The Modified Void Nucleation and Growth Model (MNAG) for Damage Evolution in BCC Ta
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
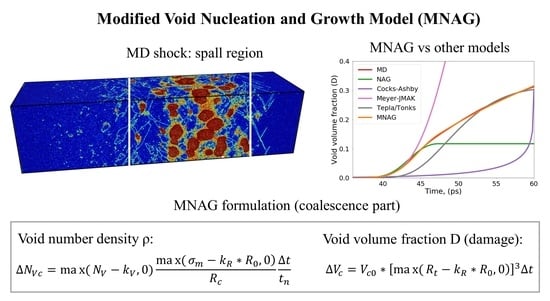
- To propose a modified NAG model, which we term as the MNAG model, to better describe void evolution at later times through the addition of a term to describe void coalescence. This robustness of this new analytical form was tested against the other commonly used damage models by using void evolution data generated from MD simulations.
- (2)
- To evaluate and compare several widely utilized semi-analytical damage models in terms of how well they could describe the void evolution behavior, as extracted from MD shock loading simulations, using single-crystal and nanocrystalline Ta as model systems.
- (3)
- To utilize the extract parameters associated with void nucleation, growth, and coalescence rates from specific simulations and to provide insights into the role of crystal orientation and grain size in dictating damage, which remained a challenge under dynamic loading.
2. Computational Methods
3. Results and Discussion
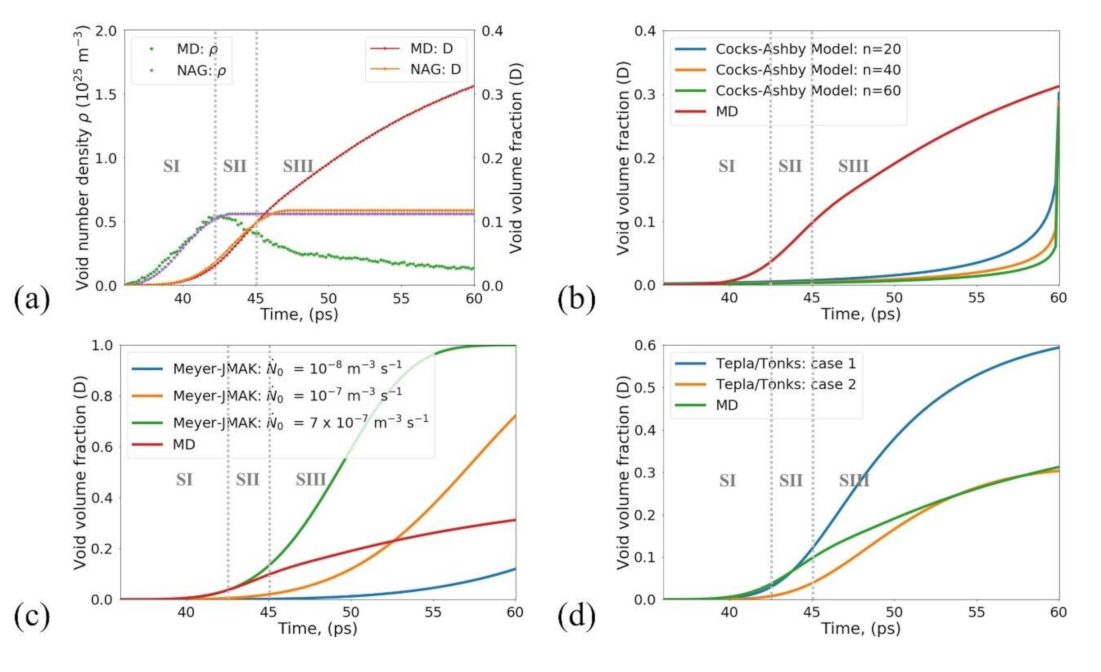
3.1. The NAG Model
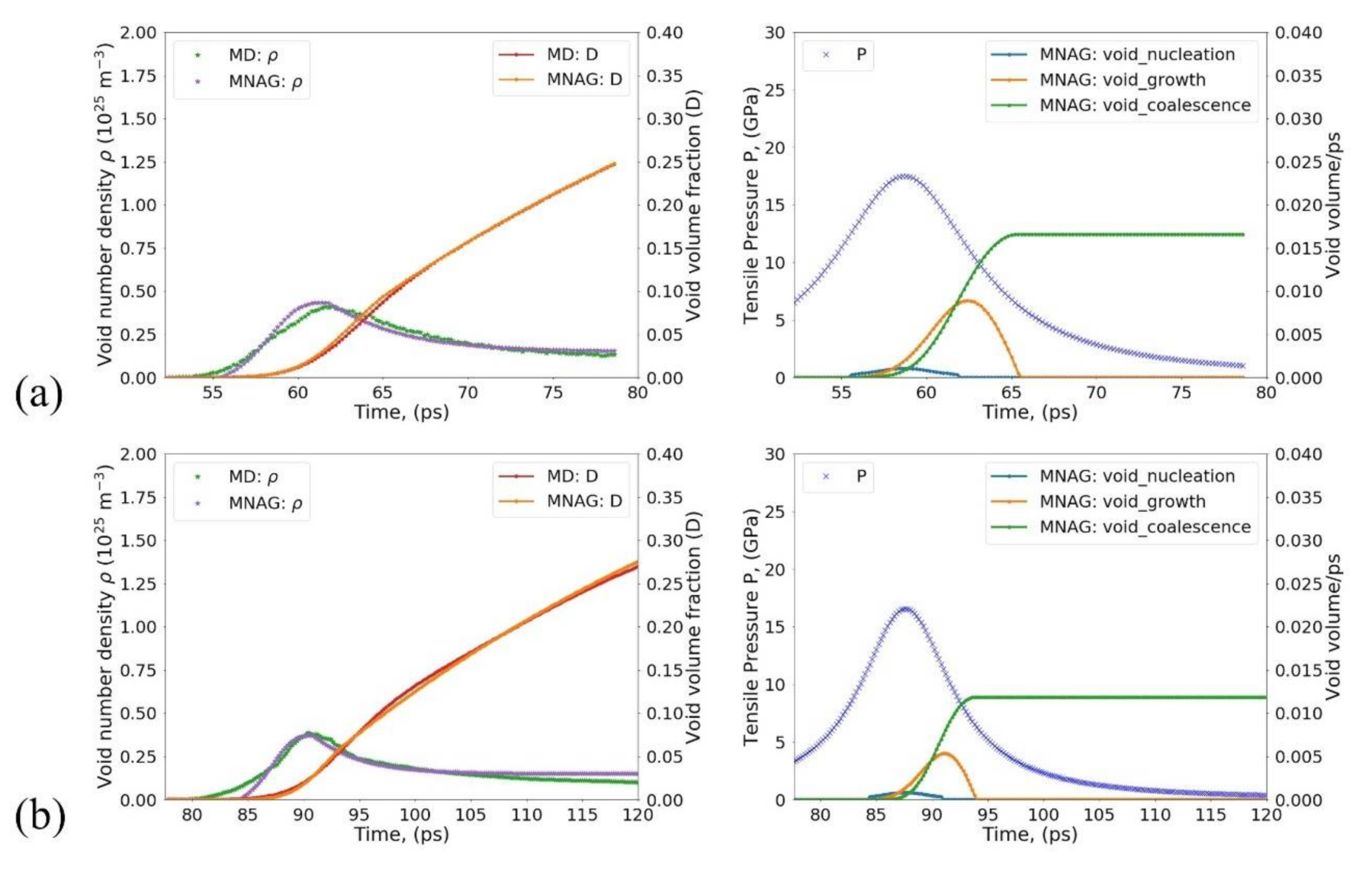
3.2. The MNAG Model
3.2.1. Void Coalescence Term
3.2.2. Stress Evolution
