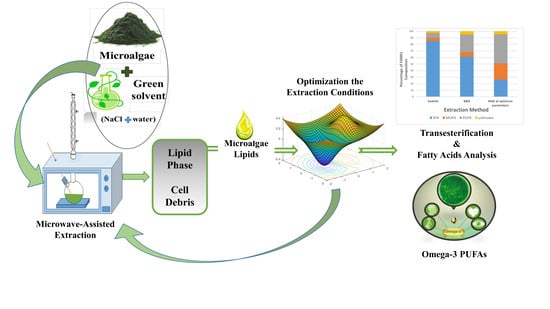
Microwave-Assisted Brine Extraction for Enhancement of the Quantity and Quality of Lipid Production from Microalgae Nannochloropsis sp.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
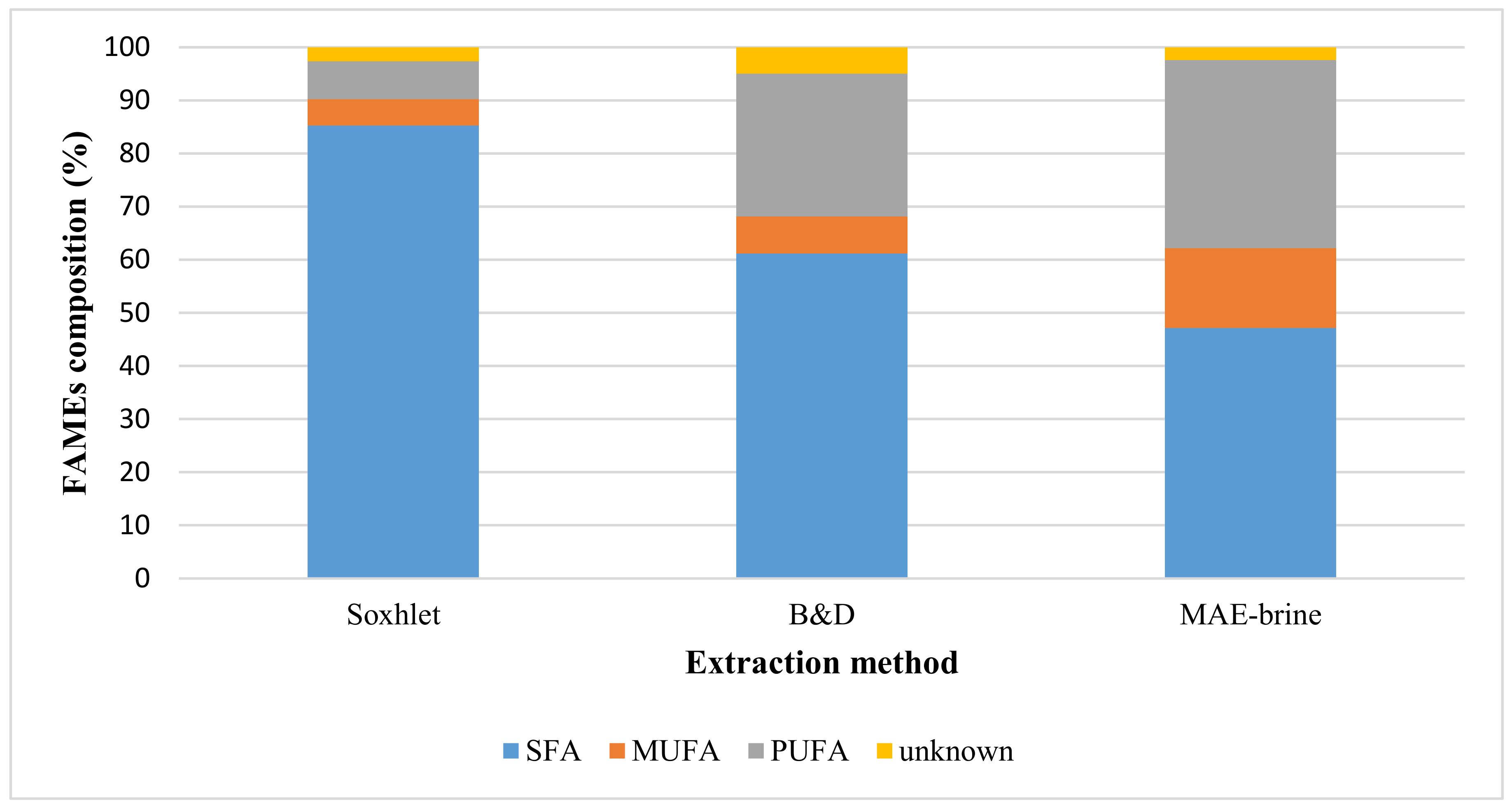
2.1. Conventional Extraction
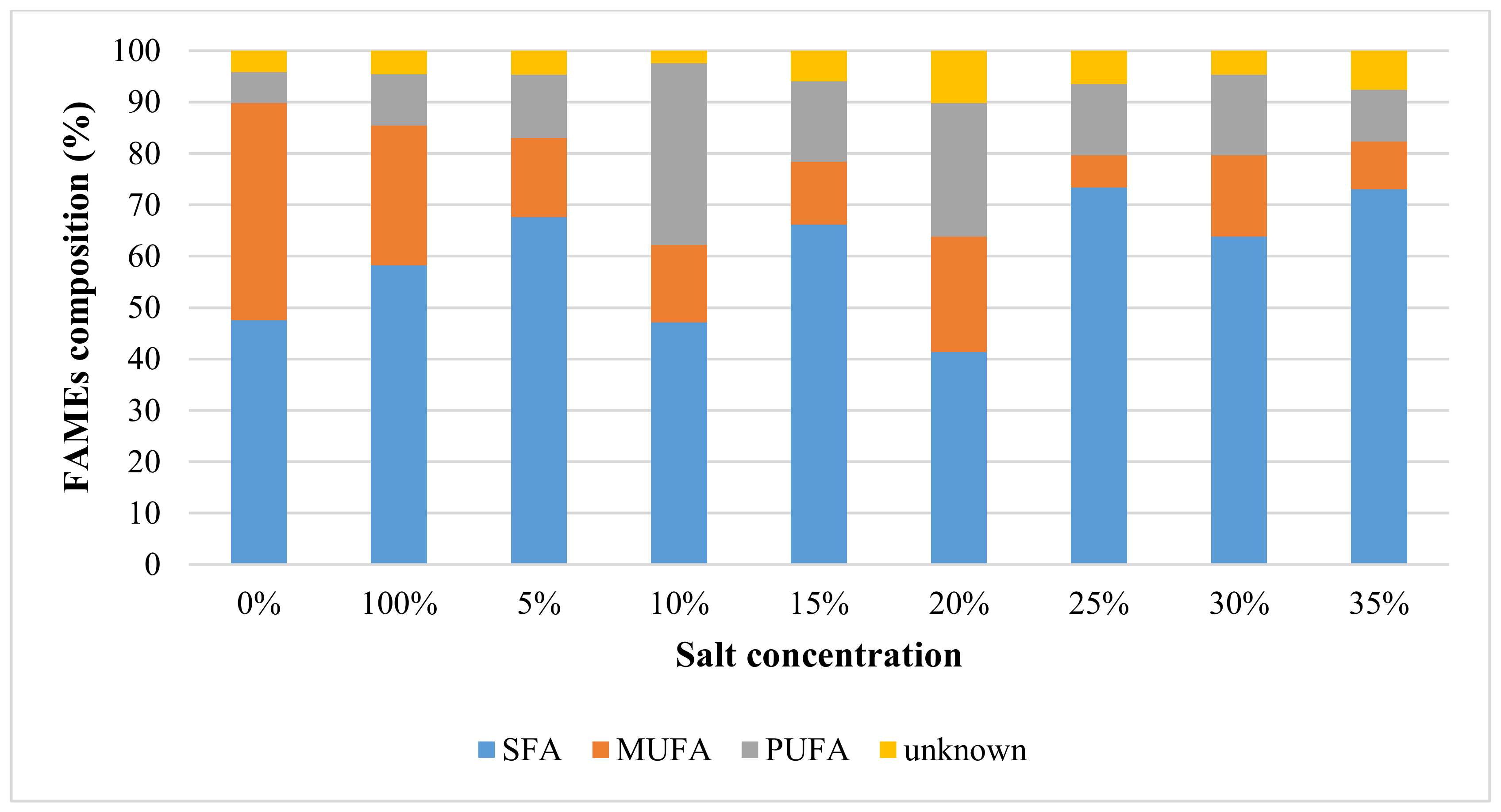
2.2. Effect of Inorganic NaCl Salt Concentration on Quantity and Quality of Lipids Using MAE
2.2.1. Lipid Extraction
2.2.2. Fatty Acid Composition
2.3. Optimization of Lipid Yield Using RSM
2.3.1. Lipid Extraction Optimization
× A × C + 3.38117E−3 × B × C + 0.032721 × A2 + 5.49845E−3 × B2 + 8.25710E−3 × C2
B2 + 8.25710E−3 × C2
2.3.2. Fatty Acid Analysis for Optimization Experiment
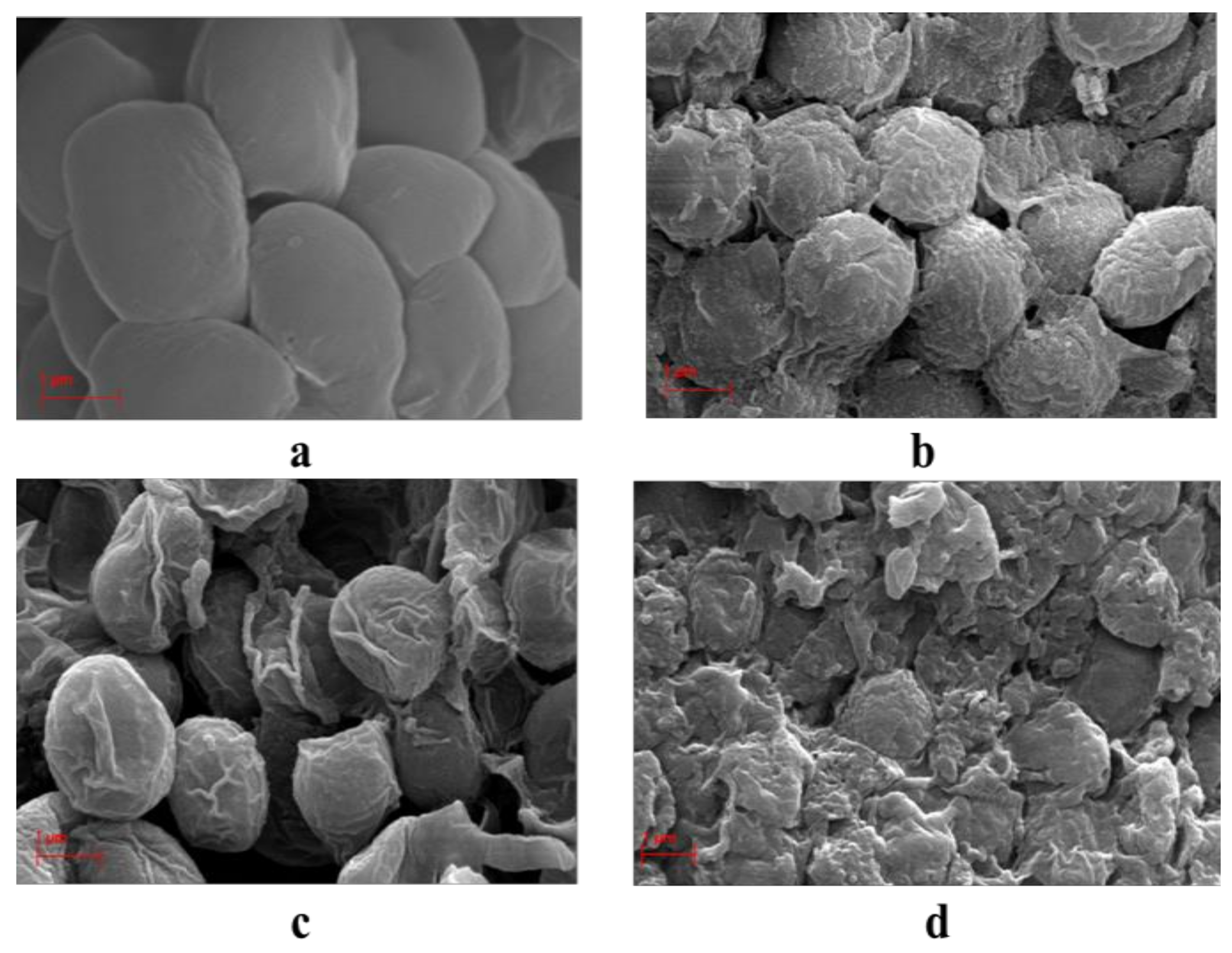
2.4. SEM Analysis
2.5. Economic Potential
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Conventional Microalgae Lipid Extraction
3.2.1. Soxhlet Extraction
3.2.2. Bligh and Dyer Extraction
3.3. Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE)
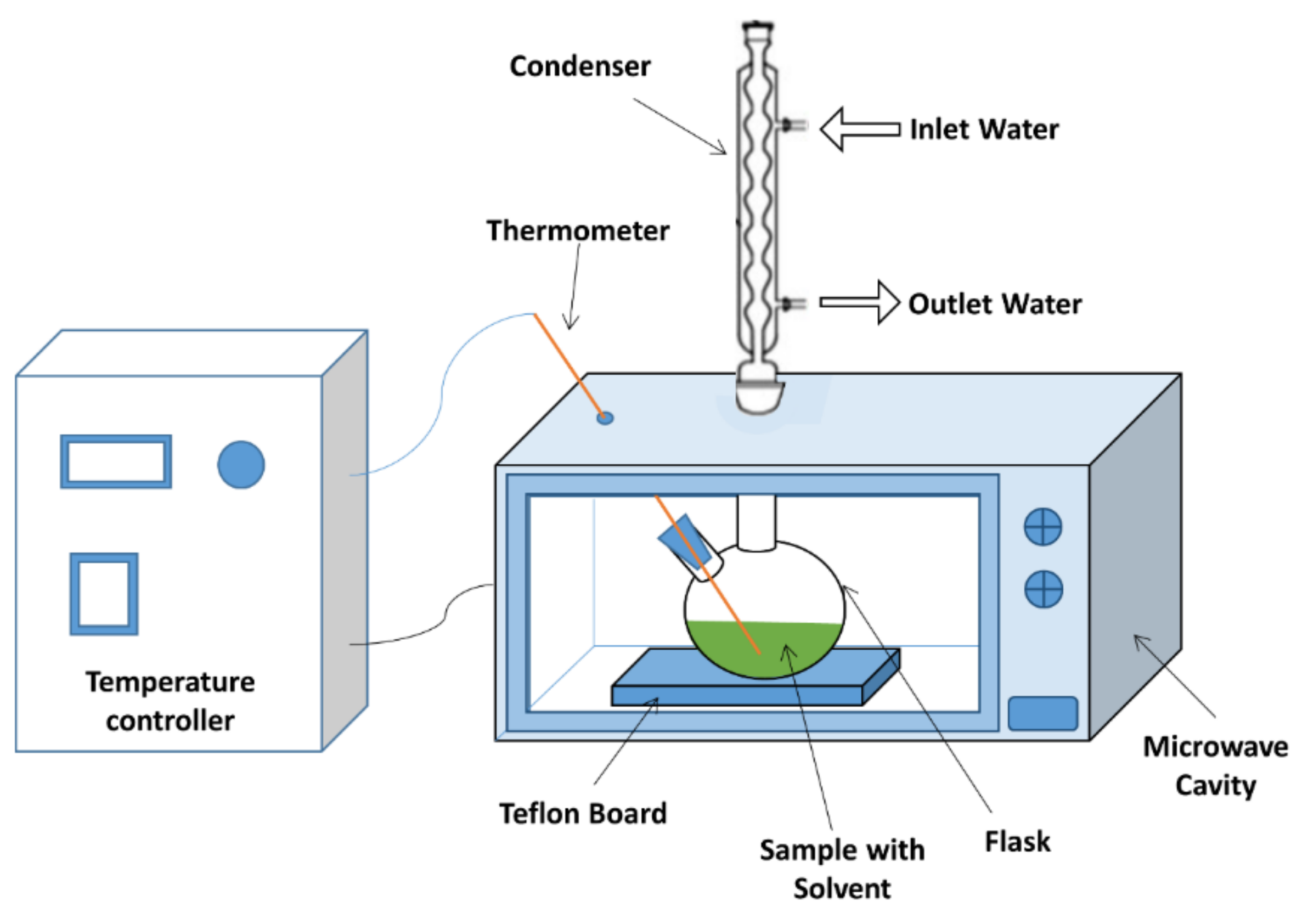
3.3.1. Microwave Extractor Setup
3.3.2. Experimental Procedures
3.3.3. Optimization Experiment and Statistical Analysis
3.3.4. Samples Post-treatment
3.4. Transesterification of Lipid
3.5. FAME Analysis Using GC-FID
3.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Handayani, N.A.; Ariyanti, D.; Hadiyanto, H. Potential production of polyunsaturated fatty acids from microalgae. Int. J. Sci. Eng. 2011, 2, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikrjukov, K.A.; Patterson, D.J. Taxonomy and phylogeny of Heliozoa. III. Actinophryids. Acta Protozool. 2001, 40, 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, I.; Gouveia, L.; Batista, A.P.; Raymundo, A.; Bandarra, N.M. Microalgae in novel food products. In Food Chemistry Research Developments; Papadoupoulos, K., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 75–112. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzaález-Delgado, A.D.; Kafarov, V. Microalgae based biorefinery: Evaluation of oil extraction methods in terms of efficiency, costs, toxicity and energy in lab-scale. ION 2013, 26, 27–39. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio-Rodríguez, N.; Beltrán, S.; Jaime, I.; Saram, M.; Sanz, M.T.; Carballido, J.R. Production of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid concentrates: A review. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, G.; Micek, A.; Marventano, S.; Castellano, S.; Mistretta, A.; Pajak, A. Dietary n-3 PUFA; fish consumption and depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 205, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Harris, W.S.; Appel, L.J.; Committee, N. Fish consumption; fish oil; omega-3 fatty acids; and cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2002, 106, 2747–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oken, E.; Kleinman, K.P.; Berland, W.E.; Simon, S.R.; Rich-Edwards, J.W.; Gillman, M.W. Decline in fish consumption among pregnant women after a national mercury advisory. Obstet. Gynecol. 