In Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial Peptide Tridecaptin M in Combination with Other Antibiotics against Multidrug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
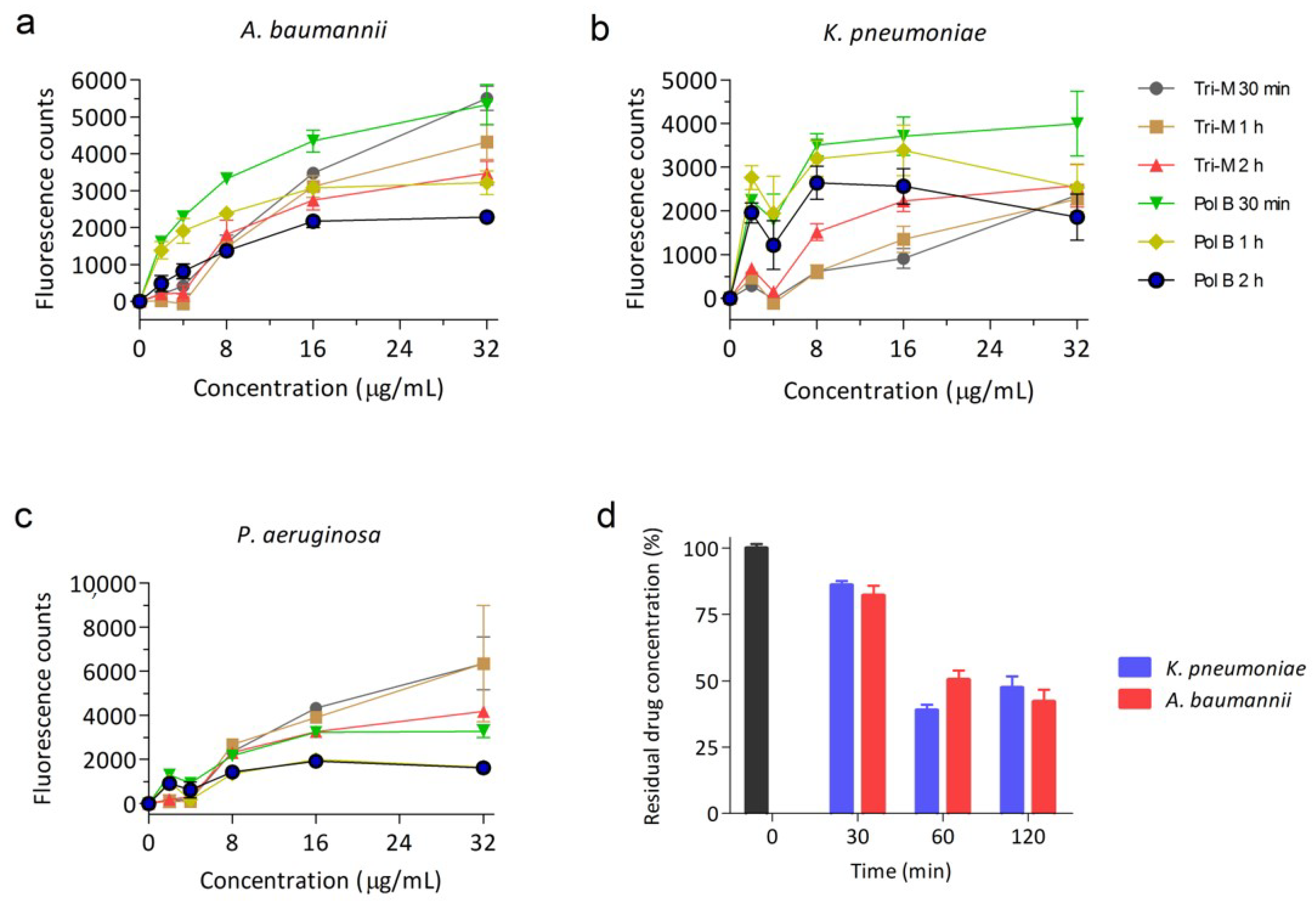
2.1. Tridecaptin M Disrupts the Outer Membrane Effectively
2.2. Synergy of Tridecaptin M with Various Antibiotics in A. baumannii
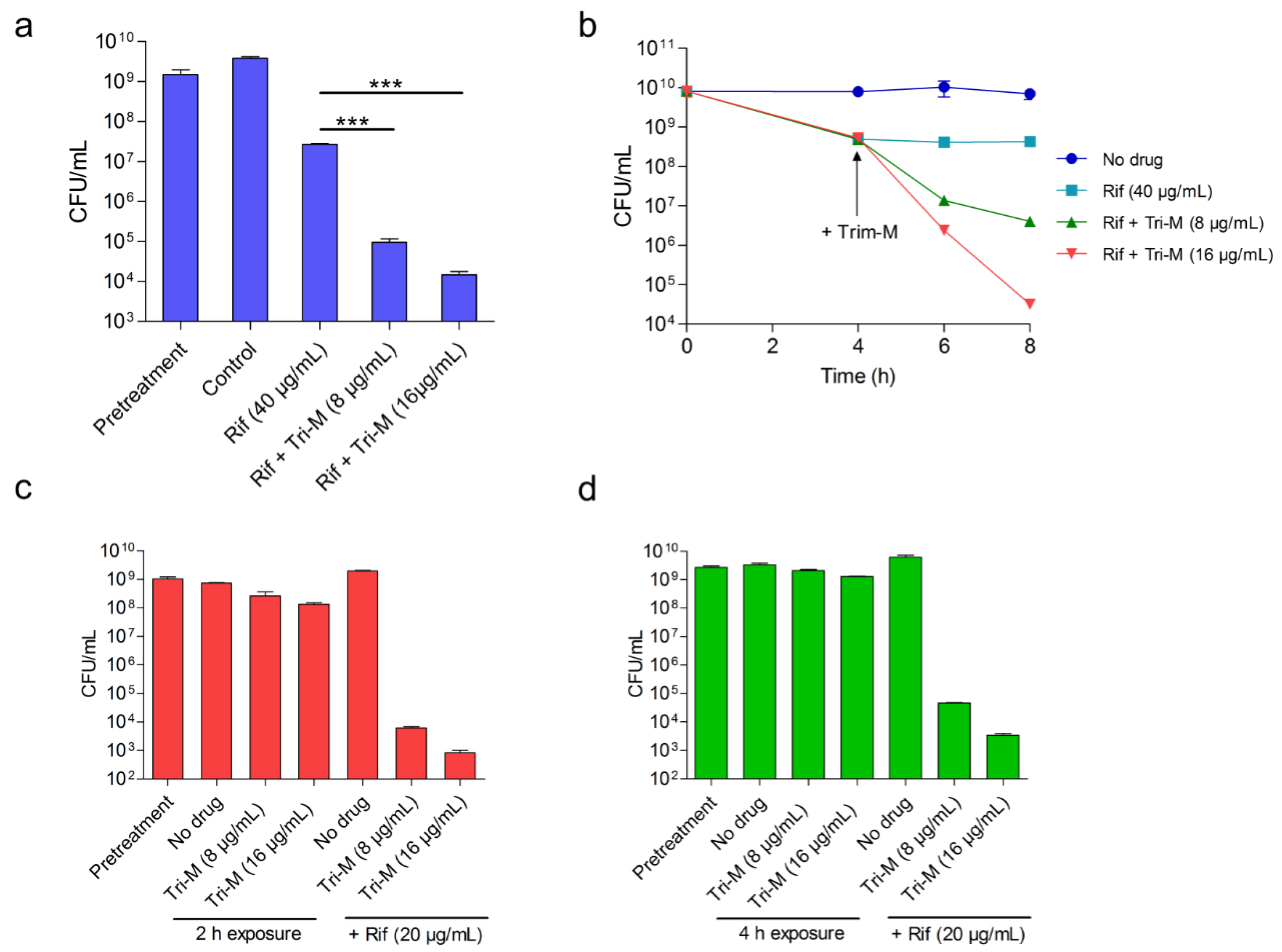
2.3. Tridecaptin M and Rifampicin Combination Shows Efficacy in Rabbit Blood
2.4. Concomitant Administration of Both Antibiotics is not Necessary for the Potentiation
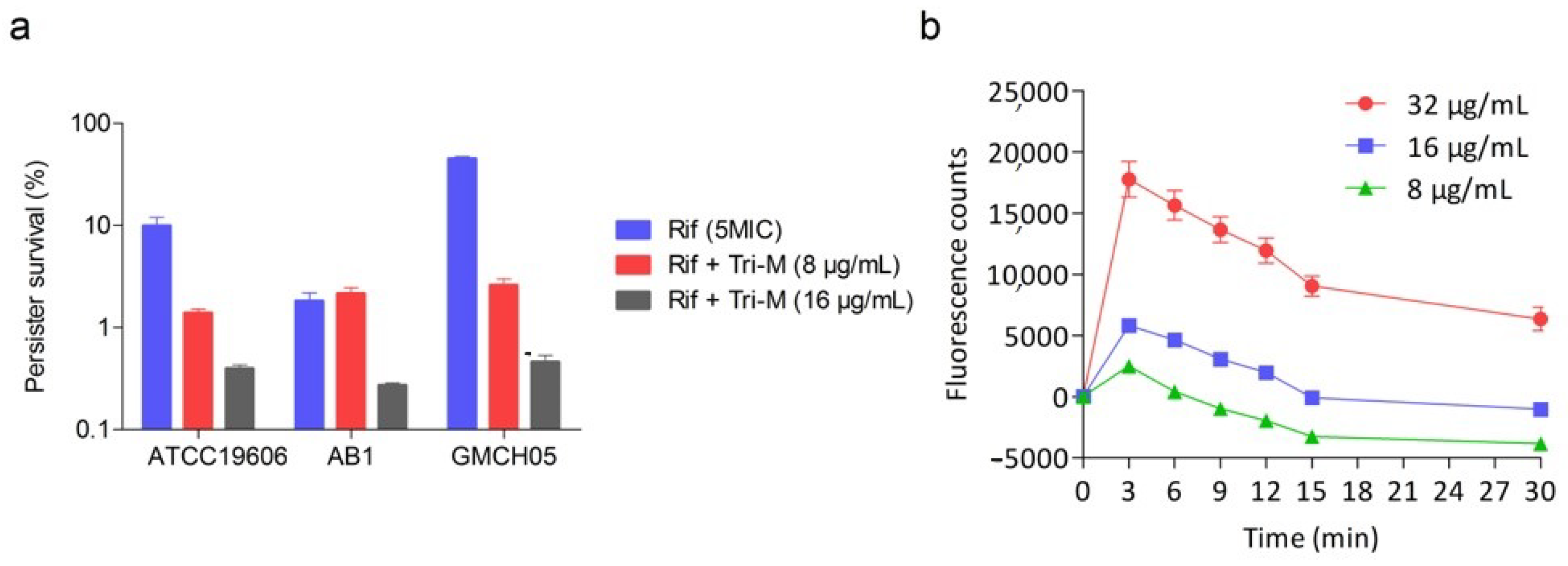
2.5. Effect of Combination Therapy on Persister Survival
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Antibiotics, Bacterial Strains, and Growth Conditions
4.2. Outer Membrane Permeabilization Assay
4.3. Tridecaptin Binding Kinetics
4.4. MIC Determination
4.5. Synergy Studies
4.6. Time-Dependent Killing Kinetics
4.7. Ex Vivo Blood Infection Model
4.8. Time-Lag Treatment Studies
4.9. Persister Assay
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Savage, P.B. Multidrug-resistant bacteria: Overcoming antibiotic permeability barriers of Gram-negative bacteria. Ann. Med. 2001, 33, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masi, M.; Réfrégiers, M.; Pos, K.M.; Pagès, J.-M. Mechanisms of envelope permeability and antibiotic influx and efflux in Gram-negative bacteria. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papp-Wallace, K.M.; Endimiani, A.; Taracila, M.A.; Bonomo, R.A. Carbapenems: Past, Present, and Future. