1H-NMR as a Structural and Analytical Tool of Intra- and Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonds of Phenol-Containing Natural Products and Model Compounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Parameters Influencing Phenol –OH Proton Exchange Rates
2.1. Effects of pH


2.2. Effects of Temperature

2.3. Effects of Solvents

3. Assignments of Phenol –OH Resonances



4. Phenol OH Proton Shieldings
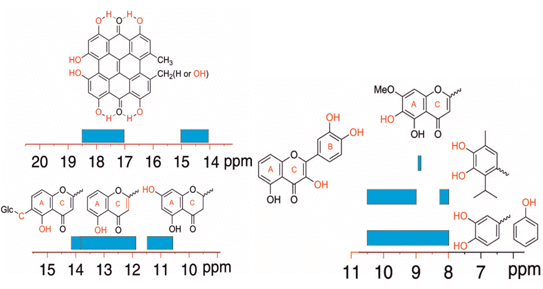
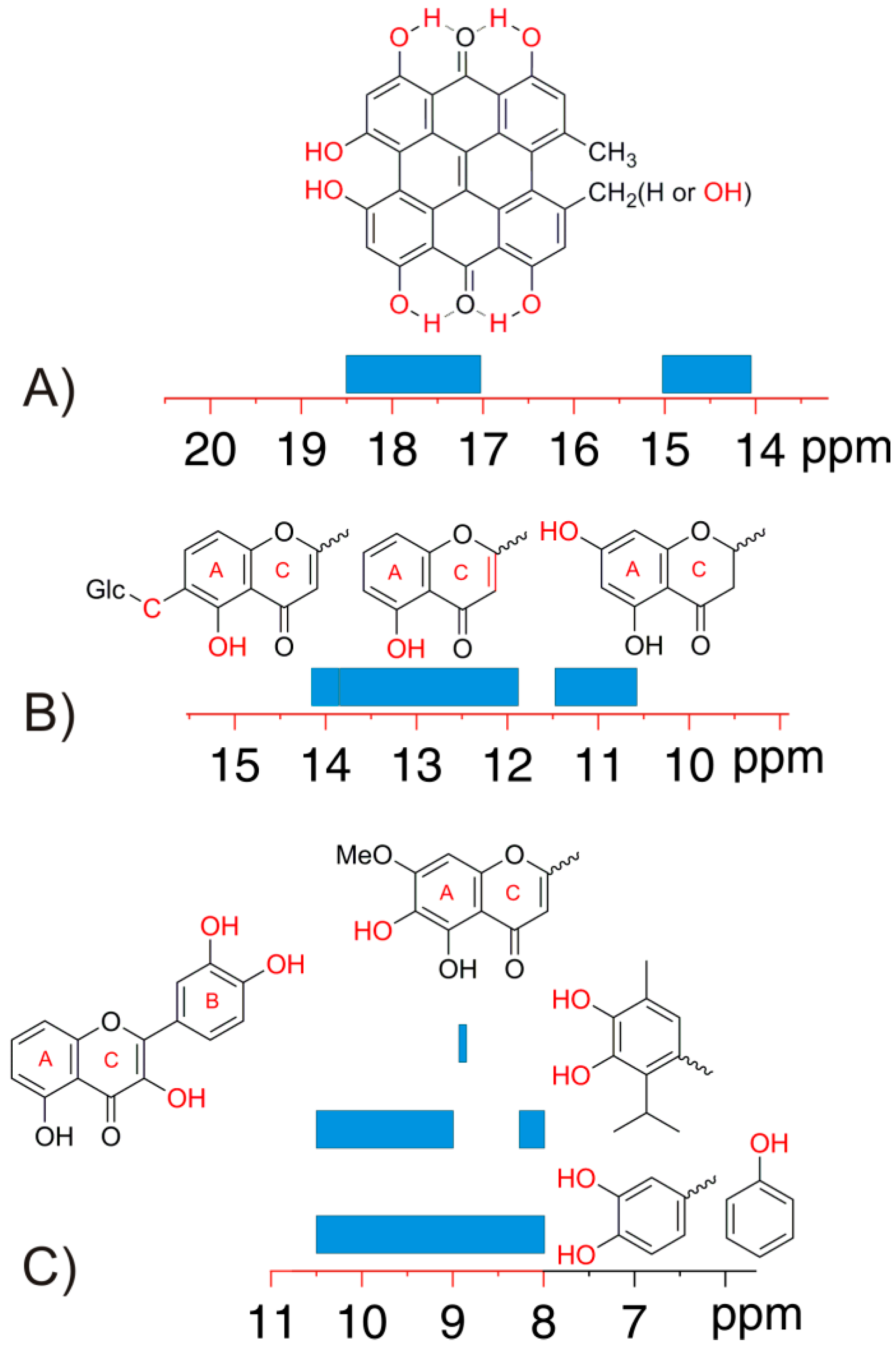
4.1. –OH Shielding Range—Effects of Hydrogen Bonding
| No. | Compound | δΟΗ | δCH | Conc., mol.% | No. | Compound | δΟΗ | Conc., mol.% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | 11.83 | 6.90 | 0.4 | 9 |  | 10.73 | 0.2 |
| 2 |  | 12.36 | 7.12 | 0.2 | 10 | 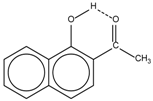 | 13.92 † | 3.3 † |
| 3 |  | - | 6.95 | 1.0 | 11 |  | 7.33 | 0.3 |
| 4 | 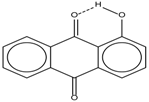 | 12.52 | - | 0.9 | 12 | 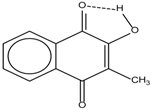 | 7.35 | 0.5 |
| 5 | 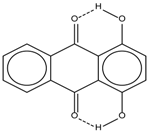 | 12.85 | 7.29 | 0.4 | 13 | 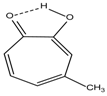 | 9.00 | 0.5 |
| 6 | 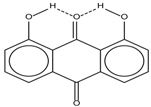 | 12.00 | - | 0.2 | 14 | 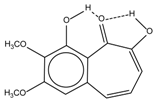 | a 8.49 b 14.71 | 1.0 |
| 7 | 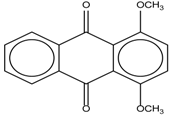 | - | 7.35 | 0.6 | 15 | 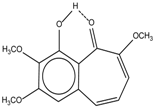 | 15.16 | 1.0 |
| 8 | 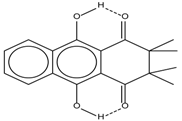 | 13.50 | - | 0.8 |


