A Potential Information Capacity Index for Link Prediction of Complex Networks Based on the Cannikin Law
Abstract
:1. Introduction
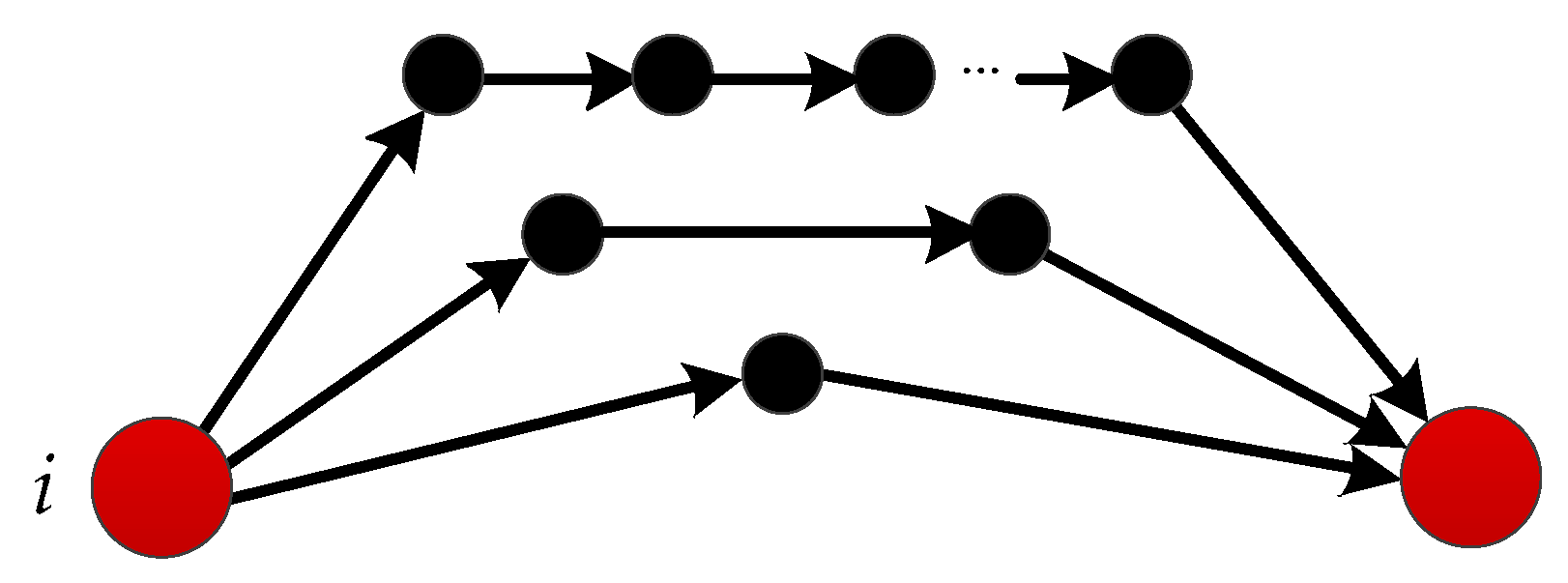
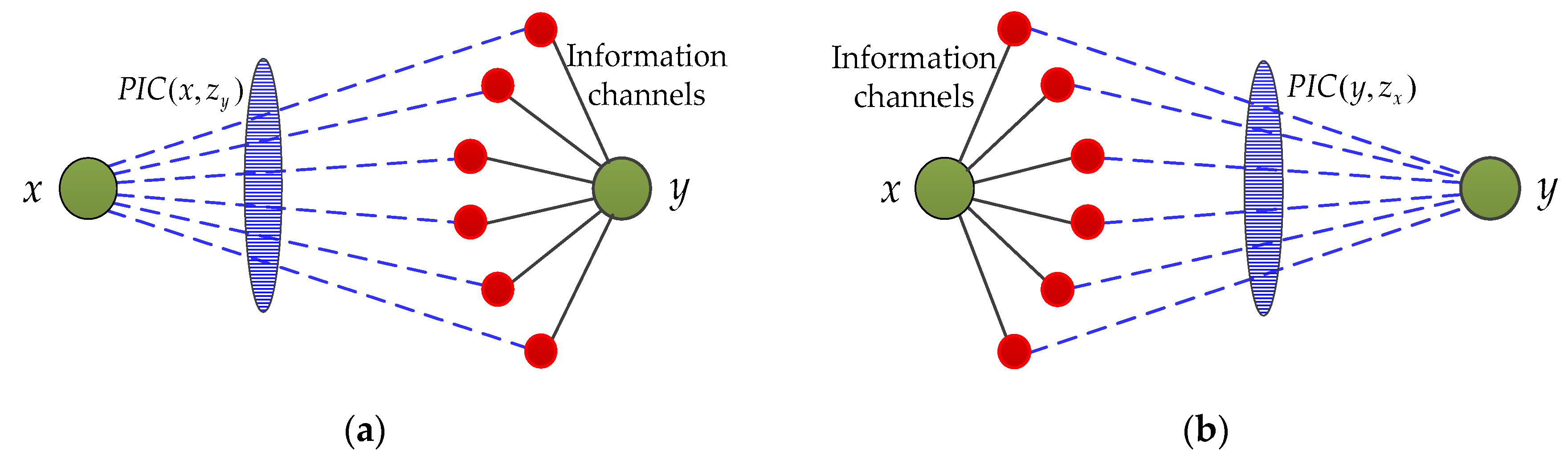
2. The Potential Information Capacity Index
2.1. Information Capacity Based on the Cannikin Law
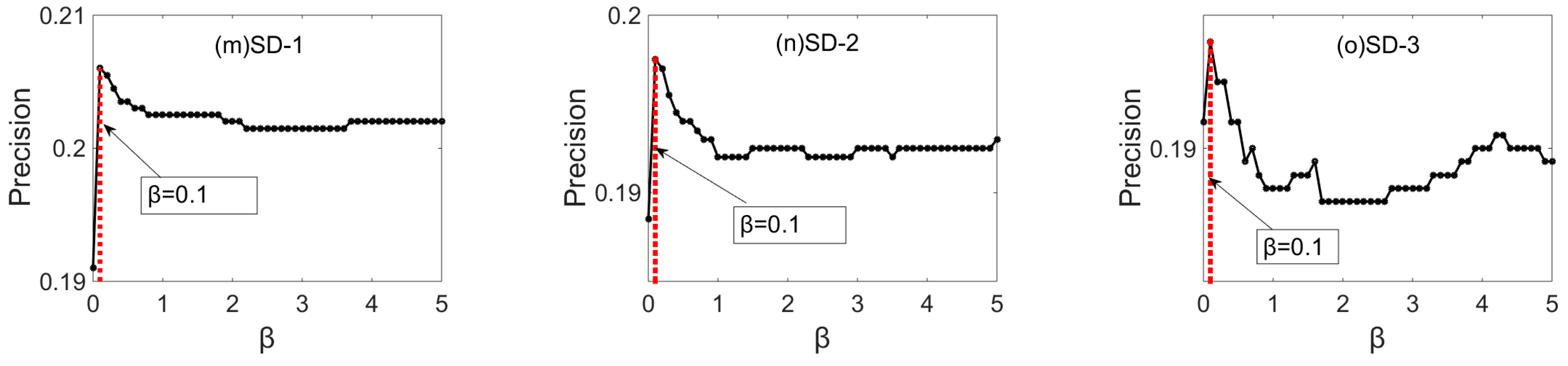
2.2. The Potential Information Capacity Index
3. Metrics and Baselines
3.1. Metrics
3.2. Baselines
- Common Neighbor (CN) index [10] calculates the similarity of two endpoints by the number of their common neighbors:is the set of neighbors of node x, and represents the common neighbors between nodes x and y.
- Resource Allocation (RA) index [12] measures the similarity of two endpoints by the received resource (information) of endpoint y through common neighbors sending by endpoint x:denotes the node degree of common neighbor z.
