The Eco-Evo Mandala: Simplifying Bacterioplankton Complexity into Ecohealth Signatures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Marine Ecosystem Health through the Microbiome
1.2. Leveraging Community Complexity for EcoHealth Assessment
1.3. Community Signals as Environment-Modulated Noise
1.3.1. Phylogenetic Trait Dynamics
1.3.2. Entropic Methods for Species Interaction Assessment
1.4. Paper Outline
2. Materials and Methods
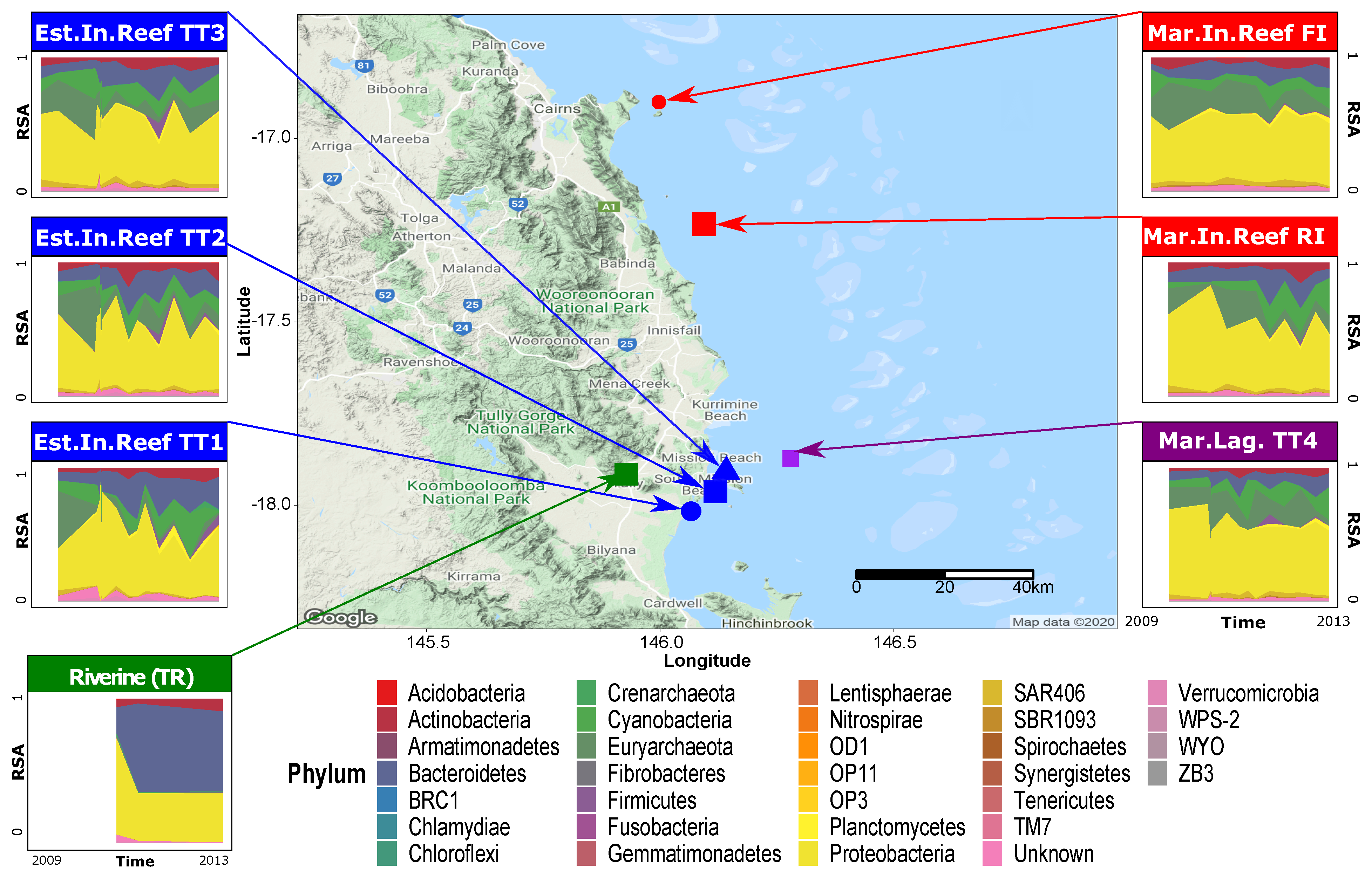
2.1. Microbiome Data
2.2. Interaction Quantification
2.3. Population Complexity Indicators
2.3.1. Probabilistic Characterization of Distributions
2.3.2. Taylor’s Law
2.4. Phylogenetic Distance
2.5. Eco-Evo Mandala
3. Results
3.1. Community Health Characterization
3.2. Intra-Community Health Characterization
3.3. Community Structural and Functional Optimality
4. Discussion
4.1. Signaling Ecosystem Optimality with Community versus Population Dynamics
4.2. Phylogenetic and Probabilistic Ecohealth Characterization
4.3. Multi-Axis Community Departure from Optimality
4.4. Habitat Inference from Bacterioplankton Organization
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salazar, G.; Cornejo-Castillo, F.M.; Benítez-Barrios, V.; Fraile-Nuez, E.; Álvarez-Salgado, X.A.; Duarte, C.M.; Gasol, J.M.; Acinas, S.G. Global diversity and biogeography of deep-sea pelagic prokaryotes. ISME J. 2016, 10, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleinteich, J.; Hildebrand, F.; Bahram, M.; Voigt, A.Y.; Wood, S.A.; Jungblut, A.D.; Küpper, F.C.; Quesada, A.; Camacho, A.; Pearce, D.A.; et al. Pole-to-pole connections: Similarities between Arctic and Antarctic microbiomes and their vulnerability to environmental change. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 5, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sunagawa, S.; Acinas, S.G.; Bork, P.; Bowler, C.; Eveillard, D.; Gorsky, G.; Guidi, L.; Iudicone, D.; Karsenti, E.; Lombard, F.; et al. Tara Oceans: Towards global ocean ecosystems biology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 428–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Zhang, W.; Ding, W.; Wang, M.; Fan, S.; Yang, B.; Mcminn, A.; Wang, M.; Xie, B.b.; Qin, Q.L.; et al. Structure and function of the Arctic and Antarctic marine microbiota as revealed by metagenomics. Microbiome 2020, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Cardozo-Mino, M.G.; Fadeev, E.; Salman-Carvalho, V.; Boetius, A. Spatial distribution of Arctic bacterioplankton abundance is linked to distinct water masses and summertime phytoplankton bloom dynamics (Fram Strait, 79° N). Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 658803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falkowski, P.G.; Fenchel, T.; Delong, E.F. The microbial engines that drive Earth’s biogeochemical cycles. Science 2008, 320, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fuhrman, J.A. Microbial community structure and its functional implications. Nature 2009, 459, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuhrman, J.A.; Cram, J.A.; Needham, D.M. Marine microbial community dynamics and their ecological interpretation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasl, B.; Bourne, D.G.; Frade, P.R.; Thomas, T.; Schaffelke, B.; Webster, N.S. Microbial indicators of environmental perturbations in coral reef ecosystems. Microbiome 2019, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bourne, D.G.; Morrow, K.M.; Webster, N.S. Insights into the coral microbiome: Underpinning the health and resilience of reef ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 70, 317–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasl, B.; Webster, N.S.; Bourne, D.G. Microbial