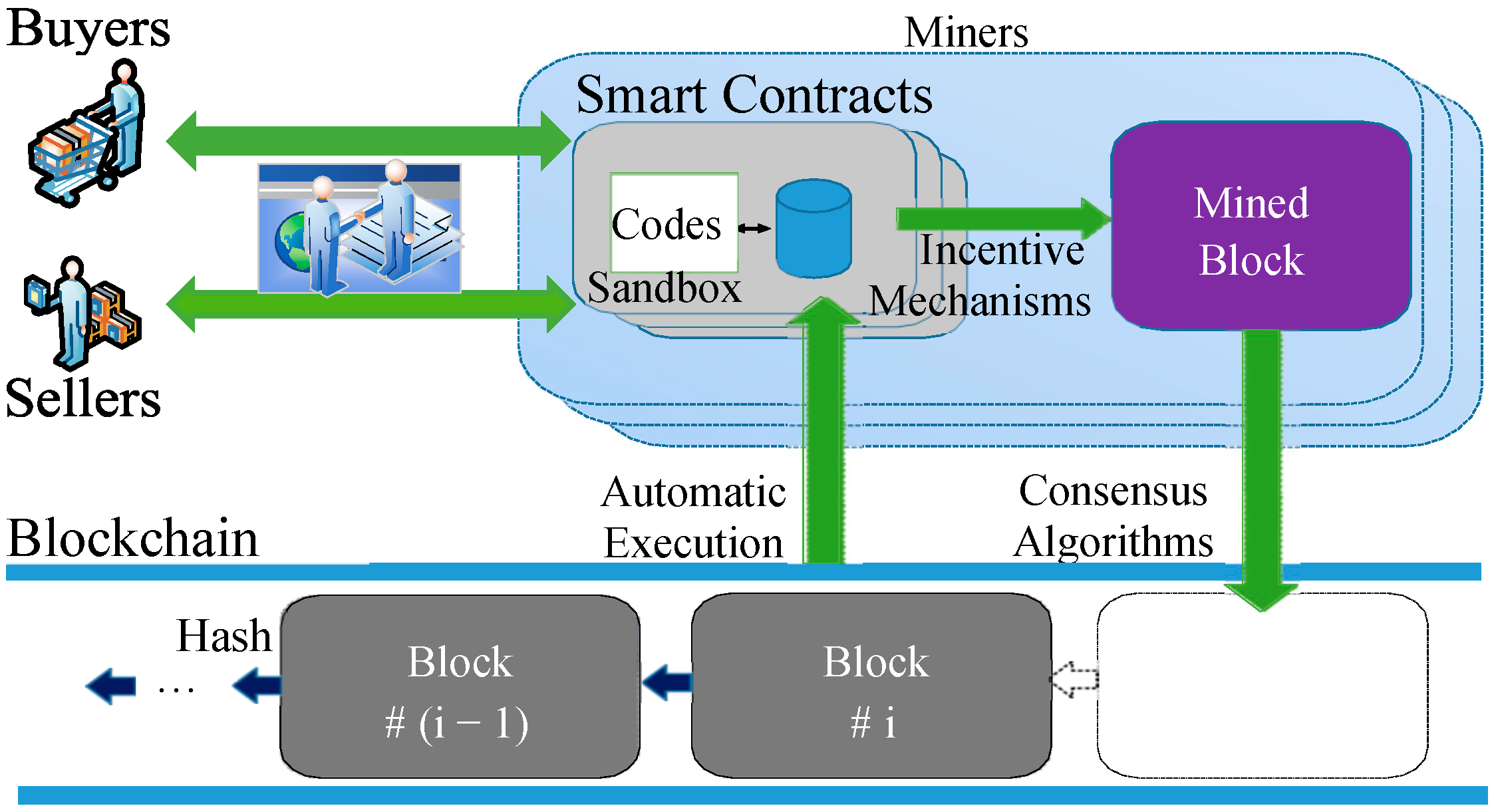
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed digital ledger technology that records transactions among multiple parties in a way that ensures recorded data are secure, transparent, and immutable [1]. In recent years, this has been applied in e-commerce [1], supply chains [2], the sharing economy [3], peer-to-peer data exchange [4], and so on. Blockchain is expected to disrupt existing e-commerce architecture and reconstruct e-commerce processes. Compared with traditional e-commerce, blockchain-based e-commerce can improve efficiency, reduce costs, enhance transparency, and realize decentralized transaction processes. As shown in Figure 1, the smart contract is a bridge between blockchain and the e-commerce domain [5,6,7]. In blockchain-based e-commerce, the smart contract is a type of program code endorsed by two parties (the seller and buyer), which is equivalent to a legal instrument in the real world. E-commerce smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement written directly into code on a blockchain. They automate and secure transactions in online commerce by ensuring that the conditions of a contract are met before the transaction is completed. This offers transparency, security, and efficiency by eliminating the need for intermediaries. Different from traditional program codes, e-commerce smart contracts generally control huge amounts of financial assets. The execution of e-commerce smart contracts in the blockchain will cost a certain amount of gas. If the gas is insufficient, the e-commerce transaction executed by a smart contract cannot be completed. Moreover, once an e-commerce smart contract is deployed on the blockchain, it cannot be modified except at a high cost, such as the hard fork. Thus, a secure e-commerce smart contract is very important for blockchain-based e-commerce. However, security vulnerabilities in smart contracts have emerged one after another, and some of them have brought huge economic losses to the real world [8]. For example, in April 2022, Akutar, a blockchain-based NFT project, lost ETH 11,539 (about USD 34 million) due to a vulnerability in the smart contract (https://beosin.com/resources/34m-locked-due-to-contract-vulnerabilities-in-akutar, accessed on 13 March 2025). At present, as analyzed in Section 2.1, the security of smart contracts is still an open problem for blockchain-based e-commerce.
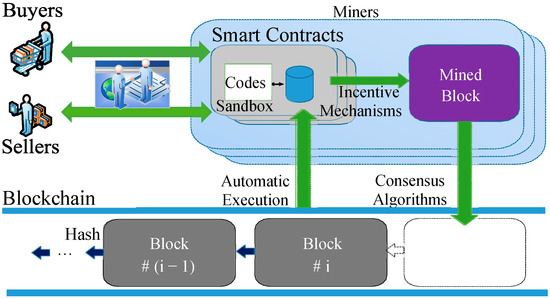
Figure 1.
Decentralized e-commerce based on blockchain.
1.1. Problem Analysis
Much of the existing work relies on static verification to address the security of smart contracts, which can provide a provable security mechanism at design time. These include theorem proving [9], symbol execution [10], and model checking [11]. Such methods can be used to ensure e-commerce smart contracts at design time, i.e., before deployment to the blockchain. These are heavyweight verification techniques that cannot consider all the situations of e-commerce smart contracts at runtime. Runtime verification [12], a lightweight verification technology, makes up for static verification. It can monitor the runtime behavior of e-commerce smart contracts and verify security properties. The core goal of runtime verification is to obtain the runtime behavior information of e-commerce smart contracts. At present, many methods achieve this by inserting instrument codes into the source codes of smart contracts. This leads to additional overheads for e-commerce smart contracts and consumes more gas at runtime. In addition, only one property can be tracked per monitor, which greatly reduces the efficiency of verification.
There is also another way to analyze the runtime behavior of e-commerce smart contracts, which is based on the traces of e-commerce smart contracts at runtime. We argue that this can be an alternative solution for runtime verification of e-commerce smart contracts. This is to say, rather than verifying smart contracts by monitoring, this aims to extract a runtime model from the traces of e-commerce smart contracts and verify the model automatically. The key to verifying e-commerce smart contracts by this method is solving how to model e-commerce smart contracts from the traces. With manual modeling, it is difficult to take into account all secure aspects of e-commerce smart contracts [13,14]. Moreover, the model’s quality completely depends on the modeler’s knowledge and understanding of e-commerce smart contracts, and this will inevitably lead to uneven model verification results. Recently, model learning [15,16,17] has developed rapidly; it automatically learns a model from the samples of observations or executions of a system. Such a model can be used for verification and analysis of an e-commerce smart contract at runtime. Model learning has been widely used in many fields, including analyzing TCP or SSH implementations [18,19], modeling automatic driving behaviors [20], and automatic generation of software behavioral models [21]. In [22], Dong et al. extracted probabilistic automata from observations to explain recurrent neural networks. The core of model learning is the learning algorithms that learn a model from a runtime system. In fact, many learning algorithms learn the system as a deterministic finite automaton (DFA) [23] or variants of DFA [24]. However, current learning algorithms have shortcomings in terms of the accuracy and expressiveness of the learned model, which are still not expressive enough for e-commerce smart contracts at runtime. Moreover, the effectiveness of the learning process, especially state merging, should be enhanced.
1.2. Our Contributions
We take Ethereum Solidity as the concrete e-commerce smart contract, which is the first Turing-complete programming language of smart contracts. We take quantitative security specification [25] in PCTL (probabilistic computation tree logic) as the verification property. We argue that model learning can be used to model runtime e-commerce smart contracts. To efficiently obtain a runtime model closer to the real situation of an e-commerce smart contract, in this paper, we propose a novel model learning method without any prior knowledge. It is a passive learning method that can learn P2TA (priced probabilistic timed automaton) as the runtime model for an e-commerce smart contract (PL4ESC) from historical events (i.e., traces). Compared to state-of-the-art passive learning methods, such as TAG [26] and RTI+ [27], PL4ESC is the most effective, as it can simultaneously model temporal and gas consumer behaviors in an e-commerce smart contract at runtime. The gas is modeled as a price on each edge of the P2TA. In addition to this, to further improve the effectiveness of PL4ESC, we designed a Genetic algorithm to merge state sequences and devise automaton reorganizing to simultaneously split time and gas behaviors. This will reduce the possibility of generating false mergers and improve the accuracy of the learned model, P2TA. Then, we integrated PL4ESC into the open-source PAT (Process Analysis Toolkit) [28,29] to implement the automated security verification of e-commerce smart contracts at runtime. The specific contributions of this paper are as follows:
(1) A new passive learning method, PL4ESC, is proposed, which can learn P2TA for runtime e-commerce smart contracts from Ethereum logs. Compared with state-of-the-art passive learning methods, it can obtain a more expressive model. It is the first work to model runtime smart contracts by passive learning. It is also the first work to automatically model the gas information of runtime smart contracts.
(2) The Genetic algorithm is designed to evolve the state-merging process, and automaton reorganizing is devised to simultaneously split the time and gas behavior information, which can enhance the accuracy and precision of the PL4ESC method.
(3) An automated security verification framework for runtime e-commerce smart contracts is implemented based on PL4ESC and the open-source PAT. It is the first automated runtime verification framework for smart contracts. Compared with instrument-based runtime verification, it avoids additional runtime overheads, improves verification efficiency, and enriches the diversity of verifiable properties.
The comparisons between PL4ESC and the state-of-the-art passive learning methods TAG [26] and RTI+ [27] are shown in Table 1. Compared with TAG, PL4ESC can learn the stochastic behaviors of e-commerce smart contracts. Compared with RTI+, PL4ESC owns simple parameters. The most important things are that the gas consumption can be learned as the price of P2TA by PL4ESC and that the accuracy of PL4ESC is improved by the Genetic algorithm and automata reorganizing. As far as we know, it is not only the first learning method that can learn P2TA from traces, but it is also the first automated runtime verification framework for e-commerce smart contracts. This will provide security guarantees for smart contracts, which will be valuable and helpful for blockchain-based e-commerce.

Table 1.
Comparisons between PL4ESC, TAG, and RTI+.
1.3. Structure of the Paper
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: In Section 2, we summarize related works about the security verification of e-commerce smart contracts and model learning methods. Section 3 defines the runtime model P2TA for e-commerce smart contracts. Section 4 shows the details of the PL4ESC method. In Section 5, we present the runtime verification framework for e-commerce smart contracts in a small-scale case. In Section 6, we analyze the Genetic algorithm and automaton reorganizing on the accuracy of PL4ESC with a large-scale case and compare it with state-of-the-art passive learning methods TAG and RTI+ in accuracy, precision, and recall. Finally, Section 7 summarizes our work and points out future directions.
2. Related Works
2.1. Security Verification of Smart Contracts
Much work has been done to ensure the security of smart contracts through formal verification technologies [29]. They can be divided into verification at design time (theorem proving, symbol execution, and model checking) and verification at runtime (runtime verification). Security verification at design time belongs to static verification, which can verify the security of e-commerce smart contracts off the blockchain. Security verification at runtime belongs to dynamic verification, which can verify the security of e-commerce smart contracts on the blockchain. In [9], a theorem-proving approach was proposed to verify Ethereum smart contracts at the level of EVM bytecode. Tsankov et al. [30] developed a tool called Securify, a security analyzer for Ethereum smart contracts, which can automatically prove that the contract behavior is secured/unsecured for the given properties. Similar work includes [31,32,33]. Reference [10] proposed a new verification approach by learning a fuzzer from symbolic execution and instantiating it to the domain of smart contracts. Reference [34] proposed a user-friendly verification framework by symbolic execution for binaries and smart contracts. In terms of model checking, Abdellatif et al. [13] modeled smart contracts as TA (timed automata) but also built simple blockchain mechanisms and simulated user behavior. This includes mining transactions in blocks and analyzing the interactions between these components by statistical models for assessing the chances of successful attacks on the smart contract. Andrychowicz et al. [14] used timed automata to describe the timed commitment of parties in Bitcoin, where the commitment protocol requires participants to exchange hashes of their committed secret values by a specified time. Reference [35] modeled smart contracts according to a three-fold modeling process, provided the translation rules from Solidity to NuSMV language, and verified the properties formalized in CTL by NuSMV. Zupan et al. [36] presented a method and a prototype tool to generate secure smart contracts based on Petri Nets. They used Petri Net to model a workflow of smart contracts and then automatically translated the model into executable smart contract code through mapping rules. While not the same as static verification, Azzopardi et al. [37] focused on runtime properties and developed a smart contract runtime verification tool, ContractLarva. The tool ContractLarva integrates monitoring code and specifications into the target smart contract and reacts at runtime once the monitor detects a violation. In [38], Abraham et al. used the K framework for runtime verification of ERC20 tokens. In [39], a model-based verification tool, solidClarva, was proposed by combining an uncertain static analysis step with runtime verification.
As mentioned above, most of the security verification works for smart contracts focus on static verification. They aim to deploy a secure smart contract on the blockchain, i.e., validate/prove correctness before the contract is deployed. However, the runtime situation of e-commerce smart contracts is complex, and static verification can hardly take into account all cases. Runtime verification is a supplement to static verification. It tracks some runtime key information by manually instrumenting source codes, which inevitably introduces additional overhead and gas costs for e-commerce smart contracts. In this paper, we propose a model learning method to model runtime e-commerce smart contracts from Ethereum logs and automated verification of security properties on the learned model.
2.2. Model Learning
There are some works about model learning for modeling an information system, such as learning automata or state machines from traces of a runtime system. An excellent survey of recent results, applications, and case studies can be found in [40]. Overall, this research can be categorized as active learning or passive learning. The former learns automata with queries; a passive learning technique learns the model of the system from its traces (i.e., inputs, outputs, and tests). A seminal work in active learning is Angluin’s work on learning DFAs with membership and equivalence queries [41]. Based on this work, many other types of models are learned, such as Mealy machines [42], symbolic /extended Mealy machines [43,44], or timed automata [45]. However, in practice, it is almost impossible to perform a complete equivalence query. As the complexity of the system increases, its model has exponential complexity, and the number of queries will also increase exponentially.
