Complexity and Entropy in Physiological Signals (CEPS): Resonance Breathing Rate Assessed Using Measures of Fractal Dimension, Heart Rate Asymmetry and Permutation Entropy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Objectives
- To conduct brief literature reviews on fractal dimension (FD) and HRA measures, and a more extensive review on resonance breathing.
- To use CEPS and DynamicalSystems.jl to analyse RRi, respiration and EDA data, and to compare results.
- To compare findings when using a variety of CEPS FD, HRA and measures based on permutation entropy (among others) to investigate whether there are marked differences between the effects of paced, self-paced and non-paced breathing on such physiological data—for example, which measures are most/least responsive to changes in breathing rate.
- To examine changes and agreement in key measures between baseline or self-paced breathing and optimal (or ‘resonance’) breathing, and explore questions such as ‘do people breathe naturally at their ideal rate?’
- To investigate the effects of parameter tuning on these measures in this context.
- To update the online CEPS ‘Primer’ and Manual to take changes in CEPS into account.
- To assess whether and which complexity and entropy measures applied to RRi and respiration data may be more effective at differentiating between resonance breathing and other breathing states than some of the more conventional HRV indices.
- To examine briefly whether age, sex, perceived stress (‘Distress’ and its converse, ‘Coping’), ‘Mindful awareness’ and two dimensions of interoceptive awareness (‘Noticing’, or awareness of body sensations, and ‘Attention regulation’, or the ability to sustain and control attention to body sensation), as well as a third dimension, ‘Self-Regulation’, may affect how CEPS measures reflect breathing state.
- To explore correlations within ‘families’ of measures, and between individual measures when applied to different data types (RRi, respiration and EDA).
- To investigate the effects of different data lengths on standard HRV and CEPS measures, with a view to determining the shortest data length that is feasible for use in further research on self-training methods of stress management.
- To explore how modifying the data in different ways (interpolation or deduplication, resampling, detrending, normalisation, multi-scaling, addition of noise) affects HRV and CEPS measures, and whether some of these methods may in fact compensate for the effects of shortening data length.
- In conclusion, to determine which measures are most useful for differentiating between resonance breathing and other breathing states, while also performing well for short data.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Reviews
2.1.1. Fractal Dimension (FD) and Heart Rate Asymmetry (HRA) Measures
Fractal Dimension
Heart Rate Asymmetry (HRA)
2.1.2. Resonance Breathing and Vagally-Mediated Heart Rate Variability (vmHRV)
2.2. Study Protocol
2.2.1. Resonant Breathing Rate Selection Using Paced Breathing
2.2.2. Ethics
COVID Risk Mitigation
2.2.3. Participants
2.2.4. Data Collection
2.2.5. Software and Data Processing
Updating CEPS for This Project
Comparison with Estimators from DynamicalSystems.jl
Other Software Used
2.2.6. Data Processing
2.2.7. Data Pre-Processing and Modification
Detrending
Data Segmentation (‘Cut Files’)
Adding Noise (‘Add Noise’)
Interpolation
Equal Resampling, Using ‘Shape-Preserving Piecewise Cubic Spline Interpolation’
2.2.8. Parameter Selection
2.2.9. Statistical Analysis
Data Distribution
Analysis of Variance 1. Welch’s ANOVA
Analysis of Variance 2. Friedman Tests, Kendall’s W and Conover Tests
Assessing Agreement. Intraclass Correlation Coefficients (ICCs) and Simple Correlations
Combining the Results of Conover Tests and ICCs
- CEPS and RR-APET measures for non-resampled RRi data;
- CEPS and DynamicalSystems.jl measures for RRi data resampled at 4 Hz;
- CEPS measures for RRi data resampled at 10 Hz;
- CEPS and DynamicalSystems.jl measures for detrended and deduplicated EDA data.
Effects of Age, Sex, Perceived Stress and Other Trait and State Measures
Correlations within ‘Families’ of Measures, and between Individual Measures
3. Results
3.1. Normality of Data
3.2. Data Resampling and Modification
3.2.1. The Effects of Data Resampling on CEPS Measures
3.2.2. The Effects of Data Modification—Mitigating for the Effects of Data Segmentation (Shortening)
3.3. Parameter Tuning
3.4. CEPS, DynamicalSystems.jl and Other Analysis of RRi, Respiration and EDA Data
3.4.1. Five-Minute ECG RRi Data—CEPS, DynamicalSystems.jl and Kubios HRV Analysis
Post-Hoc Analysis
3.4.2. Respiration Data—CEPS Analysis Only
3.4.3. EDA Data—CEPS and DynamicalSystems.jl Analysis
3.4.4. Summary of Results for RRi, Respiration and EDA Data
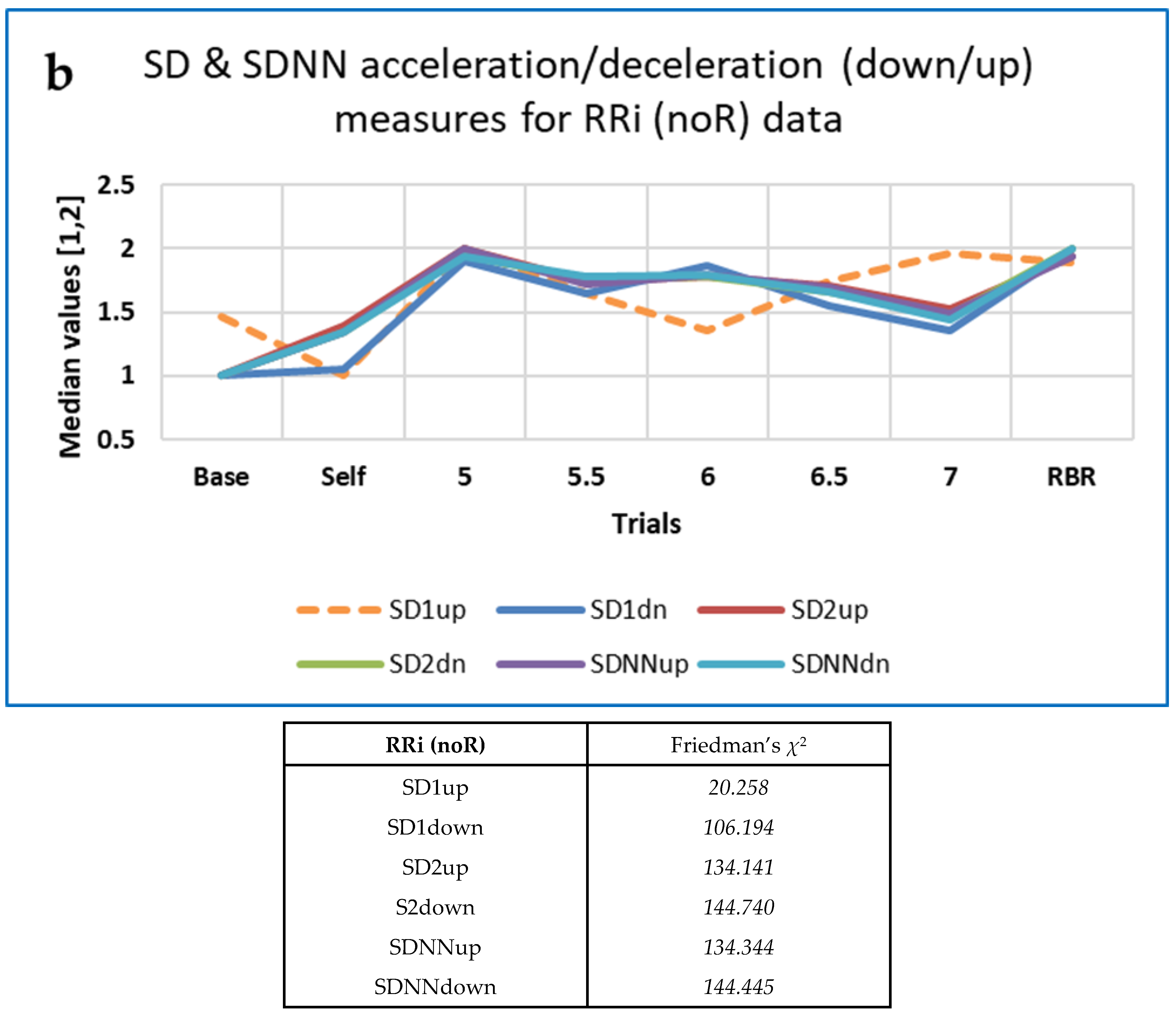
3.4.5. Some Findings on Heart Rate Asymmetry (HRA)
Correlations between HRA Indices and HRV Measures
Respiration and Asymmetry
3.4.6. Difference and Agreement between Baseline or Self-Paced Breathing and Optimal (or ‘Resonance’) Breathing or Breathing at 5 BrPM: Do Measure Values during Slow Self-Paced Breathing Predict Those of RBR?