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 4943–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jangra, M.; Randhawa, H.K.; Kaur, M.; Srivastava, A.; Maurya, N.; Patil, P.P.; Jaswal, P.; Arora, A.; Patil, P.B.; Raje, M.; et al. Purification, Characterization and in vitro Evaluation of Polymyxin A From Paenibacillus dendritiformis: An Underexplored Member of the Polymyxin Family. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velkov, T.; Gallardo-Godoy, A.; Swarbrick, J.D.; Blaskovich, M.A.T.; Elliott, A.G.; Han, M.; Thompson, P.E.; Roberts, K.D.; Huang, J.X.; Becker, B.; et al. Structure, Function, and Biosynthetic Origin of Octapeptin Antibiotics Active against Extensively Drug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria. Cell Chem. Boil. 2018, 25, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imai, Y.; Meyer, K.J.; Iinishi, A.; Favre-Godal, Q.; Green, R.; Manuse, S.; Caboni, M.; Mori, M.; Niles, S.; Ghiglieri, M.; et al. A new antibiotic selectively kills Gram-negative pathogens. Nature 2019, 576, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spellberg, B.; Bonomo, R.A. The Deadly Impact of Extreme Drug Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 42, 1289–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isler, B.; Doi, Y.; Bonomo, R.A.; Paterson, D.L. New Treatment Options against Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumanniiInfections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 