Abstract
Virtually all modern imaging devices collect electromagnetic or acoustic waves and use the energy carried by these waves to determine pixel values to create what is basically an “energy” picture. However, waves also carry “information”, as quantified by some form of entropy, and this may also be used to produce an “information” image. Numerous published studies have demonstrated the advantages of entropy, or “information imaging”, over conventional methods. The most sensitive information measure appears to be the joint entropy of the collected wave and a reference signal. The sensitivity of repeated experimental observations of a slowly-changing quantity may be defined as the mean variation (i.e., observed change) divided by mean variance (i.e., noise). Wiener integration permits computation of the required mean values and variances as solutions to the heat equation, permitting estimation of their relative magnitudes. There always exists a reference, such that joint entropy has larger variation and smaller variance than the corresponding quantities for signal energy, matching observations of several studies. Moreover, a general prescription for finding an “optimal” reference for the joint entropy emerges, which also has been validated in several studies.
1. Introduction
All applications of imaging technology begin with collection of a flux, either electromagnetic [1] or acoustic [2], and nearly all images produced by current technology, e.g., for remote sensing or medical imaging, are representations based on some type of scattered energy. The reasons for this are mainly historical, since the detectors are typically developed by physicists and electrical engineers who are intimately acquainted with the wave equation and transmission line theory where conservation of energy is a central concept. On a more practical level, transduction elements are frequently characterized in terms of energy conversion efficiencies, making it natural to think of the subsequent image formation process in terms of either electromagnetic or acoustic field energy. From this perspective, if the received energy arriving during some small interval of time must be reduced to a single number in order to compute an image pixel value, energy is the obvious choice.
For instance, in the field of medical ultrasonics, tumor detection and tissue classification with ultrasound remain a highly useful and clinically relevant approach (liver, kidney, prostate, breast, heart, eye, thyroid, pancreas, gall bladder, etc.). A number of teams, including those of Insana [3–5], Forsberg [6,7], Deng [8], and others, have pursued novel data acquisition and reduction schemes (spectral, cepstral, wavelet, elastographic, harmonic, etc.) to augment diagnostic power from traditional radio frequency data, and progress continues apace. Nevertheless, although hardware improvements in clinical imaging systems over the last 50 years have dramatically improved the ability of ultrasound to display tissue features, resident signal processing algorithms have not evolved much beyond fundamental presentation of the energy of backscattered compressional waves.
Since all detectors have a finite response time, their output is essentially an integral of the incoming flux that they measure taken over a very short time interval. As such, it is natural to ask if other integrals or functionals of the incident flux might also have utility if represented as images [9–14].
In fact, numerous experimental studies have demonstrated the utility of information theoretic quantities for this type of analysis of experimentally-measured waveforms. In the standard application of information theory, as initiated by Shannon, the random variables (i.e., waveforms, which we will denote f and g defined on [0, 1]) are assumed to have the same underlying distribution [15]. However, additional assumptions, such as differentiability, permit computation of distributions, both individual and joint, directly from the measured waveforms. Operationally, the ability to differentiate experimentally-measured waveforms, which contain noise, requires regularization. For our studies, this is accomplished using optimal smoothing splines [16]. Differentiability combined with regularization then permits computation of the distributions for individual waveforms, or pairs of waveforms in the case of joint distributions. Information-theoretic quantities may then be computed from these distributions in an approach that corresponds more closely to that initiated by Kolmogorov and Chaitan, where entropy is a measure of the intrinsic complexity of individual mathematical objects [17,18]. The underlying assumption in experimental applications of these quantities is that the waveforms, usually acquired in scattering measurements, faithfully capture the complexity of the interrogated scattering architectures. The merit of this strategy has been demonstrated in several experimental studies, which have investigated the sensitivities of several entropies for the detection of small changes in waveforms acquired in acoustic experiments [19–24].
To date, the most sensitive of these is a joint entropy of two waveforms, one acquired in an acoustic backscatter (i.e., an echo) measurement from an experimental specimen, f(t), and the other a reference, g(t), which may be obtained separately by experiment or by theoretical modeling [25]. To compute this entropy for differentiable waveforms f(t), g(t), we must calculate their joint distribution wf,g, which is not a function, but a tempered distribution [25]. Thus, calculations based on wf,g require “coarse-graining” on a uniform grid of C × C squares covering the x, y-plane to obtain a discrete joint probability distribution pC(j, k) from wf,g by integrating its product with smoothed versions of the characteristic functions of these squares (Equations 40 to 44 of [25]). This is followed by a limiting process where the grid size, C, is taken to zero. For instance, the calculation of the joint entropy begins with the following computation:
In the limit where C → 0 and f, g are piecewise differentiable functions on [0,1] (without any intervals of constancy), Equation (1) becomes [25]:
In this note we determine conditions on g(t) that maximize the sensitivity of Hf,g to small changes in f(t). This requires a lengthy calculation.
We will be comparing this sensitivity to that of the signal energy, Ef, of f(t) defined by:
Numerous studies have shown that entropy signal receivers are always at least as sensitive as Ef is to small changes in f (see Equation (5)). In fact, in many cases, it is actually much more sensitive [19–25].
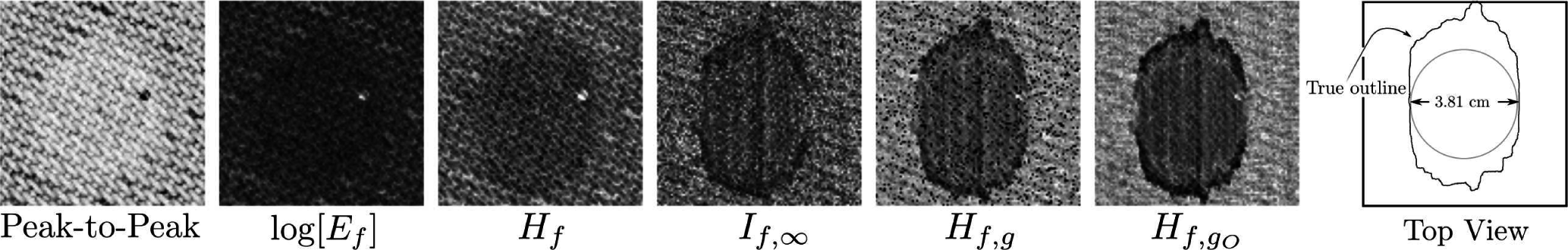
A typical result for materials characterization is shown in Figure 1 [26], which shows images of a graphite/epoxy composite laminate scanned using a 2.5-MHz transducer on a 101 × 101 point grid. The backscattered ultrasound was digitized for off-line analysis. The peak-to-peak image was produced using the peak-to-peak amplitudes of the waveforms. The rest were produced using a moving window (128 points long) analysis to produce a stack of images corresponding to different depths whose minima were then projected onto a single image-plane to permit rapid analysis of the entire image set. This projection scheme is frequently used to reduce the amount of data that must be inspected or in the case where the defect is not confined to a narrow range of depths. The Ef image was produced using Equation (3). The Hf [20], If,∞ [27], Hf,g ([25] or Equation (2)) and Hf,gO are entropy images.
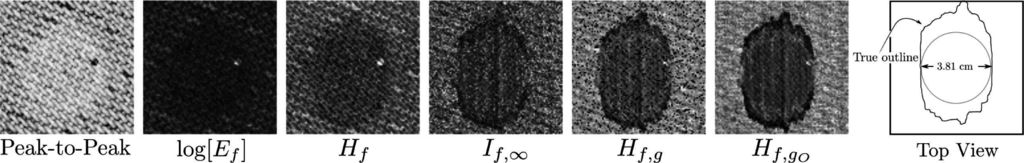
Figure 1.
Materials characterization using entropy signal receivers. The derivation of the prescription for the reference g that permits the improvement in contrast between the Hf,g and Hf,gO images is the subject of this study. (Far left) Sample diagram showing intended circular defect shape and the actual defect shape as revealed by several entropy images and verified by eventual destructive examination.
Similar results have also been obtained in medical imaging [27–38].
2. The Main Result
All of our studies have been based on the (fairly typical) situation where an experimentalist acquires waveforms of a few microseconds duration over a much greater period of time spanning minutes or longer. Thus, there are two time scales: the long experimental time scale and a much shorter measurement time scale (which we have parametrized on the interval [0, 1], the domain of f(t) and g(t)). If we denote a measurement at time t by Mt, then the sensitivity is defined by [39]:
It is essentially the noise-normalized change in a physical quantity at different measurement times. The situation also describes measurements where data (i.e., f(t), g(t)) are acquired at different times between which the measurement device has been moved; for instance, Figure 1, where the experimental times map to different spatial locations in the experimental specimen.