3.3. Parameterization of the MNAG Model
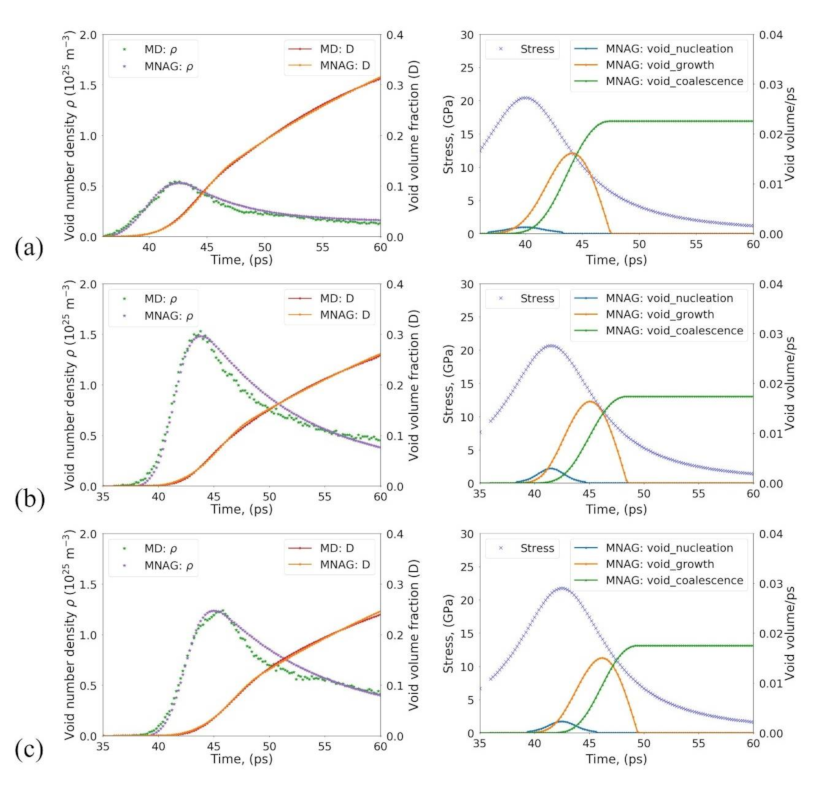
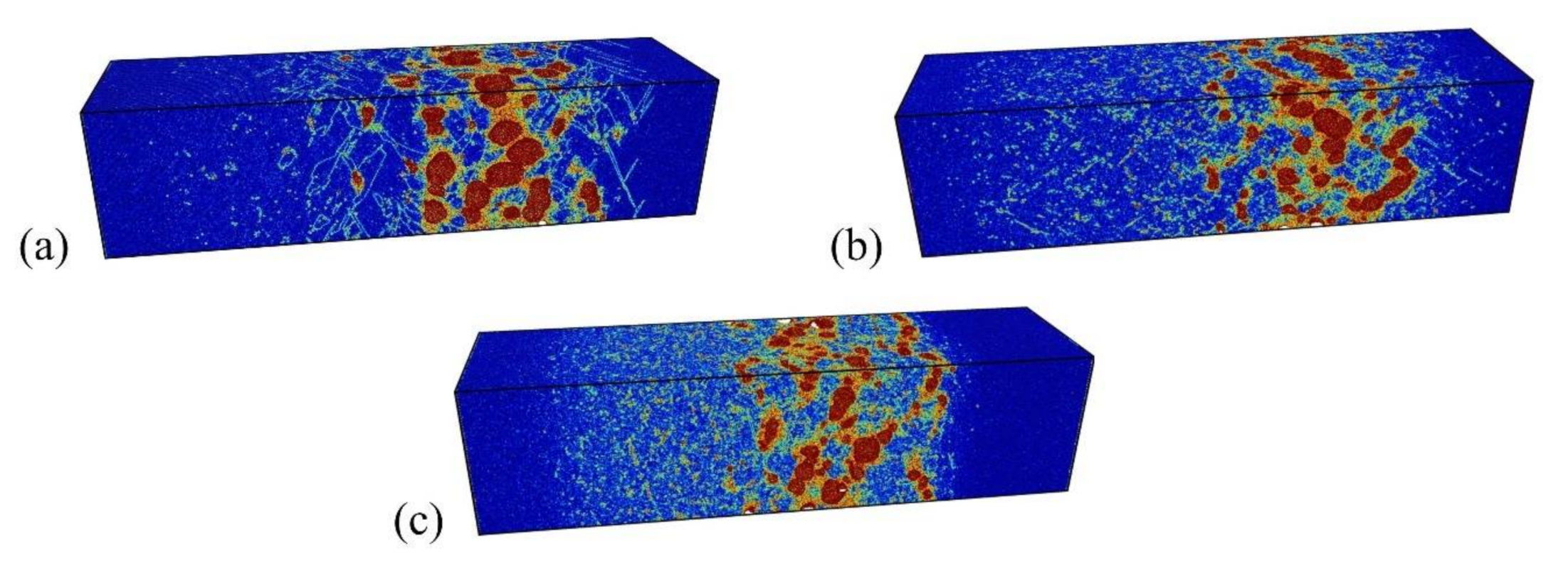
3.3.1. Single-Crystal Ta
- most significantly affected the void number density and the resulting damage due to void nucleation: the lower the value of , the higher the rate of void nucleation;
- most significantly affected the growth of existing voids at tensile stress above : the lower the value of , the higher the rate of void growth;
- most significantly affected the slope of the quasi-linear growth during the void coalescence stage: the greater value of led to a higher rate of void coalescence.