3.4.7. Results for Correlations within ‘Families’ of Measures, and between Individual Measures When Applied to Different Data Types (RRi, Respiration and EDA) Are Described in the Supplementary Materials (Section SM5.1)
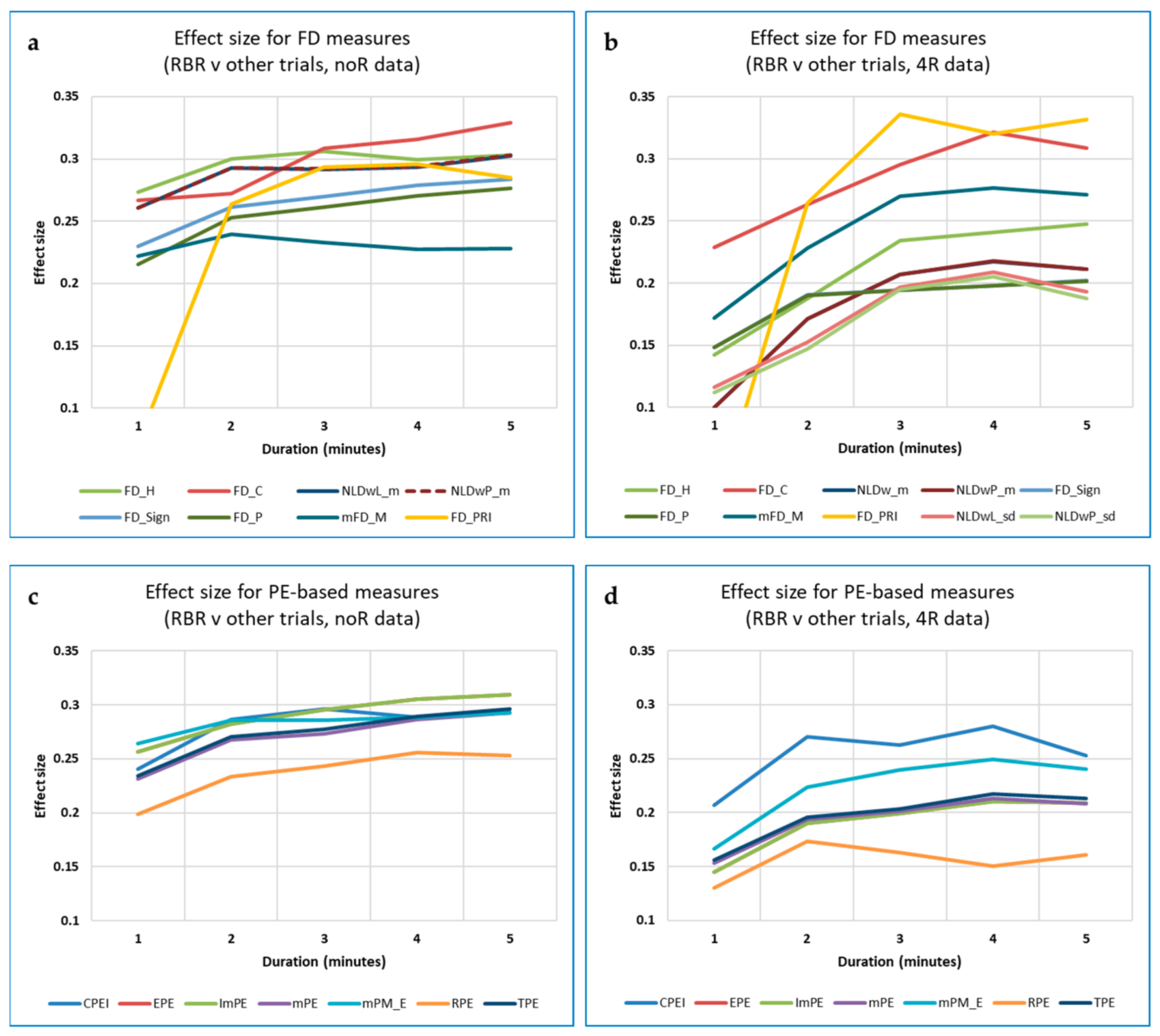
3.5. The Effects of Time
3.5.1. Data Length and Its Effect on Different Measures
Data Length and Differences in Measures between Breathing Rates
Agreements between Measures for Different Data Lengths
3.5.2. Do Nonlinear Measures Indicate RBR More Accurately than Standard HRV Measures, Especially for Short Data?
4. Discussion
4.1. General Points
4.2. Our Basic Approach
4.3. The Anxieties of Data Collection and Collaboration
4.4. Including EDA Results
4.5. An Explanation of HRA Results
4.6. Limitations
4.7. Advantages
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 4R, 10R | Data resampled at 4 Hz or 10 Hz |
| AAPE | Amplitude-aware Permutation Entropy |
| ACR5 | Autocorrelation at lag 5 |
| AE | Average entropy |
| AI | Area Index |
| Alpha1 | See DFA Alpha1 |
| Alpha2 | See DFA Alpha2 |
| ApEn | Approximate entropy |
| AR | Autoregressive |
| ASI | Asymmetric Spread Index |
| AttnEn | Attention entropy |
| AvgApEnP | Average Approximate entropy based on profiling |
| AvgSampEnP | Average Sample entropy based on profiling |
| B_ApEn | Bucket-assisted Approximate entropy |
| B_SampEn | Bucket-assisted Sample entropy |
| BBi | Breath-to-Breath interval |
| BE | Bubble Entropy |
| BrPM | Breaths Per Minute |
| C0 | C0 complexity, a representation of sequence randomness |
| C1a | Relative contribution of accelerations to short-term variance in HRA |
| C1d | Relative contribution of decelerations to short-term variance in HRA |
| C2a | Relative contribution of accelerations to long-term variance in HRA |
| C2d | Relative contribution of decelerations to long-term variance in HRA |
| CAFE | Centred and averaged fuzzy entropy |
| CCM | Complex Correlation Measure |
| CEPS | Complexity and Entropy in Physiological Signals |
| χ2 | “Chi-square” statistic from the non-parametric Friedman test |
| CI | Complexity index |
| CID | Complexity-invariant distance |
| CmSE | Composite multiscale entropy |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| CoSEn | Coefficient of Sample entropy |
| CoSiEn | Cosine Similarity Entropy |
| CPEI | Composite permutation entropy index |
| CV | Coefficient of Variation |
| CVs | Coefficients of Variation |
| D2 | Correlation Dimension |
| DE | Diffusion entropy |
| Dedup | Deduplicated |
| Δ and Δ2 | Fractal dimension estimators in DynamicalSystems.jl |
| DFA | Detrended Fluctuation Analysis |
| DFA Alpha 1 | Detrended Fluctuation Analysis short-term scaling exponent |
| DFA Alpha 2 | Detrended Fluctuation Analysis long-term scaling exponent |
| DiffEn | Differential entropy |
| DistEn | Distribution Entropy |
| DS | DynamicalSystems.jl |
| Dβ | Spectral dimension |
| Dσ | Variance dimension |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| ECG IBI | ECG Interbeat interval |
| EDA | Electrodermal activity |
| EE | Energy entropy |
| EI | Ehlers’ Index |
| EoD | Entropy of difference |
| EPE | Edge Permutation Entropy |
| EPP | Extended Poincaré Plot |
| EPP r1 | Pearson’s r at lag 1 in the Extended Poincaré Plot |
| EPP SD1_2 | SD1 at lag 2 in the Extended Poincaré Plot |
| ES | Effect size |
| ESCHA | Emergence, Self-organization, Complexity, Homeostasis and Autopoiesis (here, only Complexity has been used) |
| ESCHA_c | ESCHA for continuous data |
| ESCHA_d | ESCHA for discrete data |
| FD | Fractal Dimension |
| FD_Amp | Amplitude fractal dimension |
| FD_Box_Moisy | Box-counting fractal dimension, using Moisy’s implementation |
| FD_Box_MvdL | Box-counting fractal dimension, according to Meerwijk and van der Linden |
| FD_C | Castiglioni fractal dimension |
| FD_Dist | Distance fractal dimension |
| FD_H | Higuchi fractal dimension (for which we used ‘HFD’ in our earlier paper [4]) |
| FD_K | Katz fractal dimension |
| FD_LRI | Fractal dimension based on linear regression intersection |
| FD_M | Mandelbrot fractal dimension |
| FD_P | Petrosian fractal dimension |
| FD_PRI | Fractal dimension based on polynomial regression intersection |
| FD_S | Sevcik fractal dimension |
| FD_Sign | Sign fractal dimension |
| FFT | Fast Fourier transform |
| GI | Guzik’s index |
| GPP | Generalised Poincaré Plot |
| GridEn | Grid Entropy (or Gridded Distribution entropy) |
| GUI | Graphical user interface |
| HF | High frequency |
| HFpwr | (Lomb-Scargle)High frequency power, based on the Lomb-Scargle periodogram |
| HFpwr (Welch) | High frequency power, based on the Welch periodogram |
| HR | Heart rate |
| HRA | Heart Rate Asymmetry |
| HRMaxMin | Peak-to-trough difference in heart rate |
| HRV | Heart Rate Variability |
| Hz | Hertz (unit of frequency) |
| ICC | Intraclass Correlation Coefficient |
| ImPE | Improved multiscale Permutation Entropy |
| INbreath | Inbreath data |
| IncrEn | Increment entropy |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| Jitter_Jitt | Local jitter, or average absolute difference in length between two consecutive periods, divided by average period |
| Jitter_Jitta | Absolute jitter, or average absolute difference in length between two consecutive periods |
| Jitter_ppq5 | Average absolute difference between a period and the average of it and the two previous and two subsequent periods, divided by the average period |
| Jitter-RAP | Relative Absolute Perturbation, or average absolute difference between a period and the average of it and its two neighbours, divided by the average period |
| KLD | Kullbach-Leibler Divergence |
| kmax | Maximum interval time used in calculation of FD_H |
| L_ApEn | Lightweight Approximate entropy |
| L_SampEn | Lightweight Sample entropy |
| LF | Low frequency |
| LFBP | Low frequency band power |
| LFpwr | Low frequency power |
| LLE32 | Largest Lyapunov exponent, iteration 32 |
| LS | Lomb-Scargle |
| LZC | Lempel-Ziv complexity |
| LZPC | Lempel Ziv Permutation Complexity |
| m | Order, or embedding dimension |
| MAAS | Mindful Attention Awareness Scale |
| MAIA | Multidimensional Assessment of Interoceptive Awareness |
| MESA | Maximum Entropy Spectral Analysis |
| mFD_M | multiscale fractal dimension, according to Maragos |
| mFmDFA | multifractal multiscale detrended fluctuation analysis |
| mLZC7 | multiscale Lempel-Ziv complexity, at Scale 7 |
| MmSE | Modified multiscale Sample Entropy, at Scale indicated by number following abbreviation |
| mPE | Multiscale Permutation entropy, at Scale indicated by number following abbreviation |
| mPE1 | multiscale Permutation entropy 1 |
| mPhEn | multiscale Phase entropy |
| mPM_E | multiscale Permutation Min-entropy |
| n or N | Number |
| n.p. | Not published |
| NLD | Normalised Length Density (fractal dimension according to Kalauzi) |
| NLDiL_m | NLD based on normalisation of amplitudes for whole signal (mean, using Log model) |
| NLDiL_sd | NLD based on normalisation of amplitudes for whole signal (standard deviation, using Log model) |
| NLDiP_m | NLD fractal dimension based on normalisation of amplitudes for whole signal (mean, using Power model) |
| NLDiP_sd | NLD based on normalisation of amplitudes for whole signal (standard deviation, using Power model) |
| NLDwL_m | NLD based on normalisation of moving window amplitudes (mean, using Log model) |
| NLDwL_sd | NLD based on normalisation of moving window amplitudes (standard deviation, using Log model) |
| NLDwP_m | NLD based on normalisation of moving window amplitudes (mean, using Power model) |
| NLDwP_sd | NLD based on normalisation of moving window amplitudes (standard deviation, using Power model) |
| noR | Non-resampled |
| nu | Normalised units |
| OC | Family of ‘Other Complexity’ measures |
| OE | Family of ‘Other Entropy’ measures |
| ORDO | Open Research Data Online (Open University Repository) |
| OU | Open University |
