The Glass Transition: A Topological Perspective
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Geometric Signatures of Topological Changes
2.2. Numerical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Model
3.2. Characterization of the Phase Transition
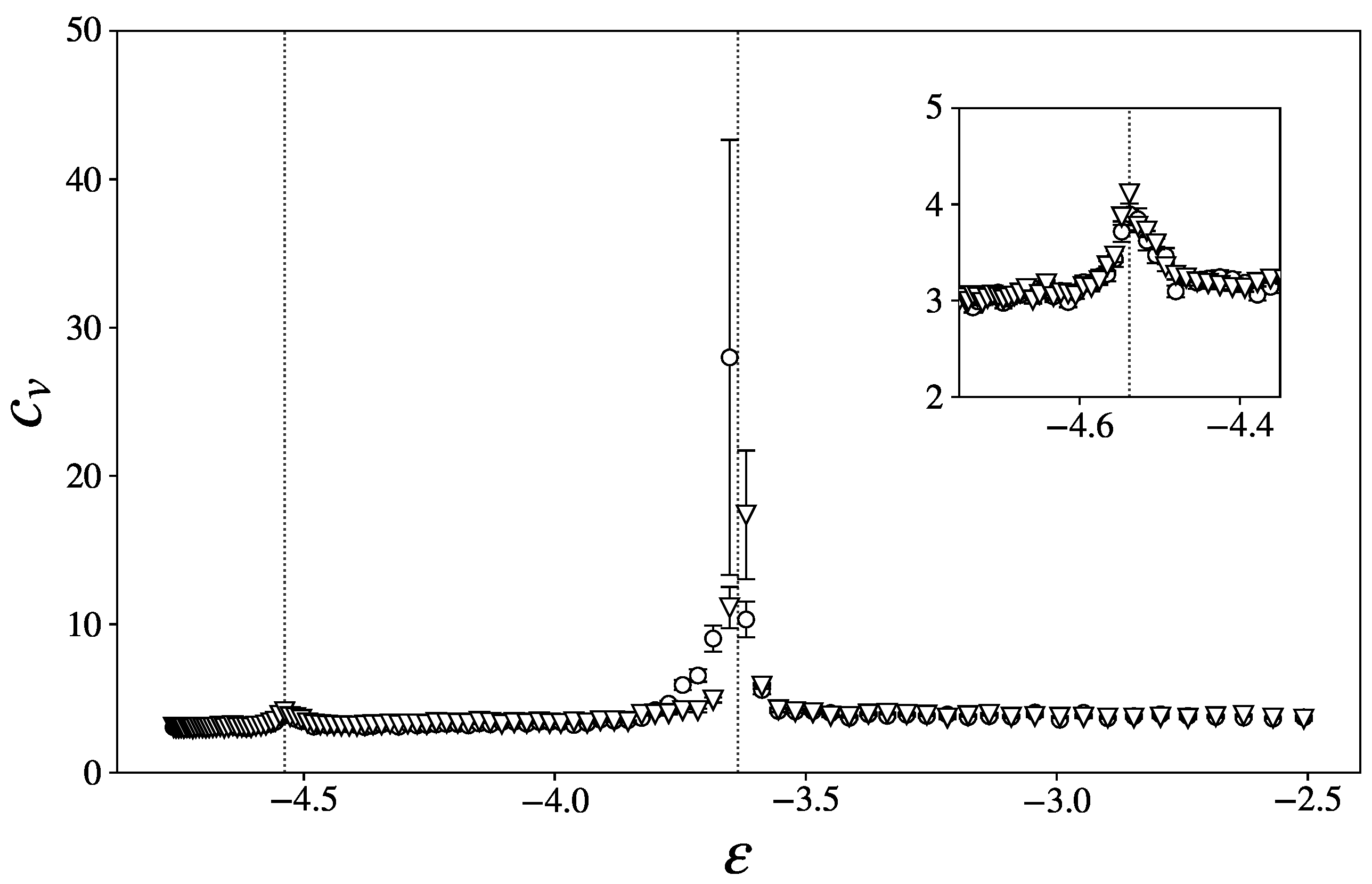
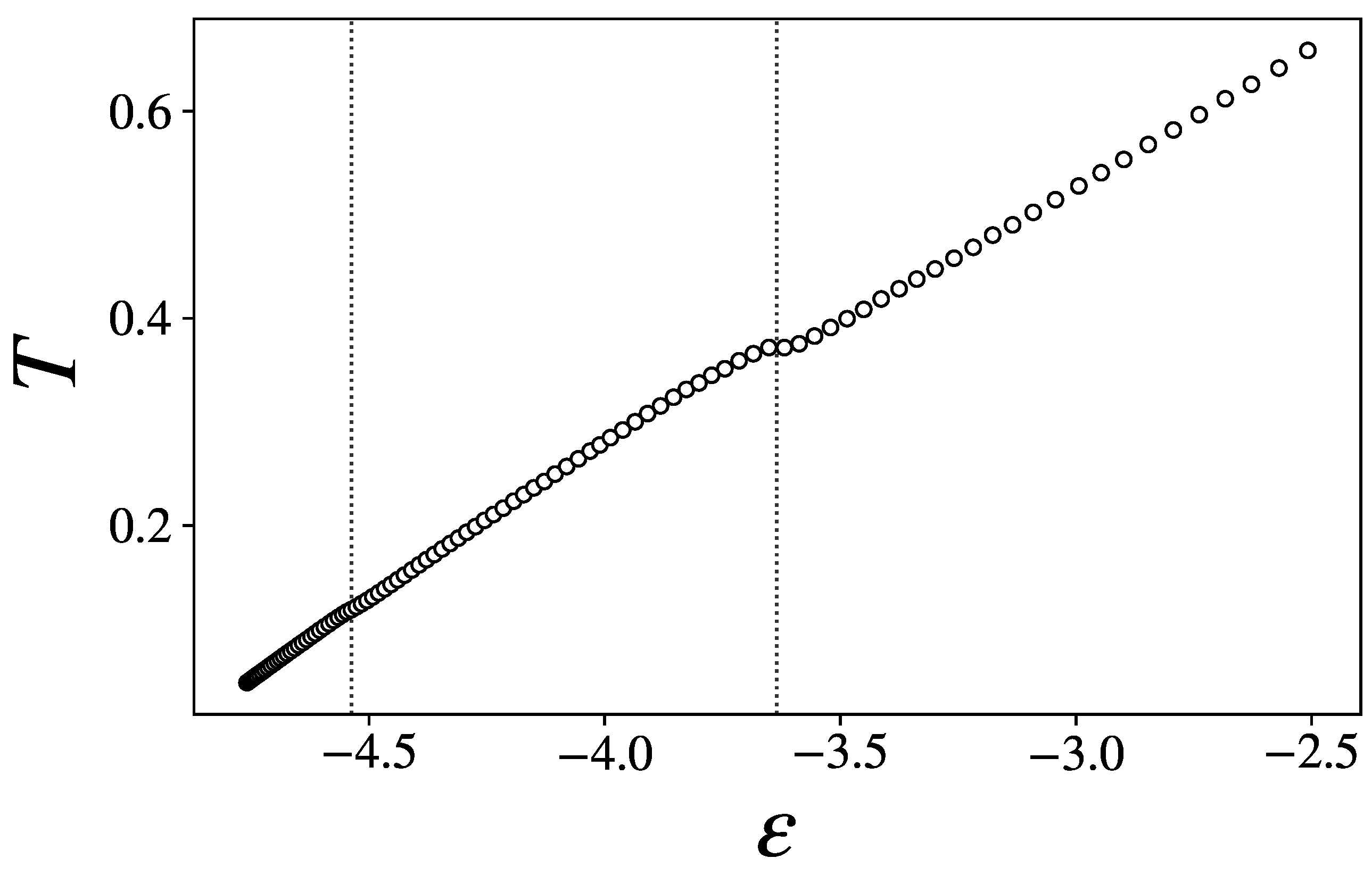
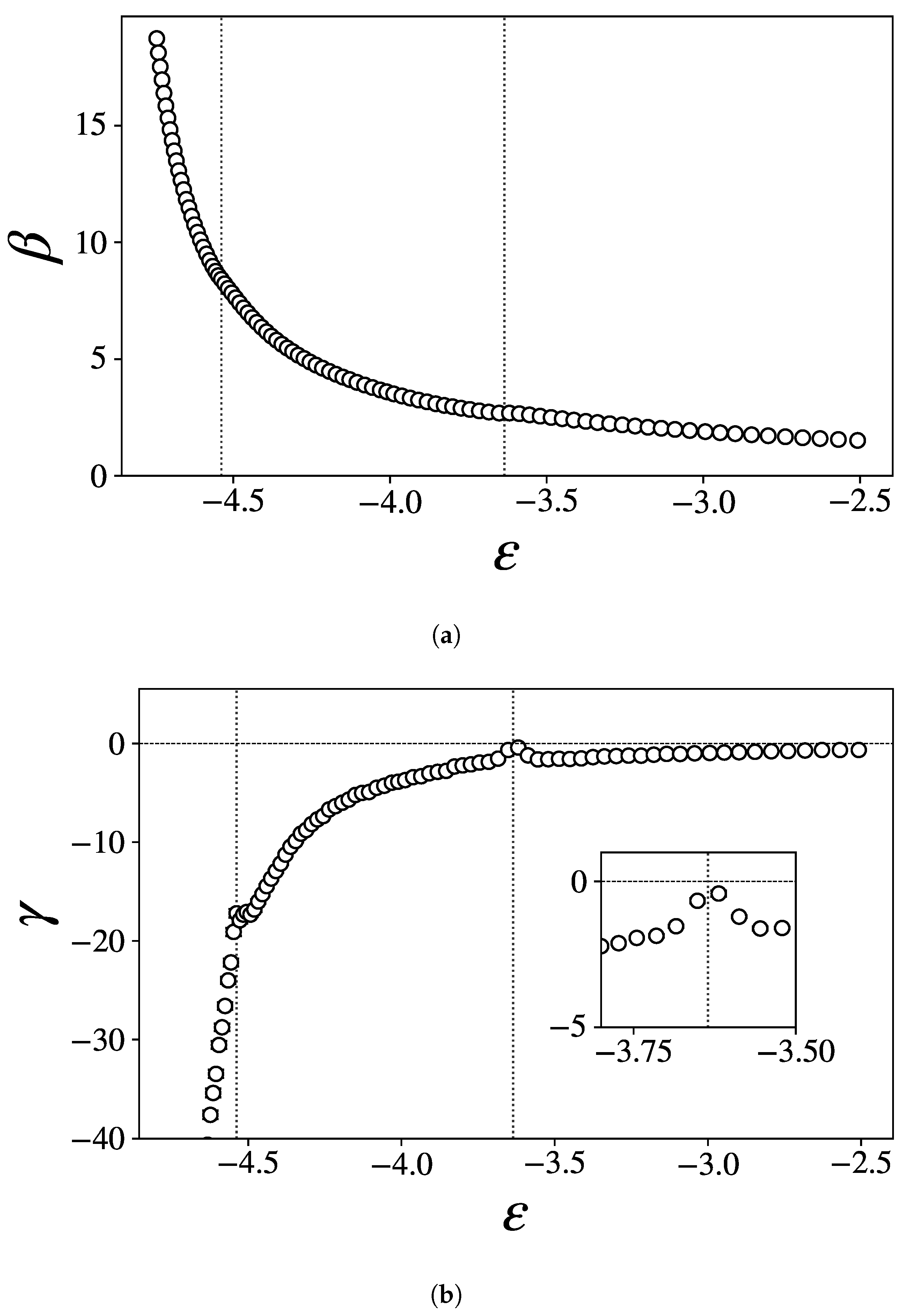
3.2.1. Specific Heat, Caloric Curve, and Entropy Derivatives
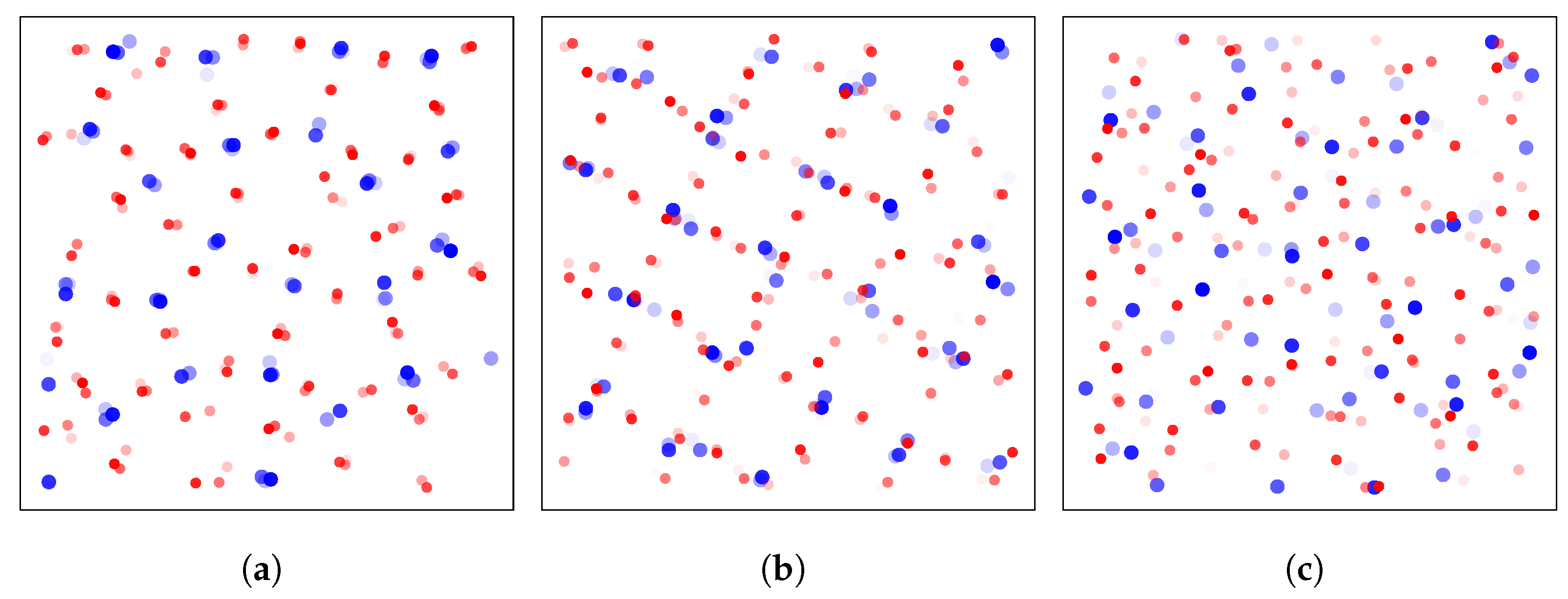
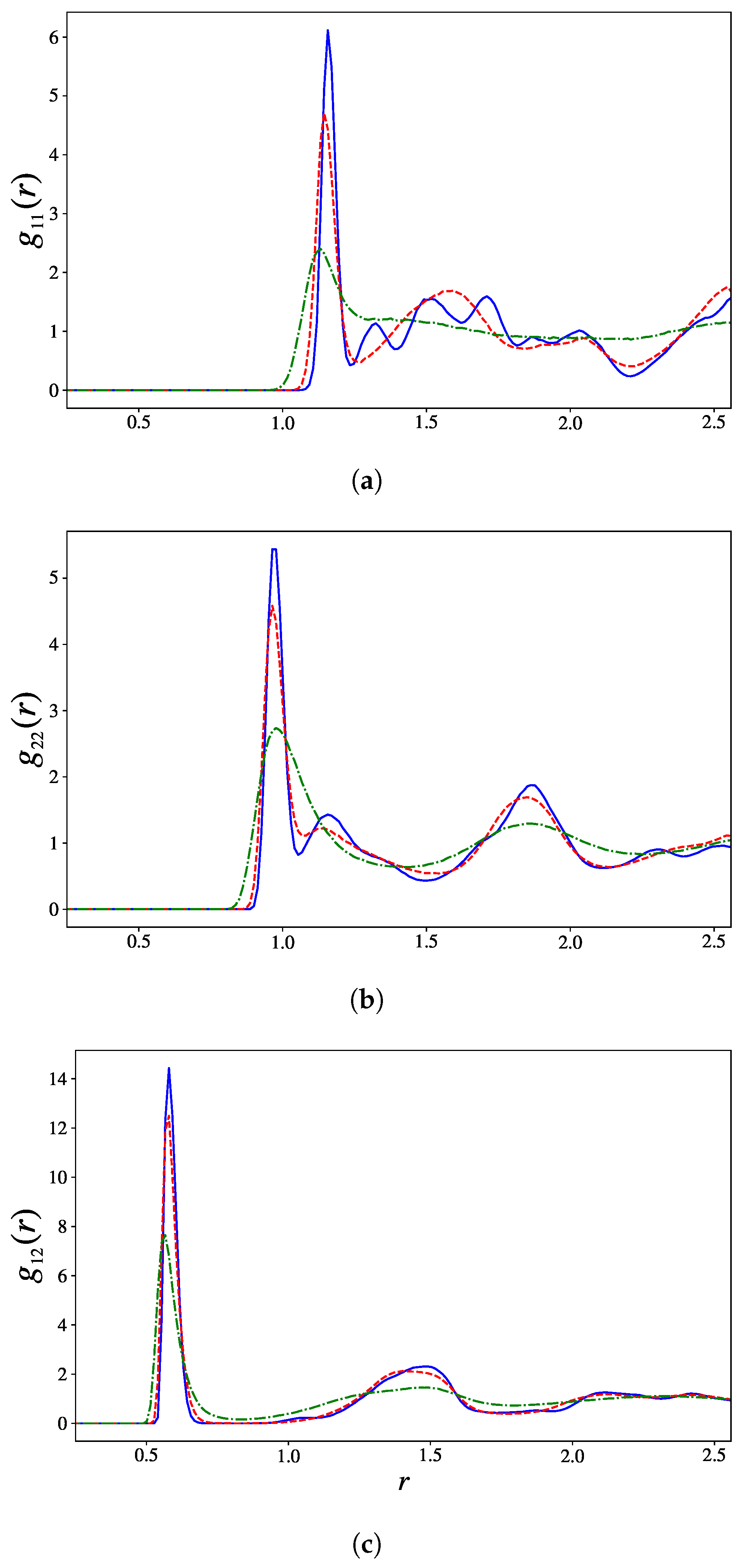
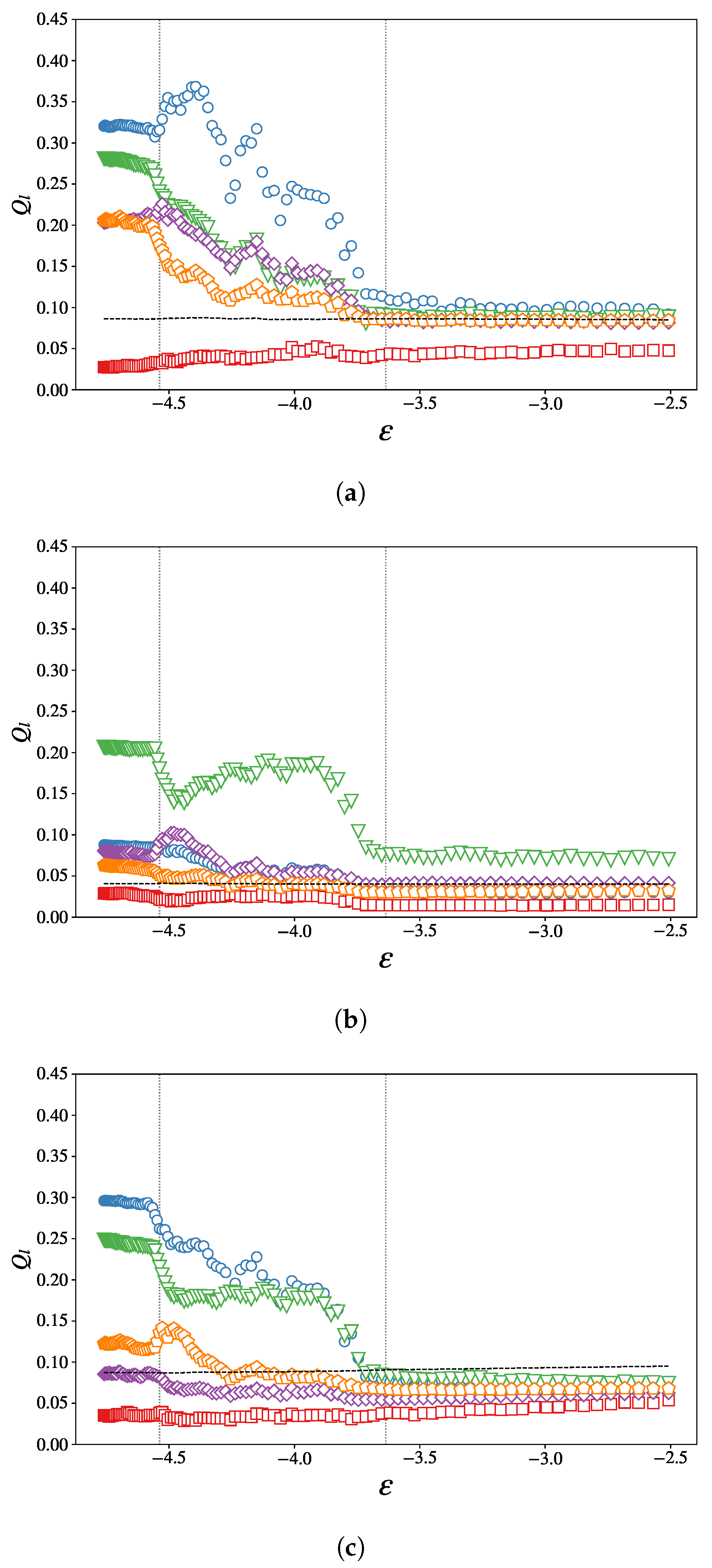
3.2.2. Translational and Orientational Order
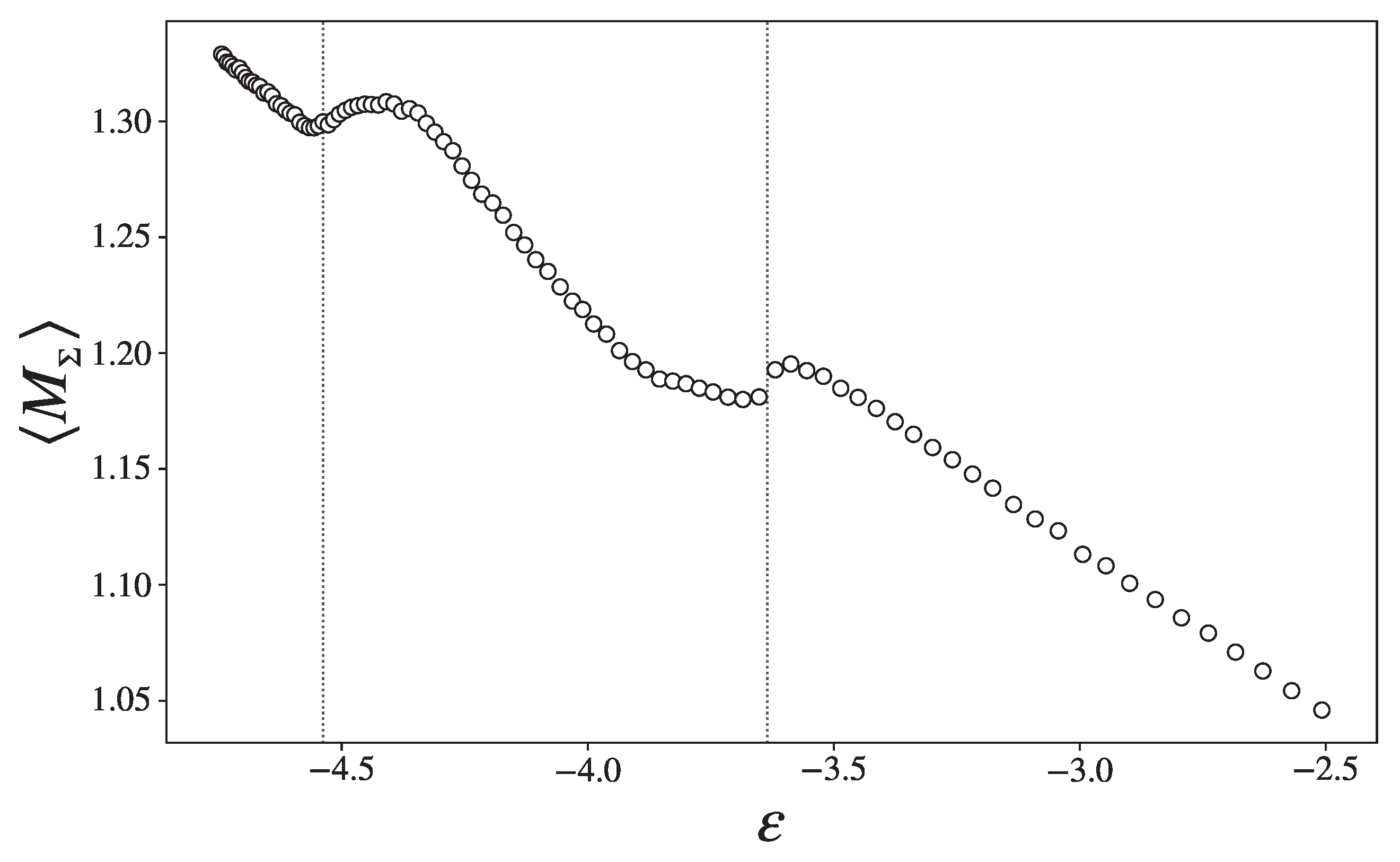
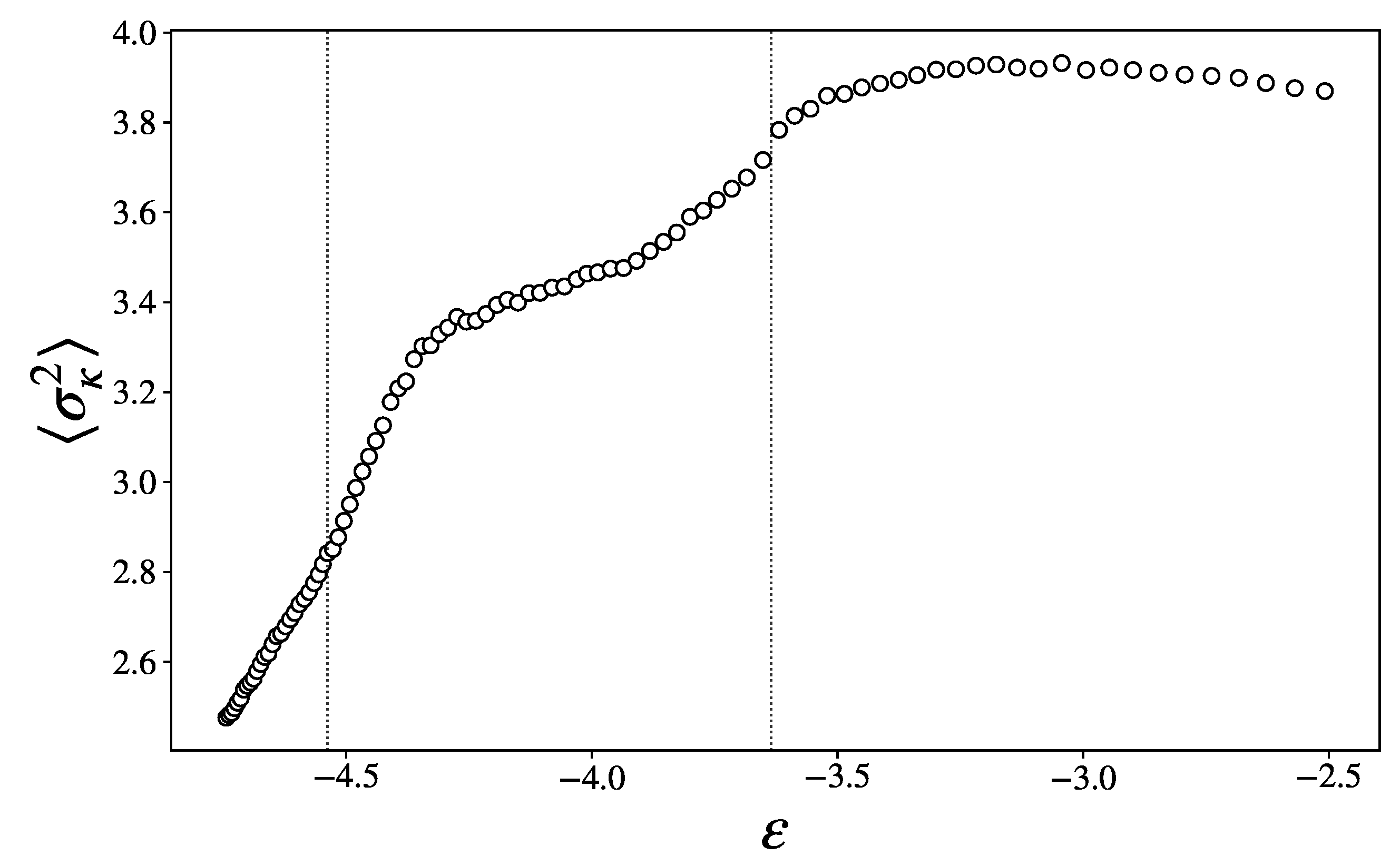
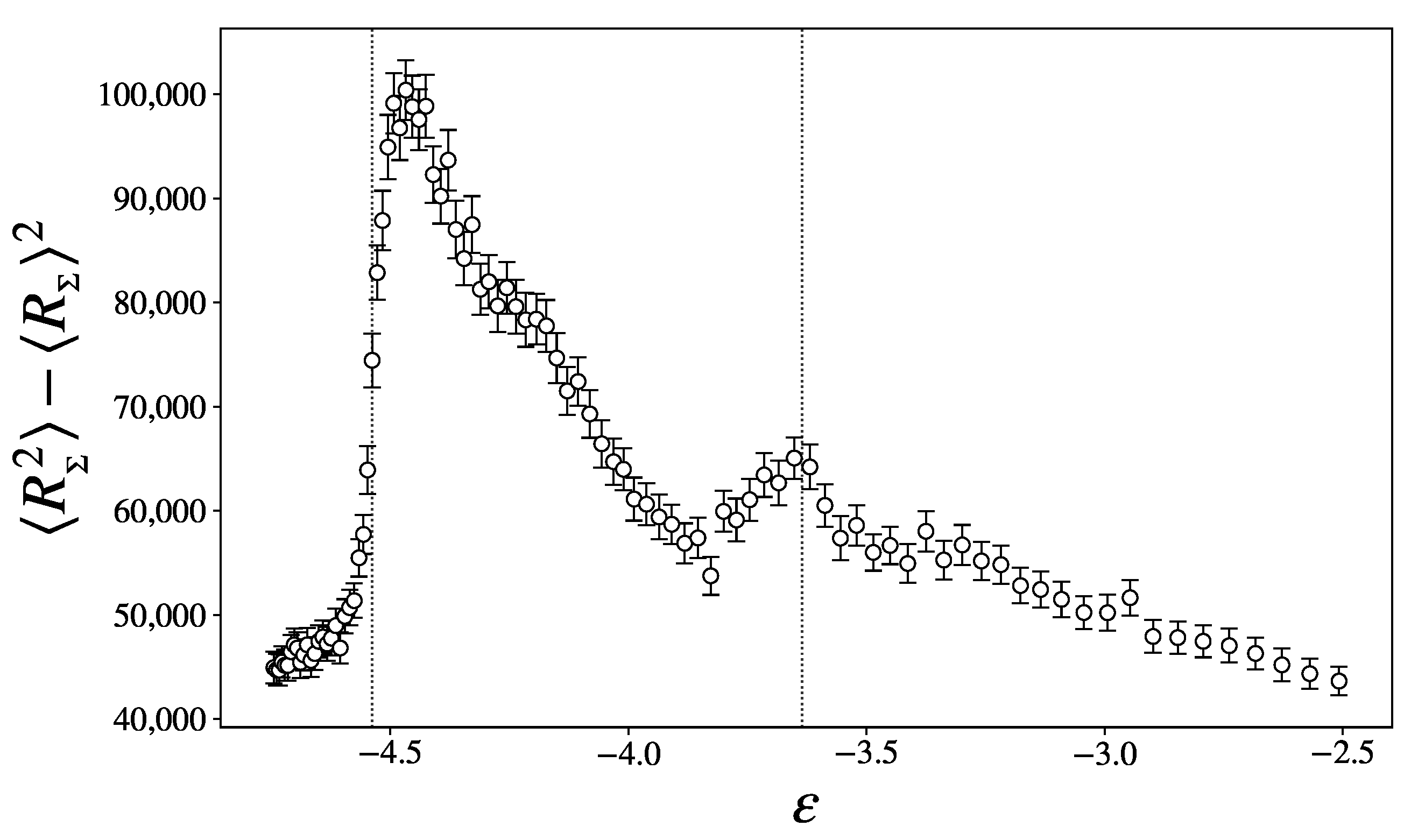
3.3. Topological Changes
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Monte Carlo Methods
| Algorithm A1: E-range optimization through U-overlap method |
 |
Appendix B. Initial Configuration, Periodic Boundary Conditions and Cutoff
References
- Pettini, M. Geometry and Topology in Hamiltonian Dynamics and Statistical Mechanics; Interdisciplinary Applied Mathematics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Volume 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angell, C. Perspective on the Glass Transition. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1988, 49, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, G. The Physics of the Glass Transition. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2000, 280, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelani, L.; Di Leonardo, R.; Ruocco, G.; Scala, A.; Sciortino, F. Saddles in the Energy Landscape Probed by Supercooled Liquids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 5356–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broderix, K.; Bhattacharya, K.K.; Cavagna, A.; Zippelius, A.; Giardina, I. Energy Landscape of a Lennard-Jones Liquid: Statistics of Stationary Points. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 5360–5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigera, T.S. Geometrical Properties of the Potential Energy of the Soft-Sphere Binary Mixture. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 124, 064502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigera, T.S.; Cavagna, A.; Giardina, I.; Parisi, G. Geometric Approach to the Dynamic Glass Transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 055502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, M. The Calculus of Variations in the Large, repr ed.; Number 18 in Colloquium Publications/American Mathematical Society; American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gori, M.; Franzosi, R.; Pettini, M. Topological Origin of Phase Transitions in the Absence of Critical Points of the Energy Landscape. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2018, 2018, 093204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cairano, L.; Gori, M.; Pettini, M. Topology and Phase Transitions: A First Analytical Step towards the Definition of Sufficient Conditions. Entropy 2021, 23, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cairano, L.; Gori, M.; Pettini, G.; Pettini, M. Hamiltonian Chaos and Differential Geometry of Configuration Space–Time. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2021, 422, 132909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, T.L. Thermodynamics of Small Systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1962, 36, 3182–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, D.H.E.; Kenney, J.F. The Microcanonical Thermodynamics of Finite Systems: The Microscopic Origin of Condensation and Phase Separations, and the Conditions for Heat Flow from Lower to Higher Temperatures. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 122, 224111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leocmach, M.; Tanaka, H. Roles of Icosahedral and Crystal-like Order in the Hard Spheres Glass Transition. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H. Bond Orientational Order in Liquids: Towards a Unified Description of Water-like Anomalies, Liquid-Liquid Transition, Glass Transition, and Crystallization: Bond Orientational Order in Liquids. Eur. Phys. J. E 2012, 35, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinisch, J.; Heuer, A. Local Properties of the Potential-Energy Landscape of a Model Glass: Understanding the Low-Temperature Anomalies. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 70, 064201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coluzzi, B.; Mézard, M.; Parisi, G.; Verrocchio, P. Thermodynamics of Binary Mixture Glasses. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 111, 9039–9052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coslovich, D.; Pastore, G. Understanding Fragility in Supercooled Lennard-Jones Mixtures. I. Locally Preferred Structures. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 127, 124504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernu, B.; Hansen, J.P.; Hiwatari, Y.; Pastore, G. Soft-Sphere Model for the Glass Transition in Binary Alloys: Pair Structure and Self-Diffusion. Phys. Rev. A 1987, 36, 4891–4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kob, W.; Andersen, H.C. Testing Mode-Coupling Theory for a Supercooled Binary Lennard-Jones Mixture I: The van Hove Correlation Function. Phys. Rev. E 1995, 51, 4626–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flenner, E.; Szamel, G. Hybrid Monte Carlo Simulation of a Glass-Forming Binary Mixture. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 73, 061505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlin, R.V. An Ising Model for Supercooled Liquids and the Glass Transition. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bel-Hadj-Aissa, G.; Gori, M.; Penna, V.; Pettini, G.; Franzosi, R. Geometrical Aspects in the Analysis of Microcanonical Phase-Transitions. Entropy 2020, 22, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, E.M.; Halicioglu, T.; Tiller, W.A. Laplace-Transform