An Irreversibility-Based Criterion to Determine the Cost Formation of Residues in a Three-Pressure-Level Combined Cycle
Abstract
:1. Introduction
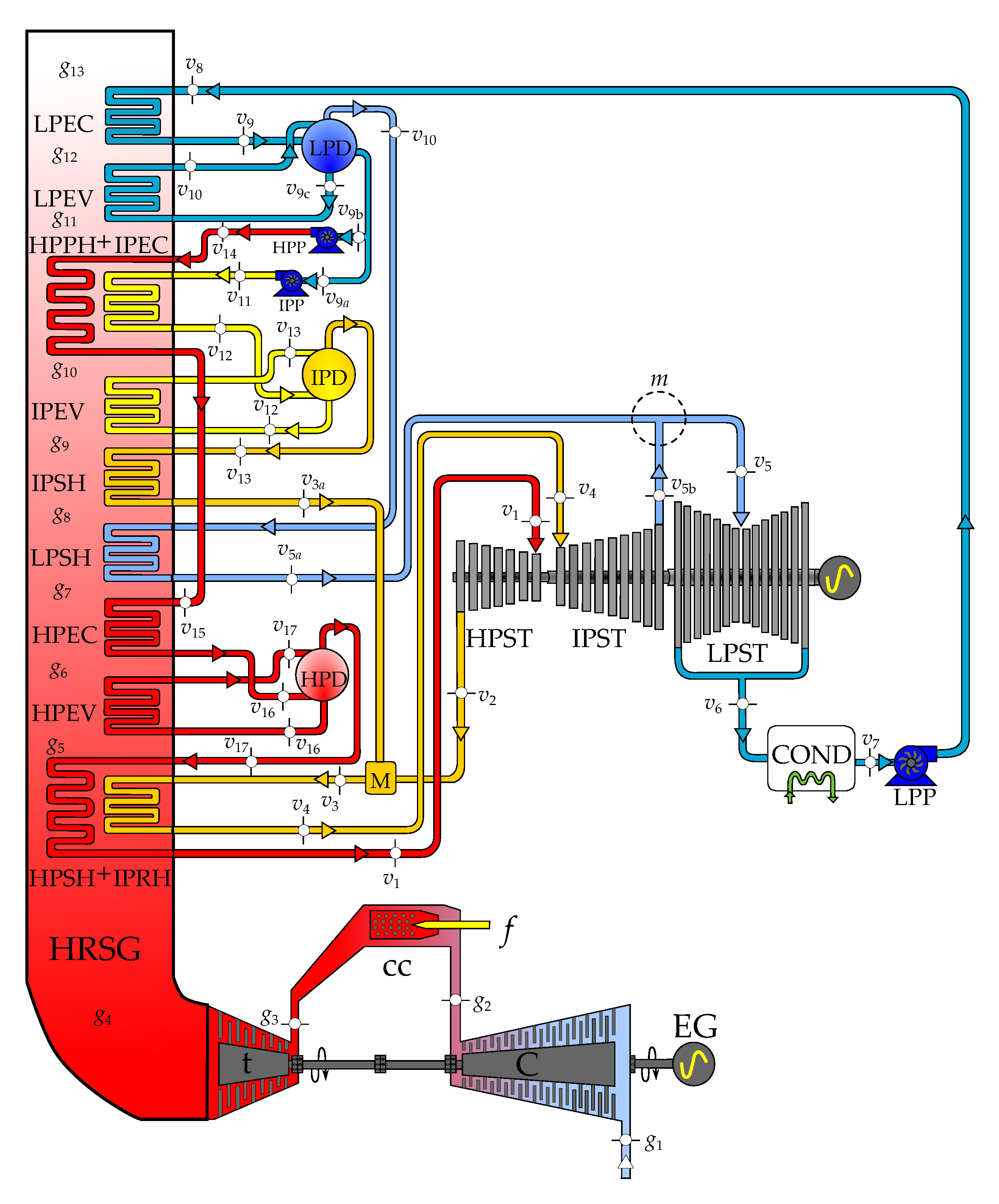
2. Thermodynamics of the Combined Cycle
2.1. Assumptions Made
- The combined cycle operates under steady-flow conditions.
- The air and combustion gas flows are assumed to behave ideally.
- The components of the combined cycle are taken into consideration as adiabatic.
- Kinetic and potential energy changes within each component are assumed to be negligible.
- The fuel physical exergy is not considered.
- Chemical exergy is neglected in the exergoeconomic analyses of all the combined cycle components.
- The operating conditions of the combined cycle, the dead state, the pinch-point difference temperatures, and the combustion parameters of the study case are presented in Table 1.
2.2. Gas Turbine
- Heat supplied to the gas turbinewhere and .
- Thermal efficiencywhere .
- Air mass flow rate used by the two simple gas turbinesIn this equation, is the power generated by the two gas turbines.
- Fuel mass flow rate fed to the pair of gas turbines
- Mass flow rate of combustion gases produced by the two Mitsubishi gas turbines
- Power supplied to the compressors of both gas turbine cycles
- Exergy flow rates for the thermodynamic states of air and combustion gases are given respectively as follows:
- The thermal exergy flow rate provided by the combustion of the natural gas iswhere and are respectively the low heating value and the adiabatic flame temperature of the natural gas.
2.3. Steam Cycle
- Net work of the steam turbines
- Net power of the steam turbine
- Recovered heat in the heat recovery steam generator
