Enhanced Magnetocaloric Properties of the (MnNi)0.6Si0.62(FeCo)0.4Ge0.38 High-Entropy Alloy Obtained by Co Substitution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
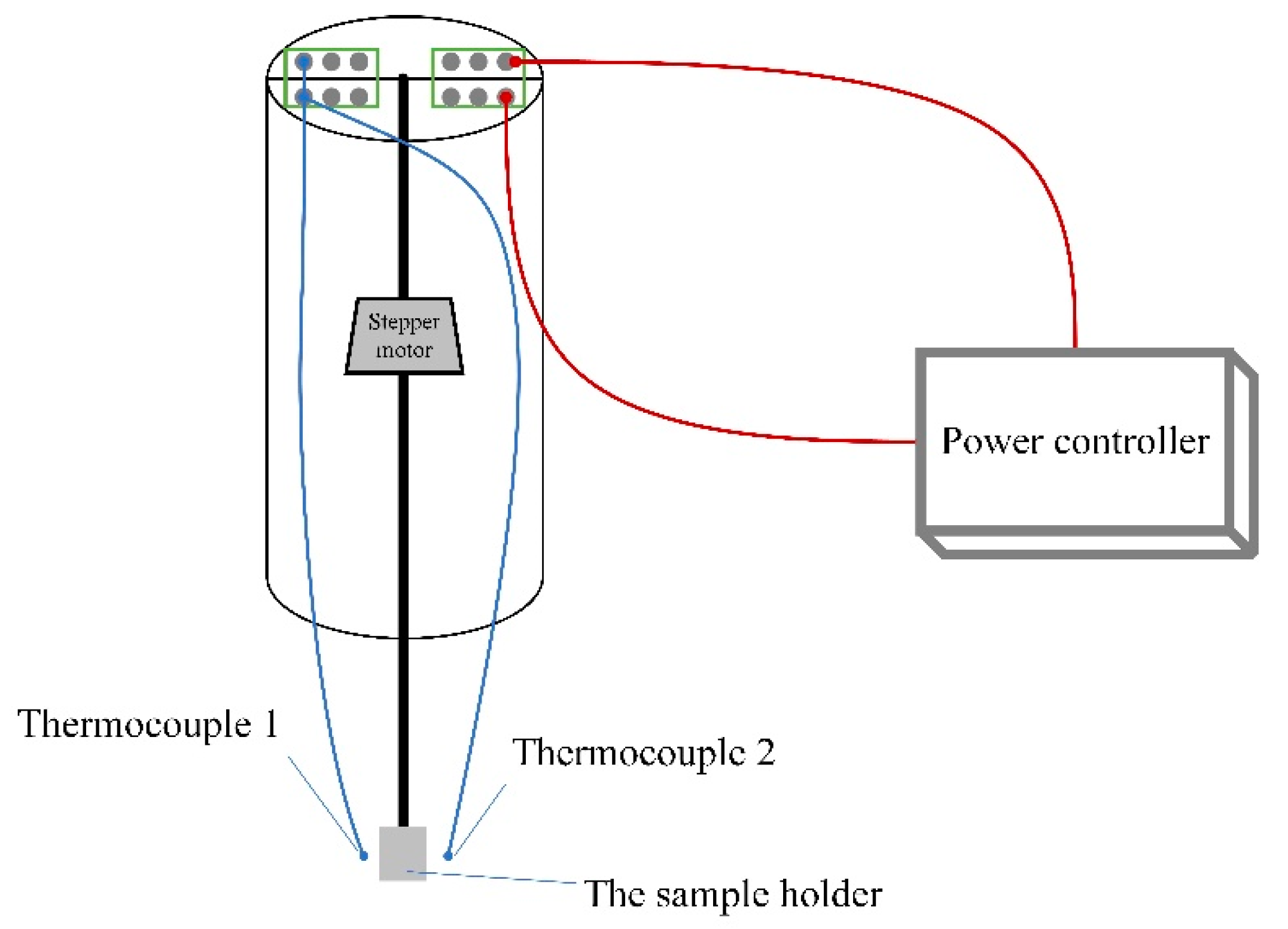
2. Experimental
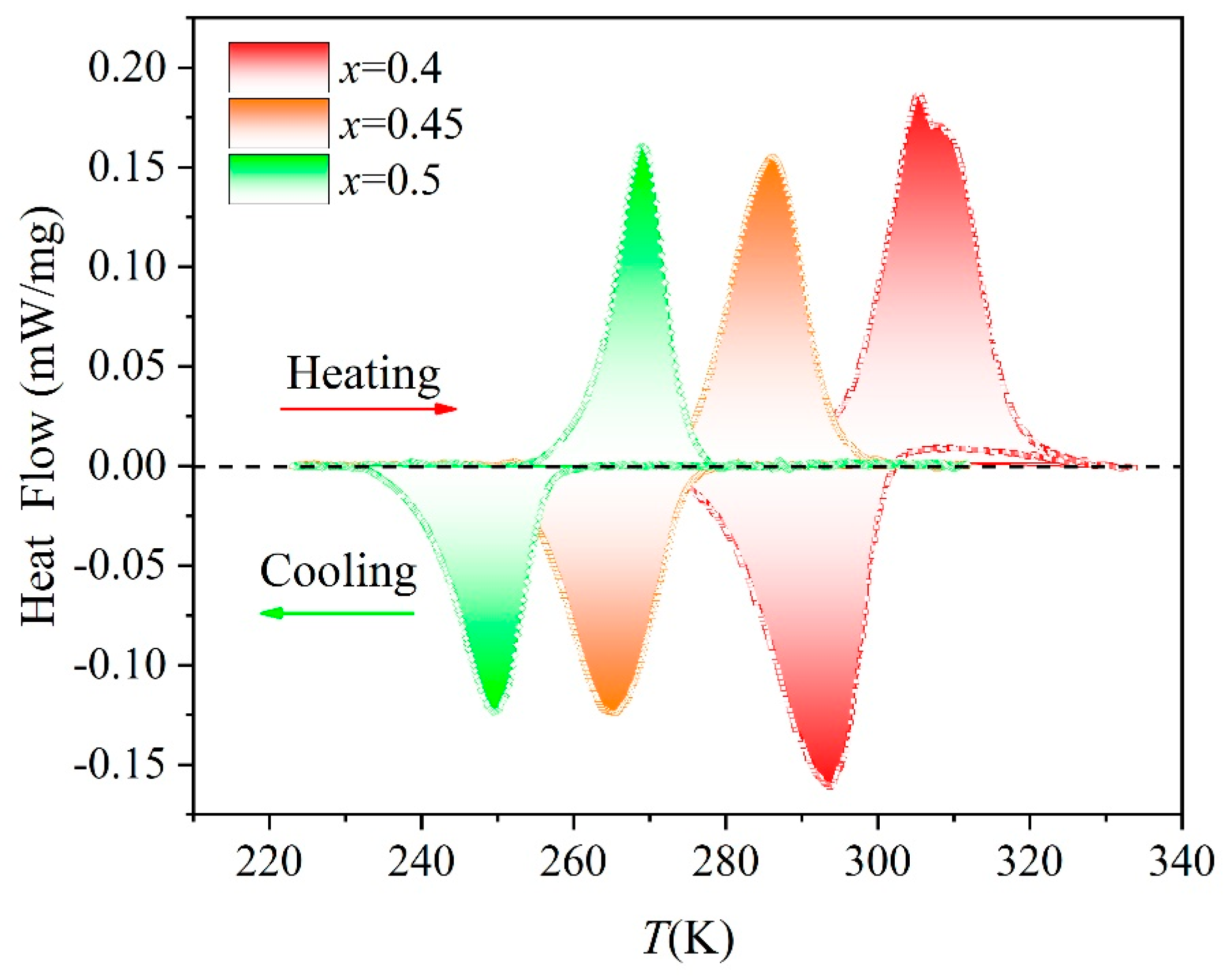
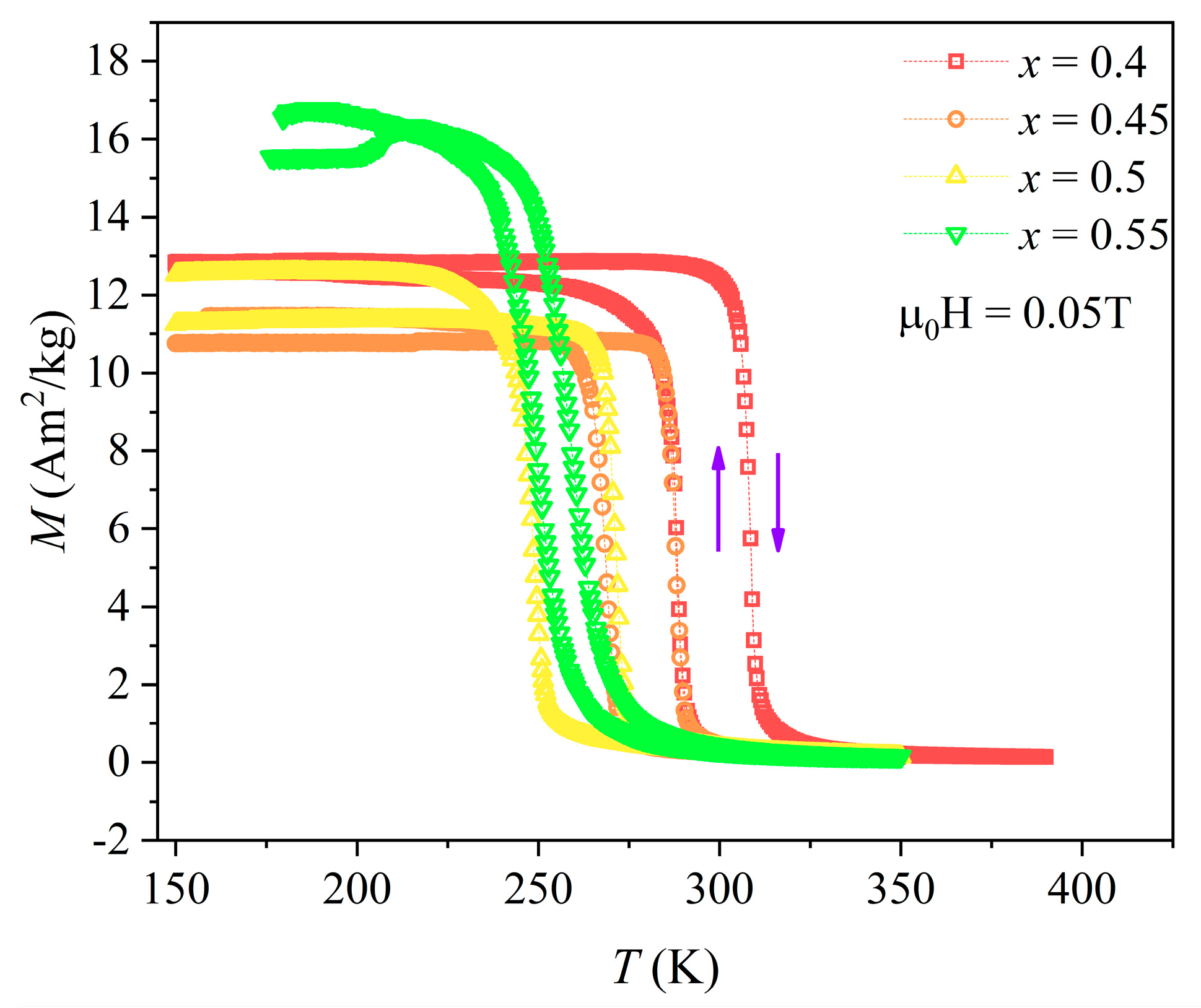
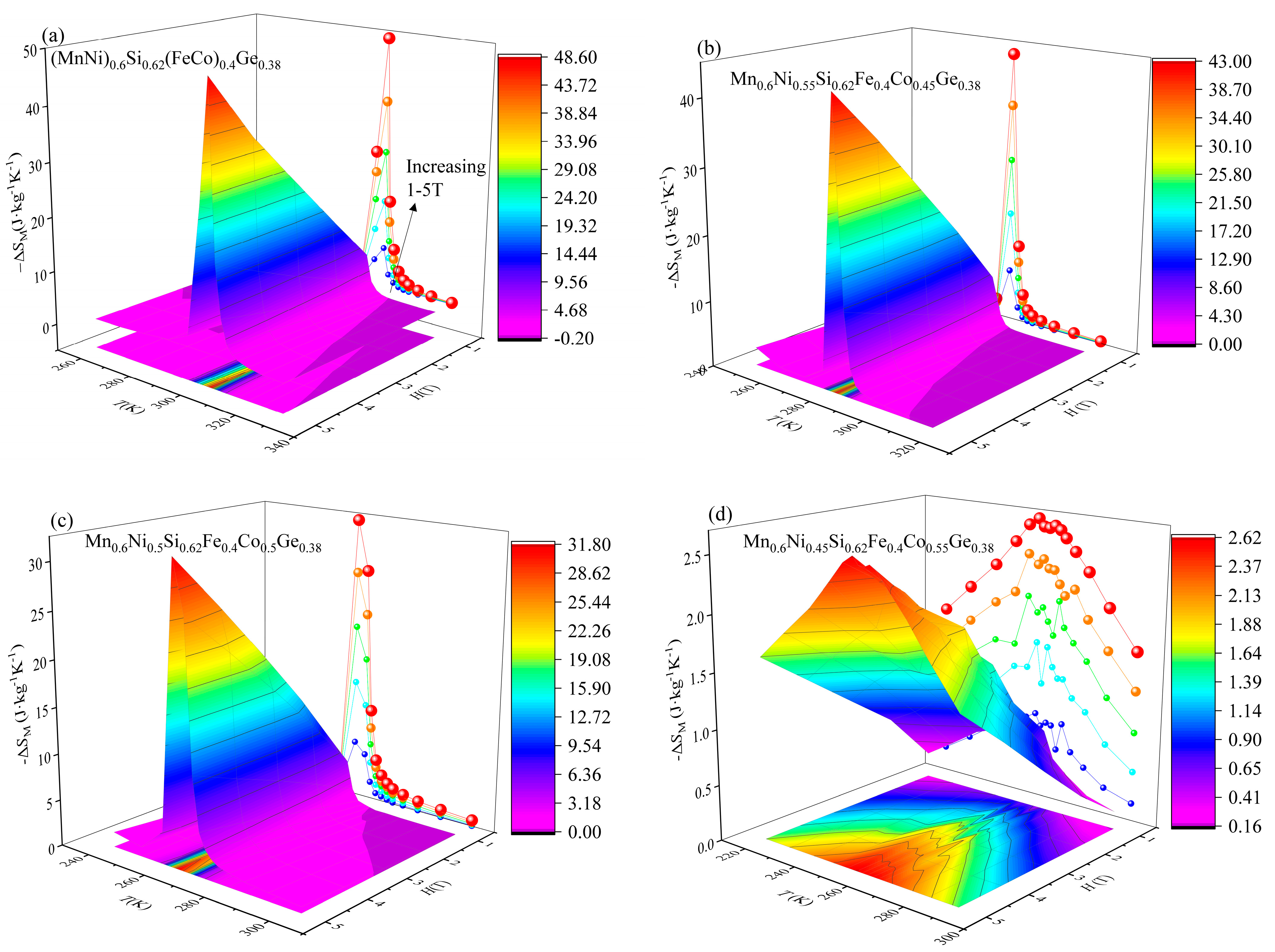
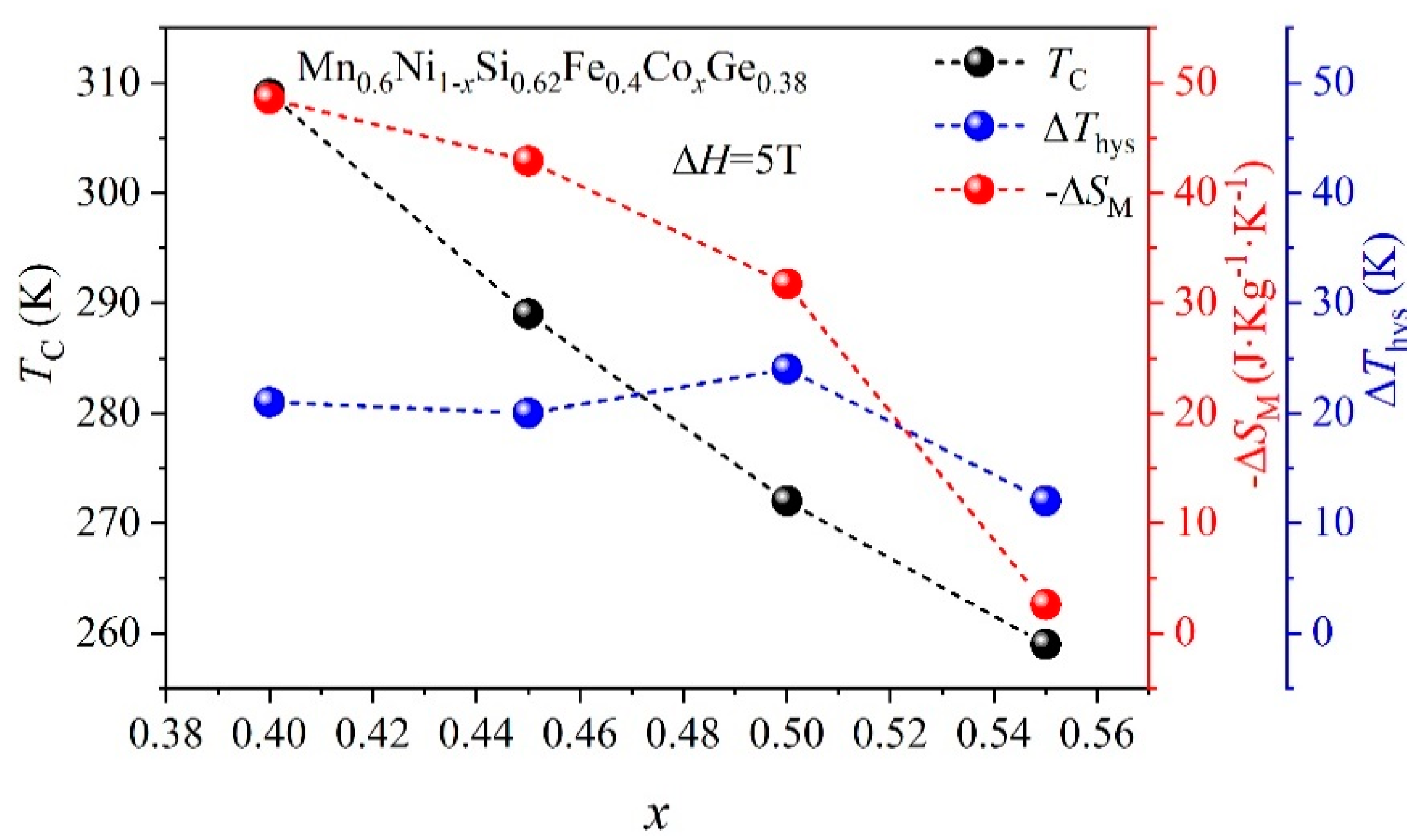
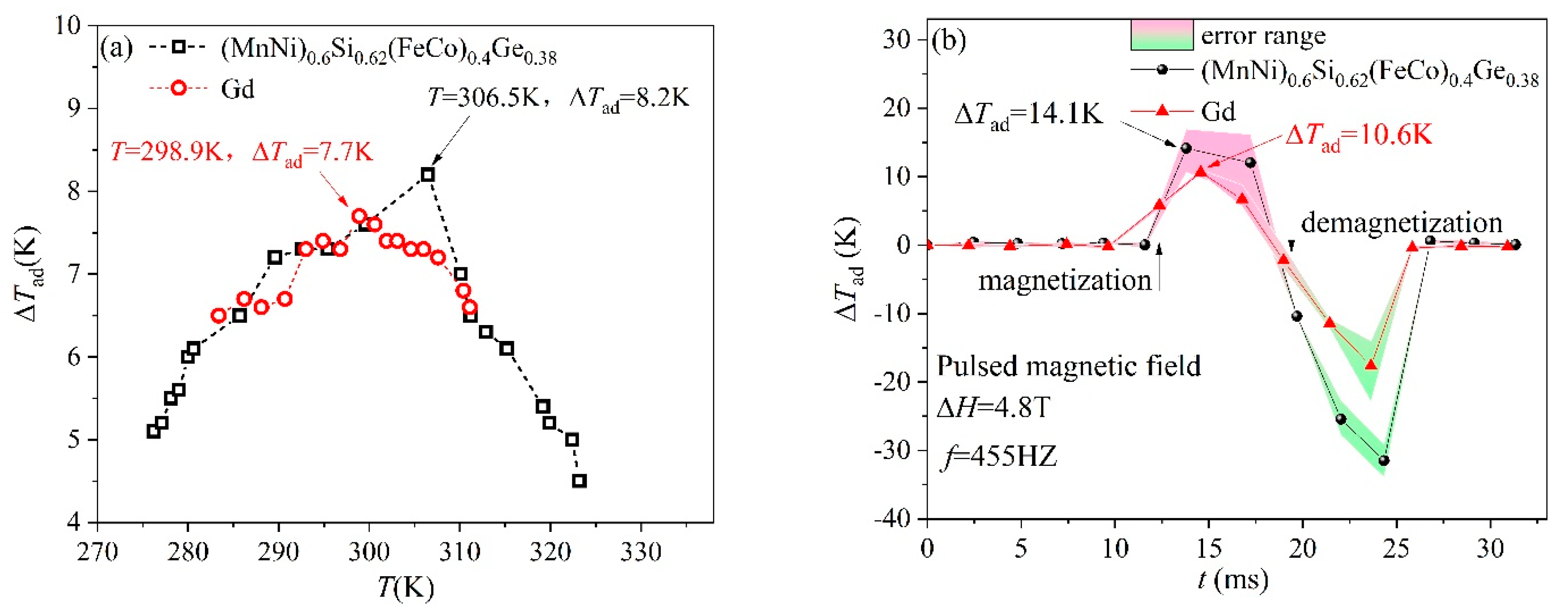
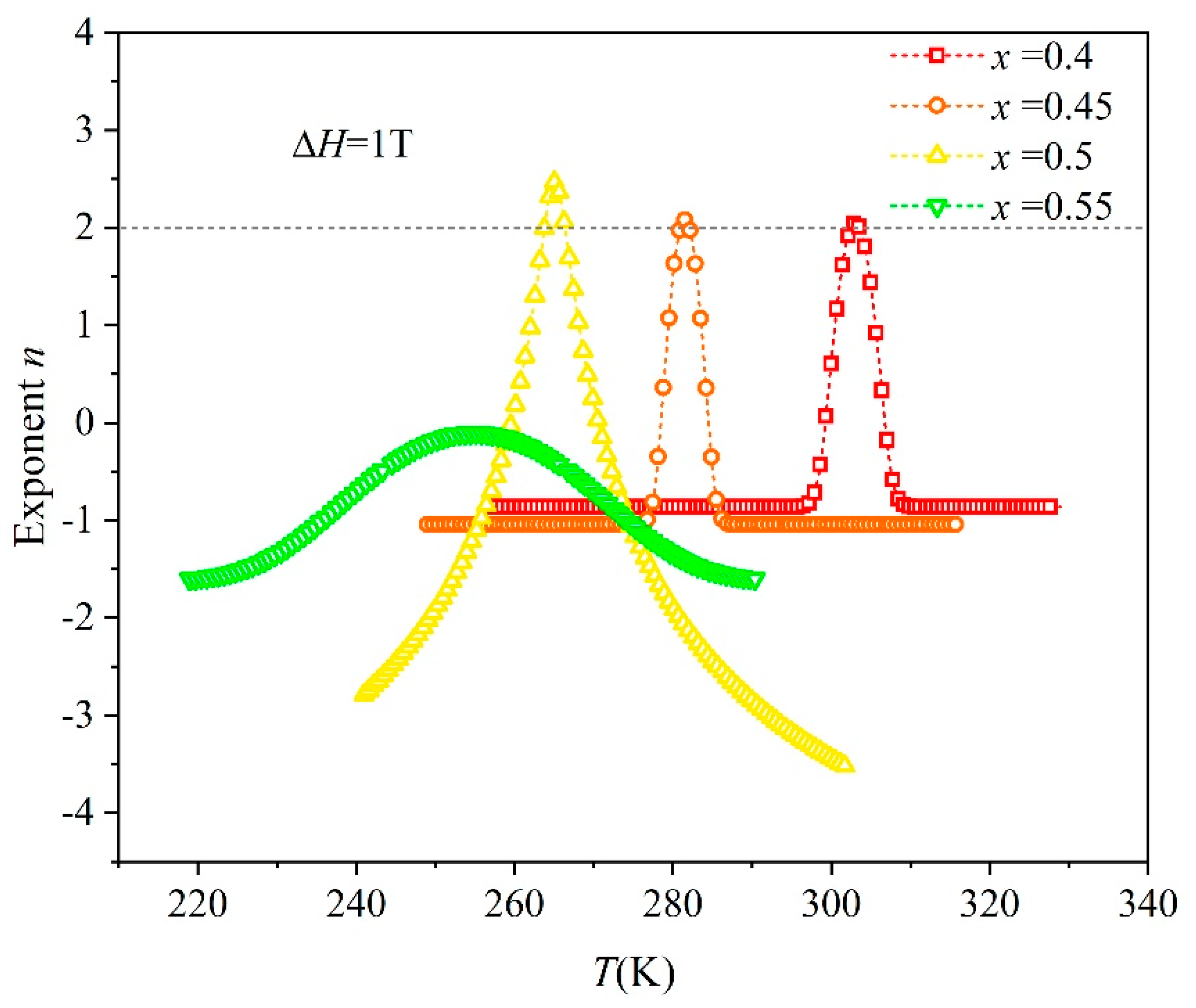
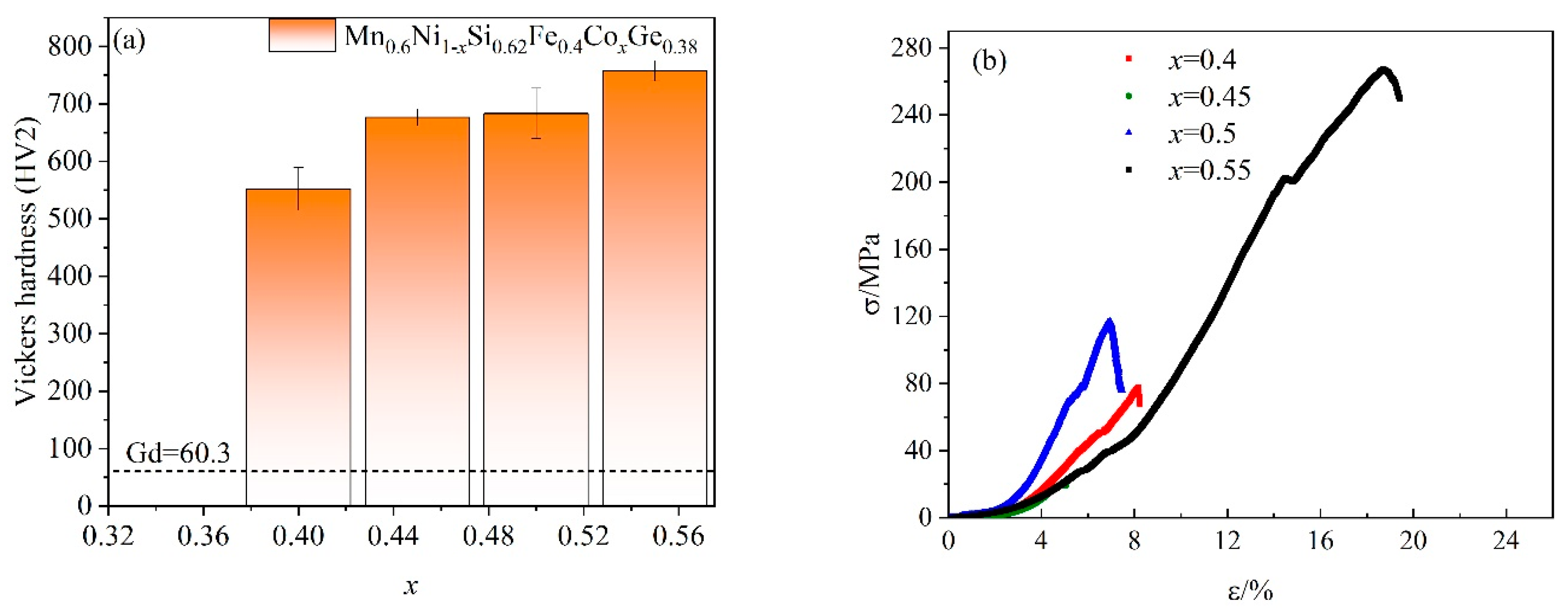
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aprea, C.; Greco, A.; Maiorino, A. Magnetic Refrigeration: A Promising New Technology for Energy Saving. Int. J. Ambient. Energy 2016, 37, 294–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S. Experimental Study on a Piston-Driven Type Magnetic Refrigeration Apparatus. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2022, 36, 3165–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitanovski, A.; Egolf, P.W. Application of Magnetic Refrigeration and its Assessment. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zou, Z.; He, B.; Liu, L.; Mao, Z. Research Progress of Doped Manganite Materials in Magnetic Refrigeration. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 771941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, I.; Sandeman, K. Solid-state Cooling with Caloric Materials. Phys. Today 2015, 68, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fähler, S. Caloric effects in Ferroic Materials: New Concepts for Cooling. Energy Technol. 