Pharmacological Aspects of Over-the-Counter Opioid Drugs Misuse
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Introduction to Opioid Drugs
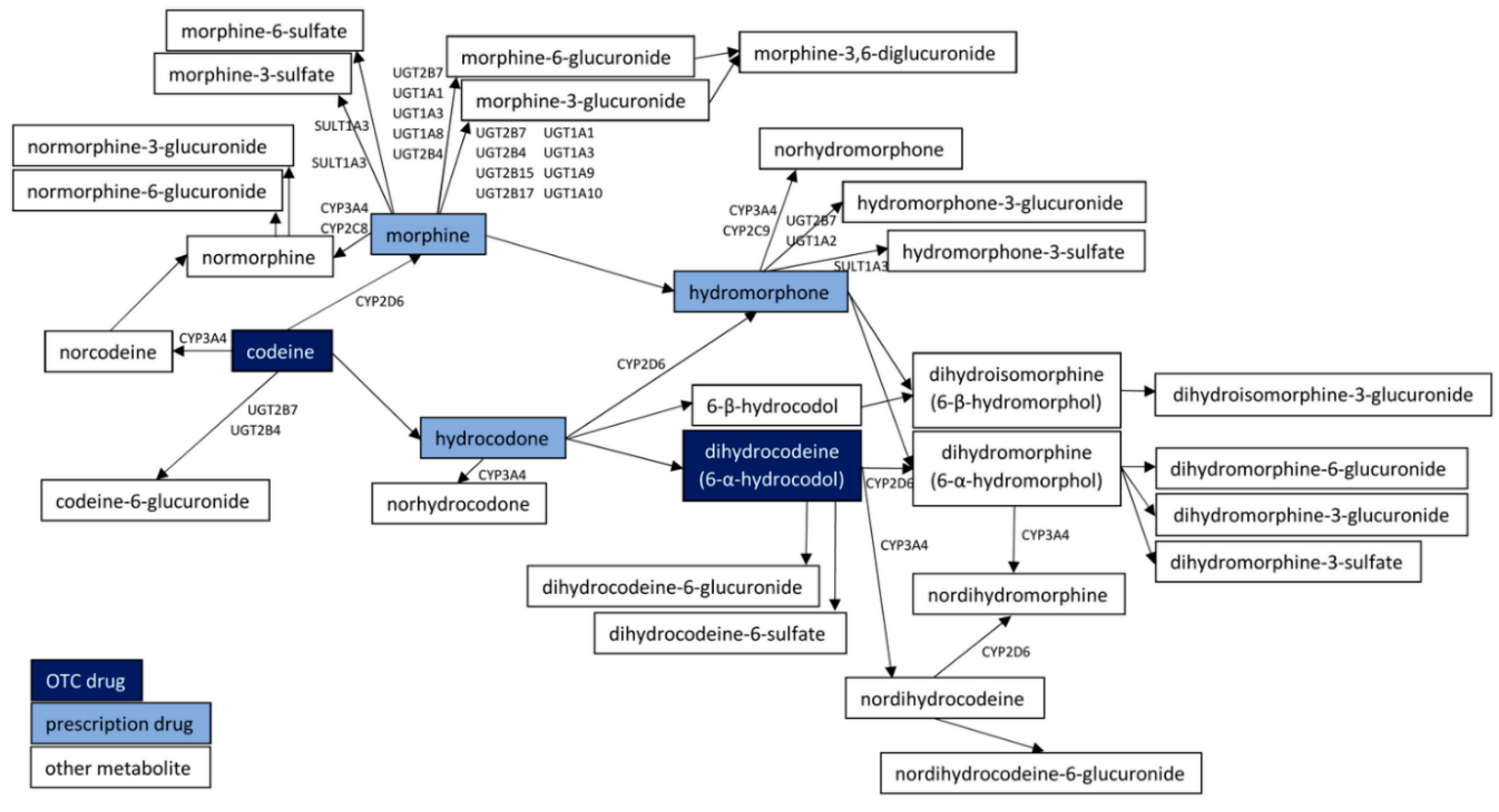
2.2. Codeine
2.3. Dihydrocodeine
2.4. Loperamide
2.5. Alternative (Non-Opioid) Antitussives Used to Treat Unproductive Cough
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
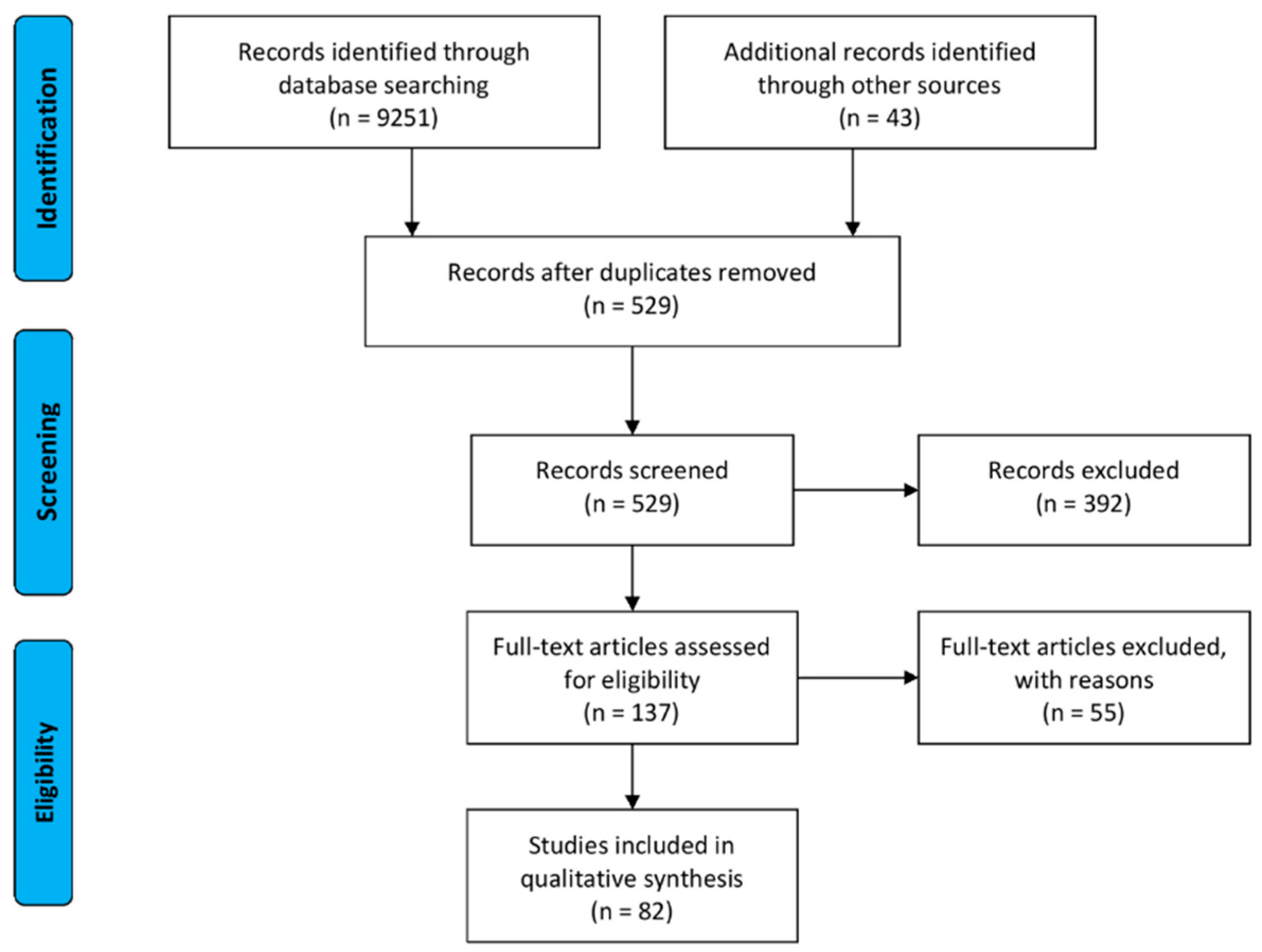
4.1. Data Source
4.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
4.3. Additional Limitations of the Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foley, M.; Breindahl, T.; Hindersson, P.; Deluca, P.; Kimergård, A. Misuse of ‘Over-The-Counter’ Codeine Analgesics: Does Formulation Play a Role? Public Health 2016, 130, 95–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DZIENNIK USTAW RZECZYPOSPOLITEJ POLSKIEJ, Poz. 2189, ROZPORZĄDZENIE MINISTRA ZDROWIA z dnia 16 grudnia 2016 r. w sprawie wykazu substancji o działaniu psychoaktywnym oraz maksymalnego poziomu ich zawartości w produkcie leczniczym, stanowiącego ograniczenie w wydawaniu produktów leczniczych w ramach jednorazowej sprzedaży. Available online: http://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/download.xsp/WDU20160002189/O/D20162189.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Foley, M.; Harris, R.; Rich, E.; Rapca, A.; Bergin, M.; Norman, I.; Van Hout, M.C. The Availability of Over-The-Counter Codeine Medicines Across the European Union. Public Health 2015, 11, 1465–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishriky, J.; Stupans, I.; Chan, V. Pharmacists’ Views on the Upscheduling of Codeine-Containing Analgesics to ‘Prescription Only’ Medicines in Australia. Int. J. Clin. Pharm 2019, 41, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, E.M.Y.; Roberts, D.M. A Spotlight on the Role, Use, and Availability of Codeine and the Implications Faced. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 11, 1057–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burns, J.M.; Boyer, E.W. Antitussives and substance abuse. Subst. Abuse Rehabil. 2013, 4, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Motyka, M.; Marcinkowski, J.T. New methods of narcotization. Part I. Drugs available without a prescription used for psychoactive purposes. Probl. Hig. Epidemiol. 2014, 95, 504–511. [Google Scholar]
- Piątek, A.; Koziarska-Rościszewska, M.; Zawilska, J.B. Recreational use of over-the-counter drugs: The doping of the brain. Alcohol. Drug Addict. 2015, 28, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubowski, P.; Puchała, Ł.; Grzegorzewski, W. Recreational use of popular OTC drugs—Pharmacological review. Farmacia 2018, 66, 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- Oelhaf, R.C.; Azadfard, M. Opioid Toxicity. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Van Hout, M.C. Kitchen chemistry: A scoping review of the diversionary use of pharmaceuticals for non-medicinal use and home production of drug solutions. Drug Test. Anal. 2014, 6, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePriest, A.Z.; Puet, B.L.; Holt, A.C.; Roberts, A.; Cone, E.J. Metabolism and Disposition of Prescription Opioids: A Review. Forensic Sci. Rev. 2015, 27, 115–145. [Google Scholar]