For evaluation of receiver sensitivities in theoretical studies, we will maximize the similar quantity:
where the product σς(t) captures the impact of Gaussian noise on the experimental measurement (ς(t) is a functional of a Brownian path (see Equation (15)) and σ is a scalar representing the signal-to-noise ratio). On the other hand, the perturbing function εη(t), where ε is small and η ∈ C1[0, 1], models the effect of the variation of the scattering architecture, as captured in Figure 1. Together, these account for the specific form of the measured function, which we write as (f + εη + σς) (t); all of these functions will be discussed fully in the next section. The experimental change referred to prior to Equation (4) is then quantified mathematically by the directional derivative:
The measure of noise is:
where all of the means are computed as Wiener integrals as discussed below. Similar definitions hold for the signal energy Ef.
After carefully-defining the quantities, f(t), η(t), σ, ς(t), in terms of a physical measurement model, having finite time resolution width Δ ≪ 1, we calculate the variations δHf+σς,g[η] and δEf+σς[η] in Section 4. The mean values of these are then calculated in Section 5 as Wiener integrals. The joint entropy is considered first in Section 4.1. After deriving the mean variation as a Wiener integral, we rewrite it in Section 5.1.1 as a Lebesgue integral. This integral represents a family of solutions to the heat equation with initial conditions defined on the real line. However, the noise-level plays the role usually held by time.
The results of the calculations may be summarized as:
Theorem 1. Suppose that f is in C3[0, 1] and there exists t0 ∈ (0, 1), such that f′(t0) = 0 and f″(t0) ≠ 0. Then, there exists C1 > 0, such that for all C2 > 0, there exists a piecewise differentiable function g, independent of η, such that:
In particular, provided η′(t0) ≠ 0, one can make arbitrarily large.
In nearly all practical situations, such a t0 exists. We prove this theorem by constructing an example reference at the end of Section 5.1.1.
There are actually many such g(t). A good way to construct examples is, roughly, to pick a zero, t0, of f′(t) and have g′(t) be a non-zero constant on one side of t0, while on the other side, it differs from f′(t) by only a small constant 1 ≫ ω > 0. In the limit as ω → 0, |δHf+σς,g[η]| > 2|η′ (t0)| log[1/ω]/f″(t0). Exact details are provided in the proof, where a bound on the size of g(t) is also provided.
On the other hand, the variation for the signal energy, provided by Equation (81), is calculated in Section 4.2. If f and η are bounded, then in the noise-free limit, it is (see Equation (51)):
which is bounded.
Thus, if η′(t0) ≠ 0, there exists g, such that:
There are many theorems describing the behavior of solutions to the heat equation for small time discussed in Section 5.1.2. These results are used in Section 6 to prove:
Theorem 2. Suppose K0 > 0 is a constant, f, η are in C1[0, 1] and g is piecewise C1[0, 1]. Let 0 < α < 1/6. Suppose that, except at finitely many points, |g′(t)| ≠|f′(t)| and |g′(t)| ≥ K0Δα.
- Then, for Δ small, there exists a constant K1 that depends on ║η′║∞, but not on g or σ, such that:
- There exists K2 > 0, that depends on ║η║∞, but not on Δ or σ, such that:
Consequently, given the freedom to choose g(t), the sensitivity of joint entropy analysis can always be made greater than that of signal energy analysis. For instance, choosing α = 1/16 and ω = Δ1/32 and setting g′(t) = f′ (t) − ω for t < t0 and g′(t) = 1 for t > t0 produces a reference that satisfies the requirement Δ1/32 ∼ |g′(t)| ≫ Δα ∼ Δ1/16 and leads to δHf+σς,g[η] ∼ η′(t0) log[Δ]/(4f″ (t0)); so that the confidence for Hf,g is O[σ−1Δ−5/16 log[Δ]], whereas the signal energy will have confidence
, since δEf+σς[η] = O[1].
3. Approach
3.1. The Physical Setup
We assume that we have an experimental system that is measured by some means, e.g., interrogated by waves, π(t), of some sort, such as microwave or ultrasonic radiation, and that we collect some portion of the waves scattered in this system to obtain both perturbed, fpert.(t), and unperturbed functions, funpert.(t), for times normalized by the appropriate choice of units to lie between zero and one. The difference |funpert.(t) − fpert.(t)| is assumed to be small and to be caused physically by a change in the system as measured at different spatial locations (as in Figure 1) and/or different times if the system is evolving. We also assume that there is Gaussian distributed noise in the system and that the noise functions for all measurements are represented by Brownian paths, which we will always denote by x(t) or, when there are multiple Brownian paths that must be distinguished, by xi(t). Moreover, we assume that these functions, which all have a variance of one, are scaled by an experimentally-determined signal-to-noise ratio, σ, which will typically have positive values much less than one-tenth.
If the system is linear, with initial impulse-response function Λ(t) and final perturbed impulse-response function Λ(t) + ελ(t), these functions may be represented mathematically as:
If the system is non-linear, these equations become approximate representations of funpert. (t) and fpert. (t) in the case where the perturbation to the system is small.
All experimental systems have finite time resolution. In addition, an experimentalist may deliberately signal average successive measurements to cancel noise. Both of these facts may be expressed using convolution of ideal experimental measurements, such those in Equation (12), with a finite measurement function, µΔ(t) of limited time duration, i.e., supp(µΔ)⊊ [0, 1]. This requires us to replace Equation (12) by:
and:
where,
with:
Physically, f(t) is the “well-behaved”, i.e., noise-free and smooth, part of the linear response of the experimental system (as described by Λ(t)) to the probing “waveform”, π(t1), while η(t) is the noise-free and smooth change in the system, resulting from the perturbation of the system, as represented by the function λ(t).
We will additionally assume that,
for later use.
Later, we will also need ς′(t):
with:
We will also assume that µΔ(t) is non-negative; typically, a unit step function of width less than one whose derivatives we will treat in the sense of distributions. We have from Equation (14):
which we will need for the evaluation of Equation (2).
3.2. Characteristics of the Measurement Window µΔ(t) Relevant to the Variation and Variance of Hf+εη+σς,g
Up to this point, we have not specified the experimental window function µΔ(t). While many different choices for this function are possible, the most common is a unit height step function of width much smaller that the total time of the experimental measurement, which we have scaled to be one. Experimental conditions usually provide for at least sixteen sample points in this window. This is motivated by the experimental goal of selecting digitizer equipment and settings so that the experimental window function is very small compared to the scale over which the input waveform exhibits significant change. Consequently, for typical measurements, we have values of ║mt║ ≪ 1/16. To make these comments more precise, we will define:
where χ(0,Δ](t) is the characteristic function of (0, Δ]. This function has finite total variation and mt(1) = µΔ(t − 1) = 0, for all t ∈ [0, 1], which we must always have for technical reasons (see the Appendix on Wiener integrals Equations (128) and (146)). Later, we will also need, for the calculation of the variance of joint entropy and its variation, the relation (jointly continuous in s and t):
and using ║mt║ to denote the L2-norm on [0, 1]:
3.3. Characteristics of the Measurement Window µΔ(t) Relevant to the Variation and Variance of Ef+εη+σς
If we define:
and:
Then, the last term in Equation (13) may be written as:
We also note for later use:
In particular, if 0 ≤ t1, t2 ≤ 1, then we have the order relation:
4. Calculation of the Variations of Joint Entropy and Signal Energy
4.1. Calculation of the Variation, δHf+σς,g(η)
We now calculate the average change in Equation (2) when f(t) is perturbed by the function εη(t) + σς(t) as shown in Equation (20). The calculation is broken into two parts.