2018, 6, 1394–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, X.; Kar-Narayan, S.; Mathur, N.D. Caloric Materials near Ferroic Phase Transitions. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, X.; Mathur, N.D. Caloric Materials for Cooling and Heating. Science 2020, 370, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vopson, M.M. The Multicaloric Effect in Multiferroic Materials. Solid State Commun. 2012, 152, 2067–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.Z.; Li, Q.; Bellaiche, L.; Scott, J.F.; Dkhil, B.; Wang, Q. Towards multicaloric effect with ferroelectrics. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 94, 214113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mañosa, L.; Stern-Taulats, E.; Gràcia-Condal, A.; Planes, A. Cross-Coupling Contribution to the Isothermal Entropy Change in Multicaloric Materials. J. Phys. Energy 2023, 5, 24016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, N.R.; Prakash, M.; Naresh, U.; Kumar, N.S.; Sarmash, T.S.; Subbarao, T.; Kumar, R.J.; Kumar, G.R.; Naidu, K.C.B. Review on Magnetocaloric Effect and Materials. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2018, 31, 1971–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegus, O.; Brück, E.; Buschow, K.H.J.; de Boer, F.R. Transition-metal-based magnetic refrigerants for room-temperature applications. Nature 2002, 415, 150–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanta, T.; Lloveras, P.; Saleheen, A.U.; Lepkowski, D.L.; Kramer, E.; Dubenko, I.; Adams, P.W.; Young, D.P.; Barrio, M.; Tamarit, J.L.; et al. Barocaloric and Magnetocaloric effects in (MnNiSi)1−x (FeCoGe)x. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 021907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Lin, J.C.; Jiang, W.B.; Yang, C.; Li, L.F.; Zhang, X.K.; Song, W.H.; Zhu, X.B.; Tong, P.; Sun, Y.P. Enhanced Mechanical Properties and Large Magnetocaloric effect in Epoxy-Bonded Mn0.98CoGe. Scr. Mater. 2018, 150, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Tao, K.; Chen, B.; Chen, H.; Qiao, K.; Yu, Z.; Cong, J.; Huang, R.; Taskaev, S.V.; Zhang, H. Low-melting Metal Bonded MM′X/In Composite with Largely Enhanced Mechanical Property and Anisotropic Negative Thermal Expansion. Acta Mater. 2022, 229, 117830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.; Zheng, S.; Pang, J.; Ma, X. High-Strength and High-Ductility AlCoCrFeNi2.1 Eutectic High-Entropy Alloy Achieved via Precipitation Strengthening in a Heterogeneous Structure. Scr. Mater. 2020, 186, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Jia, Y.; Wang, Z.; He, F.; Wei, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, J. Rapid Alloy Design from Superior Eutectic High-Entropy Alloys. Scr. Mater. 2022, 219, 114875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Shi, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P. Microstructure and Properties of Laser Cladding AlxFeCoCrNiMn High Entropy Alloy of Q345 Steel. Mater. Res. 2023, 