- Thermal efficiency of the steam cycle
2.4. Heat Recovery Steam Generator (HRSG)
- High pressure superheater and intermediate pressure reheater (HPSH + IPRH)
- High pressure evaporator (HPEV)
- High pressure economizer (HPEC)
- Low pressure superheater (LPSH)
- Intermediate pressure superheater (IPSH)
- Intermediate pressure evaporator (IPEV)
- High pressure preheater and Intermediate pressure economizer (HPPH+IPEC)
- Low pressure evaporator (LPEV)
- Low pressure economizer (LPEC)
2.5. Performance Parameters of the Combined Cycle
- The specific fuel consumption of the combined cycle is given by
- The thermal efficiency of the combined cycle is determined by the following expression
- The specific steam consumption of the combined cycle is given by
3. Exergetic Cost Analysis
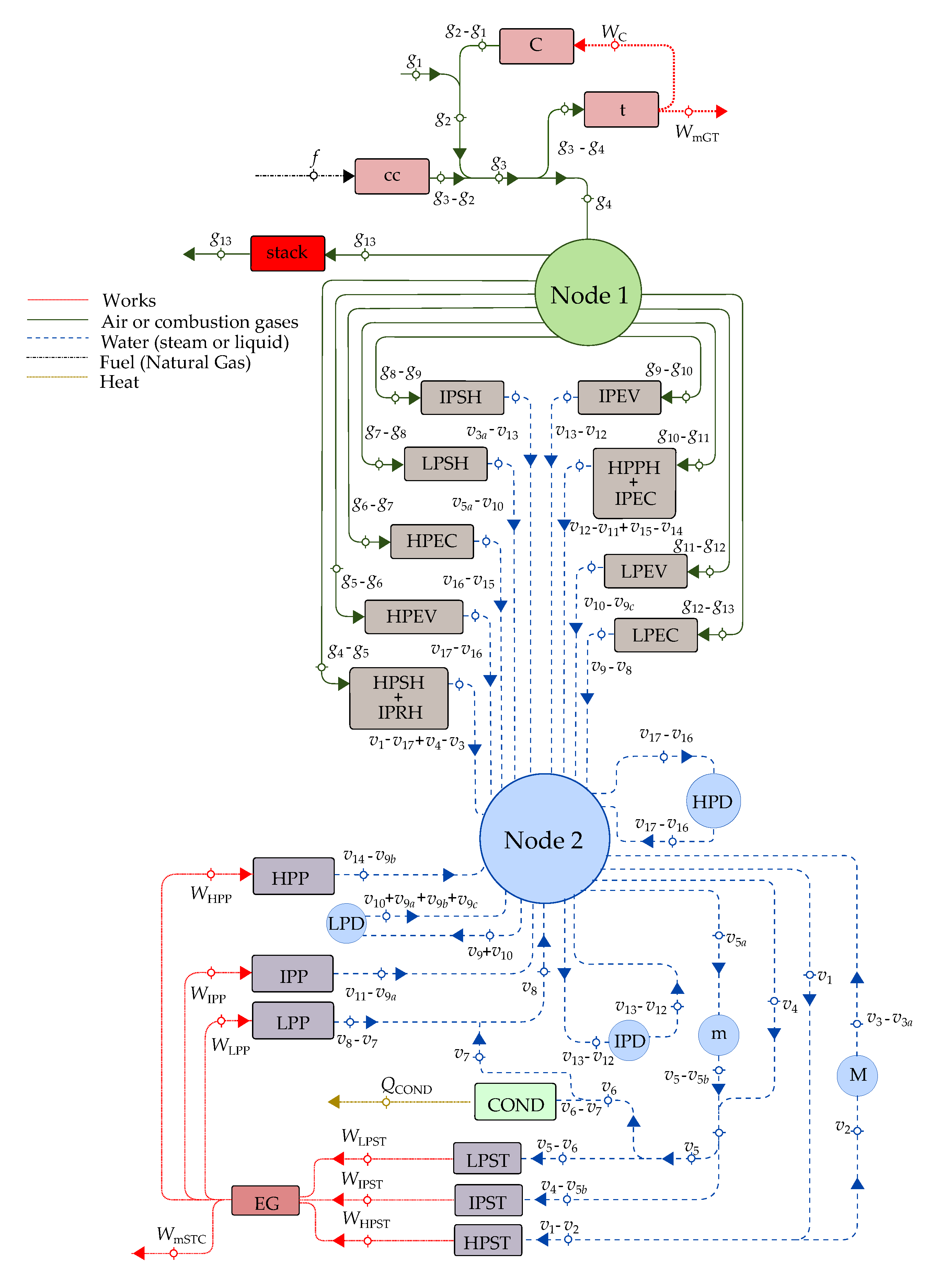
3.1. Productive Structure
3.1.1. Productive Components
3.1.2. Dissipative Components
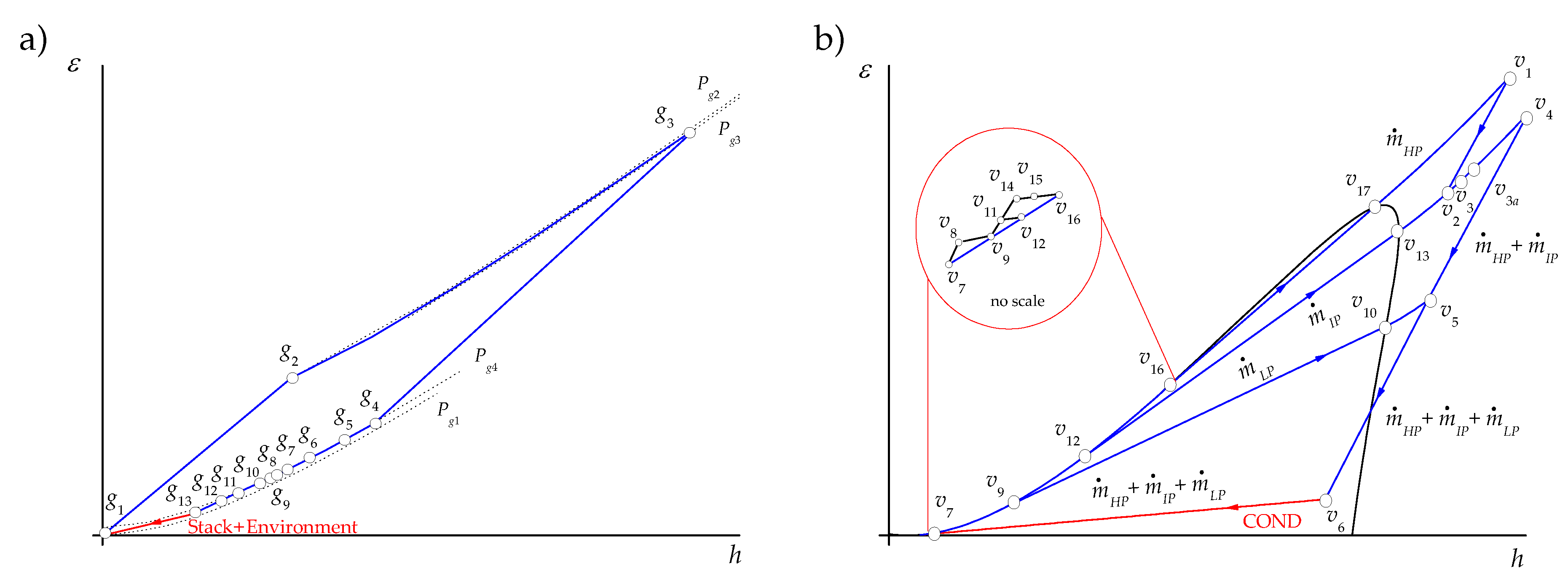
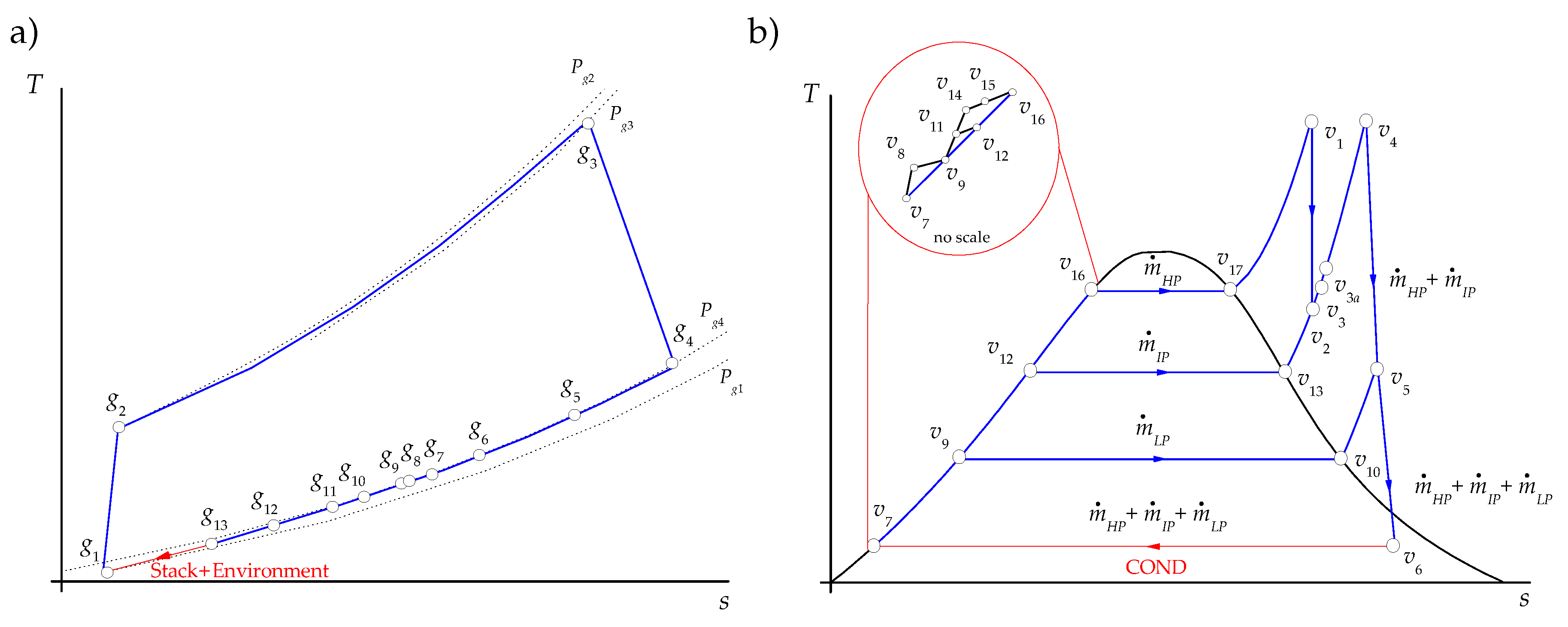
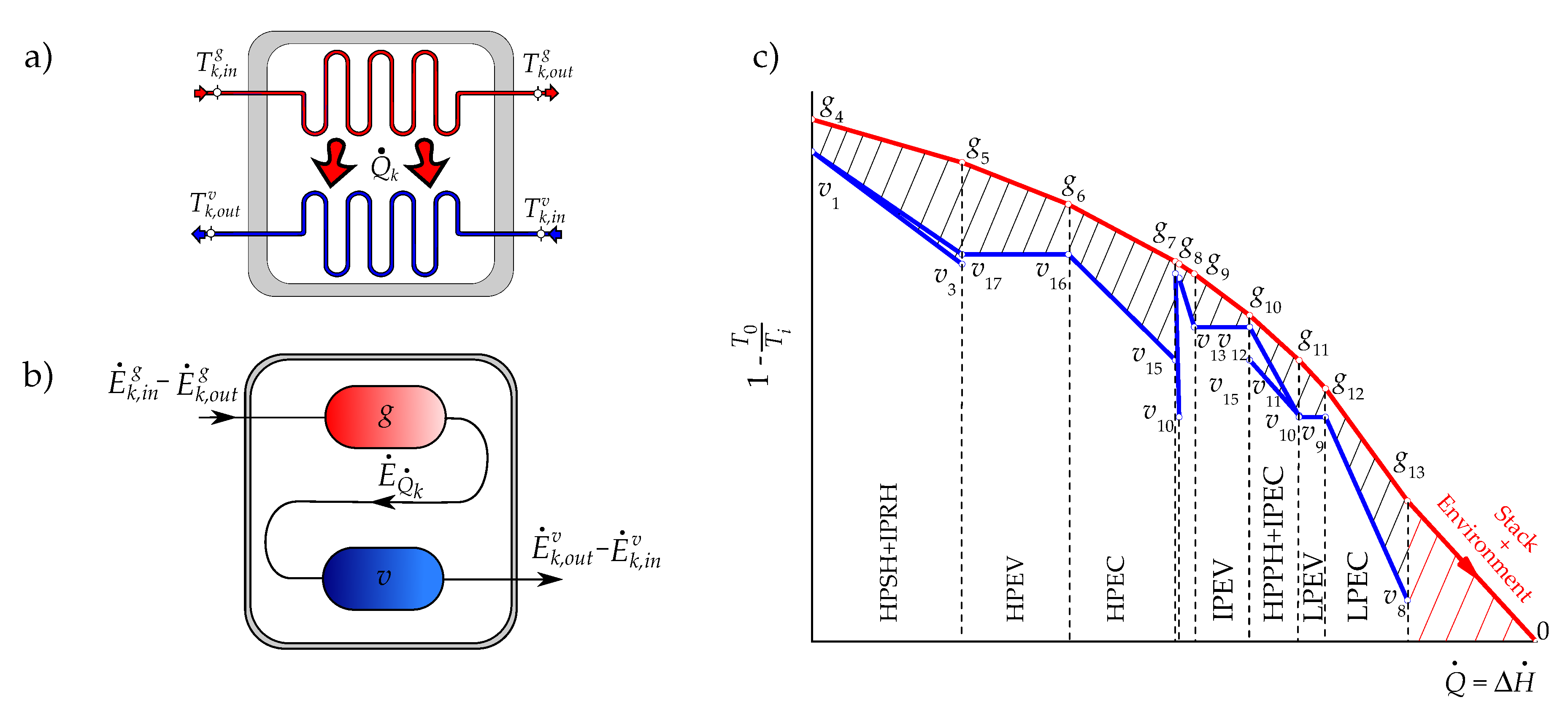
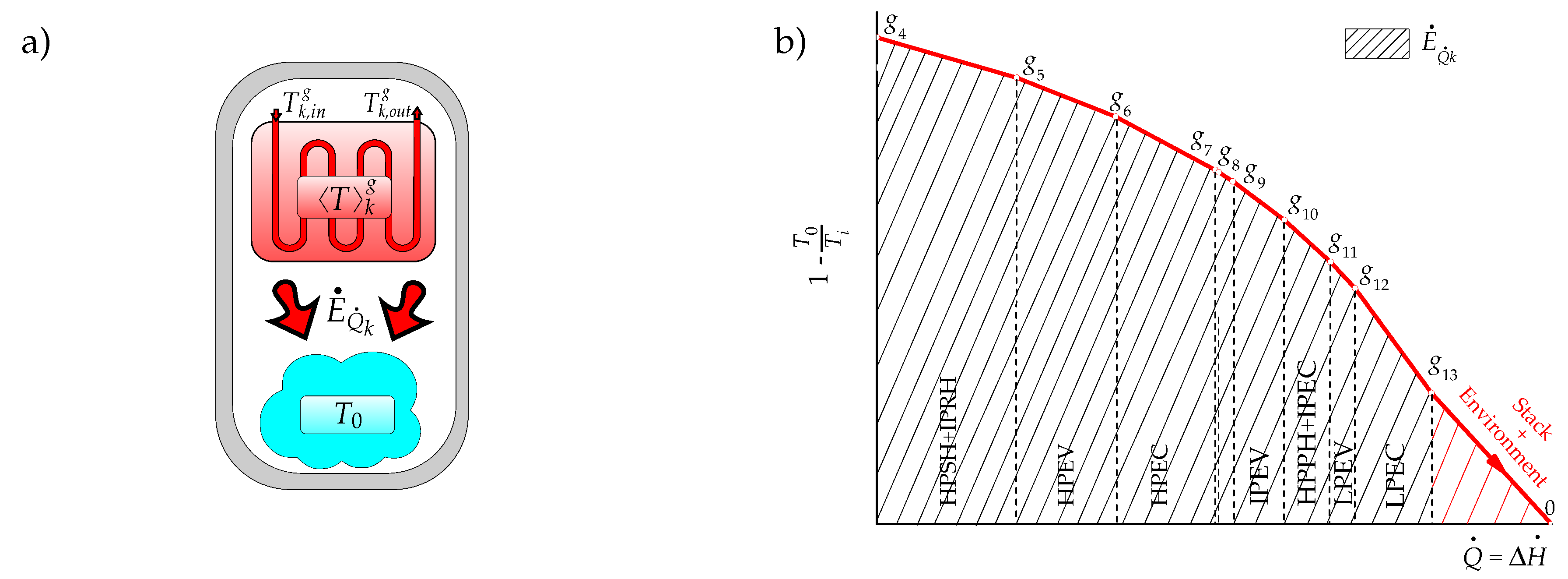
- The exergy flow rate of the exhaust gases releases to the environment through the stack. Strictly, this stream contains at least three residues: its physical exergy, the fraction of its chemical exergy associated to CO, and that associated to NOx. However, since in this work the chemical exergy of the working fluids is neglected, the residual stream of exhausted gases corresponds to their physical exergy, which also coincides with the residue associated to the formation of the power generated by the gas turbines, .It should be appointed that the HRSG, as it can be observed in Figure 2a, saves only a part of the