GC-MS Analysis of Membrane-Graded Fulvic Acid and Its Activity on Promoting Wheat Seed Germination
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemical Composition Analysis of FA-500
2.2. Influence of FA-500 on Germination Rate, Coleoptile and Radicle Length of Wheat Seed
2.3. Influence of FA-500 on the Germination Index and the Vitality Index of Wheat Seed
2.4. Influence of FA-500 on the Activity of α-Amylase and (α+β) Amylase
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of 500-FA
3.3. Chromatographic Conditions
3.3.1. MS Conditions
3.3.2. Measurement of RI
3.4. Seed Germination Process
3.5. Measurement of Activity Index
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbt, B.G.; Lankes, U.; Frimmel, F.H. Structural Characterization of Aquatic Humic Substances? The Need for a Multiple Method Approach. Aquat. Sci. 2004, 66, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavani, L.; Ciavatta, C.; Trubetskaya, O.E.; Reznikova, O.I.; Afanaseva, G.V.; Trubetskoj, O.A. Capillary zone electrophoresis of soil humic acid fractions obtained by coupling size-exclusion chromatography and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 983, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.X. Exordium. In Introduction of Humic Substances, 1st ed.; CIP: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, F.J. Structural basis of humic substances. In Humus Chemistry: Genesis, Composition, Reactions, 2nd ed.; John Wiley Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1994; p. 337. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, H.D.; Quan, Y.; Hong, L.Y. Changes of chemical properties of humic acids from crude and fungal transformed lignite. Fuel 2006, 85, 2402–2407. [Google Scholar]
- Maosz, A. Effect of fulvic and humic organic acids and calcium on growth and chlorophyll content of tree species grown under salt stress. Dendrobiology 2009, 62, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.N.; Sun, L.R.; Mao, H.; Dong, Q.U. Effects of drought-resistant fulvic acid liquid fertilizer on wheat and maize growth. Agric. Res. Arid Areas 2012, 30, 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Pandeya, S.B.; Singh, A.K.; Dhar, P. Fluence of fulvic acid on transport of iron in soils and uptake by paddy seedlings. Plant Soil 1998, 198, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepetkin, I.; Khlebnikov, A.; Kwon, B.S. Medical dfugs from humus matter: focus on mumie. Drug Dev. Res. 2002, 57, 140–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.M.; Li, B.C.; Li, P.; Liu, J.Z.; Cui, J.L.; Mei, Z.Q. Effects of Na-FA on gastrointestinal movement and gastric ulcer in mice. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2011, 34, 1565–1569. [Google Scholar]