- Mignat, C.; Wille, U.; Ziegler, A. Affinity profiles of morphine, codeine, dihydrocodeine and their glucuronides at opioid receptor subtypes. Life Sci. 1995, 56, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toll, L.; Berzetei-Gurske, I.P.; Polgar, W.E.; Brandt, S.R.; Adapa, I.D.; Rodriguez, L.; Schwartz, R.W.; Haggart, D.; O’Brien, A.; White, A.; et al. Standard binding and functional assays related to medications development division testing for potential cocaine and opiate narcotic treatment medications. NIDA Res. Monogr. 1998, 178, 440–466. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, H.; v Vormfelde, S.; Klinder, K.; Gundert-Remy, U.; Gleiter, C.H.; Skopp, G.; Aderjan, R.; Fuhr, U. Affinities of dihydrocodeine and its metabolites to opioid receptors. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2002, 91, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Knapp, B.I.; Bidlack, J.M.; Neumeyer, J.L. Synthesis and preliminary in vitro investigation of bivalent ligands containing homo- and heterodimeric pharmacophores at mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptors. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breslin, H.J.; Miskowski, T.A.; Rafferty, B.M.; Coutinho, S.V.; Palmer, J.M.; Wallace, N.H.; Schneider, C.R.; Kimball, E.S.; Zhang, S.P.; Li, J.; et al. Rationale, design, and synthesis of novel phenyl imidazoles as opioid receptor agonists for gastrointestinal disorders. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 5009–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilsky, E.J.; Calderon, S.N.; Wang, T.; Bernstein, R.N.; Davis, P.; Hruby, V.J.; McNutt, R.W.; Rothman, R.B.; Rice, K.C.; Porreca, F. SNC 80, a selective, nonpeptidic and systemically active opioid delta agonist. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1995, 273, 359–366. [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh, A.; Kimura, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Kawai, K.; Nagase, H.; Kamei, J. Potential anxiolytic and antidepressant-like activities of SNC80, a selective delta-opioid agonist, in behavioral models in rodents. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 95, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, K.J.; Rigdon, G.C.; Howard, J.L.; McNutt, R.W. A novel, potent and selective nonpeptidic delta opioid receptor agonist BW373U86. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1993, 267, 852–857. [Google Scholar]
- Fulton, B.S.; Knapp, B.I.; Bidlack, J.M.; Neumeyer, J.L. Synthesis and Pharmacological Evaluation of Hydrophobic Esters and Ethers of Butorphanol at Opioid Receptors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 4474–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, T.; Sromek, A.W.; Scrimale, T.; Bidlack, J.M.; Neumeyer, J.L. Synthesis and Binding Affinity of Novel Mono- and Bivalent Morphinan Ligands for κ, μ and δ Opioid Receptors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 2808–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Florez, D.H.Â.; Dos Santos Moreira, A.M.; da Silva, P.R.; Brandão, R.; Borges, M.M.C.; de Santana, F.J.M.; Borges, K.B. Desomorphine (Krokodil): An overview of its chemistry, pharmacology, metabolism, toxicology and analysis. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2017, 173, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, H.; Inoue, M.; Mizuno, K. New approaches to study the development of morphine tolerance and dependence. Life Sci. 2003, 74, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Oh, S.; Sung, B.; Tian, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, S.; Mao, J. Anti-morphine antibody contributes to the development of morphine tolerance in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 480, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Hout, M.C. Nod and wave: An Internet study of the codeine intoxication phenomenon. Int. J. Drug Policy 2015, 26, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hout, M.C.; Horan, A.; Santlal, K.; Rich, E.; Bergin, M. ‘Codeine is my companion’: Misuse and dependence on codeine containing medicines in Ireland. Ir. J. Psychol. Med. 2018, 35, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peechakara, B.V.; Gupta, M. Codeine. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, J.S.; Bergin, M.; Van Hout, M.C.; McGuinness, P.; De Pleissisc, J.; Rich, E.; Dada, S.; Wells, R.; Gooney, M.A. Purchasing Over-The-Counter (OTC) Medicinal Products Containing Codeine—Easy Access, Advertising, Misuse and Perceptions of Medicinal Risk. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 21, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narcotic Drugs—Estimated World Requirements for 2020. Available online: https://www.incb.org/documents/Narcotic-Drugs/Technical-Publications/2019/Narcotic_Drugs_Technical_Publication_2019_web.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Parry, C.D.H.; Rich, E.; Van Hout, M.C.; Deluca, P. Codeine misuse and dependence in South Africa: Perspectives of addiction treatment providers. S. Afr. Med. J. 2017, 107, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, H.S. Opioid Metabolism. Mayo. Clin. Proc. 2009, 84, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Opioid Equivalence Chart. Available online: https://www.gloshospitals.nhs.uk/gps/treatment-guidelines/opioid-equivalence-chart/ (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- OPIATE CONVERSION DOSES. Available online: https://www.wales.nhs.uk/sites3/Documents/814/OpiateConversionDoses%5BFinal%5DNov2010.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Nielsen, S.; Van Hout, M.C. Over-the-Counter Codeine-from Therapeutic Use to Dependence, and the Grey Areas in Between. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 34, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasche, Y.; Daali, Y.; Fathi, M.; Chiappe, A.; Cottini, S.; Dayer, P.; Desmeules, J. Codeine intoxication associated with ultrarapid CYP2D6 metabolism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 27, 2827–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.; Woodall, K.L.; Solbeck, P.; Ross, C.J.; Carleton, B.C.; Hayden, M.R.; Koren, G.; Madadi, P. Codeine-related deaths: The role of pharmacogenetics and drug interactions. Forensic Sci. Int. 2014, 239, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roussin, A.; Bouyssi, A.; Pouché, L.; Pourcel, L.; Lapeyre-Mestre, M. Misuse and Dependence on Non-Prescription Codeine Analgesics or Sedative H1 Antihistamines by Adults: A Cross-Sectional Investigation in France. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frei, M.Y.; Nielsen, S.; Dobbin, M.D.H.; Tobin, C.L. Serious morbidity associated with misuse of over-the-counter codeine-ibuprofen analgesics: A series of 27 cases. Med. J. Aust. 2010, 193, 294–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, G.M.; Robinson, S.; McCarthy, P.; Cameron, C. Misuse of over-the-counter codeine-containing analgesics: Dependence and other adverse effects. N. Z. Med. J. 2010, 123, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mill, D.; Johnson, J.L.; Cock, V.; Monaghan, E.; Hotham, E.D. Counting the cost of over-the-counter codeine containing analgesic misuse: A retrospective review of hospital admissions over a 5-year period. Drug Alcohol. Rev. 2018, 37, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimergård, A.; Deluca, P.; Hindersson, P.; Breindahl, T. How Resistant to Tampering are Codeine Containing Analgesics on the Market? Assessing the Potential for Opioid Extraction. Pain Ther. 2016, 5, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pascali, J.P.; Fais, P.; Vaiano, F.; Pigaiani, N.; D’Errico, S.; Furlanetto, S.; Palumbo, D.; Bertol, E. Internet pseudoscience: Testing opioid containing formulations with tampering potential. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 153, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hout, M.C.; Rich, E.; Dada, S.; Bergin, M. “Codeine Is My Helper”: Misuse of and Dependence on Codeine-Containing Medicines in South Africa. Qual. Health Res. 2017, 27, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gable, R.S. Comparison of acute lethal toxicity of commonly abused psychoactive substances. Addiction 2004, 99, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.; Chalmers-Watson, T.A.; Gearry, R.B. Medical image. Combination NSAID-codeine preparations and gastrointestinal toxicity. N. Z. Med. J. 2010, 1324, 92–93. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, S.; MacDonald, T.; Johnson, J.L. Identifying and treating codeine dependence: A systematic review. Med. J. Aust. 2018, 208, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Hout, M.C.; Delargy, I.; Ryan, G.; Flanagan, S.; Gallagher, H. Dependence on Over the Counter (OTC) Codeine Containing Analgesics: Treatment and Recovery with Buprenorphine Naloxone. Int. J. Ment. Addict. 2016, 14, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, T.H. Anesthesia for the 21st century. Proc. Bayl. Uni. Med. Cent. 2000, 13, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morphine SAFETY DATA SHEET. Available online: https://www.caymanchem.com/msdss/15464m.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Cichewicz, D.L.; Martin, Z.L.; Smith, F.L.; Welch, S.P. Enhancement of μ Opioid Antinociception by Oral Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol: Dose-Response Analysis and Receptor Identification. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 289, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- La Barre, J. The pharmacological properties and therapeutic use of dextromoramide. Bull. Narc. 1959, 4, 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Codeine SAFETY DATA SHEET. Available online: https://www.caymanchem.com/msdss/ISO60140m.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Eddy, N.B.; Friebel, H.; Hahn, K.J.; Halbach, H. Codeine and its Alternates for Pain and Cough Relief, 2. Alternates for Pain Relief. Bull. Wld. Hlth. Org. 1969, 40, 1–53. [Google Scholar]