63, e01110-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Yang, S.; Noh, H.; Chung, E.K.; Lee, J.I. Antimicrobials for the treatment of drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii pneumonia in critically ill patients: A systemic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, S.M.S.; Sime, F.B.; Roberts, J.A. Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections: Current evidence on treatment options and the role of pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics in dose optimisation. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 53, 726–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boral, B.; Unaldi, Ö.; Ergin, A.; Durmaz, R.; Eser, Ö.K.; Acinetobacter Study Group; The Acinetobacter Study Group; Zarakolu, P. A prospective multicenter study on the evaluation of antimicrobial resistance and molecular epidemiology of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections in intensive care units with clinical and environmental features. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2019, 18, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheah, S.-E.; Li, J.; Tsuji, B.T.; Forrest, A.; Bulitta, J.B.; Nation, R.L. Colistin and Polymyxin B Dosage Regimens against Acinetobacter baumannii: Differences in Activity and the Emergence of Resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 3921–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bassetti, M.; Peghin, M.; Vena, A.; Giacobbe, D.R. Treatment of Infections Due to MDR Gram-Negative Bacteria. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffatt, J.H.; Harper, M.; Harrison, P.F.; Hale, J.D.F.; Vinogradov, E.; Seemann, T.; Henry, R.; Crane, B.; Michael, F.S.; Cox, A.D.; et al. Colistin Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii Is Mediated by Complete Loss of Lipopolysaccharide Production. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4971–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trebosc, V.; Gartenmann, S.; Tötzl, M.; Lucchini, V.; Schellhorn, B.; Pieren, M.; Lociuro, S.; Gitzinger, M.; Tigges, M.; Bumann, D.; et al. Dissecting Colistin Resistance Mechanisms in Extensively Drug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Isolates. mBio 2019, 10, e01083-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zafer, M.M.; El-Mahallawy, H.A.; Abdulhak, A.; Amin, M.A.; Al-Agamy, M.H.; Radwan, H.H. Emergence of colistin resistance in multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli strains isolated from cancer patients. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2019, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbediwi, M.; Li, Y.; Paudyal, N.; Pan, H.; Xie, S.; Rajkovic, A.; Feng, Y.; Fang, W.; Rankin, S.C.; Yue, M.; et al. Global Burden of Colistin-Resistant Bacteria: Mobilized Colistin Resistance Genes Study (1980–2018). Microorganisms 2019, 7, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ArrayExpress — A Database of Functional Genomics Experiments. Available online: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/ (accessed on 12 November 2012).