4.1.1. The First Term
To begin with, we will focus on the first term in Equation (2). Using the terms defined above this is:
Let A(ε) denote the set of points where
. Similarly, denote the corresponding set of points where
. by B(ε). We will additionally assume that the set of critical points of f(t) and g(t) are disjoint, so that χA(ε)(t) ≠ 0 ⇒ g′(t) ≠ 0 and χB(ε)(t) ≠ 0 ⇒ f′(t) ≠ 0. The indicator functions may be expressed in terms of Heaviside functions, H(t), as:
Using these conventions, the first term in Equation (29) becomes:
Now,
where we have used the operational relation for Dirac delta functions: xδ(x) = 0. In addition, if f′(t) + εη′(t) + σς′(t) ≠ 0 (which is true if t ∈ B(ε), since the set of critical points of f(t) and g(t) are disjoint), we similarly have:
Using these relations, we differentiate Equation (31) with respect to ε as the first step in obtaining the variation, VI, of the first term:
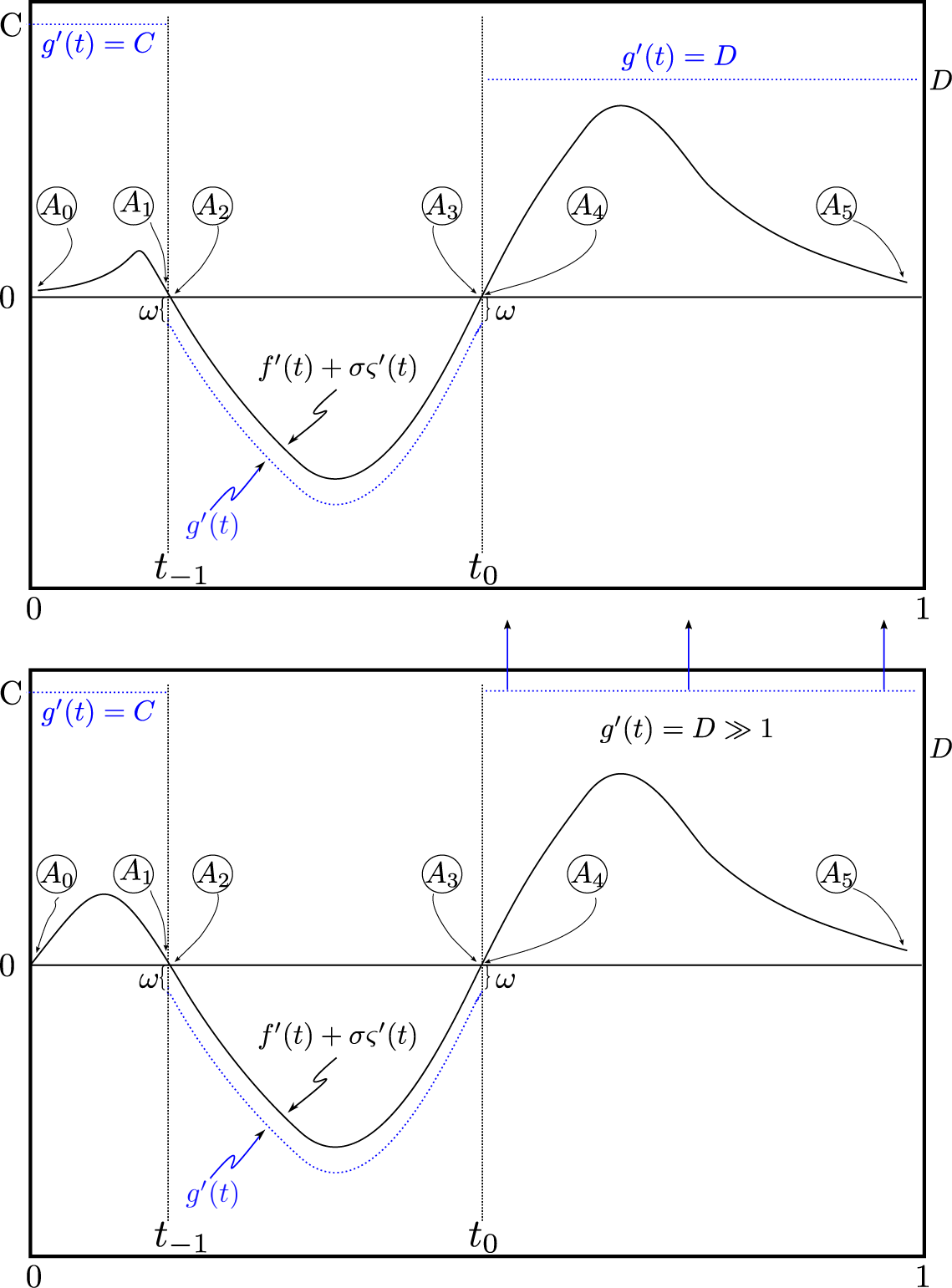
Now, it is always possible to pick a reference g(t), so that at ∂A(0) and ∂B(0), we have:
since the boundary points will either come in canceling pairs, with a contribution of ±1 at each of the boundary points (top panel of Figure 2); or there will be exact cancellations at all boundary points, but one, and the contribution from this point may be made arbitrarily small (bottom panel of Figure 2). The examples shown in Figure 2 have been chosen also to match the description of an “optimal” reference given in the Introduction after Theorem 4.
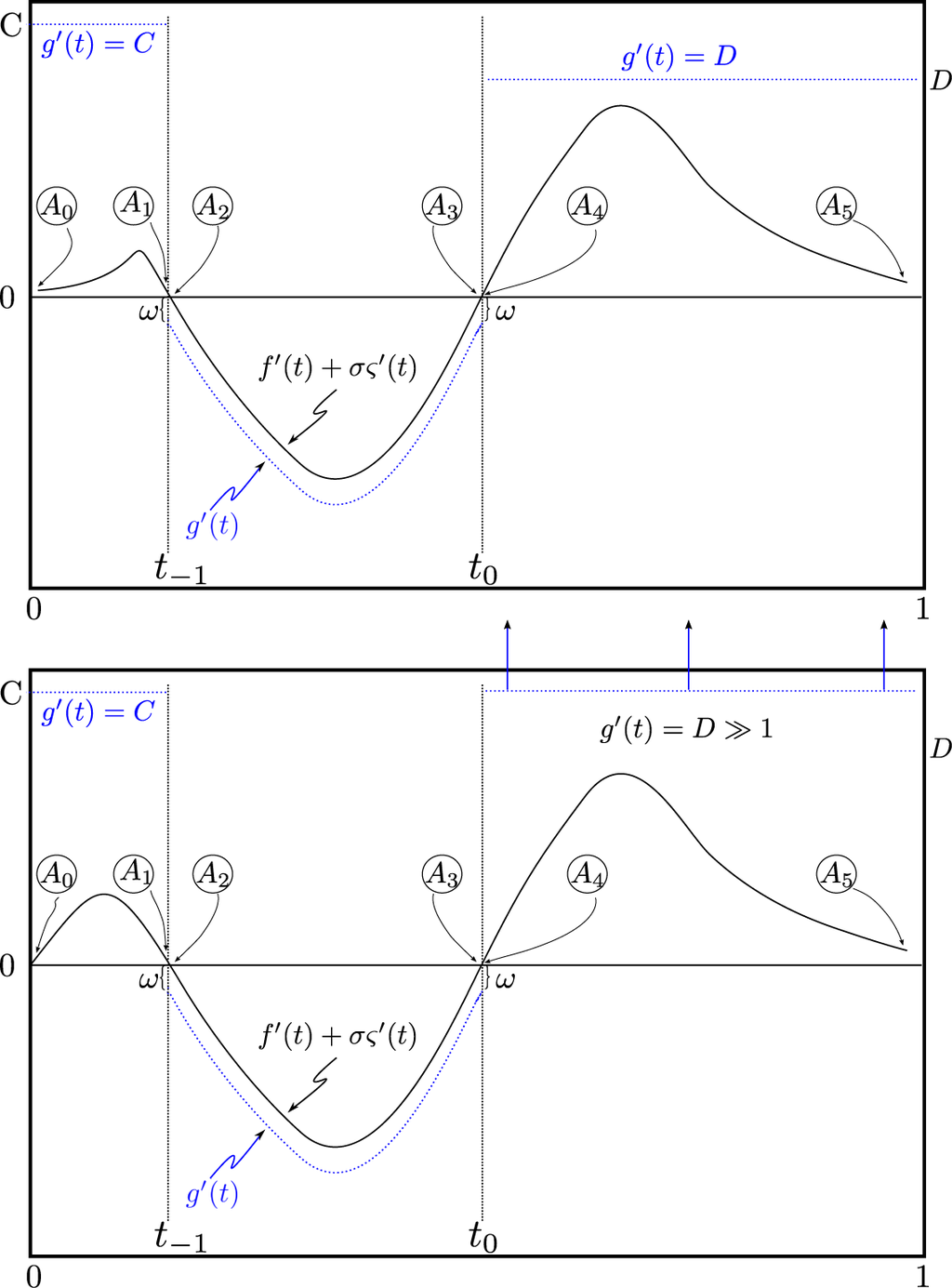
Figure 2.