exergy generated in the productive components of the gas turbine (g4 to g13) and that the stack together with the environment close the gas turbine cycle by reducing in the atmosphere the chemical and physical exergy of the exhaust gases to reach the dead state (g13 to 0). On the other hand, the coupling of the gas turbine and the steam cycle through the HRSG transfers the residue associated to the combustion gases from the gas turbine to the HRSG, since they are produced by the gas turbine and used as a resource by the HRSG.
- The exergy of wet steam leaves the low-pressure stream turbine, corresponding to state . As shown in Table 3, is the resource of the condenser, of which the productive purpose is to close the thermodynamic cycles of steam or, in other words, to destroy the exergy of wet steam by its condensation from state to . This is made by the heat exchange from steam to cooling water using the power of cooling water pump as additional resource. If the cooling water is assumed to be the dead state for water, then the residue of the condenser is .
3.2. The Exergetic Costs Model
3.2.1. The Cost Formation Process of Residues
3.2.2. Exergetic Costs Equations
- Exergetic cost equations for the external resourcesThe costs of the external resources are known
- Exergetic cost balance equation for a productive componentAccording to the conservative nature of costs, the product cost of the component i is equal to the cost of resources required to obtain it plus the cost of the residues allocated to the ith component .The cost of the resources consumed by the component i is composed by the cost of external resources and the cost of flows coming from other productive component j.