- Butler, M.S.; Paterson, D.L. Antibiotics in the clinical pipeline in October 2019. J. Antibiot. 2020, 73, 329–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Kim, M.-C.; Park, S.-J.; Kim, H.S.; Sung, H.; Kim, S.-H.; Lee, S.-O.; Choi, S.-H.; Woo, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; et al. In VitroSynergistic Activity of Antimicrobial Agents in Combination against Clinical Isolates of Colistin-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 6774–6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, W.; Wang, Y.; Cao, W.; Cao, S.; Zhang, J. In vitro evaluation of antimicrobial combinations against imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii of different MICs. J. Infect. Public Health 2018, 11, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyclit, L.; Baron, S.A.; Rolain, J.-M. Drug Repurposing to Fight Colistin and Carbapenem-Resistant Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamma, P.D.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Maragakis, L.L. Combination Therapy for Treatment of Infections with Gram-Negative Bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 450–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pachón-Ibáñez, M.E.; Fernández-Cuenca, F.; Docobo-Pérez, F.; Pachón, J. Pascual, Álvaro Prevention of rifampicin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii in an experimental pneumonia murine model, using rifampicin associated with imipenem or sulbactam. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 58, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leite, G.C.; Oliveira, M.S.; Perdigão-Neto, L.V.; Rocha, C.K.D.; Guimarães, T.; Rizek, C.; Levin, A.S.S.; Costa, S.F. Antimicrobial Combinations against Pan-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates with Different Resistance Mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, T.; Cai, Y.; Liang, B.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J. In VitroActivities of Combinations of Rifampin with Other Antimicrobials against Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 59, 1466–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pachón-Ibáñez, M.E.; Docobo-Pérez, F.; López-Rojas, R.; Domínguez-Herrera, J.; Jiménez-Mejias, M.E.; García-Curiel, A.; Pichardo, C.; Jiménez, L.; Pachón, J. Efficacy of Rifampin and Its Combinations with Imipenem, Sulbactam, and Colistin in Experimental Models of Infection Caused by Imipenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliva, A.; Garzoli, S.; De Angelis, M.; Marzuillo, C.; Vullo, V.; Mastroianni, C.M.; Ragno, R. In-Vitro Evaluation of Different Antimicrobial Combinations with and without Colistin Against Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii. Molecules 2019, 24, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giacometti, A.; Cirioni, O.; Barchiesi, F.; Fortuna, M.; Scalise, G. In-vitro activity of cationic peptides alone and in combination with clinically used antimicrobial agents against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1999, 44, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corbett, D.; Wise, A.; Langley, T.; Skinner, K.; Trimby, E.; Birchall, S.; Dorali, A.; Sandiford, S.; Williams, J.; Warn, P.; et al. Potentiation of Antibiotic Activity by a Novel Cationic Peptide: Potency and Spectrum of Activity of SPR741. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00200-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kampshoff, F.; Willcox, M.; Dutta, D. A Pilot Study of the Synergy between Two Antimicrobial Peptides and Two Common Antibiotics. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geitani, R.; Moubareck, C.A.; Touqui, L.; Sarkis, D.K. Cationic antimicrobial peptides: Alternatives and/or adjuvants to antibiotics active against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baker, K.R.; Jana, B.; Hansen, A.M.; Vissing, K.J.; Nielsen, H.M.; Franzyk, H.; Guardabassi, L. Repurposing azithromycin and rifampicin against Gram-negative pathogens by combination with peptide potentiators. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 53, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cochrane, S.A.; Findlay, B.; Bakhtiary, A.; Acedo, J.Z.; Rodriguez-Lopez, E.M.; Mercier, P.; Vederas, J.C. Antimicrobial lipopeptide tridecaptin A1selectively binds to Gram-negative lipid II. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11561–11566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cochrane, S.A.; Lohans, C.T.; Bels, M.A.; Vederas, J.C.; Van Belkum, M.J. Studies on tridecaptin B 1, a lipopeptide with activity against multidrug resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 6073–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangra, M.; Kaur, M.; Tambat, R.; Rana, R.; Maurya, S.K.; Khatri, N.; Ghafur, A.; Nandanwar, H. Tridecaptin M, a New Variant Discovered in Mud Bacterium, Shows Activity against Colistin- and Extremely Drug-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00338-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cochrane, S.A.; Vederas, J.C. Unacylated tridecaptin A1 acts as an effective sensitiser of Gram-negative bacteria to other antibiotics. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2014, 44, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangra, M.; Kaur, M.; Podia, M.; Tambat, R.; Singh, V.; Chandal, N.; Mahey, N.; Maurya, N.; Nandanwar, H. Purification and biological activity of natural variants synthesized by tridecaptin M gene cluster and in vitro drug-kinetics of this antibiotic class. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, B.; Grant, C.; Hancock, R.E.W. Use of the fluorescent probe 1-N-phenylnaphthylamine to study the interactions of aminoglycoside antibiotics with the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1984, 26, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, D.; Schmidt, S.; Derendorf, H. Importance of Relating Efficacy Measures to Unbound Drug Concentrations for Anti-Infective Agents. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Levison, M.E.; Levison, J.H. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Antibacterial Agents. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 23, 791–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, E.S.; Ko, K.S. Eradication of persister cells of Acinetobacter baumannii through combination of colistin and amikacin antibiotics. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, M.; Trent, M.S. Expanding the paradigm for the outer membrane:Acinetobacter baumanniiin the absence of endotoxin. Mol. Microbiol. 