The Diagnosis of Congestive Heart Failure Based on Generalized Multiscale Entropy-Wavelet Leaders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
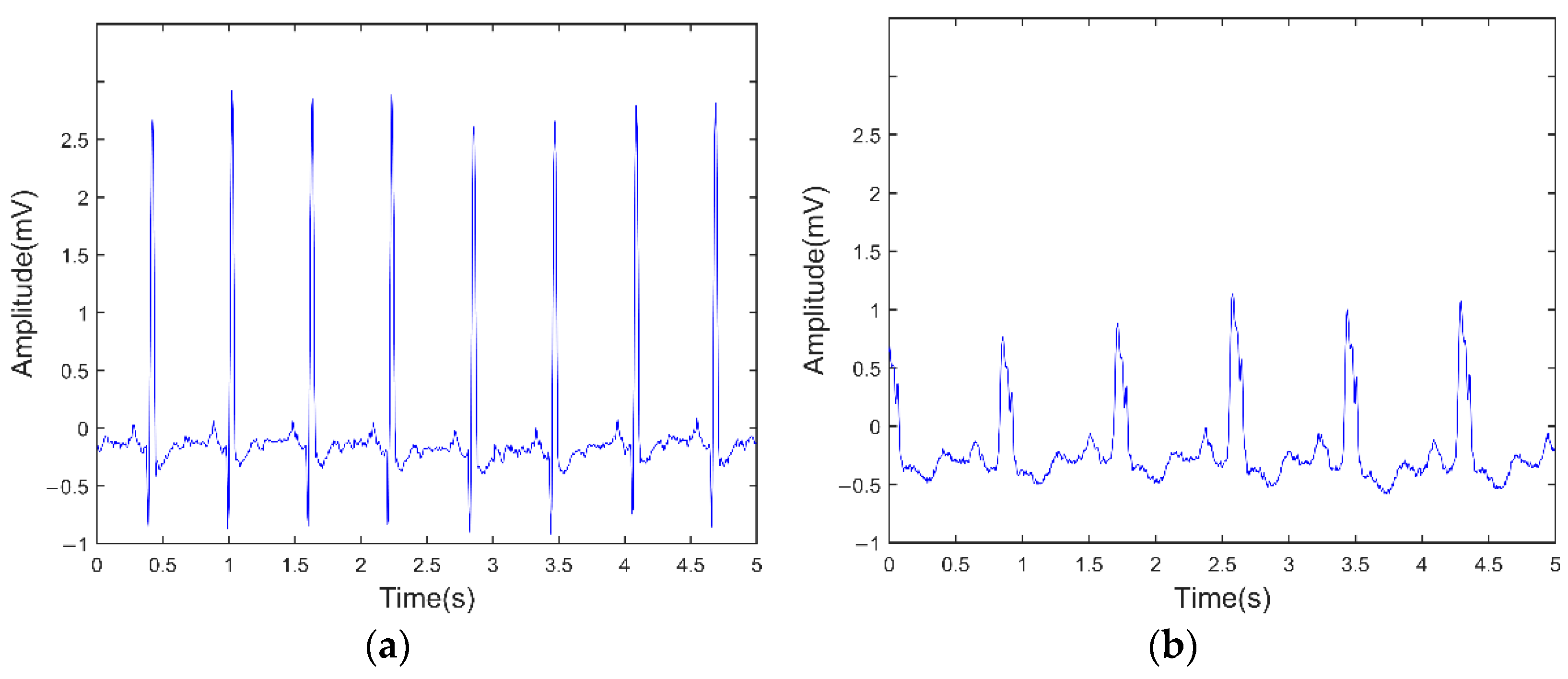
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
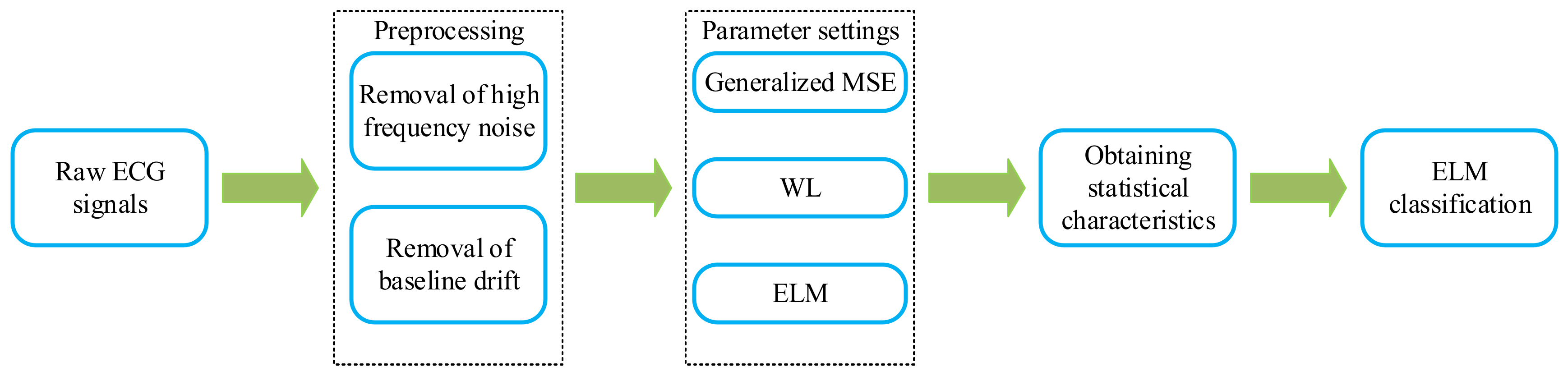
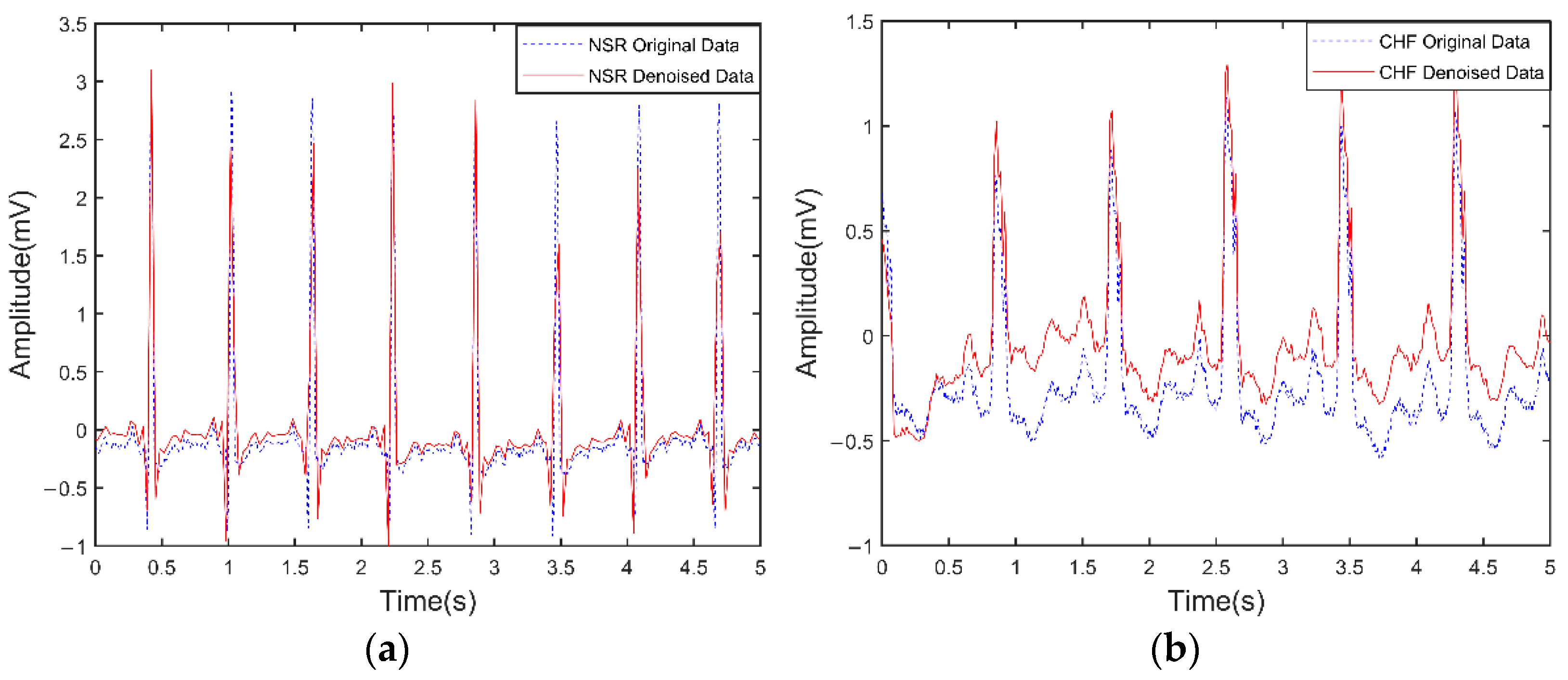
2.2.1. Pre-Processing
2.2.2. Multiscale Entropy Algorithm with the First Moment
2.2.3. Multiscale Entropy Algorithm with the Second Moment
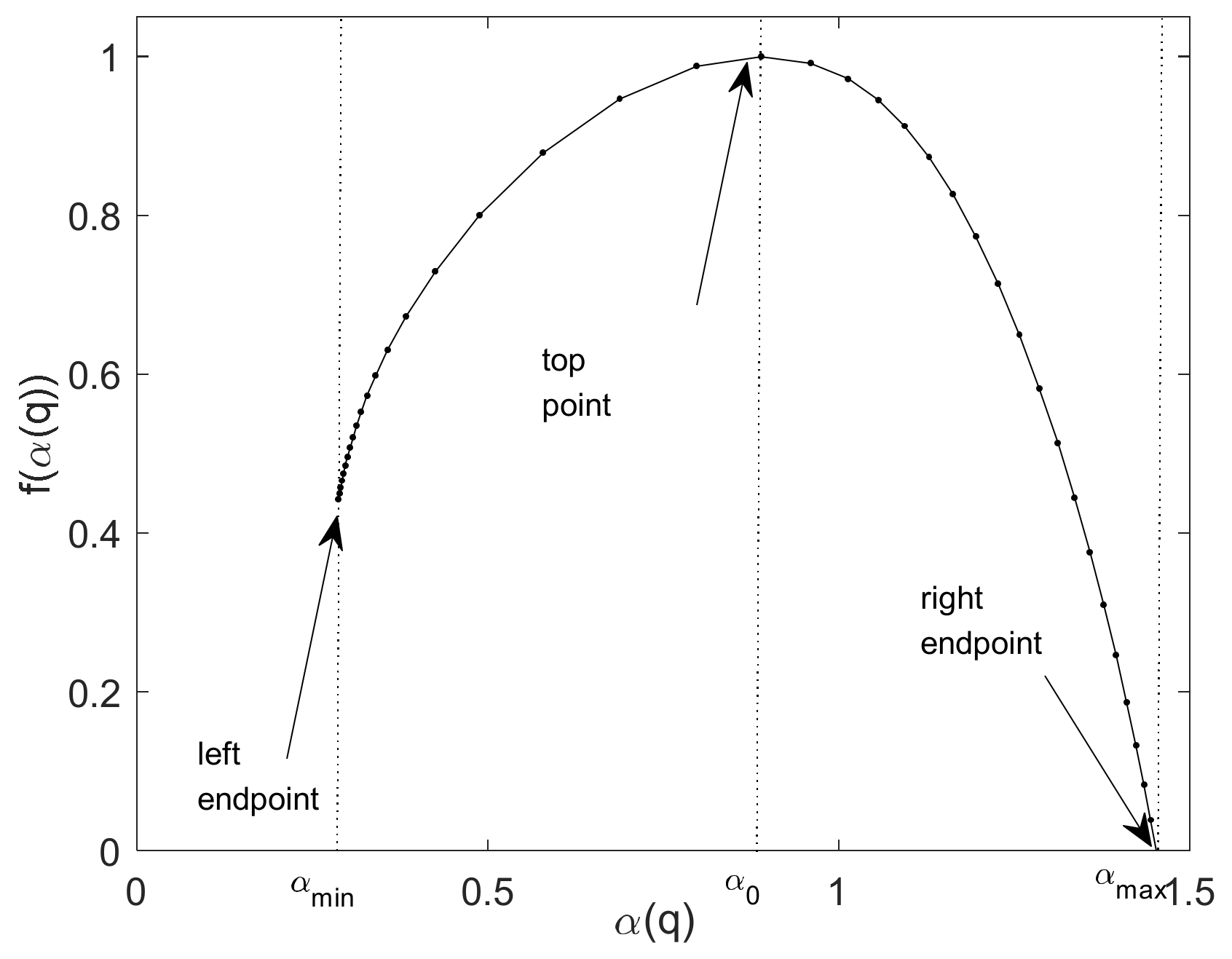
2.2.4. Wavelet Leaders Method
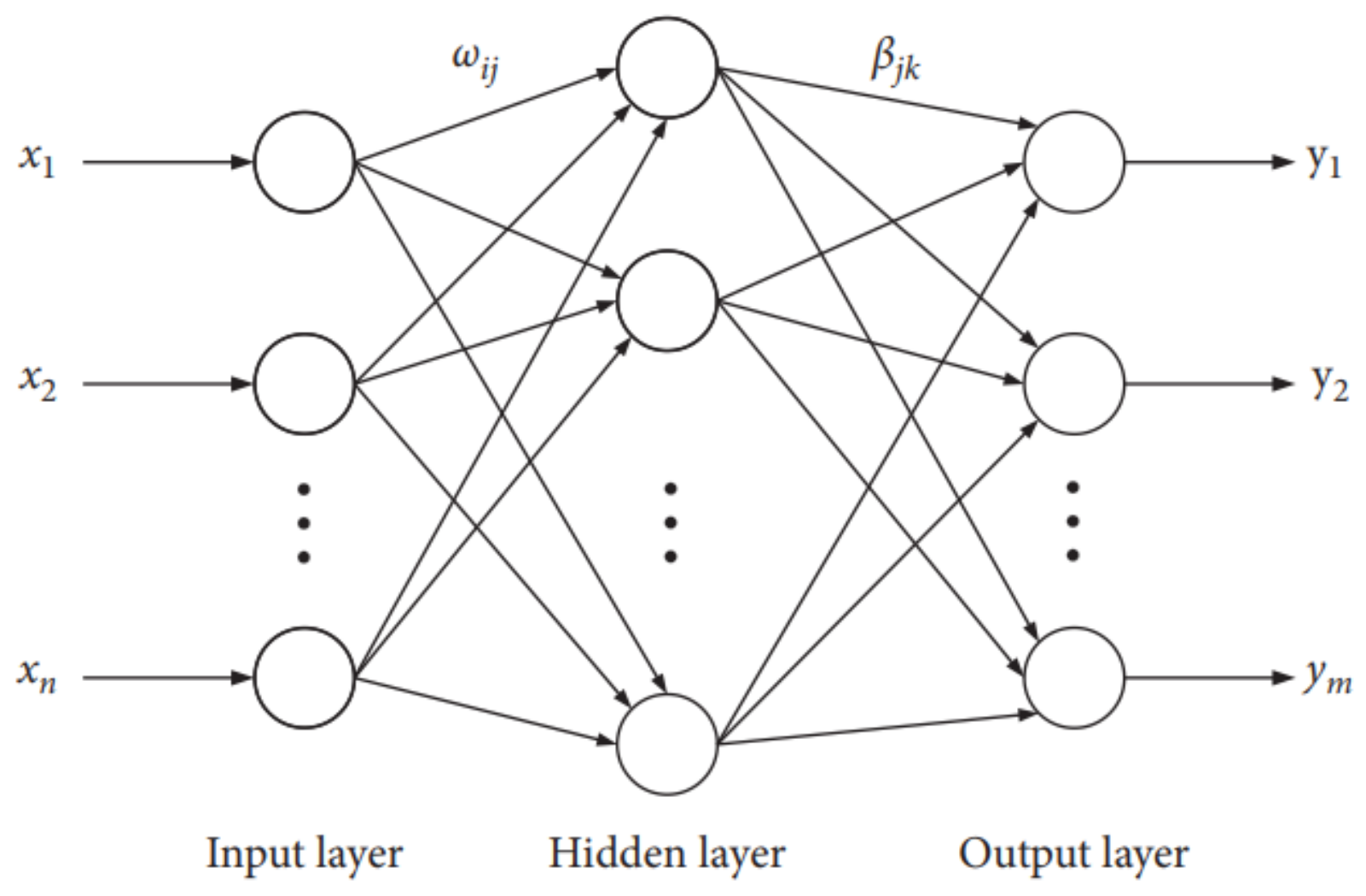
2.2.5. Extreme Learning Machine
2.2.6. K-Fold Cross-Validation
2.2.7. Evaluation Criteria
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of Parameter Settings
3.1.1. Embedded Dimensions
3.1.2. Segmentation Time
3.1.3. Scale Factor
3.1.4. Similarity Tolerance
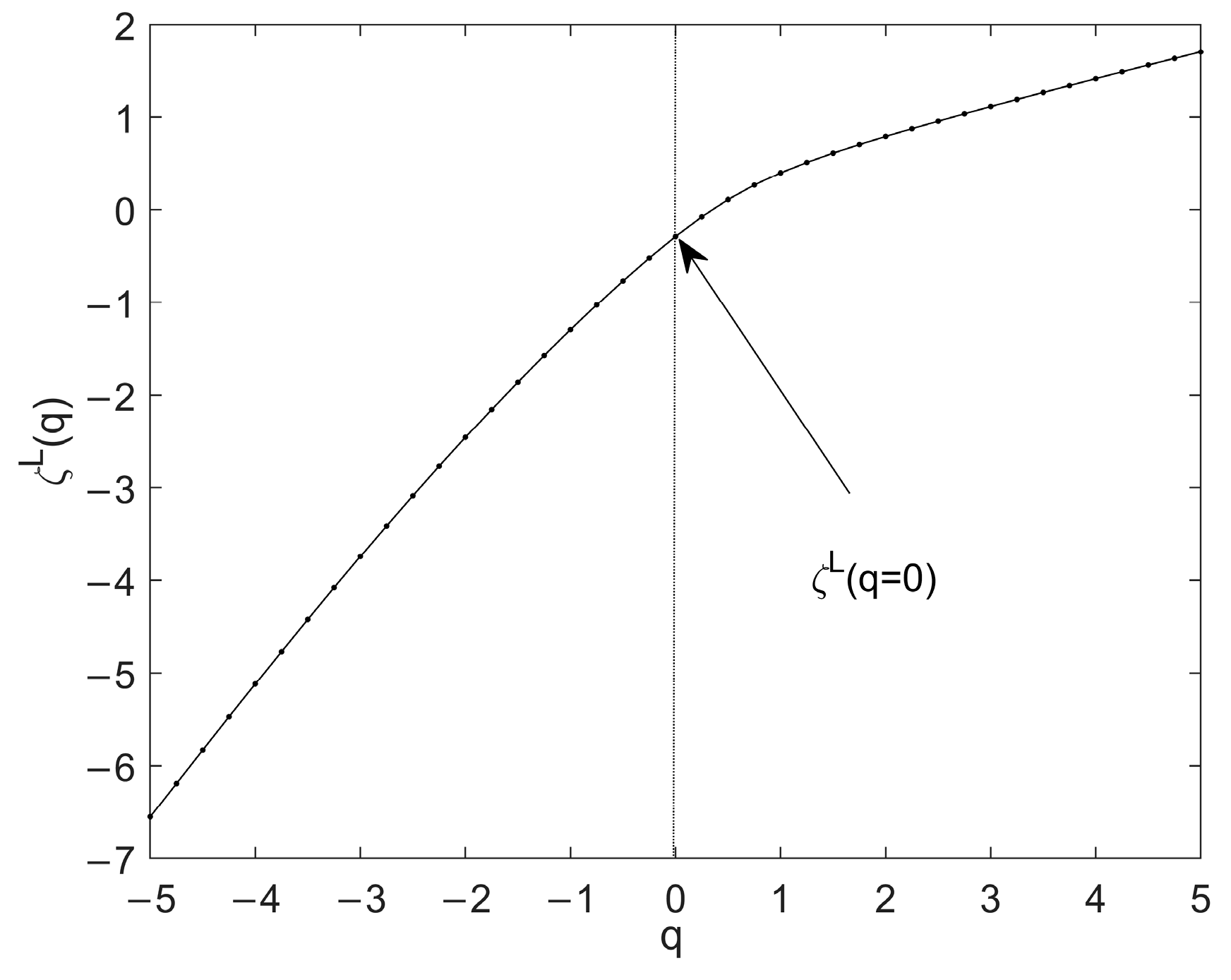
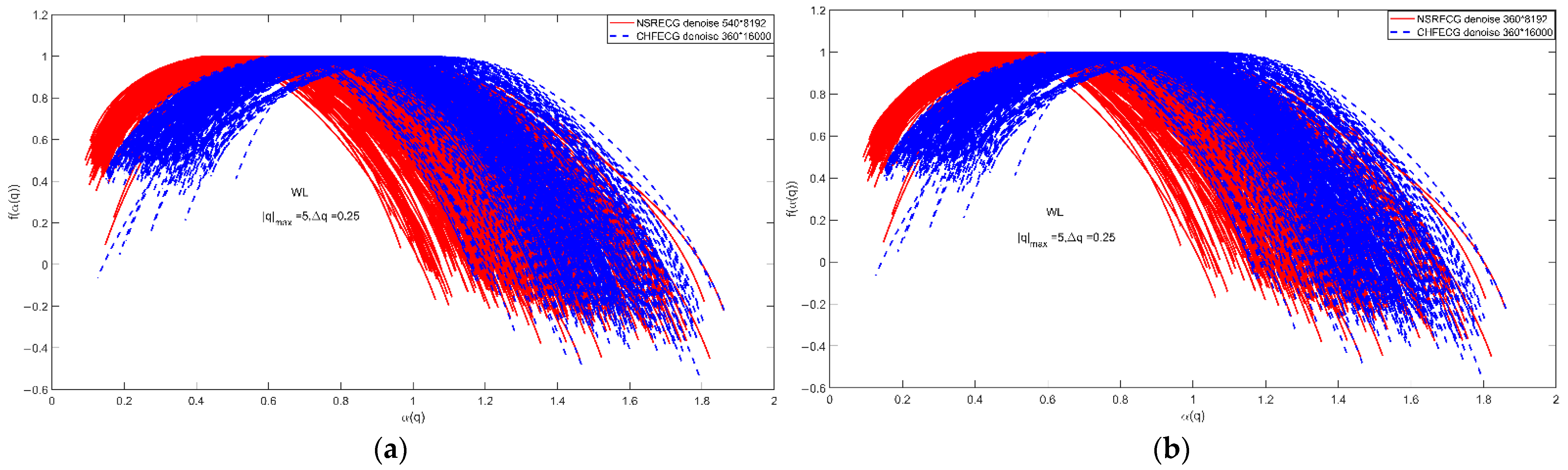
3.1.5. Multifractal Spectrum Features
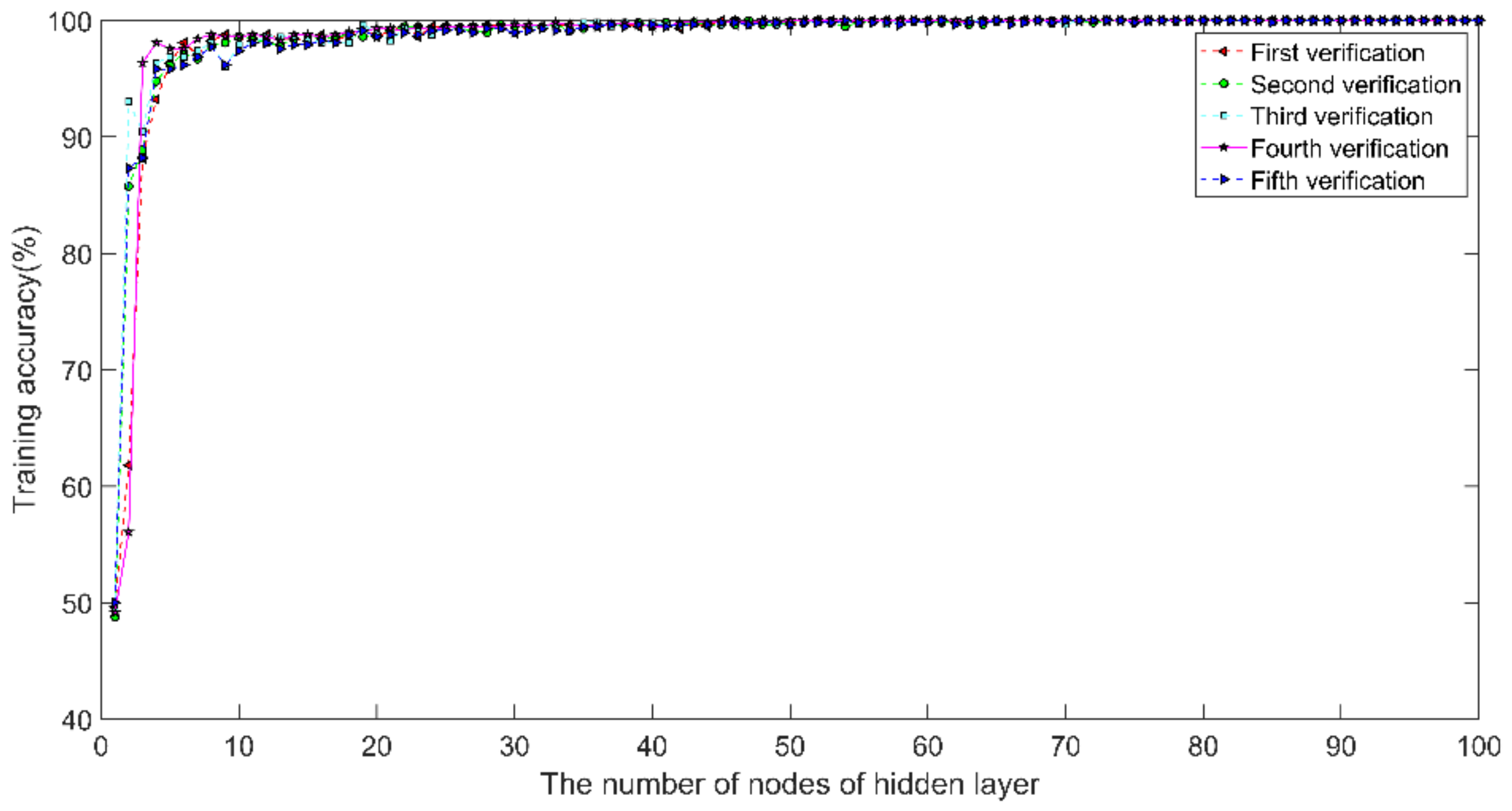
3.1.6. Number of ELM Hidden Layer Nodes
3.2. Training and Test of the CHF Classifier
3.2.1. Results of Classification
3.2.2. Results of Adding Data Segments
3.2.3. Comparison Results of Different Algorithms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Acharya, U.R.; Fujita, H.; Lih, O.S.; Adam, M.; Tan, J.H.; Chua, C.K. Automated Detection of Coronary Artery Disease Using Different Durations of ECG Segments with Convolutional Neural Network. Knowl. Based Syst. 2017, 132, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, A.; Shah, K.; Hough, O.; Hynynen, K. Focused Ultrasound-Mediated Drug Delivery through the Blood–Brain Barrier. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2015, 15, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gladding, P.; Cave, A.; Zareian, M.; Smith, K.; Hussan, J.; Hunter, P.; Erogbogbo, F.; Aguilar, Z.; Martin, D.; Chan, E.; et al. Open Access Integrated Therapeutic and Diagnostic Platforms for Personalized Cardiovascular Medicine. JPM 2013, 3, 203–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costa, M.; Goldberger, A.L.; Peng, C.