- Exergetic cost balance equation for each dissipative componentThe exergy cost balance equation for the rth dissipative component, in which the residue is released to the environment, is given bywhere and are respectively the formation and elimination costs of the residue. For the residues considered in this work, and , the formation costs are and while the elimination costs are and .
- Auxiliary equations of components with multiple productsIf a unit has a product composed of several flows, then the same unit exergetic cost can be assigned to them. In fact, even if two or more products can be identified in the same unit, their formation processes are inseparable at the level of aggregation considered, and therefore, a cost proportional to their exergy is assigned to them.
- Cost balance equations for the complete combined cycleThe cost balance equation for the entire power plant [25] is given bywhere and are respectively the exergetic costs of the external resources and the useful product of the combined cycle.
3.3. Criteria for Residues Cost Allocation
- C2: Generated irreversibilities along the process (proposed in this work),
3.3.1. Criterion of Entropy Changes in the Productive Components (C1)
3.3.2. Criterion of Irreversibilities (C2)
3.3.3. Criterion of Distributed Exergy along the Process (C3)
3.3.4. Criterion of Distributed Entropy along the Process (C4)
4. Results
4.1. Thermodynamics of the Combined Cycle
4.2. Exergy Analysis
4.3. Exergetic Costs Analysis
4.3.1. Exergetic Cost of Streams
4.3.2. Product Exergetic Costs of the Productive Components
4.3.3. Residue Formation Cost
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| C | compressor, |
| CC | combined cycle, |
| COND | condenser, |
| cc | combustion chamber, |
| CW | cooling water, |
| CSP | cooling system pump, |
| EG | electric generator, |
| GT | gas turbine, |
| HPD | high-pressure drum, |
| HPEC | high-pressure economizer, |
| HPEV | high-pressure evaporator, |
| HPP | high-pressure pump, |
| HPPH | high-pressure preheater, |
| HPSH | high-pressure superheater, |
| HPST | high-pressure steam turbine, |
| HRSG | heat recovery steam generator, |
| IPD | intermediate-pressure drum, |
| IPEC | intermediate-pressure economizer, |
| IPEV | intermediate-pressure evaporator, |
| IPP | intermediate-pressure pump, |
| IPRH | intermediate-pressure reheater, |
| IPSH | intermediate-pressure superheater, |
| IPST | intermediate-pressure steam turbine, |
| LPD | low-pressure drum, |
| LPEC | low-pressure economizer, |
| LPEV | low-pressure evaporator, |
| LPP | low-pressure pump, |
| LPSH | low-pressure superheater, |
| LPST | low-pressure steam turbine, |
| M | stream mixer, |
| m | union of steam streams, |
| SC | steam cycle, |
| ST | steam turbine, |
| t | turbine. |
Nomenclature
| c | unit exergoeconomic cost; (USD GJ), |
| specific heat capacity at constant pressure; (kJ (kgK)), | |
| set of dissipative component, | |
| exergy flow rate; (kW or MW), | |
| exergetic cost; (kW), | |
| exergoeconomic cost; (USD h), | |
| resource exergy flow rate; (kW or MW), | |
| exergetic cost of the resource; (kW or MW), | |
| fuel to air ratio; (kg kg), | |
| enthalpy flow rate; (kW or MW), | |
| h | specific enthalpy; (kJ kg), |
| irreversibility flow rate; (kW), | |
| intermediate pressure; (bar), | |
| unit exergy cost; (-), | |
| lower heat value; (kJ kg), | |
| m | mass fraction; (-), |
| mass flow rate; (kg s), | |
| set of productive components. | |
| P | pressure; (bar), |
| product exergy flow; (kW), | |
| exergetic cost of the product; (KW) | |
| heat flow rate; (kW), | |
| q | specific heat; (kJ kg), |
| R | gas constant; (kJ (kg K)), |
| residue exergy flow rate; (kW), | |
| exergetic cost of the residue; (KW) | |
| relative humidity; (%), | |
| specific fuel comsumption; (kg (kWh)), | |
| specific steam comsumption; (kg (kWh)), | |
| entropy generation; (kW), | |
| s | specific entropy; (kJ (kgK)), |
| T | temperature; (C, K), |
| turbine inlet temperature; (K), | |
| t | time; (s), |
| v | steam specific volume; (m kg) |
| power; (MW), | |
| w | work per unit of mass; (kJ kg), |
| X | stoichiometric coefficient; (%), |
| x | ratio of the particular gas constant to heat capacity of constant pressure, ; (-), |
| y | ratio of to ; (-), |
| Z | capital and operation costs; (USD h). |
| Greek symbols | |
| stoichiometric coefficient; (%), | |
| cost allocation ratio for the waste heat dissipated in the condenser; (-), | |
| exergy per unit mass; (kJ (kg)), | |
| efficiency; (%), | |
| Relative humidity; (%), | |
| excess of air; (%), | |
| cost ratio for the exhaust gases dissipated in the stack; (-), | |
| set of productive components of the gas turbine and the HRSG on the gas-side, | |
| exergoeconomic cost; (USD (h)), | |
| compression pressure ratio; (-), | |
| cost distribution ratio; (-), | |
| residue cost allocation ratio; (-). | |
| Subscripts | |
| 0 | dead state, |
| a | ambient, |
| adiabatic flame, | |
| air, | |
| control volumen, | |
| combustion gas, | |
| cooling water, | |
| D | destruction. |
| dry air, | |
| e | exit, |
| exergetic, | |
| F | resource, |
| f | fuel, |
| generation, | |
| g | gas |
| thermodynamic state of the gas turbine, | |
| thermodynamic state of the heat recovery steam generator, | |
| H | supplied |
| humid air, | |
| output of gas turbine, | |
| output of steam turbine, | |
| optimum (maximum), | |
| pinch-point, | |
| productive, | |
| r or R | residue, |
| s | steam, |
| stoichiometric, | |
| surroundings, | |
| t | turbine, |
| thermal, | |
| total, | |
| thermodynamic state of the steam cycle. | |
| Superscripts | |
| 0 | dead state, |
| air, | |
| combustion gas, | |
| g | gas, |
| irreversibility flow, | |
| productive, | |
| entropy generation, | |
| v | steam. |
Appendix A. Exergy of a Heat Exchange from a Stream with Nonconstant Temperature
References
