In Silico Evaluation of Ibuprofen and Two Benzoylpropionic Acid Derivatives with Potential Anti-Inflammatory Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Molecular Docking Studies
2.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulations, RMSD and Trajectory Analysis
2.3. Binding Free Energy
2.4. In Silico Study of Oral Bioavailability, Bioactivity and Toxicity Risk Assessment
3. Materials and Methods
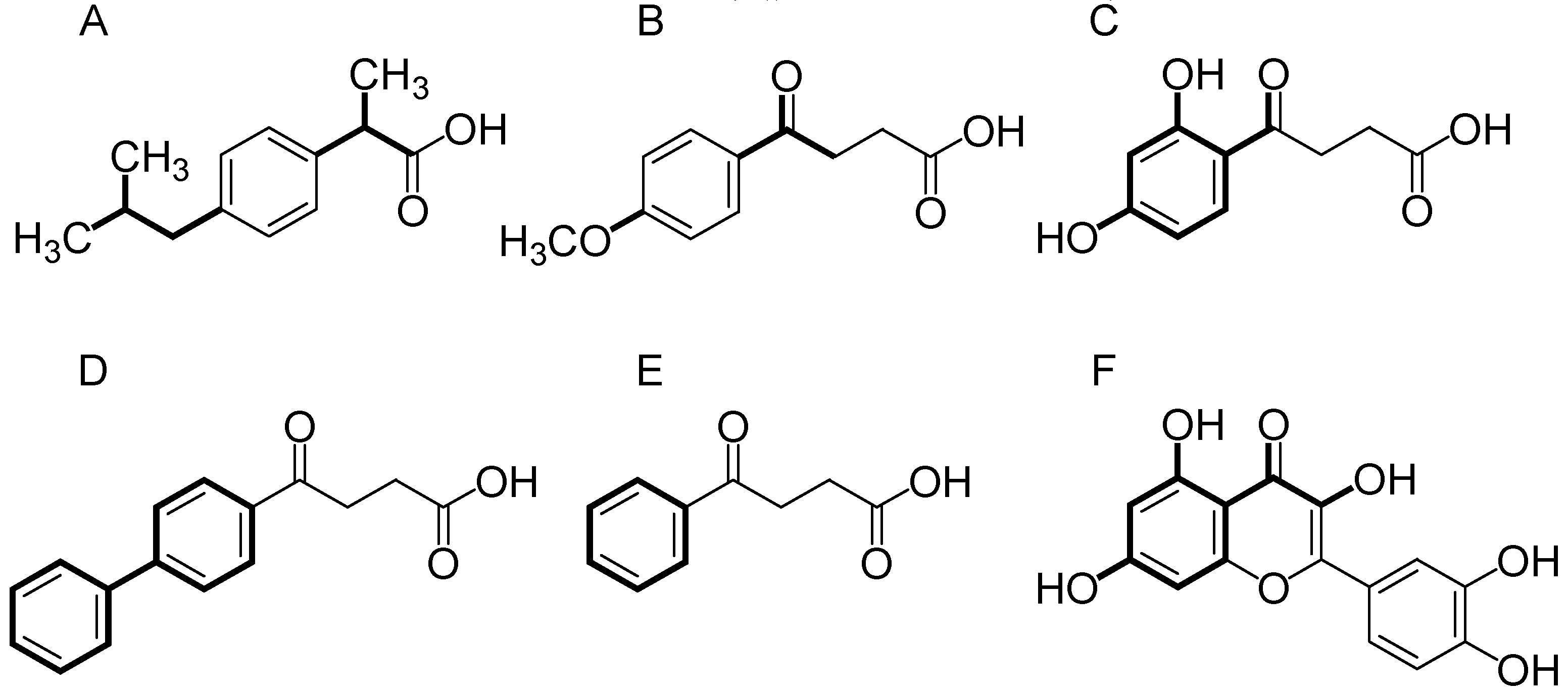
3.1. Compounds Studied
3.2. Molecular Modeling Studies
3.2.1. Molecular Docking
3.2.2. Molecular Dynamics (MD)
3.2.3. Molecular Dynamics Trajectory Analysis
3.2.4. Binding Free Energy Calculations
3.2.5. In Silico Study of Oral Bioavailability, Bioactivity and Toxicity Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chung, H.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.W.; Yu, B.P. The Inflammation Hypothesis of Aging: Molecular modulation by calorie restriction. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 928, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrero-Miliani, L.; Nielsen, O.H.; Andersen, P.S.; Girardin, S.E. Chronic inflammation: Importance of NOD2 and NALP3 in interleukin-1β generation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007, 147, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansouri, M.T.; Hemmati, A.A.; Naghizadeh, B.; Mard, S.A.; Rezaie, A.; Ghorbanzadeh, B. A study of the mechanisms underlying the anti-inflammatory effect of ellagic acid in carrageenan-induced paw edema in rats. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2015, 47, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moroni, F.; Ammirati, E.; Norata, G.D.; Magnoni, M.; Camici, P.G. The Role of Monocytes and Macrophages in Human Atherosclerosis, Plaque Neoangiogenesis, and Atherothrombosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, O.P.; Lichtnekert, J.; Anders, H.J.; Mulay, S.R. The immune system in tissue environments regaining homeostasis after injury: Is “inflammation” always inflammation? Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha e Silva, M. A brief survey of the history of inflammation. Inflamm. Res. 1978, 8, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedgwick, A.D.; Willoughby, D.A. Initiation of the inflammatory response and its prevention. Handbook Inflamm. 1985, 5, 27–47. [Google Scholar]
- Aderem, A.; Smith, K.D. A systems approach to dissecting immunity and inflammation. Semin. Immunol. 2004, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilroy, D.W.; Lawrence, T.; Perretti, M.; Rossi, A.G. Inflammatory resolution: New opportunities for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherwood, E.R.; Toliver-Kinsky, T. Mechanisms of the inflammatory response. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesth. 2004, 18, 385–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, T.; Gilroy, D.W. Chronic inflammation: A failure of resolution? Int. J. Exp Pathol. 2007, 88, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, C.N. Resolution phase of inflammation: Novel endogenous anti-inflammatory and proresolving lipid mediators and pathways. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 101–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bushra, R.; Aslam, N. An overview of clinical pharmacology of ibuprofen. Oman Med. J. 2010, 25, 155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Richy, F.; Bruyère, O.; Ethgen, O.; Rabenda, V.; Bouvenot, G.; Audran, M.; Reginster, J.Y. Time dependent risk of gastrointestinal complications induced by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug use: A consensus statement using a meta-analytic approach. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2004, 63, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, P.L.; Xavier, R.; Lu, N.; Nanda, N.N.; Dinauer, M.; Podolsky, D.K.; Seed, B. Mechanisms of NSAID-induced gastrointestinal injury defined using mutant mice. Gastroenterology 2000, 119, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, F.K.L.; Graham, D.Y. Prevention of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug gastrointestinal complications–review and recommendations based on risk assessment. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 19, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouad, A.A.; Al-Sultan, A.I.; Yacoubi, M.T.; Gomaa, W. Ameliorative effects of telmisartan in diabetic rats with indomethacin-induced gastric ulceration. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 637, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laneuville, O.; Breuer, D.K.; Dewitt, D.L.; Hla, T.; Funk, C.D.; Smith, W.L. Differential inhibition of human prostaglandin endoperoxide H synthases-1 and-2 by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1994, 271, 927–934. [Google Scholar]
- Orlando, B.J.; Lucido, M.J.; Malkowski, M.G. The structure of ibuprofen bound to cyclooxygenase-2. J. Struct. Biol. 2015, 189, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, W.L.; Urade, Y.; Jakobsson, P.J. Enzymes of the cyclooxygenase pathways of prostanoid biosynthesis. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5821–5865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMasi, J.A.; Grabowski, H.G.; Hansen, R.W. Innovation in the pharmaceutical industry: New estimates of R&D costs. J. Health Econ. 2016, 47, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Cummings, J.; Reiber, C.; Kumar, P. The price of progress: Funding and financing Alzheimer’s disease drug development. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2018, 4, 330–343. [Google Scholar]
- Drews, J.; Ryser, S. Drug Development: The role of innovation in drug development. Nat. Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kola, I. The state of innovation in drug development. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 83, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, K.C. The chemistry-biology-medicine continuum and the drug discovery and development process in academia. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.; Willett, P.; Glen, R.C.; Leach, A.R.; Taylor, R. Development and validation of a genetic algorithm for flexible docking. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 267, 727–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verdonk, M.L.; Cole, J.C.; Hartshorn, M.J.; Murray, C.W.; Taylor, R.D. Improved protein-ligand docking using GOLD. Proteins 2003, 52, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.P.; Mantoani, S.P.; DE Almeida, J.R.; Pinseta, F.R.; Semighini, E.P.; DA Silva, V.B.; DA Silva, C.H.P. Virtual Screening Strategies in Drug Design. Rev. Virtual Quim. 2012, 4, 739–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, M.Y.; Takamatsu, Y.; Ichinose, T.; Nakamura, K.; Itai, A. Effective handling of induced-fit motion in flexible docking. Proteins 2006, 63, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.S.; Costa, K.S.L.; Cruz, J.V.; Ramos, R.S.; Silva, L.B.; Brasil, D.S.B.; Tomich, C.S.; Rodrigues, C.B.; Macêdo, W.J.C. Virtual screening and statistical analysis in the design of new caffeine analogues molecules with potential epithelial anticancer activity. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 576–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, J.V.; Neto, M.F.A.; Silva, L.B.; Ramos, R.; Costa, J.; Brasil, D.S.B.; Lobato, C.C.; Costa, G.V.; Bittencourt, J.A.H.M.; Silva, C.H.T.P.; et al. Identification of novel protein kinase receptor type 2 inhibitors using pharmacophore and structure-based virtual screening. Molecules 2018, 23, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.B.R.; Ramos, R.S.; Ortiza, B.L.S.; Silva, G.M.; Giuliatti, S.; Navarrete, J.L.A.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Oil from the fruits of Pterodon emarginatus Vog.: A traditional anti-inflammatory. Study combining in vivo and in silico. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 222, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teles Fujishima, M.A.; Silva, N.S.R.; Ramos, R.S.; Batista Ferreira, E.F.; Santos, K.L.B.; Silva, C.H.T.P.; Silva, J.O.; Campos Rosa, J.M.; Santos, C.B.R. An antioxidant potential, quantum-chemical and molecular docking study of the major chemical constituents present in the leaves of Curatella americana Linn. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, J.V.; Serafim, R.B.; Silva, G.M.; Giuliatti, S.; Rosa, J.M.C.; Araújo Neto, M.F.; Leite, F.H.A.; Taft, C.A.; Silva, C.H.T.P.; Santos, C.B.R. Computational design of new protein kinase 2 inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory diseases using QSAR, pharmacophore-structure-based virtual screening and molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Model. 2018, 24, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padilha, E.C.; Serafim, R.B.; Sarmiento, D.Y.R.; Santos, C.F.; Santos, C.B.R.; Silva, C.H.T.P. New PPAR optimal activator rationally designed by computational methods. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2016, 27, 1636–1647. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, A.L.E.; Santos, G.B.; Franco, M.S.F.; Federico, L.B.; Silva, C.H.T.P.; Santos, C.B.R. Molecular modeling and statistical analysis in the design of derivatives of human dipeptidyl peptidase IV. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2018, 36, 318–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.S.; Ramos, R.S.; Costa, K.S.L.; Brasil, D.S.B.; Silva, C.H.T.P.; Ferreira, E.F.B.; Borges, R.S.; Campos, J.M.; Macêdo, W.J.C.; Santos, C.B.R. An in silico study of the antioxidant ability for two caffeine analogs using molecular docking and quantum chemical methods. Molecules 2018, 23, 2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, R.S.; Palheta, I.C.; Ota, S.S.B.; Morais, R.B.; Barros, V.A.; Ramos, R.S.; Silva, R.C.; Costa, J.S.; Silva, C.H.T.P.; Campos, J.M.; et al. Toward of Safer Phenylbutazone Derivatives by Exploration of Toxicity Mechanism. Molecules 2019, 24, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metz, C.E. Basic principles of ROC analysis. Semin. Nucl. Med. 1978, 8, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søreide, K.; Korner, H.; Søreide, J.A.S. Diagnostic accuracy and receiver-operating characteristics curve analysis in surgical research and decision making. Ann. Surg. 2011, 253, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Cheng, K.; Liu, D. Organosolv pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for enzymatic hydrolysis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 82, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truchon, J.; Bayly, C.I. Evaluating Virtual Screening Methods: Good and Bad Metrics for the “Early Recognition” Problem. J. Chem. Inf. Model 2007, 47, 488–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, V.S.; Araújo, J.S.C.; Silva, R.C.; da Costa, G.V.; Cruz, J.N.; De A. Neto, M.F.; Campos, J.M.; Santos, C.B.R.; Leite, F.H.A.; Junior, M.C.S. In Silico Study to Identify New Antituberculosis Molecules from Natural Sources by Hierarchical Virtual Screening and Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, A.; Coote, M.L.; Barakat, K. Molecular dynamicsdriven drug discovery: Leaping forward with confidence. Drug Discov. Today. 2016, 22, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, R.; Kumar, R.; Open Source Drug Discovery Consortium; Lynn, A. A GROMACS Tool for High-Throughput MM-PBSA Calculations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, P.; Lipowsky, R.; Knecht, V. Importance of Polar Solvation and Configurational Entropy for Design of Antiretroviral Drugs Targeting HIV1 Protease. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 5793–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miners, J.O.; Smith, P.A.; Sorich, M.J.; McKinnon, R.A.; Mackenzie, P.I. Predicting human drug glucuronidation parameters: Application of in vitro and in silico modeling approaches. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2004, 44, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A. Drug-like properties and the causes of poor solubility and poor permeability. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2000, 44, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapustikova, I.; Bak, A.; Gonec, T.; Kos, J.; Kozik, V.; Jampilek, J. Investigation of hydro-lipophilic properties of N alkyl phenyl hydroxynaphthalene carboxamides. Molecules 2018, 23, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kujawski, J.; Popielarska, H.; Myka, A.; Drabińska, B.; Bernard, M.K. The log P parameter as a molecular descriptor in the computer-aided drug design—An overview. Comput. Meth. Sci. Technol. 2012, 18, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, K.; Luthman, K.; Ungell, A.L.; Strandlund, G.; Beigi, F.; Lundahl, P.; Artursson, P. Evaluation of dynamic polar molecular surface area as predictor of drug absorption: Comparison with other computational and experimental predictors. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 5382–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van De Waterbeemd, H.; Gifford, E. ADMET in silico modelling: Towards prediction paradise? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Samant, L.R.; Chowdhary, A. In silico pharmacokinetics analysis and ADMET of phytochemicals of Datura metel Linn. and Cynodon dactylon Linn. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 385–388. [Google Scholar]
- de Souza, G.C.; Matias Pereira, A.C.; Viana, M.D.; Ferreira, A.M.; da Silva, I.D.R.; de Oliveira, M.M.R.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Acmella oleracea (L) R. K. Jansen Reproductive Toxicity in Zebrafish: An In Vivo and In Silico Assessment. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, G.; Coletto, L.; Sciorati, C.; Bozzolo, E.; Manunta, P.; Rovere-Querini, P.; Manfredi, A. Ion channels and transporters in inflammation: Special focus on TRP channels and TRPC6. Cells 2018, 7, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarali, H.I.G.; Hawkins, E.; Ross, G.R.; Kang, M. Ion channel remodeling in gastrointestinal inflammation. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanhehco, E.J. Potassium channel modulators as anti-inflammatory agents. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2001, 11, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, H.; Nibbs, R.; McInnes, I.; Siebert, S. Protein kinase inhibitors in the treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2014, 176, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malek, G.; Lad, E.M. Emerging roles for nuclear receptors in the pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 4617–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.; Glass, C.K. Nuclear receptors and inflammation control: Molecular mechanisms and pathophysiological relevance. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 1542–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberga, D.; Trisciuzzi, D.; Mansouri, K.; Mangiatordi, G.F.; Nicolotti, O. Prediction of Acute Oral Systemic Toxicity Using a Multifingerprint Similarity Approach. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 167, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridings, J.E.; Barratt, M.D.; Cary, R.; Earnshaw, C.G.; Eggington, C.E.; Ellis, M.K.; Judson, P.N.; Langowski, J.J.; Marchant, C.A.; Payne, M.P.; et al. Computer prediction of possible toxic action from chemical structure: An update on the DEREK system. Toxicology 1996, 106, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, S.L.; Ward, J.R. Pharmacology, clinical efficacy, and adverse effects of the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent benoxaprofen. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 1982, 2, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geneve, J.E.A.N.; Hayat-Bonan, B.; Labbe, G.; Degott, C.; Letteron, P.; Freneaux, E.; Pessayre, D. Inhibition of mitochondrial beta-oxidation of fatty acids by pirprofen. Role in microvesicular steatosis due to this nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1987, 242, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman, H.J. Hepatotoxicity: The Adverse Effects of Drugs and Other Chemicals on the Liver; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Dallas, TX, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Grillo, M.P.; Benet, L.Z. In vivo mechanistic studies on the metabolic activation of 2-phenylpropionic acid in rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 305, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, M.J.; Dickinson, R.G. Acyl glucuronide reactivity in perspective: Biological consequences. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2003, 145, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Dickinson, R.G. Bile duct ligation promotes covalent drug-protein adduct formation in plasma but not in liver of rats given zomepirac. Life Sci. 2000, 68, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpignato, C. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: How do they damage gastroduodenal mucosa? Dig. Dis. 1995, 13, 9–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, G.A.; Purmalis, A.; Vandermeer, D.A.; Denlinger, R.H. The propionic acids. Gastrointestinal toxicity in various species. Toxicol. Pathol. 1988, 16, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, M.T.D.; Basketter, D.A. Multivariate QSAR analysis of a skin sensitization database. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 1994, 2, 159–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, C.L. Contact sensitivity to topical antimicrobials. Contact Dermat. 1989, 21, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basketter, D.A.; Flyvholm, M.A.; Menne, T. Classification criteria for skin-sensitizing chemicals: A commentary. Contact Dermat. 1999, 40, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, M. Sensitization potency of some phenolic compounds. J. Dermatol. 1982, 9, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, M.D.; Basketter, D.A. Possible origin of the skin sensitisation potential of isoeugenol and related compounds. (I) Preliminary studies of potential reaction mechanisms. Contact Dermat. 1992, 27, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.S. The propionic acids: A personal perspective. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1992, 32, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, R.; Grennan, D.M.; Palmer, D.G. Fenbufen compared with indomethacin in osteoarthrosis. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 1978, 5, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekka, E.; Ayalogu, E.O.; Lewis, D.F.V.; Gibson, G.G.; Ioannides, C. Induction of hepatic microsomal CYP4A activity and of peroxisomal β-oxidation by two non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Arch. Toxicol. 1994, 68, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, M.; Skonberg, C.; Hansen, S.H. Inhibition of ATP synthesis by fenbufen and its conjugated metabolites in rat liver mitochondria. Toxicol. In Vitro 2016, 31, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, P.E.S.; Sena, C.B.C.; Machi, B.M.; Pinto, L.C.; Montenegro, R.C.; Borges, R.S.; Bastos, G.N.T.; do Nascimento, J.L.M. Study of anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties of 3-benzoyl-propionic acid. Pará Res. Med. J. 2017, 1, e07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.; Cramer, R.D.; Opdenbosch, N.V. Validation of the general purpose tripos 5.2 force field. J. Comput. Chem. 1989, 10, 982–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, J.; Marsili, M. Iterative Partial Equalization of Orbital Electronegativity—A Rapid Access to Atomic Charges. Tetrahedron 1980, 36, 3219–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masek, B.B. SYBYL-X 2.0; Tripos Inc.: St. Louis, MO, USA.