(Top) An example of where boundary points can be balanced exactly, A0,…, A5 ∈ ∂A(0), ∂B(0) = ∅. The cancellations may be enumerated as follows: the contribution to Equation (36) from A0, A1 cancels that from A4, A5 if
; the contribution from A2 of −1 cancels that from A3, which is +1. C, D can always be scaled, so that C > |f′(t) + σς′(t)|, for t ∈ (0, t−1), and similarly for D with t ∈ (t0, 1). The addition of additional pairs of zero-crossings for f′(t) + σς′(t) will lead to the same structure of canceling pairs. (Bottom) The case where the terms in Equation (36) from boundary points A4, A5 cannot be canceled exactly. Their contribution can, however, be made arbitrarily small by increasing the constant D.
Thus, VI (Equation (35)) becomes:
where we have written χA(t) and χB(t) for χA(0)(t) and χB(0)(t), respectively. Finally, we rewrite Equation (30):
in terms of f′(t), g′(t), η′(t) and ς′(t), using Equation (20), and set ε = 0 to find:
This permits us to use Expression (37) to write:
4.1.2. Logarithmic Term
Similarly, VII, the variation for the logarithmic part of Equation (2), is obtained by first computing the derivative:
As in the case for the first term, the variations at ∂A(ε) and ∂B(ε) cancel in pairs, since |f′(t) + εη′(t) + σς′(t)| = |g′(t)| at the boundary points; hence, the derivative is:
Now, we set ε = 0 to obtain the variation, VII, for the logarithmic part:
4.1.3. Total Variation
The total variation, V, is now:
where:
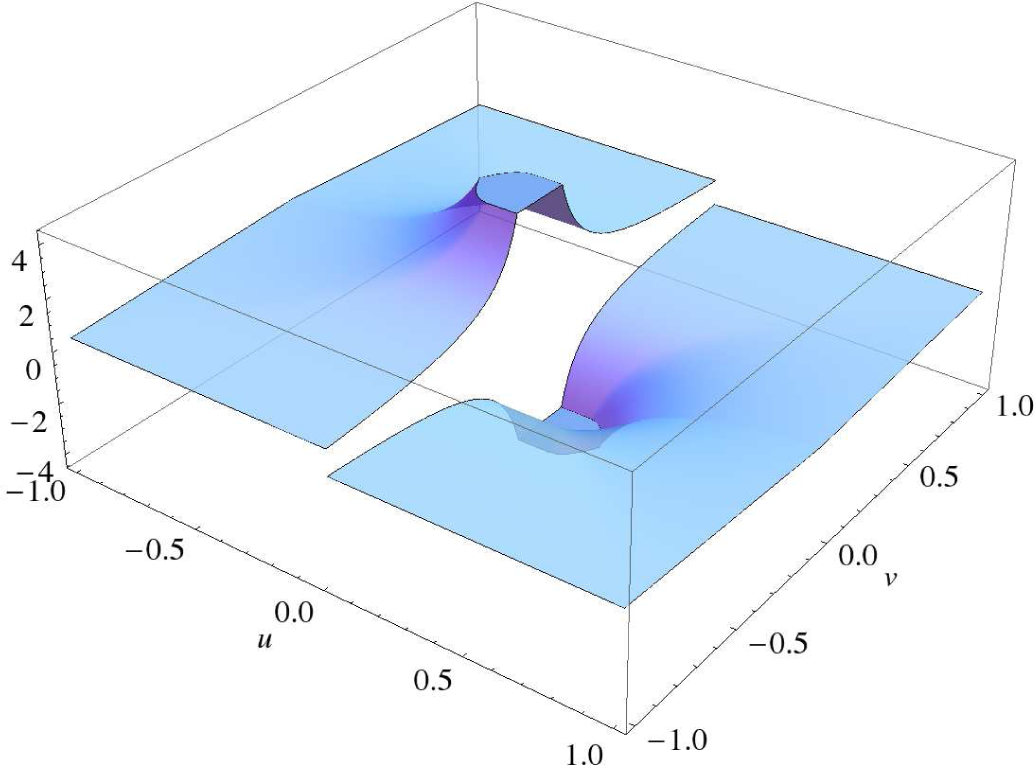
is continuous in u for fixed v and continuous in v, except for a discontinuity across v = 0. Figure 3 contains a plot of a typical G(u, v). Moreover, for fixed v, G(u, v) is an odd function of u, a fact that will be significant later.
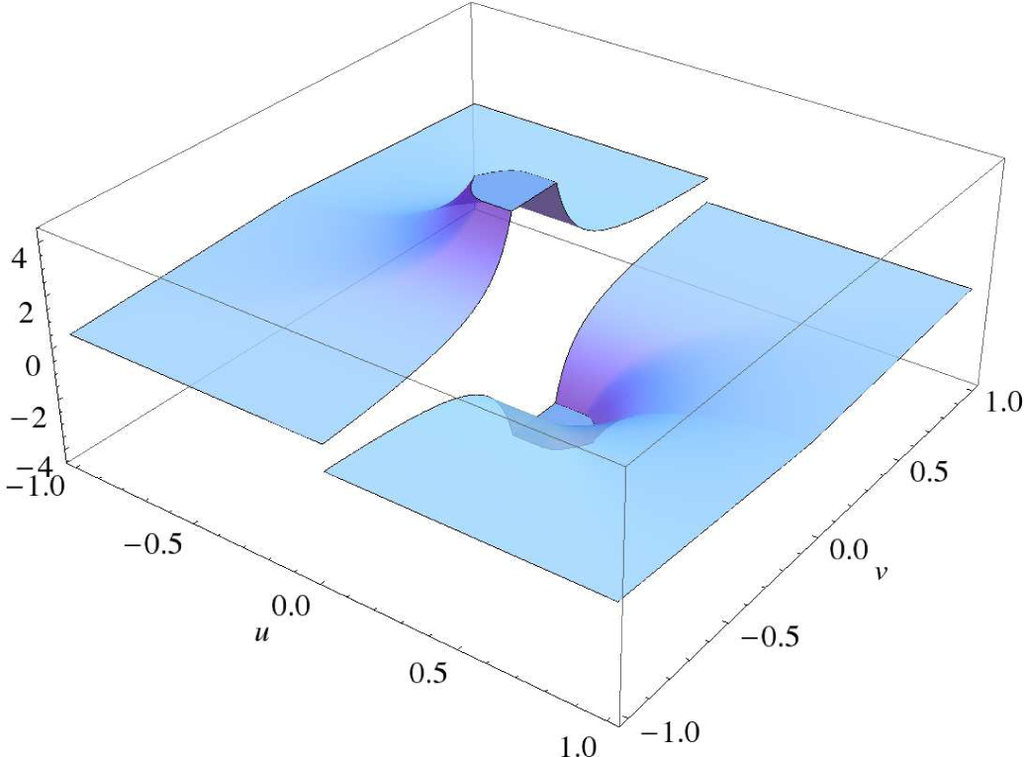
Figure 3.
A plot of G(u, v).
For later use, we record the alternate forms of G(u, v):
and:
We also record for later use the first and second partial derivatives of G(u, v) with respect to u,
which is continuous in u and, therefore, yields upon further differentiation with respect to u the distribution-free second partial derivative,
4.2. Calculation of the Variation, δEf+σς(η), for Ef
We now wish to characterize the signal receiver for energy, which is given by Equation (3). The perturbed signal receiver value is:
Following the usual steps, we differentiate with respect to ε:
The variation δEf+σς[η] is now given by:
5. Calculation of the Average Variations of Joint Entropy and Signal Energy
5.1. Calculation of the Average Variation, ⟨δHf+σς,g(η)⟩, by Wiener Integration
We now compute the average variation or expectation value of the variation over the space of noise functions, i.e., we may average Equation (43) over the Brownian paths. This is obtained from the Wiener integral of
and is:
The function G(u, v) is continuous in u for all v; hence (Theorem 29.6 on page 443 of [40]), we can interchange the order of evaluation of integration, so:
Finally,
where the last integral is obtained by the change of variables:
This can be further simplified as:
where, based on the discussion above, typical experimental conditions will lead to σ being on the order of 10−6.