- Adamic–Adar (AA) index [11] weights the common neighbors according to the node degree, and punishes the common neighbors with big degree:This method considers that the contribution of common neighbors with low node degree are weighted higher than that of nodes with high node degree, and the weighting scheme used by AA index is the reciprocal of the logarithm of node degree [10].
- CAR index [13] believes that the link is more likely to exist between two nodes if their common-first-neighbors are members of a strongly inner-linked cohort:denotes the sub-set of the neighbors of node z, and all these neighbors of node z are also the common neighbors of nodes x and y.
- Local Path (LP) index [14] considers the longer paths with length 3 between endpoints based on the common neighbors:denotes the adjust parameter for longer paths, and A is the adjacency matrix.
- Katz index [15] calculates the similarity between two nodes by considering all the paths between them:here, is the adjust parameter for paths, and is the set of paths with length l between nodes x and y.
- Average Commute Time (ACT) [17] calculates the similarity between two nodes by the average number of steps required by random walks between them:denotes the pseudo-inverse of matrix L = D − A, and is the corresponding entry in .
- Cosine Similarity Time (Cos+) [19] calculates the similarity between nodes based on the angle between the random walk vectors:
4. Data
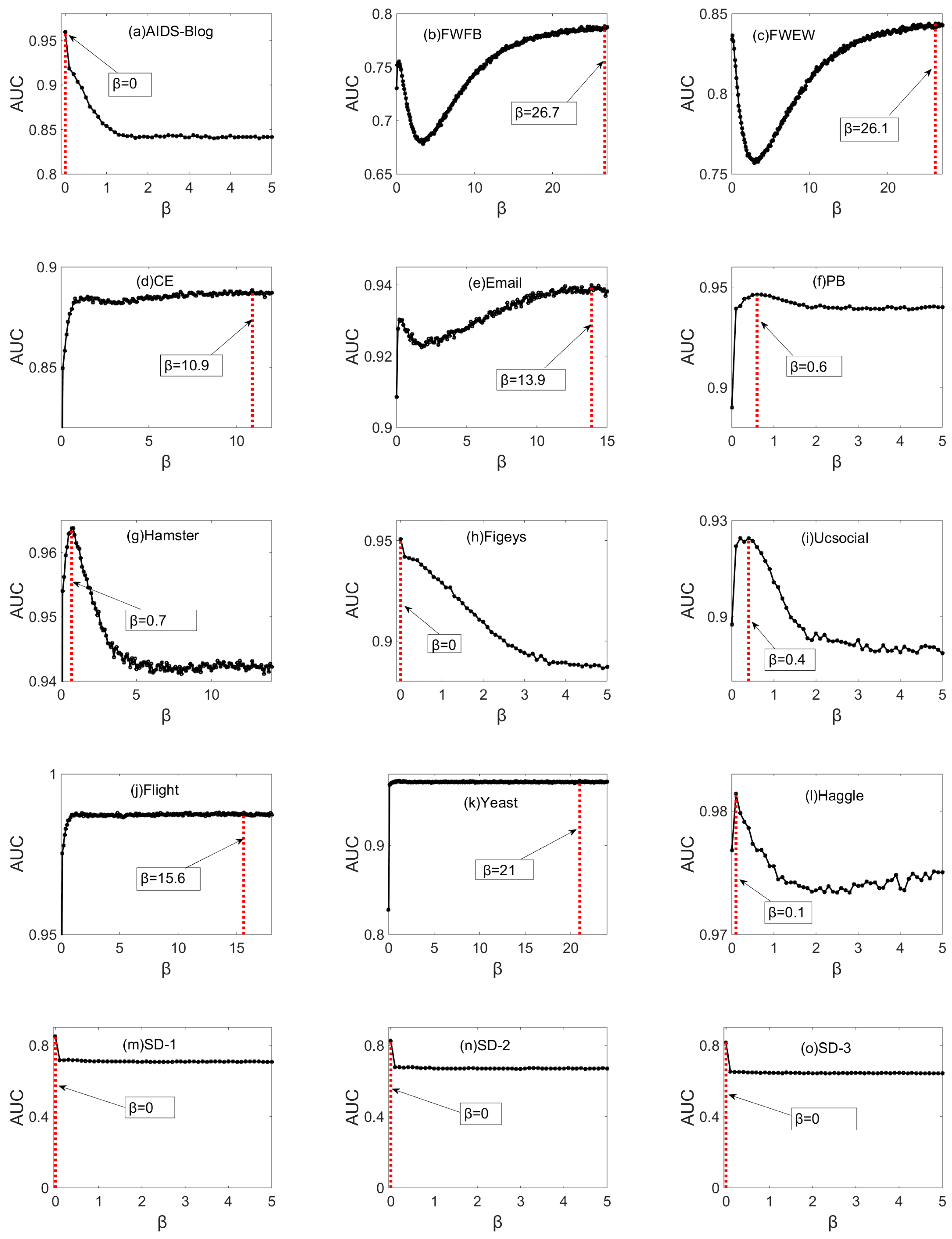
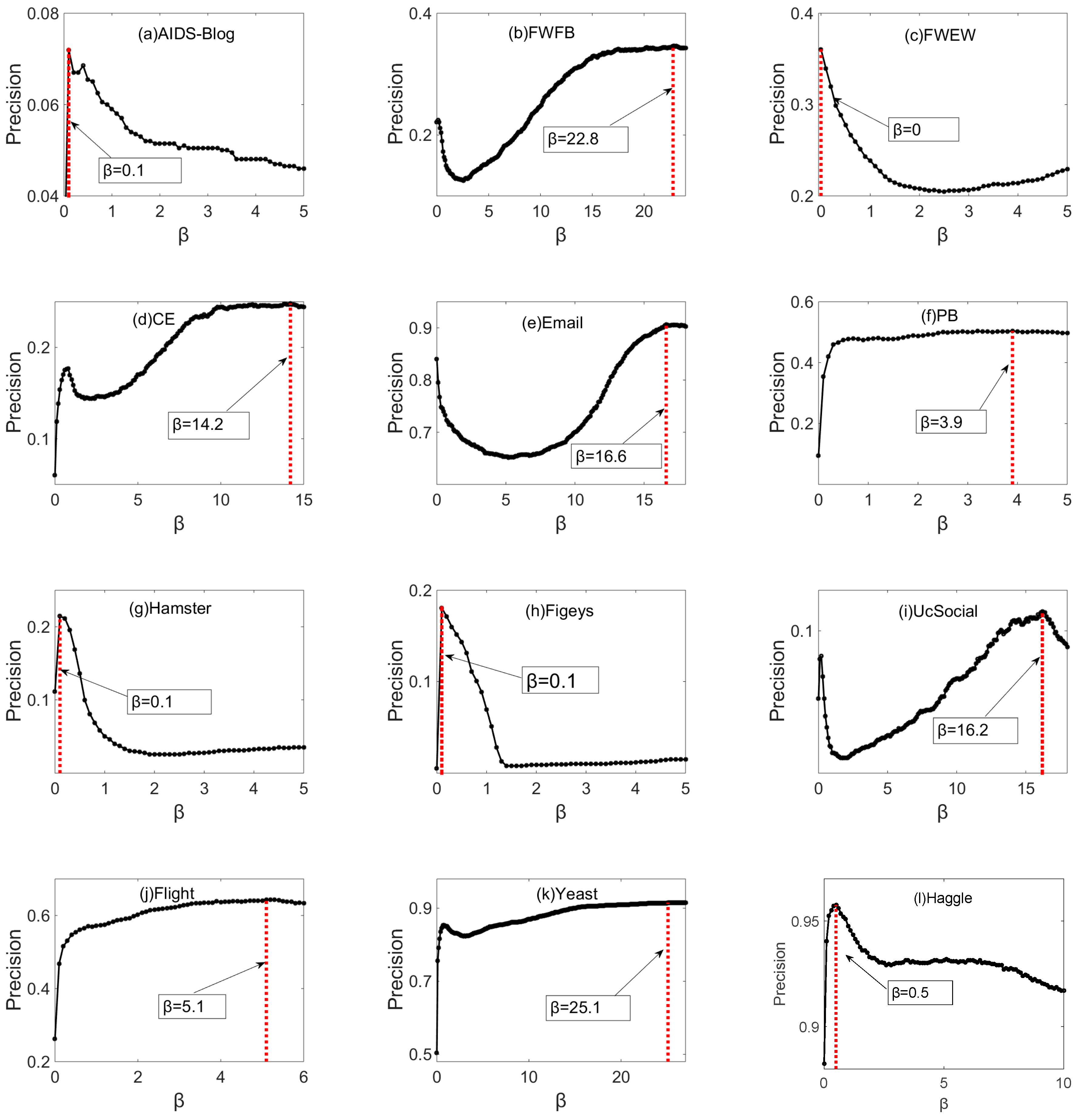
5. Results
5.1. AUC Results
5.2. Precision Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gosak, M.; Markovič, R.; Dolenšek, J.; Rupnik, M.S.; Marhl, M.; Stožer, A.; Perc, M. Network science of biological systems at different scales: A review. Phys. Life Rev. 2018, 24, 118–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, L.; Du, R.; Wang, C.; Chen, L.; Tian, L.; Stanley, H.E. A novel hybrid method of forecasting crude oil prices using complex network science and artificial intelligence algorithms. Appl. Energy 2018, 220, 480–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Interdonato, R.; Atzmueller, M.; Gaito, S.; Kanawati, R.; Largeron, C.; Sala, A. Feature-rich networks: Going beyond complex network topologies. Appl. Netw. Sci. 2019, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ji, X.; Liu, C.; Bai, Y. Extended resource allocation index for link prediction of complex network. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2017, 479, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ji, X.; Liu, C.; Guo, H. A complex network evolution model for network growth promoted by information transmission. Acta Phys. Sin. 2014, 63, 158902. [Google Scholar]