| OUTbreath | Outbreath data |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| PE | Family of measures based on ‘Permutation entropy’ |
| PI | Porta’s index |
| PJSC | Permutation Jensen-Shannon complexity |
| PLFP | Peak low frequency power |
| PLZC | Permutation Lempel Ziv Complexity |
| pNN50 | percentage of absolute differences in successive ECG NN values > 50 ms |
| PNS | Parasympathetic nervous system index, from Kubios HRV |
| PP | Peak-to-peak |
| PPG | Photoplethysmography |
| PSS | Perceived Stress Scale |
| PTSD | post-traumatic stress disorder |
| QR | Quick response |
| QSE | Quadratic Sample entropy |
| r1 and r2 | See EPP r1 and EPP r2 |
| RBA | Resonant breathing assessment |
| RBR | Resonance breathing rate |
| RCmDE3 | Refined Composite multiscale Dispersion Entropy at lag 3 |
| RE | Rényi entropy |
| RespR | median Outbreath-to-Inbreath ratio |
| rest | Breathing trials other than RBR |
| RMSSD | Root mean square of successive differences between normal heartbeats |
| RoCV | Robust Coefficient of Variation |
| RoSlope | Robust Slope |
| RPDE | Recurrence period density entropy |
| RPE | Rényi Permutation Entropy |
| RQA | Family of measures based on recurrence quantification analysis |
| RQA DET | Recurrence Quantification Analysis: Determinism |
| RQA Lmax | Recurrence Quantification Analysis: Max diagonal line length |
| RQA Lmean | Recurrence Quantification Analysis: Mean diagonal line length |
| RQA RTmax | Recurrence Quantification Analysis: Max recurrence time |
| RQA Vmax | Recurrence Quantification Analysis: Max vertical line length |
| RQA Vmean | Recurrence Quantification Analysis: Mean vertical line length |
| RR-APET | Python-based Heart rate variability analysis software |
| RRi | ECG RR interval |
| RSA | Respiratory sinus arrhythmia |
| RSP | Respiration |
| SampEn | Sample entropy |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SD1 | Standard Deviation of Poincaré Plot scattergram (minor axis) |
| SD1_2 | See EPP SD1_2 |
| SD1down | SD1 for the number of points below the Poincaré Plot line of identity |
| SD1up | SD1 for the number of points above the Poincaré Plot line of identity |
| SD2 | Standard Deviation of Poincaré Plot scattergram (major axis) |
| SD2down | SD2 for the number of points below the Poincaré Plot line of identity |
| SD2up | SD2 for the number of points above the Poincaré Plot line of identity |
| SDNN | Standard deviation of the interbeat intervals of normal sinus beats |
| SDNNdown | Deceleration-related part of HRV measure SDNN (Standard Deviation of interbeat interval of normal sinus beats) |
| SDNNup | Acceleration-related part of HRV measure SDNN (Standard Deviation of interbeat interval of normal sinus beats) |
| Shimmer_apq3 | Average absolute difference between amplitude of a period and the mean amplitudes of its two neighbours, divided by the average amplitude |
| Shimmer_apq5 | Average absolute difference between amplitude of a period and the mean amplitudes of it and its four nearest neighbours, divided by the average amplitude |
| Shimmer_ShdB | Average absolute difference of base 10 logarithm of the amplitude difference between two consecutive periods |
| Shimmer_Shim | Average absolute difference between amplitudes of two consecutive periods, divided by the average amplitude |
| SI | Slope index |
| SlopeEn | Slope entropy |
| SNS | Sympathetic nervous system index, from Kubios HRV |
| SpEn | Spectral entropy |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for Social Science |
| SQA | Symmetry Quantification Analysis |
| SymDyn | Symbolic Dynamics |
| Tangle | Temporal complexity metric |
| TE | Tsallis entropy |
| T_E | Tone_entropy (either T_E Tone or T_E Entropy) |
| Totpwr | Total power |
| TPE | Tsallis Permutation Entropy |
| UCFB | University Campus of Football Business |
| VM | Volatility Method |
| vmHRV | Vagally mediated HRV |
| vmHRVBF | Vagally-mediated heart rate variability biofeedback |
| W | Kendall’s coefficient of concordance |
| wavent (or WE) | Wavelet entropy |
References
- Li, P. EZ Entropy: A Software Application for the Entropy Analysis of Physiological Time-Series. Biomed. Eng. Online 2019, 18, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azami, H.; Faes, L.; Escudero, J.; Humeau-Heurtier, A.; Silva, L.E.V. Entropy Analysis of Univariate Biomedical Signals: Review and Comparison of Methods. In Frontiers in Entropy across the Disciplines: Panorama of Entropy: Theory, Computation, and Applications; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, 2020; pp. 233–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humeau-Heurtier, A. Entropy Analysis in Health Informatics. In Intelligent Systems Reference Library; Springer Science and Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 192, pp. 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayor, D.; Panday, D.; Kandel, H.K.; Steffert, T.; Banks, D. CEPS: An Open Access Matlab Graphical User Interface (GUI) for the Analysis of Complexity and Entropy in Physiological Signals. Entropy 2021, 23, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flood, M.W.; Grimm, B. EntropyHub: An Open-Source Toolkit for Entropic Time Series Analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datseris, G.; Kottlarz, I.; Braun, A.P.; Parlitz, U. Estimating the Fractal Dimension: A Comparative Review and Open Source Implementations. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.05937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datseris, G. DynamicalSystems.Jl: A Julia Software Library for Chaos and Nonlinear Dynamics. J. Open Source Softw. 2018, 3, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalauzi, A.; Bojić, T.; Rakić, L. Extracting Complexity Waveforms from One-Dimensional Signals. Nonlinear Biomed. Phys. 2009, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platiša, M.M.; Radovanović, N.N.; Kalauzi, A.; Pavlović, S. Generalized Poincaré Plots Analysis of Cardiac Interbeat Intervals in Heart Failure. In Proceedings of the 15th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2022), Virtual, 9–11 February 2022; pp. 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigolini, P.; Palatella, L.; Raffaelli, G. Asymmetric Anomalous Diffusion: An Efficient Way to Detect Memory in Time Series. Fractals 2001, 9, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelinek, H.F.; Tuladhar, R.; Culbreth, G.; Bohara, G.; Cornforth, D.; West, B.J.; Grigolini, P. Diffusion Entropy vs. Multiscale and Rényi Entropy to Detect Progression of Autonomic Neuropathy. Front. Physiol. 2021, 11, 607324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce-Flores, M.; Frausto-Solís, J.; Santamaría-Bonfil, G.; Pérez-Ortega, J.; González-Barbosa, J.J. Time Series Complexities and Their Relationship to Forecasting Performance. Entropy 2020, 22, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harte, D. Multifractals: Theory and Applications; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T. Approach to an Irregular Time Series on the Basis of the Fractal Theory. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1988, 31, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, M.J. Fractals and the Analysis of Waveforms. Comput. Biol. Med. 1988, 18, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglioni, P. What Is Wrong in Katz’s Method? Comments on: “A Note on Fractal Dimensions of Biomedical Waveforms”. Comput. Biol. Med. 2010, 40, 950–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosian, A. Kolmogorov Complexity of Finite Sequences and Recognition of Different Preictal EEG Patterns. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems, Lubbock, TX, USA, 9–10 June 1995; pp. 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevcik, C. A Procedure to Estimate the Fractal Dimension of Waveforms. Complex. Int. 1998, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Moisy, F. Boxcount. Available online: https://uk.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/13063-boxcount (accessed on 23 July 2022).
