Reaction of bis[(2-chlorocarbonyl)phenyl] Diselenide with Phenols, Aminophenols, and Other Amines towards Diphenyl Diselenides with Antimicrobial and Antiviral Properties †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
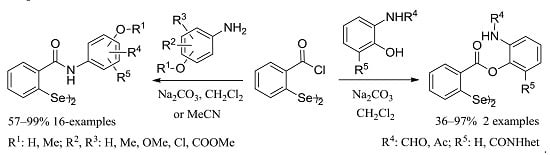
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Antimicrobial Activity
2.3. Antiviral Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis
General Information
3.2. Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity
3.3. Evaluation of Antiviral Activity and Cytotoxicity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wirth, T. Organoselenium Chemistry in Stereoselective Reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 3740–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudendahl, D.M.; Santoro, S.; Shahzad, S.A.; Santi, C.; Wirth, T. Green Chemistry with Selenium Reagents: Development of Efficient Catalytic Reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 8409–8411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Back, T. Oxidations Catalyzed by Seleninic Acids and Anhydrides, their Precursors and Congeners. Curr. Green Chem. 2016, 3, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Huang, J.; Huang, H.; Zhao, X. Organoselenium-Catalyzed Synthesis of Oxygen- and Nitrogen-Containing Heterocycles. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Rao, G.K.; Saleem, F.; Singh, A.K. Organoselenium ligands in catalysis. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 11949–11977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Młochowski, J.; Wójtowicz-Młochowska, H. Developments in Synthetic Application of Selenium(IV) Oxide and Organoselenium Compounds as Oxygen Donors and Oxygen-Transfer Agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 10205–10243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Młochowski, J.; Kloc, K.; Lisiak, R.; Potaczek, P.; Wójtowicz, H. Developments in the chemistry of selenaheterocyclic compounds of practical importance in synthesis and medicinal biology. Arkivoc 2007, 6, 14–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, C. Organoselenium Chemistry: Between Synthesis and Biochemistry; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, UAE, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pacuła, A.J.; Mangiavacchi, F.; Sancineto, L.; Lenardão, E.J.; Ścianowski, J.; Santi, C. Selenium Containing Compounds from Poison to Drug Candidates: A Review on the GPx-like Activity. Curr. Chem. Biol. 2015, 9, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano-Garcia, M. Organoselenium Compounds as Potential Therapeutic and Chemopreventive Agents: A Review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 1657–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mugesh, G.; du Mont, W.W.; Sies, H. Chemistry of biologically important synthetic organoselenium compounds. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 2125–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, A.P.; Gandin, V. Selenium compounds as therapeutic agents in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 1642–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azad, G.K.; Tomar, R.S. Ebselen, a promising antioxidant drug: Mechanisms of action and targets of biological pathways. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 4865–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, T. Small Organoselenium Compounds: More than just Glutathione Peroxidase Mimics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 10074–10076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, C.W.; Rocha, J.B. Toxicology and pharmacology of selenium: Emphasis on synthetic organoselenium compounds. Arch. Toxicol. 2011, 85, 1313–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninomiya, M.; Garud, D.R.; Koketsu, M. Biologically significant selenium-containing heterocycles. