Risk Neutral Measure Determination from Price Ranges: Single Period Market Models
Abstract
:1. Preliminaries and Problem Statement
2. The Method of Maximum Entropy with Errors in the Data
2.1. The Standard Method of Maximum Entropy
2.2. Nested Sequence of Entropy Maximization Problems
2.3. Maxentropic Density Reconstruction from Data with Errors
3. Numerical Examples
3.1. Risk Neutral Prices from Option Prices: Discrete Case
3.2. Simple Continuous Example: The Risk Free Rate Is Uncertain
3.3. Only the Bid-Ask Prices of the Asset Are Known
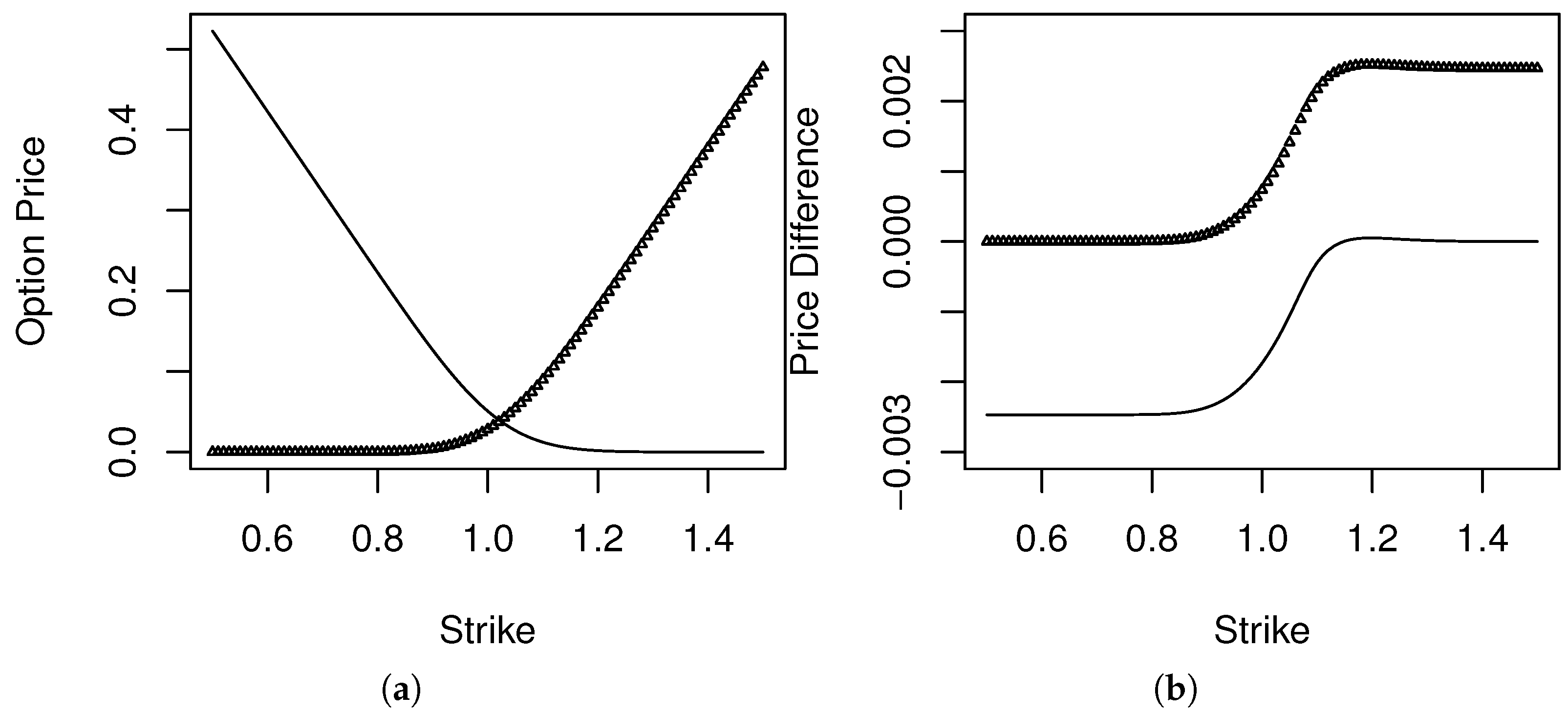
3.4. Risk Neutral Measures from Option Prices
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elliott, R.J.; Kopp, P.E. Mathematics of Financial Markets; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Pliska, R.S. Introduction to Mathematical Finance; Blackwell Publishers: Malden, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gzyl, H.; Mayoral, S. A method for determining risk aversion functions from uncertain market prices of risk. Insur. Math. Econ. 2010, 47, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, J.; Saá-Requejo, J. Beyond arbitrage: Good-deal asset price bounds and incomplete markets. J. Polit. Econ. 2000, 108, 79–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Peña, V.; Ibragimov, R.; Jordan, S. Option Bounds. J. Appl. Probab. 2004, 41, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aspremont, A.; El Ghaoui, L. Static arbitrage bounds on basket option prices. Math. Prog. A 2006, 106, 467–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, J.; Saynac, X.; Vera, J.C.; Zuluaga, L.F. Computing general static-arbitrage bounds for European basket options via Dantzig-Wolfe decomposition. Algorithmic Oper. Res. 2010, 5, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Reynaerts, H.; Vanmaele, M.; Dhaene, J.; Deelstra, G. Bounds for the price of a European-style Asian option in a binary tree model. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2006, 168, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tankov, P. Improved Freéchet bounds and model free pricing of multi-asset options. J. Appl. Probab. 2011, 48, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigelböck, M.; Labordère, P.H.; Penkner, F. Model independent bounds for option process: A mass transport approach. Financ. Stoch. 2013, 17, 477–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borwein, J.; Choksi, R.; Marechal, P. Probability distributions from assets inferred from option prices via the principle of maximum entropy. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2003, 14, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brody, D.C.; Buckley, I.R.; Constantinou, I.C.; Meister, B.K. Entropy calibration revisited. Phys. Lett. A 2005, 337, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchen, P.W.; Kelly, M. The maximum entropy distribution of an asset inferred from option prices. J. Financ. Quant. Anal. 1996, 31, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritelli, M. The minimal entropy martingale measure and the valuation problem in incomplete markets. Math. Financ. 2000, 10, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulko, L. The entropy theory of stock option pricing. Int. J. Theor. Appl. Financ. 1999, 2, 331–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacod, J.; Protter, P. Risk-neutral compatibility with option prices. Financ. Stoch. 2010, 14, 285–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, C.; Schneider, L. Maximum entropy distributions inferred from option portfolios on an asset. Financ. Stoch. 2012, 16, 293–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutzer, M. A simple non-parametric approach to derive security valuation. J. Financ. 