- Torres, C.; Valero, A. Curso de Doctorado (Termoeconomía); Universidad de Zaragoza, Departamento de Ingeniería Mecánica: Zaragoza, Spain, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, C.; Valero, A.; Rangel, V.; Zaleta, A. On the cost formation process of the residues. Energy 2008, 33, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo, A.; Valero, A.; Torres, C. Allocation of waste cost in thermoeconomic analysis. Energy 2012, 45, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, Z.; Sharma, S.; Mian, A.; Lin, T.E.; Tsatsaronis, G.; Maréchal, F.; Yang, Y. A Review of Evaluation, Optimization and Synthesis of Energy Systems: Methodology and Application to Thermal Power Plants. Energies 2019, 12, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frangopoulos, C.A. Thermo-economic functional analysis and optimization. Energy 1987, 12, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, M.; Valero, A. Thermoeconomic analysis of gas turbine cogeneration systems. In Proceedings of the 1993 ASME Winter Annual Meeting, New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–3 December 1993; pp. 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, J.A.; de Oliveira Junior, S. Unit exergy cost and CO2 emissions of offshore petroleum production. Energy 2018, 147, 757–766. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano, M.; Valero, A. Theory of the exergetic cost. Energy 1993, 18, 939–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Spakovsky, M.R. Application of engineering functional analysis to the analysis and optimization of the CGAM problem. Energy 1994, 19, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Gama Cerqueira, S.A.A.; Nebra, S.A. Cost attribution methodologies in cogeneration systems. Energy Convers. Manag. 1999, 40, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Li, C. A novel evaluation of heat-electricity cost allocation in cogenerations based on entropy change method. Energy Policy 2013, 60, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, R.G.; de Faria, P.R.; Santos, J.J.; da Silva, J.A.; Flórez-Orrego, D. Thermoeconomic modeling for CO2 allocation in steam and gas turbine cogeneration systems. Energy 2016, 117, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Nascimento, M.; Lora, E.; Reyes, A.M. On the negentropy application in thermoeconomics: a fictitious or an exergy component flow? Int. J. Thermodyn. 2009, 12, 163. [Google Scholar]
- Valero, A.; Correas, L.; Zaleta, A.; Lazzaretto, A.; Verda, V.; Reini, M.; Rangel, V. On the thermoeconomic approach to the diagnosis of energy system malfunctions: Part 2. Malfunction definitions and assessment. Energy 2004, 29, 1889–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, A.; Usón, S.; Torres, C.; Valero, A. Application of thermoeconomics to industrial ecology. Entropy 2010, 12, 591–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyyedi, S.M.; Ajam, H.; Farahat, S. A new criterion for the allocation of residues cost in exergoeconomic analysis of energy systems. Energy 2010, 35, 3474–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyyedi, S.M.; Khaleghib, M.; Hashemi-Tilehnoeec, M. Allocating the Residues Cost of a Typical HTGR Directly Integrated with Steam Cycle Using Distributed Entropy Method. Arab J. Nuclear Sci. Appl. 2019, 52, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Song, D.; Liu, W.; Liu, W. Exergy and exergoeconomic analyses with modeling for CO2 allocation of coal-fired CHP plants. Energy 2018, 152, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yu, Z.; Song, D. Exergy-based analysis combined with LCA for waste heat recovery in coal-fired CHP plants. Energy 2019, 169, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk, N.; Mongia, H. Semianalytical correlations for NOx, CO, and UHC emissions. In ASME 1992 International Gas Turbine and Aeroengine Congress and Exposition; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: Cologne, Germany, 1992; p. V003T06A023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivkin, S.L.; Wagman, D.D. Thermodynamic Properties of Gases; Hemisphere Publishing Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Lazzaretto, A.; Tsatsaronis, G. SPECO: A systematic and general methodology for calculating efficiencies and costs in thermal systems. Energy 2006, 31, 1257–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, A.; Lozano, M.; Muñoz, M.A.; Lozano, M.; Muñoz, M. A general theory of exergy saving I, II and III. In Computed Aided Engineering and Energy Systems: Second Law Analysis and Modelling; ASME Book: New York, NY, USA, 1986; Volume AES 2–3, pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Piacentino, A. Application of advanced thermodynamics, thermoeconomics and exergy costing to a Multiple Effect Distillation plant: In-depth analysis of cost formation process. Desalination 2015, 371, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balli, Ö. Thermodynamic, thermoeconomic and environmental performance analyses of a high bypass turbofan engine used on commercial aircrafts. Sakarya Univ. J. Sci. 2019, 23, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, A. The thermodynamic process of cost formation. In Exergy, Energy System Analysis and Optimization-Volume II: Thermoeconomic Analysis Modeling, Simulation and Optimization in Energy Systems; EOLSS Publications: Oxford, UK, 2009; Volume 2, p. 35. [Google Scholar]
- Frangopoulos, C.A. Thermoeconomic Functional Analysis: A Method for Optimal Design or Improvement of Complex Thermal Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Dogonchi, A.S.; Seyyedi, S. Two New Alternative Options for Residues Cost Distribution Ratio. J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. Control 2018, 1, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.; Sheng, D.; Chen, J.; Li, W.; Wan, A.; Chen, H. Exergoeconomic analysis of a combined cycle system utilizing associated gases from steel production process based on structural theory of thermoeconomics. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 51, 476–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R. On the Gouy–Stodola theorem of thermodynamics for open systems. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Educ. 2017, 45, 194–206. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, C.C. Symbolic thermoeconomic analysis of energy systems. In Exergy, Energy System Analysis and Optimization-Volume II: Thermoeconomic Analysis Modeling, Simulation and Optimization in Energy Systems; EOLSS Publications: Oxford, UK, 2009; Volume 2, p. 61. [Google Scholar]
- Valero, A.; Usón, S.; Torres, C.; Stanek, W. Theory of exergy cost and thermo-ecological cost. In Thermodynamics for Sustainable Management of Natural Resources; Stanek, W., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; Chapter 7; pp. 167–202. [Google Scholar]