26, e20220154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, N.; Xing, B.; Yin, S. An Assessment of the High-Temperature Oxidation Resistance of Selected Thermal Sprayed High Entropy Alloy Coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2022, 31, 1386–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.X.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.Q.; Huang, M.Z.; Xiang, H.M.; Xue, L.Y.; Jiang, Z.M.; Zhao, Z.G.; Wei, L.F.; Zheng, Y.; et al. High-Entropy (Sm0.2Eu0.2Gd0.2Dy0.2Er0.2)2Hf2O7 Ceramic with Superb Resistance to Radiation-Induced Amorphization. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 155, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.G.; Du, J.P.; Yu, P.J.; Li, R.; Shinzato, S.H.; Peng, Q.; Ogata, S. Chemical Ordering effect on the Radiation Resistance of a CoNiCrFeMn High-Entropy Alloy. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2022, 214, 111764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.G.; Jo, Y.H.; Park, J.M.; Choi, W.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, B.; Sohn, S.S.; Lee, S. Effects of Annealing Temperature on Microstructures and Tensile Properties of a Single FCC Phase CoCuMnNi High-Entropy Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 812, 152111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J. Alloy Design Strategies and Future Trends in High-Entropy Alloys. JOM 2013, 65, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.Y.; Franco, V. Pushing the Limits of Magnetocaloric High-Entropy Alloys. APL Mater. 