- Anandakrishnan, R.; Aguilar, B.; Onufriev, A.V. H++ 3.0: Automating pK prediction and the preparation of biomolecular structures for atomistic molecular modeling and simulations. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2012, 40, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SYSTAT. Available online: http://www.sigmaplot.co.uk/products/sigmaplot/sigmaplot-details.php (accessed on 12 April 2018).
- Lätti, S.; Niinivehmas, S.; Pentikäinen, O. Rocker: Open source, easy-to-use tool for AUC and enrichment calculations and ROC visualization. J. Cheminformatics 2016, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Aalten, D.M.; Bywater, R.; Findlay, J.B.; Hendlich, M.; Hooft, R.W.; Vriend, G. PRODRG, a program for generating molecular topologies and unique molecular descriptors from coordinates of small molecules. J. Comput. Aided. Mol. Des. 1996, 10, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A.E.; Berendsen, H.J. GROMACS: Fast, flexible, and free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Grigera, J.R.; Straatsma, T.P. The missing term in effective pair potentials. J. Phys. Chem. 1987, 91, 6269–6271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laboratory for Molecular Modeling and Dynamics. Available online: http://lmdm.biof.ufrj.br/software/hbmap2grace/index.html (accessed on 12 May 2018).
- Hess, B.; Kutzner, C.; van der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS 4: Algorithms for Highly Efficient, Load-Balanced, and Scalable Molecular Simulation. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2008, 4, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuh, R. Grace: A cross-platform micromagnetic simulator on graphics processing units. SoftwareX 2015, 3, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Wagoner, J.A.; Baker, N.A. Assessing implicit models for nonpolar mean solvation forces: The importance of dispersion and volume terms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8331–8336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drwal, M.N.; Banerjee, P.; Dunkel, M.; Wettig, M.R.; Preissner, R. ProTox: A web server for the in silico prediction of rodent oral toxicity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W53–W58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sithambaram, S.; Othman, H.H. Acute and sub-acute dermal toxicity studies of Morinda citrifolia L. fruit extract in sprague dawley rats. Asian J. Pharm Clin Res. 2015, 8, 400–408. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds not available from the authors. |






| Fitness Function | BEDROC (α = 16.1) |
|---|---|
| ASP | 0.37 |
| ChemSCORE | 0.29 |
| ChemPLP | 0.43 |
| GoldSCORE | 0.54 |
| Ligand | EvdW (Kcal/mol) | Eelec (Kcal/mol) | EMM (Kcal/mol) | Gpolar (Kcal/mol) | Gnonpolar (Kcal/mol) | ΔGBind (Kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ibuprofen | −35.07 | 0.10 | −34.97 | 9.52 | −3.24 | −28.69 |
| MBPA | −33.30 | −4.41 | −37.41 | 5.40 | −3.21 | −35.52 |
| DHBPA | −34.25 | −3.43 | −37.68 | 16.91 | −3.23 | −24.01 |
| Name | MW a (<500 Da) | Molecular Formula | HBA b (≤10) | HBD c (≤5) | Log P d (≤5) | MPSA e (Å2) | MV f (Å3) | NRB g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ibuprofen | 206.28 | C13H18O2 | 2 | 1 | 3.46 | 37.30 | 211.19 | 4 |