indicators as a diagnostic tool for assessing water quality and climate stress in coral reef ecosystems. Mar. Biol. 2017, 164, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasl, B.; Bourne, D.G.; Frade, P.R.; Webster, N.S. Establishing microbial baselines to identify indicators of coral reef health. Microbiol. Aust. 2018, 39, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roitman, S.; Pollock, F.J.; Medina, M. Coral microbiomes as bioindicators of reef health. In Population Genomics: Marine Organisms; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 39–57. [Google Scholar]
- Astudillo-García, C.; Hermans, S.M.; Stevenson, B.; Buckley, H.L.; Lear, G. Microbial assemblages and bioindicators as proxies for ecosystem health status: Potential and limitations. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 6407–6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, R.C.; Williams, G.J.; Turner, J.R. Towards developing a mechanistic understanding of coral reef resilience to thermal stress across multiple scales. Curr. Clim. Chang. Rep. 2018, 4, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patrick, C.J.; McCluney, K.E.; Ruhi, A.; Gregory, A.; Sabo, J.; Thorp, J.H. Multi-scale biodiversity drives temporal variability in macrosystems. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2021, 19, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Convertino, M. Optimal microbiome networks: Macroecology and criticality. Entropy 2019, 21, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bak, P.; Tang, C.; Wiesenfeld, K. Self-organized criticality. Phys. Rev. A 1988, 38, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavender-Bares, K.K.; Rinaldo, A.; Chisholm, S.W. Microbial size spectra from natural and nutrient enriched ecosystems. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneghan, R.F.; Hatton, I.A.; Galbraith, E.D. Climate change impacts on marine ecosystems through the lens of the size spectrum. Emerg. Top. Life Sci. 2019, 3, 233–243. [Google Scholar]
- Barabási, A.L.; Bonabeau, E. Scale-free networks. Sci. Am. 2003, 288, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Iturbe, I.; Rinaldo, A. Fractal River Basins: Chance and Self-Organization; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo, J.; Grilli, J.; Suweis, S.; Munoz, M.A.; Banavar, J.R.; Maritan, A. Information-based fitness and the emergence of criticality in living systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10095–10100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zimatore, G.; Tsuchiya, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Kasperski, A.; Giuliani, A. Self-organization of whole-gene expression through coordinated chromatin structural transition. Biophys. Rev. 2021, 2, 031303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolov, S.; Yankulova, E.; Wolkenhauer, O.; Petrov, V. Principal difference between stability and structural stability (robustness) as used in systems biology. Nonlinear Dyn. Psychol. Life Sci. 2007, 11, 413–433. [Google Scholar]
- Scheffer, M.; Bascompte, J.; Brock, W.A.; Brovkin, V.; Carpenter, S.R.; Dakos, V.; Held, H.; Van Nes, E.H.; Rietkerk, M.; Sugihara, G. Early-warning signals for critical transitions. Nature 2009, 461, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Convertino, M. Temperature increase drives critical slowing down of fish ecosystems. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinello, M.; Hidalgo, J.; Maritan, A.; Di Santo, S.; Plenz, D.; Munoz, M.A. Neutral theory and scale-free neural dynamics. Phys. Rev. X 2017, 7, 041071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Convertino, M. Inferring ecosystem networks as information flows. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, G.; Xu, Q.; Tang, J.; Li, X.; Wen, J.; Liu, H.; Tang, C.; Dong, K.; et al. Phylogenetic responses of marine free-living bacterial community to Phaeocystis globosa bloom in Beibu Gulf, China. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, L.; González-Díaz, P.; Armenteros, M.; Ferrer, V.M.; Bretos, F.; Bartels, E.; Santoro, A.E.; Apprill, A. Microbial signatures of protected and impacted Northern Caribbean reefs: Changes from Cuba to the Florida Keys. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 499–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varkey, D.; Mazard, S.; Jeffries, T.C.; Hughes, D.J.; Seymour, J.; Paulsen, I.T.; Ostrowski, M. Stormwater influences phytoplankton assemblages within the diverse, but impacted Sydney Harbour estuary. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0209857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Jiang, X.; Jing, Z.; Li, G.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, C.; Liu, J.; Tan, Y. Spatial and seasonal distributions of bacterioplankton in the Pearl River Estuary: The combined effects of riverine inputs, temperature, and phytoplankton. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 125, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries, T.C.; Schmitz Fontes, M.L.; Harrison, D.P.; Van-Dongen-Vogels, V.; Eyre, B.D.; Ralph, P.J.; Seymour, J.R. Bacterioplankton dynamics within a large anthropogenically impacted urban estuary. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Angly, F.E.; Heath, C.; Morgan, T.C.; Tonin, H.; Rich, V.; Schaffelke, B.; Bourne, D.G.; Tyson, G.W. Marine microbial communities of the Great Barrier Reef lagoon are influenced by riverine floodwaters and seasonal weather events. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.M.; Segata, N. Multiple levels of the unknown in microbiome research. BMC Biol. 2019, 17, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martiny, J.B.; Jones, S.E.; Lennon, J.T.; Martiny, A.C. Microbiomes in light of traits: A phylogenetic perspective. Science 2015, 350, aac9323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Louca, S.; Parfrey, L.W.; Doebeli, M. Decoupling function and taxonomy in the global ocean microbiome. Science 2016, 353, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, T. Measuring information transfer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cullen, C.M.; Aneja, K.K.; Beyhan, S.; Cho, C.E.; Woloszynek, S.; Convertino, M.; McCoy, S.J.; Zhang, Y.; Anderson, M.Z.; Alvarez-Ponce, D.; et al. Emerging priorities for microbiome research. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carr, A.; Diener, C.; Baliga, N.S.; Gibbons, S.M. Use and abuse of correlation analyses in microbial ecology. ISME J. 2019, 13, 2647–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coenen, A.R.; Weitz, J.S. Limitations of correlation-based inference in complex virus-microbe communities. mSystems 2018, 3, e00084-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, J.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Pan, Y.; Li, M. Patterns and processes of free-living and particle-associated bacterioplankton and archaeaplankton communities in a subtropical river-bay system in South China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2020, 65, S161–S179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaneveld, J.R.; Burkepile, D.E.; Shantz, A.A.; Pritchard, C.E.; McMinds, R.; Payet, J.P.; Welsh, R.; Correa, A.M.; Lemoine, N.P.; Rosales, S.; et al. Overfishing and nutrient pollution interact with temperature to disrupt coral reefs down to microbial scales. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.P.; Kerry, J.T.; Álvarez-Noriega, M.; Álvarez-Romero, J.G.; Anderson, K.D.; Baird, A.H.; Babcock, R.C.; Beger, M.; Bellwood, D.R.; Berkelmans, R.; et al. Global warming and recurrent mass bleaching of corals. Nature 2017, 543, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lizier, J.T. JIDT: An information-theoretic toolkit for studying the dynamics of complex systems. Front. Robot. AI 2014, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gillespie, C.S. Fitting heavy tailed distributions: The poweRlaw package. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1407.3492. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, L.; Woiwod, I. Temporal stability as a density-dependent species characteristic. J. Anim. Ecol. 1980, 49, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jombart, T.; Dray, S. adephylo: Exploratory analyses for the phylogenetic comparative method. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1907–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margalef, R. Life-forms of phytoplankton as survival alternatives in an unstable environment. Oceanol. Acta 1978, 1, 493–509. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, V.I.; Yawata, Y.; Stocker, R. A foraging mandala for aquatic microorganisms. ISME J. 2019, 13, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glibert, P.M. Margalef revisited: A new phytoplankton mandala incorporating twelve dimensions, including nutritional physiology. Harmful Algae 2016, 55, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauchinger, F. Self-Organized Criticality in the Gut Microbiome. Ph.D. Thesis, Uniwien, Vienna, Austria, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, S.; Schlaeppi, K.; van der Heijden, M.G. Keystone taxa as drivers of microbiome structure and functioning. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousef, M.; Kumar, A.; Bakir-Gungor, B. Application of biological domain knowledge based feature selection on gene expression data. Entropy 2021, 23, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, L.P.; Song, C.; Saavedra, S. Merging dynamical and structural indicators to measure resilience in multispecies systems. J. Anim. Ecol. 2021, 90, 2027–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, M.; Roik, A.; Porter, A.; Zubier, K.; Mudarris, M.S.; Ormond, R.; Voolstra, C.R. Coral microbial community dynamics in response to anthropogenic impacts near a major city in the central Red Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 105, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruce, T.; Meirelles, P.M.; Garcia, G.; Paranhos, R.; Rezende, C.E.; de Moura, R.L.; Filho, R.F.; Coni, E.O.; Vasconcelos, A.T.; Amado Filho, G.; et al. Abrolhos bank reef health evaluated by means of water quality, microbial diversity, benthic cover, and fish biomass data. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinsdale, E.A.; Pantos, O.; Smriga, S.; Edwards, R.A.; Angly, F.; Wegley, L.; Hatay, M.; Hall, D.; Brown, E.; Haynes, M.; et al. Microbial ecology of four coral atolls in the Northern Line Islands. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Overmann, J.; Lepleux, C. Marine Bacteria and Archaea: Diversity, adaptations, and culturability. In The Marine Microbiome; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 21–55. [Google Scholar]