-K. Multiscale Entropy Analysis of Complex Physiologic Time Series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 068102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costa, M.; Goldberger, A.L.; Peng, C.-K. Multiscale Entropy Analysis of Biological Signals. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 71, 021906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.-D.; Wu, C.-W.; Lin, S.-G.; Lee, K.-Y.; Peng, C.-K. Analysis of Complex Time Series Using Refined Composite Multiscale Entropy. Phys. Lett. A 2014, 378, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humeau-Heurtier, A. The Multiscale Entropy Algorithm and Its Variants: A Review. Entropy 2015, 17, 3110–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Hu, J.; Liu, F.; Cao, Y. Multiscale Entropy Analysis of Biological Signals: A Fundamental Bi-Scaling Law. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, M.; Goldberger, A. Generalized Multiscale Entropy Analysis: Application to Quantifying the Complex Volatility of Human Heartbeat Time Series. Entropy 2015, 17, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Gao, R. Multiscale Entropy Analysis of the Differential RR Interval Time Series Signal and Its Application in Detecting Congestive Heart Failure. Entropy 2017, 19, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, K.; Maghsoudi, F. Classification of 7 Arrhythmias from ECG Using Fractal Dimensions. J. Bioinform. Syst. Biol. 2019, 2, 053–065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowiec, D.; Dudkowska, A.; Galaska, R.; Rynkiewicz, A. Multifractal Analysis of Normal RR Heart-Interbeat Signals in Power Spectra Range. 2007. Available online: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.q-bio/0702047 (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Chakraborty, M.; Das, T.; Ghosh, D. Comparative Analysis of Different Fractal Methods in Studying Post-Ictal ECG Signals of Epilepsy Patient. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE First International Conference on Control, Measurement and Instrumentation (CMI), Kolkata, India, 8–10 January 2016; IEEE: Kolkata, India, 2016; pp. 219–223. [Google Scholar]