- Meerwijk, E.L.; Ford, J.M.; Weiss, S.J. Resting-State EEG Delta Power Is Associated with Psychological Pain in Adults with a History of Depression. Biol. Psychol. 2015, 105, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizlaitienė, I. Fractal Modeling of Speech Signals. Master’s Thesis, Vilnius Universitetas, Vilnius, Lithuania, 2021. Available online: https://epublications.vu.lt/object/elaba:81590289/81590289.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Maragos, P. Fractal Signal Analysis Using Mathematical Morphology. Adv. Electron. Electron Phys. 1994, 88, 199–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlatintsi, A.; Maragos, P. Multiscale Fractal Analysis of Musical Instrument Signals with Application to Recognition. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2013, 21, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsner, W. A Unified Approach to Fractal Dimensions. J. Inf. Technol. Res. 2008, 1, 62–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Cheong, K.H. The Fractal Dimension of Complex Networks: A Review. Inf. Fusion 2021, 73, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, T.; Ribeiro, M.; Teixeira, A.; Castro, L.; Antunes, L.; Costa-Santos, C. Nonlinear Methods Most Applied to Heart-Rate Time Series: A Review. Entropy 2020, 22, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabási, A.L.; Stanley, H.E. Fractal Concepts in Surface Growth. Z. Für Phys. Chem. 1995, 193, 218–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassberger, P.; Procaccia, I. Characterization of Strange Attractors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1983, 50, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gneiting, T.; Ševčíková, H.; Percival, D.B. Estimators of Fractal Dimension: Assessing the Roughness of Time Series and Spatial Data. Stat. Sci. 2012, 27, 247–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ševčíková, H.; Percival, D.; Gneiting, T. Estimation of Fractal Dimensions: Package ‘Fractaldim’. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=fractaldim (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Mieszkowski, D.; Kośmider, M.; Krauze, T.; Guzik, P.; Piskorski, J. Asymmetric Detrended Fluctuation Analysis Reveals Asymmetry in the RR Intervals Time Series. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Mech. 2016, 15, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.H.; Herrera-Diestra, J.L.; Chavez, M. Detection of Time Reversibility in Time Series by Ordinal Patterns Analysis. Chaos 2018, 28, 123111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czippelova, B.; Chladekova, L.; Uhrikova, Z.; Zibolen, M.; Javorka, K.; Javorka, M. Is the Time Irreversibility of Heart Rate Present Even in Newborns? In Proceedings of the 2014 8th Conference of the European Study Group on Cardiovascular Oscillations, ESGCO 2014, Trento, Italy , 25–28 May 2014; pp. 15–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, C.K.; Khandoker, A.H.; Gubbi, J.; Palaniswami, M. Complex Correlation Measure: A Novel Descriptor for Poincaré Plot. Biomed. Eng. Online 2009, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ehlers, C.L.; Havstad, J.; Prichard, D.; Theiler, J. Low Doses of Ethanol Reduce Evidence for Nonlinear Structure in Brain Activity. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 7474–7486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzik, P.; Piskorski, J.; Krauze, T.; Wykretowicz, A.; Wysocki, H. Heart Rate Asymmetry by Poincaré Plots of RR Intervals. Biomed. Tech. 2006, 51, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskorski, J.; Guzik, P. Geometry of the Poincaré Plot of RR Intervals and Its Asymmetry in Healthy Adults. Physiol. Meas. 2007, 28, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, A.; Guzzetti, S.; Montano, N.; Gnecchi-Ruscone, T.; Furlan, R.; Malliani, A. Time Reversibility in Short-Term Heart Period Variability. In Proceedings of the Computers in Cardiology Conference, Valencia, Spain, 17–20 September 2006; Volume 33, pp. 77–80. [Google Scholar]
- Karmakar, C.; Khandoker, A.; Palaniswami, M. Analysis of Slope Based Heart Rate Asymmetry Using Poincaré Plots. In Proceedings of the Computing in Cardiology Conference, Krakow, Poland, 9–12 September 2012; Volume 39, pp. 949–952. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.; Li, P.; Ji, L.; Yao, L.; Karmakar, C.; Liu, C. Area Asymmetry of Heart Rate Variability Signal. Biomed. Eng. Online 2017, 16, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, C.K.; Khandoker, A.H.; Gubbi, J.; Palaniswami, M. Defining Asymmetry in Heart Rate Variability Signals Using a Poincaré Plot. Physiol. Meas. 2009, 30, 1227–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohila, A.; Sharma, A. Asymmetric Spread of Heart Rate Variability. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 60, 101985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chladekova, L.; Czippelova, B.; Turianikova, Z.; Tonhajzerova, I.; Calkovska, A.; Baumert, M.; Javorka, M. Multiscale Time Irreversibility of Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Variability during Orthostasis. Physiol. Meas. 2012, 33, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czippelova, B.; Chladekova, L.; Uhrikova, Z.; Javorka, K.; Zibolen, M.; Javorka, M. Time Irreversibility of Heart Rate Oscillations in Newborns—Does It Reflect System Nonlinearity? Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2015, 19, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshvarpour, A.; Goshvarpour, A. Asymmetry of Lagged Poincare Plot in Heart Rate Signals during Meditation. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2021, 11, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Ramirez, J.; Echeverria, J.C.; Meraz, M.; Rodriguez, E. Asymmetric Acceleration/Deceleration Dynamics in Heart Rate Variability. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2017, 479, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskorski, J.; Kosmider, M.; Mieszkowski, D.; Krauze, T.; Wykretowicz, A.; Guzik, P. Properties of Asymmetric Detrended Fluctuation Analysis in the Time Series of RR Intervals. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2018, 491, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskorski, J.; Guzik, P. Compensatory Properties of Heart Rate Asymmetry. J. Electrocardiol. 2012, 45, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurosaka, C.; Maruyama, T.; Yamada, S.; Hachiya, Y.; Ueta, Y.; Higashi, T. Estimating Core Body Temperature Using Electrocardiogram Signals. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porges, S.W. A Phylogenetic Journey through the Vague and Ambiguous Xth Cranial Nerve: A Commentary on Contemporary Heart Rate Variability Research. Biol. Psychol. 2007, 74, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.; Jang, K.I.; Lee, S.H. Heart and Brain Interaction of Psychiatric Illness: A Review Focused on Heart Rate Variability, Cognitive Function, and Quantitative Electroencephalography. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2019, 17, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appelhans, B.M.; Luecken, L.J. Heart Rate Variability as an Index of Regulated Emotional Responding. Rev. Gen. Psychol. 2006, 10, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayer, J.F.; Åhs, F.; Fredrikson, M.; Sollers, J.J.; Wager, T.D. A Meta-Analysis of Heart Rate Variability and Neuroimaging Studies: Implications for Heart Rate Variability as a Marker of Stress and Health. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ask, T.F.; Lugo, R.G.; Sütterlin, S. The Neuro-Immuno-Senescence Integrative Model (NISIM) on the Negative Association between Parasympathetic Activity and Cellular Senescence. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaschillo, E.; Lehrer, P.M.; Rishe, N.; Konstantinov, M. Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback as a Method for Assessing Baroreflex Function: A Preliminary Study of Resonance in the Cardiovascular System. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2002, 27, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaschillo, E.G.; Vaschillo, B.; Pandina, R.J.; Bates, M.E. Resonances in the Cardiovascular System Caused by Rhythmical Muscle Tension. Psychophysiology 2011, 48, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shaffer, F.; Meehan, Z.M. A Practical Guide to Resonance Frequency Assessment for Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrer, P.M.; Vaschillo, E.; Vaschillo, B.; Lu, S.E.; Eckberg, D.L.; Edelberg, R.; Shih, W.J.; Lin, Y.; Kuusela, T.A.; Tahvanainen, K.U.O.; et al. Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback Increases Baroreflex Gain and Peak Expiratory Flow. Psychosom. Med. 2003, 65, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrer, P.M.; Vaschillo, E.; Vaschillo, B.; Lu, S.E.; Scardella, A.; Siddique, M.; Habib, R.H. Biofeedback Treatment for Asthma. Chest 2004, 126, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrer, P.; Vaschillo, E.; Lu, S.E.; Eckberg, D.; Vaschillo, B.; Scardella, A.; Habib, R. Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback: Effects of Age on Heart Rate Variability, Baroreflex Gain, and Asthma. Chest 2006, 129, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, M.J.; Pike, K.C.; Budzynski, H.K. Psychosocial Nursing Therapy Following Sudden Cardiac Arrest: Impact on Two-Year Survival. Nurs. Res. 2001, 50, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.C.; Lin, I.M.; Fan, S.Y.; Chien, C.L.; Lin, T.H. One-Year Cardiovascular Prognosis of the Randomized, Controlled, Short-Term Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback Among Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. Int. J. Behav. Med. 2018, 25, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucker, T.L.; Samuelson, K.W.; Muench, F.; Greenberg, M.A.; Gevirtz, R.N. The Effects of Respiratory Sinus Arrhythmia Biofeedback on Heart Rate Variability and Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Symptoms: A Pilot Study. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2009, 34, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzoli, S.F.M.; Marzorati, C.; Gatti, D.; Monzani, D.; Mazzocco, K.; Pravettoni, G. A Meta-Analysis on Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback and Depressive Symptoms. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firth, A.M.; Cavallini, I.; Sütterlin, S.; Lugo, R.G. Mindfulness and Self-Efficacy in Pain Perception, Stress and Academic Performance. The Influence of Mindfulness on Cognitive Processes. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 2019, 12, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goessl, V.C.; Curtiss, J.E.; Hofmann, S.G. The Effect of Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback Training on Stress and Anxiety: A Meta-Analysis. Psychol. Med. 2017, 47, 2578–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevirtz, R. The Promise of Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback: Evidence-Based Applications. Biofeedback 2013, 41, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Xiang, Q.; Fu, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Chen, S.; Shao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, T. Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback Decreases Blood Pressure in Prehypertensive Subjects by Improving Autonomic Function and Baroreflex. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2012, 18, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leganes-Fonteneau, M.; Bates, M.E.; Muzumdar, N.; Pawlak, A.; Islam, S.; Vaschillo, E.; Buckman, J.F. Cardiovascular Mechanisms of Interoceptive Awareness: Effects of Resonance Breathing. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2021, 169, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwerdtfeger, A.R.; Schwarz, G.; Pfurtscheller, K.; Thayer, J.F.; Jarczok, M.N.; Pfurtscheller, G. Heart Rate Variability (HRV): From Brain Death to Resonance Breathing at 6 Breaths per Minute. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020, 131, 676–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rominger, C.; Graßmann, T.M.; Weber, B.; Schwerdtfeger, A.R. Does Contingent Biofeedback Improve Cardiac Interoception? A Preregistered Replication of Meyerholz, Irzinger, Withoft, Gerlach, and Pohl (2019) Using the Heartbeat Discrimination Task in a Randomised Control Trial. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, D.; Matthews, J.J.L.; Chen, J.J.; Mah, L. Increased Exhalation to Inhalation Ratio during Breathing Enhances High-Frequency Heart Rate Variability in Healthy Adults. Psychophysiology 2021, 58, e13905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Diest, I.; Verstappen, K.; Aubert, A.E.; Widjaja, D.; Vansteenwegen, D.; Vlemincx, E. Inhalation/Exhalation Ratio Modulates the Effect of Slow Breathing on Heart Rate Variability and Relaxation. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2014, 39, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.; Bigger, J.T.; Camm, A.J.; Kleiger, R.E.; Malliani, A.; Moss, A.J.; Schwartz, P.J. Heart Rate Variability: Standards of Measurement, Physiological Interpretation, and Clinical Use. Eur. Heart J. 1996, 17, 354–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, M.L.; Van Roon, A.; Riese, H.; Thio, C.; Oostenbroek, E.; Westrik, I.; De Geus, E.J.C.; Gansevoort, R.; Lefrandt, J.; Nolte, I.M.; et al. Validity of (Ultra-)Short Recordings for Heart Rate Variability Measurements. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.; Kamarck, T.; Mermelstein, R. A Global Measure of Perceived Stress. J. Health Soc. Behav. 1983, 24, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.W.; Ryan, R.M. The Benefits of Being Present: Mindfulness and Its Role in Psychological Well-Being. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2003, 84, 822–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.; Lamis, D.A.; Bagge, C.L.; Freedenthal, S.; Barnes, S.M. The Mindful Attention Awareness Scale: Further Examination of Dimensionality, Reliability, and Concurrent Validity Estimates. J. Pers. Assess. 2016, 98, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehling, W.E.; Price, C.; Daubenmier, J.J.; Acree, M.; Bartmess, E.; Stewart, A. The Multidimensional Assessment of Interoceptive Awareness (MAIA). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Choudhary, G.I.; Rahardja, S.; Franti, P. Classification of Interbeat Interval Time-Series Using Attention Entropy. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udhayakumar, R.K.; Karmakar, C.; Palaniswami, M. Approximate Entropy Profile: A Novel Approach to Comprehend Irregularity of Short-Term HRV Signal. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 88, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udhayakumar, R.K.; Karmakar, C.; Palaniswami, M. Understanding Irregularity Characteristics of Short-Term HRV Signals Using Sample Entropy Profile. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 2569–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manis, G.; Sassi, R. A Python Library with Fast Algorithms for Popular Entropy Definitions. In Proceedings of the Computing in Cardiology Conference, Brno, Czech Republic, 13–15 September 2021; Volume 48, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, E.; Cai, Z.; Gu, F. Mathematical Foundation of a New Complexity Measure. Appl. Math. Mech. 2005, 26, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Girault, J.M.; Humeau-Heurtier, A. Centered and Averaged Fuzzy Entropy to Improve Fuzzy Entropy Precision. Entropy 2018, 20, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Ghiran, I.; Peng, C.K.; Nicholson-Weller, A.; Goldberger, A.L. Complex Dynamics of Human Red Blood Cell Flickering: Alterations with in Vivo Aging. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2008, 78, 020901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, G.E.A.P.A.; Keogh, E.J.; Tataw, O.M.; De Souza, V.M.A. CID: An Efficient Complexity-Invariant Distance for Time Series. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2014, 28, 634–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.D.; Wu, C.W.; Lin, S.G.; Wang, C.C.; Lee, K.Y. Time series analysis using composite multiscale entropy. Entropy 2013, 15, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, D.E.; Moorman, J.R. Accurate Estimation of Entropy in Very Short Physiological Time Series: The Problem of Atrial Fibrillation Detection in Implanted Ventricular Devices. Am. J. Physiol. Hear. Circ. Physiol. 2011, 300, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanwimalueang, T.; Mandic, D.P. Cosine Similarity Entropy: Self-Correlation-Based Complexity Analysis of Dynamical Systems. Entropy 2017, 19, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsen, E.; Sleigh, J.W.; Dahan, A. Permutation Entropy of the Electroencephalogram: A Measure of Anaesthetic Drug Effect. Br. J. Anaesth. 2008, 101, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugiumtzis, D.; Tsimpiris, A. Measures of Analysis of Time Series (MATS): A MATLAB Toolkit for Computation of Multiple Measures on Time Series Data Bases. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.C.; Jiao, Y.Y.; Lu, B.L. Differential Entropy Feature for EEG-Based Vigilance Estimation. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS, Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 6627–6630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakopoulos, T.; Pikrakis, A. Introduction to Audio Analysis: A MATLAB Approach; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shu, L.; Liao, X. Edge Permutation Entropy: An Improved Entropy Measure for Time-Series Analysis. In Proceedings of the 45th IECON Proceedings (Industrial Electronics Conference), Lisbon, Portugal, 14–17 October 2019; Volume 2019, pp. 5998–6003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, N.; Maldonado, C.; Gershenson, C. Information Measures of Complexity, Emergence, Self-Organization, Homeostasis, and Autopoiesis. In Guided Self-Organization: Inception; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 19–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scargle, J.D. Studies in Astronomical Time Series Analysis. II—Statistical Aspects of Spectral Analysis of Unevenly Spaced Data. Astrophys. J. 1982, 263, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, J.W.; Tukey, J.W. An Algorithm for the Machine Calculation of Complex Fourier Series. Math. Comput. 1965, 19, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Peng, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Yin, C.; Yao, L. Novel Gridded Descriptors of Poincaré Plot for Analyzing Heartbeat Interval Time-Series. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 109, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, A.; Xu, N.; Xue, J. Increment Entropy as a Measure of Complexity for Time Series. Entropy 2016, 18, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, J.P.; Oliveira, C.; Lopes, C. Vocal Acoustic Analysis—Jitter, Shimmer and HNR Parameters. Procedia Technol. 2013, 9, 1112–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zozor, S.; Mateos, D.; Lamberti, P.W. Mixing Bandt-Pompe and Lempel-Ziv Approaches: Another Way to Analyze the Complexity of Continuous-State Sequences. Eur. Phys. J. B 2014, 87, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burg, J.P. Maximum Entropy Spectral Analysis. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Castiglioni, P.; Faini, A. A Fast DFA Algorithm for Multifractal Multiscale Analysis of Physiological Time Series. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.D.; Wu, C.W.; Lee, K.Y.; Lin, S.G. Modified Multiscale Entropy for Short-Term Time Series Analysis. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2013, 392, 5865–5873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunino, L.; Soriano, M.C.; Rosso, O.A. Distinguishing Chaotic and Stochastic Dynamics from Time Series by Using a Multiscale Symbolic Approach. Phys. Rev. E-Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2012, 86, 046210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Liang, Z.; Li, X.; Voss, L.J.; Sleigh, J.W. Permutation Lempel-Ziv Complexity Measure of Electroencephalogram in GABAergic Anaesthetics. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 36, 2483–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, D.E. Improved Entropy Rate Estimation in Physiological Data. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 1463–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, M.; McSharry, P.; Roberts, S.; Costello, D.; Moroz, I. Exploiting Nonlinear Recurrence and Fractal Scaling Properties for Voice Disorder Detection. Nat. Preced. 2007, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauregui, M.; Zunino, L.; Lenzi, E.K.; Mendes, R.S.; Ribeiro, H.V. Characterization of Time Series via Rényi Complexity–Entropy Curves. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2018, 498, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lad, F.; Sanfilippo, G.; Agrò, G. Extropy: Complementary Dual of Entropy. Stat. Sci. 2015, 30, 40–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inouye, T.; Shinosaki, K.; Sakamoto, H.; Toi, S.; Ukai, S.; Iyama, A.; Katsuda, Y.; Hirano, M. Quantification of EEG Irregularity by Use of the Entropy of the Power Spectrum. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1991, 79, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girault, J.M. Recurrence and Symmetry of Time Series: Application to Transition Detection. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2015, 77, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulder, R.G.; Daniel, K.E.; Teachman, B.A.; Boker, S.M. Tangle: A Metric for Quantifying Complexity and Erratic Behavior in Short Time Series. Psychol. Methods 2022, 27, 82–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunino, L.; Pérez, D.G.; Martín, M.T.; Garavaglia, M.; Plastino, A.; Rosso, O.A. Fractional Brownian Motion, Fractional Gaussian Noise, and Tsallis Permutation Entropy. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2008, 387, 6057–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernaola-Galván, P.A.; Gómez-Extremera, M.; Romance, A.R.; Carpena, P. Correlations in Magnitude Series to Assess Nonlinearities: Application to Multifractal Models and Heartbeat Fluctuations. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 96, 032218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosso, O.A.; Blanco, S.; Yordanova, J.; Kolev, V.; Figliola, A.; Schürmann, M.; Baar, E. Wavelet Entropy: A New Tool for Analysis of Short Duration Brain Electrical Signals. J. Neurosci. Methods 2001, 105, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, K.H.; Datseris, G.; Kurths, J.; Kiss, I.Z.; Ocampo-Espindola, J.L.; Marwan, N. A Unified and Automated Approach to Attractor Reconstruction. New J. Phys. 2021, 23, 033017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassberger, P. Grassberger-Procaccia Algorithm. Scholarpedia 2007, 2, 3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandt, C.; Pompe, B. Permutation Entropy: A Natural Complexity Measure for Time Series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 174102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panday, D.; Mayor, D.; Kandel, H.; ProcessSignals. Detection of Real EGG and BVP Peaks from Noisy Biosignals: An Innovative MATLAB-Based Graphical User Interface (GUI). Abstract for a Poster Presentation, GUI. Available online: http://electroacupuncture.qeeg.co.uk/processsignals (accessed on 28 September 2022).
