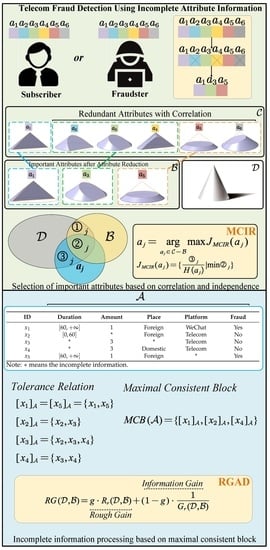
TFD-IIS-CRMCB: Telecom Fraud Detection for Incomplete Information Systems Based on Correlated Relation and Maximal Consistent Block
Abstract
Share and Cite
Li, R.; Chen, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, K.; Wang, B.; Hu, X. TFD-IIS-CRMCB: Telecom Fraud Detection for Incomplete Information Systems Based on Correlated Relation and Maximal Consistent Block. Entropy 2023, 25, 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25010112
Li R, Chen H, Liu S, Wang K, Wang B, Hu X. TFD-IIS-CRMCB: Telecom Fraud Detection for Incomplete Information Systems Based on Correlated Relation and Maximal Consistent Block. Entropy. 2023; 25(1):112. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25010112
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ran, Hongchang Chen, Shuxin Liu, Kai Wang, Biao Wang, and Xinxin Hu. 2023. "TFD-IIS-CRMCB: Telecom Fraud Detection for Incomplete Information Systems Based on Correlated Relation and Maximal Consistent Block" Entropy 25, no. 1: 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25010112
APA StyleLi, R., Chen, H., Liu, S., Wang, K., Wang, B., & Hu, X. (2023). TFD-IIS-CRMCB: Telecom Fraud Detection for Incomplete Information Systems Based on Correlated Relation and Maximal Consistent Block. Entropy, 25(1), 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25010112