- Cornejo, A.; Jiménez, J.M.; Caballero, L.; Melo, F.; Maccioni, R.B. Fulvic acid inhibits aggregation and promotes disassembly of tau fibrils associated with Alzheimer’s. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2011, 27, 143–153. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, Y.Y.; Li, B.C.; He, J.; Li, Y.M.; Cui, J.L.; Zhang, S.H.; Mei, Z.Q. Study on Extraction and Sober-up Effect of Fulvic Acid (FA). Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2010, 22, 144–148. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.D.; Fang, X.W.; Klaus, S.R.; Ana, M.C.; Lakhwinder, S.H.; Michael, L.T. Molecular-scale heterogeneity of humic acid in particle-size fractions of two Iowa soils. Geoderma 2007, 140, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Huang, W.L.; Peng, P.A.; Sheng, J.Y.; Fu, J.M. Characterization of humic acids fractionated by ultrafiltration. Org. Geochem. 2004, 35, 1025–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yu, Z.; Ran, Y.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J.M.; Peng, P.; Huang, W. Characteristics for the molecular weight distribution of the Pahokee peat humic acids and the effects on the sorption of phenanthrene. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2004, 24, 587–594. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Qin, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, H.; He, J.; Li, S.; Li, B.C. The Effect of Brown Coal Distillate on the Germination of Wheat. Life Sci. Res. 2014, 18, 423–430. [Google Scholar]
- Piccolo, A.; Nardi, S.; Coxcheri, G. Structural characteristics of humic substances as related to nitrate uptake and growth regulation in plant systems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1992, 24, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, W.Y.; Liu, B. Study on the activity and mechanism of humic acid from different sources: I. The sample preparation and structure determination of humic acid and its effect on plant seed germination. Humic Acid 2000, 1, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.H.; Li, B.C.; Zhang, H.F.; Liu, J.Z.; He, J.; Dai, W.F.; Li, P. Physicochemical Properties of Humic Acid Separated from Chemolysis Brown Coal from Xundian Yunnan. J. Kunming Univ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 35, 98–102. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; He, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhuang, W.; Li, B.C. Effects of lignite-derived sodium fulvate on angiogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Latin Am. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 33, 1252–1257. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.L. Influence of humic acids on physiological activities of plants. Chin. Bull. Bot. 2000, 17, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Liu, K.H.; Lan, J.K. Humic acid and it’s significant in protection of soil environment. J. Guangxi Acad. Sci. 2001, 17, 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, A.; Li, C.; Gao, Z.; Stanley, C.A.; Matschinsky, F.M. Glutam inolysis and insulin secretion: From bedside to bench and back. Diabetes 2002, 51, S421–S426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Buettger, C.; Kwagh, J.; Matter, A.; Daikhin, Y.; Nissim, I.B.; Collins, H.W.; Yudkoff, M.; Stanley, C.A.; Matschinsky, F.M. A signaling role of glutamine in insulin secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 13393–13401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gismondi, A.; Canini, A. Microsatellite analysis of Latial Olea europaea L. Cultivars. Plant Biosyst. 