| Compound | 3 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 3′ | 4′ | 5′ | C-2−C-3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin (1) | OH | OH | H | OH | H | OH | OH | H | double | |||||||||
| Luteolin (2) | H | OH | H | OH | H | OH | OH | H | double | |||||||||
| Myricetin (3) | OH | OH | H | OH | H | OH | OH | OH | double | |||||||||
| Kaempferol (4) | OH | OH | H | OH | H | H | OH | H | double | |||||||||
| Chrysin (5) | H | OH | H | OH | H | H | H | H | double | |||||||||
| Genkwanin (6) | H | OH | H | OCH3 | H | H | OH | H | double | |||||||||
| Apigenin (7) | H | OH | H | OH | H | H | OH | H | double | |||||||||
| 4′,5,6-Trihydroxy-7-methoxyflavone (8) | H | OH | OH | OCH3 | H | H | OH | H | single | |||||||||
| 5,6-Dihydroxy-4′,7-dimethoxyflavone (9) | H | OH | OH | OCH3 | H | H | OCH3 | H | single | |||||||||
| 5,6-Dihydroxy-3′,4′,7-trimethoxyflavone (10) | H | OH | OH | OCH3 | H | OCH3 | OCH3 | H | single | |||||||||
| 4′,5,6-Trihydroxy-7,8-dimethoxyflavone (11) | H | OH | OH | OCH3 | OCH3 | H | OH | H | single | |||||||||
| Naringenin (12) | H | OH | H | OH | H | H | OH | H | single | |||||||||
| Eriodictyol (13) | H | OH | H | OH | H | OH | OH | H | single | |||||||||
| Aromadendrin (14) | OH | OH | H | OH | H | H | OH | H | single | |||||||||
| Taxifolin (15) | OH | OH | H | OH | H | OH | OH | H | single | |||||||||
| Tamarixetin (16) | OH | OH | H | OH | H | OH | OCH3 | H | double | |||||||||
| 3′,4′,5,7-Tetrahydroxy-3-methoxyflavone (17) | OCH3 | OH | H | OH | H | OH | OH | H | double | |||||||||
| 3′,5,7-Trihydroxy-3,4′-dimethoxyflavone (18) | OCH3 | OH | H | OH | H | H | OCH3 | H | double | |||||||||
| 3,5,7-Trihydroxy-3′,4′,5′-trimethoxyflavone (19) | OH | OH | H | OH | H | OCH3 | OCH3 | OCH3 | double | |||||||||