| MBPA | 208.21 | C11H12O4 | 4 | 1 | 1.30 | 63.60 | 189.18 | 5 |
| DHBPA | 210.19 | C10H10O5 | 5 | 3 | 0.68 | 94.83 | 179.67 | 4 |
| Name | GPCR | Ion Channel Modulator | Kinase Inhibitor | Nuclear Receptor Ligand | Protease Inhibitor | Enzyme Inhibitor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ibuprofen | −0.17 | −0.01 | −0.72 | 0.05 | −0.21 | 0.12 |
| MBPA | −0.35 | −0.22 | −0.82 | −0.34 | −0.53 | 0.00 |
| DHBPA | −0.19 | −0.09 | −0.68 | −0.04 | −0.43 | 0.20 |
| No | Name | LD50 Toxic a | Toxicity Class b |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ibuprofen | 299 mg/kg | III |
| 2 | MBPA | 700 mg/kg | IV |
| 3 | DHBPA | 700 mg/kg | IV |
| Compounds | Toxicity Prediction Alert (Lhasa Prediction) | Toxicophoric Group | Toxicity Alert | Toxicity Prediction (Custom Prediction) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ibuprofen | Hepatotoxicity in human, mouse and rat | 2-arylacetic or 3-arylpropionic acid | PLAUSIBLE | Nothing to declare |
| Irritation of the gastrointestinal tract in human, mouse and rat | alpha-substituted propionic acid or ester | |||
| MBPA | Skin sensitization in human, mouse and rat | Substituted phenol or precursor | PLAUSIBLE | Nothing to declare |
| DHBPA | Thyroid toxicity in human, mouse and rat | Resorcinol or 3-aminophenol | PROBABLE | Nothing to declare |
| Skin sensitization in human, mouse and rat | Resorcinol or 3-aminophenol | PLAUSIBLE |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bittencourt, J.A.H.M.; Neto, M.F.A.; Lacerda, P.S.; Bittencourt, R.C.V.S.; Silva, R.C.; Lobato, C.C.; Silva, L.B.; Leite, F.H.A.; Zuliani, J.P.; Rosa, J.M.C.; et al. In Silico Evaluation of Ibuprofen and Two Benzoylpropionic Acid Derivatives with Potential Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Molecules 2019, 24, 1476. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081476
Bittencourt JAHM, Neto MFA, Lacerda PS, Bittencourt RCVS, Silva RC, Lobato CC, Silva LB, Leite FHA, Zuliani JP, Rosa JMC, et al. In Silico Evaluation of Ibuprofen and Two Benzoylpropionic Acid Derivatives with Potential Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Molecules. 2019; 24(8):1476. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081476
Chicago/Turabian StyleBittencourt, José A. H. M., Moysés F. A. Neto, Pedro S. Lacerda, Renata C. V. S. Bittencourt, Rai C. Silva, Cleison C. Lobato, Luciane B. Silva, Franco H. A. Leite, Juliana P. Zuliani, Joaquín M. C. Rosa, and et al. 2019. "In Silico Evaluation of Ibuprofen and Two Benzoylpropionic Acid Derivatives with Potential Anti-Inflammatory Activity" Molecules 24, no. 8: 1476. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081476
APA StyleBittencourt, J. A. H. M., Neto, M. F. A., Lacerda, P. S., Bittencourt, R. C. V. S., Silva, R. C., Lobato, C. C., Silva, L. B., Leite, F. H. A., Zuliani, J. P., Rosa, J. M. C., Borges, R. S., & Santos, C. B. R. (2019). In Silico Evaluation of Ibuprofen and Two Benzoylpropionic Acid Derivatives with Potential Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Molecules, 24(8), 1476. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081476