5.1.1. The Average Variation, ⟨δHf+σς,g[η]⟩, and the Heat Equation
We observe that the bracketed term in Equation (58) is the Green’s function for the heat equation [41,42], defined on ℝ, i.e.,
Thus, we have:
where:
is a point on one member of a family of heat surfaces that are determined by the heat equations,
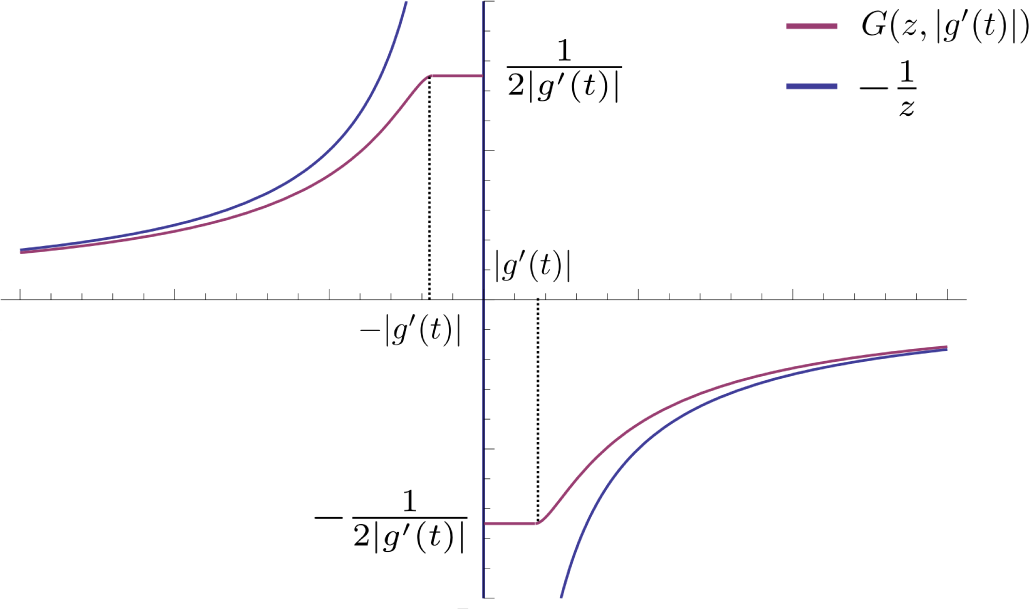
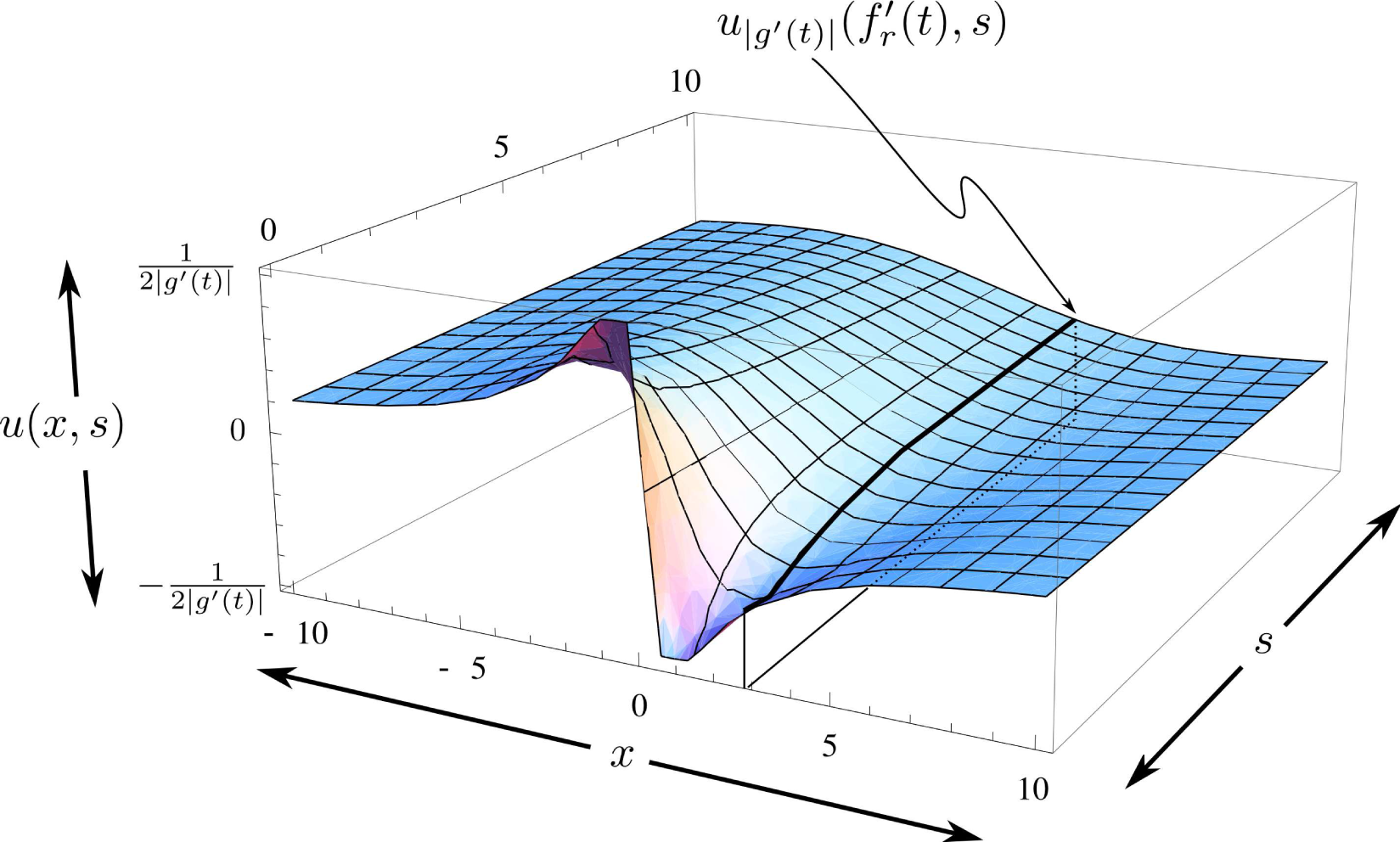
with different (in fact, |g′(t)|-dependent) “initial conditions” (i.e., at s = 0) defined by G (z, |g′(t)|). A typical example is shown in Figure 4.
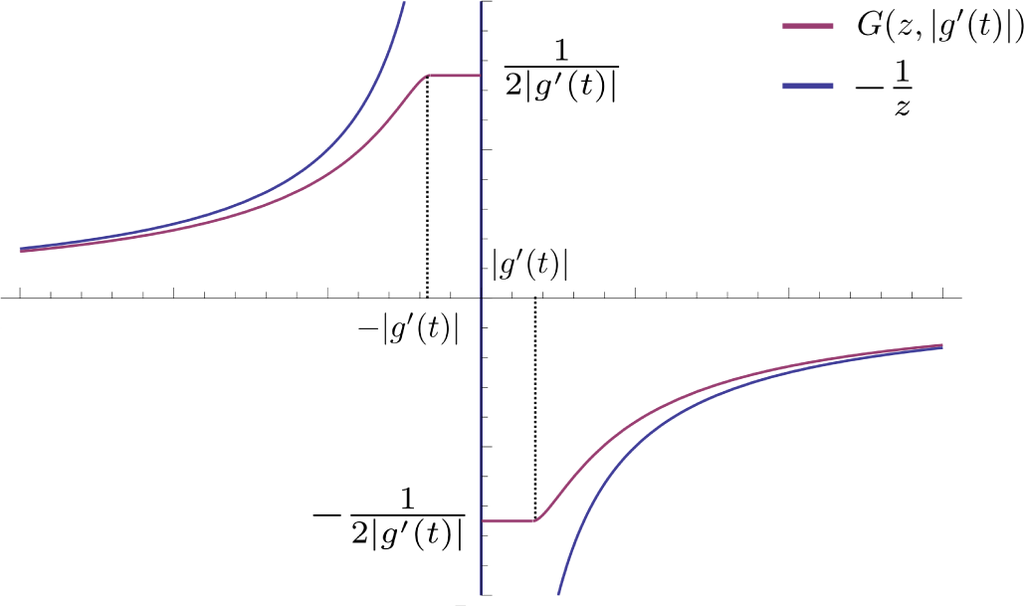
Figure 4.
A typical initial condition from Equation (78) is shown by the purple curve. Many different initial conditions, such as the one shown, define different “heat”-surfaces, which, in turn, define the average variation ⟨δHf+σς.g[η]⟩ via the inner z-integral in Equation (60). Also shown is the curve
.