2021, 9, 080702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.Y.; Franco, V. Review on Magnetocaloric High-Entropy Alloys: Design and Analysis Methods. J. Mater. Res. 2022, 38, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.Y.; Díaz-García, Á.; Moreno-Ramírez, L.M.; Franco, V. Increased magnetocaloric response of FeMnNiGeSi high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2021, 212, 116931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Tong, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.J.; Ma, L.; Suo, H.L.; Lu, Z.P. Rare-earth high-entropy alloys with giant magnetocaloric effect. Acta Mater. 2017, 125, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.G.; Chen, X.L.; Wang, H.Y.; Da, S.; Wang, G.; Qiu, Z.G.; Zeng, D.C.; Xia, Q.B. Giant magnetocaloric effects of MnNiSi-based high-entropy alloys near room temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 966, 171483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazela, W.; Szytuła, A.; Todorović, J.; Tomkowicz, Z.; Zięba, A. Crystal and Magnetic Structure of NiMnGe. Phys. Status Solidi 1976, 38, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Taani, H.; Tarawneh, K.; Al-Khatatbeh, Y.; Hamad, B. The High-Pressure Stability of Ni2In-type Structure of ZrO2 with Respect to OII and Fe2P-type Phases: A First-Principles Study, IOP Conference Series. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 305, 12016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, D.; Li, Z.; Cong, J.