- Lok, C. Mining the microbial dark matter. Nat. News 2015, 522, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, D.; Liu, L.; He, S. Application of in situ cultivation in marine microbial resource mining. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2021, 3, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Madamwar, D.; Incharoensakdi, A. Bloom dynamics of cyanobacteria and their toxins: Environmental health impacts and mitigation strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magurran, A.E.; Henderson, P.A. Explaining the excess of rare species in natural species abundance distributions. Nature 2003, 422, 714–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frade, P.R.; Glasl, B.; Matthews, S.A.; Mellin, C.; Serrão, E.A.; Wolfe, K.; Mumby, P.J.; Webster, N.S.; Bourne, D.G. Spatial patterns of microbial communities across surface waters of the Great Barrier Reef. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Oppen, M.J.; Bongaerts, P.; Frade, P.; Peplow, L.M.; Boyd, S.E.; Nim, H.T.; Bay, L.K. Adaptation to reef habitats through selection on the coral animal and its associated microbiome. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 2956–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apprill, A.; Weber, L.G.; Santoro, A.E. Distinguishing between microbial habitats unravels ecological complexity in coral microbiomes. mSystems 2016, 1, e00143-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meirelles, P.M.; Soares, A.C.; Oliveira, L.; Leomil, L.; Appolinario, L.R.; Francini-Filho, R.B.; de Moura, R.L.; de Barros Almeida, R.T.; Salomon, P.S.; Amado-Filho, G.M.; et al. Metagenomics of coral reefs under phase shift and high hydrodynamics. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, B.S.; Fernandez, V.I.; Stocker, R. Motility drives bacterial encounter with particles responsible for carbon export throughout the ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2019, 4, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falter, J.L.; Lowe, R.J.; Zhang, Z.; McCulloch, M. Physical and biological controls on the carbonate chemistry of coral reef waters: Effects of metabolism, wave forcing, sea level, and geomorphology. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, C.E.T.; Kim, D.Y.; Sachdeva, R.; Caron, D.A.; Fuhrman, J.A. Top-down controls on bacterial community structure: Microbial network analysis of bacteria, T4-like viruses and protists. ISME J. 2014, 8, 816–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Du, X.P.; Zeng, Y.H.; Zhu, J.M.; Zhang, S.J.; Cai, Z.H.; Zhou, J. The communities and functional profiles of virioplankton along a salinity gradient in a subtropical estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodinger, F.; Endo, H.; Takano, Y.; Li, Y.; Tominaga, K.; Isozaki, T.; Blanc-Mathieu, R.; Gotoh, Y.; Tetsuya, H.; Taniguchi, E.; et al. Year-round dynamics of amplicon sequence variant communities differ among eukaryotes, Mimiviridae, and prokaryotes in a coastal ecosystem. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galbraith, E.; Convertino, M. The Eco-Evo Mandala: Simplifying Bacterioplankton Complexity into Ecohealth Signatures. Entropy 2021, 23, 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23111471
Galbraith E, Convertino M. The Eco-Evo Mandala: Simplifying Bacterioplankton Complexity into Ecohealth Signatures. Entropy. 2021; 23(11):1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23111471
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalbraith, Elroy, and Matteo Convertino. 2021. "The Eco-Evo Mandala: Simplifying Bacterioplankton Complexity into Ecohealth Signatures" Entropy 23, no. 11: 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23111471
APA StyleGalbraith, E., & Convertino, M. (2021). The Eco-Evo Mandala: Simplifying Bacterioplankton Complexity into Ecohealth Signatures. Entropy, 23(11), 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23111471