In passive learning, the key is how to merge the states. Evolutionary algorithms for DFA learning have been investigated in [46]. In [23], DFA can be learned with a smart state labeling evolutionary algorithm. Compared with pure evolutionary algorithms, state merging is more widely used in passive learning, such as evidence-driven state merging (EDSM) [47] and its improved version [48]. In addition to learning DFA, some works have also extended passive learning to model complex systems with richer semantics, including Moore machines [49], extended finite state machines [50], probabilistic automata [24], etc. There are also works that focus on temporal information and learn timed automata from timed sequences. For example, a passive learning method for more general stochastic timed systems has been proposed in [51]. They targeted learning generalized semi-Markov processes from sample executions of stochastic discrete-event systems. In [52], Mao et al. proposed to learn continuous-time Markov chains through state merging. RTI+ [27] passively learns probabilistic deterministic real-time automaton (PDRTA) via EDSM from a sequence of positive time stamp events. The notions of clock and guard are also reduced to an acceptable delay interval between two consecutive events, and the probability of their occurrence is added to each transition. Timed K-Tail (TKT) [53] is a specification mining technology that can capture nested operations of duration in information systems, in which a timed trace is included for each operation. The TKT algorithm is based on the passive learning technique, k-Tail [54], which defines the current state by computing the future behavior, and states with the same future behavior should be merged. Similarly, the TAG algorithm inherits this type of state-merging method. Compared with the RTI+ algorithm, the TAG algorithm can easily balance the precision and recall of the learned model by controlling the unique K value [26].
As stated above, many works have made corresponding contributions to passive learning. Some works focus on the accuracy of models, from simple state merging to EDSM, transition splitting, etc., while others aim to learn more expressive models, from deterministic finite automata (DFA) to probabilistic finite automata (PFA) to timed automata (TA) and even probabilistic timed automata (PTA). The ideal passive learning method is to learn a model that is small enough, accurate enough, and expressive. However, modeling e-commerce smart contracts brings new challenges to passive learning. Different from traditional e-commerce systems, this needs a more expressive runtime model, as the gas consumed by the runtime e-commerce smart contract should be considered in the learned model. Moreover, the efficiency of the learning process should be enhanced, given that the e-commerce smart contracts will consume gas at runtime.
3. Runtime Model of E-Commerce Smart Contract
The runtime behavior of smart e-commerce contracts is complex and diverse. It needs an expressive model to model its runtime behaviors. We argue that the P2TA (priced probability timed automata) [55] is an appropriate formal model to describe the runtime of an e-commerce smart contract. It can simultaneously simulate the stochastic action, time, and gas consumed at runtime. In this section, we present the syntactic and semantics of P2TA and the corresponding relationship between this and runtime e-commerce smart contracts.
3.1. Clocks, Guards, and Probability
Let be the time domain of either the non-negative reals or naturals. The clock is a real value variable taken from the time domain , which can be used to measure the elapse of time. Let be a finite set of clocks. For a clock , a clock valuation is a mapping . Let V be a set of clock valuations, that is, V. For any , the clock valuation denotes the time increment of the values in by d. Assuming , we use to denote the clock valuation obtained from by resetting the clocks x to 0.
A guard is a conjunction of inequalities, where the value of a single clock is compared to an integer. Formally, the set Guards() of guards is defined by the grammar: x C < x C ≤ x , where is the clock, and is a positive rational number.
A discrete probability distribution for events over a finite state set S is a function S × → [0, 1], i.e., every event has a value P(S =|s) given the current state s, and , where .
3.2. Priced Probabilistic Timed Automata for an E-Commerce Smart Contract
We define the components in priced probabilistic timed automata for e-commerce smart contracts. A priced probabilistic timed automaton (P2TA) for an e-commerce smart contract is an 8-tuple P2TA = (L, l, Act, X, inv, , H, E), where L is a finite set of states and l is the initial state; Act is the set of smart contract events (which is equivalent to the actions performed by the smart contract); X is the only clock, which is reset in every transition; inv: L → Guards(X) is the invariant condition; is a probability distribution; H: L Act → is the price function, which provides a price rate to every location L, and a price to every action act; the price of taking the timed move (a, t) from state (S, ) is then defined by H(S)·t + H(a); and E L × Act × Guards(X) × (L × Act) × × L × H is a set of edges. For a specific edge e = (L1, a, g, h, p, L2) E, L1 and L2 denote the two states of the smart contract, a is an action, g is a guard, and h and p denote the price and probability, respectively. It means that the e-commerce smart contract executes from state L1 to state L2 by action a with the probability p when guard g is satisfied, and the gas consumption for this transition is the price h.
Let P2TA = (L, l, Act, X, inv, , H, E) be a priced probabilistic timed automaton for an e-commerce smart contract. The semantics of P2TA is the priced state transition system with time, the probabilistic PSTS = (S, s, Act, , H, , Steps) consists of a set of states S = , an initial state s = (l0, 0) S, a set Act of actions, and a time domain , while H is a price function, representing the price increment at state transition, and is the state transition probability and a transition relation with probabilistic and time Steps S × (Act ) × × H × S. Formally, a path of a PSTS is a finite sequence of probabilistic transitions and is defined as: , , is a specific value of , , and .
The set of steps contains two types of transitions: time transitions and discrete transitions. Discrete transition: for with in an e-commerce smart contract, there exists a transition such that the valuation satisfies Guard(X) and .
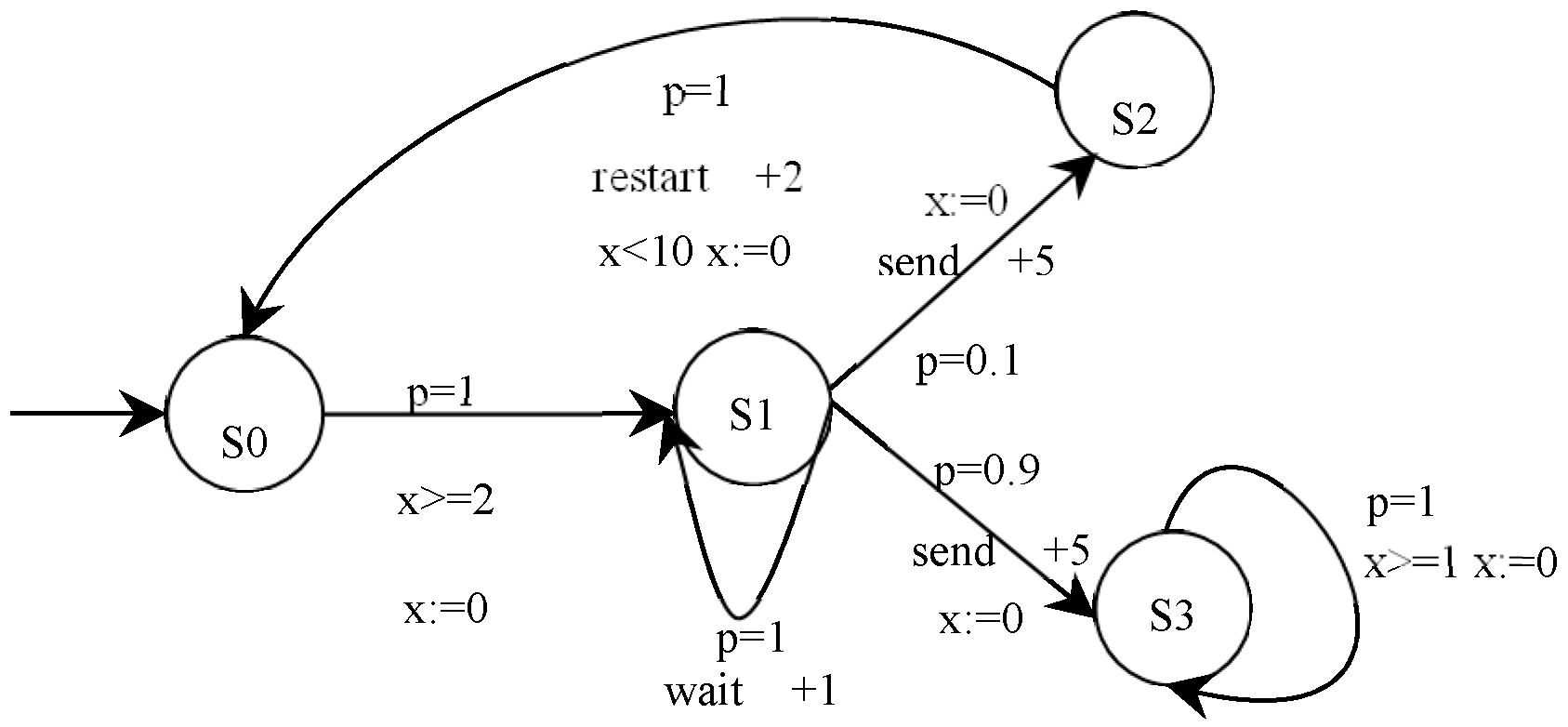
Figure 2 shows a toy P2TA example of an e-commerce smart contract for communication between a buyer and a seller. The contract has four states: S0 is the initial state, S1 denotes the buyer trying to send a message to the seller, S2 means sending fails, and S3 denotes sending success. In this P2TA, from initial state S0, the buyer starts to try and send the message to the seller with gas 3; then, a nondeterministic choice happens between (a) waiting a step with gas 1 because the channel is unready and (b) sending the message with gas 5; if the latter occurs, it sends successfully with a probability of 0.9 and stops with gas 1. If it is the former, the send fails with a probability of 0.1 and restarts with gas 2. A single clock x measures the time between each event. As a result of the function execution, an event is triggered, and the state of the e-commerce smart contract changes, such as (S1, send, g [0, 1], h = 5, p = 0.1, S2), which means that the e-commerce smart contract holds on state S1 for less than 1 time unit and jumps from state S1 to state S2 by executing the action “send” with a probability of p = 0.1 and a gas consumption +5.
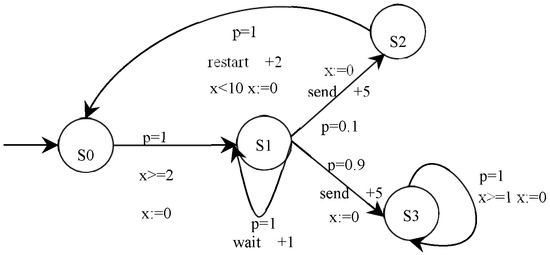
Figure 2.
A toy P2TA for an e-commerce smart contract.
4. Passive Learning P2TA for Runtime E-Commerce Smart Contracts
This section proposes the passive learning method for modeling the runtime behaviors of e-commerce smart contracts (PL4ESC for short). It learns P2TA (priced probabilistic timed automaton) from the runtime traces of an e-commerce smart contract without any prior knowledge. Compared to state-of-the-art passive learning methods, it can learn a more expressive model with stochastic behaviors, such as the time and gas consumed for runtime e-commerce smart contracts. Firstly, PL4ESC produces an automaton, which is basically a graphical representation of the input sample with all its redundancies. Then, it merges the states with these structural redundant parts to obtain a more compact P2TA. After size reduction, the temporal values are recomputed, which may be necessary to refine the automaton in splitting and reorganizing. In general, after obtaining the initialized automaton, PL4ESC merges all valid states to reduce the automaton, ignoring the time and gas values. We argue that states with the same k-future value can form a valid merger. The optimal sequence of state merging is selected according to the Genetic algorithm, which greatly reduces the probability of incorrect mergers. When no states can be merged, PL4ESC attempts to split and reorganize the automata with more detailed constraints in the transitions. Compared with TAG, PL4ESC splits the time and price simultaneously, which avoids information loss caused by multiple splits of an edge through automaton reorganization. Each transition is associated with a probability corresponding to the proportion of transition taken in the input sample. These probabilities are initialized in the automaton initializing and updated after each merging, thus splitting or reorganizing with respect to the new distribution. We will illustrate the details of the PL4ESC method in the following, including automaton initializing, Genetic algorithm-based state merging, splitting, and reorganizing.
4.1. Automaton Initializing
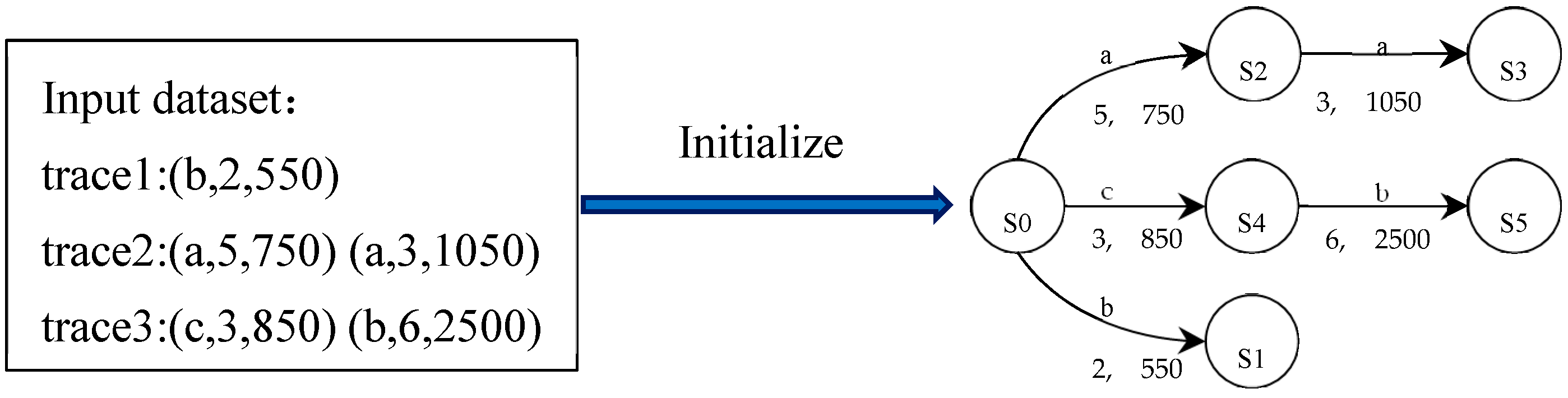
Multiple events in the Ethereum logs constitute the runtime traces of a runtime e-commerce smart contract, which are the inputs used for PL4ESC. Formally, a runtime trace of a runtime e-commerce smart contract is a finite sequence, constituted by events in chronological order, which can be expressed as , where . Act represents a specific action of the event, which forms the alphabet of the learned model P2TA. Time and Gas are the time and gas consumed in this event, respectively. The initial automaton is represented as an augmented prefix tree acceptor (APTA). It is created from the input, where each path represents a specific sequence containing time and gas. The initial automaton is absolutely consistent with the input, and its size (i.e., the number of states) is equal to the number of Acts in the input. In Figure 3, we show the initial automaton with input {trace1, trace2, trace3}.
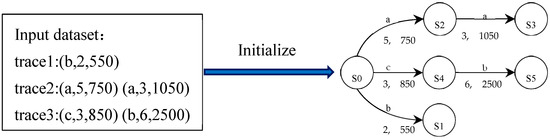
Figure 3.