- Piña-Vega, R.; Valtierra-Rodriguez, M.; Perez-Ramirez, C.A.; Amezquita-Sanchez, J.P. EARLY PREDICTION OF SUDDEN CARDIAC DEATH USING FRACTAL DIMENSION AND ECG SIGNALS. Fractals 2021, 29, 2150077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, E.; Figliola, A. Wavelet Leaders: A New Method to Estimate the Multifractal Singularity Spectra. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2009, 388, 2793–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahmunah, V.; Oh, S.L.; Wei, J.K.E.; Ciaccio, E.J.; Chua, K.; San, T.R.; Acharya, U.R. Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Congestive Heart Failure Using ECG Signals—A Review. Phys. Med. 2019, 62, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acharya, U.R.; Fujita, H.; Oh, S.L.; Hagiwara, Y.; Tan, J.H.; Adam, M.; Tan, R.S. Deep Convolutional Neural Network for the Automated Diagnosis of Congestive Heart Failure Using ECG Signals. Appl. Intell. 2019, 49, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baim, D.S.; Colucci, W.S.; Monrad, E.S.; Smith, H.S.; Wright, R.F.; Lanoue, A.; Gauthier, D.F.; Ransil, B.J.; Grossman, W.; Braunwald, E. Survival of Patients with Severe Congestive Heart Failure Treated with Oral Milrinone. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1986, 7, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldberger, A.L.; Amaral, L.A.N.; Glass, L.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Ivanov, P.C.; Mark, R.G.; Mietus, J.E.; Moody, G.B.; Peng, C.-K.; Stanley, H.E. PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: Components of a New Research Resource for Complex Physiologic Signals. Circulation 2000, 101, E215–E220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.; Shen, C.; Chen, L. Deep Fault Recognizer: An Integrated Model to Denoise and Extract Features for Fault Diagnosis in Rotating Machinery. Appl. Sci. 2016, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Tmeme, A.; Woo, W.L.; Dlay, S.S.; Gao, B. Underdetermined Convolutive Source Separation Using GEM-MU With Variational Approximated Optimum Model Order NMF2D. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2017, 25, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Nima, R.R.O.; Abdullah, M.A.M.; Al-Kaltakchi, M.T.S.; Dlay, S.S.; Woo, W.L.; Chambers, J.A. Finger Texture Biometric Verification Exploiting Multi-Scale Sobel Angles Local Binary Pattern Features and Score-Based Fusion. Digit. Signal Process. 2017, 70, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Tomar, H.; Mehla, V.K.; Komaragiri, R.; Kumar, M. Stationary Wavelet Transform Based ECG Signal Denoising Method. ISA Trans. 2021, 114, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurek, S.; Grabowski, W.; Kosmider, M.; Jurga, S.; Guzik, P.; Piskorski, J. Bootstrapping the Empirical Bounds on the Variability of Sample Entropy in 24-Hour ECG Recordings for 1 Hour Segments. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Mech. 2018, 17, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouahabi, A.; Femmam, S. Wavelet-Based Multifractal Analysis of 1-D and 2-D Signals: New Results. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2011, 69, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonarduzzi, R.; Wendt, H.; Jaffard, S.; Roux, S.G.; Torres, M.E.; Abry, P. Extending Multifractal Analysis to Negative Regularity: P-Exponents and P-Leaders. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Florence, Italy, 4–9 May 2014; IEEE: Florence, Italy, 2014; pp. 305–309. [Google Scholar]
- Jaffard, S.; Melot, C.; Leonarduzzi, R.; Wendt, H.; Abry, P.; Roux, S.G.; Torres, M.E. P-Exponent and p-Leaders, Part I: Negative Pointwise Regularity. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2016, 448, 300–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mallat, S. A wavelet tour of signal processing. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 1998, 628, 998. [Google Scholar]