- Lü, L.; Zhou, T. Link prediction in complex networks: A survey. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2011, 390, 1150–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lü, L.; Medo, M.; Yeung, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, T. Recommender systems. Phys. Rep. 2012, 519, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yerneni, S.; Khan, K.I.; Wei, Q. IAS: Interaction specific GO term associations for predicting protein–protein interaction networks. IEEE ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2018, 15, 1247–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xu, B.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, X. Link prediction in social networks: The state-of-the-art. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2015, 58, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitzenmacher, M. A brief history of generative models for power law and lognormal distributions. Internet Math. 2004, 1, 226–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamic, L.A.; Adar, E. Friends and neighbors on the Web. Soc. Netw. 2003, 25, 211–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, T.; Lü, L.; Zhang, Y.C. Predicting missing links via local information. Eur. Phys. J. 2009, 71, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cannistraci, C.V.; Alanis-Lobato, G.; Ravasi, T. From link-prediction in brain connectomes and protein interactomes to the local-community-paradigm in complex networks. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lü, L.; Jin, C.H.; Zhou, T. Similarity index based on local paths for link prediction of complex networks. Phys. Rev. 2009, 80, 046122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, L. A new status index derived from sociometric analysis. Psychometrika 1953, 18, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeh, G.; Widom, J. SimRank: A measure of structural-context similarity. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 23–26 July 2002; pp. 271–279. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, D.J.; Randic, M. Resistance distance. J. Math. Chem. 1993, 12, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y. Mean commute time for random walks on hierarchical scale-free networks. Internet Math. 2012, 8, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouss, F.; Pirotte, A.; Renders, J.M.; Saerens, M. Random-walk computation of similarities between nodes of a graph with application to collaborative recommendation. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2007, 19, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Qu, B.; Chen, B.; Hanjalic, A.; Wang, H. Modelling of information diffusion on social networks with applications to WeChat. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2018, 496, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, D.; Liao, X.; Shen, H.; Cheng, X.; Chen, G. Dynamic node immunization for restraint of harmful information diffusion in social networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2018, 503, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzaferagic, M.; Kaminski, N.; McBride, N.; Macaluso, I.; Marchetti, N. A functional complexity framework for the analysis of telecommunication networks. J. Complex Netw. 2018, 6, 971–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Guo, X.; Jiang, W.; Ding, H.; Li, T.; Xu, X. Exploring the node importance and its influencing factors in the railway freight transportation network in china. J. Adv. Transp. 2019, 2019, 1493206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avena-Koenigsberger, A.; Misic, B.; Sporns, O. Communication dynamics in complex brain networks. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 19, 17–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yang, F.; Tang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Hu, R. Link prediction in complex networks based on the interactions among paths. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2018, 510, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S. Link prediction based on local information considering preferential attachment. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2016, 443, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, H. Interpretation of cannikin law in human resource management. J. Nanning Teach. Coll. 2009, 67, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Hanely, J.; McNeil, B. The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 1982, 143, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Huang, R.; Li, P. USI-AUC: An evaluation criterion of community detection based on a novel link-prediction method. Intell. Data Anal. 2018, 22, 439–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herlocker, J.; Konstann, J.; Terveen, K.; Riedl, J. Evaluating collaborative filtering recommender systems. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 2004, 22, 5–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuan, P.M.; Ali, M.; Khang, T.D.; Dey, N. Link prediction in co-authorship networks based on hybrid content similarity metric. Appl. Intell. 2018, 48, 2470–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, H. Improving local clustering based top-L link prediction methods via asymmetric link clustering information. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2018, 492, 1859–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gopal, S. The evolving social geography of blogs. In Societies and Cities in the Age of Instant Access; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 275–294. [Google Scholar]
