Multi-Task Transformer with Adaptive Cross-Entropy Loss for Multi-Dialect Speech Recognition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Multi-Task Transformer
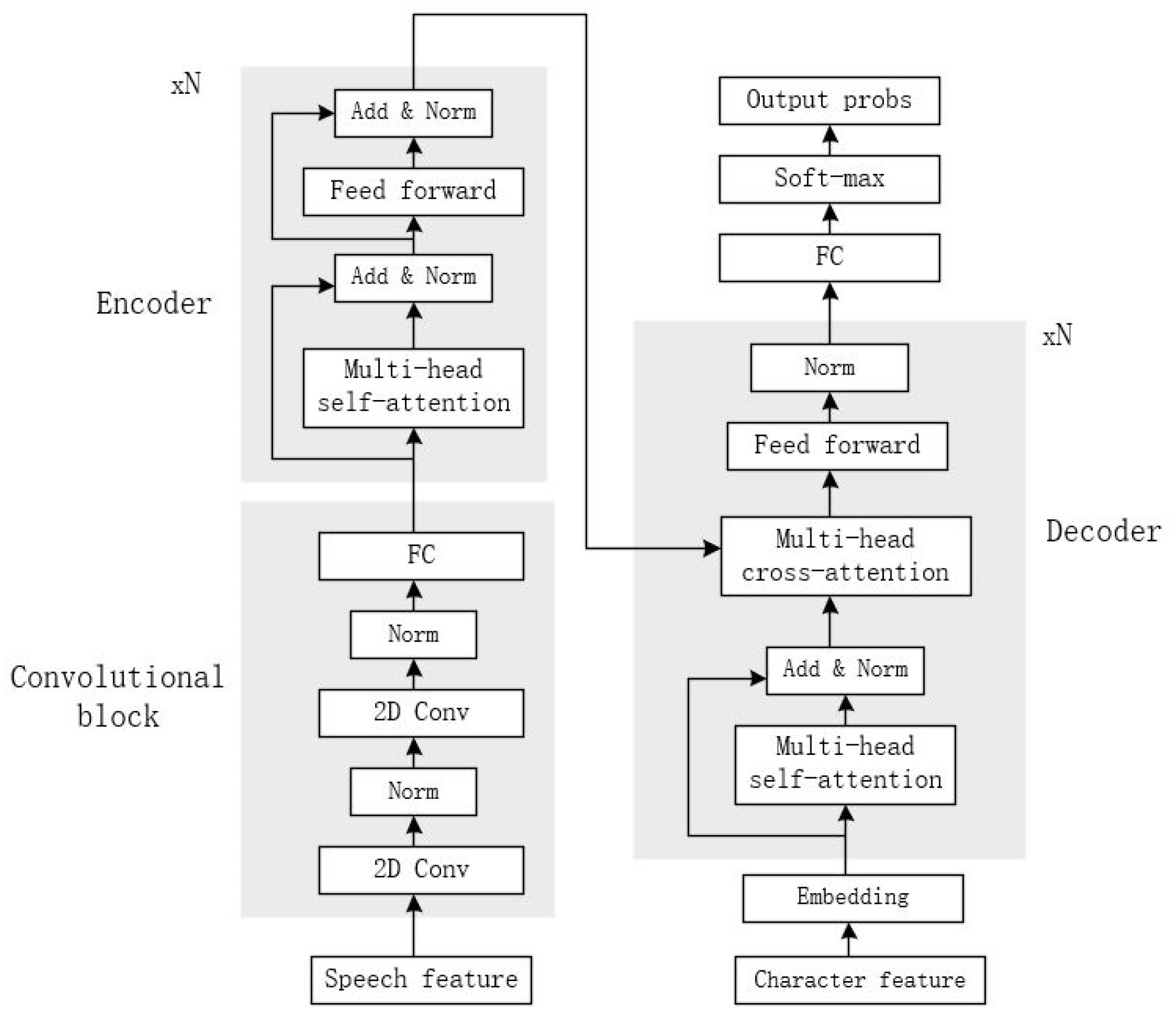
3.1. Speech-Transformer
3.1.1. Convolutional Block
3.1.2. Encoder
3.1.3. Decoder
3.2. Soft-MTL Transformer
Auxiliary Cross-Attention
3.3. Adaptive Cross-Entropy Loss
4. Experiment
4.1. Data
4.2. Settings
4.3. Experimental Results
4.3.1. Single-Task Transformer vs. Multi-Task Transformer
4.3.2. Adaptive Cross-Entropy Loss Experiment
4.3.3. Dialect ID Recognition Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moritz, N.; Hori, T.; Le, J. Streaming automatic speech recognition with the transformer model. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 6074–6078. [Google Scholar]
- Kriman, S.; Beliaev, S.; Ginsburg, B.; Huang, J.; Kuchaiev, O.; Lavrukhin, V.; Leary, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. Quartznet: Deep automatic speech recognition with 1d time-channel separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 6124–6128. [Google Scholar]
- Synnaeve, G.; Xu, Q.; Kahn, J.; Likhomanenko, T.; Grave, E.; Pratap, V.; Sriram, A.; Liptchinsky, V.; Collobert, R. End-to-end asr: From supervised to semi-supervised learning with modern architectures. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.08460. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.; Li, J. Recent progresses in deep learning based acoustic models. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2017, 4, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainath, T.N.; Weiss, R.J.; Wilson, K.W.; Li, B.; Narayanan, A.; Variani, E.; Bacchiani, M.; Shafran, I.; Senior, C.; Kim, C.; et al. Multichannel signal processing with deep neural networks for automatic speech recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2017, 25, 965–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, T.; Chang, E. Accent issues in large vocabulary continuous speech recognition. Int. J. Speech Technol. 2004, 7, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Xu, S.; Xu, B. Speech-Transformer: A No-Recurrence Sequence-to-Sequence Model for Speech Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vergyri, D.; Lamel, L.; Gauvain, J.L. Automatic speech recognition of multiple accented English data. In Proceedings of the Eleventh Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Chiba, Japan, 26–30 September 2010; pp. 1652–1655. [Google Scholar]
- Shetty, V.M.; NJ, M.S.M. Improving the Performance of Transformer Based Low Resource Speech Recognition for Indian Languages. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 8279–8283. [Google Scholar]
- Siohan, O.; Rybach, D. Multitask learning and system combination for automatic speech recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 13–17 December 2015; pp. 589–595. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Yin, M.; You, Y.; Yu, K. Multi-task joint-learning of deep neural networks for robust speech recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 13–17 December 2015; pp. 310–316. [Google Scholar]