Since for small noise, s, the heat kernel is approximated well by a Dirac delta function, we might expect that in the limit s → 0+:
in which case, Equation (60) becomes:
which we will shortly show is unbounded for certain choices of g(t). A good way to construct such g(t) is to pick a zero of f′(t) and have g′(t) differ only slightly from f′(t) on one side of the zero and differ greatly from it on the other side. Referring back to Equation (78), if we assume that |g′(t)| ≩ 0, then G(z, |g′(t)|) ∈ L2 [ℝ], and there are a large number of theorems describing the behavior of u|g′(t)|(x, s). In particular, a limiting form of Theorem 5 in Chapter 5 on page 67 of [42], where the vertical sides are pushed out to ±∞, guarantees that as s → 0, u|g′(t)|(z, s) → G(z, |g′(t)|).
5.1.2. The Structure of the Solution-Surfaces Associated with ⟨δHf+σς,g[η]⟩
Figure 4 also illustrates the useful inequality:
With this result, we are now ready to prove:
Theorem 3. Suppose that f is in C3[0, 1] and there exists t0 ∈ (0, 1), such that f′(t0) = 0 and f′′(t0) ≠ 0. Then, there exists C1 > 0, such that for all C2 > 0, there exists a piecewise differentiable function g, independent of η, such that:
In particular, provided η′(t0) ≠ 0, one can make arbitrarily large.
Proof. We shall consider the case f″(t0) > 0; the other case is similar.
Choose ξ > 0 and small enough that f′∈ C2[0, 1] and strictly increasing on [t0 − ξ, t0 + ξ], so that:
We define:
where ω > 0 is chosen small.
We extend g to be piecewise C3[0, 1] off(t0 − ξ, t0 + ξ) and such that g′(t) ≥ 1 for all t ∈ [0, 1]\[t0 − ξ, t0 + ξ), except possibly finitely many points where it does not exist. The exact details of the extension do not matter, since contributions from the extension will be negligible compared to those from (t0 − ξ, t0 + ξ), as long as we do not choose a reference g(t) that does not violate the conditions discussed after Equation (36). Figure 2 illustrates how the extension might be chosen in one case.
We break the integral in Equation (64) into an integral over [t0 − ξ, t0 + ξ] and its compliment. The latter piece is bounded by:
where:
The integral over [t0 − ξ, t0 + ξ] becomes:
The term ξη′(t0) may be incorporated into C1║η′║∞ by increasing C1 slightly. By Equation (67), we have:
Finally, g does not depend on η. This completes the proof. □
We note, however, that in order to keep the variance of the variation small, so that we maintain high sensitivity (Equation (5)), we must keep
as indicated in Equation (109). This provides a practical bound on the magnitude of the variation.
We also record for later use the calculation of the maximum magnitudes of the first and second partial derivatives of G(u, v) with respect to u as:
and:
Given the structure of the integral in Equation (61), we see that u|g′(t)|(f′(t), s) → 0 as s → ∞. Moreover,
A later analysis of the signal energy Ef will reveal a different “initial condition” (these “initial conditions” refer to the noise-free case), which characterizes that receiver.
We note that G (z, |g′(t)|) is determined by the mathematical form of the signal receiver, in this case Hf,g, as well as the reference waveform g′(t).
As shown in Figure 4, the supremum of the initial conditions may be made arbitrarily large by making g′(t) smaller. The effect of this change is reflected in the structure of the solution (heat) surface, as shown in Figure 5. The figure also shows that for all z and s:
which is consistent with the maximum property for solutions to the heat equation (discussed in Chapter 2, Section 3 of [42]).
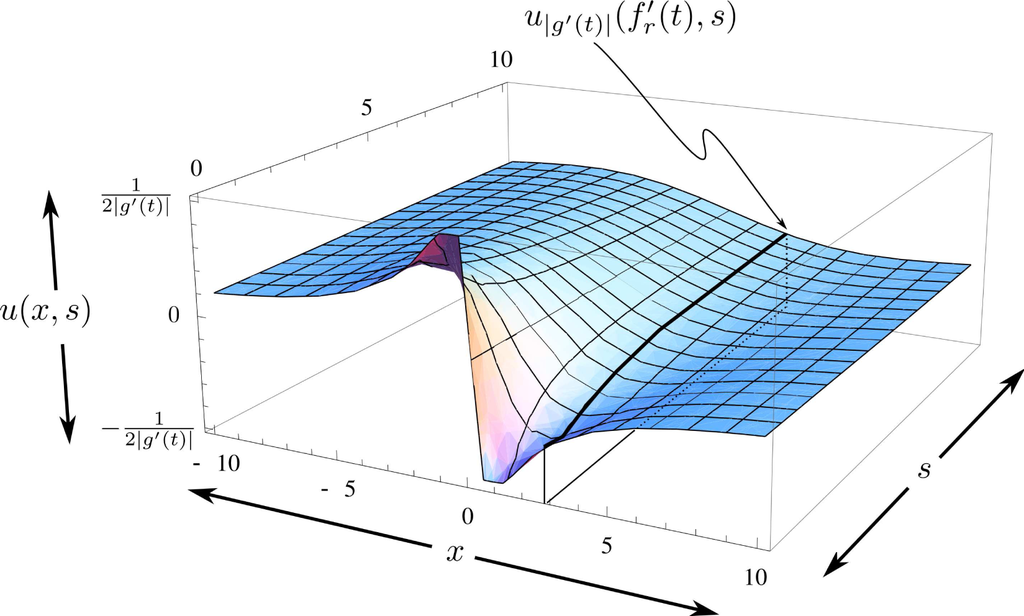
Figure 5.
Typical solution surface for Equation (62) resulting from the initial conditions shown in Figure 4. The heavy purple line represents a typical u|g′(t)|(f′(t),s). Many lines, such as the one shown, each from a potentially different solution-surface (determined by different initial conditions, such as shown in Figure 4), determine the “heat”-surface that defines the average variation ⟨δHf+σς,g[η]⟩ via Equation (60). The resulting surface inherits properties of the different solution surfaces, e.g., for negative values of x, the “heat”-surface is positive; for positive values of x it is negative, as s → ∞ the “heat”-surface decays to zero, as discussed after Equation (61). Surface shown for |g′(t)| = 0.5.
5.2. Calculation of the Average Variation ⟨δEf+σς(η)⟩
From Equation (51), the average variation is the Wiener integral:
which becomes:
which has no dependence on the noise level σ and, thus, no heat surface.
We also observe that the integral in Equation (81) is the variation for the signal energy receiver in the noise-free analysis.
6. The Variances of the Variations
In this section, we perform the calculations required to prove:
Theorem 4. Suppose K0 > 0 is a constant, f, η are in C1[0, 1] and g is piecewise C1[0, 1]. Let 0 < α < 1/6. Suppose that, except at finitely many points, |g′(t)| ≠ |f′(t)| and |g′(t)| ≥ K0Δα.
- Then, there exists a constant K1 that depends on ║η′║∞, but not on g or σ, such that:
- There exists K2 > 0, that depends on ║η║∞, but not on Δ or σ, such that:
We break the proof into two parts.
Proof. Part I: Calculation of the variance of δHf+σς,g[η]
Expanding the square as a double integral (and using Equation (18) for ς′(t) and Equation (19) for mt), the Wiener integral may be written as:
where, since G(u, v) is jointly continuous in u, v, as before, we can interchange the order of integrations. The inner Wiener integral may be replaced by a Lebesgue integral, using Equation (146). It becomes:
where (from Equation (143)):
We also point out for later use that calculation of the maximum of n2(t1, t2)2 shows:
Substituting this into Equation (84), we obtain:
As a double check of the result, we observe that as s1, s2→0+, the heat-kernels in the first and second terms approach Dirac delta functions centered at f′(t), f′(t1) and f′(t2), i.e., δ(z−f′(t)), δ(z1− f′(t1)) and δ(z2− f′(t2)), respectively, and:
as expected.
We now rewrite the right-hand side of Equation (92) in terms of solutions of the heat equation, as was done following Equation (60), and find that Equation (92) equals:
where:
where we have used the change of variables:
and Equation (61) to go from the first to the second equations.
We now observe that, by Equation (22),
when |t1 − t2| > Δ, in which case:
and so, Equation (94) may be written as:
The functions appearing in Equation (98) are based on integrals that have the form:
where limiting behavior as si → 0 for i = 1, 2 may be found using a Laplace expansion, as described in Equation 6.4.35 of Bender and Orszag [43], and Equation (99) holds, provided h is C5 in a neighborhood of a.
Consequently, we see that, after rewriting the first integral as a product of a t1 and a t2 integral and using Equations (90), the difference of the first and the last terms in Equation (98) is of order σ4 in the limit s1, s2 → 0 and may therefore be dropped.
