A Time-Varying Information Measure for Tracking Dynamics of Neural Codes in a Neural Ensemble
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Computational Framework
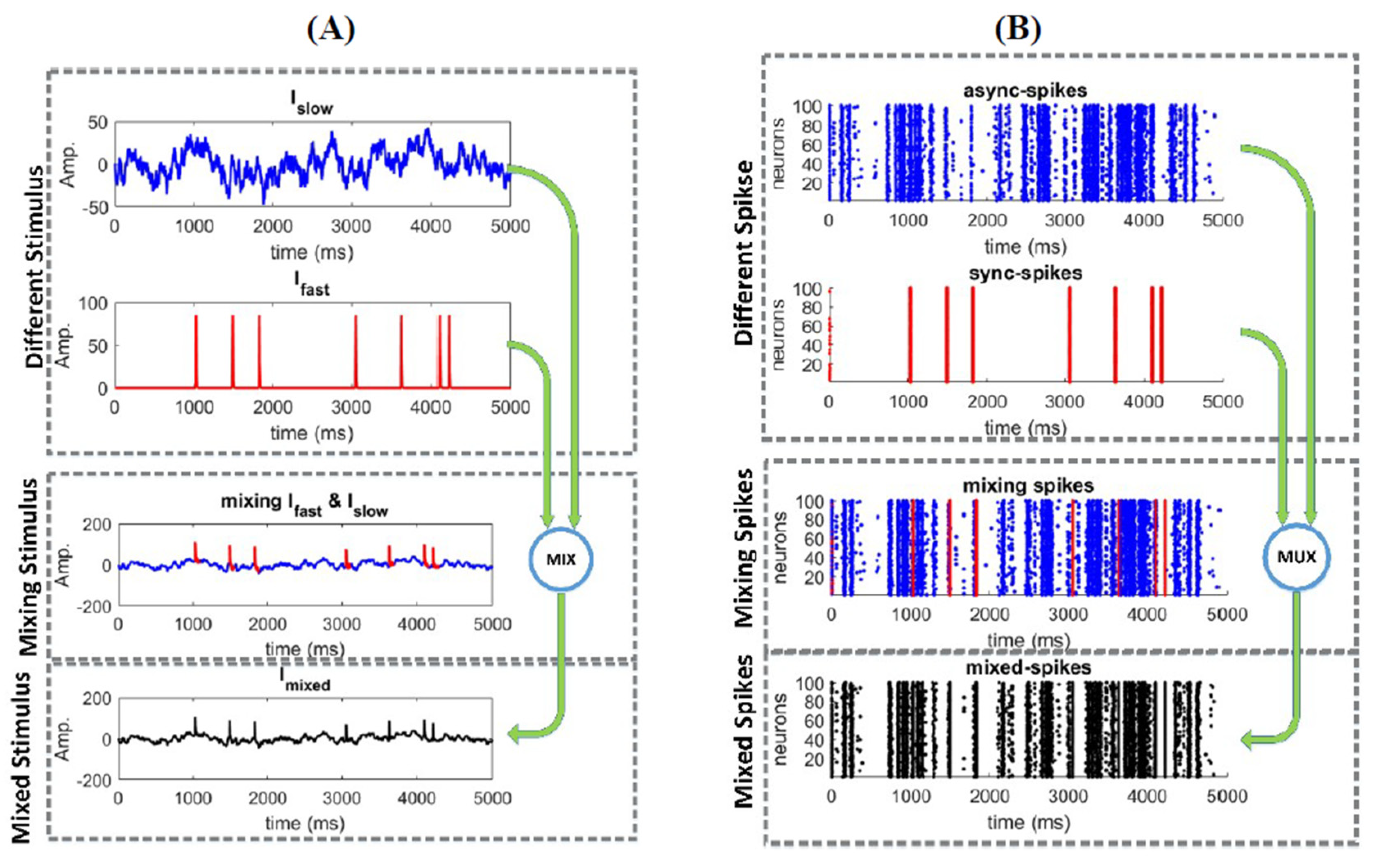
2.1. Responses of a Homogeneous Neural Ensemble to a Mixed Stimulus
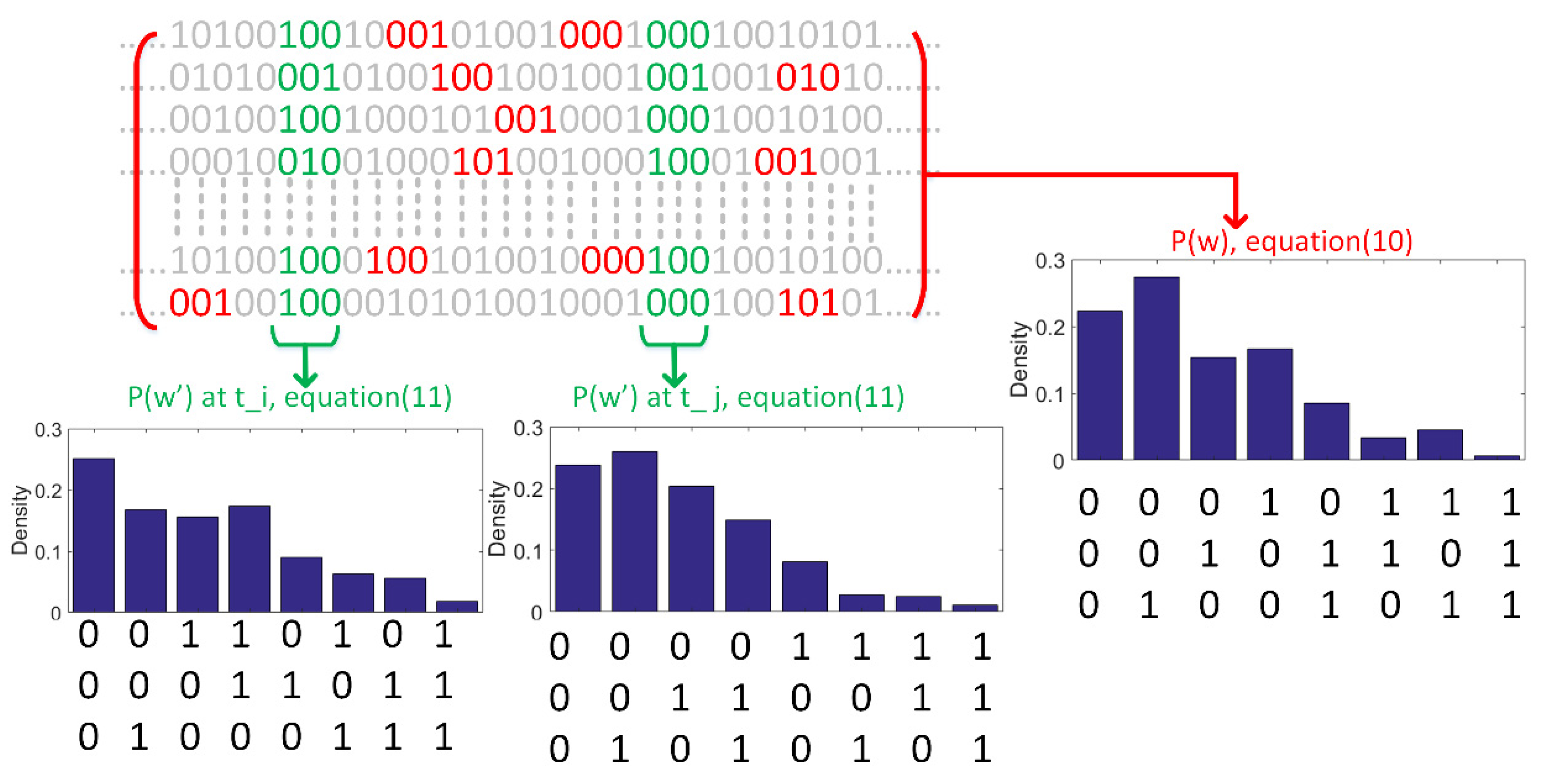
2.2. Probability Density Estimation
3. Results
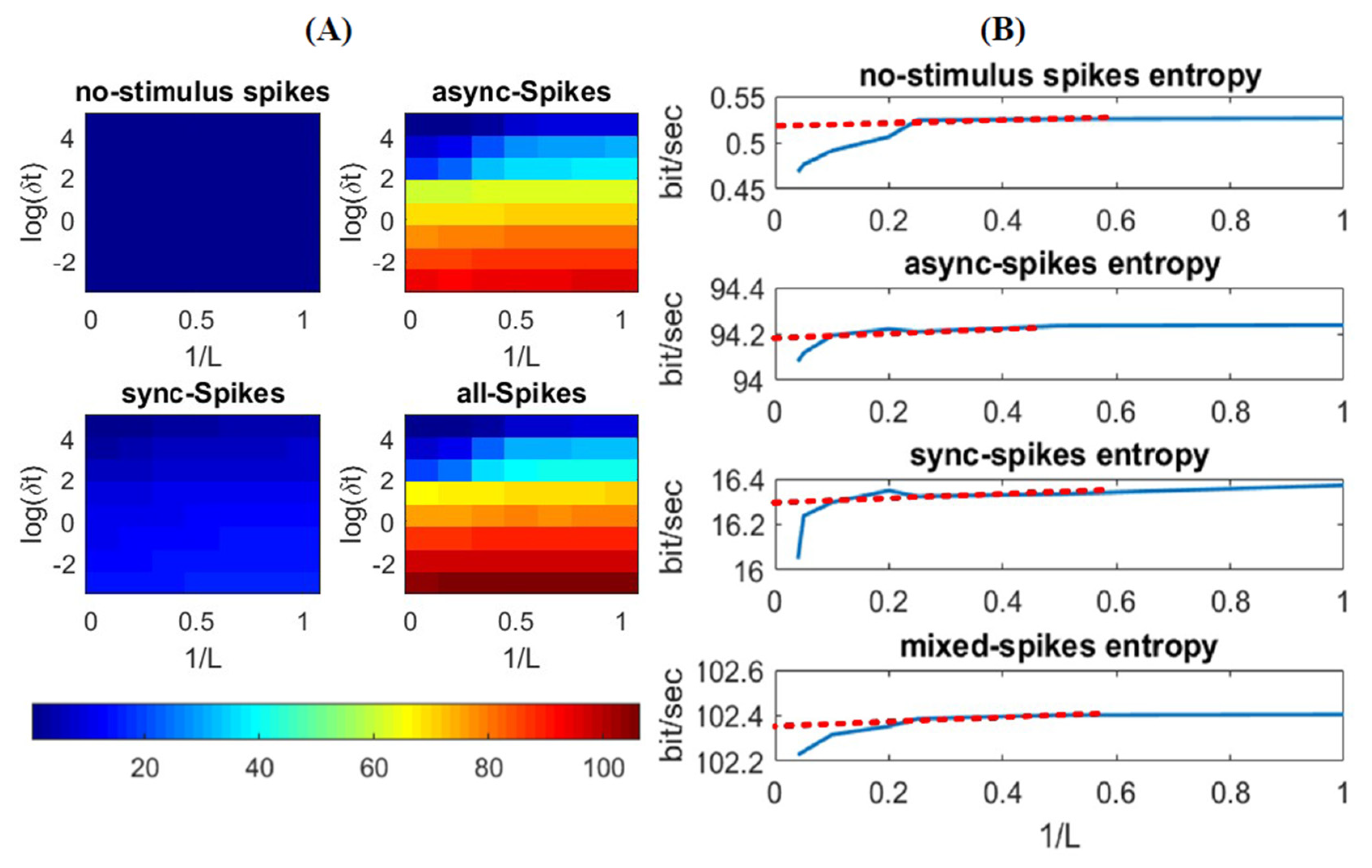
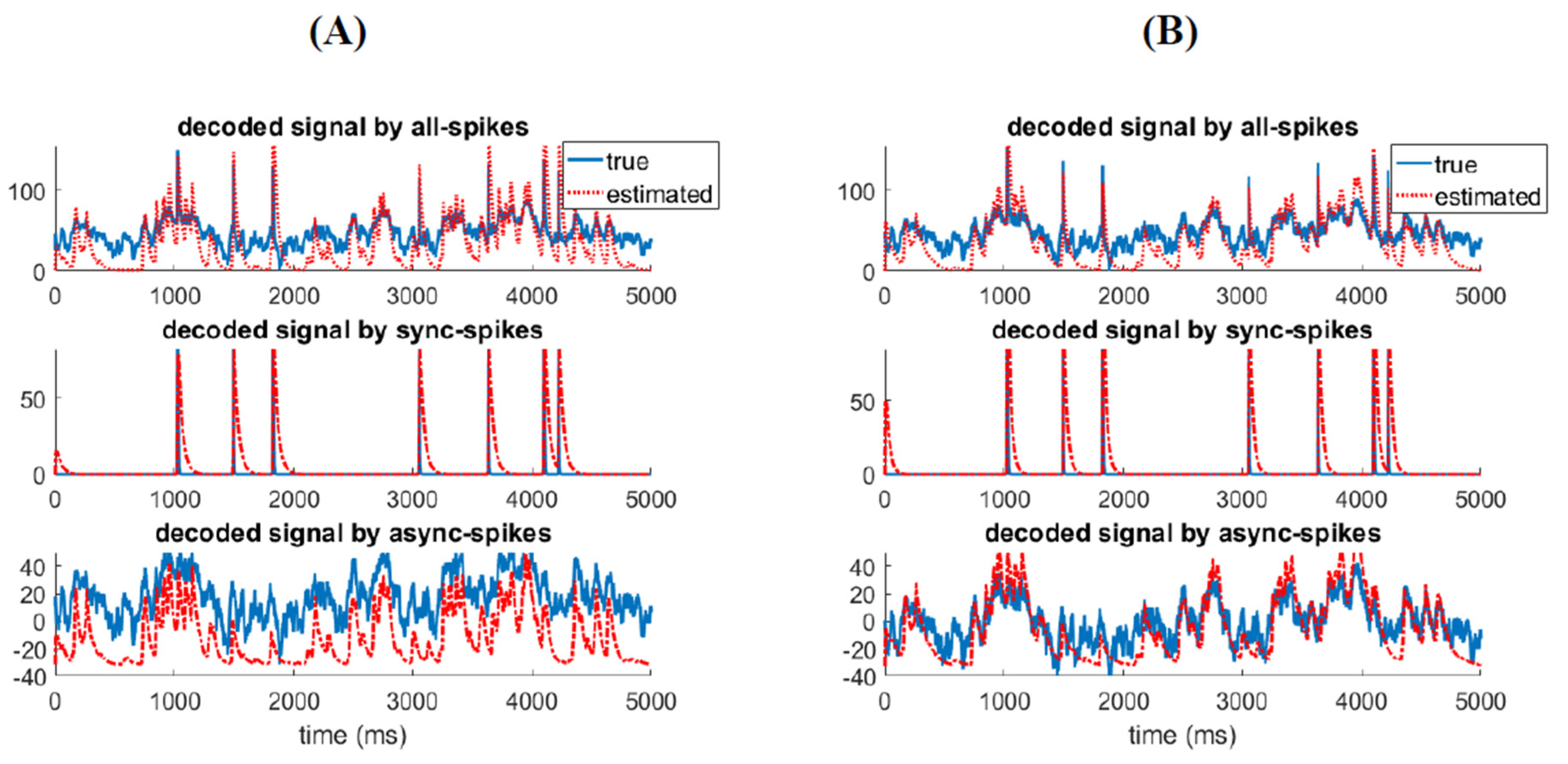
3.1. Information Underlying Synchronous and Asynchronous Spikes Are Distinctively Separable
3.2. Different Types of Spikes in a Multiplexed Code Carry Different Amounts of Information
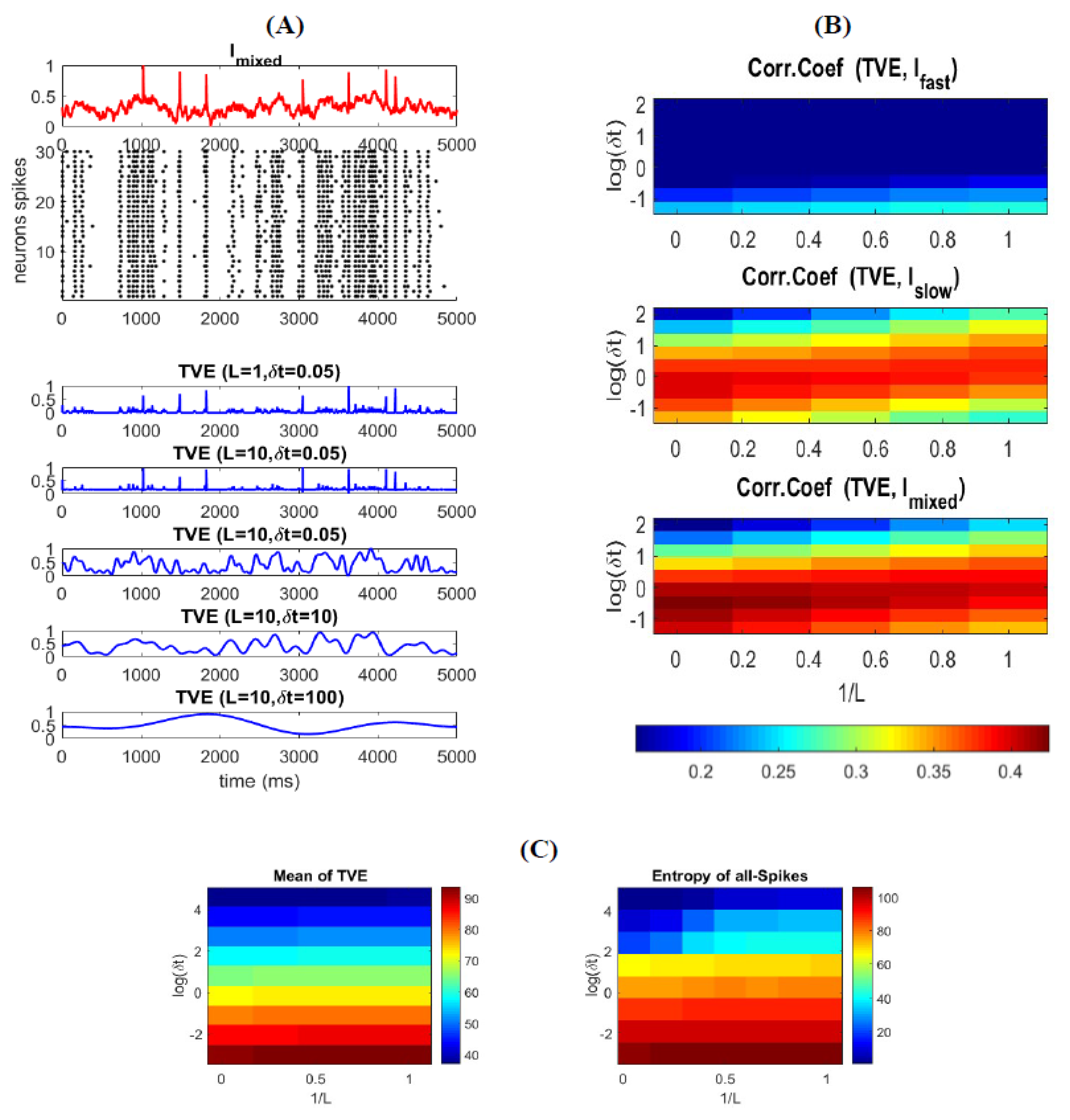
3.3. Time-Varying Entropy (TVE) Measure
3.4. Relatinship between Mixed Stimulus and Spike Patterns
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zuo, Y.; Safaai, H.; Notaro, G.; Mazzoni, A.; Panzeri, S.; Diamond, M.E. Complementary contributions of spike timing and spike rate to perceptual decisions in rat S1 and S2 cortex. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panzeri, S.; Harvey, C.D.; Piasini, E.; Latham, P.E.; Fellin, T. Cracking the neural code for sensory perception by combining statistics, intervention, and behavior. Neuron 2017, 93, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runyan, C.A.; Piasini, E.; Panzeri, S.; Harvey, C.D. Distinct timescales of population coding across cortex. Nature 2017, 548, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremkow, J.; Aertsen, A.; Kumar, A. Gating of signal propagation in spiking neural networks by balanced and correlated excitation and inhibition. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 15760–15768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montemurro, M.A.; Panzeri, S.; Maravall, M.; Alenda, A.; Bale, M.R.; Brambilla, M.; Petersen, R.S. Role of precise spike timing in coding of dynamic vibrissa stimuli in somatosensory thalamus. J. Neurophysiol. 2007, 98, 1871–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Panzeri, S.; Petersen, R.S.; Schultz, S.R.; Lebedev, M.; Diamond, M.E. The role of spike timing in the coding of stimulus location in rat somatosensory cortex. Neuron 2001, 29, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, M.; Roth, A.; Beeren, L.; Häusser, M.; Latham, P.E. Sensitivity to perturbations in vivo implies high noise and suggests rate coding in cortex. Nature 2010, 466, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieke, F.; Warlland, D.; van Steveninck, R.R.; Bialek, W. Spikes: Exploring the Neural Code; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Abeles, M.; Purt, Y.; Bergman, H.; Vaadia, E. Synchronization in neuronal transmission and its importance for information processing. Prog. Brain Res. 1994, 102, 395–404. [Google Scholar]
- Diesmann, M.; Gewaltig, M.-O.; Aertsen, A.J.N. Stable propagation of synchronous spiking in cortical neural networks. Nature 1999, 402, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzeri, S.; Brunel, N.; Logothetis, N.K.; Kayser, C. Sensory neural codes using multiplexed temporal scales. Trend Neurosci. 