- Wendt, H.; Roux, S.G.; Jaffard, S.; Abry, P. Wavelet Leaders and Bootstrap for Multifractal Analysis of Images. Signal Process. 2009, 89, 1100–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kantelhardt, J.W. Fractal and Multifractal Time Series. 2008. Available online: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.0804.0747 (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Ihlen, E.A.F. Multifractal Analyses of Response Time Series: A Comparative Study. Behav. Res. 2013, 45, 928–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.-B.; Zhu, Q.-Y.; Siew, C.-K. Extreme Learning Machine: Theory and Applications. Neurocomputing 2006, 70, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xi, C. Rolling Bearing Fault Diagnosis Based on MFDFA-SPS and ELM. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 4034477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richman, J.S.; Moorman, J.R. Physiological Time-Series Analysis Using Approximate Entropy and Sample Entropy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 278, H2039–H2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leonarduzzi, R.; Wendt, H.; Abry, P.; Jaffard, S.; Melot, C.; Roux, S.G.; Torres, M.E. P-Exponent and p-Leaders, Part II: Multifractal Analysis. Relations to Detrended Fluctuation Analysis. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2016, 448, 319–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffard, S.; Abry, P.; Roux, S. Function Spaces Vs. Scaling Functions: Tools for Image Classification. In Mathematical Image Processing; Springer Proceedings in Mathematics; Bergounioux, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 5, pp. 1–39. ISBN 978-3-642-19603-4. [Google Scholar]
- Abry, P.; Jaffard, S.; Wendt, H. Irregularities and Scaling in Signal and Image Processing: Multifractal Analysis. In Fractals and Dynamics in Mathematics, Science, and the Arts: Theory and Applications; World Scientific: Singapore, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 31–116. ISBN 978-981-4366-06-9. [Google Scholar]