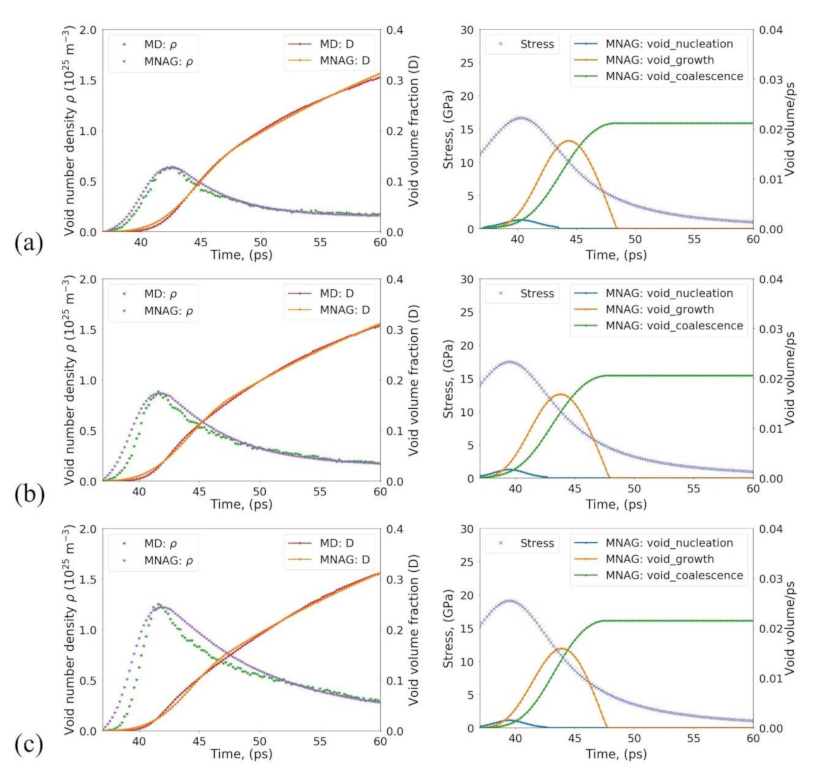
3.3.2. Nanocrystalline Ta
3.4. The MNAG Model: Comparison to Other Models
3.5. The MNAG Model: Size Effects
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, H.J.; Segurado, J.; Rodríguez de la Fuente, O.; Pabón, B.M.; Llorca, J. Molecular Dynamics Modeling and Simulation of Void Growth in Two Dimensions. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 21, 075010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, P.; Yuan, L.; Shivpuri, R.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, D.; Guo, B. Evolution of Spherical Nanovoids within Copper Polycrystals during Plastic Straining: Atomistic Investigation. Int. J. Plast. 2018, 100, 122–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segurado, J.; Llorca, J. An Analysis of the Size Effect on Void Growth in Single Crystals Using Discrete Dislocation Dynamics. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segurado, J.; Llorca, J. Discrete Dislocation Dynamics Analysis of the Effect of Lattice Orientation on Void Growth in Single Crystals. Int. J. Plast. 2010, 26, 806–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Segurado, J.; Lebensohn, R.A.; Llorca, J.; Tomé, C.N. Multiscale Modeling of Plasticity Based on Embedding the Visco-plastic Self-consistent Formulation in Implicit Finite Elements. Int. J. Plast. 2012, 28, 124–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanel, G.I. Spall Fracture: Methodological Aspects, Mechanisms and Governing Factors. Int. J. Fract. 2010, 163, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, M.A.; Aimone, C.T. Dynamic Fracture (Spalling) of Metals. Prog. Mater. Sci. 1983, 28, 1–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remington, T.; Hahn, E.; Zhao, S.; Flanagan, R.; Mertens, J.; Sabbaghianrad, S.; Langdon, T.; Wehrenberg, C.; Maddox, B.; Swift, D.; et al. Spall Strength Dependence on Grain Size and Strain Rate in Tantalum. Acta Mater. 2018, 158, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dongare, A.M.; Rajendran, A.M.; LaMattina, B.; Zikry, M.A.; Brenner, D.W. Atomic Scale Simulations of Ductile Failure Micromechanisms in Nanocrystalline Cu at High Strain Rates. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 80, 104108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Escobedo, J.P.; Dennis-Koller, D.; Cerreta, E.K.; Patterson, B.M.; Bronkhorst, C.A.; Hansen, B.L.; Tonks, D.; Lebensohn, R.A. Effects of Grain Size and Boundary Structure on the Dynamic Tensile Response of Copper. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 033513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fensin, S.; Escobedodiaz, J.P.; Brandl, C.; Cerreta, E.; Gray, G.; Germann, T.C.; Valone, S.M. Effect of Loading Direction on Grain Boundary Failure under Shock Loading. Acta Mater. 2014, 64, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minich, R.W.; Cazamias, J.U.; Kumar, M.; Schwartz, A.J. Effect of Microstructural Length Scales on Spall Behavior of Copper. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2004, 35, 2663–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.A.; Li, S.F.; Rhee, M.; Barton, N.R. Modeling the Effects of Grain and Porosity Structure on Copper Spall Response. J. Dyn. Behav. Mater. 2018, 4, 464–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Luscher, D.; Wilkerson, J. A Dislocation-based Crystal Plasticity Framework for Dynamic Ductile Failure of Single Crystals. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2017, 108, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Luscher, D.; Wilkerson, J. The Role of Elastic and Plastic Anisotropy in Intergranular Spall Failure. Acta Mater. 