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 2968–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, S.; Azeredo, J.B.; Nascimento, V.; Sancineto, L.; Braga, A.L.; Santi, C. The green Side of the Moon: Ecofriendly Aspects of Organoselenium Chemistry. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 31521–31535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granda, J.M.; Piekielska, K.; Wąsińska, M.; Kawecka, N.; Giurg, M. Synthesis of 7- and 8-Functionalized 2-Aminophenoxazinones via Cyclocondensation of 2-Aminophenols. Synthesis 2015, 47, 3321–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denmark, S.E.; Chi, H.M. Lewis Base Catalyzed, Enantioselective, Intramolecular Sulfenoamination of Olefins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 8915–8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamata, Y.; Hashimoto, T.; Maruoka, K. A Chiral Electrophilic Selenium Catalyst for Highly Enantioselective Oxidative Cyclization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 5206–5209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancineto, L.; Tidei, C.; Bagnoli, L.; Marini, F.; Lenardão, E.J.; Santi, C. Selenium Catalyzed Oxidation of Aldehydes: Green Synthesis of Carboxylic Acids and Esters. Molecules 2015, 20, 10496–10510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Li, D.; Xiong, K.; Ge, Y.; Jin, H.; Zhang, G.; Hong, M.; Tian, Y.; Yin, J.; Zeng, H. Inhibition of thioredoxin reductase by a novel series of bis-1,2-benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-ones: Organoselenium compounds for cancer therapy. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 3816–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, V.; Ferreira, N.L.; Canto, R.F.; Schott, K.L.; Waczuk, E.P.; Sancineto, L.; Santi, C.; Rocha, J.B.; Braga, A.L. Synthesis and biological evaluation of new nitrogen-containing diselenides. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 87, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaaban, S.; Negm, A.; Sobh, M.A.; Wessjohann, L.A. Organoselenocyanates and symmetrical diselenides redox modulators: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plano, D.; Karelia, D.N.; Pandey, M.K.; Spallholz, J.E.; Amin, S.; Sharma, A.K. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Novel Selenium (Se-NSAID) Molecules as Anticancer Agents. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 1946–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Węglarz-Tomczak, E.; Burda-Grabowska, M.; Giurg, M.; Mucha, A. Identification of methionine aminopeptidase 2 as a molecular target of the organoselenium drug ebselen and its derivatives/analogues: Synthesis, inhibitory activity and molecular modeling study. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 5254–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartori, G.; Jardim, N.S.; Marcondes Sari, M.H.; Dobrachinski, F.; Pesarico, A.P.; Rodrigues, L.C., Jr.; Cargnelutti, J.; Flores, E.F.; Prigol, M.; Nogueira, C.W. Antiviral Action of Diphenyl Diselenide on Herpes Simplex Virus 2 Infection in Female BALB/c Mice. J. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 117, 1638–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Weiner, W.S.; Schroeder, C.E.; Simpson, D.S.; Hanson, A.M.; Sweeney, N.L.; Marvin, R.K.; Ndjomou, J.; Kolli, R.; Isailovic, D.; et al. Ebselen inhibits hepatitis C virus NS3 helicase binding to nucleic acid and prevents viral replication. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 2393–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thenin-Houssier, S.; de Vera, I.M.S.; Pedro-Rosa, L.; Brady, A.; Richard, A.; Konnick, B.; Opp, S.; Buffone, C.; Fuhrmann, J.; Kota, S.; et al. Ebselen, a Small-Molecule Capsid Inhibitor of HIV-1 Replication. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 2195–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancineto, L.; Mariotti, A.; Bagnoli, L.; Marini, F.; Desantis, J.; Iraci, N.; Santi, C.; Pannecouque, C.; Tabarrini, O. Design and Synthesis of DiselenoBisBenzamides (DISeBAs) as Nucleocapsid Protein 7 (NCp7) Inhibitors with anti-HIV Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 9601–9614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietka-Ottlik, M.; Potaczek, P.; Piasecki, E.; Mlochowski, J. Crucial Role of Selenium in the Virucidal Activity of Benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-ones and Related Diselenides. Molecules 2010, 15, 8214–8228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wójtowicz, H.; Chojnacka, M.; Młochowski, J.; Palus, J.; Syper, L.; Hudecova, D.; Uher, M.; Piasecki, E.; Rybka, M. Functionalized alkyl and aryl diselenides as antimicrobial and antiviral agents: Synthesis and properties. II Farmaco 2003, 58, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wójtowicz, H.; Kloc, K.; Maliszewska, I.; Młochowski, J.; Piętka, M.; Piasecki, E. Azaanalogues of ebselen as antimicrobial and antiviral agents: Synthesis and properties. II Farmaco 2004, 59, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piętka-Ottlik, M.; Wójtowicz-Młochowska, H.; Kołodziejczyk, K.; Piasecki, E.; Młochowski, J. New Organoselenium Compounds Active against Pathogenic Bacteria, Fungi and Viruses. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 56, 1423–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piętka-Ottlik, M.; Burda-Grabowska, M.; Woźna, M.; Waleńska, J.; Kaleta, R.; Zaczyńska, E.; Piasecki, E.; Giurg, M. Synthesis of new alkylated and methoxylated analogues of ebselen with antiviral and antimicrobial properties. Arkivoc 2017, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, T.N.; Osman, H.; Werngren, J.; Hoffner, S.; Engman, L.; Holmgren, A. Ebselen and analogs as inhibitors of Bacillus anthracis thioredoxin reductase and bactericidal antibacterials targeting Bacillus species, Staphylococcus aureus and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1860, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.J.; Xue, Z.; Xiao, Q.; Hou, A.X.; Liu, Y. Antibacterial activities of novel diselenide-bridged bis(porphyrin)s on Staphylococcus aureus investigated by microcalorimetry. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2008, 125, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosseti, I.B.; Wagner, C.; Fachinetto, R.; Taube Junior, P.; Costa, M.S. Candida albicans growth and germ tube formation can be inhibited by simple diphenyl diselenides [(PhSe)2, (MeOPhSe)2, (p-Cl-PhSe)2, (F3CPhSe)2] and diphenyl ditelluride. Mycoses 2011, 54, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denardi, L.B.; Mario, D.A.; de Loreto, E.S.; Nogueira, C.W.; Santurio, J.M.; Alves, S.H. Antifungal activities of diphenyl diselenide alone and in combination with fluconazole or amphotericin B against Candida glabrata. Mycopathologia 2013, 176, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loreto, E.S.; Mario, D.A.; Santurio, J.M.; Alves, S.H.; Nogueira, C.W.; Zeni, G. In vitro antifungal evaluation and structure-activity relationship of diphenyl diselenide and synthetic analogues. Mycoses 2011, 54, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chassot, F.; Pozzebon Venturini, T.; Baldissera Piasentin, F.; Morais Santurio, J.; Estivalet Svidzinski, T.I.; Hartz Alves, S. Antifungal activities of diphenyl diselenide and ebselen against echinocandin-susceptible and -resistant strains of Candida parapsilosis. New Microbiol. 2016, 39, 301–303, ISN 1121–7138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Venturini, T.P.; Chassot, F.; Loreto, É.S.; Keller, J.T.; Azevedo, M.I.; Zeni, G.; Santurio, J.M.; Alves, S.H. Antifungal activities of diphenyl diselenide and ebselen alone and in combination with antifungal agents against Fusarium spp. Med. Mycol. 2016, 54, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancineto, L.; Piccioni, M.; De Marco, S.; Pagiotti, R.; Nascimento, V.; Braga, A.L.; Santi, C.; Pietrella, D. Diphenyl diselenide derivatives inhibit microbial biofilm formation involved in wound infection. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrella, D. Antimicrobial Activity of Organoselenium Compounds. In Organoselenium Chemistry: Between Synthesis and Biochemistry; Santi, C., Ed.; Bentham Books: Sharjah, UAE, 2014; pp. 328–344. [Google Scholar]