2010, 33, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, H.R.; Cowan, J.D. Excitatory and inhibitory interactions in localized populations of model neurons. Biophys. J. 1972, 12, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstner, W.; Kistler, W.M. Spiking Neuron Models: Single Neurons, Populations, Plasticity; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Rotter, S.; Aertsen, A. Conditions for propagating synchronous spiking and asynchronous firing rates in a cortical network model. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 5268–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiroga, R.Q.; Panzeri, S.J.N.R.N. Extracting information from neuronal populations: Information theory and decoding approaches. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lankarany, M.; Al-Basha, D.; Ratté, S.; Prescott, S.A. Differentially synchronized spiking enables multiplexed neural coding. Nat. Acad. Sci. 2019, 116, 10097–10102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Rotter, S.; Aertsen, A. Spiking activity propagation in neuronal networks: Reconciling different perspectives on neural coding. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, R.C.; Victor, J.; Shapley, R. The use of m-sequences in the analysis of visual neurons: Linear receptive field properties. Vis. Neurosci. 1997, 14, 1015–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinagel, P.; Reid, R.C. Temporal coding of visual information in the thalamus. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 5392–5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillow, J.W.; Shlens, J.; Paninski, L.; Sher, A.; Litke, A.M.; Chichilnisky, E.J.; Simoncelli, E.P. Spatio-temporal correlations and visual signalling in a complete neuronal population. Nature 2008, 454, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, A.M.; Schoffelen, J.