2003, 102, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adarme-Vega, T.C.; Lim, D.K.; Timmins, M.; Vernen, F.; Li, Y.; Schenk, P.M. Microalgal biofactories: A promising approach towards sustainable omega-3 fatty acid production. Microb. Cell Factories 2012, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Yoo, C.; Jun, S.Y.; Ahn, C.Y.; Oh, H.M. Comparison of several methods for effective lipid extraction from microalgae. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, S75–S77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Naghdi, F.G.; Garg, S.; Adarme-Vega, T.C.; Thurecht, K.J.; Ghafor, W.A. A comparative study: The impact of different lipid extraction methods on current microalgal lipid research. Microb. Cell Factories 2014, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Arora, N.; Nanda, M.; Pruthi, V. Different cell disruption and lipid extraction methods from microalgae for biodiesel production. In Microalgae Biotechnology for Development of Biofuel and Wastewater Treatment; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 265–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjith Kumar, R.; Hanumantha Rao, P.; Arumugam, M. Lipid extraction methods from microalgae: A comprehensive review. Front. Energy Res. 2015, 2, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safafar, H.; Ljubic, A.; Møller, P.; Jacobsen, C. Two-step direct transesterification as a rapid method for the analysis of fatty acids in microalgae biomass. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2019, 121, 1700409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.; Omar, R.; Ethaib, S.; Mazlina, M.S.; Biak, D.A.; Aisyah, R.N. Microwave-assisted extraction of lipid from fish waste. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2017; Volume 206, p. 012096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, S.; Tyagi, R.D.; Drogui, P.; Surampalli, R.Y. Ultrasonication assisted lipid extraction from oleaginous microorganisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 158, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, H.; Al-Zuhair, S.; Al-Marzouqi, A.H.; Haik, Y.; Farid, M. Effective extraction of microalgae lipids from wet biomass for biodiesel production. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 66, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, G.P.; Balducchi, R.; Mehariya, S.; Martino, M.; Larocca, V.; Di Sanzo, G. Selective Extraction of ω-3 fatty acids from Nannochloropsis sp. using supercritical CO2 extraction. Molecules 2019, 24, 2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethaib, S.; Omar, R.; Kamal, S.M.; Biak, D.A. Microwave-assisted pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass: A review. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2015, 2, 97–109. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, D.; Dvoretsky, S.; Temnov, M.; Akulinin, E.; Peshkova, E. Enhanced lipid extraction from microalgae Chlorella vulgaris biomass: Experiments; modelling; optimization. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2016, 49, 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Amarni, F.; Kadi, H. Kinetics study of microwave-assisted solvent extraction of oil from olive cake using hexane: Comparison with the conventional extraction. Innov. Food Sci. & Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refaat, A.; El Sheltawy, S.; Sadek, K. Optimum reaction time; performance and exhaust emissions of biodiesel produced by microwave irradiation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. & Technol. 2008, 5, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koberg, M.; Cohen, M.; Ben-Amotz, A.; Gedanken, A. Bio-diesel production directly from the microalgae biomass of Nannochloropsis by microwave and ultrasound radiation. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 4265–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabakaran, P.; Ravindran, A. A comparative study on effective cell disruption methods for lipid extraction from microalgae. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 53, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.P.F.D.S.; Costa, M.C.; Lopes, A.C.; Neto, E.F.A.; Leitão, R.C.; Mota, C.R.; Dos Santos, A.B. Comparison of pretreatment methods for total lipids extraction from mixed microalgae. Renew. Energy 2014, 63, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Yin, J.; Gao, Z.; Huang, H.; Ji, X.-J.; Dou, C. Disruption of Chlorella vulgaris Cells for the Release of Biodiesel-Producing Lipids: A Comparison of Grinding, Ultrasonication, Bead Milling, Enzymatic Lysis, and Microwaves. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 164, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermúdez Menéndez, J.M.; Arenillas, A.; Menéndez Díaz, J.Á.; Boffa, L.; Mantegna, S.; Binello, A. Optimization of microalgae oil extraction under ultrasound and microwave irradiation. J. Chem. Technol. & Biotechnol. 2014, 89, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garoma, T.; Janda, D. Investigation of the effects of microalgal cell concentration and electroporation, microwave and ultrasonication on lipid extraction efficiency. Renew. Energy 2016, 86, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criado, M.R.; Pereiro, I.R.; Torrijos, R.C.; Pereiro, I.R. Optimization of a microwave-assisted extraction method for the analysis of polychlorinated biphenyls in ash samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 985, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethaib, S.; Omar, R.; Mustapa Kamal, S.M.; Awang Biak, D.R.; Syam, S.; Harun, M.Y. Microwave-assisted pretreatment of sago palm bark. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2017, 37, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metaxas, A.; Meredith, R.J. Industrial Microwave Heating; IET; Peter Peregrinus Ltd.: London, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Thostenson, E.; Chou, T.-W. Microwave processing: Fundamentals and applications. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1999, 30, 1055–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete, A.; Mato, R.; Cocero, M.; Mato, R.; Alonso, M.J.C. A predictive approach in modeling and simulation of heat and mass transfer during microwave heating. Application to SFME of essential oil of Lavandin Super. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 68, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veggi, P.C.; Martínez, J.; Meireles, M.A.A. Fundamentals of Microwave Extraction. In Food Engineering Series; Springer Science and Business Media LLC/Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 15–52. [Google Scholar]
- Gilman, L.B.; Engelhart, W.G. Recent advances in microwave sample preparation. Spectroscopy 1989, 4, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kunlan, L.; Lixin, X.; Jun, L.; Jun, P.; Guoying, C.; Zuwei, X. Salt-assisted acid hydrolysis of starch to d-glucose under microwave irradiation. Carbohydr. Res. 2001, 331, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miadonye, A.; Lin, S. Investigation on enhanced microwave demulsification using inorganic salts. Eur. Chem. Bull. 2015, 4, 414–419. [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel, C.; Gabriel, S.; Grant, E.H.; Halstead, B.S.J.; Mingos, D.M.P. Dielectric parameters relevant to microwave dielectric heating. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1998, 27, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, T.; Wentz, F. The complex dielectric constant of pure and sea water from microwave satellite observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2004, 42, 1836–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sukenik, A.; Zmora, O.; Carmeli, Y. Biochemical quality of marine unicellular algae with special emphasis on lipid composition. II. Nannochloropsis sp. Aquaculture 1993, 117, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grima, E.M.; Medina, A.R.; Giménez, A.G.; Perez, J.A.S.; Camacho, F.G.; Sánchez, J.L.G. Comparison between extraction of lipids and fatty acids from microalgal biomass. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1994, 71, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, H.; Barreira, L.; Figueiredo, F.; Custodio, L.; Vizetto-Duarte, C.; Polo, C.; Rešek, E.; Engelen, A.; Varela, J. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids of Marine Macroalgae: Potential for Nutritional and Pharmaceutical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1920–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsubaki, S.; Oono, K.; Onda, A.; Yanagisawa, K.; Azuma, J.-I. Microwave-assisted hydrothermal hydrolysis of cellobiose and effects of additions of halide salts. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 123, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.-A.; Cheng, Y.-M.; Huang, J.-W.; Jen, J.-F.; Huang, Y.-S.; Yu, C.-C. Effects of ultrasonic and microwave pretreatments on lipid extraction of microalgae. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 37, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.-X.; Lu, S.-W.; Cao, G.