Consequently, we focus attention on the remaining integrals. Equation (99) enables this refinement of the limiting form of Equation (63):
where the n-th-partial derivative of G(u, v) with respect to the first argument is denoted by G(n)(u, v) and is guaranteed to exist for all n at all but finitely many points by the assumption that |g′(t)| ≠ |f′(t)| at all but finitely many points. Moreover, since |g′(t)| is bounded away from zero by hypothesis, there is a uniform bound on G(4) (f′(t), |g′(t)|) offthe set of points where |g′(t)| = |f′(t)|.
Consider the second integral in Equation (98). The term in brackets becomes (ignoring those finitely many points where G(f′(t), |g′(t)|) might be non-smooth, because |f′(t)| = |g′(t)|), and using Equation (90) to replace s1, s2:
We next consider the third integral in Equation (98), by Equations (95) and (100) as s2 → 0,
with:
defined as indicated to simplify notation. Applying Equation (99) to Equation (102), we find that Λ(t1, t2, s1, s2) is asymptotic to:
Since
and
, Λ(t1, t2, s1, s2) becomes:
where we used Equation (90) to write the error term as a function of σ.
Using (105) and (90), the difference between the second and third integrals appearing in Equation (98) gives:
to accuracy O[σ4]. This may be further simplified, introducing errors of O[2Δ] by truncating the upper bound of integration for t1 in the last two integrals from 1 to 1−2Δ, so that by Equation (23), ║mt║ = 1, and the last two pieces cancel, leaving:
Focusing on the product of integrals in the second row, we see that at the cost of an additional error term of O[Δ], we may replace ║mt║ by 1 in the t1 integral and then use Schwartz’s inequality to bound the integral by the norms shown. To bound the t2 integral, we use Equations (17) and (75) to obtain:
Focusing next on the integrals in the first row of the inequality, we use Schwartz’s inequality to bound the t1 integral and Equations (17), (76) and (89) to bound the t2 integral to obtain:
Since the reference satisfies the constraint:
where α > 0, then we have:
This simplifies to our final bound:
where
is a constant independent of g, η, Δ and σ. Let
, and we are done.
Part II: Calculation of the variance of δEf+σς[η] The variance of the variation, δEf+σς[η], is:
Recalling Equations (81) and (51) and using Equation (13) for ς(t) and Equation (16) for Mt, the Wiener integral on the right-hand side of Equation (112) becomes:
Using Equation (146), the right-hand side may be written in terms of Lebesgue integrals as:
where (from Equation (143)):
Note that the first term in Equation (118) may be calculated exactly as:
which, by Equation (81), cancels the −⟨δEf+σς[η]⟩2 appearing in Equation (112).
We now rewrite Ω as:
In the second integral the z1 integration is of an odd integrand over a symmetric interval and, hence, vanishes, so that we obtain after some rearrangement and simplification of the remaining Gaussian integrals:
where we have used Equation (116) to obtain the last equation.
Inserting the limiting form of the integral into Expression (117) of small positive s1, s2 into Equation (112) and using Equation (119), we obtain:
where K2 is a constant independent of Δ and σ, but depending on η.
This completes the proof of the theorem. □
7. A Short List of Wiener Integrals
7.1. The First Wiener Integral
The first type of Wiener integral is described by the following:
Theorem 5. Let ρ(t) be real and of bounded variation on [0, 1] and the ρ be normalized, such that:
Let:
and let F (u) be a (real or complex) measurable function defined on −∞ < u < ∞. Then, a necessary and sufficient condition that:
be a Wiener measurable function of x(•) over C0[0, 1] is that:
be of class L1 on −∞ < u < ∞. Moreover, if this condition is satisfied,
We derive this equation below. Published results of a similar form may be found in [40], Theorem 29.7 (n = 1 case and assuming that ρ is normalized to unity). Other references are either Koval’chick [44] (page 106, Equation (13)) or Cameron and Martin [45] (page 393, Equation (6.3)). The same result is derived by an argument that will be familiar to many physicists in Paley, Wiener and Zygmund (see [46] Equation (2.11)), although the result derived there also assumes that the ρ is normalized to one. There is a difference of
between the result contained in Equation (128) and the older references [44,46], due to use of different definitions of the normal distribution used to define the Brownian motion on which the Wiener measure is based.
7.1.1. Random Variables Derivation
We want to calculate:
ς′(t) is a Gaussian random variable with zero mean, so
, where σ2 = EW (ς′(t)2). From this:
7.2. The Second Wiener Integral
The second type of Wiener integral we need is:
where ρi(1) = 0 for each index i and the ρi are orthonormal.
Similar versions of this integral appear in many sources, for instance in Koval’chick [44] (page 107, Equation (14)), which contains (after transcription into the modern conventions):
This form appears to be derivable from Equation (131) using integration by parts. Specifically,
We would formally transform this into the form of Equation (131) by the following steps:
First observe that the integral in Equation (133) is equal to:
Next, use the facts that we have assumed that ρi(1) = 0 and, additionally, that the Brownian paths are normalized according to x(0) = 0, so that (classical) integration by parts of the integrals in the first line of Equation (134) would yield:
Although this “derivation” shows that the two forms are equivalent, as desired, it overlooks the fact that the integrals in Equation (132) cannot be classical integrals. In fact, Wiener [47] (p. 68) states that integrals of the form:
are actually Itō integrals. The correct integration-by-parts formula in this case is:
where [X, Y]t is the quadratic covariation process with:
where P ranges over partitions of the interval [0, t] and the norm, ║P║, of the partition, t0 <⋯< tn, is the mesh, i.e., max{|ti − ti−1| : i = 1,…, n}.
However, in the case where Y is of bounded variation:
so that Equation (137) reduces to the classical integration by parts formula. Thus, the derivation above is (accidentally) correct.
The number of sources containing detailed derivations of these equations in English appears to be limited. The only source we have been able to locate is Paley, Wiener and Zygmund, which is completely self-contained and contains the equivalent of our Equation (131) (see Equation (2.14) in [46]), although the result derived there assumes that the measure is normalized to one and uses a slightly different notation for the Brownian paths.
We need to compute Wiener integrals like those on the left-hand side of Equation (131) in the case where the ρk(t) are not orthonormal. Moreover, we only need to consider the special form:
To apply Equation (131), we use the Gram–Schmidt process to obtain an orthonormal family ν1(t), ν2(t) from the original ρ1(t), ρ2(t). Using the short-hand notation:
The Gram–Schmidt process is:
where:
which is expressed in matrix form:
or:
This permits us to rewrite Equation (140) as:
to which (since the νk(1) = 0, k = 1, 2) we may now apply Equation (131) to obtain:
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by NIH EB002168, 5R21EB018095 and NSF DMS1300280. The research was carried out at the Washington University Department of Mathematics and the School of Medicine.
Author Contributions
The paper was conceived by M.S. Hughes, J.E. McCarthy and S.A. Wickline. The theorems and proofs are primarily due to Hughes, McCarthy and P.J. Bruillard. The experimental results are due to Hughes, J.N. Marsh and S.A. Wickline. The introduction and background sections were written primarily by Marsh, Wickline and Hughes. The manuscript was drafted by all authors and all have read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Young, S.; Driggers, R.; Jacobs, E. Signal Processing and Perfromance Analysis for Imaging Systems; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Carson, P.L.; Abbott, J.G.; Harris, G.R.; Lewin, P. Acoustic output Measurement and Labeling Standard for Diagnostic Ultrasound Equipment; American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Insana, M. Ultrasonic imaging of microscopic structures in living organs. Int. Rev. Exp. Pathol. 1996, 36, 73–92. [Google Scholar]
- Chaturvedi, P.; Insana, M. Error bounds on ultrasonic scatterer size estimates. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1996, 100, 392–399. [Google Scholar]
- Madsen, E.; Insana, M.; Zagzebski, J. Method of data reduction for accurate determination of acoustic backscatter coefficients. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1984, 76, 913–923. [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg, F.; Liu, J.; Merton, D. Gray scale second harmonic imaging of acoustic emission signals improves detection of liver tumors in rabbits. J Ultras. Med. 2000, 19, 557–563. [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg, F.; Dicker, A.P.; Thakur, M.L.; Rawool, N.M.; Liu, J.B.; Shi, W.T.; Nazarian, L.N. Comparing contrast-enhanced ultrasound to immunohistochemical markers of angiogenesis in a human melanoma xenograft model: Preliminary results. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2002, 28, 445–451. [Google Scholar]
- Lizzi, F.L.; Feleppa, E.J.; Alam, S.K.; Deng, C.X. Ultrasonic spectrum analysis for tissue evaluation. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2003, 24, 637–658. [Google Scholar]
- Ciancio, A. Analysis of Time Series with Wavelets. Int. J. Wavel. Multiresolut. Inf. Process 2007, 5, 241–256. [Google Scholar]
- Rukun, S.; Subanar; Rosadi, D; Suharto. The Adequateness of Wavelet Based Model for Time Series. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2007, 423, 241–256. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, C.; Pipiras, V. Long range Dependence, Unbalanced Haar Wavelet Transformation and Changes in Local Mean Level. Int. J. Wavel. Multiresolut. Inf. Process 2009, 7, 23–58. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Park, J. Efficient Similarity Search for Multi-Dimensional Time Sequences. Int. J. Wavel. Multiresolut. Inf. Process 2010, 8, 343–357. [Google Scholar]
- Aman, S.; Chelmis, C.; Prasanna, V.K. Influence-Driven Model for Time Series Prediction from Partial Observations, Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Austin, TX, USA, 25–30 January 2015; pp. 601–607.