-M. A tutorial review of functional connectivity analysis methods and their interpretational pitfalls. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borst, A.; Theunissen, F.E. Information theory and neural coding. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasini, E.; Panzeri, S. Information Theory in Neuroscience. Entropy 2019, 21, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, C.F.; Zador, A.M. Information through a spiking neuron. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; NIPS: San Diego, CA, USA, 1996; pp. 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, M.I.J.S. Graphical models. Statist. Sci. 2004, 19, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belghazi, M.I.; Baratin, A.; Rajeswar, S.; Ozair, S.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.; Hjelm, R.D. Mine: Mutual information neural estimation. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholmsmässan, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Timme, N.M.; Lapish, C.J.E. A tutorial for information theory in neuroscience. eNuro 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cover, T.M.; Thomas, J.A. Elements of Information Theory (Wiley Series in Telecommunications and Signal Processing), 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Walters-Williams, J.; Li, Y. Estimation of mutual information: A survey. In International Conference on Rough Sets and Knowledge Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pirschel, F.; Kretzberg, J. Multiplexed population coding of stimulus properties by leech mechanosensory cells. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 3636–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destexhe, A.; Rudolph, M.; Fellous, J.M.; Sejnowski, T.J. Fluctuating synaptic conductances recreate in vivo-like activity in neocortical neurons. Neuroscience 2001, 107, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, C.; Lecar, H. Voltage oscillations in the barnacle giant muscle fiber. Biophys. J. 1981, 35, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khubieh, A.; Rudolph, M.; Fellous, J.M.; Sejnowski, T.J. Regulation of cortical dynamic range by background synaptic noise and feedforward inhibition. Neuroscience 2016, 26, 3357–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratté, S.; Hong, S.; De Schutter, E.; Prescott, S.A. Impact of neuronal properties on network coding: Roles of spike initiation dynamics and robust synchrony transfer. Neuron 2013, 78, 758–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, S.A.; De Koninck, Y.; Sejnowski, T.J. Biophysical basis for three distinct dynamical mechanisms of action potential initiation. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2008, 4, e1000198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destexhe, A.; Rudolph, M.; Paré, D. The high-conductance state of neocortical neurons in vivo. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalizi, C. Advanced Data Analysis from an Elementary Point of View; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Cruz, F. Kullback-Leibler divergence estimation of continuous distributions. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE international symposium on information theory, Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Van Kerm, P. Adaptive kernel density estimation. Stata J. 2003, 3, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, G.; Franceschini, A. A multidimensional version of the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1987, 225, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, F.J., Jr. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for goodness of fit. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1951, 46, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, S.P.; Koberle, R.; van Steveninck, R.R.R.; Bialek, W. Entropy and information in neural spike trains. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seber, G.A.; Lee, A.J. Linear Regression Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; Volume 329. [Google Scholar]
- Hasanzadeh, N.; Rezaei, M.; Faraz, S.; Popovic, M.R.; Lankarany, M. Necessary Conditions for Reliable Propagation of Time-Varying Firing Rate. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Black, M.J.; Gao, Y.; Bienenstock, E.; Serruya, M.; Shaikhouni, A.; Donoghue, J.P. Inferring hand motion from multi-cell recordings in motor cortex using a Kalman filter. In Proceedings of the SAB’02-Workshop on Motor Control in Humans and Robots: On the Interplay of Real Brains and Artificial Devices, Edinburgh, UK, 10 August 2002; pp. 66–73. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Black, M.J.; Gao, Y.; Bienenstock, E.; Serruya, M.; Shaikhouni, A.; Donoghue, J.P. Neural decoding of cursor motion using a Kalman filter. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Cubero, R.J.; Marsili, M.; Roudi, Y. Multiscale relevance and informative encoding in neuronal spike trains. J. Comput. Neurosci. 2020, 48, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillow, J.W.; Aoi, M.C. Is population activity more than the sum of its parts? Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 1196–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimazaki, H.; Shinomoto, S. Kernel bandwidth optimization in spike rate estimation. J. Comput. Neurosc. 2010, 29, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, G.F.; Cunningham, J.P. Structure in neural population recordings: An expected byproduct of simpler phenomena? Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rezaei, M.R.; Popovic, M.R.; Lankarany, M. A Time-Varying Information Measure for Tracking Dynamics of Neural Codes in a Neural Ensemble. Entropy 2020, 22, 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22080880
Rezaei MR, Popovic MR, Lankarany M. A Time-Varying Information Measure for Tracking Dynamics of Neural Codes in a Neural Ensemble. Entropy. 2020; 22(8):880. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22080880
Chicago/Turabian StyleRezaei, Mohammad R., Milos R. Popovic, and Milad Lankarany. 2020. "A Time-Varying Information Measure for Tracking Dynamics of Neural Codes in a Neural Ensemble" Entropy 22, no. 8: 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22080880
APA StyleRezaei, M. R., Popovic, M. R., & Lankarany, M. (2020). A Time-Varying Information Measure for Tracking Dynamics of Neural Codes in a Neural Ensemble. Entropy, 22(8), 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22080880