2017, 107, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, S.E.; Melander, R.J.; Brackett, C.M.; Scott, A.J.; Chandler, C.E.; Nguyen, C.M.; Minrovic, B.M.; Harrill, S.E.; Ernst, R.K.; Manoil, C.; et al. Small Molecule Potentiation of Gram-Positive Selective Antibiotics against Acinetobacter baumannii. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.; Schneider-Futschik, E.K.; Paulin, O.K.; Allobawi, R.; Crawford, S.; Zhou, Q.T.; Hanif, A.; Baker, M.A.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J. An effective strategy targeting polymyxin-resistant Gram-negative pathogens: Polymyxin B in combination with the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor sertraline. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 1436–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassetti, M.; Repetto, E.; Righi, E.; Boni, S.; Diverio, M.; Molinari, M.P.; Mussap, M.; Artioli, S.; Ansaldi, F.; Durando, P.; et al. Colistin and rifampicin in the treatment of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 61, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Motaouakkil, S.; Charra, B.; Hachimi, A.; Nejmi, H.; Benslama, A.; Elmdaghri, N.; Belabbes, H.; Benbachir, M. Colistin and rifampicin in the treatment of nosocomial infections from multiresistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Infect. 2006, 53, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saballs, M.; Pujol, M.; Tubau, F.; Peña, C.; Montero, A.; Domínguez, M.A.; Gudiol, F.; Ariza, J. Rifampicin/imipenem combination in the treatment of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 58, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante-Mangoni, E.; Signoriello, G.; Andini, R.; Mattei, A.; De Cristoforo, M.; Murino, P.; Bassetti, M.; Malacarne, P.; Petrosillo, N.; Galdieri, N.; et al. Colistin and Rifampicin Compared With Colistin Alone for the Treatment of Serious Infections Due to Extensively Drug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: A Multicenter, Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Z.; Qin, W.; Lin, J.; Fang, S.; Qiu, J. Antibacterial Mechanisms of Polymyxin and Bacterial Resistance. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayne, P. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: 25th Informational Supplement M100-S25; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tambat, R.; Jangra, M.; Mahey, N.; Chandal, N.; Kaur, M.; Chaudhary, S.; Verma, D.K.; Thakur, K.G.; Raje, M.; Jachak, S.; et al. Microbe-Derived Indole Metabolite Demonstrates Potent Multidrug Efflux Pump Inhibition in Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, K.R.; Brynildsen, M.P.; Collins, J.J. Metabolite-enabled eradication of bacterial persisters by aminoglycosides. Nature 2011, 473, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Sample Availability: Sample of the compound tridecaptin Mis available from the authors. |
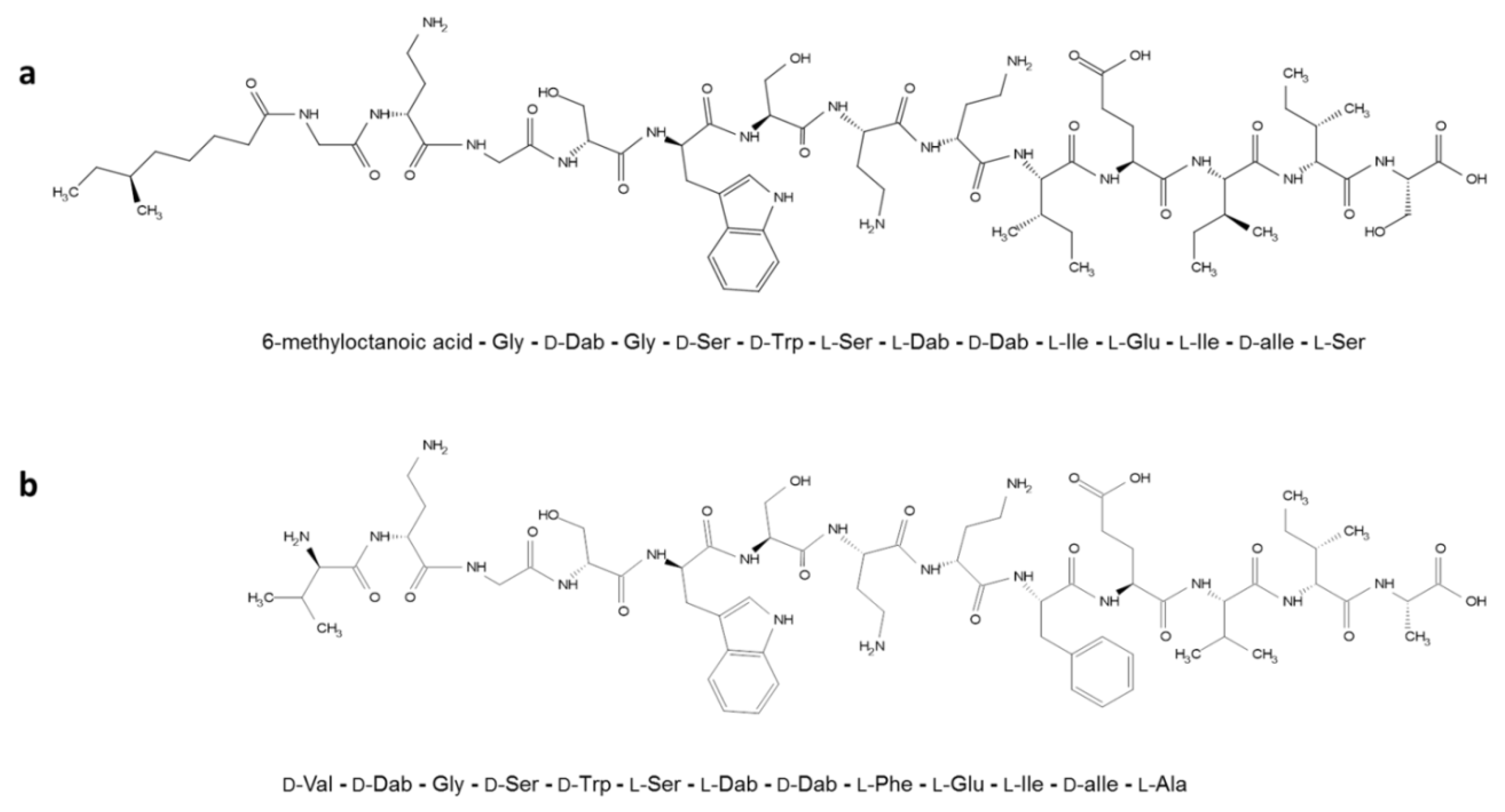


| Strain | Tri-M MIC (µg/mL) | Antibiotic | Tri-M Concentration (µg/mL) | MIC (µg/mL) | Potentiation Factor | FICI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. baumannii ATCC 19606 | 32 | Vancomycin | 0 | 128 | ||
| 2 | 128 | 1 | - | |||
| 4 | 32 | 4 | 0.375 | |||
| 8 | 8 | 16 | 0.312 | |||
| Rifampicin | 0 | 4 | ||||
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 0.562 | |||
| 4 | 1 | 4 | 0.375 | |||