4.2. Effects of Solvents
| Compound | δDMSO-d6 | δAcetone-d6 | Δδ(δDMSO-d6 − δAcetone-d6) | δCD3CN | Δδ(δDMSO-d6 − δCD3CN) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin (1) | C-5 OH | 12.52 | 12.18 | 0.34 | 12.01 | 0.51 |
| C-7 OH | 10.80 | 9.61 | 1.19 | 8.11 | 2.69 | |
| C-3 OH | 9.37 | 7.97 | 1.40 | 7.02 | 2.35 | |
| C-3′ OH | 9.32 | 8.41 | 0.91 | 7.02 | 2.30 | |
| C-4′ OH | 9.61 | 8.58 | 1.03 | 7.27 | 2.34 | |
| Kaempferol (4) | C-5 OH | 12.45 | 12.19 | 0.26 | 12.02 | 0.43 |
| C-7 OH | 10.82 | 9.63 | 1.19 | 8.00 | 2.82 | |
| C-3 OH | 9.37 | 8.03 | 1.34 | 7.01 | 2.36 | |
| C-4′ OH | 10.11 | 9.00 | 1.11 | 7.59 | 2.52 | |
| Genkwanin (6) | C-5 OH | 12.95 | 13.03 | −0.08 | 12.95 | 0.00 |
| C-4′ OH | 10.56 | 9.26 | 1.30 | 7.70 | 2.86 | |
| Oleuropein (20) | C-5′ OH | 8.74 | 7.75 | 0.99 | 6.71 | 2.03 |
| C-6′ OH | 8.68 | 7.73 | 0.95 | 6.56 | 2.12 | |
| C-2′′ OH | 5.14 | 4.46 | 0.68 | 3.48 | 1.66 | |
| C-3′′ OH | 5.02 | 4.32 | 0.70 | 3.48 | 1.54 | |
| C-4′′ OH | 4.96 | 4.25 | 0.71 | 3.37 | 1.59 | |
| C-6′′ OH | 4.48 | 3.67 | 0.81 | 2.92 | 1.56 | |
| Hydroxytyrosol (21) | C-3 OH | 8.72 | 7.68 | 1.04 | 6.53 | 2.19 |
| C-4 OH | 8.63 | 7.65 | 0.98 | 6.51 | 2.12 | |
| C-8 OH | 4.60 | 3.54 | 1.06 | 2.60 | 2.00 |
4.3. Temperature Effects of Phenol OH Protons

4.4. Theoretical Calculations
| Compound | Δδ/ΔΤ a,b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMSO-d6 | Acetone-d6 | CD3CN | ||
| Quercetin (1) | C-5 OH | −2.0 (−2.4) | −2.9 (−3.4) | −1.5 (−2.1) |
| C-7 OH | −5.4 (−5.8) | −11.1 (−11.6) | −9.9 (−10.5) | |
| C-3 OH | −8.0 (−8.4 | −11.6 (−12.1) | −4.4 (−5.0) | |
| C-3′ OH | −6.3 (−6.7) | −8.4 (−8.9) | −6.7 (−7.3) | |
| C-4′ OH | −6.5 (−6.9) | −11.2 (−11.7) | −8.0 (−8.6) | |
| Kaempferol (4) | C-5 OH | −2.0 (−2.4) | −3.1 (−3.6) | −1.3 (−1.9) |
| C-7 OH | −5.8 (−6.2) | −10.7 (−11.2) | −9.6 (−10.2) | |
| C-3 OH | −8.2 (−8.6) | −11.8 (−12.3) | −4.1 (−4.7) | |
| C-4′ OH | −5.7 (−6.1) | −10.1 (−10.6) | −6.7 (−7.3) | |
| Genkwanin (6) | C-5 OH | −2.1 (−2.5) | −1.4 (−1.8) | −0.8 (−1.4) |
| C-4′ OH | −8.9 (−9.3) | −8.9 (−9.3) | −8.5 (−9.1) | |
| Oleuropein (20) | C-5′ OH | −7.0 (−7.4) | −9.2 (−9.7) | −7.5 (−8.1) |
| C-6′ OH | −6.9 (−7.3) | −9.1 (−9.6) | −7.3 (−7.9) | |
| C-2′′ OH | −6.9 (−7.3) | −9.6 (−10.1) | −5.6 (−6.2) | |
| C-3′′ OH | −7.0 (−7.4) | −8.7 (−9.2) | −5.0 (−5.6) | |
| C-4′′ OH | −6.2 (−6.6) | −8.2 (−8.7) | −5.0 (−5.6) | |
| C-6′′ OH | −6.3 (−6.7) | −8.7 (−9.2) | −7.2 (−7.8) | |
| Hydroxytyrosol (21) | C-3 OH | −7.8 (−8.2) | −9.6 (−10.1) | −6.7 (−7.3) |
| C-4 OH | −7.6 (−8.0) | −9.3 (−9.8) | −6.3 (−6.9) | |
| C-8 OH | −6.2 (−6.6) | −8.7 (−9.2) | −5.3 (−5.9) | |