Technique for Deriving Thermodynamic Equations from the Classical Microcanonical Ensemble. Phys. Rev. A 1985, 32, 3030–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cairano, L.; Capelli, R.; Bel-Hadj-Aissa, G.; Pettini, M. Topological Origin of the Protein Folding Transition. Phys. Rev. E 2022, 106, 054134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bel-Hadj-Aissa, G.; Gori, M.; Franzosi, R.; Pettini, M. Geometrical and Topological Study of the Kosterlitz–Thouless Phase Transition in the XY Model in Two Dimensions. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2021, 2021, 023206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkall, U. Inequalities of Willmore Type for Submanifolds. Math. Z. 1986, 193, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overholt, M. Fluctuation of Sectional Curvature for Closed Hypersurfaces. Rocky Mt. J. Math. 2002, 32, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coslovich, D.; Pastore, G. Dynamics and Energy Landscape in a Tetrahedral Network Glass-Former: Direct Comparison with Models of Fragile Liquids. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 285107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigera, T.S.; Parisi, G. Fast Monte Carlo Algorithm for Supercooled Soft Spheres. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 63, 045102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettini, G.; Gori, M.; Franzosi, R.; Clementi, C.; Pettini, M. On the Origin of Phase Transitions in the Absence of Symmetry-Breaking. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2019, 516, 376–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnabel, S.; Seaton, D.T.; Landau, D.P.; Bachmann, M. Microcanonical Entropy Inflection Points: Key to Systematic Understanding of Transitions in Finite Systems. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 84, 011127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, K.; Bachmann, M. Classification of Phase Transitions by Microcanonical Inflection-Point Analysis. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 180601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, M. Novel Concepts for the Systematic Statistical Analysis of Phase Transitions in Finite Systems. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 487, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lévy, L.P. Critical Dynamics of Metallic Spin Glasses. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 38, 4963–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, E. Spin Glass Experiments. In Encyclopedia of Condensed Matter Physics, 2nd ed.; Chakraborty, T., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2024; pp. 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchiat, H. Determination of the Critical Exponents in the Ag Mn Spin Glass. J. Phys. 1986, 47, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malthe-Sørenssen, A. Finite Size Scaling. In Percolation Theory Using Python; Malthe-Sørenssen, A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behringer, H.; Pleimling, M.; Hüller, A. Finite-Size Behaviour of the Microcanonical Specific Heat. J. Phys. Math. Gen. 2005, 38, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhardt, P.J.; Nelson, D.R.; Ronchetti, M. Bond-Orientational Order in Liquids and Glasses. Phys. Rev. B 1983, 28, 784–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errington, J.R.; Debenedetti, P.G.; Torquato, S. Quantification of Order in the Lennard-Jones System. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 118, 2256–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdes, L.C.; Affouard, F.; Descamps, M.; Habasaki, J. Mixing Effects in Glass-Forming Lennard-Jones Mixtures. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 130, 154505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truskett, T.M.; Torquato, S.; Debenedetti, P.G. Towards a Quantification of Disorder in Materials: Distinguishing Equilibrium and Glassy Sphere Packings. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 62, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.J.; Barkema, G.T. Monte Carlo Methods in Statistical Physics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, J.R. Microcanonical Ensemble Monte Carlo Method. Phys. Rev. A 1991, 44, 4061–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustig, R. Microcanonical Monte Carlo Simulation of Thermodynamic Properties. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 109, 8816–8828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hukushima, K. Domain-Wall Free Energy of Spin-Glass Models: Numerical Method and Boundary Conditions. Phys. Rev. E 1999, 60, 3606–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozada, I.; Aramon, M.; Machta, J.; Katzgraber, H.G. Effects of Setting the Temperatures in the Parallel Tempering Monte Carlo Algorithm. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 100, 043311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holian, B.L.; Evans, D.J. Shear Viscosities Away from the Melting Line: A Comparison of Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Molecular Dynamics. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 78, 5147–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vesperini, A.; Franzosi, R.; Pettini, M. The Glass Transition: A Topological Perspective. Entropy 2025, 27, 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27030258
Vesperini A, Franzosi R, Pettini M. The Glass Transition: A Topological Perspective. Entropy. 2025; 27(3):258. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27030258
Chicago/Turabian StyleVesperini, Arthur, Roberto Franzosi, and Marco Pettini. 2025. "The Glass Transition: A Topological Perspective" Entropy 27, no. 3: 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27030258
APA StyleVesperini, A., Franzosi, R., & Pettini, M. (2025). The Glass Transition: A Topological Perspective. Entropy, 27(3), 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27030258