Automaton initializing with the input sample.
4.2. Genetic Algorithm-Based State Merging
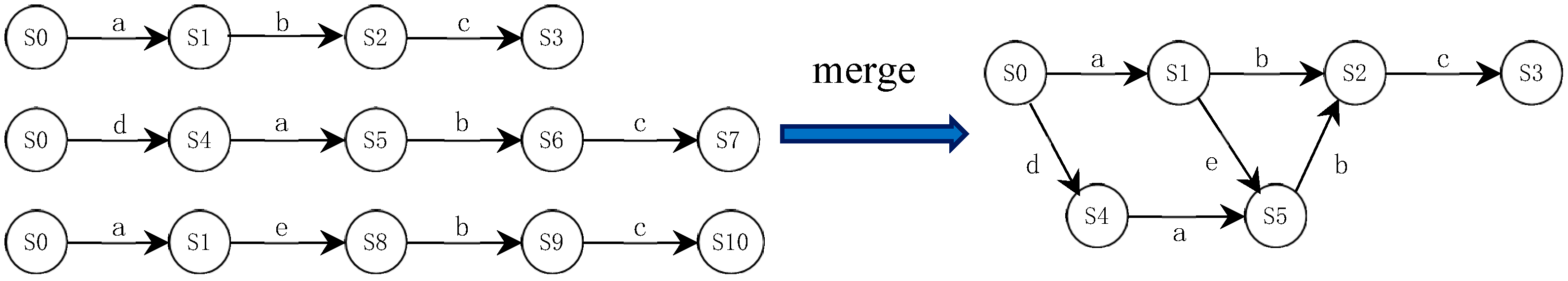
The general passive learning process is actually a process of state merging, which aims to reduce the size of an initial automaton. The key is to determine what type of states should be merged and how to balance the size and accuracy of the learned model. Undoubtedly, as the length of the merged sequence increases, the error of the learned model will also increase. The K-Tail [53] algorithm considers that a state is defined by its possible future behavior. Thus, for a given history (i.e., string prefix), the current state reached by the history is determined by its possible future. Two or more strings can share a common prefix, which are separated from each other and provide multiple futures for a single history. The “k-future” is defined as the next k actions, where k is an important parameter for merging. If two different states have the same “k-future”, they belong to an equivalence class and should be merged. As shown in Figure 4, merging two equivalent states from an equivalence class consists of accumulating their outgoing and incoming transitions and deleting the others. The initial automaton may have multiple valid mergers, and randomly merging states will lead to an accuracy decrease in the final learned model. Evidence-driven state merging (EDSM) [47] explicitly emphasizes that the choice of the first merged states has an important impact on the learned model. It uses heuristics to score state merging and prioritizes the highest score. Coste [56] regards state merging as a graph coloring problem. Each state in the augmented prefix tree acceptor (APTA) will be mapped to a state in the corresponding targeted determining finite automaton (DFA). If different colors are assigned to each state in the APTA, it will be mapped to one of these colors. EDSM may produce an incompatible color merger, i.e., the wrong model was learned.
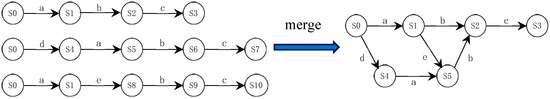
Figure 4.
State merging process based on k-future and deterministic conditions.
John et al. [57] pointed out that merging with large reductions is more likely to contain color-compatible mergers. Ideal state merging comprises finding the longest possible color-compatible merge sequence from a smaller merge space, which is more conducive to obtaining a low-error model. Inspired by the works of [57], we designed a Genetic algorithm (GA) to evolve the states merging process, as shown in Algorithm 1. First, the search space is expanded to the whole valid mergers, where it makes sense to increase the diversity of the population while including all color-compatible mergers. Second, adding the probability of being selected for each valid merger ensures that mergers with large reductions are more likely to be merged earlier. In the above processes, the merging sequence composed of multiple valid mergers is represented as a chromosome, and multiple chromosomes constitute a population. We introduce two concepts that will be used in the state merging based on GA as follows:
Reduction Count (RC) is defined as:
where denotes the size of the initial automaton, and is the size of the merged automaton.
Genetic probability (GPmerge) indicates the probability of a valid merger being selected and is defined as:
Genetic probability expresses the ratio of the Reduction Count of this state merging to the Reduction Count of all valid merging.
A valid merging with a larger GPmerge is more likely to occur in the chromosome, i.e., it is more likely to be preferentially merged. This ensures both the diversity and universality of chromosomes while allowing merging with a larger RC to be performed preferentially. In other words, it ensures that both the size and the error of the learned model are as small as possible. This is in keeping with the experimental results of [57]. The specific process of Genetic algorithm-based state merging is as follows:
(1) Creating a Reduction Table (RT). We first calculate the k-future of each state in the initial automaton (e.g., an augmented prefix tree acceptor). States with the same k-future can form a valid merger, and the RT is a set of all valid mergers in the initial automaton.
(2) Population initialization. First, we extract some valid mergers from the RT to form a chromosome with a length of L. The probability of each valid merger being extracted is GPmerge. For example, the probability of a valid merger X being extracted into the chromosome from RT is GPX. Multiple such chromosomes make up the initial population. It is important to note that we should avoid situations where the preceding merger in the chromosome makes the subsequent merger empty or invalid.
(3) Fitness evaluation. Intuitively, a chromosome that contains more color-compatible mergers is a good individual. However, during the actual learning process, we do not know which merger is color compatible; the only thing we can be sure of is that they are more likely to be found at the head of the chromosome. The fitness of a chromosome is calculated in two steps. First, we merge the states in the initial automaton according to the order in the chromosome to obtain a partial hypothesis (automaton with one or more valid mergers). Secondly, the states in the partial hypothesis continue to be merged until the final automaton is obtained, and its size is calculated as m. The chromosome fitness score is defined as:
where n + 1= . The ideal final learned model contains only one state for each letter in the alphabet. The chromosome with a lower score is a more suitable selection than the chromosome with a higher score.
(4) Crossover. We use a variant of uniform crossover in the GA. Two chromosomes are selected as parents, and then a new chromosome (an offspring) is formed by randomly selecting a number L of valid mergers from the parents.
(5) Mutation. We randomly select a valid merger in an existing chromosome and replace it with a merger from the reduction table. It is also still randomly selected according to the probability of being selected.
(6) Selection. We randomly select a certain number of chromosomes from the population with the same probability and allow them to participate in the competition. The chromosome with a low fitness score will enter the sub-population or be used for parental selection in the crossover operations. The equal probability avoids the results from falling into local optima.
(7) New generation. The new population consists of four parts, defined as: Pnew = Psel + Pcro + Pmut + CHRO. Psel is the best individual in previous generations of the population (the last 30% of chromosomes in the fitness score); Pcro is the new individual obtained by crossover; Pmut is the new individual obtained by mutation; CHRO is a new chromosome generated from the Reduction Table, which ensures that the number of chromosomes in the new population is always the same as the initial population.
(8) Termination condition. The GA terminates either when a chromosome with a fitness score of zero is found or when a maximum number of generations have elapsed. In the second case, the final hypothesis corresponding to the fittest chromosome is returned.
| Algorithm 1: State merging based on GA |
| Input: An augmented prefix tree A, Reduction Table RT |
| Output: A P2TA merge(A) such that L(A) ⊆ L(merge(A)) and |merge(A)| < |A| |
| 1: Creating some chromosomes from RT(the number is p, length is L) |
| 2: i = 0, Score ≠ 0 |
| 3: While (!(i >= I) and !(Score==0) ) |
| 4: Fitness evaluate: |
| 5: for each chromosome from Population do |
| 6: Merging all valid merges from chromosome in A => a part hypothesis PH |
| 7: if Si and Sj will be merged do |
| 8: for all t ∈ Ein(Sj) do |
| 9: Replace t = (S, act, g, h, p, Sj) with (S, act, g, h, p, Si) |
| 10: for all t ∈ Eout(Sj) do |
| 11: Replace t = (Sj, act, g, h, p, S) with (Si, act, g, h, p, S) |
| 12: Delete Sj |
| 13: Merging the remaining valid merges by EDSM in PH => a final hypothesis FH |
| 14: |
| 15: Crossover, Mutation, Selection |
| 16: New generation |
| 17: i++ |
| 18: A is the P2TA corresponding to the chromosome with the lowest fitness score |
| 19: return merge(A) |
4.3. Splitting and Reorganizing
(1) Splitting
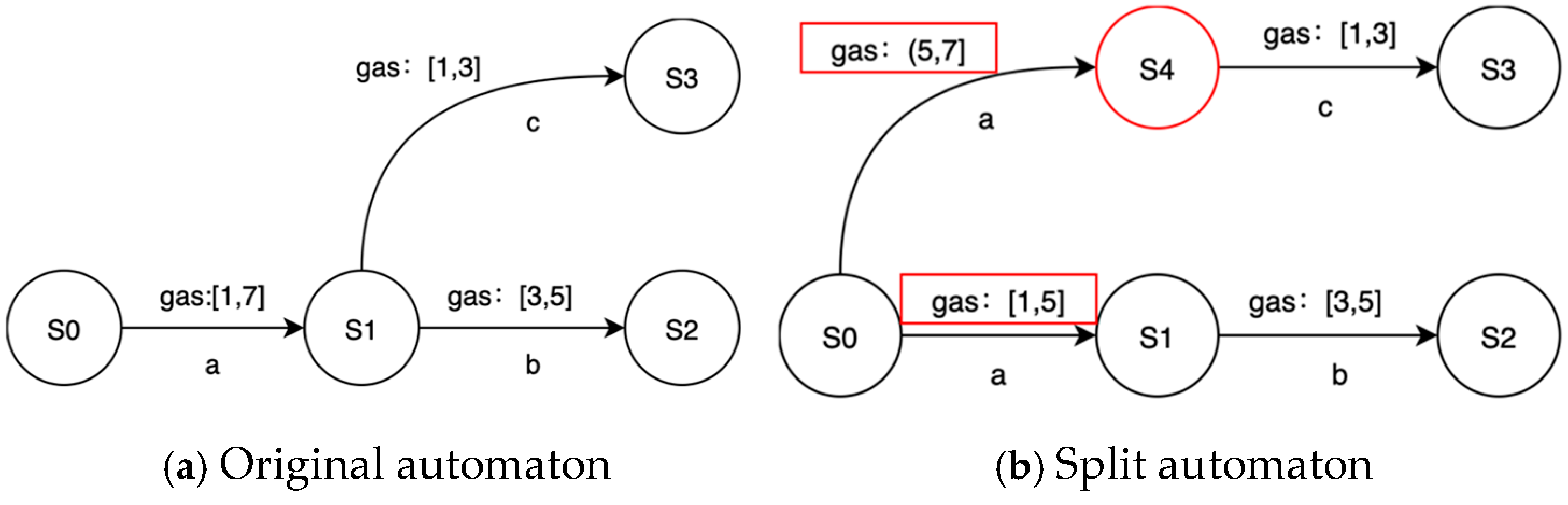
The purpose of splitting is to obtain more sensitive and detailed transitions in the learned model P2TA. PL4ESC extends the time guards’ splitting to simultaneously split the time and price guards. In the learning process, the specific gas consumed at each transition should be modeled. The condition of splitting depends on whether there is a more refined guard for a certain transition. Let us consider an edge e and guard [min, max] (here, guard may be the time or price) to be on the state s1 to s2, and let s2 lead to different parts of the automaton: part 1 and part 2. Given an input sequence, if a timed transition e from s1 to s2 is always going to part 1 with a delay in [min, v], while others lead to part 2 with a delay in [v + 1, max], v [min, max], then the transition e can be split. A new state, s3, reached from s1, is created, such that s2 leads to part 1 and s3 to part 2. Both transitions from s are labeled by the same action but are associated with different guards [min, v] and [v + 1, max]. We take the splitting transition with the gas interval as an example, which is shown in Figure 5.
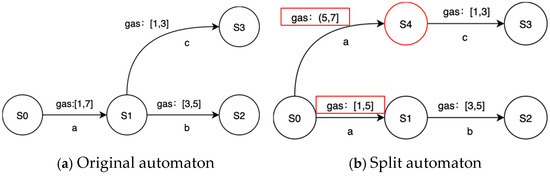
Figure 5.
A toy example of splitting.
Formally, the states and transitions needed to be split can be defined as follows. Let A, B, C, and D be the states of a P2TA if there exists a unique transition , such that at least and hold, then B and e are a state and transition that requires splitting, respectively. Let e = () be a transition from state S to A, g = [g1, g2] be a time interval, h = [h1, h2] be a gas consumption interval, and the splitting trigger conditions can be classified as two types: (1) There exists t < g2, such that when g = [g1, t], holds, then transition e is split according to the time interval. (2) There exists t < h2, such that when h = [h1, t], holds, then transition e is split according to the gas consumption interval. The key to splitting is how to quickly find critical value t in the guard interval. We adopted the KDE (kernel density estimation) method to determine the value of t. The determined process is as follows:
- Number Extraction: Select a guard [min, max] from the edge to be split. During the initialization of the automaton, in order to obtain a more generalized automaton, we extend the discrete data in a runtime trajectory with a continuous interval. In order to ensure the accuracy of splitting and reduce the interference of irrelevant data, we need to extract all the discrete data that actually exists in the runtime trajectory from the guards. Note that the time and gas consumption need to be handled separately.
- Sorting: Sort all the extracted numbers for subsequent analysis.
- Kernel Density Estimation: Use the kernel density estimation method to estimate the probability density function of the data.
- Finding Density Saddle Points: Search multiple density saddle points on the density curve. These saddle points will divide the data into multiple parts.
- Determining the Boundary Value: The value corresponding to each saddle point is taken as the boundary value, and the data are divided into multiple parts. Each part forms a new guard interval.
- Validate: Kernel density estimation often results in multiple saddle points. A single saddle point will divide the discrete data into two parts. The number of saddle points selected depends primarily on the output number of the node to be split, but the actual situation may not require such a large number of nodes. After determining the number of saddle points to be selected, we can obtain the value of t.