2013, 147, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gismondi, A.; Impei, S.; Di Marco, G.; Crespan, M.; Leonardi, D.; Canini, A. Detection of new genetic profiles and allelic variants in improperly classified grapevine accessions. Genome 2014, 57, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, M.J.; Nguyen, T.M.; Waterman, A.; McMichael, G.L.; Chalmers, K.J. Application of multiplex-ready PCR for fluorescence-based SSR genotyping in barley and wheat. Mol. Breed. 2008, 21, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoagland, D.R.; Arnon, D.I. The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Calif. Agric. Exp. Stat. 1950, 347, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.H.; Wong, P.K. Correlation relationships between physic-chemical properties and gas chromatographic retention index of polychlorinated-dibenzofurans. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.J.; Liu, H.X.; Zhang, R.S.; Chun, X.X.; Xiao, J.Y.; Man, C.L.; Zhi, D.H.; Bo, T.F. QSPR prediction of GC retention indices for nitrogen-containing polycyclic aromatic compounds from heuristically computed molecular descriptors. Talanta 2005, 68, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.Y. Determination of amylase activity. In Modern Plant Physiology Laboratory Manual, 1st ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1999; pp. 123–124. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, W.Y.; Liu, B. Study on the activity and mechanism of humic acid from different sources: II. The effect of humic acid on enzyme activity, respiration and photosynthesis of plants. Humic Acid 2000, 2, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, M.A. Absorption of metals on sedimentary and peat humic acids. Chem. Geol. 1974, 13, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Nobili, M.D.; Aviad, T. Stimulatory effects of humic substances on plant growth. In Soil Organic Matter in Sustainable Agriculture, 1st ed.; Magdoff, F., Weil, R.R., Eds.; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 103–124. [Google Scholar]
- Nardi, S.; Pizzeghello, D.; Reniero, F.; Muscolo, A. Biological activity of humic substances extracted from soils under different vegetation cover. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1999, 30, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscolo, A.; Cutrupi, S.; Nardi, S. IAA detection in humic substances. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 1199–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, M.C.; Fábregas, R.; Méndez, J. Inhibitory Effect of Soil Humic Acids on Indoleacetic Acid Oxidase. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1971, 3, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, M.C.; Olmedo, M.G.; Méndez, J. Inhibition of enzymatic indoleacetic acid oxidation by soil fulvic acids. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1972, 4, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