- Keshavarzian, S.; Rocco, M.V.; Gardumi, F.; Colombo, E. Practical approaches for applying thermoeconomic analysis to energy conversion systems: Benchmarking and comparative application. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 150, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, A.B.; Nebra, S.A.; Santos, J.J.C.; Donatelli, J.L.M. Application of an alternative thermoeconomic approach to a two-stage vapour compression refrigeration cascade cycle. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2015, 37, 903–913. [Google Scholar]
- Keenan, J.H.; Keyes, F.G.; Hill, P.G.; Moore, J.G. Steam Tables; Thermodynamic Properties of Water, Including Vapor, Liquid and Soild Phases; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ganapathy, V. Industrial Boilers and Heat Recovery Steam Generators; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]

| Gas Turbine | Fuel | Ambient Conditions | ||||||||||||||
| (MW) | (°C) | (-) | (-) | (-) | (-) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (°C) | (bar) | (%) | |||
| 139.2 | 1300 | 16 | 0.88 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 2 | 1 | 88 | 9 | 3 | 25 | 1.013 | 45 | |||
| Pinch-point temperature | ||||||||||||||||
| Steam cycle | differences, | |||||||||||||||
| LPEV | IPEV | HPEV | ||||||||||||||
| (°C) | (bar) | (bar) | (bar) | (bar) | (-) | (-) | (-) | (°C) | (°C) | (°C) | (°C) | (°C) | (°C) | |||
| 525.8 | 106.3 | 25.2 | 4.1 | 0.08 | 0.88 | 0.85 | 0.60 | 15 | 30.23 | 30.18 | 22.37 | 15 | 84.51 | |||
| Combustion parameters of Equation (9) | ||||||||||||||||
| m | n | |||||||||||||||
| 4.3 | 1.15 | 10.74 | 0.986 | 0.014 | 1.396 | 1.139 | 2.510 | 20.047 | 3.106 | 0.010 | 4.77 × | 0.011 | ||||
| Component | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gas turbine cycle | ||||
| C | ||||
| cc | ||||
| t | ||||
| Heat recovery steam generator | ||||
| HPSH+IPRH | ||||
| HPEV | ||||
| HPEC | ||||
| LPSH | ||||
| IPSH | ||||
| IPEV | ||||
| HPPH+IPEC | ||||
| LPEV | ||||
| LPEC | ||||
| Steam cycle | ||||
| HPST | ||||
| IPST | ||||
| LPST | ||||
| LPP | ||||
| IPP | ||||
| HPP | ||||
| LPD | 0 | |||
| IPD | 0 | |||
| HPD | 0 | |||
| m | ||||
| M | ||||
| Electric generator | ||||
| EG | 0 | |||
| Component | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gas-side residue | |||||
| Stack | 0 | ||||
| Steam-side residue | |||||
| COND | |||||
| Component | Exergetic Costs Balances | Auxiliary Equations |
|---|---|---|
| Gas turbine cycle | ||
| External | ||
| resources | ||
| C | ||
| t | ||
| Heat recovery steam generator | ||
| HPSH+IPRH | ||
| HPEV | ||
| HPEC | ||
| LPSH | ||
| IPSH | ||
| IPEV | ||
| HPPH+IPEC | ||
| LPEV | ||
| LPEC | ||
| Steam cycle | ||
| HPST | ||
| IPST | ||
| LPST | ||
| LPP | ||
| IPP | ||
| HPP | ||
| LPD | ||
| m | ||
| M | ||
| COND | ||
| EG | ||
| Thermodynamic States | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | T | P | v | s | h | X | |||||
| (°C) | (bar) | (-) | (MW) | (MW) | |||||||
| Gas turbine cycle | |||||||||||
| f | 25.00 | 16.21 | 9.37 | 43,275.51 | 15.36 | 664.79 | 664.79 | 0.14 | |||
| 25.00 | 1.01 | 0.853 | 6.76 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 626.82 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 4.24 | ||
| 433.77 | 16.21 | 0.126 | 6.90 | 445.37 | 404.49 | 626.82 | 253.54 | 279.17 | 4.32 | ||
| 1300.00 | 15.89 | 0.292 | 7.80 | 1618.70 | 1231.00 | 642.18 | 790.52 | 1039.50 | 5.01 | ||
| 617.58 | 1.02 | 2.565 | 7.88 | 750.46 | 338.09 | 642.18 | 217.11 | 481.93 | 5.06 | ||
| 279.17 | |||||||||||
| 278.40 | |||||||||||
| 489.28 | 1.02 | 2.200 | 7.71 | 597.33 | 237.89 | 642.18 | 152.77 | 383.59 | 4.95 | ||
| 374.28 | 1.02 | 1.870 | 7.52 | 460.07 | 156.19 | 642.18 | 100.30 | 295.45 | 4.83 | ||
| 299.46 | 1.02 | 1.655 | 7.39 | 376.39 | 110.11 | 642.18 | 70.71 | 241.71 | 4.75 | ||
| 292.51 | 1.02 | 1.636 | 7.38 | 368.62 | 106.00 | 642.18 | 68.07 | 236.72 | 4.74 | ||
| Heat recovery steam generator | |||||||||||
| 290.50 | 1.02 | 1.632 | 7.38 | 366.37 | 104.76 | 642.18 | 67.28 | 235.28 | 4.74 | ||
| 262.57 | 1.02 | 1.553 | 7.33 | 335.14 | 88.99 | 642.18 | 57.15 | 215.22 | 4.70 | ||
| 231.48 | 1.02 | 1.465 | 7.27 | 301.18 | 72.49 | 642.18 | 46.55 | 193.41 | 4.67 | ||
| 164.16 | 1.01 | 1.271 | 7.13 | 227.66 | 40.92 | 642.18 | 26.28 | 146.20 | 4.58 | ||
| 98.62 | 1.01 | 1.081 | 6.97 | 156.82 | 16.68 | 642.18 | 10.71 | 100.71 | 4.48 | ||
| Steam cycle | |||||||||||
| 525.80 | 127.38 | 0.026 | 6.54 | 3410.26 | 1464.34 | SW | 76.78 | 112.43 | 261.84 | 0.50 | |
| 328.25 | 32.06 | 0.081 | 6.62 | 3058.97 | 1088.92 | SW | 76.78 | 83.61 | 234.86 | 0.51 | |
| 321.60 | 32.06 | 0.079 | 6.60 | 3042.57 | 1080.69 | SW | 88.06 | 95.17 | 267.94 | 0.58 | |
| 278.75 | 32.06 | 0.071 | 6.40 | 2930.98 | 1027.20 | SW | 11.29 | 11.59 | 33.08 | 0.07 | |
| 525.80 | 32.06 | 0.113 | 7.28 | 3512.97 | 1347.96 | SW | 88.06 | 118.71 | 309.37 | 0.64 | |
| 246.67 | 3.53 | 0.671 | 7.43 | 2959.35 | 749.43 | SW | 21.99 | 16.48 | 65.08 | 0.16 | |
| 246.67 | 3.53 | 0.671 | 7.43 | 2959.35 | 749.43 | SW | 88.06 | 66.00 | 260.62 | 0.65 | |
| 246.67 | 3.53 | 0.671 | 7.43 | 2959.35 | 749.43 | SW | 110.06 | 82.48 | 325.70 | 0.82 | |
| 41.03 | 0.08 | 17.167 | 7.67 | 2397.81 | 115.22 | 0.926 | 110.06 | 12.68 | 263.90 | 0.84 | |
| 41.03 | 0.08 | 0.001 | 0.59 | 171.85 | 1.65 | 0 | 110.06 | 0.18 | 18.91 | 0.06 | |
| 41.07 | 3.53 | 0.001 | 0.59 | 172.24 | 1.94 | CLW | 110.06 | 0.21 | 18.96 | 0.06 | |
| 139.16 | 3.53 | 0.001 | 1.73 | 585.60 | 74.19 | 0 | 110.06 | 8.16 | 64.45 | 0.19 | |
| 139.16 | 3.53 | 0.001 | 1.73 | 585.60 | 74.19 | 0 | 11.29 | 0.84 | 6.61 | 0.02 | |
| 139.16 | 3.53 | 0.001 | 1.73 | 585.60 | 74.19 | 0 | 76.78 | 5.70 | 44.96 | 0.13 | |
| 139.16 | 3.53 | 0.001 | 1.73 | 585.60 | 74.19 | 0 | 21.99 | 1.63 | 12.88 | 0.04 | |
| 139.16 | 3.53 | 0.520 | 6.94 | 2732.36 | 668.58 | 1 | 21.99 | 14.70 | 60.09 | 0.15 | |
| 139.59 | 32.06 | 0.001 | 1.73 | 589.24 | 77.37 | CLW | 11.29 | 0.87 | 6.65 | 0.02 | |
| 237.57 | 32.06 | 0.001 | 2.68 | 1025.95 | 231.57 | 0 | 11.29 | 2.61 | 11.58 | 0.03 | |
| 237.57 | 32.06 | 0.062 | 6.16 | 2803.23 | 971.30 | 1 | 11.29 | 10.96 | 31.64 | 0.07 | |
| 140.38 | 127.38 | 0.001 | 1.74 | 601.28 | 88.14 | CLW | 76.78 | 6.77 | 46.17 | 0.13 | |
| 191.85 | 127.38 | 0.001 | 2.24 | 821.10 | 158.76 | CLW | 76.78 | 12.19 | 63.04 | 0.17 | |
| 329.28 | 127.38 | 0.002 | 3.54 | 1520.98 | 468.90 | 0 | 76.78 | 36.00 | 116.78 | 0.27 | |
| 329.28 | 127.38 | 0.013 | 5.45 | 2669.03 | 1048.77 | 1 | 76.78 | 80.52 | 204.92 | 0.42 | |
| 0.04 | |||||||||||
| 0.04 | |||||||||||
| 1.20 | |||||||||||