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, S.; Jiang, P.; Cong, D.; Zheng, X.; Qiao, K.; et al. Large Enhancement of Magnetocaloric Effect Induced by Dual Regulation Effects of Hydrostatic Pressure in Mn0.94Fe0.06NiGe Compound. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 114, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SzytuŁa, A.; Pȩdziwiatr, A.T.; Tomkowicz, Z.; Bażela, W. Crystal and magnetic structure of CoMnGe, CoFeGe, FeMnGe and NiFeGe. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1981, 25, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.K.; Wang, W.; Feng, L.; Zhu, W.; Li, G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Wu, G.; Jiang, C.; Xu, H.; et al. Stable magnetostructural coupling with tunable magnetoresponsive effects in hexagonal ferromagnets. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.Q.; Zhang, C.L.; Nie, Y.G.; Shi, H.F.; Ye, E.J.; Han, Z.D.; Wang, D.H. Tunable magneto-structural phase transition and magnetocaloric effect in Mn1−xNi1−xCo2xSi1−xGex system. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 698, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.J.; Liu, E.K.; Zhang, H.G.; Zhang, Y.J.; Chen, J.L.; Wang, W.H.; Zhang, H.W.; Wu, G.H.; Yu, S.Y. Phase diagram, ferromagnetic martensitic transformation and magnetoresponsive properties of Fe-doped MnCoGe alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 332, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Zheng, Z.G.; Lei, L.; Qiu, Z.G.; Zeng, D.C. Simple Practical System for Directly Measuring Magnetocaloric effects under Large Magnetic Fields. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2020, 91, 065102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, P.B.D.; Terashima, K.; Yamamoto, T.D.; Iwasaki, S.; Matsumoto, R.; Adachi, S.; Saito, Y.; Takeya, H.; Takano, Y. Effect of Dy substitution in the giant magnetocaloric properties of HoB2. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2021, 21, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.G.; Chen, X.L.; Liu, J.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Da, S.; Qiu, Z.G.; Zeng, D.C. Dynamical Response of Gadolinium in Alternating Magnetic Fields up to 9Hz. Int. J. Refrig. 2023, 146, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.Y.; Franco, V.; Moreno-Ramírez, L.M.; Conde, A.; Karpenkov, D.Y.; Radulov, I.; Skokov, K.P.; Gutfleisch, O. A Quantitative Criterion for Determining the Order of Magnetic Phase Transitions Using the Magnetocaloric Effect. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
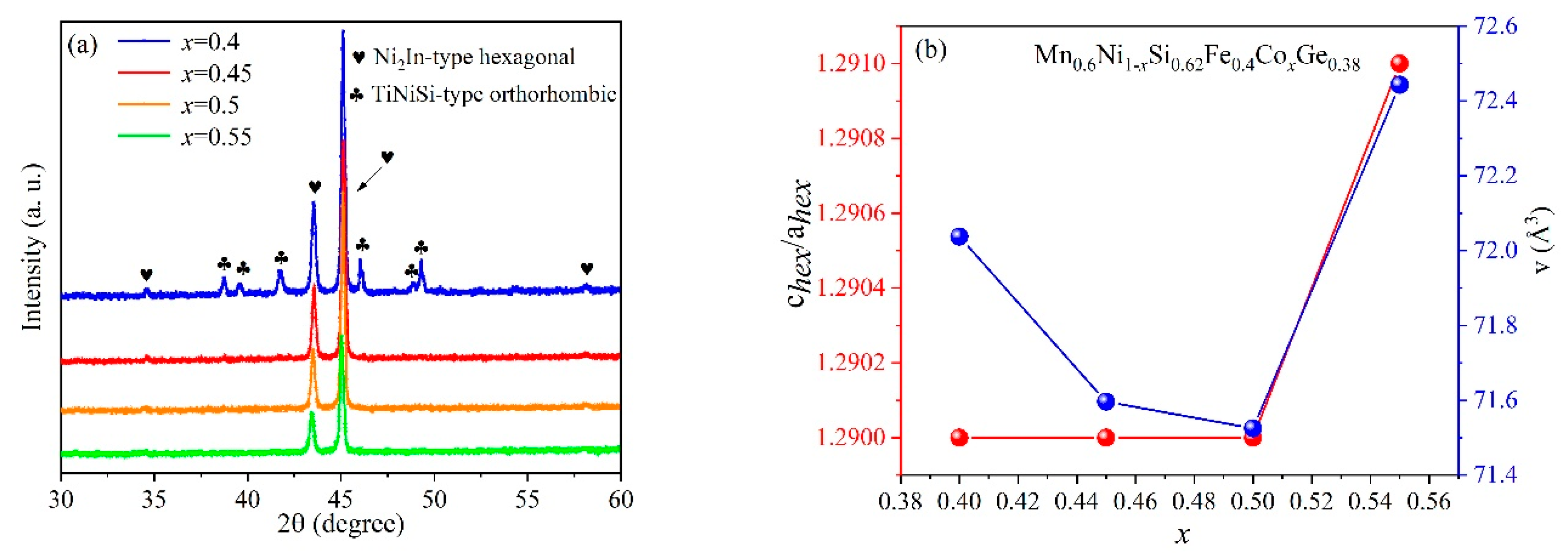

| x = 0.4 | x = 0.45 | x = 0.5 | x = 0.55 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni2In-type phase (%) | 98.6 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| TiNiSi-type phase (%) | 1.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ahex, bhex (Å) | 4.010 | 4.002 | 4.000 | 4.017 |
| chex (Å) | 5.172 | 5.161 | 5.161 | 5.184 |
| chex/ahex | 1.290 | 1.290 | 1.290 | 1.291 |
| aorth (Å) | 6.010 | - | - | - |
| borth (Å) | 3.645 | - | - | - |