-Y. SALT-ASSISTED MICROWAVE DEMULSIFICATION. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2004, 191, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binner, E.; Robinson, J.; Silvester, S.; Kingman, S.; Lester, E. Investigation into the mechanisms by which microwave heating enhances separation of water-in-oil emulsions. Fuel 2014, 116, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, V.; Mohan, Y.; Hemalatha, S. Microwave assisted extraction—An innovative and promising extraction tool for medicinal plant research. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2007, 1, 7–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, N.S.; Nassar, A.M.; Zaki, N.N.; Gharieb, H.K. Formation of fluid heavy oil-in-water emulsions for pipeline transportation. Fuel 1999, 78, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafizadeh, S.; Kamran, M. Emulsification of heavy crude oil in water for pipeline transportation. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2010, 71, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King PM, N.K.; Joyce, E.; Mason, T. Ultrasonic disruption of algae cells. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, University Park, MD, USA, 24 May 2012; Volume 1433, pp. 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravotto, G.; Boffa, L.; Mantegna, S.; Perego, P.; Avogadro, M.; Cintas, P. Improved extraction of vegetable oils under high-intensity ultrasound and/or microwaves. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2008, 15, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakesh, S.; Dhar, D.W.; Prasanna, R.; Saxena, A.K.; Saha, S.; Shukla, M.; Sharma, K. Cell disruption methods for improving lipid extraction efficiency in unicellular microalgae. Eng. Life Sci. 2015, 15, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Oca, M.G.M.; Viêgas, C.V.; Lemões, J.S.; Miyasaki, E.K.; Morón-Villarreyes, J.A.; Primel, E.G.; Abreu, P.C. Production of FAMEs from several microalgal lipidic extracts and direct transesterification of the Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Biomass- Bioenergy 2011, 35, 1533–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.-L.; Harrata, K.A.; Yao, L.; Gerde, J.A.; Wang, T. Microalgae Lipid Characterization. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 1773–1787. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Rios, S.D.; Castañeda, J.; Torras, C.; Farriol, X.; Salvadó, J. Lipid extraction methods from microalgal biomass harvested by two different paths: Screening studies toward biodiesel production. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 133, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, J.; Theegala, C. Microwave assisted lipid extraction from microalgae using biodiesel as co-solvent. Algal Res. 2013, 2, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, A.; Patil, C.; Moholkar, V.S.; Moholkar, P.V. Mechanistic Assessment of Microalgal Lipid Extraction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 2979–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virot, M.; Tomao, V.; Giniès, C.; Visinoni, F.; Chemat, F. Microwave-integrated extraction of total fats and oils. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1196, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Yu, T.; Li, T.; Zhou, J.; Cen, K. Using wet microalgae for direct biodiesel production via microwave irradiation. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 131, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sostaric, M.; Klinar, D.; Bricelj, M.; Golob, J.; Berovič, M.; Likozar, B. Growth, lipid extraction and thermal degradation of the microalga Chlorella vulgaris. New Biotechnol. 2012, 29, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, T.; Nichols, P.D.; McMeekin, T.A. Evaluation of extraction methods for recovery of fatty acids from lipid-producing microheterotrophs. J. Microbiol. Methods 2000, 43, 107–116. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Not available. |







| Microalgae | Protein | Carbohydrate | Lipids |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anabaena cylindrical | 43–56 | 25–30 | 4–7 |
| Chlamydomonas rheinhardii | 48 | 17 | 21 |
| Chlorella vulgaris | 38 | 33 | 5 |
| Diacronema vlkianum | 57 | 32 | 6 |
| Dunaliella salina | 39–61 | 14–18 | 14–20 |
| Haematococcus pluvialis | 48 | 27 | 15 |
| Isochrysis galbana | 50–56 | 10–17 | 12–14 |
| Scenedesmus obiquus | 6–20 | 33–64 | 11–21 |
| Spirulina maxima | 46–63 | 8–14 | 4–9 |
| Spirulina platensis | 52 | 15 | 3 |
| Nannochloropsis sp. | 64 | 3 | 23 |
| Microalgae | Extraction Method | Solvent | Lipid Yield (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Botryococcus sp., Chlorella vulgaris, Scenedesmus sp. | Autoclave Microwave Ultrasound | Chloroform/ methanol (1:1 v/v) | 5.4–11.9 10–28.6 6.1–8.8 | [10] |
| Nannochloropsis sp. | Microwave Ultrasound | Chloroform/ methanol (2:1 v/v) | 32.8 18.9 | [25] |
| Chlorella sp. | Microwave Autoclave | Chloroform/ methanol (2:1 v/v) | 38 24 | [26] |
| Mixed culture | Microwave Autoclave Ultrasound Electroflotation | chloroform/ methanol/ water (1:2:0.8 v/v) | 33.7 15.4 13.3 24.8 | [27] |
| Chlorella vulgaris | Grinding Ultrasound beadmilling Microwave | Chloroform/ methanol (1:1 v/v) | 6 15 10 18 | [28] |
| N. gaditana | Microwave Ultrasound | Chloroform/ methanol/ water (1:2:1 v/v/v) | 39 36 | [29] |
| C. vulgaris | Ultrasound Microwave | Chloroform/ methanol/ water (2:2:1.8 v/v/v) | 26.4 28.9 | [30] |
| FAs | FAMEs (mg/g) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 1% | 5% | 10% | 15% | 20% | 25% | 30% | 35% | |
| C14:0 | 0.26 | 0.63 | 1.10 | 4.02 | 1.88 | 2.97 | 1.46 | 1.21 | 0.80 |
| C14:1 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.31 | 0.16 | 0.22 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.08 |
| C16:0 | 1.12 | 2.97 | 7.10 | 9.19 | 13.95 | 4.68 | 9.51 | 7.60 | 5.51 |
| C16:1 | 0.92 | 1.24 | 0.71 | 0.51 | 0.82 | 0.59 | 0.16 | 1.14 | 0.03 |
| C18:0 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.89 | 0.08 | 0.07 |
| C18:1 | 0.24 | 0.11 | 0.60 | 1.14 | 0.97 | 2.42 | 0.15 | 0.72 | 0.43 |