| 1:1 PhOH+ solvent complex | DFT/B3LYP 6-31+G(d) geometry optimization, gas phase | DFT/B3LYP 6-31+G(d) geometry optimization, CPCM | DFT/B3LYP 6-311++G(d,p) geometry optimization, gas phase | DFT/B3LYP 6-311++G(d,p) geometry optimization, CPCM | Experimental values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PhOH + CHCl3 | 3.96 | 4.61 | 3.85 | 4.49 | 4.65 |
| PhOH + MeCN | 6.43 | 6.80 | 6.42 | 6.79 | 6.90 |
| PhOH + acetone | 8.60 | 8.95 | 8.48 | 8.83 8.71 a | 8.29 |
| PhOH + DMSO | 9.02 | 9.31 | 9.08 | 9.37 | 9.36 |



4.5. Calculated vs Experimental 1H Chemical Shifts


5. Spin-Coupling Constants

6. Correlation of Phenol OH 1H Chemical Shifts with Heteronuclear Chemical Shifts

7. Phenol –OH Diffusion Coefficients
8. Deuterium Isotope Effects
9. Applications to Natural Products

9.1. Mixture Analysis



| Extract | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methanol | 7.0 ± 0.4 | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 2.9 ± 0.3 | 3.4 ± 0.2 | 36.9 ± 3.0 | ND c | 32.9 ± 2.0 |
| Aqueous | 1.3 ± 0.1 | ND c | 0.2 ± 0.05 | 0.4 ± 0.05 | 9.2 ± 1.1 | 7.2 ± 0.2 | ND c |


9.2. Determination of Total Phenolics
- (i)
- a 1D 1H-NMR spectrum was obtained in DMSO-d6;
- (ii)
- a subsequent 1H-NMR spectrum was recorded with irradiation of the residual H2O resonance and
- (iii)
- 1H-NMR spectra were recorded with the addition of a progressively increased amount of NaHCO3 salt.
10. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
| Sample | Total Phenolic Content/ mg CAE g−1 | Ae d | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FC a | FCcorr b | 1H-NMR c | ||
| Sage e | 82 ± 8 | 66 | 55 | 0.83 |
| Rosemary e | 97 ± 9 | 80 | 135 | 1.69 |
| Oregano | 211 ± 10 | 197 | 303 | 1.54 |
| Ligustrum lucidum (MeOH extract) | 61 ± 4 | 40 | 35 | 0.88 |
| Ligustrum lucidum (H2O extract) | 65 ± 3 | 45 | 15 | 0.33 |
| Ligustrum lucidum e | 98 ± 8 | 89 | 115 | 1.29 |

Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeffrey, G.A.; Sanger, S.W. Hydrogen Bonding in Biological Structures; Springer Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Scheider, S. Hydrogen Bonding: A Theoretical Perspective; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Perrin, C.L.; Nielson, J.B. “Strong” hydrogen bonds in chemistry and biology. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 1997, 48, 511–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilli, P.; Pretto, L.; Bertolasi, V.; Gilli, G. Predicting hydrogen-bond strengths from acid-base molecular properties. The pKa slide rule: Toward the solution of a long-lasting problem. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunther, H. NMR Spectroscopy: Basic Principles, Concepts and Applications in Chemistry, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- De Dios, A.C. Ab initio calculations of the NMR chemical shift. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 1996, 29, 229–278. [Google Scholar]
- Casu, B.; Reggiani, M.; Gallo, G.G.; Vigevani, A. Hydrogen bonding and conformation of glucose and polyglucoses in dimethyl-sulphoxide solution. Tetrahedron 1966, 22, 3061–3083. [Google Scholar]
- Poppe, L.; van Halbeek, H. NMR spectroscopy of hydroxyl protons in supercooled carbohydrates. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 1994, 1, 215–216. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, B.; Lerner, L. Observation of hydroxyl protons of sucrose in aqueous solution: No evidence for persistent intramolecular hydrogen bonds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 4827–4829. [Google Scholar]
- Bekiroglu, S.; Sandström, A.; Kenne, L.; Sandström, C. Ab initio and NMR studies on the effect of hydration on the chemical shift of hydroxy protons in carbohydrates using disaccharides and water/methanol/ethers as model systems. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2004, 2, 200–205. [Google Scholar]
- Shapetko, N.N.; Shigorin, D.N. NMR study of intramolecular hydrogen bond protons in quinoid structures. J. Struct. Chem. 1967, 8, 474–476. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, P.E.; Spanget-Larsen, J. NMR and IR Spectroscopy of Phenols. In Chemistry of Phenols; Rappoport, Z., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Eigen, M. Proton transfer, acid-base catalysis, and enzymatic hydrolysis. Part I: Elementary processes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1964, 3, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englander, S.W.; Kallenbach, N.R. Hydrogen exchange and structural dynamics of proteins and nucleic acids. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1983, 16, 521–655. [Google Scholar]
- Wuthrich, K. NMR of Proteins and Nucleic Acids; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Charisiadis, P.; Primikyri, A.; Exarchou, V.; Tzakos, A.; Gerothanassis, I.P. Unprecedented ultra-high-resolution hydroxy group 1H-NMR spectroscopic analysis of plant extracts. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2462–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charisiadis, P.; Exarchou, V.; Troganis, A.N.; Gerothanassis, I.P. Exploring the “forgotten” –OH-NMR spectral region in natural products. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 3589–3591. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Ahmadd, A. Spectrophotometric and spectroscopic studies of charge transfer complex of 1-naphthylamine as an electron donor with picric acid as an electron acceptor in different polar solvents. J. Mol. Struct. 2010, 977, 197–202. [Google Scholar]
- Zesławska, E.; Stürzebecher, J.; Oleksyn, B.J. Geometry of GPPE binding to picrate and to the urokinase type plasminogen activator. Biorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 6212–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exarchou, V.; Troganis, A.; Gerothanassis, I.P.; Tsimidou, M.; Boskou, D. Do strong intramolecular hydrogen bonds persist in aqueous solution? Variable temperature gradient 1H, 1H-13C GE-HSQC and GE-HMBC-NMR studies of flavonols and flavones in organic and aqueous mixtures. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 7423–7429. [Google Scholar]
- Tolstoy, P.M.; Koeppe, B.; Denisov, G.S.; Limbach, H.H. Combined NMR and UV-vis spectroscopy in the solution state: Study of the geometries of strong OHO hydrogen bonds of phenols with carboxylic acids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 5745–5747. [Google Scholar]
- Koeppe, B.; Tolstoy, P.M.; Limbach, H.-H. Reaction pathways of proton transfer in hydrogen-bonded phenol-carboxylate complexes explored by combined UV-vis and NMR spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 7897–7908. [Google Scholar]