- Schellekens, K.H.L.; Awouters, F.; Artois, K.S.K.; Frederickx, R.E.J.; Hendrickx, H.M.R.; van Bruggen, W.; Niemegeers, C.J.E. R 62 818, a new analgesic: A comparative study with codeine. Drug Dev. Res. 1986, 8, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loperamide (hydrochloride) SAFETY DATA SHEET. Available online: https://www.caymanchem.com/msdss/14875m.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Niemegeers, C.J.; McGuire, J.L.; Heykants, J.J.; Janssen, P.A. Dissociation between opiate-like and antidiarrheal activities of antidiarrheal drugs. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1979, 210, 327–333. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, D.E. Loperamide: A pharmacological review. Rev. Gastroenterol. Disord. 2007, 7, S11–S18. [Google Scholar]
- Halpert, A.G.; Olmstead, M.C.; Beninger, R.J. Mechanisms and abuse liability of the anti-histamine dimenhydrinate. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2002, 26, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, L.L.; Rømsing, J.; Dalhoff, K. A Danish Survey of Antihistamine Use and Poisoning Patterns. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 120, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnich, L.E.; Stogner, J.M.; Miller, B.L.; Marcum, C.D. Purple drank prevalence and characteristics of misusers of codeine cough syrup mixtures. Addict. Behav. 2013, 38, 2445–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parker, S.D.; De Gioannis, A.; Page, C. Chronic promethazine misuse and the possibility of dependence: A brief review of antihistamine abuse and dependence. J. Subst. Use 2013, 18, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grund, J.P.; Latypov, A.; Harris, M. Breaking worse: The emergence of krokodil and excessive injuries among people who inject drugs in Eurasia. Int. J. Drug Policy 2013, 24, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katselou, M.; Papoutsis, I.; Nikolaou, P.; Spiliopoulou, C.; Athanaselis, S. A “krokodil” emerges from the murky waters of addiction. Abuse trends of an old drug. Life Sci. 2014, 102, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, E.A.; Grund, J.P.; Afonso, C.M.; Netto, A.D.; Carvalho, F.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J. The harmful chemistry behind krokodil (desomorphine) synthesis and mechanisms of toxicity. Forensic Sci. Int. 2015, 249, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, E.A.; Soares, J.X.; Afonso, C.M.; Grund, J.C.; Agonia, A.S.; Cravo, S.M.; Netto, A.D.P.; Carvalho, F.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J. The harmful chemistry behind “krokodil”: Street-like synthesis and product analysis. Forensic Sci. Int. 2015, 257, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahr, M.; Freudenmann, R.W.; Hiemke, C.; Gunst, I.M.; Connemann, B.J.; Schönfeldt-Lecuona, C. “Krokodil”: Revival of an old drug with new problems. Subst. Use Misuse 2012, 47, 861–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppert, W.; Woroń, J. Dihydrocodeine: Safety concerns. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 9, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jurna, I.; Kömen, W.; Baldauf, J.; Fleischer, W. Analgesia by dihydrocodeine is not due to formation of dihydromorphine: Evidence from nociceptive activity in rat thalamus. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 281, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar]