| C18:1 | 0.04 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 1.64 | 0.55 | 0.80 | 0.37 | 0.08 | 0.06 |
| C18:2 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.24 | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.87 | 0.37 | 0.32 | 0.17 |
| C18:3 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.30 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.03 |
| C20:0 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| C20:1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.12 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.00 |
| C20:2 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.62 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.03 |
| C20:4 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.27 | 1.16 | 0.68 | 0.93 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.17 |
| C20:3 | 0.00 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.04 |
| C20:5 | 0.14 | 0.45 | 1.19 | 8.15 | 2.87 | 4.02 | 1.78 | 1.71 | 0.64 |
| C22:0 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.34 | 0.21 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.08 |
| C22:1 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.68 | 0.28 | 0.24 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.18 |
| C24:0 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.42 | 0.27 | 0.17 | 0.10 |
| C22:6 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| C24:1 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.06 |
| Unknown | 0.11 | 0.22 | 0.34 | 0.58 | 1.46 | 1.20 | 0.47 | 0.36 | 0.51 |
| SFA | 1.44 | 3.75 | 8.35 | 13.86 | 16.21 | 8.44 | 12.26 | 9.22 | 6.61 |
| MUFA | 1.28 | 1.76 | 1.91 | 4.41 | 2.98 | 4.58 | 1.05 | 2.29 | 0.84 |
| PUFA | 0.18 | 0.65 | 1.52 | 10.42 | 3.84 | 5.31 | 2.31 | 2.26 | 0.91 |
| Omega-3 | 0.15 | 0.51 | 1.23 | 8.54 | 2.99 | 4.24 | 1.89 | 1.76 | 0.67 |
| Runs | Coded Parameters | Process Parameters | Lipid Yield (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | Solid Loading (%) | Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | ||
| 1 | −1 | −1 | +1 | 10 | 70 | 25 | 5.10 ± 0.04 |
| 2 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 10 | 70 | 10 | 3.91 ± 0.02 |
| 3 | +1 | +1 | −1 | 20 | 90 | 10 | 5.03 ± 0.01 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | −α | 15 | 80 | 5 | 3.84 ± 0.10 |
| 5 | 0 | −α | 0 | 15 | 60 | 17.5 | 2.10 ± 0.11 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 80 | 17.5 | 5.42 ± 0.03 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 80 | 17.5 | 3.18 ± 0.03 |
| 8 | −1 | +1 | −1 | 10 | 90 | 10 | 9.30 ± 0.03 |
| 9 | +1 | −1 | +1 | 20 | 70 | 25 | 2.64 ± 0.05 |
| 10 | −1 | +1 | +1 | 10 | 90 | 25 | 9.95 ± 0.02 |
| 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 80 | 17.5 | 3.2 ± 0.03 |
| 12 | −α | 0 | 0 | 5 | 80 | 17.5 | 8.75 ± 0.10 |
| 13 | +α | 0 | 0 | 25 | 80 | 17.5 | 2.56 ± 0.04 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | +α | 15 | 80 | 30 | 5.47 ± 0.03 |
| 15 | 0 | +α | 0 | 15 | 100 | 17.5 | 7.68 ± 0.12 |