- Dutta, I.; Banerjee, R.; Bit, S.D. Energy Efficient Audio Compression Scheme Based on Red Black Wavelet Lifting for Wireless Multimedia Sensor Network, Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), Mysore, India, 22–25 August 2013; 45, pp. 1070–1075.
- Shannon, C.; Weaver, W. The Mathematical Theory of Communication; University of Illinois Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Reinsch, C.H. Smoothing by Spline Functions. Numer. Math. 1967, 10, 177–183. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Vitanyi, P. An Introduction to Kolmogorov Complexity and Its Applications; Texts in Computer Science; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chaitin, G. Algorithmic Information Theory; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, M.S. A Comparison of Shannon Entropy versus Signal Energy for Acoustic Detection of Artificially Induced Defects in Plexiglass. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1992, 91, 2272–2275. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, M.S. Analysis of Ultrasonic Waveforms Using Shannon Entropy, Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Tucson, AZ, USA, 20–23 October 1992; pp. 1205–1209.
- Hughes, M.S. Analysis of Digitized Waveforms Using Shannon Entropy. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1993, 93, 892–906. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, M.S. NDE Imaging of Flaws Using Rapid Computation of Shannon Entropy, Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Baltimore, MD, USA, 31 October–3 November 1993; pp. 697–700.
- Hughes, M.S. Analysis of digitized waveforms using Shannon entropy. II. High-speed Algorithms based on Green’s functions. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1994, 95, 2582–2588. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, M.S.; Marsh, J.N.; Hall, C.S.; Savery, D.; Lanza, G.M.; Wickline, S.A. Characterization of Digital Waveforms Using Thermodynamic Analogs: Applications to Detection of Materials Defects. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 2005, 52, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, M.S.; McCarthy, J.; Marsh, J.; Wickline, S. Joint entropy of continuously differentiable ultrasonic waveforms. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 133, 283–300. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, M.S.; McCarthy, J.; Marsh, J.; Wickline, S. High Sensitivity Imaging of Resin-Rich Regions in Graphite/Epoxy Laminates using an Optimized Joint-Entropy-based Signal Receiver. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, M.S.; McCarthy, J.E.; Wickerhauser, M.V.; Marsh, J.N.; Arbeit, J.M.; Fuhrhop, R.W.; Wallace, K.D.; Thomas, T.; Smith, J.; Agyem, K.; et al. Real-time Calculation of a Limiting form of the Renyi Entropy Applied to Detection of Subtle Changes in Scattering Architecture. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 126, 2350–2358. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, M.S.; Marsh, J.N.; Hall, C.S.; Savoy, D.; Scott, M.J.; Allen, J.S.; Lacy, E.K.; Carradine, C.; Lanza, G.M.; Wickline, S.A. In vivo ultrasonic detection of angiogenesis with site-targeted nanoparticle contrast agents using measure-theoretic signal receivers, Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Montréal, Canada, 23–27 August 2004; pp. 1106–1109.
- Hughes, M.S.; Marsh, J.N.; Arbeit, J.; Neumann, R.; Fuhrhop, R.W.; Lanza, G.M.; Wickline, S.A. Ultrasonic Molecular Imaging of Primordial Angiogenic Vessels in Rabbit and Mouse Models With αvβ3-integrin Targeted Nanoparticles Using Information-Theoretic Signal Detection: Results at High Frequency and in the Clinical Diagnostic Frequency Range, Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 18–21 September 2005; pp. 617–620.
- Hughes, M.S.; Marsh, J.; Woodson, A.; Lacey, E.; Carradine, C.; Lanza, G.M.; Wickline, S.A. Characterization of Digital Waveforms Using Thermodynamic Analogs: Detection of Contrast Targeted Tissue in MDA435 Tumors Implanted in Athymic Nude Mice, Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 18–21 September 2005; pp. 373–376.
- Hughes, M.S.; Marsh, J.; Lanza, G.M.; Wickline, S.A.; McCarthy, J.; Wickerhauser, V.; Maurizi, B.; Wallace, K. Improved signal processing to detect cancer by ultrasonic molecular imaging of targeted nanoparticles. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 129, 3756–3767. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, M.S.; Marsh, J.N.; Zhang, H.; Woodson, A.K.; Allen, J.S.; Lacy, E.K.; Carradine, C.; Lanza, G.M.; Wickline, S.A. Characterization of Digital Waveforms Using Thermodynamic Analogs: Detection of Contrast-Targeted Tissue In Vivo. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 2006, 53, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, M.S.; McCarthy, J.E.; Marsh, J.N.; Arbeit, J.M.; Neumann, R.G.; Fuhrhop, R.W.; Wallace, K.D.; Znidersic, D.R.; Maurizi, B.N.; Baldwin, S.L.; et al. Properties of an entropy-based signal receiver with an application to ultrasonic molecular imaging. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 121, 3542–3557. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, M.S.; Marsh, J.; Wallace, K.; Donahue, T.; Connolly, A.; Lanza, G.M.; Wickline, S.A. Sensitive Ultrasonic Detection of Dystrophic Skeletal Muscle in Patients with Duchenne’s Muscular Dystrophy using an Entropy-Based Signal Receiver. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2007, 33, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, M.S.; McCarthy, J.E.; Marsh, J.N.; Arbeit, J.M.; Neumann, R.G.; Fuhrhop, R.W.; Wallace, K.D.; Thomas, T.; Smith, J.; Agyem, K.; et al. Application of Renyi Entropy for ultrasonic molecular imaging. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 125, 3141–3145. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, M.S.; Marsh, J.; Agyem, K.; McCarthy, J.; Maurizi, B.; Wickerhauser, M.; Wallance, K.D.; Lanza, G.; Wickline, S. Use of smoothing splines for analysis of backscattered ultrasonic waveforms: Application to monitoring of steroid treatment of dystrophic mice. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 2011, 58, 2361–2369. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, J.N.; McCarthy, J.E.; Wickerhauser, M.; Arbeit, J.M.; Fuhrhop, R.W.; Wallace, K.D.; Lanza, G.M.; Wickline, S.A.; Hughes, M.S. Application of Real-Time Calculation of a Limiting Form of the Renyi Entropy for Molecular Imaging of Tumors. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 2010, 57, 1890–1895. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, J.N.; Wallace, K.D.; Lanza, G.M.; Wickline, S.A.; Hughes, M.S.; McCarthy, J.E. Application of a limiting form of the Renyi entropy for molecular imaging of tumors using a clinically relevant protocol, Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, San Diego, CA, USA, 11–14 October 2010; pp. 53–56.
- Sackett, D.L. Why randomized controlled trials fail but needn’t: 2. Failure to employ physiological statistics, or the only formula a clinician-trialist is ever likely to need (or understand!). Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2001, 165, 1226–1237. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, J.C. Stochastic Processes and the Wiener Integral; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Cannon, J.R. The One-Dimensional Heat Equation; Addison-Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Widder, D.V. The Heat Equation; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Bender, C.M.; Orszag, S.A. Advanced Mathematical Methods for Scientists and Engineers; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Koval’chik, I. The Wiener Integral. Russ. Math. Surv. 1963, 18, 97–134. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, R.H.; Martin, W.T. Transformations of Weiner Integrals Under Translations. Ann. Math. 1944, 45, 386–396. [Google Scholar]
- Paley, R.E.A.C.; Wiener, N.; Zygmund, A. Notes on Random Functions. Math. Z. 1933, 37, 651–672. [Google Scholar]
- Wiener, N.; Siegel, A.; Rankin, B.; Martin, W.T. Differential Space, Quantum Systems, and Prediction; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).