- Ammon, S.; Hofmann, U.; Griese, E.U.; Gugeler, N.; Mikus, G. Pharmacokinetics of dihydrocodeine and its active metabolite after single and multiple oral dosing. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 48, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Asmari, A.I.; Anderson, R.A. The role of dihydrocodeine (DHC) metabolites in dihydrocodeine-related deaths. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2010, 34, 476–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, P.; Ashraf, H.; Root, T.R. Drug dependence caused by dihydrocodeine. Br. Med. J. 1978, 1, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dihydrocodeine SAFETY DATA SHEET. Available online: https://www.caymanchem.com/msdss/15460m.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Borron, S.W.; Watts, S.H.; Tull, J.; Baeza, S.; Diebold, S.; Barrow, A. Intentional Misuse and Abuse of Loperamide: A New Look at a Drug with “Low Abuse Potential”. J. Emerg. Med. 2017, 53, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, A.; Hendrickson, R.G.; Chia-Chi Chen, B.; Valentod, M. Severe loperamide toxicity associated with the use of cimetidine to potentiate the “high”. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 36, 1527.e3–1527.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schifano, F.; Chiappini, S. Is there such a thing as a ‘lope’ dope? Analysis of loperamide-related European Medicines Agency (EMA) pharmacovigilance database reports. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lasoff, D.R.; Koh, C.H.; Corbett, B.; Minns, A.B.; Cantrell, F.L. Loperamide Trends in Abuse and Misuse over 13 Years: 2002–2015. Pharmacotherapy 2017, 37, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, H.; Panahi, L.; Tapia, D.; Tran, A.; Bowman, J.D. Loperamide misuse and abuse. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 2017, 57, S45–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vakkalanka, J.P.; Charlton, N.P.; Holstege, C.P. Epidemiologic Trends in Loperamide Abuse and Misuse. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2017, 69, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DrugBank. Available online: https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00836 (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/3955#section=Chemical-and-Physical-Properties (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Stanciu, C.N.; Gnanasegaram, S.A. Loperamide, the “Poor Man’s Methadone”: Brief Review. J. Psychoact. Drugs 2017, 49, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.E.; Juurlink, D.N. Clinical Review: Loperamide Toxicity. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2017, 70, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montesinos, R.N.; Moulari, B.; Gromand, J.; Beduneau, A.; Lamprecht, A.; Pellequer, Y. Coadministration of P-glycoprotein modulators on loperamide pharmacokinetics and brain distribution. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2014, 42, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marraffa, J.M.; Holland, M.G.; Sullivan, R.W.; Morgan, B.W.; Oakes, J.A.; Wiegand, T.J.; Hodgman, M.J. Cardiac conduction disturbance after loperamide abuse. Clin. Toxicol. 2014, 52, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Compton, D.R.; Vaz, R.J.; Rampe, D. Proarrhythmic mechanisms of the common anti-diarrheal medication loperamide: Revelations from the opioid abuse epidemic. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs. Arch. Pharmacol. 2016, 389, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, A.; Bodar, V.; Malekzadegan, M.; Singh, S.; Frumkin, W.; Mangla, A.; Doshi, K. Loperamide Induced Life Threatening Ventricular Arrhythmia. Case Rep. Cardiol. 2016, 2016, 5040176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eggleston, W.; Clark, K.H.; Marraffa, J.M. Loperamide Abuse Associated with Cardiac Dysrhythmia and Death. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2017, 69, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, R.; Heiner, J.; Villarreal, J.; Strote, J. Loperamide dependence and abuse. BMJ Case Rep. 2015, 2015, bcr2015209705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniulaityte, R.; Carlson, R.; Falck, R.; Cameron, D.; Perera, S.; Chen, L.; Sheth, A. “I Just Wanted to Tell You That Loperamide WILL WORK”: A Web-Based Study of Extra-Medical Use of Loperamide. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2013, 130, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trends in Annual Prevalence of Use of Various Drugs for Grades 8, 10, and 12 Combined. Available online: http://monitoringthefuture.org/data/19data/19drtbl6.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Monte, A.A.; Chuang, R.; Bodmer, M. Dextromethorphan, chlorphenamine and serotonin toxicity: Case report and systematic literature review. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2010, 70, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linn, K.A.; Long, M.T.; Pagel, P. “Robo-tripping”: Dextromethorphan abuse and its anesthetic implications. Anesth. Pain Med. 2014, 4, e20990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overdose Death Rates, Drug Overdoses Data Document.xls. Available online: https://www.drugabuse.gov/drug-topics/trends-statistics/overdose-death-rates (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- World Health Organization Model List of Essential Medicines. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/325771/WHO-MVP-EMP-IAU-2019.06-eng.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- PubMed.gov. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- ScienceDirect.com, Science, Health and Medical Journals, Full Text Articles and Books. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/ (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Springer Link. Available online: https://link.springer.com/ (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Wiley Online Library, Scientific Research Articles, Journals, Books, and Reference Works. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/ (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Prisma Transparent Reporting of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. Available online: http://www.prisma-statement.org/ (accessed on 20 August 2020).