- McConnell, M.; Schwerin, B.; So, S.; Richards, B. RR-APET—Heart Rate Variability Analysis Software. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 185, 105127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; RStudio Team: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pohlert, T. PMCMRplus: Calculate Pairwise Multiple Comparisons of Mean Rank Sums Extended. 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=PMCMRplus (accessed on 29 January 2023).
- Patil, I. Visualizations with Statistical Details: The “ggstatsplot” Approach. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datseris, G.; Parlitz, U. Nonlinear Dynamics: A Concise Introduction Interlaced with Code; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Garcia, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S. Enhancing Stochastic Resonance by Adaptive Colored Noise and Particle Swarm Optimization: An Application to Steering Control. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, AIM, Sapporo, Japan, 11–15 July 2022; Volume 2022, pp. 1700–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beinecke, J.; Heider, D. Gaussian Noise Up-Sampling Is Better Suited than SMOTE and ADASYN for Clinical Decision Making. BioData Min. 2021, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MATLAB. Interpn: Interpolation for 2-D Gridded Data in Meshgrid Format. Available online: https://uk.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/interpn.html (accessed on 8 November 2022).
- Marshall, S. Strip the Willow; Penguin: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- MATLAB. Signal Processing Toolbox. Available online: https://uk.mathworks.com/help/signal/index.html?s_tid=hc_product_card (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Li, P.; Karmakar, C.; Yan, C.; Palaniswami, M.; Liu, C. Classification of 5-S Epileptic EEG Recordings Using Distribution Entropy and Sample Entropy. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, E.; Marquier, B. Friedman Test in SPSS (Non-Parametric Equivalent to Repeated Measures ANOVA). Available online: https://www.sheffield.ac.uk/media/35112/download?attachment (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Tomczak, M.; Tomczak, E. The Need to Report Effect Size Estimates Revisited. An Overview of Some Recommended Measures of Effect Size. Trends Sport Sci. 2014, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Spencer, N.; (University of Hertfordshire, Hatfield, UK). Personal Communication, 2022.
- Conover, W.J. Practical Nonparametric Statistics, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Laerd, A.; Laerd, M. Linear Regression Analysis in SPSS Statistics—Procedure, Assumptions and Reporting the Output. Available online: https://statistics.laerd.com/spss-tutorials/linear-regression-using-spss-statistics.php (accessed on 22 October 2022).
- Tarvainen, M.P.; Niskanen, J.P.; Lipponen, J.A.; Ranta-aho, P.O.; Karjalainen, P.A. Kubios HRV—Heart Rate Variability Analysis Software. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2014, 113, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes del Paso, G.A.; Langewitz, W.; Mulder, L.J.M.; van Roon, A.; Duschek, S. The Utility of Low Frequency Heart Rate Variability as an Index of Sympathetic Cardiac Tone: A Review with Emphasis on a Reanalysis of Previous Studies. Psychophysiology 2013, 50, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubios. HRV in Evaluating ANS Function. Available online: https://www.kubios.com/hrv-ans-function/ (accessed on 10 November 2022).
- Baevsky, R.M.; Berseneva, A.P. Anwendungen des System Kardivar zur Feststellung des Stressniveaus und des Anpassungsvermögens des Organismus; Messungsstandards und Physiologische Interpretation: Moscow, Russia; Prague, Czech Republic, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Liu, C.; Li, K.; Zheng, D.; Liu, C.; Hou, Y. Assessing the Complexity of Short-Term Heartbeat Interval Series by Distribution Entropy. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2015, 53, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datseris, G.; Isensee, J.; Pech, S.; Gál, T. DrWatson: The Perfect Sidekick for Your Scientific Inquiries. J. Open Source Softw. 2020, 5, 2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabeti, M.; Katebi, S.; Boostani, R. Entropy and Complexity Measures for EEG Signal Classification of Schizophrenic and Control Participants. Artif. Intell. Med. 2009, 47, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenier, P.; Parent, A.C.; Huard, D.; Anctil, F.; Chaumont, D. An Assessment of Six Dissimilarity Metrics for Climate Analogs. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 733–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
























| Name | Abbrev. | Selected References | PubMed | Google Scholar | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Date 1st | N | Date 1st | |||
| Higuchi | FD_H | Higuchi 1988 [14] | 153 (116) | 1994 | 5180 (1610) | 1988 |
| Katz | FD_K | Katz 1988 [15] | 34 (16) | 1994 | 6620 (436) | 1985 |
| Castiglioni | FD_C | Castiglioni 2010 [16] | 3 (5) | 2010 | 561 (13) | 2010 |
| Mandelbrot | FD_M | Castiglioni 2010 [16] | 33 (42) | 1975 | 46,400 (108) | 1967 |
| Petrosian | FD_P | Petrosian 1995 [17] | 5 (8) | 2010 | 876 (296) | 1995 |
| Sevcik | FD_S | Sevcik 1998 [18] | 4 (4) | 2009 | 534 (79) | 1998 |
| Box-count [Moisy] | FD_Box_M | Moisy 2022 [19] | 370 (40) | 1990 | 34,410 (2029) | c. 1985 |
| Meerwijk/ van der Linden | FD_Box_MvdL | Meerwijk et al. 2015 [20] | 2 (0) | 2014 | 11 (0) | 2015 |
| Kalauzi | NLDwL NLDwP NLDiL NLDiP | Kalauzi et al. 2009 [8] | 7 (0) | 2005 | 243 (0) | 2009 |
| Tamulevičius, Kizlaitienė | FD_Amp FD_Dist FD_Sign FD_LRI FD_PRI | Kizlaitienė 2021 [21] | 0 (0) | n/a | 1 (0) | 2021 |
| Maragos | mFD_M | Maragos 1994; [22] Zlatintsi and Maragos 2013 [23] | 2 (0) | 1999 | 829 (4) | 1993 |
| Kinsner | Dβ Dσ | Kinsner 2008 [24] | 1 (1) | 2001 | 691 (2) | 1989 |
| Name | Abbrev. | Selected References | PubMed | Google Scholar | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Date 1st | N | Date 1st | |||
| Ehlers’ Index | EI | Ehlers et al. 1998 [35] | 4 (4) | 2009 | 59 (37) | 2006 |
| Guzik’s Index | GI | Guzik et al. 2006 [36] | 24 (9) | 2006 | 1 (63) | 2008 |
| Porta’s Index | PI | Porta et al. 2006 [38] | 15 (11) | 2012 | 188 (123 a) | 2006 |
| Slope Index (Karmakar) | SI | Karmakar et al. 2012 [39] | 4 (4) | 2015 | 28 (b) | 2012 |
| Area Index (Karmakar) | AI | Yan et al. 2017 [40] | 3 (2 b) | 2017 | 17 (b) | 2017 |
| Asymmetric Spread Index (Rohila) | ASI | Rohila and Sharma 2020 [42] | 0 | n/a | 2 | 2020 |
| Deceleration contributions | SD1up, SD2up | Guzik et al. 2006 2006 [36] | 1 | 2007 | 8, 0 (69, 12 b) | 2006 |
| Acceleration contributions | SD1down, SD2down c | Guzik et al. 2006 2006 [36] | 0 | n/a | 0, 0 (23, 12 b) | n/a |
| SD1up2/SD12, SD2up2/SD22 | C1a, C2a | Guzik et al. 2006 2006 [36] (adapted by Rohila)d | 1 | 2022 | 5 | 2021 |
| SD1dn2/SD12, SD2dn2/SD22 | C1d, C2d | Guzik et al. 2006 2006 [36] (adapted by Rohila) | 1 | 2022 | 5 | 2021 |
| √((SD1up2 + SD2up2)/2) | SDNNup | Piskorski and Guzik 2012 [48] | 1 | 2022 | 17 | 2021 |
| √((SD1down2 + SD2down2)/2) | SDNNdown | Piskorski and Guzik 2012 [48] | 1 | 2022 | 17 | 2021 |