- Gerould, S.; Higer, A. U.S. geological survey program on the south Florida ecosystem. U.S. Geol. Surv. Publicaion 1999, 99, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ulanowicz, R.E.; DeAngelis, D.L. Network analysis of trophic dynamics in south Florida ecosystems. US Geol. Surv. Program South Fla. Ecosyst. 2005, 114, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Watts, D.J.; Strogatz, S.H. Collective dynamics of “small-world” networks. Nature 1998, 393, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimera, R.; Danon, L.; Diaz-Guilera, A.; Giralt, F.; Arenas, A. Self-similar community structure in a network of human interactions. Phys. Rev. 2003, 68, 065103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adamic, L.A.; Glance, N. The political blogosphere and the 2004 US election: Divided they blog. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Link Discovery, Chicago, IL, USA, 21–24 August 2005; pp. 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Lü, L.; Pan, L.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, Y.C.; Stanley, H.E. Toward link predictability of complex networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2325–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ewing, R.M.; Chu, P.; Elisma, F.; Li, H.; Taylor, P.; Climie, S. Large-scale mapping of human protein–protein interactions by mass spectrometry. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2007, 3, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opsahl, T.; Panzarasa, P. Clustering in weighted networks. Soc. Netw. 2009, 31, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opsahl, T.; Agneessens, F.; Skvoretz, J. Node centrality in weighted networks: Generalizing degree and shortest paths. Soc. Netw. 2010, 32, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, L.; Xue, H.; Zhu, X.; Lu, H.; Zhang, J.; Sun, S.; Ling, L.; Zhang, N.; et al. Topological structure analysis of the protein–protein interaction network in budding yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 2443–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaintreau, A.; Hui, P.; Crowcroft, J.; Diot, C.; Gass, R.; Scott, J. Impact of human mobility on opportunistic forwarding algorithms. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2007, 6, 606–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y. Consensus in averager-copier-voter networks of moving dynamical agents. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2017, 27, 023116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Y. Resilient multiscale coordination control against adversarial nodes. Energies 2018, 11, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y. On the delayed scaled consensus problems. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Datasets | C | r | H | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AIDS | 146 | 180 | 2.47 | 3.42 | 0.052 | −0.725 | 5.99 |