1996, 51, 1633–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackwerth, J.C. Option implied risk neutral distributions and implied binomial trees: A literature Review. J. Derivatives 1999, 7, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkings, R.I.; Rubinstein, M.; Daniel, G.J. Reconstruction of the density function implicit in option prices from incomplete and noisy data. In Maximum Entropy and Bayesian Methods; Hanson, K.M., Silver, R.N., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Tapiero, O.J. A maximum (non-extensive) entropy approach to equity options bid-ask spread. Phys. A 2013, 392, 3051–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Celis, O.; Luang, L.; Lemmes, D.; Tempères, J.; Cuyt, A. Determining and benchmarking risk neutral distributions from implied option prices. Appl. Math. Comp. 2015, 258, 372–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, E.; Gzyl, H.; Mayoral, S. Density reconstructions with errors in the data. Entropy 2014, 16, 3257–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyahara, Y. Option Pricing in Incomplete Markets: Modeling Based on Geometric Levy Processes and Minimal Entropy Martingale Measures; World Scientific Press: Singapore, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.; Cai, R.; Tong, C. Applications of entropy in finance: A review. Entropy 2013, 15, 4909–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esscher, F. On the Probability Function in the Collective Theory of Risk. Skandinavisk Aktuarietidskrift 1932, 15, 175–195. [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes, E.T. Information theory and statistical mechanics. Phys. Rev. 1957, 106, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullback, S. Information Theory and Statistics; Dover Publications Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Csizsar, I. I-divergence geometry of probability distributions and minimization problems. Ann. Probab. 1975, 3, 620–630. [Google Scholar]
- Borwein, J.; Lewis, A. Convex Analysis and Non-Linear Optimization; CMS Books in Mathematics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gzyl, H.; Velásquez, Y. Linear Inverse Problems: The Maximum Entropy Connection; World Scientific Press: Singapore, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Varadhan, R.; Gilbert, D.P. BB: An R Package for Solving a Large System of Nonlinear Equations and for Optimizing a High-Dimensional Nonlinear Objective Function. J. Stat. Softw. 2009, 32, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.M.; Rubio, G. Economía Financiera; Antoni Bosch Editores: Barcelona, Spain, 2011. [Google Scholar]



| Strike Price | 2550 | 2600 | 2650 | 2700 | 2750 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Option price | 73 | 47 | 31 | 20 | 10 |
| Strike Price | 2550 | 2600 | 2650 | 2700 | 2750 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Option price | [69.2, 76.8] | [44.6, 49.4] | [29.4, 32.6] | [19, 21] | [9.5, 10.5] |
| State | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level | 2850 | 2750 | 2700 | 2650 | 2600 | 2550 |
| Range |
| 0.6102 | 0.4326 | 0.3642 | 0.6976 | 1.3362 | 2.5593 | |
| 0.1017 | 0.0709 | 0.1661 | 0.1163 | 0.2227 | 0.4265 | |
| q(from prices) | 1/10 | 1/10 | 1/50 | 1/10 | 1/5 | 0.48 |
| 76.752 | [69.2, 76.8] |
| 48.645 | [44.6, 49.4] |
| 31.349 | [29.4, 32.6] |
| 19.392 | [19.0, 21.0] |
| 10.070 | [09.5, 10.5] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gzyl, H.; Molina, G.; Ter Horst, E. Risk Neutral Measure Determination from Price Ranges: Single Period Market Models. Entropy 2018, 20, 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20070508
Gzyl H, Molina G, Ter Horst E. Risk Neutral Measure Determination from Price Ranges: Single Period Market Models. Entropy. 2018; 20(7):508. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20070508
Chicago/Turabian StyleGzyl, Henryk, German Molina, and Enrique Ter Horst. 2018. "Risk Neutral Measure Determination from Price Ranges: Single Period Market Models" Entropy 20, no. 7: 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20070508
APA StyleGzyl, H., Molina, G., & Ter Horst, E. (2018). Risk Neutral Measure Determination from Price Ranges: Single Period Market Models. Entropy, 20(7), 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20070508