- Koeppe, B.; Guo, J.; Tolstoy, P.M.; Denisov, G.S.; Limbach, H.H. Solvent and H/D isotope effects on the proton transfer pathways in heteroconjugated hydrogen-bonded phenol-carboxylic acid anions observed by the combined UV-vis and NMR spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 7553–7566. [Google Scholar]
- Shenderovich, I.G.; Burtsev, A.P.; Denisov, G.S.; Golubev, N.S.; Limbach, H.H. Influence of the temperature-dependent dielectric constant on the H/D isotope effects on the NMR chemical shifts and the hydrogen bond geometry of the collidine-HF complex in CDF3/CDClF2 solution. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2001, 39, S91–S99. [Google Scholar]
- Kontogianni, V.; Primikyri, A.; Exarchou, V.; Charisiadis, P.; Tzakos, A.; Gerothanassis, I.P. Hydrogen bonding probes of phenol –OH groups: Shielding ranges, solvent effects and temperature coefficients of 1H-NMR shieldings and –OH diffusion coefficients. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 1013–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Porte, A.L.; Gutowsky, H.S.; Hunsberger, I.M. The determination of double-bond character in cyclic systems. V. Proton chemical shifts in chelated derivatives of benzene, naphthalene and phenanthrene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1960, 82, 5057–5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolasi, V.; Gilli, P.; Ferretti, V.; Gilli, G. Intramolecular O-H•••O hydrogen bonds assisted by resonance. Correlation between crystallographic data and 1H-NMR chemical shifts. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2 1997, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilli, G.; Bellucci, F.; Ferretti, V.; Bertolasi, V. Evidence for resonance-assisted hydrogen bonding from crystal-structure correlations on the enol form of the β-diketone fragment. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Falk, H.; Roth, L. From the photosensitizer hypericin to the photoreceptor stentorin—the chemistry of phenantroperylene quinines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 3117–3136. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, G. How the body’s “garbage disposal” may inactivate drugs. Science 2001, 291, 35–37. [Google Scholar]
- Skalkos, D.; Tatsis, E.; Gerothanassis, I.P.; Troganis, A. Towards a consensus structure of hypericin in solution: Direct evidence for a single tautomer and different ionization states in protic and nonprotic solvents by the use of variable temperature gradient 1H-NMR. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 4925–4929. [Google Scholar]
- Dax, T.G.; Falk, H.; Kapinus, E.I. Ein nachweis für die struktur des 1,6-dioxo-tautomeren des hypericin. Monatch. Chem. 1999, 130, 827–831. [Google Scholar]
- Smirnov, A.; Fulton, D.B.; Andreotti, A.; Petrich, J.W. Exploring ground-state heterogeneity of hypericin and hypocrellin A and B: Dynamic and 2D ROESY NMR study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 7979–7988. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, D.; Frolow, F.; Kapinus, D.; Lavie, B.; Lavie, G.; Meruelo, D.; Mazur, Y. Acidic properties of hypericin and its octahydroxy analogue in the ground and excited states. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1994, 7, 891–892. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, T.K.; Zhao, Q.; Mildvan, A.S. NMR studies of strong hydrogen bonds in enzymes and in a model compound. J. Mol. Struct. 2000, 552, 97–109. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, T.K.; Mildvan, A.S. High-precision measurement of hydrogen bond lengths in proteins by nuclear magnetic resonance methods. Proteins 1999, 35, 275–282. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Abeygunawardana, C.; Giltis, A.G.; Mildvan, A.S. Hydrogen bonding at the active site of Δ5−3-ketosteroid isomerase. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 14614–14626. [Google Scholar]
- McDermott, A.; Ridenour, C.F. In proton chemical shift measurements in biological solids. In Encyclopedia of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance; Wiley: Sussex, England, 1996; pp. 3820–3825. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimi, Y.; Maeda, H.; Hatanaka, M.; Mizuno, K. Intramolecular 9-membered hydrogen bonding of 2-arylmethylphenols having carbonyl groups at 2′-position. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 9425–9431. [Google Scholar]
- Castelano, R.K.; Li, Y.; Homan, E.A.; Lampkins, A.J.; Marín, I.V.; Abboud, K.A. Seven-membered intramolecular hydrogen bonding of phenols: Database analysis and phloroglucinol model compounds. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 2012, 4483–4492. [Google Scholar]
- Siskos, M.; Kontogianni, V.G.; Tsiafoulis, C.; Tzakos, A.; Gerothanassis, I.P. Investigation of solute-solvent interactions in phenol compounds: Accurate ab initio calculations of solvent effects on 1H-NMR shieldings. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 7400–7411. [Google Scholar]