2019, 168, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuitiño, A.; Ortiz, M. Ductile Fracture by Vacancy Condensation in fcc Single Crystals. Acta Mater. 1996, 44, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubarda, V.; Schneider, M.; Kalantar, D.; Remington, B.; Meyers, M. Void Growth by Dislocation Emission. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 1397–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remington, T.P.; Remington, B.A.; Hahn, E.N.; Meyers, M.A. Deformation and Failure in Extreme Regimes by High-energy Pulsed Lasers: A Review. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 688, 429–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krasnikov, V.; Mayer, A. Plasticity Driven Growth of Nanovoids and Strength of Aluminum at High Rate Tension: Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Continuum Modeling. Int. J. Plast. 2015, 74, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanthraj, P.; Zikry, M. Dislocation-density Mechanisms for Void Interactions in Crystalline Materials. Int. J. Plast. 2012, 34, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkerson, J. On the Micromechanics of Void Dynamics at Extreme Rates. Int. J. Plast. 2017, 95, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, J.R.; Thomson, R. Ductile vs. Brittle Behaviour of Crystals. Philos. Mag. 1974, 29, 73–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, M.A.; Traiviratana, S.; Lubarda, V.A.; Benson, D.J.; Bringa, E.M. The Role of Dislocations in the Growth of Nanosized Voids in Ductile Failure of Metals. Jom 2009, 61, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traiviratana, S.; Bringa, E.M.; Benson, D.J.; Meyers, M.A. Void Growth in Metals: Atomistic Calculations. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 3874–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubarda, V.A. Emission of Dislocations from Nanovoids under Combined Loading. Int. J. Plast. 2011, 27, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Cui, Z. A 3-D Model for Void Evolution in Viscous Materials under Large Compressive Deformation. Int. J. Plast. 2015, 74, 192–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkerson, J.; Ramesh, K. A Dynamic Void Growth Model Governed by Dislocation Kinetics. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2014, 70, 262–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshe, E.; Eliezer, S.; Dekel, E.; Ludmirsky, A.; Henis, Z.; Werdiger, M.; Goldberg, I.B.; Eliaz, N.; Eliezer, D. An Increase of the Spall Strength in Aluminum, Copper, and Metglas at Strain Rates Larger Than 107 s−1. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 83, 4004–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Besson, J. Damage of Ductile Materials Deforming under Multiple Plastic or Viscoplastic Mechanisms. Int. J. Plast. 2009, 25, 2204–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocks, A.; Ashby, M. On Creep Fracture by Void Growth. Prog. Mater. Sci. 1982, 27, 189–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, D.R.; Seaman, L.; Shockey, D.A. Dynamic Failure in Solids. Phys. Today 1977, 30, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaman, L.; Curran, D.R.; Shockey, D.A. Computational Models for Ductile and Brittle Fracture. J. Appl. Phys. 1976, 47, 4814–4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shockey, D.A.; Seaman, L.; Curran, D.R. The Micro-statistical Fracture Mechanics Approach to Dynamic Fracture Problems. Int. J. Fract. 1985, 27, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonks, D.L.; Zurek, A.K.; Thissell, W.R.; Rivera, J.M.; Hixson, R.S. Importance of Deviatoric Stress in Modeling Void Growth in Ductile Fracture; Los Alamos National Lab.: Los Alamos, NM, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Addessio, F.L.; Johnson, J.N. Rate-dependent Ductile Failure Model. J. Appl. Phys. 1993, 74, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.N. Dynamic Fracture and Spallation in Ductile Solids. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 2812–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dekel, E.; Eliezer, S.; Henis, Z.; Moshe, E.; Ludmirsky, A.; Goldberg, I.B. Spallation Model for the High Strain Rates Range. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 84, 4851–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuksin, A.Y.; Norman, G.E.; Pisarev, V.V.; Stegailov, V.V.; Yanilkin, A.V. Theory and Molecular Dynamics Modeling of Spall Fracture in Liquids. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 174101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, T.; Hayden, M.; Roe, C. Effects of the Stress State on Plasticity and Ductile Failure of an Aluminum 5083 Alloy. Int. J. Plast. 2009, 25, 2366–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garajeu, M.; Michel, J.; Suquet, P. A Micromechanical Approach of Damage in Viscoplastic Materials by Evolution in Size, Shape and Distribution of Voids. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2000, 183, 223–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurson, A.L. Continuum Theory of Ductile Rupture by Void Nucleation and Growth: Part I—Yield Criteria and Flow Rules for Porous Ductile Media. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 1977, 99, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keralavarma, S.; Benzerga, A. A Constitutive Model for Plastically Anisotropic Solids with Non-spherical Voids. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2010, 58, 874–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keralavarma, S.; Hoelscher, S.; Benzerga, A. Void Growth and Coalescence in Anisotropic Plastic Solids. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2011, 48, 1696–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Gao, X.; Srivatsan, T.S. Modeling of Void Growth in Ductile Solids: Effects of Stress Triaxiality and Initial Porosity. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2004, 71, 379–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebensohn, R.A.; Escobedo, J.P.; Cerreta, E.K.; Dennis-Koller, D.; Bronkhorst, C.A.; Bingert, J.F. Modeling Void Growth in Polycrystalline Materials. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 6918–6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecarme, L.; Tekog, L.C.; Pardoen, T. Void Growth and Coalescence in Ductile Solids with Stage III and Stage IV Strain Hardening. Int. J. Plast. 2011, 27, 1203–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.; Besson, J.; Forest, S.; Tanguy, B.; Latourte, F.; Bosso, E. An Elastoviscoplastic Model for Porous Single Crystals at Finite Strains and Its Assessment Based on Unit Cell Simulations. Int. J. Plast. 2016, 84, 58–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardoen, T.; Hutchinson, J. An Extended Model for Void Growth and Coalescence. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2000, 48, 2467–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tvergaard, V. Material Failure by Void Growth to Coalescence. Adv. Appl. Mech. 1989, 27, 83–151. [Google Scholar]