| 26.97 | |||||||||||
| 48.75 | |||||||||||
| 61.80 | |||||||||||
| 1.74 | |||||||||||
| 134.48 | |||||||||||
| 12.50 | |||||||||||
| Gas Turbine | |||||||||
| (kg) | (kg) | (kg/s) | (kJ/kg) | (kJ/kg) | (kg/kWh) | (%) | (%) | ||
| 1GT | 313.40 | 7.68 | 321.08 | 444.14 | 1,262.87 | 0.1986 | 35.16 | 40.25 | |
| 2GT | 626.81 | 15.36 | 642.17 | 444.14 | 1,262.87 | 0.1986 | 35.16 | 40.25 | |
| HRSG | Steam cycle | ||||||||
| (MW) | (kg/s) | (kg/s) | (kJ/kg) | (kJ/kg) | (MW) | (kg/kWh) | (%) | (%) | |
| 387.00 | 76.77 | 11.28 | 21.99 | 1,751.65 | 134.48 | 2.05 | 34.75 | 82.65 | |
| Combined cycle with a arrangement | |||||||||
| (kg) | (MW) | (kg/kWh) | (kg/kWh) | (%) | (%) | ||||
| 15.36 | 412.88 | 0.67 | 0.13 | 54.30 | 62.15 | ||||
| Component | Gas Side | Steam Side | Combined Cycle | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (MW) | (MW) | (MW) | (MW) | (MW) | (%) | (MW) | (MW) | (MW) | (MW) | (MW) | (%) | (MW) | (%) | |||
| Gas turbine cycle | ||||||||||||||||
| C | 279.17 | 253.54 | 25.62 | 25.62 | 90.82 | 25.62 | 90.82 | |||||||||
| cc | 664.79 | 536.98 | 127.81 | 223.35 | 80.77 | 127.81 | 80.77 | |||||||||
| t | 573.41 | 557.57 | 15.84 | 15.84 | 97.24 | 15.84 | 97.24 | |||||||||
| GT | 664.79 | 495.51 | 169.28 | 264.82 | 74.54 | 169.28 | 74.54 | |||||||||
| Heat recovery steam generator | ||||||||||||||||
| HPSH+IPRH | 64.35 | 62.65 | 1.69 | −33.99 | 97.37 | 62.65 | 55.44 | 7.21 | 42.89 | 88.50 | 8.90 | 86.17 | ||||
| HPEV | 52.47 | 50.61 | 1.85 | −35.68 | 96.47 | 50.61 | 44.52 | 6.09 | 43.62 | 87.96 | 7.95 | 84.86 | ||||
| HPEC | 29.59 | 27.37 | 2.21 | −24.15 | 92.52 | 27.37 | 23.81 | 3.56 | 29.92 | 86.99 | 5.77 | 80.48 | ||||
| LPSH | 2.64 | 2.38 | 0.26 | −2.35 | 89.97 | 2.38 | 1.78 | 0.60 | 3.21 | 74.81 | 0.86 | 67.31 | ||||
| IPSH | 0.79 | 0.68 | 0.11 | −0.65 | 85.76 | 0.68 | 0.63 | 0.05 | 0.81 | 92.71 | 0.16 | 79.51 | ||||
| IPEV | 10.13 | 9.17 | 0.96 | −9.93 | 90.52 | 9.17 | 8.35 | 0.82 | 11.71 | 91.03 | 1.78 | 82.40 | ||||
| HPPH+IPEC | 10.59 | 9.30 | 1.29 | −11.22 | 87.77 | 9.30 | 7.16 | 2.13 | 14.64 | 77.05 | 3.43 | 67.63 | ||||
| LPEV | 20.28 | 17.17 | 3.11 | −26.93 | 84.67 | 17.17 | 13.07 | 4.10 | 34.14 | 76.13 | 7.21 | 64.46 | ||||
| LPEC | 15.56 | 11.74 | 3.82 | −29.93 | 75.44 | 11.74 | 7.95 | 3.79 | 37.54 | 67.71 | 7.61 | 51.09 | ||||
| HRSG | 217.11 | 191.08 | 15.32 | −174.82 | 88.01 | 191.08 | 162.72 | 28.36 | 218.50 | 85.16 | 85.16 | 74.95 | ||||
| HRSG+GT | 664.79 | 480.19 | 184.60 | 90.00 | 72.23 | |||||||||||
| Stack | 10.71 | 0.00 | 10.71 | 0.00 | 0 | |||||||||||
| Steam cycle | ||||||||||||||||
| HPST | 28.82 | 26.97 | 1.85 | 1.85 | 93.57 | 1.85 | 93.57 | |||||||||
| IPST | 52.71 | 48.75 | 3.96 | 3.96 | 92.50 | 3.96 | 92.50 | |||||||||
| LPST | 69.80 | 61.80 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 88.54 | 8.00 | 88.54 | |||||||||
| LPP | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 74.74 | 0.01 | 74.74 | |||||||||
| IPP | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 87.44 | 0.01 | 87.44 | |||||||||
| HPP | 1.20 | 1.07 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 88.99 | 0.13 | 88.99 | |||||||||
| LPD | 22.87 | 22.87 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 100.00 | |||||||||
| IPD | 8.35 | 8.35 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 100.00 | |||||||||
| HPD | 44.52 | 44.52 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 100.00 | |||||||||
| m | 82.48 | 82.48 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 100.00 | |||||||||
| M | 95.20 | 95.17 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 99.97 | 0.03 | 99.97 | |||||||||
| SC | 406.04 | 392.06 | 13.98 | 13.98 | 96.56 | 13.98 | 96.56 | |||||||||
| HRSG+SC | 42.34 | 232.48 | 96.56 | 99.14 | 96.56 | |||||||||||
| COND | 14.25 | 12.50 | 1.75 | −232.48 | 1.75 | |||||||||||
| Productive | Cost Allocation Ratios for the Exhaust | Cost Allocation Ratios for the Waste | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gases Dissipated in the Stack, (-) | Heat Dissipated in the Condenser, (-) | |||||||
| Component | Criterion | |||||||
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | |
| Gas turbine cycle | ||||||||
| C | 0.191 | 0.139 | 0.321 | 0.262 | ||||
| cc | 1.992 | 0.693 | 0.679 | 0.738 | ||||
| t | 0.118 | 0.086 | ||||||
| Heat recovery steam generator | ||||||||
| HPSH+IPRH | −0.253 | 0.009 | 0.184 | 0.172 | 0.337 | 0.252 | ||
| HPEV | −0.265 | 0.010 | 0.188 | 0.144 | 0.271 | 0.227 | ||
| HPEC | −0.180 | 0.012 | 0.129 | 0.084 | 0.145 | 0.140 | ||
| LPSH | −0.017 | 0.001 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.011 | 0.013 | ||
| IPSH | −0.005 | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.004 | ||
| IPEV | −0.074 | 0.005 | 0.050 | 0.019 | 0.051 | 0.052 | ||
| HPPH+IPEC | −0.083 | 0.007 | 0.063 | 0.050 | 0.044 | 0.058 | ||
| LPEV | −0.200 | 0.017 | 0.147 | 0.097 | 0.079 | 0.125 | ||
| LPEC | −0.223 | 0.021 | 0.161 | 0.089 | 0.048 | 0.122 | ||
| Steam cycle | ||||||||
| HPST | 0.008 | 0.044 | ||||||
| IPST | 0.017 | 0.093 | ||||||
| LPST | 0.034 | 0.188 | ||||||
| LPP | 0.000 | 0.000255 | 0.000195 | 0.000107 | ||||
| IPP | 0.000 | 0.000122 | 0.000218 | 0.000101 | ||||
| HPP | 0.001 | 0.00312 | 0.006514 | 0.002955 | ||||
| LPD | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||||
| IPD | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||||
| HPD | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||||
| m | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||||
| M | 0.000119 | 0.000654 | 0.00367 | 0.00326 | ||||
| Total | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Stream | Exergetic Costs,(MW) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Criterion | ||||
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | |
| Gas turbine cycle | ||||
| f | 664.789 | 664.789 | 664.789 | 664.789 |
| 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| 401.823 | 388.937 | 392.003 | 391.159 | |
| 1096.199 | 1063.710 | 1066.608 | 1066.608 | |
| 301.064 | 292.141 | 292.937 | 292.937 | |
| 398.991 | 386.935 | 387.368 | 387.368 | |
| 397.894 | 385.871 | 386.303 | 386.303 | |
| Heat recovery steam generator (gas side) | ||||
| 211.838 | 205.559 | 206.119 | 206.119 | |
| 139.083 | 134.961 | 135.328 | 135.328 | |
| 98.056 | 95.150 | 95.409 | 95.409 | |
| 94.393 | 91.595 | 91.845 | 91.845 | |
| 93.293 | 90.528 | 90.774 | 90.774 | |
| 79.243 | 76.894 | 77.104 | 77.104 | |
| 64.556 | 62.643 | 62.813 | 62.813 | |