- Saenger, W.; Betzel, C.; Hingerty, B.; Brown, G.M. Flip-flop hydrogen bonding in a partially disordered system. Nature 1982, 296, 581–583. [Google Scholar]
- Domagala, S.; Munshi, P.; Ahmed, M.; Guillot, B.; Jelsch, C. Structural analysis and multipole modelling of quercetin monohydrate—A quantitative and comparative study. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Sci. 2011, 67, 63–78. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, R.J.; Mobli, M. An NMR, IR and theoretical investigation of 1H chemical shifts and hydrogen bonding in phenols. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2007, 45, 865–877. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, R.A.; Mennucci, B.; Tomasi, J. Ab initio calculations of 17O NMR-chemical shifts for water. The limits of PCM theory and the role of hydrogen-bond geometry and cooperativity. J. Phys. Chem. A 2004, 108, 5851–5863. [Google Scholar]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar]
- Wehrli, F.W. Proton-coupled 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectra involving 13C-1H spin-spin coupling to hydroxyl-protons, a complementary assignment aid. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1975, 16, 663–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.E. Carbon-hydrogen spin-spin coupling constants. Prog. NMR Spectrosc. 1981, 14, 175–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, E.V.; Agrawal, P. Keto-enol tautomerism in 2-acetyltetralone: A reinvestigation. Magn. Reson. Chem. 1994, 32, 499–499. [Google Scholar]
- Borisov, E.V.; Zhang, W.; Bolvig, S.; Hansen, P.E. nJ(13C,O1H) coupling constants of intramolecularly hydrogen-bonded compounds. Magn. Reson. Chem. 1998, 36, 5104–5110. [Google Scholar]
- Jaccard, G.; Lauterwein, J. Intramolecular hydrogen bonds of the C=O---H–O type as studied by 17O-NMR. Helv. Chim. Acta 1986, 69, 1469–1485. [Google Scholar]
- Gerothanassis, I.P. Oxygen-17 NMR spectroscopy: Basic principles and applications (Part II). Prog. NMR Spectrosc. 2010, 57, 1–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerothanassis, I.P. Oxygen-17 NMR spectroscopy: Basic principles and applications (Part I). Progr. NMR Spectrosc. 2010, 56, 95–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Y.; Avram, L.; Frish, L. Diffusion NMR spectroscopy in supramolecular and combinatorial chemistry: An old parameter- new insights. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 520–554. [Google Scholar]
- Primikyri, A.; Kyriakou, E.; Charisiadis, P.; Tsiafoulis, C.; Tzakos, A.G.; Gerothanassis, I.P. Fine-tuning of the diffusion dimension of –OH groups for high resolution DOSY NMR applications in crude enzymatic transformations and mixtures of organic compounds. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 6887–6891. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.S.; Hong, K.S.; Cho, J.H.; Volkov, V.I.; Lee, C.H. Chemical exchange of hydroxyl protons in quercetin measured by pulsed field gradient NMR. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2008, 35, 261–270. [Google Scholar]
- Bolvig, S.; Hansen, P.E. Isotope effects on chemical shifts as an analytical tool in structural studies of intramolecular hydrogen bonded compounds. Curr. Org. Chem. 2000, 4, 19–54. [Google Scholar]
- Etzlstorfer, C.; Falk, H.; Mayr, E.; Schwarzinger, S. Concerning the acidity and hydrogen bonding of hydroxyphenanthroperylene quinones like fringelite D, hypericin, and stentorian. Monatch. Chem. 1996, 127, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, K. On Line LC-NMR and Related Techniques; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hostettmann, K.; Wolfender, J.L. Bioactive Compounds from Natural Sources—Isolation, Characterization and Biological Properties; Tringali, C., Ed.; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Exarchou, V.; Godejohann, M.; van Beek, T.A.; Gerothanassis, I.P.; Vervoort, J. LC-UV-solid phase extraction-NMR-MS combined with a cryogenic flow probe and its application to the identification of compounds present in Greek oregano. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 6288–6294. [Google Scholar]
- Exarchou, V.; Krucker, M.; van Beek, T.A.; Vervoort, J.; Gerothanassis, I.P.; Albert, K. LC-NMR coupling technology: Recent advancements and applications in natural products analysis. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2005, 43, 681–687. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, I.A.; Schommer, S.C.; Hodis, B.; Robb, K.A.; Tonelli, M.; Westler, W.M.; Sussman, M.R.; Markley, J.L. Method for determining molar concentrations of metabolites in complex solutions from two-dimensional 1H-13C-NMR spectra. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 9385–9390. [Google Scholar]