| FWFB | 128 | 2075 | 32.42 | 1.78 | 0.335 | −0.112 | 1.24 |
| FWEW | 69 | 880 | 25.51 | 1.64 | 0.552 | −0.298 | 1.27 |
| CE | 297 | 2148 | 14.46 | 2.46 | 0.308 | −0.163 | 1.80 |
| 167 | 5784 | 69.26 | 1.87 | 0.541 | −0.295 | 1.66 | |
| PB | 1222 | 16717 | 27.36 | 2.74 | 0.361 | −0.221 | 2.97 |
| Hamster | 1858 | 12534 | 13.49 | 3.39 | 0.090 | −0.085 | 3.36 |
| Figeys | 2239 | 6432 | 5.76 | 3.98 | 0.040 | −0.331 | 9.75 |
| UcSocial | 1899 | 13838 | 14.57 | 3.06 | 0.109 | −0.188 | 3.82 |
| Flight | 2939 | 30501 | 20.75 | 4.18 | 0.255 | 0.051 | 5.22 |
| Yeast | 2375 | 11693 | 9.85 | 5.10 | 0.378 | 0.469 | 3.48 |
| Haggle | 274 | 2124 | 15.5 | 2.42 | 0.566 | −0.474 | 3.66 |
| SD-1 | 800 | 1727 | 4.32 | 3.14 | 0.211 | −0.242 | 6.14 |
| SD-2 | 1200 | 2527 | 4.21 | 3.27 | 0.172 | −0.229 | 6.99 |
| SD-3 | 2000 | 4123 | 4.12 | 3.40 | 0.144 | −0.220 | 8.43 |
| Datasets | CN | RA | AA | CAR | LP 1 | LP 2 | Katz 1 | Katz 2 | ACT | Cos+ | PIC-0.9 | PIC-Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AIDS | 0.599 | 0.611 | 0.612 | 0.599 | 0.834 | 0.834 | 0.851 | 0.850 | 0.957 | 0.591 | 0.857 | 0.960 |
| FWFB | 0.604 | 0.613 | 0.605 | 0.621 | 0.622 | 0.670 | 0.622 | 0.681 | 0.725 | 0.655 | 0.733 | 0.788 |
| FWEW | 0.693 | 0.709 | 0.700 | 0.693 | 0.713 | 0.736 | 0.712 | 0.743 | 0.787 | 0.505 | 0.793 | 0.844 |
| CE | 0.852 | 0.873 | 0.868 | 0.851 | 0.870 | 0.870 | 0.869 | 0.868 | 0.748 | 0.860 | 0.883 | 0.888 |
| 0.923 | 0.928 | 0.924 | 0.921 | 0.923 | 0.923 | 0.922 | 0.920 | 0.902 | 0.910 | 0.926 | 0.940 | |
| PB | 0.925 | 0.930 | 0.928 | 0.924 | 0.936 | 0.940 | 0.937 | 0.934 | 0.892 | 0.928 | 0.946 | 0.946 |
| Hamster | 0.813 | 0.818 | 0.817 | 0.814 | 0.934 | 0.940 | 0.934 | 0.938 | 0.869 | 0.960 | 0.963 | 0.964 |
| Figeys | 0.566 | 0.569 | 0.569 | 0.566 | 0.887 | 0.901 | 0.884 | 0.898 | 0.915 | 0.837 | 0.931 | 0.951 |
| UcSocial | 0.782 | 0.787 | 0.786 | 0.783 | 0.891 | 0.902 | 0.892 | 0.902 | 0.896 | 0.869 | 0.915 | 0.924 |
| Flight | 0.969 | 0.972 | 0.971 | 0.968 | 0.984 | 0.983 | 0.982 | 0.980 | 0.907 | 0.989 | 0.987 | 0.988 |
| Yeast | 0.916 | 0.917 | 0.916 | 0.915 | 0.970 | 0.970 | 0.972 | 0.972 | 0.899 | 0.972 | 0.972 | 0.972 |
| Haggle | 0.962 | 0.963 | 0.962 | 0.962 | 0.970 | 0.970 | 0.970 | 0.970 | 0.959 | 0.909 | 0.976 | 0.981 |
| SD-1 | 0.646 | 0.647 | 0.649 | 0.647 | 0.708 | 0.709 | 0.705 | 0.704 | 0.571 | 0.267 | 0.710 | 0.848 |
| SD-2 | 0.621 | 0.622 | 0.622 | 0.621 | 0.672 | 0.671 | 0.667 | 0.668 | 0.538 | 0.266 | 0.673 | 0.825 |
| SD-3 | 0.603 | 0.602 | 0.602 | 0.602 | 0.648 | 0.648 | 0.645 | 0.643 | 0.519 | 0.281 | 0.647 | 0.815 |
| Datasets | CN | RA | AA | CAR | LP 1 | LP 2 | Katz 1 | Katz 2 | ACT | Cos+ | PIC-0.4 | PIC-Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AIDS | 0.013 | 0.029 | 0.028 | 0.013 | 0.054 | 0.054 | 0.055 | 0.055 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.069 | 0.072 |