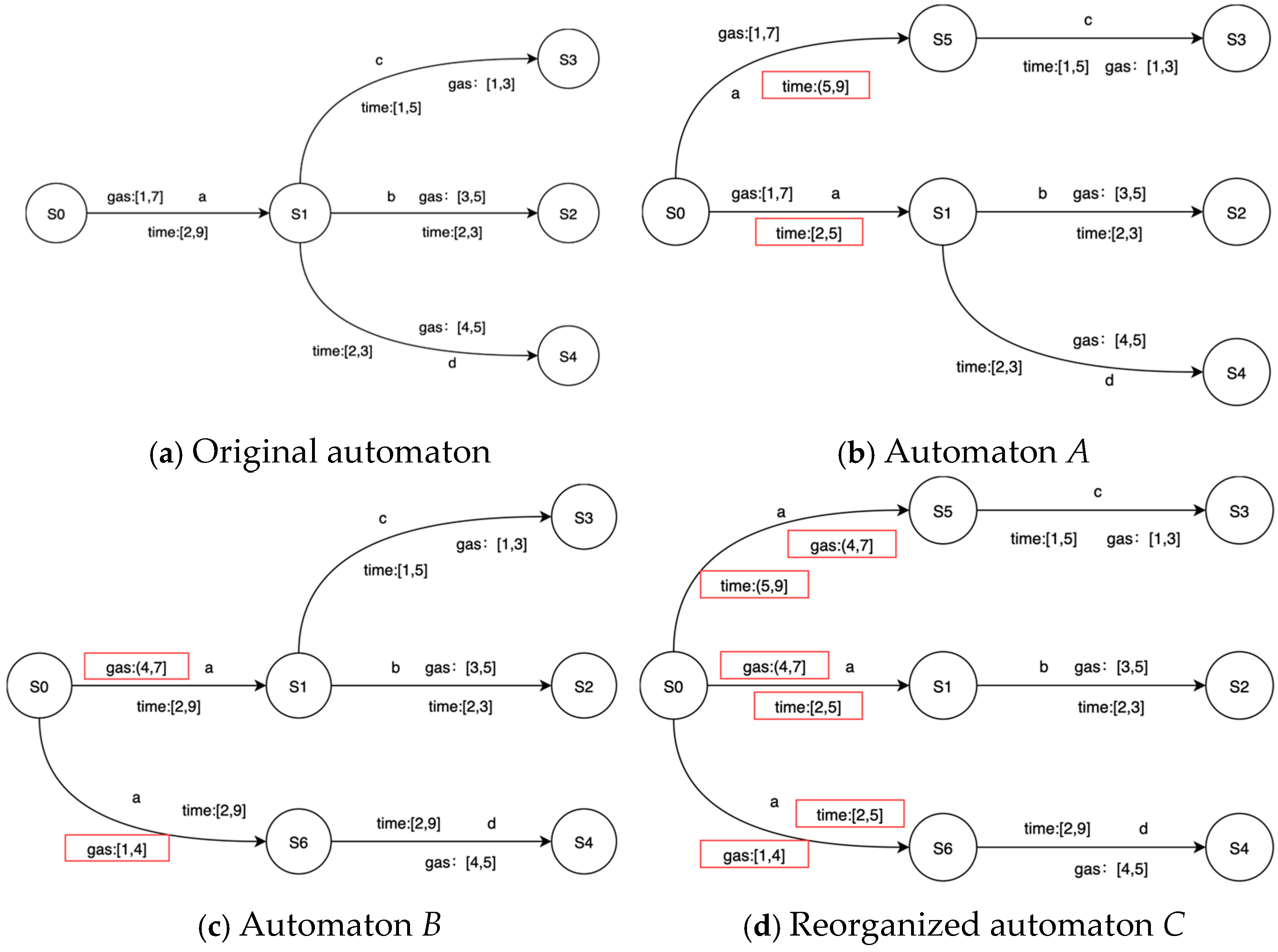
(2) Reorganizing
In the splitting process, if an edge satisfies both splitting conditions of time and price, and the future states are inconsistent, a conflict is bound to occur. PL4ESC perfectly avoids this type of conflict through automaton reorganization. It is important to note that reorganizing automaton applies to edges that both satisfy the time guard and price guard splitting conditions. After the operation of splitting the edge, the recombination of time and gas consumption guards is bound to occur. When an edge simultaneously meets the splitting conditions of both time and gas consumption, in order to avoid the confusion and conflicts caused by the recombination, we always split one type completely before proceeding with another type. Consider an automaton, as shown in Figure 6, which has the following three paths: S0->S1->S2, S0->S1->S3, and S0->S1->S4. The transition between S0 and S1 simultaneously satisfies the conditions of time division and gas consumption. The time interval [2, 9] can be divided into two sub-intervals: [2, 5] and (5, 9]; the gas consumption interval [1, 7] can be divided into two sub-intervals: [1, 4] and (4, 7]. Suppose the transition is first split according to the time intervals. The guard (5, 9] ensures that state S1 always reaches state S3, while the guard [2, 5] makes state S1 always reach states S2 and S4, and automaton A is obtained. Then, the gas consumption interval is divided, where the guard [1, 4] makes state S1 always reach state S4, and the guard (4, 7] makes state S1 always reach states S2 and S3, and finally, automaton B is obtained. The reorganization takes the union of the two states and replaces the initial guard with a guard with higher sensitivity, which can obtain reorganized automaton C.
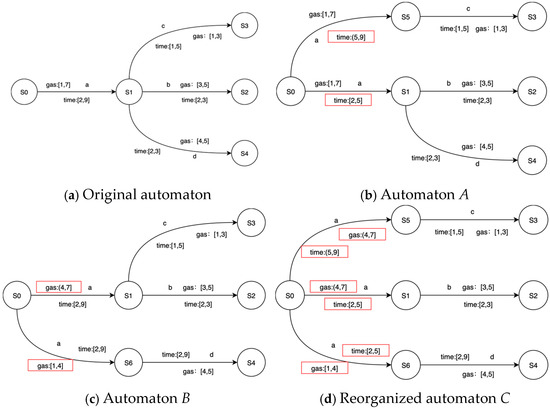
Figure 6.
A toy example of reorganizing.
Algorithm 2 shows the automaton reorganizing process. Assume that A and B are two automata from the same transition splitting. B will be a complement to A, i.e., information that is specific to B will be added to A.
| Algorithm 2: Automaton reorganizing |
| Input: P2TA A and B |
| Output: P2TA A |
| 1: Let A and B be the result of the transition T = (S1, a, g, h, p, S2) edge splitting |
| 2: Let S3 is a new state in A and S4 is a new state in B |
| 3: edge |
| 4: |
| 5: edge |
| 6: |
| 7: Reorganizing operation: |
| 8: add Bt1 to edge in A, |
| 9: At2 = (S1, a, g1,h1, p, S2) |
| 10: let state S is a child node of states S2 and S4 with action b |
| 11: replace (S2, b, g, h, p, S) with (S4, a, g, h, p, S) |
| 12: delete B |
| 13: end for |
| 14: A = Probability_Update(A) |
| 15: Return A |
(3) Complete example of splitting and reorganizing
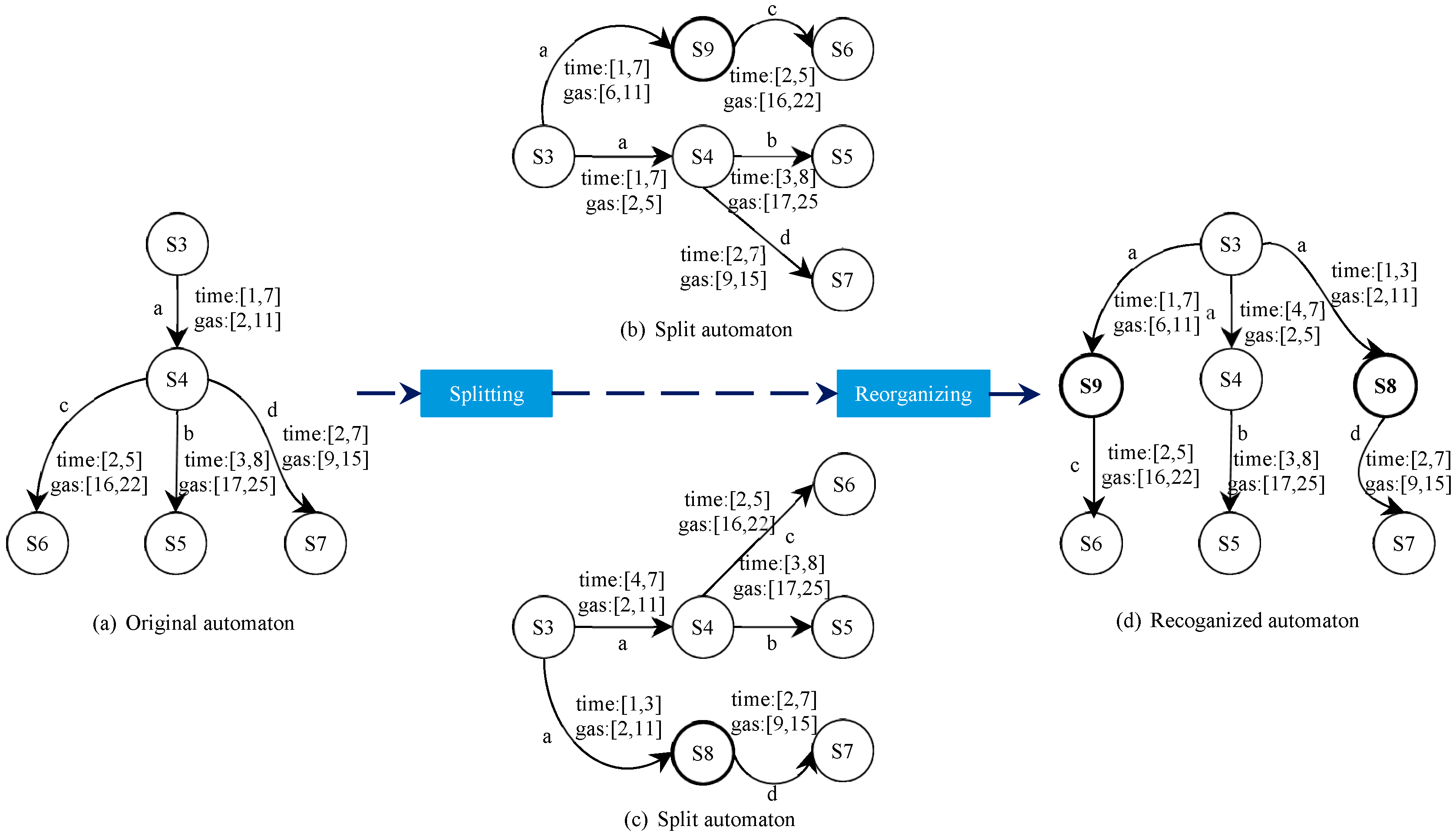
In Figure 7a, for example, states S3 to S4 via the edge labeled with a, we find that S4 moves to state S5 through the edge labeled b with time guard [3, 8] and time guard [2, 7] to state S7. Figure 7b shows the result of splitting. As shown in Figure 7, each transition is split based on the input sequence, which makes the automaton more accurate with respect to time and gas information. It divides a large time guard into several smaller guards and additionally assigns a new path to a particular guard to reach a new state. Our approach is to split the same edge twice, which will result in two different automata, as shown in Figure 7b,c. The final P2TA will be obtained by reorganizing two different automata, as shown in Figure 7d.
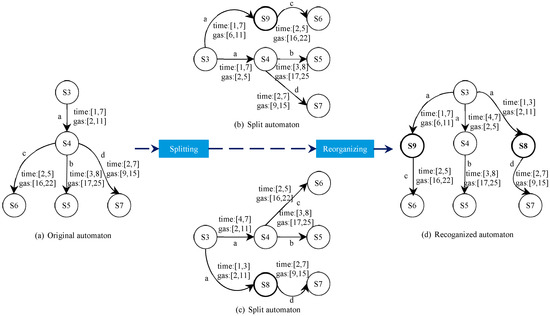
Figure 7.
A splitting and reorganizing process.
5. Automated Runtime Verification of E-Commerce Smart Contracts
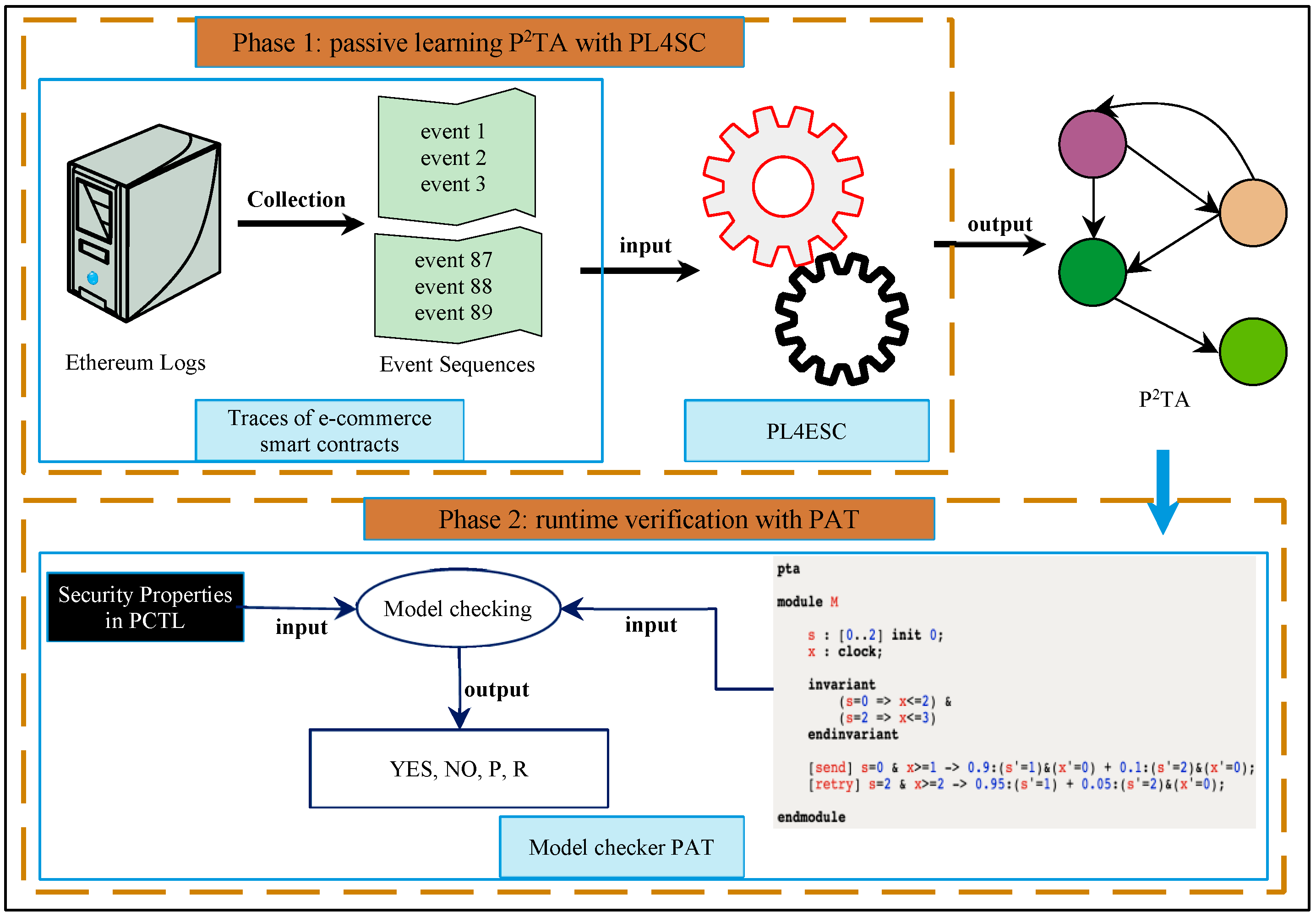
We orthogonally integrated PL4ESC with the open-source model checker PAT (National University of Singapore, Singapore) [28,29] to automatically verify runtime e-commerce smart contracts, as shown in Figure 8. The verification framework can be divided into two components: learning and model checking. In the learning phase, we first extracted the runtime events of a runtime e-commerce smart contract from the Ethereum logs and transactions. PL4ESC accepts these as input and outputs of a learned model for e-commerce smart contracts, i.e., P2TA. In the model-checking phase, the model checker PAT is used to verify and analyze the security properties of runtime e-commerce smart contracts on the level of the learned runtime model P2TA. The model-checking algorithm of P2TA is in the style of explicit-state exploration. The symbolic edition (implicit-state exploration) of the P2TA model-checking algorithm is under development, which will be open-source on the PAT website. Model checker PAT is a popular automatic process verification and analysis tool that can verify many qualitative or quantitative properties (e.g., security, fairness, and liveness) of a process with stochastic, concurrent, and real-time behaviors. It has been used to verify a variety of business process systems, such as in the fields of management, computing, business, and service. Thus far, it has 4370+ registered users from 1341+ organizations in 150 countries and regions. In PAT, the security properties of e-commerce smart contracts can be specified by PCTL (probabilistic computation tree logic), such as, “What is the probability of a e-commerce smart contract failure resulting in a shutdown within 4 h?”, “What is the worst probability of e-commerce smart contract error termination in all possible initial configurations?”, “What is the expected gas consumed after 30 min in the e-commerce smart contract?”, or “What is the expected worst-case gas required for the e-commerce smart contract to terminate?”.