- Exarchou, V.; Troganis, A.; Gerothanassis, I.P.; Tsimidou, M.; Boskou, D. Analysis of phenolic acids in complex phenolic mixtures by the use of variable temperature two dimensional 1H-1H COSY, 1H-13C HMQC and 1H-13C HMBC gradient enhanced NMR spectroscopy: Application to methanolic extracts of several oregano species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kontogianni, V.G.; Exarchou, V.; Troganis, A.; Gerothanassis, I.P. Rapid and novel discrimination and quantification of oleanolic and ursolic acids in complex plant extracts using two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy-comparison with HPLC methods. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 635, 188–195. [Google Scholar]
- Novoa-Carballal, R.; Fernandez-Megia, E.; Jimenez, C.; Riguera, R. NMR methods for unravelling the spectra of complex mixtures. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 78–98. [Google Scholar]
- Robinette, S.L.; Brüschweiler, R.; Schroeder, F.C.; Edison, A.S. NMR in metabolomics and natural products research: Two sides of the same coin. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 288–297. [Google Scholar]
- Charisiadis, P.; Tsiafoulis, C.G.; Exarchou, V.; Tzakos, A.G.; Gerothanassis, I.P. Rapid and direct low micromolar NMR method for the simultaneous detection of hydrogen peroxide and phenolics in plant extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 4508–4513. [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakou, E.; Primikyri, A.; Charisiadis, P.; Katsoura, M.; Gerothanassis, I.P.; Stamatis, H.; Tzakos, A.G. Unexpected enzyme-catalyzed regioselective acylation of flavonoid aglycones and rapid product screening. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 1739–1742. [Google Scholar]
- Neratzaki, A.A.; Tsiafoulis, C.G.; Charisiadis, P.; Kontogianni, V.G.; Gerothanassis, I.P. Novel determination of the total phenolic content in crude plant extracts by the use of 1H-NMR of the –OH spectral region. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 688, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Tsiafoulis, C.; Gerothanassis, I.P. A novel NMR method for the determination and monitoring of evolution of hydrogen peroxide in aqueous solution. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 3371–3375. [Google Scholar]
- Tatsis, E.; Exarchou, V.; Troganis, A.; Gerothanassis, I.P. 1H-NMR determination of hypericin and pseudohypericin in complex natural mixtures by the use of strongly deshielded OH groups. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 607, 219–226. [Google Scholar]
- Tatsis, E.C.; Boeren, S.; Exarchou, V.; Troganis, A.N.; Vervoort, J.; Gerothanassis, I.P. Identification of the major constituents of hypericum perforatum by LC/SPE/NMR and/or LC/MS. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 383–393. [Google Scholar]
- Lomas, J.S. 1H-NMR spectra of butane-1,4-diol and other 1,4-diols: DFT calculation of shifts and coupling constants. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2014, 52, 87–97. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, W.; Carmichael, I.; Serianni, A.S. DFT and NMR studies of 2JCOH, 3JHCOH, and 3JCCOH spin-couplings in saccharides: C-O torsional bias and H-bonding in aqueous solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 72, 7071–7082. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Charisiadis, P.; Kontogianni, V.G.; Tsiafoulis, C.G.; Tzakos, A.G.; Siskos, M.; Gerothanassis, I.P. 1H-NMR as a Structural and Analytical Tool of Intra- and Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonds of Phenol-Containing Natural Products and Model Compounds. Molecules 2014, 19, 13643-13682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190913643
Charisiadis P, Kontogianni VG, Tsiafoulis CG, Tzakos AG, Siskos M, Gerothanassis IP. 1H-NMR as a Structural and Analytical Tool of Intra- and Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonds of Phenol-Containing Natural Products and Model Compounds. Molecules. 2014; 19(9):13643-13682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190913643
Chicago/Turabian StyleCharisiadis, Pantelis, Vassiliki G. Kontogianni, Constantinos G. Tsiafoulis, Andreas G. Tzakos, Michael Siskos, and Ioannis P. Gerothanassis. 2014. "1H-NMR as a Structural and Analytical Tool of Intra- and Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonds of Phenol-Containing Natural Products and Model Compounds" Molecules 19, no. 9: 13643-13682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190913643
APA StyleCharisiadis, P., Kontogianni, V. G., Tsiafoulis, C. G., Tzakos, A. G., Siskos, M., & Gerothanassis, I. P. (2014). 1H-NMR as a Structural and Analytical Tool of Intra- and Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonds of Phenol-Containing Natural Products and Model Compounds. Molecules, 19(9), 13643-13682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190913643