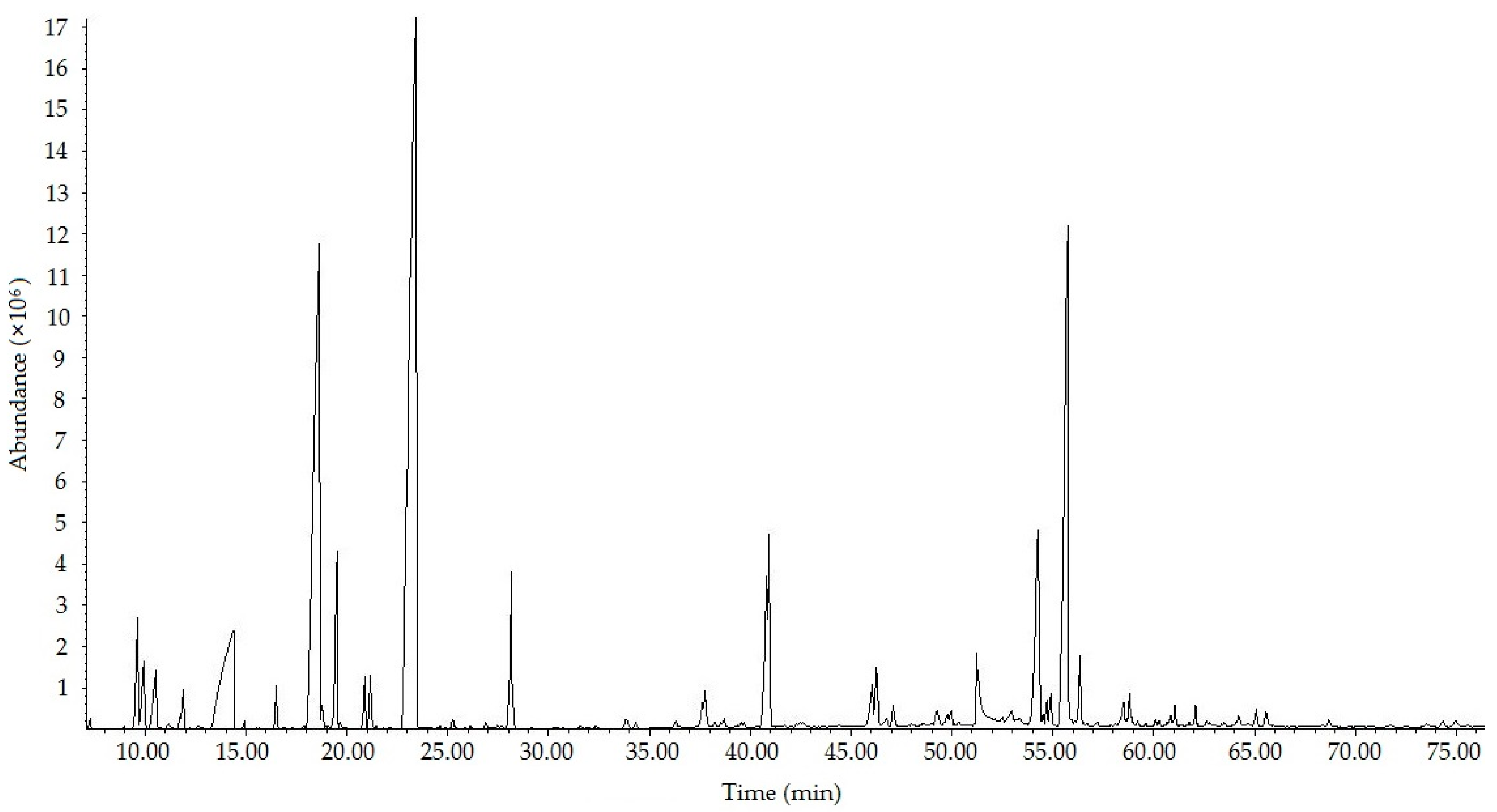






| NO. | Compound | Retention Time (min) | Molecular Formula | Similarity (%) | RI | Area Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1,5-Hexadiene-3-ol | 9.633 | C6H10O | 85.9 | 1032 | 1.425 |
| 2 | Ethyl glycolate | 10.545 | C4H8O3 | 98.7 | 1055 | 3.927 |
| 3 | Acetic acid | 11.694 | C2H4O2 | 93.9 | 1084 | 0.104 |
| 4 | Methoxyacetic acid | 11.739 | C3H6O3 | 92.6 | 1085 | 0.121 |
| 5 | Ethyl methyl ether | 11.796 | C3H8O | 95.6 | 1087 | 0.487 |
| 6 | Propan-1-ol | 11.825 | C3H8O | 96.8 | 1088 | 0.157 |
| 7 | Propanedioic acid, oxo-, ethyl methyl ester | 11.870 | C6H8O5 | 96.0 | 1091 | 0.224 |
| 8 | Diethyl oxalate | 14.388 | C6H10O4 | 98.3 | 1144 | 6.745 |
| 9 | Propanedioic acid, methyl, ethyl ester | 16.509 | C6H10O4 | 92.6 | 1190 | 0.394 |
| 10 | Diethyl malonate | 18.655 | C7H12O4 | 96.3 | 1233 | 17.156 |
| 11 | Glucose | 18.784 | C6H12O6 | 74.8 | 1236 | 0.323 |
| 12 | Ethyl levulinate | 19.520 | C7H12O3 | 91.8 | 1251 | 2.117 |
| 13 | Butanedioic acid, ethyl methyl ester | 20.897 | C7H12O4 | 94.9 | 1278 | 0.532 |
| 14 | Diethyl methylsuccinate | 21.188 | C9H16O4 | 93.7 | 1284 | 0.666 |
| 15 | Diethyl succinate | 23.452 | C8H14O4 | 92.7 | 1334 | 29.512 |
| 16 | Ethyl 4-acetylbutyrate | 25.256 | C8H14O3 | 97.1 | 1376 | 0.119 |
| 17 | Diethyl glutarate | 28.145 | C9H16O4 | 82.5 | 1522 | 2.235 |
| 18 | Hexanedioic acid diethyl ester | 33.825 | C10H18O4 | 82.2 | 1732 | 0.202 |
| 19 | Ethyl 3-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoate | 36.317 | C8H16O3 | 91.8 | 1784 | 0.133 |
| 20 | 3-(methylthio)-propionaldehyde | 37.628 | C4H8OS | 77.9 | 1811 | 0.487 |
| 21 | Maleic acid diethyl ester | 40.808 | C8H14O5 | 98.0 | 1879 | 2.658 |
| 22 | Succinic acid, 2-hydroxy-3-methyl-, diethyl ester | 46.054 | C9H16O5 | 86.3 | 1993 | 0.829 |
| 23 | Diethyl 3-hydroxyglutarate | 46.762 | C9H16O5 | 91.7 | 2009 | 0.159 |
| 24 | Diethyl 2-acetylglutarate | 49.274 | C11H18O5 | 83.6 | 2067 | 0.331 |
| 25 | Ethyl 2-ethylacetoacetate | 49.781 | C8H14O3 | 83.0 | 2078 | 0.170 |
| 26 | Ethyl oxamate | 49.987 | C4H7NO3 | 87.5 | 2083 | 0.231 |
| 27 | 2-(1-Ethoxyethoxy)-3-methysuccinic acid, diethyl ester | 51.244 | C13H24O6 | 87.8 | 2112 | 0.397 |
| 28 | 6-desoxy-l-gulitol | 51.303 | C6H14O5 | 80.1 | 2115 | 1.282 |
| 29 | d-glucosiduronic acid | 52.522 | C6H10O7 | 80.1 | 2143 | 0.226 |
| 30 | Levulinic acid | 52.995 | C5H8O3 | 86.4 | 2154 | 0.470 |
| 31 | d-manno-2-Heptulose | 53.376 | C7H14O7 | 81.4 | 2163 | 0.249 |
| 32 | Ethyl hydrogen malonate | 54.294 | C5H8O4 | 98.1 | 2185 | 5.070 |
| 33 | Tetraethylene glycol di-2-ethylhexoate | 54.528 | C24H46O7 | 83.0 | 2190 | 0.156 |
| 34 | Ethyl(2-tetrahydropyranyl)acetate | 54.702 | C9H16O3 | 78.7 | 2195 | 0.230 |