- Pesarico, A.P.; Sartori, G.; dos Santos, C.F.; Neto, J.S.; Bortolotto, V.; Santos, R.C.; Nogueira, C.W.; Prigol, M. 2,2′-Dithienyl diselenide pro-oxidant activity, accounts for antibacterial and antifungal activities. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 168, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosseti, I.B.; Taube Junior, P.; de Campos, C.B.; da Rocha, J.B.; Costa, M.S. Biofilm formation by Candida albicans is inhibited by 4,4-dichloro diphenyl diselenide (pCl-PhSe)2. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2014, 11, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plano, D.; Baquedano, Y.; Moreno-Mateos, D.; Font, M.; Jiménez-Ruiz, A.; Palop, J.A.; Sanmartín, C. Selenocyanates and diselenides: A new class of potent antileishmanial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 3315–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Vlamis-Gardikas, A.; Kandasamy, K.; Zhao, R.; Gustafsson, T.N.; Engstrand, L.; Hoffner, S.; Engman, L.; Holmgren, A. Inhibition of bacterial thioredoxin reductase: An antibiotic mechanism targeting bacteria lacking glutathione. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macegoniuk, K.; Grela, E.; Palus, J.; Rudzińska-Szostak, E.; Grabowiecka, A.; Biernat, M.; Berlicki, Ł. 1,2-Benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-one Derivatives As a New Class of Bacterial Urease Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 8125–8133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, G.; Hardej, D.; Santoro, M.; Lau-Cam, C.; Billack, B. Evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of ebselen: Role of the yeast plasma membrane H+-ATPase. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2007, 21, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billack, B.; Pietka-Ottlik, M.; Santoro, M.; Nicholson, S.; Młochowski, J.; Lau-Cam, C. Evaluation of the antifungal and plasma membrane H+-ATPase inhibitory action of ebselen and two ebselen analogs in S. cerevisiae cultures. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2010, 25, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orie, N.N.; Warren, A.R.; Basaric, J.; Lau-Cam, C.; Piętka-Ottlik, M.; Młochowski, J.; Billack, B. In vitro assessment of the growth and plasma membrane H+ -ATPase inhibitory activity of ebselen and structurally related selenium- and sulfur-containing compounds in Candida albicans. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welter, A.; Fischer, H.; Christiaens, L.; Wendel, A.; Etschenberg, E.; Dereu, N.; Kuhl, P.; Graf, E. Diselenobis-Benzoic Acid Amides of Primary and Secondary Amines and Processes for the Treatment of Diseases in Humans Caused by a Cell Injury. U.S. Patent 4873350, 10 October 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Welter, A.; Christiaens, L.; Wirtz-Peitz, F. Benzisoselenazolones and Process for the Treatment of Rheumatic and Arthritic Diseases Using Them. U.S. Patent 4418069, 29 November 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Osajda, M.; Mlochowski, J. The reactions of 2-(chloroseleno)benzoyl chloride with nucleophiles. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 7531–7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhabak, K.P.; Mugesh, G. Synthesis, Characterization, and Antioxidant Activity of Some Ebselen Analogues. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 4594–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Yan, J.; Poon, J.F.; Singh, V.P.; Lu, X.; Karlsson, O.M.; Engman, L.; Kumar, S. Multifunctional Antioxidants: Regenerable Radical-Trapping and Hydroperoxide-Decomposing Ebselenols. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3729–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, M.P.; Smith, R.A.J. Mitochondrially Targeted Antioxidants. U.S. Patent 0227957, 13 October 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Młochowski, J.; Kloc, K.; Syper, L.; Inglot, A.D.; Piasecki, E. Aromatic and Azaaromatic Diselenides, Benzisoselenazolones and Related Compounds as Immunomodulators Active in Humans: Synthesis and Properties. Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1993, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlochowski, J.; Gryglewski, R.J.; Inglot, A.D.; Jakubowski, A.; Juchniewicz, L.; Kloc, K. Synthesis and Properties of 2-Carboxyalkyl-1,2-benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-ones and Related Organoselenium Compounds as Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitors and Cytokine Inducers. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 1996, 1751–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, J.; Saba, S.; Canto, R.F.; Frizon, T.E.; Hassan, W.; Waczuk, E.P.; Jan, M.; Back, D.F.; Da Rocha, J.B.; Braga, A.L. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 2-picolylamide-based diselenides with non-bonded interactions. Molecules 2015, 20, 10095–10109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küppers, J.; Schulz-Fincke, A.C.; Palus, J.; Giurg, M.; Skarżewski, J.; Gütschow, M. Convergent Synthesis of Two Fluorescent Ebselen-Coumarin Heterodimers. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkrishna, S.J.; Bhakuni, B.S.; Kumar, S. Copper catalyzed/mediated synthetic methodology for ebselen and related isoselenazolones. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 9565–9575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Li, P.; Sun, Z.; Yang, S.; Wang, B.; Hana, K. A fluorescent probe for rapid detection of thiols and imaging of thiols reducing repair and H2O2 oxidative stress cycles in living cells. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 391–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieske, J.S. Antimycyn A. In Antibiotics. Mechanism of Action; Gottlieb, D., Shaw, P.D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1967; Volume 1, pp. 542–584. [Google Scholar]
- Sheu, C.W.; Freese, E. Lipopolysaccharide Layer Protection of Gram-Negative Bacteria against Inhibition by Long-Chain Fatty Acids. J. Bacteriol. 1973, 115, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ngo, H.X.; Shrestha, S.K.; Green, K.D.; Garneau-Tsodikova, S. Development of ebsulfur analogues as potent antibacterials against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 6298–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, P.T.; Schauerte, J.A.; Wisser, K.C.; Ding, H.; Lee, E.L.; Steel, D.G.; Gafni, A. Amyloid-beta membrane binding and permeabilization are distinct processes influenced separately by membrane charge and fluidity. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 386, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, D.K.; Kollef, M.H.; Seiler, S.M.; Fridkin, S.K. The Epidemiology of Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus Colonization in a Medical Intensive Care Unit. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2003, 24, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manavathu, E.K.; Cutright, J.L.; Chandrasekar, P.H. Organism-Dependent Fungicidal Activities of Azoles. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 3018–3021. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gallis, H.A.; Drew, R.H.; Pickard, W.W. Amphotericin B: 30 Years of Clinical Experience. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1990, 12, 308–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Mao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xie, K.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Jiang, X.; Shen, J. Synthesis of N-(3-Cyano-7-ethoxy-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinolin-6-yl)acetamide. Heterocycles 2011, 83, 2851–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2008 Reference Method for Broth Dilutionantifungal Susceptibility Testing of Yeast Approved Standard, M27-A3 28, 3rd ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 4–10 are available from the authors. |

| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | X | Rx Time (h) | Yield (%) | m.p. (°C) | m.p. lit (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4a | 2-OH | - | - | - | 96 | 92 | 233.5–236.5 | 235–238 [53] |
| 4b | 3-OH | - | - | - | 60 | 84 | 285.5–287.0 | 285–286 [53] |
| 4c | 4-OH | - | - | - | 120 | 73 | 271.0–272.0 | 282–284 [53] |
| 4d | 2-OH | 4-Me | - | - | 24 | 60 | 221.0–223.5 | - |
| 4e | 2-OH | 5-Me | - | - | 96 | 89 | 191.5–194.5 | - |
| 4f | 2-OH | 6-Me | - | - | 168 | 88 | 264.0–267.0 | - |
| 4g | 2-OH | 4-Cl | - | - | 96 | 59 | 230.0–234.0 | - |
| 4h | 2-OH | 5-Cl | - | - | 48 | 63 | 219.5–221.5 | - |
| 4i | 2-OH | 5-COOMe | - | - | 72 | 57 | 281.0–282.0 | - |
| 4j | 3-OH | 4-OMe | - | - | 120 | 94 | 232.5–236.5 | - |
| 4k | 2-OMe | - | - | - | 168 | 94 | 211.0–214.0 | 216–217 [53] |
| 4l | 3-OMe | - | - | - | 72 | 98 | 221.0–223.0 | 221–223 [35] |
| 4m | 4-OMe | - | - | - | 48 | 94 | 285.5–287.5 | 290–292 [53] |
| 4n | 2-OMe | 4-Ome | - | - | 168 | 99 | 211.0–213.5 | - |
| 4o | 3-OMe | 4-OMe | - | - | 96 | 72 | 231.5–234.5 | 235 [53] |
| 4p | 3-OMe | 4-OMe | 5-OMe | - | 96 | 76 | 193.0–195.0 | - |
| 5 | - | - | - | - | 120 | 85 | 149.0–152.0 | - |
| 6 | - | - | - | - | 120 | 100 | 296.5 dec. | - |
| 7 | - | - | - | - | 96 | 36 | 178.0–181.0 | - |
| 8 | - | - | - | - | 240 | 97 | >300 | - |
| 10a | 2-OH | - | - | CH | 20 | 40 | 195.5–197.5 | 194–196 [54] |
| 10b | 6-OH | - | - | N | 2 | 65 | 229.0 dec. | 199–201 [55] a |
| 10c | 2-OMe | - | - | CH | 24 | 71 | 189.0–191.5 | 172–174 [63] |
| 10d | 3-OMe | - | - | CH | 2 | 65 | 166.0–168.0 | 165.5–167.5 [35] |
| 10e | 4-OMe | - | - | CH | 20 | 70 | 180.0–181.0 | 180.5–181.5 [35] |
| 10f | 2-OMe | 4-Ome | - | CH | 6 | 65 | 240.5–242.5 | - |
| 10g | 3-OMe | 4-Ome | - | CH | 48 | 68 | 159.0–161.0 | - |
| Compound | Gram-Positive Bacteria a | Gram-Negative Bacteria a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | S. epidermidis | E. faecalis | E. hirae | E. coli | P. aeruginosa | |
| 4a | 16 | 8 | 4 | 8 | >128 | >128 |
| 4b | 16 | 8 | 2 | 8 | >128 | >128 |
| 4c | 16 | 16 | 2 | 8 | >128 | >128 |
| 4d | >128 | 128 | 2 | 4 | >128 | >128 |
| 4e | 16 | 16 | 1 | 2 | 64 | >128 |
| 4f | >128 | >128 | 4 | 8 | >128 | >128 |
| 4g | 128 | 64 | 2 | 4 | >128 | >128 |
| 4h | >128 | 128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 4i | >128 | 128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 4j | >128 | 128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 4k | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 4l | >128 | 128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 4m | >128 | >128 | 8 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 4n | >128 | 128 | 4 | 64 | >128 | >128 |
| 4o | >128 | 128 | 16 | 64 | >128 | >128 |
| 4p | >128 | 128 | 4 | 32 | >128 | >128 |
| 5 | >128 | 128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 6 | >128 | 128 | 4 | 8 | >128 | >128 |
| 7 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 10a | 8 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 32 | >128 |
| 10b | 8 | 4 | 1 | 2 | >128 | >128 |
| 10c | 32 | 32 | 2 | 8 | 128 | >128 |
| 10d | >128 | 128 | 16 | 32 | >128 | >128 |
| 10e | >128 | 128 | 4 | 32 | >128 | >128 |
| 10f | 64 | 64 | 2 | 4 | >128 | >128 |
| 10g | 64 | 32 | 2 | 8 | >128 | >128 |
| Ebs | 64 | 32 | 2 | 8 | 128 | >128 |
| AMC | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| AMP | 4 | >128 | 16 | >128 | 16 | >128 |
| CHK | >128 | >128 | 128 | 128 | 2 | >128 |
| ERM | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | 64 | >128 |
| STR | 32 | 128 | >128 | >128 | 32 | 128 |
| NAT | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | 16 | 32 |
| Compound | Yeasts a | Fungi a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| C. albicans | C. glabrata | A. niger | |