| 36.436 | 35.356 | 35.452 | 35.452 | |
| 14.852 | 14.412 | 14.451 | 14.451 | |
| Heat recovery steam generator (steam side) | ||||
| Steam cycle | ||||
| 191.648 | 194.021 | 201.492 | 200.559 | |
| 142.514 | 144.279 | 149.835 | 149.141 | |
| 171.194 | 174.535 | 180.021 | 179.647 | |
| 28.677 | 30.238 | 30.083 | 30.414 | |
| 208.322 | 211.659 | 219.759 | 218.362 | |
| 37.434 | 38.942 | 37.982 | 39.775 | |
| 115.822 | 117.677 | 122.181 | 121.404 | |
| 153.256 | 156.619 | 160.163 | 161.179 | |
| 23.562 | 24.079 | 24.624 | 24.780 | |
| 0.181 | 0.181 | 0.181 | 0.181 | |
| 0.267 | 0.277 | 0.275 | 0.273 | |
| 22.880 | 23.978 | 22.633 | 24.726 | |
| 2.346 | 2.459 | 2.321 | 2.536 | |
| 15.962 | 16.728 | 15.789 | 17.249 | |
| 4.572 | 4.791 | 4.523 | 4.941 | |
| 33.660 | 34.979 | 34.115 | 35.840 | |
| 2.428 | 2.547 | 2.412 | 2.623 | |
| 13.249 | 14.887 | 13.810 | 14.090 | |
| 27.555 | 29.129 | 28.905 | 29.238 | |
| 18.366 | 19.310 | 18.465 | 19.826 | |
| 22.684 | 22.709 | 22.580 | 24.273 | |
| 64.499 | 65.002 | 66.563 | 68.137 | |
| 138.351 | 139.697 | 144.952 | 145.348 | |
| 0.085 | 0.089 | 0.089 | 0.089 | |
| 0.082 | 0.085 | 0.085 | 0.085 | |
| 2.389 | 2.497 | 2.493 | 2.493 | |
| 49.348 | 50.944 | 51.658 | 51.419 | |
| 92.957 | 96.547 | 97.579 | 96.958 | |
| 130.618 | 137.727 | 135.539 | 136.399 | |
| 266.894 | 278.918 | 278.486 | 278.486 | |
| 3.473 | 3.629 | 3.623 | 3.623 | |
| 26.853 | 27.527 | 28.066 | 28.222 | |
| Criterion | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component | |||||||||||||||||||
| (MW) | (MW) | (MW) | (MW) | ||||||||||||||||
| Gas turbine | |||||||||||||||||||
| C | 398.99 | 401.82 | 2.83 | 386.935 | 388.937 | 2.002 | 387.368 | 392.003 | 4.635 | 387.368 | 391.159 | 3.791 | |||||||
| cc | 664.79 | 694.38 | 29.59 | 664.789 | 674.773 | 9.984 | 664.789 | 674.605 | 9.816 | 664.789 | 675.449 | 10.660 | |||||||
| t | 795.13 | 796.89 | 1.75 | 771.569 | 772.806 | 1.238 | 773.671 | 773.671 | 0.000 | 773.671 | 773.671 | 0.000 | |||||||
| Heat recovery steam generator | |||||||||||||||||||
| HPSH+IPRH | 89.23 | 90.42 | −3.76 | 4.95 | 86.582 | 91.448 | 0.124 | 4.743 | 86.818 | 96.279 | 0.000 | 9.462 | 86.818 | 93.926 | 0 | 7.109 | |||
| HPEV | 72.76 | 73.85 | −3.94 | 5.04 | 70.599 | 74.695 | 0.145 | 3.952 | 70.791 | 78.389 | 0.000 | 7.598 | 70.791 | 77.211 | 0 | 6.420 | |||
| HPEC | 41.03 | 41.81 | −2.67 | 3.46 | 39.811 | 42.293 | 0.173 | 2.309 | 39.919 | 43.983 | 0.000 | 4.064 | 39.919 | 43.864 | 0 | 3.944 | |||
| LPSH | 3.66 | 3.77 | −0.26 | 0.37 | 3.555 | 3.964 | 0.021 | 0.388 | 3.564 | 3.868 | 0.000 | 0.303 | 3.564 | 3.935 | 0 | 0.370 | |||
| IPSH | 1.10 | 1.12 | −0.07 | 0.09 | 1.068 | 1.109 | 0.009 | 0.032 | 1.071 | 1.178 | 0.000 | 0.108 | 1.071 | 1.177 | 0 | 0.106 | |||
| IPEV | 14.05 | 14.31 | −1.10 | 1.35 | 13.633 | 14.242 | 0.075 | 0.534 | 13.670 | 15.095 | 0.000 | 1.425 | 13.670 | 15.148 | 0 | 1.477 | |||
| HPPH+IPEC | 14.69 | 15.14 | −1.24 | 1.69 | 14.252 | 15.739 | 0.101 | 1.386 | 14.290 | 15.513 | 0.000 | 1.222 | 14.290 | 15.914 | 0 | 1.624 | |||
| LPEV | 28.12 | 29.09 | −2.98 | 3.94 | 27.287 | 30.188 | 0.243 | 2.658 | 27.361 | 29.592 | 0.000 | 2.231 | 27.361 | 30.899 | 0 | 3.538 | |||
| LPEC | 21.58 | 22.61 | −3.31 | 4.34 | 20.944 | 23.701 | 0.299 | 2.458 | 21.001 | 22.358 | 0.000 | 1.357 | 21.001 | 24.453 | 0 | 3.452 | |||
| HRSG | 286.21 | 292.13 | −19.32 | 25.24 | 277.729 | 297.377 | 1.188 | 18.460 | 278.486 | 306.254 | 0.000 | 27.769 | 278.486 | 306.527 | 0 | 28.041 | |||
| Stack | 14.85 | 14.85 | 14.412 | 14.412 | 14.451 | 14.451 | 14.451 | 14.451 | |||||||||||
| Steam cycle | |||||||||||||||||||
| HPST | 49.13 | 49.35 | 0.21 | 49.742 | 50.944 | 1.202 | 51.658 | 51.658 | 0.000 | 51.419 | 51.419 | 0.000 | |||||||
| IPST | 92.50 | 92.96 | 0.46 | 93.982 | 96.547 | 2.565 | 97.579 | 97.579 | 0.000 | 96.958 | 96.958 | 0.000 | |||||||
| LPST | 129.69 | 130.62 | 0.92 | 132.540 | 137.727 | 5.186 | 135.539 | 135.539 | 0.000 | 136.399 | 136.399 | 0.000 | |||||||
| LPP | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.089 | 0.096 | 0.007 | 0.089 | 0.094 | 0.005 | 0.089 | 0.092 | 0.003 | |||||||
| IPP | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.085 | 0.089 | 0.003 | 0.085 | 0.091 | 0.006 | 0.085 | 0.088 | 0.003 | |||||||
| HPP | 2.39 | 2.40 | 0.02 | 2.497 | 2.582 | 0.086 | 2.493 | 2.676 | 0.183 | 2.493 | 2.576 | 0.083 | |||||||
| LPD | 56.54 | 56.54 | 0.00 | 58.957 | 58.957 | 0.000 | 56.748 | 56.748 | 0.000 | 60.566 | 60.566 | 0.000 | |||||||
| IPD | 14.31 | 14.31 | 0.00 | 14.242 | 14.242 | 0.000 | 15.095 | 15.095 | 0.000 | 15.148 | 15.148 | 0.000 | |||||||
| HPD | 73.85 | 73.85 | 0.00 | 74.695 | 74.695 | 0.000 | 78.389 | 78.389 | 0.000 | 77.211 | 77.211 | 0.000 | |||||||
| m | 153.26 | 153.26 | 0.00 | 156.619 | 156.619 | 0.000 | 160.163 | 160.163 | 0.000 | 161.179 | 161.179 | 0.000 | |||||||
| M | 171.19 | 171.19 | 0.00 | 174.517 | 174.535 | 0.018 | 179.918 | 180.021 | 0.103 | 179.555 | 179.647 | 0.092 | |||||||
| COND | 26.85 | 26.85 | 27.527 | 27.527 | 28.066 | 28.066 | 28.222 | 28.222 | |||||||||||
| EG | 272.92 | 272.92 | 285.217 | 285.217 | 284.776 | 284.776 | 284.776 | 284.776 | |||||||||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Denise, L.-M.H.; Vicente, T.-G.E.; Sergio, C.-H.; Martín, S.-P.; Teresa, L.-A.; Raúl, L.-L. An Irreversibility-Based Criterion to Determine the Cost Formation of Residues in a Three-Pressure-Level Combined Cycle. Entropy 2020, 22, 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22030299
Denise L-MH, Vicente T-GE, Sergio C-H, Martín S-P, Teresa L-A, Raúl L-L. An Irreversibility-Based Criterion to Determine the Cost Formation of Residues in a Three-Pressure-Level Combined Cycle. Entropy. 2020; 22(3):299. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22030299
Chicago/Turabian StyleDenise, Lugo-Méndez Helen, Torres-González Edgar Vicente, Castro-Hernández Sergio, Salazar-Pereyra Martín, López-Arenas Teresa, and Lugo-Leyte Raúl. 2020. "An Irreversibility-Based Criterion to Determine the Cost Formation of Residues in a Three-Pressure-Level Combined Cycle" Entropy 22, no. 3: 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22030299
APA StyleDenise, L.-M. H., Vicente, T.-G. E., Sergio, C.-H., Martín, S.-P., Teresa, L.-A., & Raúl, L.-L. (2020). An Irreversibility-Based Criterion to Determine the Cost Formation of Residues in a Three-Pressure-Level Combined Cycle. Entropy, 22(3), 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22030299