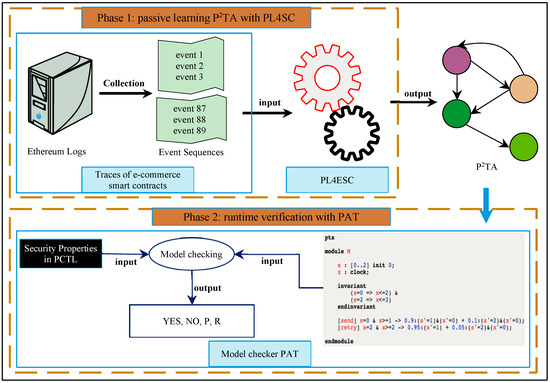
Figure 8.
A passive learning-based automated runtime verification framework of e-commerce smart contracts.
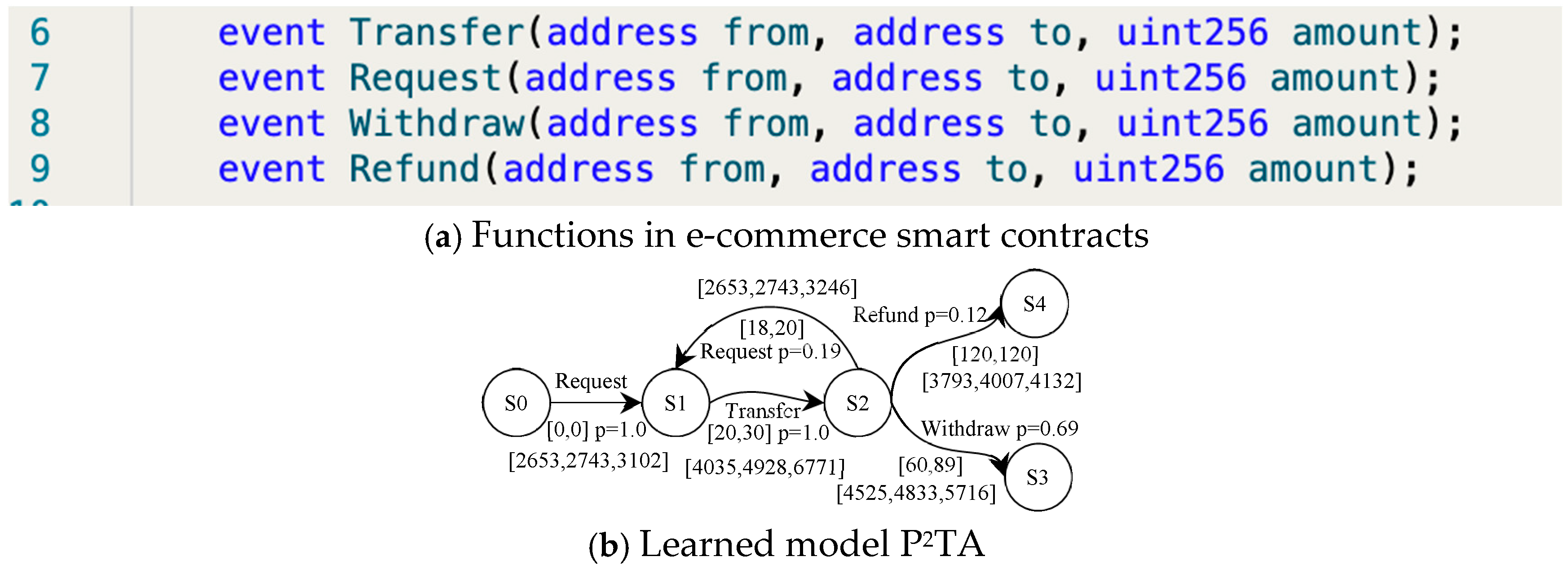
Let us consider a simple smart e-commerce contract for delegated transfers. It specifies some amount and time issues in the transfer and receipt process: (1) The recipient initiates a request to receive money, and the transferring party must transfer the money within a specified period of time after receiving the request. (2) If the transfer amount is less than the required minimum amount, the request must be initiated again and transferred again within the specified time. (3) If the minimum amount is met, the recipient should withdraw from the contract within the specified time limit (not earlier and not later). (4) If the recipient does not withdraw the money within the specified time, the amount in the contract will be returned. We have simply implemented the contract in the Ethernet Smart Contract Editor. The execution of the contract is completed by a number of specific functions, which will be triggered when the function is called, as in Figure 9a.
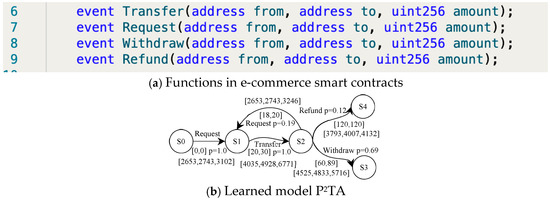
Figure 9.
The P2TA model for the delegated transfer smart contract.
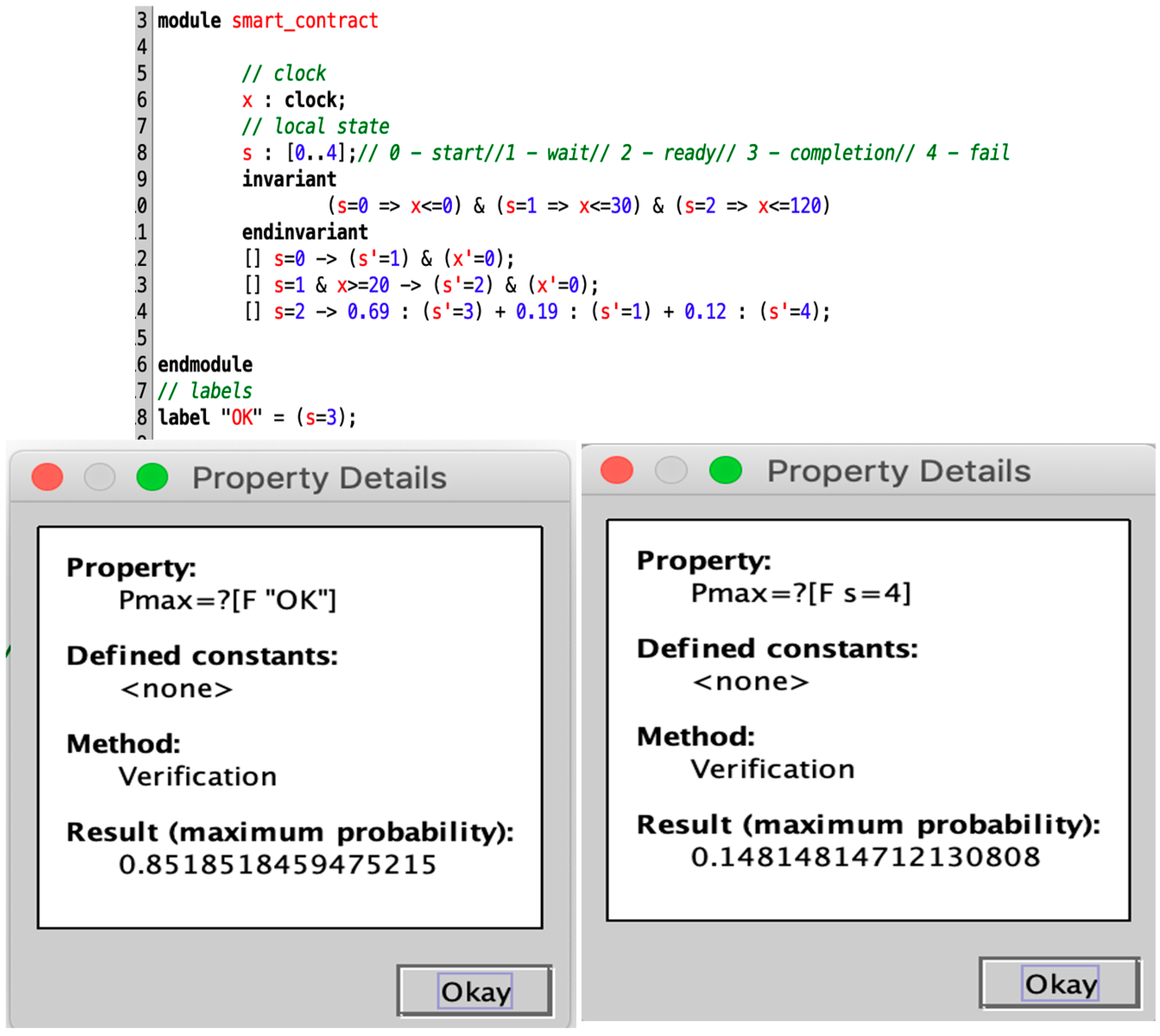
The e-commerce smart contract is randomly executed 100 times in Blockchain Ethereum. PL4ESC learns a runtime model P2TA from the traces, as shown in Figure 9b. In PL4ESC, the parameters are set as follows: k = 2 for “k-future”, population size P = 50, iterations I = 30, crossover rate CR = 0.6, mutation rate MR = 0.05, and elitism rate ER = 30%. Theoretically, Ethereum EVM specifies the amount of gas required for different operations in the contract (including reading and writing of data, state changes, etc.). However, the reality is that users will always provide more gas in order to have their transactions packaged as quickly as possible. Therefore, multiple prices are accumulated on each edge of the learned P2TA. They are formally expressed as a gas interval, which contains all gas consumptions for the action on this edge. We only show three kinds of meaningful values: minimum, maximum, and average. In the verification process, we can just pick one of the values according to the requirements. Figure 10 is the verification result of Figure 9b. It shows the maximum probability with which the smart contract reaches state S3 and state S4, respectively. We only demonstrate the verification of the quantitative properties related to probability.
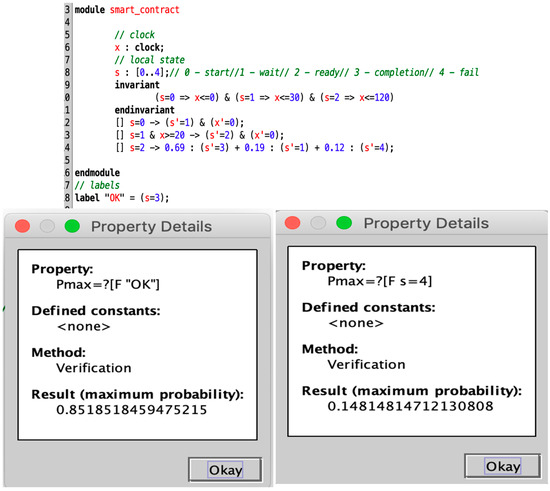
Figure 10.
Automated verification of P2TA for runtime e-commerce smart contracts.
6. Case Study
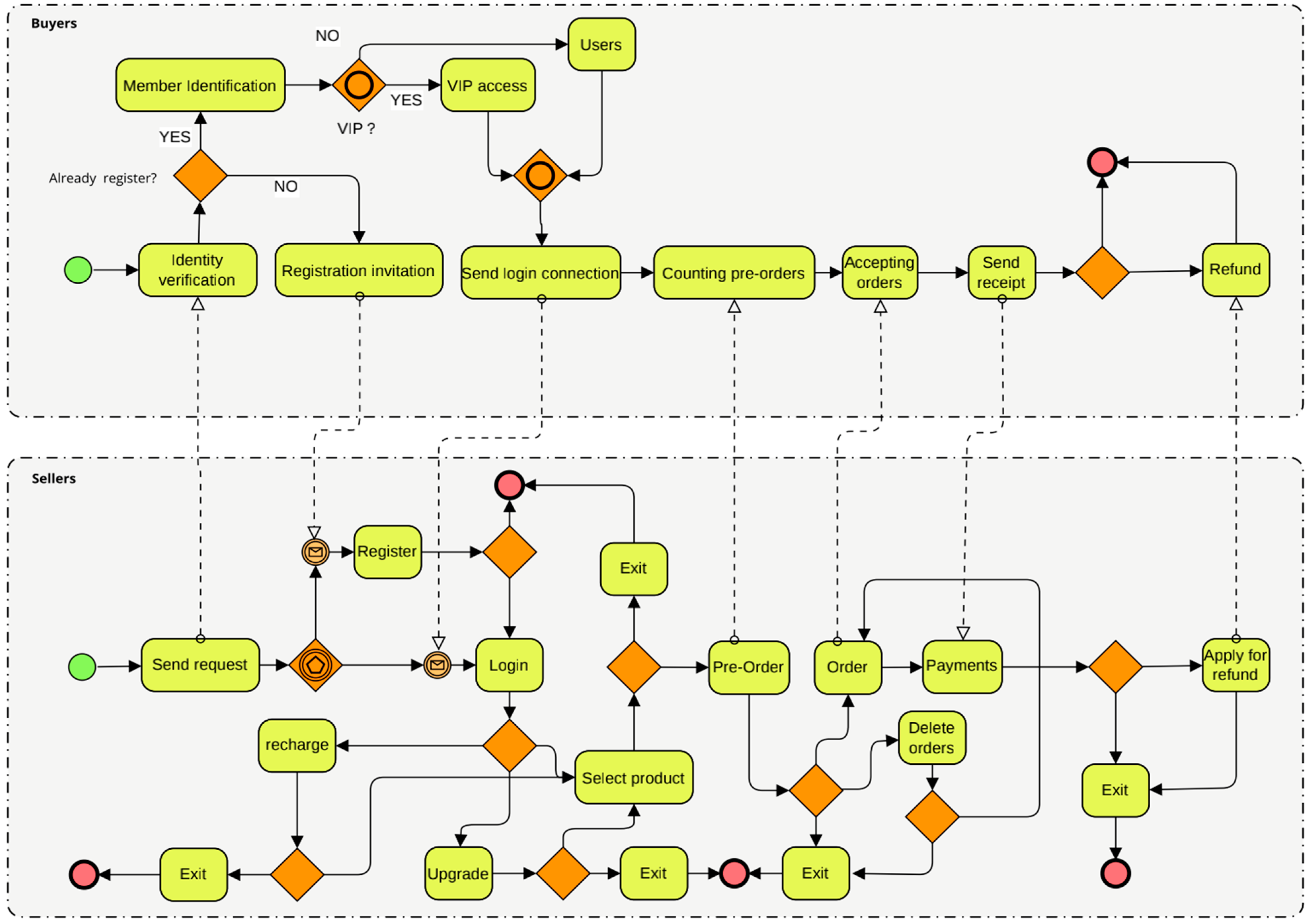
In this section, we make a quantitative evaluation of the performance of PL4ESC through an e-commerce smart contract case. The BPMN (Business Process Modeling Notation) of this e-commerce smart contract is shown in Figure 11, which can generate smart contract Solidity code automatically by Caterpillar [58]. It realizes the service composition [59] function of online shopping. We want to answer the two following questions through the experiments: (1) What is the effect of the Genetic algorithm or automaton reorganization on the accuracy of the learned model by the PL4ESC method? (2) Is PL4ESC able to infer precise models that reflect the runtime behaviors of e-commerce smart contracts compared with state-of-the-art passive learning methods?