- Thanda, A.; Venkatesan, S.M. Multi-task Learning of Deep Neural Networks for Audio Visual Automatic Speech Recognition. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1701.02477. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Mak, B.K.W. Multitask Learning of Deep Neural Networks for Low-resource Speech Recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2015, 23, 1172–1183. [Google Scholar]
- Krishna, K.; Toshniwal, S.; Livescu, K. Hierarchical Multitask Learning for CTC-based Speech Recognition. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.06234v2. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, J. Multi-Task and Transfer Learning in Low-Resource Speech Recognition. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ruder, S. An Overview of Multi-Task Learning in Deep Neural Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05098v1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Yue, J.; Xu, X.; Wu, L.; Li, X. End-to-End based Tibetan Multitask Speech Recognition. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 162519–162529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, I.; Shrivastava, A.; Gupta, A.; Hebert, M. Cross-Stitch Networks for Multi-Task Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3994–4003. [Google Scholar]
- Ruder, S.; Bingel, J.; Augenstein, I.; Søgaard, A. Sluice Networks: Learning What to Share between Loosely Related Tasks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.08142v1. [Google Scholar]
- Vandenhende, S.; Georgoulis, S.; Van Gansbeke, W.; Proesmans, M.; Dai, D.; Van Gool, L. Multi-Task Learning for Dense Prediction Tasks: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 3614–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Badrinarayanan, V.; Lee, C.Y.; Rabinovich, A. Gradnorm: Gradient normalization for adaptive loss balancing in deep multitask networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Beijing, China, 14–16 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, A.; Gal, Y.; Cipolla, R. Multi-task learning using uncertainty to weigh losses for scene geometry and semantics. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Johns, E.; Davison, A.J. End-to-end multi-task learning with attention. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.10704. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Haque, A.; Huang, D.A.; Yeung, S.; Fei-Fei, L. Dynamic task prioritization for multitask learning. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 282–299. [Google Scholar]
- Désidéri, J.-A. Multiple-gradient descent algorithm for multi-objective optimization. Competes Rendus Math. 2012, 350, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.; Sak, H. Multi-accent speech recognition with hierarchical grapheme based models. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017; pp. 4815–4819. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, A.; Upreti, M.; Jyothi, P. Improved accented speech recognition using accent embeddings and multi-task learning. In Proceedings of the Interspeech, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018; pp. 2454–2458. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Kumar, K.; Wu, J. Multi-Dialect Speech Recognition in English Using Attention on Ensemble of Experts. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021-2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–12 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chennupati, S.; Sistu, G.; Yogamani, S.; A Rawashdeh, S. MultiNet++:Multi-stream Feature Aggregation and Geometric Loss Strategy for Multi-task Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Open Speech and Language Resource. Available online: http://www.openslr.org/124/ (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Mozilla Common Voice. Available online: https://commonvoice.mozilla.org/en/datasets/ (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]