- Daqrouq, K.; Dobaie, A. Wavelet Based Method for Congestive Heart Failure Recognition by Three Confirmation Functions. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2016, 2016, 7359516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sudarshan, V.K.; Acharya, U.R.; Oh, S.L.; Adam, M.; Tan, J.H.; Chua, C.K.; Chua, K.P.; Tan, R.S. Automated Diagnosis of Congestive Heart Failure Using Dual Tree Complex Wavelet Transform and Statistical Features Extracted from 2 s of ECG Signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 83, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xia, M. An Effective Method for CHF Diagnosis via Attention-Based RNN Using ECG Signals. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Communication, Image and Signal Processing (CCISP), Chengdu, China, 13–15 November 2020; IEEE: Chengdu, China, 2020; pp. 209–213. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Si, Y.; Yang, W.; Huang, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, R. Inter-Patient Congestive Heart Failure Detection Using ECG-Convolution-Vision Transformer Network. Sensors 2022, 22, 3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, T.; Wei, K.; Liu, G.; Liu, B. Similarity Changes Analysis for Heart Rate Fluctuation Regularity as a New Screening Method for Congestive Heart Failure. Entropy 2021, 23, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, C.; Liu, R. Detection of Small Floating Target on Sea Surface Based on Gramian Angular Field and Improved EfficientNet. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Number of 64 s ECG Segments | ||
|---|---|---|
| Type (Database) | Unbalanced | Balanced |
| A | B | |
| Normal (NSR) | 540 | 360 |
| CHF (BIDMC) | 360 | 360 |
| Number of ELM Hidden Layer Nodes (%) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K-Fold | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 60 | 65 | 70 |
| 1 | 98.61 | 99.48 | 98.96 | 99.65 | 99.65 | 100 | 99.65 | 99.83 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 2 | 98.78 | 99.48 | 99.48 | 99.31 | 99.48 | 99.65 | 99.83 | 99.83 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 3 | 98.96 | 99.48 | 99.65 | 99.83 | 99.83 | 99.65 | 99.65 | 99.83 | 100 | 99.83 | 99.65 |