- Molinari, A.; Wright, T. A Physical Model for Nucleation and Early Growth of Voids in Ductile Materials under Dynamic Loading. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2005, 53, 1476–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, T.; Ramesh, K. Dynamic Void Nucleation and Growth in Solids: A Self-consistent Statistical Theory. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2008, 56, 336–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, T.; Ramesh, K. Statistically Informed Dynamics of Void Growth in Rate Dependent Materials. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2009, 36, 1242–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, S.; Warrier, M.; Chaturvedi, S.; Chavan, V.M. Temperature Sensitivity of Void Nucleation and Growth Parameters for Single Crystal Copper: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2011, 19, 025007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zeng, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Ding, J. Atomic-scale Modeling of the Void Nucleation, Growth, and Coalescence in Al at High Strain Rates. Mech. Mater. 2019, 135, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hahn, E.N.; Dongare, A.M.; Fensin, S.J. Understanding and Predicting Damage and Failure at Grain Boundaries in BCC Ta. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 126, 165902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravelo, R.; Germann, T.C.; Guerrero, O.; An, Q.; Holian, B.L. Shock-induced Plasticity in Tantalum Single crystals: In-teratomic Potentials and Large-scale Molecular-dynamics Simulations. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 88, 134101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plimpton, S. Fast Parallel Algorithms for Short-Range Molecular Dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, S. Visualization and Analysis of Atomistic Simulation Data with OVITO–the Open Visualization Tool. Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2010, 18, 015012. [Google Scholar]
- Dongare, A.; Rajendran, A.M.; LaMattina, B.; Zikry, M.A.; Brenner, D.W. Atomic Scale Studies of Spall Behavior in Nanocrystalline Cu. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 113518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelchner, C.L.; Plimpton, S.J.; Hamilton, J.C. Dislocation Nucleation and Defect Structure during Surface Indentation. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 58, 11085–11088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobi, S.; Zaretsky, E.; Shvarts, D. Experimental Examination and Numerical NAG Model Analysis of Spall Sensitivity to Microstructure in Copper. Le J. Phys. Colloq. 2000, 10, 9–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsini, V.; Zikry, M. Void Growth and Interaction in Crystalline Materials. Int. J. Plast. 2001, 17, 1393–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Brauer, A.; Rai, N.; Nixon, M.; Udaykumar, H. Modeling Impact-induced Damage and Debonding Using Level Sets in a Sharp Interface Eulerian Framework. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2018, 115, 1108–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Paradis, P.-F.; Okada, J.T.; Kumar, M.V.; Watanabe, Y. Viscosity of Molten Mo, Ta, Os, Re, and W Measured by Electrostatic Levitation. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2013, 65, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Tzafestas, S.G. Learning Algorithms for Neural Networks with the Kalman Filters. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 1990, 3, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, E.N.; Fensin, S.J.; Germann, T.C.; Gray, G.T. Orientation Dependent Spall Strength of Tantalum Single Crystals. Acta Mater. 2018, 159, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringa, E.M.; Traiviratana, S.; Meyers, M.A. Void Initiation in Fcc Metals: Effect of Loading Orientation and Nanocrystalline Effects. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 4458–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocks, A.C.F.; Ashby, M.F. Intergranular Fracture during Power-law Creep under Multiaxial Stresses. Met. Sci. 1980, 14, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.A.; Mehl, R.F. Reaction Kinetics in Processes of Nucleation and Growth. Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 1939, 135, 416–442. [Google Scholar]