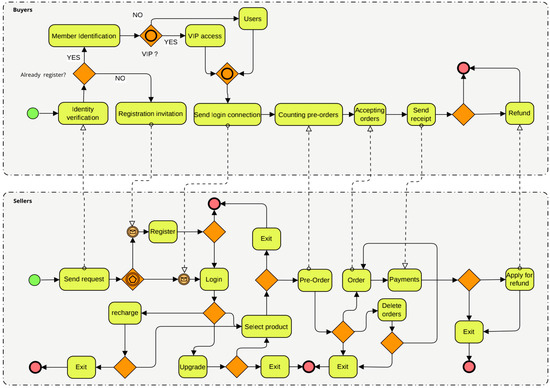
Figure 11.
E-commerce smart contract in BPMN.
6.1. Experimental Setup
The e-commerce smart contract is randomly executed 8000 times in the Blockchain Private Ethereum with 30 nodes. The experiment environment for PL4ESC is a MacBook Pro (Apple, State of Texas, USA) with an Intel Core i5 (Intel, California, USA) processor clocked at 2.4 GHz and a memory of 8 GB 2133 MHz LPDDR3. We selected some trace data from the Ethereum logs of this smart contract. As shown in Table 2, the data are selected according to the two following aspects: the alphabet size (the number of different event actions) and the number of traces in a smart contract. The selected data can be divided into six categories according to the alphabet size: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, or 12, or according to the number of traces: 100, 500, 1000, 2000, or 3000. When the input data contain more alphabets, it may increase the size and complexity of the learned model significantly, but it is helpful to learn models with higher precision. On the other hand, we can gain more knowledge about e-commerce smart contracts by learning from a large-sized alphabet. In the experiment, we used the controlled variable method. That is, we observed the performance of PL4ESC under different numbers of traces with a fixed alphabet size. Alternatively, we observed the performance of PL4ESC for different alphabet sizes with a fixed number of traces. The parameter K of the TAG algorithm is fixed to 2, and the value of the likelihood ratio test of RTI+ is set to 0.05 by default.

Table 2.
Factors in the dataset.
We chose accuracy, precision, and recall as the evaluation indicators. They are the most important performance indicators of passive learning methods. Let TP (True Positive) indicate that a positive sample is judged to be positive, TN (True Negative) indicate that a negative sample is judged to be negative, FN (False Negative) indicate that a positive sample is judged to be negative, and FP (False Positive) indicate that a negative sample is judged to be positive. Then, accuracy, precision, and recall are defined as follows:
6.2. Experimental Results and Analysis
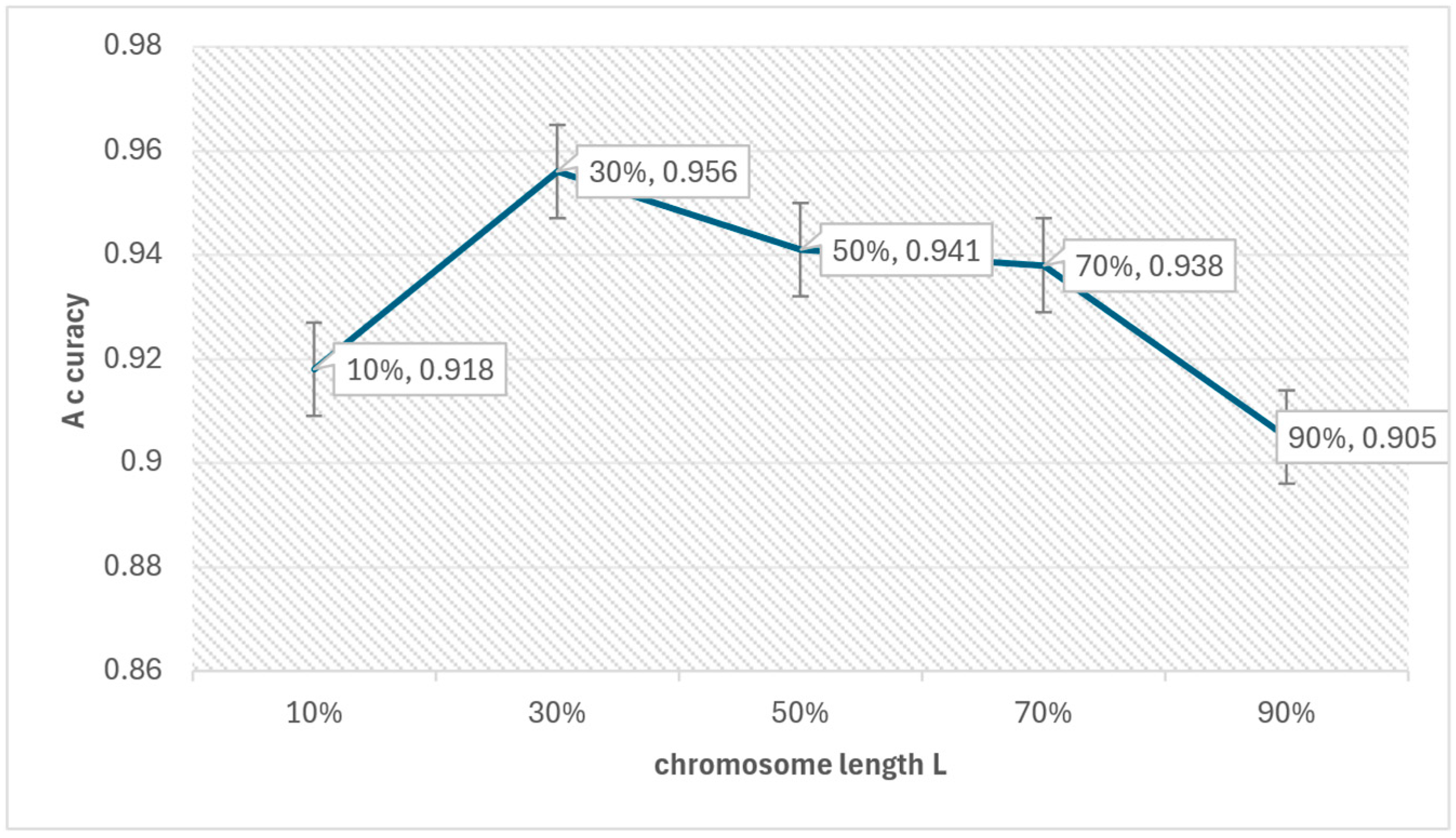
We first show the impact of the GA parameters on the PL4ESC method. PL4ESC requires setting the initial parameters of the Genetic algorithm, including k in “k-future”, population P, iterations I, crossover rate CR, mutation rate MR, elite rate ER, and length of chromosome L. The most important parameters we need to consider are k and L. All other parameters can be selected with appropriate values based on experience. The choice of k has a direct impact on which states will be merged, but we will not study the specific impact of k on the algorithm in this paper. Much work has been conducted to demonstrate that making k = 2 will be the best choice. What we care about is how parameter L affects the accuracy of PL4ESC. The longer the chromosome, the more color-compatible mergers it may contain, but it also increases the probability of incorrect mergers. Obviously, it is the key parameter that affects the accuracy of the learned model. We evaluated its specific impact via a dataset containing 1000 traces and an alphabet size of 6. These data are divided into two parts, of which 70% are used to learn the runtime model and 30% are used for testing. The other parameters in the learning process are fixed as P = 100, I = 100, CR = 0.7, MR = 0.02, and ER = 0.4. We then evaluated the accuracy of PL4ESC when the length of L is 10%, 30%, 50%, 70%, and 90% of all valid mergers in the reduced table, respectively. The results are shown in Figure 12.
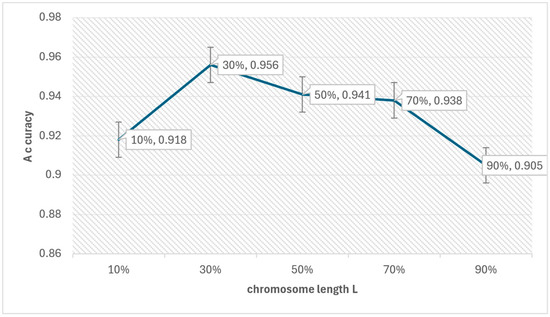
Figure 12.
Effect of chromosome length on accuracy.
From Figure 12, we can see that the accuracy of PL4ESC is highest when chromosome L contains 30% of the valid mergers. When L is 10%, the color-compatible combinations that are contained in the chromosomes are very limited, so the accuracy is low. As the length of L increases, color-compatible mergers increase. The Genetic algorithm enables these compatible mergers to be executed preferentially, which will rapidly improve the accuracy. However, when L continues to increase or even includes all valid mergers, color-incompatible mergers may decrease. This is bound to result in a false part hypothesis, which will reduce the accuracy of the learned P2TA model.
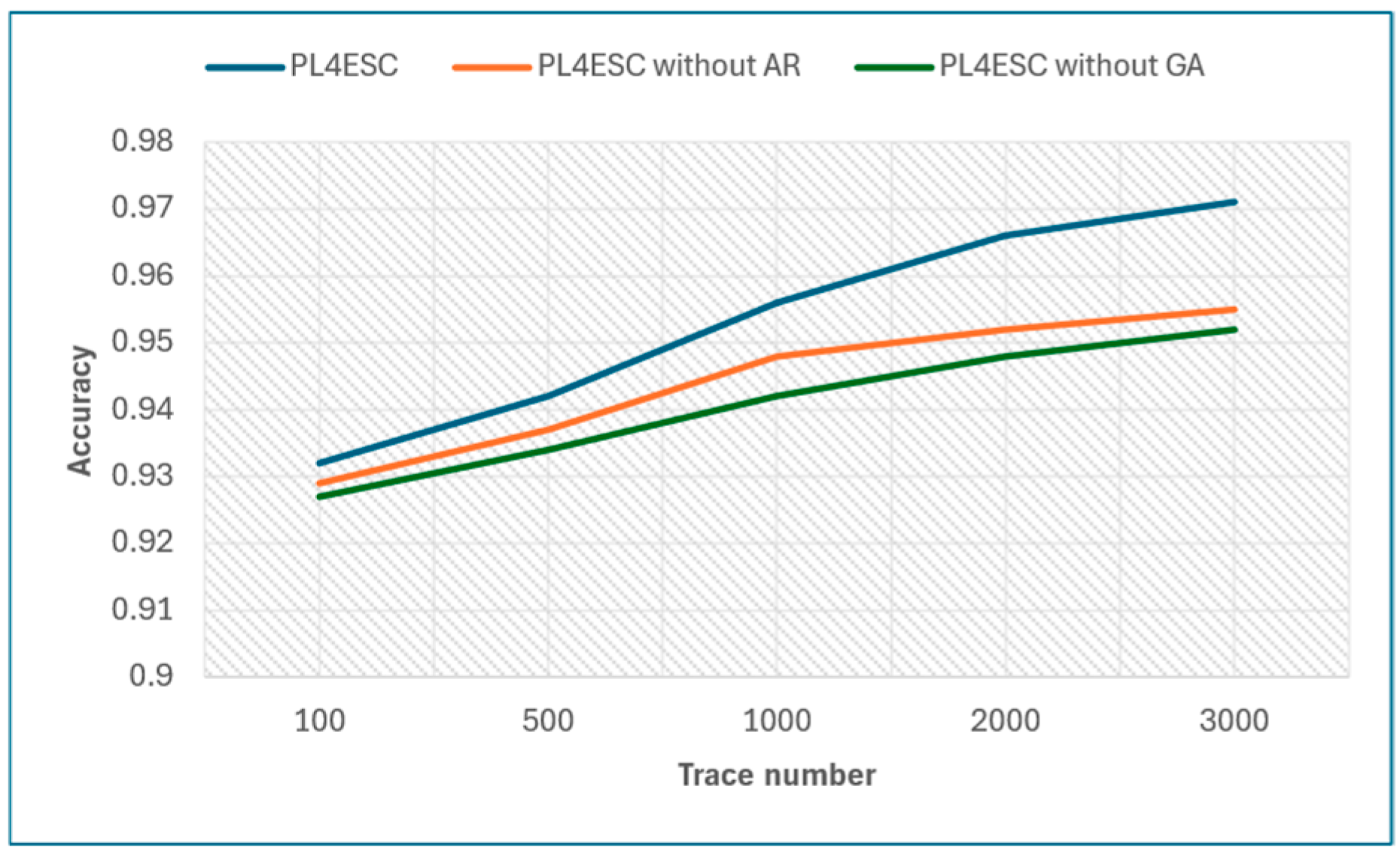
Next, we show the impact of the Genetic algorithm (GA) and automaton reorganizing (AR) on PL4ESC. Specifically, we compared the accuracy of the learned model P2TA by PL4ESC, PL4ESC without a Genetic algorithm, and PL4ESC without automaton reorganizing for the same dataset. The specific data are shown in Table 3. Figure 13 shows the accuracy of three algorithms, in which the size of the alphabet is fixed at 6, and the number of traces are 100, 500, 1000, 2000, and 3000, respectively. From it, we can see that PL4ESC always maintains the highest accuracy compared with PL4ESC without the Genetic algorithm and PL4ESC without automaton reorganizing because the Genetic algorithm provides an optimal sequence of state mergers, which significantly reduces the merging of color incompatibilities. This directly determines the accuracy of the learned model P2TA. When the trace number is small, the learned model accuracy of PL4ESC without automaton reorganizing is close to PL4ESC. However, as the number of traces continues to increase, the accuracy growth rate of PL4ESC without automaton reorganizing decreases rapidly. This is because the splitting condition is triggered frequently as the traces increase. At some point, this can lead to a false time guard or gas guard, which reduces the automaton’s ability to recognize the traces.

Table 3.
Accuracy of PL4ESC, PL4ESC without GA, and PL4ESC without AR.
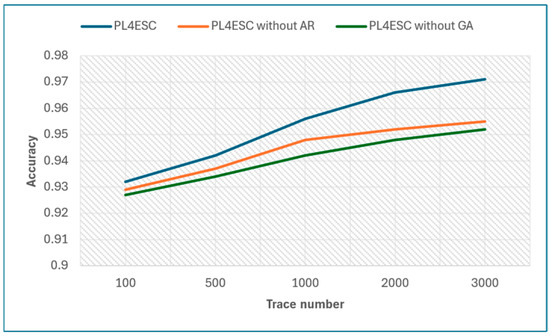
Figure 13.
Accuracy of PL4ESC, PL4ESC without GA, and PL4ESC without AR.