| 4a | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 4b | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 4c | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 4d | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 4e | 32 | 32 | 128 |
| 4f | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 4g | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 4h | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 4i | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 4j | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 4k | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 4l | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 4m | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 4n | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 4o | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 4p | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 5 | >128 | >128 | - |
| 6 | >128 | >128 | - |
| 7 | >128 | >128 | - |
| 10a | 16 | 16 | >128 |
| 10b | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 10c | 16 | 32 | 64 |
| 10d | >128 | >128 | - |
| 10e | 64 | >128 | - |
| 10f | 16 | 64 | 64 |
| 10g | 32 | 64 | - |
| Ebselen | 32 | 64 | 16 |
| AMC | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| KLK | >128 | >128 | - |
| ITC | >128 | >128 | - |
| NAT | 64 | 64 | - |
| AMB | 1 | 1 | - |
| Compound | TCCD50 a | HHV-1 | EMCV | VSV | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC b | I c | MIC b | I c | MIC b | I c | ||
| 4a | 4.9 | 40 | 0.12 | 10 | 0.49 | >1000 | <0.005 |
| 4c | 3.7 | 2 | 1.8 | 60 | 0.06 | >1000 | <0.004 |
| 4d | 4.9 | 2 | 2.5 | >1000 | <0.005 | >1000 | <0.005 |
| 4e | 4.9 | 2 | 2.5 | 6 | 0.82 | >1000 | <0.005 |
| 4f | 9.8 | 4 | 2.5 | >1000 | <0.01 | >1000 | <0.01 |
| 4g | 4.9 | 2 | 2.5 | 40 | 0.12 | >1000 | <0.005 |
| 4h | 4.9 | 6 | 0.82 | >1000 | <0.005 | >1000 | <0.005 |
| 4i | 7.3 | 20 | 0.37 | 20 | 0.37 | >1000 | <0.07 |
| 4j | 4.9 | 4 | 1.2 | 20 | 0.25 | >1000 | <0.005 |
| 4k | 312 | 6 | 52 | 400 | 0.78 | >1000 | <0.31 |
| 4n | 58 | 2 | 29 | 600 | 0.10 | >1000 | <0.06 |
| 4o | 4.9 | 2 | 2.5 | 8 | 0.61 | >1000 | <0.005 |
| 4p | 2.4 | 4 | 0.61 | 8 | 0.30 | 200 | 0.01 |
| 5 | 4.9 | 200 | 0.02 | 10 | 0.49 | >1000 | <0.005 |
| 7 | 15 | 20 | 0.75 | 400 | 0.04 | 600 | 0.03 |
| 10c | 9.8 | 4 | 2.5 | 8 | 1.2 | >1000 | <0.01 |
| 10f | 156 | 2 | 78 | 200 | 0.78 | >1000 | <0.16 |
| Ebselen | 15 | 2 | 7.5 | 10 | 1.5 | >1000 | <0.02 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giurg, M.; Gołąb, A.; Suchodolski, J.; Kaleta, R.; Krasowska, A.; Piasecki, E.; Piętka-Ottlik, M. Reaction of bis[(2-chlorocarbonyl)phenyl] Diselenide with Phenols, Aminophenols, and Other Amines towards Diphenyl Diselenides with Antimicrobial and Antiviral Properties. Molecules 2017, 22, 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22060974
Giurg M, Gołąb A, Suchodolski J, Kaleta R, Krasowska A, Piasecki E, Piętka-Ottlik M. Reaction of bis[(2-chlorocarbonyl)phenyl] Diselenide with Phenols, Aminophenols, and Other Amines towards Diphenyl Diselenides with Antimicrobial and Antiviral Properties. Molecules. 2017; 22(6):974. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22060974
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiurg, Mirosław, Anna Gołąb, Jakub Suchodolski, Rafał Kaleta, Anna Krasowska, Egbert Piasecki, and Magdalena Piętka-Ottlik. 2017. "Reaction of bis[(2-chlorocarbonyl)phenyl] Diselenide with Phenols, Aminophenols, and Other Amines towards Diphenyl Diselenides with Antimicrobial and Antiviral Properties" Molecules 22, no. 6: 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22060974
APA StyleGiurg, M., Gołąb, A., Suchodolski, J., Kaleta, R., Krasowska, A., Piasecki, E., & Piętka-Ottlik, M. (2017). Reaction of bis[(2-chlorocarbonyl)phenyl] Diselenide with Phenols, Aminophenols, and Other Amines towards Diphenyl Diselenides with Antimicrobial and Antiviral Properties. Molecules, 22(6), 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22060974