| 4 | 99.31 | 99.48 | 99.65 | 99.48 | 99.48 | 99.83 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 5 | 98.61 | 99.13 | 98.96 | 99.48 | 99.65 | 99.83 | 99.65 | 99.83 | 99.83 | 100 | 100 |
| Predicted | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | CHF | ACC (%) | PPV (%) | SEN (%) | SPEC (%) | F1 (%) | ||
| Original | Normal | 539 | 1 | 99.56 | 99.44 | 99.81 | 99.17 | 99.62 |
| CHF | 3 | 357 | ||||||
| Predicted | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | CHF | ACC (%) | PPV (%) | SEN (%) | SPEC (%) | F1 (%) | ||
| Original | Normal | 360 | 0 | 99.72 | 99.46 | 100 | 99.44 | 99.73 |
| CHF | 2 | 358 | ||||||
| Dataset | TP | TN | FP | FN | ACC (%) | PPV (%) | SEN (%) | SPEC (%) | F1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 539 | 357 | 3 | 1 | 99.56 | 99.44 | 99.81 | 99.17 | 99.62 |
| C | 1789 | 1486 | 14 | 11 | 99.24 | 99.22 | 99.39 | 99.07 | 99.30 |
| D | 7153 | 5969 | 31 | 47 | 99.41 | 99.57 | 99.35 | 99.48 | 99.46 |
| Dataset | Running Time (s) |
|---|---|
| A | 731.45 |
| C | 3107.80 |
| D | 11,825.24 |
| Algorithm | Fold1 (%) | Fold2 (%) | Fold3 (%) | Fold4 (%) | Fold5 (%) | OA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Generalized MSE + ELM | 92.22 | 98.33 | 97.22 | 96.11 | 95.00 | 95.78 |
| WL + ELM | 98.33 | 99.44 | 98.33 | 97.78 | 99.44 | 98.67 |
| Generalized MSE-WL + KNN | 95.00 | 98.33 | 95.00 | 97.78 | 97.22 | 96.67 |
| Generalized MSE-WL + SVM | 97.22 | 97.78 | 97.22 | 96.67 | 96.11 | 97.00 |
| Generalized MSE-WL + ELM (Set A) | 99.44 | 100 | 100 | 98.89 | 99.44 | 99.56 |
| Reference | Year | Number of ECG Data | Method | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daqroup and Dobaie [38] | 2016 | CHF: 140 Normal: 152 | ▪Wavelet Packet Transform ▪Feature Extraction | Acc—92.60% |
| Sundarshan et al. [39] | 2017 | CHF: 25,328 Normal: 59,624 CHF: 25,328 Normal: 25,328 | ▪Denoising and baseline removal ▪Dual tree complex wavelet transform ▪KNN classifier (2-s ECG segment) | Acc—98.42% Sen—97.04% Spec—99.01% Acc—97.94% Sen—98.19% Spec—97.69% |