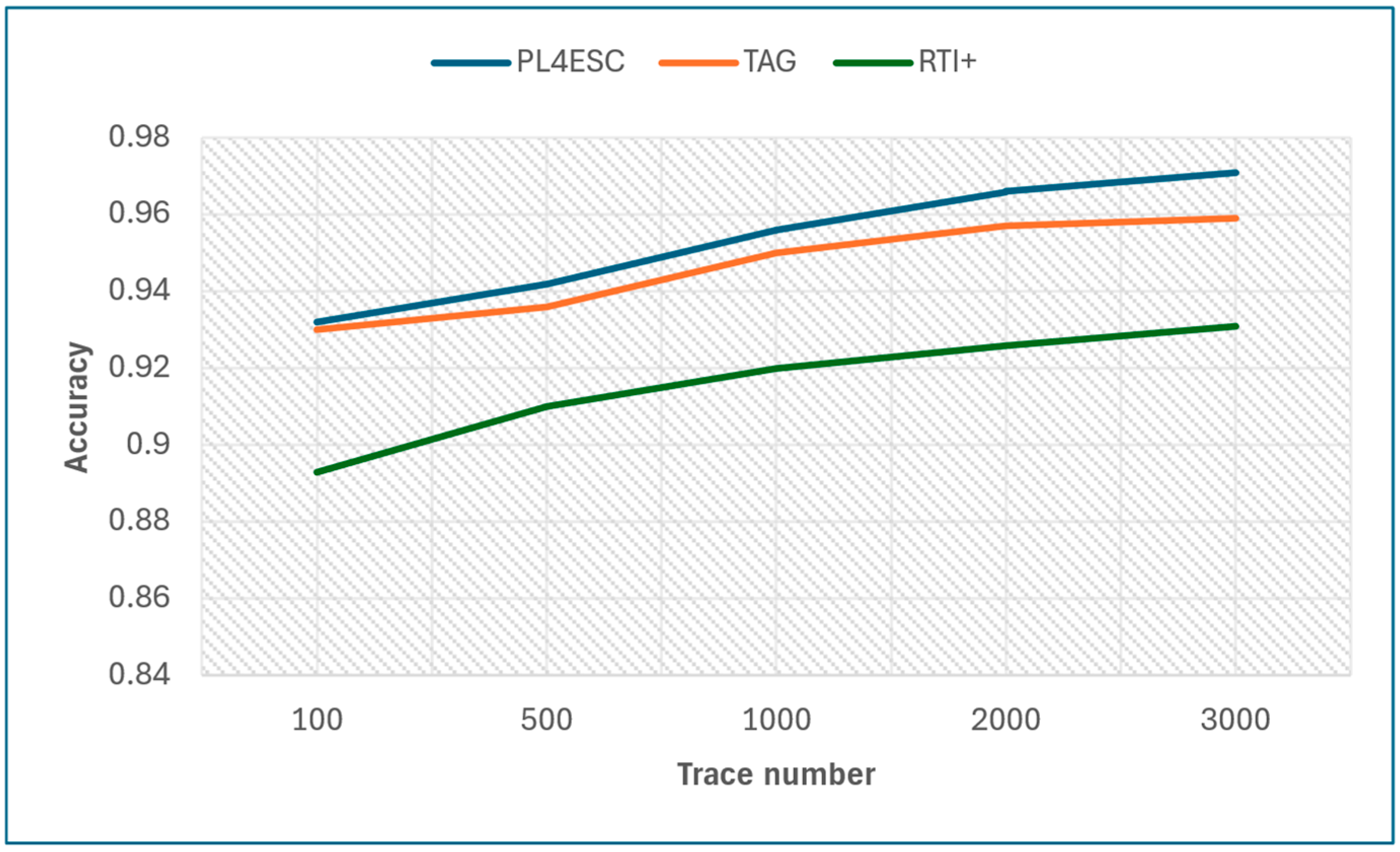
Finally, we compare PL4ESC with the state-of-the-art passive learning methods TAG and RTI+. In passive learning, the number of traces plays a decisive role in the accuracy of the learned model, and the size of the alphabet plays a decisive role in precision and recall. The specific experiment results are shown in Table 4. Figure 14 shows the learned model accuracy of the three methods on various trace numbers under the same moderate alphabet size (i.e., six letters). PL4ESC outperforms the state-of-the-art passive learning methods, which maintain the highest accuracy on all five datasets, with an average score of 0.953. This is because the Genetic algorithm can effectively achieve state merging for large datasets. The TAG method has an average score of 0.946, and the average score of RTI+ is 0.916. The TAG method recursively merges states with the same k-future by a deep or breadth search. This increases the probability of color-incompatibility merging. There are several reasons why the accuracy of the RTI+ algorithm is low. On the one hand, color-compatible mergers may not be included in high-scoring merges, or there is a certain probability that a wrong result will be chosen when selecting two mergers with the same score. On the other hand, it is the bad management of time limits that leads to too wide guards.

Table 4.
Accuracy of PL4ESC, TAG, and RTI+.
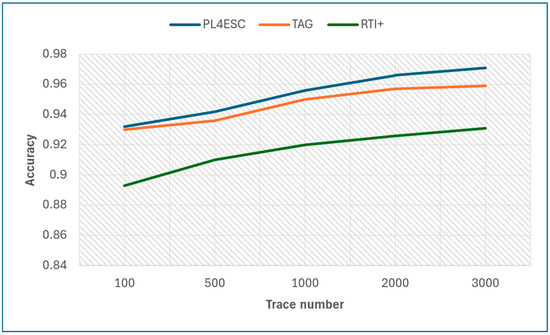
Figure 14.
Accuracy of PL4ESC, TAG, and RTI+.
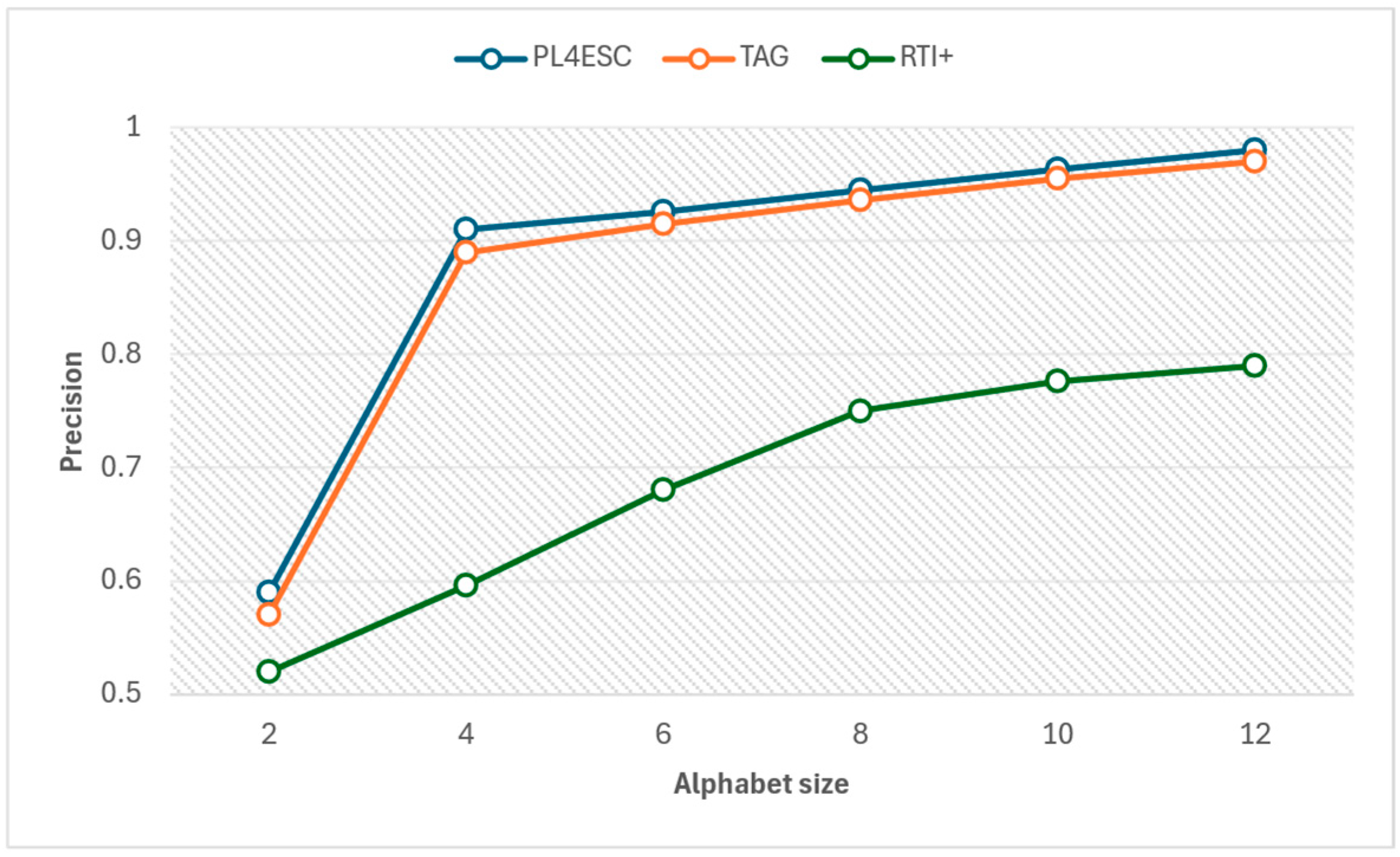
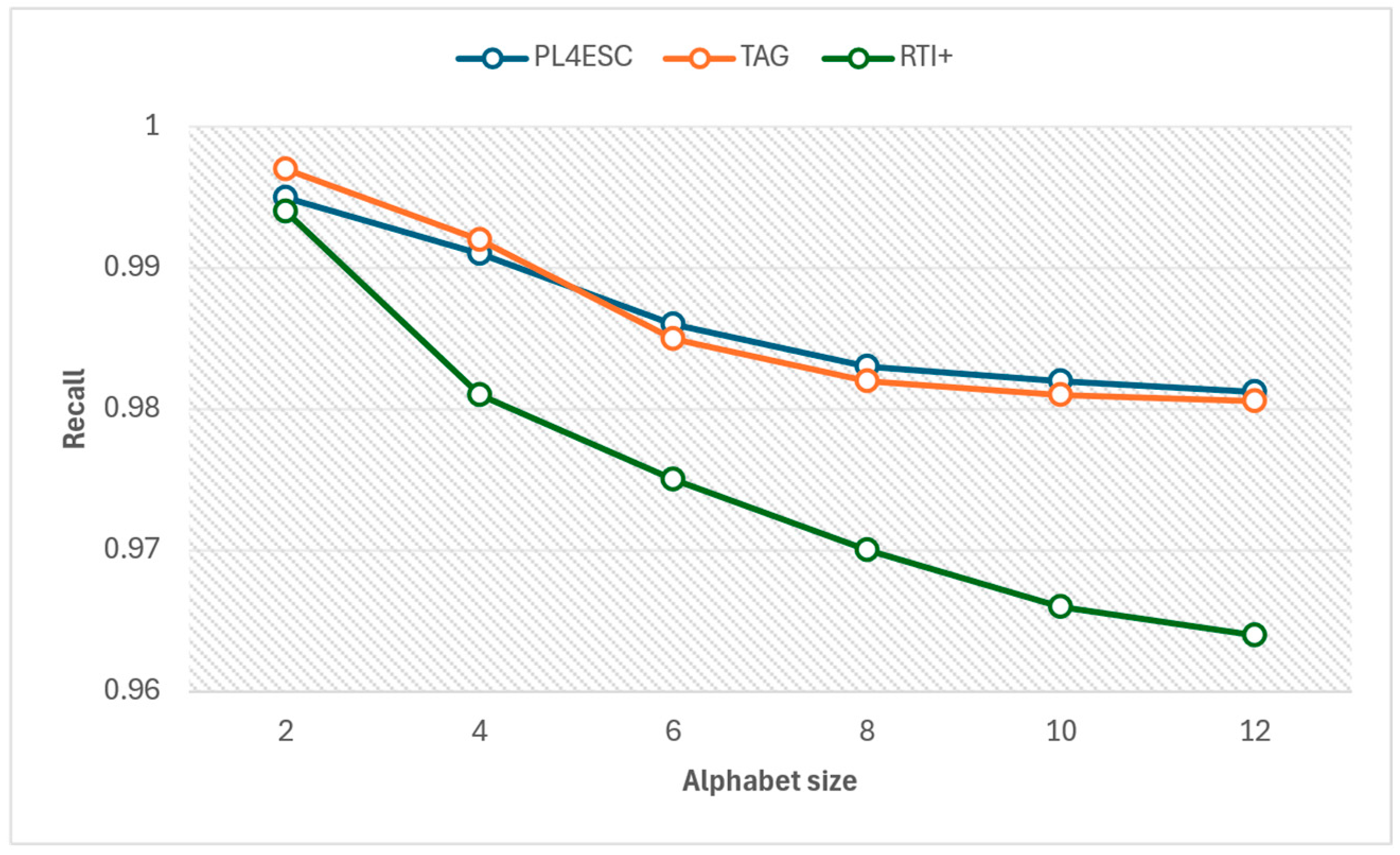
An ideal runtime model P2TA of an e-commerce smart contract should accept a sufficient number of positive samples and reject negative samples. To avoid the negative impact of experiment data imbalance on accuracy, we compared the precision and recall of three methods for different alphabet sizes at the same number of 1000 traces, as shown in Figure 15 and Figure 16. The specific experiment results are shown in Table 5 and Table 6. The larger the alphabet, the more optional operations are represented by the passive learning methods. When the input dataset contains a large variety of events, it helps to learn models with higher precision. The passive learning methods can gain more knowledge about e-commerce smart contracts by learning from more alphabets. Therefore, precision increases as the size of the alphabet increases, and recall decreases as the size of the alphabet increases. The TAG method has a higher recall than PL4ESC until the alphabet size is 6. This is because the model (P2TA) learned by PL4ESC is more complex than the timed automaton (TA), which makes it more difficult for PL4ESC to identify runtime traces. However, PL4ESC always maintains the best precision, as it adopts Genetic algorithm-based state merging and automaton reorganizing.
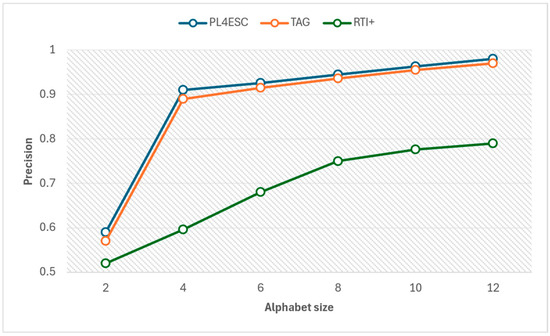
Figure 15.
Precision of PL4ESC, TAG, and RTI+.
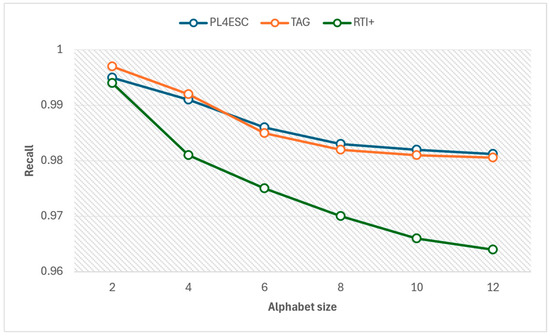
Figure 16.