| 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 80 | 17.5 | 3.87 ± 0.03 |
| 17 | +1 | −1 | −1 | 20 | 70 | 10 | 2.43 ± 0.10 |
| 18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 80 | 17.5 | 3.77 ± 0.02 |
| 19 | +1 | +1 | +1 | 20 | 90 | 25 | 7.81 ± 0.02 |
| 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 80 | 17.5 | 2.82 ± 0.04 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | Df | Mean Square | F-Ratio | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 106.65 | 9 | 11.85 | 13.25 | 0.0002 |
| Linear | |||||
| A | 31.57 | 1 | 31.57 | 35.31 | 0.0001 |
| B | 54.90 | 1 | 54.90 | 61.40 | <0.0001 |
| C | 4.20 | 1 | 4.20 | 4.70 | 0.0555 |
| Interaction | |||||
| AB | 0.76 | 1 | 0.76 | 0.85 | 0.3785 |
| AC | 0.16 | 1 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.6777 |
| BC | 0.51 | 1 | 0.51 | 0.58 | 0.4656 |
| Quadratic | |||||
| A2 | 9.64 | 1 | 9.64 | 10.79 | 0.0082 |
| B2 | 4.36 | 1 | 4.36 | 4.87 | 0.0518 |
| C2 | 3.11 | 1 | 3.11 | 3.48 | 0.0918 |
| Residual | 8.94 | 10 | 0.89 | ||
| Lack of Fit | 4.65 | 5 | 0.93 | 1.08 | 0.4662 |
| Pure Error | 4.29 | 5 | 0.86 | ||
| Cor Total | 115.60 | 19 | |||
| Economic Evaluations | Extraction Method Costs (USD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Soxhlet | B&D | MAE-Brine | |
| Microalgae biomass | 2220.00 | 555.00 | 620.00 |
| Chemicals | 8000.00 | 825.00 | 100.00 |
| Electricity | 463.99 | Not applicable | 54.03 |
| Total | 10,683.99 | 1380.00 | 774.03 |
| Variables | Levels | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coded | Actual | −α | −1 | 0 | +1 | +α |
| A | Solid loading (%) | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 |
| B | Extraction temperature (°C) | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 |
| C | Extraction time (min) | 5 | 10 | 17.5 | 25 | 30 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zghaibi, N.; Omar, R.; Mustapa Kamal, S.M.; Awang Biak, D.R.; Harun, R. Microwave-Assisted Brine Extraction for Enhancement of the Quantity and Quality of Lipid Production from Microalgae Nannochloropsis sp. Molecules 2019, 24, 3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193581
Zghaibi N, Omar R, Mustapa Kamal SM, Awang Biak DR, Harun R. Microwave-Assisted Brine Extraction for Enhancement of the Quantity and Quality of Lipid Production from Microalgae Nannochloropsis sp. Molecules. 2019; 24(19):3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193581
Chicago/Turabian StyleZghaibi, Nour, Rozita Omar, Siti Mazlina Mustapa Kamal, Dayang Radiah Awang Biak, and Razif Harun. 2019. "Microwave-Assisted Brine Extraction for Enhancement of the Quantity and Quality of Lipid Production from Microalgae Nannochloropsis sp." Molecules 24, no. 19: 3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193581
APA StyleZghaibi, N., Omar, R., Mustapa Kamal, S. M., Awang Biak, D. R., & Harun, R. (2019). Microwave-Assisted Brine Extraction for Enhancement of the Quantity and Quality of Lipid Production from Microalgae Nannochloropsis sp. Molecules, 24(19), 3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193581