| Acharya et al. [17] | 2018 | CHF: 30,000 Normal: 70,308 CHF: 30,000 Normal: 30,000 | ▪KNN classifier ▪11-layer deep CNN (2-s ECG segment) | Acc—95.98% Sen—96.52% Spec—95.75% Acc—94.40% Sen—94.68% Spec—94.12% |
| Jahmunah et al. [16] | 2019 | CHF: 30,000 Normal: 70,308 CHF: 30,000 Normal: 30,000 | ▪Fuzzy entropy ▪Rényi entropy ▪Higuchi Fractal Dimension ▪Kraskov entropy, energy ▪Frequency localized filter banks ▪Quadratic support vector machine (QSVM) ▪10-fold cross validation (2-s ECG segment) | Acc: > 99.66% Sen: > 99.82% Spec: > 99.28% |
| Yue Zhang and Ming Xia [40] | 2020 | CHF: 53,857 Normal: 58,675 | ▪Detected R peaks ▪RNN | Acc = 99.17% Sen = 99.40% Spec = 98.96% |
| Taotao Liu et al. [41] | 2022 | CHF: 36,000 Normal: 30,000 | ▪Feature Extraction ▪ECVT-Net ▪CNN | Acc: 98.88% Pre: 98.84% Sen: 98.94% |
| Zeming Liu et al. [42] | 2022 | 1 min length of RR segment | ▪Multi-feature—fApEn_IBS + IBS + LF/HF ▪Random Forces | Acc = 99.0% Sen = 97.8% Spec = 100.0% |
| Proposed Method | 2022 | CHF: 540 Normal: 360 CHF: 360 Normal: 360 | ▪The generalized multiscale entropy (MSE) ▪Wavelet leaders (WL) ▪ELM classifier (64-s ECG segment) | Acc—99.56% Sen—99.81% Spec—99.17% Acc—99.72% Sen—100% Spec—99.44% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Xi, C. The Diagnosis of Congestive Heart Failure Based on Generalized Multiscale Entropy-Wavelet Leaders. Entropy 2022, 24, 1763. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24121763
Yang J, Xi C. The Diagnosis of Congestive Heart Failure Based on Generalized Multiscale Entropy-Wavelet Leaders. Entropy. 2022; 24(12):1763. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24121763
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Juanjuan, and Caiping Xi. 2022. "The Diagnosis of Congestive Heart Failure Based on Generalized Multiscale Entropy-Wavelet Leaders" Entropy 24, no. 12: 1763. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24121763
APA StyleYang, J., & Xi, C. (2022). The Diagnosis of Congestive Heart Failure Based on Generalized Multiscale Entropy-Wavelet Leaders. Entropy, 24(12), 1763. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24121763