| Age | Female | Male | All |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18–24 | 2 | 4 | 6 |
| 25–34 | 3 | 6 | 9 |
| 35–44 | 6 | 4 | 10 |
| 45–54 | 3 | 5 | 8 |
| 55–64 | 3 | 3 | 6 |
| 65–74 | 0 | 3 | 3 |
| 75–84 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Total | 18 | 26 | 44 |
| Measure | Original Author/s | Provider | Source Code | Institution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AttnEn | Yang et al. 2020 [80] | EntropyHub | MATLAB | Xi’an |
| AvgApEnP | Udhayakumar et al. 2017 [81] | Karmakar | MATLAB | Melbourne |
| AvgSampEnP | Udhayakumar et al. 2018 [82] | Karmakar | MATLAB | Melbourne |
| (B_ApEn) | Manis and Sassi 2021 [83] | Published paper | Python | Ioannina/ Milano |
| (B_SampEn) | Manis and Sassi 2021 [83] | Published paper | Python | Ioannina/ Milano |
| (C0) | Shen et al. 2005 [84] | (Panday) | tbc | Fudan |
| CAFE | Girault and Humeau-Heurtier 2018 [85] | Girault | MATLAB | Angers |
| CI * | Costa et al. 2008 [86] | Panday | MATLAB | Harvard |
| (CID) | Batista et al. 2013 [87] | Published paper | MATLAB | California (Riverside) |
| CmSE | Wu et al. 2013 [88] | Published paper | MATLAB | Taipei |
| CoSEn | Lake 2011 [89] | Liu | MATLAB | Virginia (Charlottesville) |
| CoSiEn | Chanwimalueang and Mandic 2017 [90] | EntropyHub | MATLAB | Imperial (London) |
| CPEI | Olofsen et al. 2008 [91] | Published paper | MATLAB | Leiden/ Auckland |
| DE * | Grigolini et al. 2001 [10] | Culbreth | MATLAB | North Texas (Denton) |
| DFA Alpha | Kugiumtzis and Tsimpiris 2010 [92] | Published paper | MATLAB | Thessaloniki |
| DiffEn * | Shi et al. 2013 [93] | (Panday) | MATLAB | Shanghai |
| (EE) | Giannakopoulos and Pikrakis [94] | Mathworks | MATLAB | Agia Paraskevi |
| EPE | Huo et al. 2019 [95] | Huo | MATLAB | Lincoln |
| ESCHA * | Fernández et al. 2014 [96] | Santamaría Bonfil | R | CONACYT-INEEL, Cuernavaca |
| FastLomb * | Scargle 1982 [97] | Mathworks | MATLAB | California (Berkeley) |
| FFT * | Cooley and Tukey 1965 [98] | Mathworks | MATLAB | IBM, New York |
| GPP * | Platiša et al. 2022 [9] | Kalauzi | MATLAB | Belgrade |
| GridEn | Yan et al. 2019 [99] | EntropyHub | MATLAB | Shandong |
| IncrEn | Liu et al. 2016 [100] | EntropyHub | MATLAB | Changzhou |
| Jitter_Jitt | Teixeira et al. 2013 [101] | Teixeira | MATLAB | Bragança |
| Jitter_Jitta | Teixeira et al. 2013 [101] | Teixeira | MATLAB | Bragança |
| Jitter_ppq5 | Teixeira et al. 2013 [101] | Teixeira | MATLAB | Bragança |
| Jitter_RAP | Teixeira et al. 2013 [101] | Teixeira | MATLAB | Bragança |
| L_ApEn * | Manis and Sassi 2021 [83] | Published paper | Python | Ioannina/ Milano |
| L_SampEn * | Manis and Sassi 2021 [83] | Published paper | Python | Ioannina/ Milano |
| LZPC * | Zozor et al. 2014 [102] | GitHub | C | Grenoble/ Córdoba |
| MESA * | Burg 1975 [103] | Dowse | MATLAB | Stanford |
| mFmDFA * | Castiglioni and Faini 2019 [104] | Castiglioni | MATLAB | Milano |
| MmSE | Wu et al. 2013 [105] | Published paper | MATLAB | Taipei |
| mPhEn | Panday n.p. | Panday | MATLAB | Hertfordshire |
| PJSC | Zunino et al. 2012 [106] | Zunino | MATLAB | La Plata |
| PLZC * | Bai et al. 2015 [107] | Published paper | MATLAB | Yanshan |
| QSE * | Lake 2011 [108] | (Panday) | MATLAB | Virginia (Charlottesville) |
| (RPDE) | Little et al. 2007 [109] | GitHub: hctsa | MATLAB | Oxford |
| RPE | Jauregui et al. 2018 [110] | Zunino | MATLAB | Maringá |
| SEx | Lad et al. 2015 [111] | Sanfilippo/Panday | MATLAB | Canterbury, NZ/Palermo |
| Shimmer_Shim | Teixeira et al. 2013 [101] | Teixeira | MATLAB | Bragança |
| Shimmer_ShdB | Teixeira et al. 2013 [101] | Teixeira | MATLAB | Bragança |
| Shimmer_apq3 | Teixeira et al. 2013 [101] | Teixeira | MATLAB | Bragança |
| Shimmer_apq5 | Teixeira et al. 2013 [101] | Teixeira | MATLAB | Bragança |
| SpEn | Inouye et al. 1991 [112] | Mathworks | MATLAB | Osaka |
| SQA * | Girault 2015 [113] | Girault | MATLAB | Angers |
| SymDyn * | Various (see Primer) | (Panday) | MATLAB | Various |
| (Tangle) | Moulder et al. 2022 [114] | GitHub | R | Virginia (Charlottesville) |
| TPE | Zunino et al. 2008 [115] | Zunino | MATLAB | La Plata |
| VM * | Bernaola- Galván et al. 2017 [116] | Bernaola- Galván/ Panday | Fortran | Málaga |
| (WE) | Rosso et al. 2001 [117] | Mathworks | MATLAB | Buenos Aires |
| Data Type | 95%/N | FD | HRA | PE | RQA | OC | OE | ALL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| noR | 95th % | 11.348 | 9.927 | 11.908 | 5.223 | 6.761 | 7.178 | 8.838 |
| N | 22 | 40 | 8 | 17 | 51 | 54 | 192 | |
| RRi 4R | 95th % | 9.697 | 8.848 | 9.971 | 5.864 | 5.267 | 8.831 | 9.038 |
| N | 22 | 40 | 10 | 19 | 51 | 54 | 196 | |
| RRi 10R | 95th % | 8.288 | 9.566 | 9.384 | 6.229 | 9.414 | 9.262 | 9.089 |
| N | 22 | 40 | 8 | 19 | 48 | 51 | 188 |
| Data Type | χ2/W | FD | HRA | PE | RQA | OC | OE | ALL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| noR | χ2 | 96.597 | 106.888 | 139.596 | 28.953 | 55.626 | 50.863 | 62.795 |
| W | 0.310 | 0.350 | 0.448 | 0.093 | 0.178 | 0.163 | 0.202 | |
| RRi 4R | χ2 | 78.813 | 92.505 | 114.482 | 33.286 | 103.706 | 86.055 | 78.813 |
| W | 0.253 | 0.297 | 0.367 | 0.103 | 0.333 | 0.276 | 0.253 | |
| RRi 10R | χ2 | 63.412 | 113.907 | 108.155 | 38.291 | 102.892 | 103.603 | 95.832 |
| W | 0.203 | 0.365 | 0.347 | 0.123 | 0.330 | 0.332 | 0.307 |
| Data Type | Measures and χ2 Range | FD | HRA | PE | RQA | OC | OE | Best |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| noR | Measures | mFD_M FD_PRI NLDw_mL NLDw_mP FD_C FD_Dist | EPP SD1 (4–7) | CPEI mPM_E PJSC | n/a | n/a | T_E_Ent | mFD_M |
| χ2 range | 161.208–200.023 | 151.920–178.916 | 150.519–161.949 | 173.660 | 200.023 | |||
| RRi 4R | Measures | FD_PRI FD_H mFD_M | n/a | n/a | n/a | LLE32–36 | FE MmSE2, MmSE5 AE | FD_PRI |
| χ2 | 167.676–197.728 | 156.084–170.126 | 150.084–158.552 | 197.728 | ||||
| RRi 10R | Measures | FD_PRI | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | BE | FD_PRI |
| χ2 | 198.906 | 158.334 | 198.906 | |||||
| Kubios HRV | General | HRA | Time domain | Freq domain | OC | OE | Best | |
| RRi 4R | Measures | PLFP | SD2 SD2/SD1 | SDNN | LFpwr (AR/LS) Totpwr (AR/LS) | DFA alpha1 | SampEnApEn | PLFP [AR LFpwr] |
| χ2 | 201.714 | 164.605–165.441 | 155.624 | 154.964–181.803 | 167.895 | 155.865–157.280 | 201.714 [181.803] |
| 5-min RRi | Measures | noR | 4R | 10R |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline-RBR ↑ | SDNNdown SD2down PJSC T_E_ENT EPP SD1_3 EPP SD1_4 EPP SD1_5 EPP SD1_6 EPP SD1_7 EPP SD2_5 AE | 0.809 (12.829) (43 ↑) 0.879 (13.934) (44 ↑) 0.914 (14.483) (43 ↑) 0.868 (13.758) (43 ↑) 0.913 (14.470) (43 ↑) 0.915 (14.502) (43 ↑) 0.956 (15.151) (43 ↑) 0.966 (15.310) (43 ↑) | 0.824 (12.733) (43 ↑) 0.830 (12.828) (43 ↑) 0.801 (12.392) (43 ↑) 0.955 (14.084) (42 ↑) | 0.806 (12.624) (43 ↑) 0.806 (12.624) (43 ↑) (6.796) (35 ↑) (7.899) (39 ↑) (11.964) (43 ↑) (9.074) (39 ↑) |
| Baseline-RBR ↓ | FD_C FD_H mFD_M FD_PRI EPP R6 CPEI EPE ImPE mPE1 mPM_E TPE FE MmSE2 | 0.893 (15.151) (44 ↓) 1.000 (15.841) (44 ↓) 0.904 (14.327) (43 ↓) 0.933 (14.790) (44 ↓) 0.847 (13.423) (43 ↓) 0.845 (13.387) (44 ↓) 0.811 (12.859) (43 ↓) 0.811 (12.859) (43 ↓) 0.812 (12.877) (43 ↓) 0.856 (13.562) (43 ↓) 0.809 (12.826) (43 ↓) | 0.851 (13.151) (44 ↓) 0.994 (15.356) (44 ↓) 1.000 (15.453) (44 ↓) 1.000 (15.392) (44 ↓) 0.800 (12.364) (44 ↓) 0.821 (12.693) (43 ↓) | (7.534) (37 ↓) (10.150) (43 ↓) (12.106) (44 ↓) 1.000 (15.541) (44 ↓) (8.641) (40 ↓) (10.304) (41 ↓) (9.903) (42 ↓) (9.903) (42 ↓) (10.301) (43 ↓) (8.820) (40 ↓) (10.59) (42 ↓) (4.380) (35 ↓) (9.609) (41 ↓) |