| Language | Dialect | Training Data (Hours) | Training Utterances | Test Data (Hours) | Test Utterances |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tibetan | Ü-Tsang | 23.74 | 20,594 | 2.98 | 2575 |
| Amdo | 18.93 | 17,286 | 2.36 | 2161 | |
| Kham | 2.61 | 2373 | 0.33 | 269 | |
| Chinese | Mandarin | 34.66 | 23,755 | 2.46 | 1126 |
| Cantonese | 12.96 | 6695 | 1.63 | 961 | |
| Hokkien | 7.74 | 9967 | 0.69 | 1074 |
| Model | CER(%) | SER(%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese Test Data | Tibetan Data | |||||
| Mandarin | Cantonese | Hokkien | Ü-Tsang | Amdo | Kham | |
| Single-dialect Transformer | 32.72 | 63.20 | 94.43 | 14.96 | 8.90 | 107.73 |
| Multi-dialect Transformer | 25.44 | 13.05 | 52.97 | 8.96 | 4.26 | 24.33 |
| Hard-MTL Transformer | 34.78 | 13.96 | 60.15 | 9.53 | 4.74 | 40.64 |
| Soft-MTL Transformer | 23.31 | 11.44 | 53.74 | 7.86 | 3.07 | 29.40 |
| CER(%) | SER(%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese Test Data | Tibetan Test Data | |||||
| Mandarin | Cantonese | Hokkien | Ü-Tsang | Amdo | Kham | |
| Manually weighting | 23.31 | 11.44 | 53.74 | 7.86 | 3.07 | 29.40 |
| Uncertainty weighting [22] | 48.13 | 32.49 | 66.03 | 12.88 | 8.51 | 42.27 |
| DWA [23] | 46.31 | 24.16 | 54.37 | 12.06 | 6.67 | 44.22 |
| Adaptive Soft-MTL Transformer | 24.06 | 11.22 | 51.36 | 5.67 | 2.70 | 26.48 |
| Model | Recognition Accuracy(%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese Test Data | Tibetan Test Data | |||||
| Mandarin | Cantonese | Hokkien | Ü-Tsang | Amdo | Kham | |
| Hard-MTL Transformer | 99.73 | 99.19 | 98.21 | 99.38 | 99.58 | 99.32 |
| Soft-MTL Transformer | 99.93 | 99.71 | 97.87 | 99.73 | 99.86 | 96.62 |
| Adaptive Soft-MTL Transformer | 99.73 | 99.34 | 97.31 | 99.85 | 99.91 | 100.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dan, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Bi, X.; Wu, L.; Ji, Q. Multi-Task Transformer with Adaptive Cross-Entropy Loss for Multi-Dialect Speech Recognition. Entropy 2022, 24, 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24101429
Dan Z, Zhao Y, Bi X, Wu L, Ji Q. Multi-Task Transformer with Adaptive Cross-Entropy Loss for Multi-Dialect Speech Recognition. Entropy. 2022; 24(10):1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24101429
Chicago/Turabian StyleDan, Zhengjia, Yue Zhao, Xiaojun Bi, Licheng Wu, and Qiang Ji. 2022. "Multi-Task Transformer with Adaptive Cross-Entropy Loss for Multi-Dialect Speech Recognition" Entropy 24, no. 10: 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24101429
APA StyleDan, Z., Zhao, Y., Bi, X., Wu, L., & Ji, Q. (2022). Multi-Task Transformer with Adaptive Cross-Entropy Loss for Multi-Dialect Speech Recognition. Entropy, 24(10), 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24101429