| corth (Å) | 6.939 | - | - | - |
| aorth/borth | 1.649 | - | - | - |
| vhex (Å3) | 72.037 | 71.596 | 71.525 | 72.443 |
| vorth (Å3) | 152.013 | - | - | - |
| Rwp-hex (%) | 5.976 | 6.138 | 5.036 | 3.380 |
| Rwp-orth (%) | 3.369 | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Z.; Huang, P.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Da, S.; Wang, G.; Qiu, Z.; Zeng, D. Enhanced Magnetocaloric Properties of the (MnNi)0.6Si0.62(FeCo)0.4Ge0.38 High-Entropy Alloy Obtained by Co Substitution. Entropy 2024, 26, 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26090799
Zheng Z, Huang P, Chen X, Wang H, Da S, Wang G, Qiu Z, Zeng D. Enhanced Magnetocaloric Properties of the (MnNi)0.6Si0.62(FeCo)0.4Ge0.38 High-Entropy Alloy Obtained by Co Substitution. Entropy. 2024; 26(9):799. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26090799
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Zhigang, Pengyan Huang, Xinglin Chen, Hongyu Wang, Shan Da, Gang Wang, Zhaoguo Qiu, and Dechang Zeng. 2024. "Enhanced Magnetocaloric Properties of the (MnNi)0.6Si0.62(FeCo)0.4Ge0.38 High-Entropy Alloy Obtained by Co Substitution" Entropy 26, no. 9: 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26090799
APA StyleZheng, Z., Huang, P., Chen, X., Wang, H., Da, S., Wang, G., Qiu, Z., & Zeng, D. (2024). Enhanced Magnetocaloric Properties of the (MnNi)0.6Si0.62(FeCo)0.4Ge0.38 High-Entropy Alloy Obtained by Co Substitution. Entropy, 26(9), 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26090799