Recall of PL4ESC, TAG, and RTI+.

Table 5.
Precision of PL4ESC, TAG, and RTI+.

Table 6.
Recall of PL4ESC, TAG, and RTI+.
7. Conclusions and Future Work
As a novel computing paradigm, blockchain will bring great changes to e-commerce. Secure smart contracts are the key foundation for blockchain-based e-commerce. In this work, we devoted ourselves to the automated verification of the security of e-commerce smart contracts at runtime. Firstly, we proposed a passive learning method, PL4ESC, to learn a P2TA from historical events of e-commerce smart contracts without any prior knowledge. The Genetic algorithm is designed to evolve state merging, and automaton reorganizing is devised to simultaneously split time and gas behaviors. Then, we integrated PL4ESC with the model checker PTA to verify the security properties of runtime e-commerce smart contracts. We demonstrated the feasibility and effectiveness of this runtime verification framework by various scales of smart contract cases. The experimental results show that PL4ESC is better at accuracy and precision than the state-of-the-art passive learning methods TAG or RTI+. As far as we know, this is not only the first model learning method that can learn a priced probabilistic timed automaton for a system but it is also the first automatic runtime verification framework for verifying smart contracts. On the one hand, this expands the capabilities of passive learning for modeling and analyzing the security of an information system; on the other hand, it also improves and expands the formal verification methods for smart contracts. However, this work has some limitations: (a) PL4ESC belongs to the passive learning paradigm so that its efficiency may not be too high; (b) PL4ESC solely focuses on the security properties of smart e-commerce contracts, which can be expanded to liveness, fairness, and so on. In addition, since the Genetic algorithm is a bio-heuristic approximation algorithm, the efficiency of state merging can be further improved by niche, adaptive, or parallel Genetic algorithms or by combining Genetic algorithms with simulated annealing. Additionally, the laws between the accuracy and population size (P), crossover rate (CR), mutation rate (MR), and elitism rate (ER), respectively, can be analyzed further; the correctness and robustness of PL4ESC need to analyze and validate further; the PL4ESC method may fail to explore all valid merge combinations, if the initial population or reduction table is biased, which may be prevented by diversity-promoting mechanisms in the initial population generation; and evaluation metrics, edge cases, and dataset dependence should also be discussed further. In the future, we will develop a symbolic edition of PL4ESC and a P2TA model-checking algorithm. At the same time, we will apply it to verify more complex properties of smart e-commerce contracts at runtime.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.L., Y.M. and S.Z.; methodology, Y.L., Y.M. and S.Z.; software, S.Z.; validation, Y.L., Y.M. and S.Z.; formal analysis, Y.L. and Y.M.; investigation, S.Z.; resources, S.Z.; data curation, S.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.L. and S.Z.; writing—review and editing, Y.L., Y.M. and S.Z.; visualization, S.Z.; supervision, Y.L. and Y.M.; project administration, Y.M.; funding acquisition, Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by The National Social Science Fund of China under Grant No. 24BGL111.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the conclusions of this article can be made available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Huang, J.; Xu, B.; Yan, X. Selling mode choice and blockchain adoption in an e-commerce platform with information disclosure. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 2023, 62, 101331. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Gaur, V.; Liu, J. Supply chain transparency and blockchain design. Manag. Sci. 2024, 70, 3245–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Hua, G.; Teunter, R.H.; Cheng, T.; Shen, Z.M. The effects of tokenization on ride-hailing blockchain platforms. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2023; early view. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlec, M.M.; In, H.P. DataMesh+: A Blockchain-Powered Peer-to-Peer Data Exchange Model for Self-Sovereign Data Marketplaces. Sensors 2024, 24, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlec, M.M.; In, H.P. Blockchain-Based Decentralized Storage Systems for Sustainable Data Self-Sovereignty: A Comparative Study. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Fan, Z.P.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, M. Blockchain Technology Application in an E-commerce Supply Chain: Privacy Protection and Sales Mode Selection. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2024, 71, 8060–8074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmolino, K.; Arnett, M.; Kosba, A.; Miller, A.; Shi, E. Step by step towards creating a safe smart contract: Lessons and insights from a cryptocurrency lab. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Financial Cryptography and Data Security, Christ Church, Barbados, 26 February 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 79–94. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Ma, Y. DL4SC: A novel deep learning-based vulnerability detection framework for smart contracts. Autom. Softw. Eng. 2024, 31, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Amani, S.; Bégel, M.; Bortin, M.; Staples, M. Towards verifying ethereum smart contract bytecode in Isabelle/HOL. In Proceedings of the 7th ACM SIGPLAN International Conference on Certified Programs and Proofs, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 8–9 January 2018; pp. 66–77. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Balunović, M.; Ambroladze, N.; Tsankov, P.; Vechev, M. Learning to fuzz from symbolic execution with application to smart contracts. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, London, UK, 11–15 November 2019; pp. 531–548. [Google Scholar]
- Osterland, T.; Rose, T. Model checking smart contracts for Ethereum. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2020, 63, 101129. [Google Scholar]
- Falcone, Y.; Krstić, S.; Reger, G.; Traytel, D. A taxonomy for classifying runtime verification tools. Int. J. Softw. Tools Technol. Transf. 2021, 23, 255–284. [Google Scholar]
- Abdellatif, T.; Brousmiche, K.L. Formal verification of smart contracts based on users and blockchain behaviors models. In Proceedings of the 9th IFIP International Conference on New Technologies, Mobility and Security (NTMS), Paris, France, 26–28 February 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Tolmach, P.; Li, Y.; Lin, S.W.; Liu, Y. Formal analysis of composable DeFi protocols. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Financial Cryptography and Data Security, Virtual Event, 5 March 2021; pp. 149–161. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, H.; Chen, Y.; Jaeger, M.; Nielsen, T.D.; Larsen, K.G.; Nielsen, B. Learning probabilistic automata for model checking. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Quantitative Evaluation of Systems, Aachen, Germany, 5–8 September 2011; pp. 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, Y.M.Y.; Sagiv, M.; Shoham, S.; Wilcox, J.R. Learning the boundary of inductive invariants. Proc. ACM Program. Lang. 2021, 5, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Vaandrager, F. Model learning. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiterău-Broştean, P.; Janssen, R.; Vaandrager, F. Combining model learning and model checking to analyze TCP implementations. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computer Aided Verification, Toronto, ON, Canada, 17–23 July 2016; pp. 454–471. [Google Scholar]
- Tijssen, M.; Poll, E.; de Ruiter, J. Automatic Modeling of SSH Implementations with State Machine Learning Algorithms. Bachelor’s Thesis, Radboud University, Nijmegen, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Verwer, S.; Wang, J. MOHA: A multi-mode hybrid automaton model for learning car-following behaviors. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 20, 790–796. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzoli, D.; Mariani, L.; Pezzè, M. Automatic generation of software behavioral models. In Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Software Engineering, Leipzig, Germany, 10–18 May 2008; pp. 501–510. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, G.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Dai, T.; Dong, J.S.; Wang, X. Towards interpreting recurrent neural networks through probabilistic abstraction. In Proceedings of the 35th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering (ASE), Melbourne, Australia, 21–25 December 2020; pp. 499–510. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, S.M.; Reynolds, T.J. Learning deterministic finite automata with a smart state labeling evolutionary algorithm. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2005, 27, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, D. A novel learning algorithm for Büchi automata based on family of DFAs and classification trees. Inf. Comput. 2021, 281, 104678. [Google Scholar]
- Ndukwu, U. Generating counterexamples for quantitative safety specifications in probabilistic B. J. Log. Algebr. Program. 2012, 81, 26–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornanguer, L.; Largouët, C.; Rozé, L.; Termier, A. TAG: Learning Timed Automata from Logs. In Proceedings of the 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI’22), Virtually, 22 February–1 March 2022; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Verwer, S.; Weerdt, M.; Witteveen, C. A likelihood-ratio test for identifying probabilistic deterministic real-time automata from positive data. In International Colloquium on Grammatical Inference; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 203–216. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Dong, J.S. PAT 3: An extensible architecture for building multi-domain model checkers. In Proceedings of the 22nd Annual International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering, Hiroshima, Japan, 29 November–2 December 2011; pp. 190–199. [Google Scholar]
- Tolmach, P.; Li, Y.; Lin, S.W.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z. A survey of smart contract formal specification and verification. ACM Comput. Surv. 2021, 54, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Tsankov, P.; Dan, A.; Drachsler-Cohen, D.; Gervais, A.; Buenzli, F.; Vechev, M. Securify: Practical security analysis of smart contracts. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Toronto, ON, Canada, 15–19 October 2018; pp. 67–82. [Google Scholar]
- Kalra, S.; Goel, S.; Dhawan, M.; Sharma, S. Zeus: Analyzing safety of smart contracts. In Proceedings of the Network and Distributed System Security Symposium, San Diego, CA, USA, 18–21 February 2018; Internet Society: Reston, VA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Antonino, P.; Roscoe, A.W. Solidifier: Bounded model checking solidity using lazy contract deployment and precise memory modelling. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual ACM Symposium on Applied Computing (SAC’21), Virtual, 22–26 March 2021; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1788–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdu, Á.; Jovanović, D. solc-verify: A modular verifier for solidity smart contracts. In Proceedings of the 11th Working Conference on Verified Software: Theories, Tools, and Experiments, New York, NY, USA, 13–14 July 2019; pp. 161–179. [Google Scholar]
- Mossberg, M.; Manzano, F.; Hennenfent, E.; Groce, A.; Grieco, G.; Feist, J.; Brunson, T.; Dinaburg, A. Manticore: A user-friendly symbolic execution framework for binaries and smart contracts. In Proceedings of the 34th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering (ASE), San Diego, CA, USA, 11–15 November 2019; pp. 1186–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Nehai, Z.; Piriou, P.Y.; Daumas, F. Model-checking of smart contracts. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Internet of Things (iThings) and IEEE Green Computing and Communications (GreenCom) and IEEE Cyber, Physical and Social Computing (CPSCom) and IEEE Smart Data (SmartData), Halifax, NS, Canada, 30 July–3 August 2018; pp. 980–987. [Google Scholar]
- Zupan, N.; Kasinathan, P.; Cuellar, J.; Sauer, M. Secure smart contract generation based on petri nets. In Blockchain Technology for Industry 4.0; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 73–98. [Google Scholar]
- Azzopardi, S.; Ellul, J.; Pace, G.J. Monitoring smart contracts: Contractlarva and open challenges beyond. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Runtime Verification, Limassol, Cyprus, 10–13 November 2018; pp. 113–137. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, M.; Jevitha, K.P. Runtime verification and vulnerability testing of smart contracts. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Computing and Data Sciences, Singapore, 12–13 April 2019; pp. 333–342. [Google Scholar]
- Azzopardi, S.; Colombo, C.; Pace, G. Model-based static and runtime verification for ethereum smart contracts. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Model-Driven Engineering and Software Development, Vienna, Austria, 25–27 February 2021; pp. 323–348. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Sun, H.; Zhao, Y. Model learning: A survey of foundations, tools and applications. Front. Comput. Sci. 2021, 15, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Angluin, D. Learning regular sets from queries and counterexamples. Inf. Comput. 1987, 75, 87–106. [Google Scholar]
- Shahbaz, M.; Groz, R. Inferring mealy machines. In International Symposium on Formal Methods; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 207–222. [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson, B. Learning of automata models extended with data. In Proceedings of the International School on Formal Methods for the Design of Computer, Communication and Software Systems, Bertinoro, Italy, 13–18 June 2011; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 327–349. [Google Scholar]
- Cassel, S.; Howar, F.; Jonsson, B.; Steffen, B. Learning extended finite state machines. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Software Engineering and Formal Methods (SFFM 2014), Grenoble, France, 1–5 September 2014; pp. 250–264. [Google Scholar]
- An, J.; Chen, M.; Zhan, B.; Zhan, N.; Zhang, M. Learning One-Clock Timed Automata. In Tools and Algorithms for the Construction and Analysis of Systems. TACAS 2020; Biere, A., Parker, D., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 12078, pp. 444–462. [Google Scholar]
- Dupont, P. Regular grammatical inference from positive and negative samples by genetic search: The GIG method. In International Colloquium on Grammatical Inference; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; pp. 236–245. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, K.J.; Pearlmutter, B.A.; Price, R.A. Results of the abbadingo one DFA learning competition and a new evidence-driven state merging algorithm. In Grammatical Inference; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, K. Evidence Driven State Merging with Search; Rapport technique TR98–139; NECI: Mansfield, MA, USA, 1998; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Giantamidis, G.; Tripakis, S.; Basagiannis, S. Learning Moore machines from input–output traces. Int. J. Softw. Tools Technol. Transf. 2021, 23, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Walkinshaw, N.; Taylor, R.; Derrick, J. Inferring extended finite state machine models from software executions. Empir. Softw. Eng. 2016, 21, 811–853. [Google Scholar]
- Matos Pedro, A.; Crocker, P.A.; Sousa, S.M. Learning stochastic timed automata from sample executions. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Leveraging Applications of Formal Methods, Verification and Validation: Technologies for Mastering Change-Volume Part I (ISoLA’12), Heraclion, Greece, 15–18 October 2012; pp. 508–523. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, H.; Chen, Y.; Jaeger, M.; Nielsen, T.D.; Larsen, K.G.; Nielsen, B. Learning deterministic probabilistic automata from a model checking perspective. Mach. Learn. 2016, 105, 255–299. [Google Scholar]
- Pastore, F.; Micucci, D.; Mariani, L. Timed k-tail: Automatic inference of timed automata. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Software Testing, Verification and Validation (ICST), Tokyo, Japan, 13–17 March 2017; pp. 401–411. [Google Scholar]
- Biermann, A.W.; Feldman, J.A. On the synthesis of finite-state machines from samples of their behavior. IEEE Trans. Comput. 1972, 100, 592–597. [Google Scholar]
- Jurdziński, M.; Kwiatkowska, M.; Norman, G.; Trivedi, A. Concavely-priced probabilistic timed automata. In CONCUR 2009-Concurrency Theory: 20th International Conference, CONCUR 2009, Bologna, Italy, 1–4 September 2009. Proceedings; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 5710. [Google Scholar]
- Coste, F.; Nicolas, J. Regular inference as a graph coloring problem. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Grammatical Inference, Automata Induction, and Language Acquisition (ICML’97), Nashville, TN, USA, 12 July 1997; pp. 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Guillaumier, K.; Abela, J. Learning DFAs by Evolving Short Sequences of Merges. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Grammatical Inference (ICGI’20), Online, 23–27 August 2021; PMLR: London, UK, 2021; pp. 217–236. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Han, T.; Chen, T.; Zhou, S. Probabilistic analysis of QoS-aware service composition with explicit environment models. IET Softw. 2020, 14, 59–71. [Google Scholar]
- Lòpez-Pintado, O.; García-Bañuelos, L.; Dumas, M.; Weber, I.; Ponomarev, A. Caterpillar: A business process execution engine on the Ethereum blockchain. Softw. Pract. Exp. 2019, 49, 1162–1193. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).