| FWFB | 0.085 | 0.081 | 0.083 | 0.084 | 0.092 | 0.124 | 0.092 | 0.129 | 0.000 | 0.032 | 0.204 | 0.347 |
| FWEW | 0.149 | 0.169 | 0.157 | 0.146 | 0.162 | 0.189 | 0.162 | 0.194 | 0.134 | 0.000 | 0.289 | 0.361 |
| CE | 0.133 | 0.127 | 0.138 | 0.138 | 0.140 | 0.141 | 0.140 | 0.140 | 0.000 | 0.074 | 0.164 | 0.248 |
| 0.708 | 0.709 | 0.717 | 0.703 | 0.713 | 0.708 | 0.713 | 0.697 | 0.000 | 0.617 | 0.746 | 0.906 | |
| PB | 0.419 | 0.250 | 0.379 | 0.488 | 0.428 | 0.459 | 0.428 | 0.456 | 0.000 | 0.339 | 0.467 | 0.504 |
| Hamster | 0.018 | 0.006 | 0.012 | 0.037 | 0.021 | 0.064 | 0.021 | 0.081 | 0.000 | 0.023 | 0.169 | 0.215 |
| Figeys | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.024 | 0.008 | 0.009 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.000 | 0.007 | 0.152 | 0.181 |
| UcSocial | 0.034 | 0.028 | 0.032 | 0.061 | 0.034 | 0.046 | 0.034 | 0.050 | 0.000 | 0.007 | 0.067 | 0.110 |
| Flight | 0.515 | 0.356 | 0.451 | 0.621 | 0.522 | 0.561 | 0.522 | 0.552 | 0.000 | 0.037 | 0.547 | 0.644 |
| Yeast | 0.694 | 0.499 | 0.709 | 0.683 | 0.700 | 0.755 | 0.700 | 0.741 | 0.000 | 0.249 | 0.836 | 0.915 |
| Haggle | 0.892 | 0.890 | 0.889 | 0.882 | 0.894 | 0.933 | 0.894 | 0.944 | 0.000 | 0.823 | 0.957 | 0.958 |
| SD-1 | 0.201 | 0.091 | 0.173 | 0.202 | 0.203 | 0.203 | 0.203 | 0.203 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.204 | 0.206 |
| SD-2 | 0.191 | 0.116 | 0.166 | 0.191 | 0.193 | 0.193 | 0.194 | 0.194 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.195 | 0.198 |
| SD-3 | 0.188 | 0.123 | 0.158 | 0.187 | 0.189 | 0.189 | 0.189 | 0.189 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.191 | 0.194 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Liu, S.; Chen, H.; Wang, K. A Potential Information Capacity Index for Link Prediction of Complex Networks Based on the Cannikin Law. Entropy 2019, 21, 863. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21090863
Li X, Liu S, Chen H, Wang K. A Potential Information Capacity Index for Link Prediction of Complex Networks Based on the Cannikin Law. Entropy. 2019; 21(9):863. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21090863
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xing, Shuxin Liu, Hongchang Chen, and Kai Wang. 2019. "A Potential Information Capacity Index for Link Prediction of Complex Networks Based on the Cannikin Law" Entropy 21, no. 9: 863. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21090863
APA StyleLi, X., Liu, S., Chen, H., & Wang, K. (2019). A Potential Information Capacity Index for Link Prediction of Complex Networks Based on the Cannikin Law. Entropy, 21(9), 863. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21090863