| Data Type | Measures and χ2 Range | FD | HRA | PE | RQA | OC | OE | Best |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INbreath | Measures | 3 | n/a | 7 | n/a | 18 | 18 | MmSE13 |
| χ2 range | 155.115–166.382 | 154.082–187.089 | 150.490–190.092 | 159.045–192.043 | 192.043 | |||
| OUTbreath | Measures | 3 | 7 | 7 | 1 | 17 | 19 | MmSE13 |
| χ2 | 157.528–159.289 | 151.338–167.358 | 160.749–188.632 | 167.753 | 151.639–188.884 | 150.950–195.610 | 195.610 | |
| Peak-Peak (PP) | Measures | 1 | 8 | 7 | n/a | 17 | 22 | ImPE |
| χ2 | 168.048 | 177.494–184.878 | 171.671–191.663 | 150.569–191.249 | 152.381–190.565 | 191.663 | ||
| Raw RSP | Measures | FD_PRI | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | FD_PRI |
| χ2 | 154.064 | 154.064 |
| Data Type | Measures | Friedman’s χ2 | Kendall’s W |
|---|---|---|---|
| RRi (noR) | mFD_M FD_H | 200.023 195.703 | 0.642 0.628 |
| RRi (4R) | FD_PRI LLE34 | 197.728 170.126 | 0.633 0.546 |
| RRi (10R) | FD_PRI BE | 198.906 158.334 | 0.637 0.508 |
| RSP (IN) | LLE42 EoD | 190.092 188.255 | 0.251 0.600 |
| RSP (OUT) | LLE43 TPE | 188.884 188.642 | 0.250 0.605 |
| RSP (PP) | ImPE ESCHA_d | 191.663 191.249 | 0.613 0.612 |
| RSP (Raw) | FD_PRI FD_LRI | 154.064 122.040 | 0.493 0.389 |
| EDA | RMSSD EPP SD1_1 | 29.035 28.824 | 0.093 0.924 |
| Kubios HRV | PLFP LFpwr (AR) | 201.714 181.803 | 0.647 0.583 |
| Data Type | Measures | Friedman’s χ2 | Kendall’s W |
|---|---|---|---|
| RRi (4R) | Wavent Perment4 | 135.429 118.979 | 0.440 0.386 |
| RSP (Raw) | Wavent Perment4 | 66.910 51.835 | 0.217 0.168 |
| EDA | Wavent Delta2 | 16.609 15.214 | 0.054 0.049 |
| 4R 5-min | Pair | S | 10R 5-min | Pair | S | NoR 5-min | All Base_5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FD_PRI | Base_5 | 19.013 | FD_PRI | Base_5 | 19.508 | mFD_M | 19.334 |
| FD_PRI | Base_5.5 | 15.826 | FD_PRI | Base_5.5 | 15.614 | FD_PRI | 19.163 |
| mFD_M | Base_RBR | 15.453 | FD_PRI | Base_RBR | 15.541 | FD_H | 18.672 |
| FD_PRI | Base_RBR | 15.392 | MmSE11 | Base_5 | 13.933 | NLDwL_m | 16.566 |
| FD_H | Base_RBR | 15.356 | MmSE10 | Base_5 | 13.888 | NLDwP_m | 16.521 |
| Medians | 15.453 | 15.541 | 18.672 |
| IN 5-min | All Base_5 | OUT 5-min | All Base_5 | PP 5-min | All Base_5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IncrEn | 18.037 | ImPE | 17.907 | ImPE | 18.302 |
| EoD | 17.898 | Discrete_CS | 17.873 | Discrete_CS | 18.224 |
| KLD | 17.898 | IncrEn | 17.867 | EoD | 18.096 |
| ImPE | 17.849 | TPE | 17.833 | KLD | 18.096 |
| Discrete_CS | 17.713 | mPM_E | 17.794 | mPM_E | 18.057 |
| Medians | 17.898 | 17.867 | 18.096 |
| RSP 5-min | Pair | S | EDA 5-min | Pair | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FD_PRI | Base_5 | 14.349 | GridEn | Base_6 | 5.250 |
| FD_PRI | Base_RBR | 12.08 | Jitta | Base_5 | 4.829 |
| FD_PRI | Base_5.5 | 11.620 | RMSSD | Base_5 | 4.730 |
| FD_PRI | 7_5 | 9.627 | EPP SD1_1 | Base_5 | 4.728 |
| FD_LRI | Base_5 | 11.091 | EPP SD1_2 | Base_5 | 4.728 |
| Medians | 11.620 | 4.730 |
| Conover S | Self to RBR | Base to RBR | Self to 5 BrPM | Base to 5 BrPM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RRi (4R) (225) | 4.601 | 7.386 | 4.091 | 7.129 |
| RRi (10R) (209) | 5.267 | 8.536 | 5.007 | 8.538 |
| RRi (noR) (219) | 3.673 | 6.105 | 3.182 | 6.084 |
| RSP raw (99) | 2.549 | 3.307 | 3.069 | 3.277 |
| RSP_IN (196) | 2.770 | 7.507 | 4.270 | 8.723 |
| RSP_OUT (197) | 4.250 | 8.070 | 4.676 | 9.094 |
| RSP_PP (197) | 4.180 | 7.794 | 5.389 | 9.548 |
| EDA (89) | 0.812 | 1.732 | 0.892 | 1.865 |
| RRi (noR) (219) | RRi (4R) (224) | RR-APET (25) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mFD_M | 194.4 0.624 13.327 | SD2down | 185.6 0.595 12.828 | SD2 | 139.7 0.448 12.319 |
| FD_H | 187.8 0.602 15.239 | mFD_M | 156.8 0.503 13.562 | SDNN | 136.7 0.439 12.132 |
| FD_PRI | 187.7 0.601 14.790 | Alpha1 | 132.8 0.426 10.251 | ||
| EPP SD1_7 | 176.2 0.565 14.691 | ||||
| NLDwL_m | 172.1 0.552 14.435 | ||||
| NLDwP_m | 171.8 0.551 14.541 | ||||
| EPP SD1_6 | 170.7 0.548 15.300 | ||||
| FD_C | 161.8 0.519 13.508 | ||||
| CPEI | 157.0 0.504 13.043 | ||||
| RRi (noR) (220) | RRi (4R) (220) | RR-APET (24) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PJSC (↑) | 199 (162) | FD_C (↓) | 191 (157) | SD2 (↑) | 215 (172) |
| RoCV (↑) | 191 (154) | mFD_M (↓) | 191 (155) | SDNN (↑) | 214 (172) |
| EPP SD1_6 (↑) | 188 (150) | AE (↑) | 191 (154) | Alpha1 (↑) | 213 (171) |
| ACR5 (↓) | 187 (151) | RCmDE7 (↓) | 190 (156) | LFpwr (↑) | 211 (170) |
| EPP SD1_5 (↑) | 187 (149) a | Q3 (↑) | 188 (153) | ||
| mPE (↓) | 186 (153) | FD_H (↓) | 187 (152) | ||
| EPP r5 (↓) | 186 (150) | LLE32 (↑) | 187 (150) | ||
| EPE (↓) | 185 (152) | LLE33 (↑) | 187 (149) | ||
| ImPE (↓) | 185 (152) | RoCV (↑) | 185 (149) | ||
| AE (↑) | 185 (149) a | LLE31 (↑) | 183 (146) | ||
| EoD (↓) | 184 (151) | RCmDE6 (↓) | 182 (151) | ||
| KLD (↓) | 184 (151) | SD2down and SDNNdown (↑) | 182 (146) | ||
| MPM_E (↓) | 184 (149) | LLE30 (↑) | 182 (145) | ||
| Top 12 Measures | ICC | Median CV | Count |
|---|---|---|---|
| FD_H (NoR) | 0.947 | 0.003 | 32 |
| NLDwL_m (NoR) | 0.944 | 0.001 | 32 |
| NLDwP_m (NoR) | 0.944 | 0.001 | 32 |
| Q3 (4R) | 0.910 | 0.008 | 32 |
| CPEI (NoR) | 0.897 | 0.008 | 32 |
| mFD_M (4R) | 0.894 | 0.016 | 32 |
| mFD_M (NoR) | 0.889 | 0.003 | 32 |
| LLE33 (4R) | 0.767 | 0.011 | 32 |
| LLE32 (4R) | 0.747 | 0.011 | 32 |
| Alpha1 | 0.823 | 0.018 | 31 |
| LLE30 (4R) | 0.737 | 0.012 | 31 |
| LLE31 (4R) | 0.730 | 0.014 | 31 |
| Bottom five measures | ICC | Median CV | Count |
| PJSC (NoR) | 0.786 | 0.038 | 15 |
| EoD (NoR) | 0.849 | 0.069 | 11 |
| KLD (NoR) | 0.849 | 0.069 | 11 |
| ACR5 (NoR) | 0.864 | 0.124 | 2 |
| EPP R5 (NoR) | 0.862 | 0.138 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mayor, D.; Steffert, T.; Datseris, G.; Firth, A.; Panday, D.; Kandel, H.; Banks, D. Complexity and Entropy in Physiological Signals (CEPS): Resonance Breathing Rate Assessed Using Measures of Fractal Dimension, Heart Rate Asymmetry and Permutation Entropy. Entropy 2023, 25, 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25020301
Mayor D, Steffert T, Datseris G, Firth A, Panday D, Kandel H, Banks D. Complexity and Entropy in Physiological Signals (CEPS): Resonance Breathing Rate Assessed Using Measures of Fractal Dimension, Heart Rate Asymmetry and Permutation Entropy. Entropy. 2023; 25(2):301. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25020301
Chicago/Turabian StyleMayor, David, Tony Steffert, George Datseris, Andrea Firth, Deepak Panday, Harikala Kandel, and Duncan Banks. 2023. "Complexity and Entropy in Physiological Signals (CEPS): Resonance Breathing Rate Assessed Using Measures of Fractal Dimension, Heart Rate Asymmetry and Permutation Entropy" Entropy 25, no. 2: 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25020301
APA StyleMayor, D., Steffert, T., Datseris, G., Firth, A., Panday, D., Kandel, H., & Banks, D. (2023). Complexity and Entropy in Physiological Signals (CEPS): Resonance Breathing Rate Assessed Using Measures of Fractal Dimension, Heart Rate Asymmetry and Permutation Entropy. Entropy, 25(2), 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25020301