| 35 | Ethyl hydrogen succinate | 55.784 | C6H10O4 | 96.0 | 2221 | 11.388 |
| 36 | Diethyl 4-oxopimelate | 56.370 | C11H18O5 | 81.5 | 2236 | 0.846 |
| 37 | Succinic acid imide | 58.522 | C4H5NO2 | 84.2 | 2288 | 0.412 |
| 38 | 4-Dihexylcarbamoyl-butyric acid | 58.819 | C17H33NO3 | 81.4 | 2296 | 0.581 |
| 39 | Hexanedioic acid, 3-oxo-, diethyl ester | 60.846 | C10H16O5 | 86.4 | 2347 | 0.518 |
| 40 | Monoethyl itaconate | 61.055 | C7H10O4 | 87.7 | 2353 | 0.272 |
| 41 | Diethyl 2-aminomalonate | 62.080 | C7H13NO4 | 84.7 | 2379 | 0.277 |
| 42 | dl-glutamine | 64.203 | C5H10N2O3 | 81.4 | 2430 | 0.233 |
| 43 | 2-Ethyl-3-formylaminosuccinic acid, di-t-butyl ester | 65.068 | C15H27NO5 | 83.7 | 2449 | 0.235 |
| 44 | Isobutyl 3-(perhydro-5-oxo-2-furyl)propionate | 65.568 | C11H18O4 | 78.5 | 2461 | 0.216 |
| 45 | Diethyl allylmalonate | 68.679 | C10H16O4 | 81.8 | 2523 | 0.146 |
| 46 | Cis-9,10-Epoxyoctadecanamide | 74.336 | C18H35N2O2 | 82.2 | 2615 | 0.128 |
| 47 | Dodecanoic acid, 2-(2-hydroxyethoxy)ethyl ester | 74.975 | C16H32O4 | 81.9 | 2623 | 0.174 |
| Treatment | Germination Rate/(%) | Length of Coleoptile/mm | Length of Radicle/mm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yannong 19 | Luyuan 301 | Yannong 19 | Luyuan 301 | Yannong 19 | Luyuan 301 | |
| Control | 91.5 ± 0.3 | 78.0 ± 1.2 | 29.3 ± 0.3 | 28.9 ± 0.4 | 36.4 ± 0.2 | 34.1 ± 0.3 |
| 0.3‰ | 92.0 ± 0.4 | 76.0 ± 0.6 * | 29.7 ± 0.1 | 30.0 ± 0.2 | 35.1 ± 2.0 | 35.0 ± 0.4 |
| 0.5‰ | 92.5 ± 0.8 | 83.0 ± 2.5 | 32.0 ± 0.4 | 30.7 ± 0.7 * | 41.9 ± 0.6 * | 39.5 ± 0.7 * |
| 0.7‰ | 82.5 ± 2.9 * | 78.8 ± 0.8 | 30.2 ± 0.8 | 29.2 ± 0.6 | 40.6 ± 1.4 | 38.3 ± 0.4 * |
| 0.9‰ | 83.0 ± 1.2 * | 77.5 ± 1.5 | 36.1 ± 1.2 * | 27.6 ± 0.4 | 36.1 ± 0.4 | 35.4 ± 0.5 |
| Sample | The Water Content (%) | The Ash Content (%) | The Total HA Content (%) | The Free HA Content (%) | The FA Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eshan brown coal | 18.30 | 13.16 | 51.29 | 53.25 | 1.07 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Xiang, C.; Li, B. GC-MS Analysis of Membrane-Graded Fulvic Acid and Its Activity on Promoting Wheat Seed Germination. Molecules 2016, 21, 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21101363
Qin Y, Zhu H, Zhang M, Zhang H, Xiang C, Li B. GC-MS Analysis of Membrane-Graded Fulvic Acid and Its Activity on Promoting Wheat Seed Germination. Molecules. 2016; 21(10):1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21101363
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Yi, Hui Zhu, Mi Zhang, Huifen Zhang, Cheng Xiang, and Baocai Li. 2016. "GC-MS Analysis of Membrane-Graded Fulvic Acid and Its Activity on Promoting Wheat Seed Germination" Molecules 21, no. 10: 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21101363
APA StyleQin, Y., Zhu, H., Zhang, M., Zhang, H., Xiang, C., & Li, B. (2016). GC-MS Analysis of Membrane-Graded Fulvic Acid and Its Activity on Promoting Wheat Seed Germination. Molecules, 21(10), 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21101363