| 8 | 0.25 | 16 | 0.312 | |||
| K. pneumoniae ATCC 700603 | 4 | Vancomycin | 0 | 128 | ||
| 0.25 | 128 | 1 | - | |||
| 0.5 | 128 | 1 | - | |||
| 1.0 | 128 | 1 | - | |||
| Rifampicin | 0 | 32 | ||||
| 0.25 | 32 | 1 | - | |||
| 0.5 | 32 | 1 | - | |||
| 1.0 | 32 | 1 | - | |||
| P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 256 | Vancomycin | 0 | 256 | ||
| 4 | 256 | 1 | - | |||
| 8 | 256 | 1 | - | |||
| 16 | 256 | 1 | - | |||
| Rifampicin | 0 | 64 | ||||
| 4 | 32 | 2 | 0.515 | |||
| 8 | 32 | 2 | 0.531 | |||
| 16 | 32 | 2 | 0.562 |
| Strain | Antibiotic | MIC (µg/mL) at Tridecaptin Concentration (µg/mL) | Fold Reduction in MIC at Tri-M (8 µg/mL) | FICI at Tri-M (8 µg/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 4 | 8 | ||||
| A. baumanniiATCC 19606 | Rifampicin | 4 | 1 | 0.25 | 16 | 0.31 |
| Vancomycin | 128 | 32 | 8 | 16 | 0.31 | |
| Clarithromycin | 64 | 16 | 4 | 16 | 0.31 | |
| Imipenem | 128 | 16 | 16 | 8 | 0.37 | |
| Ceftazidime | 32 | 8 | 1 | 32 | 0.28 | |
| A. baumanniiATCC 2803 | Rifampicin | 256 | 64 | 64 | 4 | 0.5 |
| Vancomycin | 64 | 64 | 16 | 4 | 0.5 | |
| Clarithromycin | 64 | 64 | 64 | 1 | - | |
| Imipenem | 256 | 256 | 256 | 1 | - | |
| Ceftazidime | 128 | 16 | 8 | 16 | 0.31 | |
| A. baumanniiAB1 | Rifampicin | 8 | 0.5 | 0.125 | 64 | 0.27 |
| Vancomycin | 256 | 32 | 16 | 16 | 0.31 | |
| Clarithromycin | 128 | 128 | 128 | 1 | - | |
| Imipenem | 256 | 256 | 256 | 1 | - | |
| Ceftazidime | 128 | 128 | 128 | 1 | - | |
| A. baumanniiAB2 | Rifampicin | 256 | 16 | 8 | 32 | 0.28 |
| Vancomycin | 256 | 32 | 16 | 16 | 0.31 | |
| Clarithromycin | 128 | 128 | 128 | 1 | - | |
| Imipenem | 256 | 125 | 256 | 1 | - | |
| Ceftazidime | 128 | 128 | 128 | 1 | - | |
| A. baumanniiGMCH05 | Rifampicin | 8 | 0.125 | 0.03 | 256 | 0.25 |
| Vancomycin | 256 | 8 | 8 | 32 | 0.28 | |
| Clarithromycin | 128 | 128 | 128 | 1 | - | |
| Imipenem | 256 | 128 | 128 | 2 | - | |
| Ceftazidime | 128 | 4 | 4 | 32 | 0.28 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jangra, M.; Raka, V.; Nandanwar, H. In Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial Peptide Tridecaptin M in Combination with Other Antibiotics against Multidrug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Molecules 2020, 25, 3255. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25143255
Jangra M, Raka V, Nandanwar H. In Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial Peptide Tridecaptin M in Combination with Other Antibiotics against Multidrug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Molecules. 2020; 25(14):3255. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25143255
Chicago/Turabian StyleJangra, Manoj, Vrushali Raka, and Hemraj Nandanwar. 2020. "In Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial Peptide Tridecaptin M in Combination with Other Antibiotics against Multidrug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii" Molecules 25, no. 14: 3255. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25143255
APA StyleJangra, M., Raka, V., & Nandanwar, H. (2020). In Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial Peptide Tridecaptin M in Combination with Other Antibiotics against Multidrug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Molecules, 25(14), 3255. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25143255