- Avrami, M. Kinetics of Phase Change. I General Theory. J. Chem. Phys. 1939, 7, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avrami, M. Kinetics of Phase Change. II Transformation-Time Relations for Random Distribution of Nuclei. J. Chem. Phys. 1940, 8, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avrami, M. Granulation, Phase Change, and Microstructure Kinetics of Phase Change. III. J. Chem. Phys. 1941, 9, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, A.N. On the Statistical Theory of the Crystallization of Metals. Bull. Acad. Sci. USSR Math. Ser. 1937, 1, 355–359. [Google Scholar]
- Cocks, A. Inelastic Deformation of Porous Materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1989, 37, 693–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| MNAG Parameters | Regime | Initial Value | Calibrated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Void nucleation | 1.5 × 1022 m−3 ps−1 | No | |
| Void nucleation | × 0.7 | No | |
| Void nucleation | 5 GPa | Yes | |
| Void nucleation | 1 | Yes | |
| Void growth | 5 GPa | Yes | |
| Void growth | 20 GPa ps | No | |
| Void coalescence | 1.5 × 1024 m−3 | No | |
| Void coalescence | 1 | Yes | |
| Void coalescence | 5 × 10−9 m | Yes | |
| Void coalescence | 1025 m−3 ps−1 | Yes | |
| Stress evolution | 3 ps | Yes |
| Parameters | (001) | (110) | (111) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 × 1022 m−3 ps−1 | 1.5 × 1022 m−3 ps−1 | 1.5 × 1022 m−3 ps−1 | |
| 14.32 GPa | 14.47 GPa | 15.24 GPa | |
| 4.38 GPa | 2.34 GPa | 2.72 GPa | |
| 2.39 | 2.05 | 2.06 | |
| 6.32 GPa | 7.01 GPa | 7.44 GPa | |
| 20 GPa ps | 20 GPa ps | 20 GPa ps | |
| 1.5 × 1024 m−3 | 1.5 × 1024 m−3 | 1.5 × 1024 m−3 | |
| 1.12 | 1.28 | 1.51 | |
| 4.63 × 10−9 m | 7.41 × 10−9 m | 8.23 × 10−9 m | |
| 3.05 × 1025 m−3 ps−1 | 3.01 × 1025 m−3 ps−1 | 2.95 × 1025 m−3 ps−1 | |
| 4 ps | 6.5 ps | 7.5 ps |
| Parameters | 20 nm | 10 nm | 5 nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 × 1022 m−3 ps−1 | 1.5 × 1022 m−3 ps−1 | 1.5 × 1022 m−3 ps−1 | |
| 11.66 GPa | 12.24 GPa | 13.38 GPa | |
| 2.87 GPa | 2.46 GPa | 2.33 GPa | |
| 2.35 | 2.05 | 1.77 | |
| 4.57 GPa | 4.57 GPa | 5.17 GPa | |
| 20 GPa ps | 20 GPa ps | 20 GPa ps | |
| 1.5 × 1024 m−3 | 1.5 × 1024 m−3 | 1.5 × 1024 m−3 | |
| 0.64 | 0.62 | 0.79 | |
| 3.71 × 10−9 m | 4.52 × 10−9 m | 7.24 × 10−9 m | |
| 3.15 × 1025 m−3 ps−1 | 3.18 × 1025 m−3 ps−1 | 3.16 × 1025 m−3 ps−1 | |
| 3.5 ps | 2.5 ps | 2.5 ps |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Luscher, D.J.; Fensin, S.J. The Modified Void Nucleation and Growth Model (MNAG) for Damage Evolution in BCC Ta. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3378. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083378
Chen J, Luscher DJ, Fensin SJ. The Modified Void Nucleation and Growth Model (MNAG) for Damage Evolution in BCC Ta. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(8):3378. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083378
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jie, Darby J. Luscher, and Saryu J. Fensin. 2021. "The Modified Void Nucleation and Growth Model (MNAG) for Damage Evolution in BCC Ta" Applied Sciences 11, no. 8: 3378. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083378
APA StyleChen, J., Luscher, D. J., & Fensin, S. J. (2021). The Modified Void Nucleation and Growth Model (MNAG) for Damage Evolution in BCC Ta. Applied Sciences, 11(8), 3378. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083378