| Receptor Type | Main Effects of Receptor Agonism | Receptor Agonist | Receptor Type Selectivity 1 | Ref. |
| µ (mu) |
| morphine (reference) | µ/δ: 0.006–0.040 µ/κ: 0.023–0.059 | [13,14,15,16] |
| codeine (OTC drug) | µ/δ: 0.049–0.051 µ/κ: 0.033–0.044 | [13,15] | ||
| dihydrocodeine (OTC drug) | µ/δ: 0.036–0.055 µ/κ: 0.018–0.023 | [13,15] | ||
| loperamide (OTC drug) | µ/δ: 0.003 | [17] | ||
| δ (delta) |
| morphine (reference) | δ/µ: 25.000–159.091 | [13,14,15,16] |
| SNC80 2 | δ/µ: 0.002 | [18,19] | ||
| BW373U86 3 | δ/µ: 0.120 | [20] | ||
| κ (kappa) |
| morphine (reference) | κ/µ: 16.950–42.636 | [13,14,15,16] |
| butorphanol 4 | κ/µ: 0.545 | [21,22] | ||
| pentazocine 4 | κ/µ: 0.564–0.772 | [14] | ||
| nalorphine 5 | κ/µ: 0.667–0.895 | [14] |
| Mouse | Rat | |||||||||
| Drug | LD50 (mg/kg) | ED50 (mg/kg) | Therapeutic Index | LD50 (mg/kg) | ED50 1 (mg/kg) | Therapeutic Index | ||||
| Morphine (reference) | 524 | [50] | 28.8 | [51] | 18.2–21.2 | 335 | [50] | N/A | N/A | |
| 610 | [52] | |||||||||
| Codeine | 250 | [45,53] | 43.2 | [54] | 1.8–5.8 | 266 427 | [45] [53] | 69.3 | [55] | 3.8–6.2 |
| 139.9 | [51] | |||||||||
| Loperamide | 105 | [56] | N/A | N/A | 185 | [56] | 0.15 | [57] | 102–1233 | |
| 0.61 | [58] | |||||||||
| 1.81 | [57,58] | |||||||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sobczak, Ł.; Goryński, K. Pharmacological Aspects of Over-the-Counter Opioid Drugs Misuse. Molecules 2020, 25, 3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173905
Sobczak Ł, Goryński K. Pharmacological Aspects of Over-the-Counter Opioid Drugs Misuse. Molecules. 2020; 25(17):3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173905
Chicago/Turabian StyleSobczak, Łukasz, and Krzysztof Goryński. 2020. "Pharmacological Aspects of Over-the-Counter Opioid Drugs Misuse" Molecules 25, no. 17: 3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173905
APA StyleSobczak, Ł., & Goryński, K. (2020). Pharmacological Aspects of Over-the-Counter Opioid Drugs Misuse. Molecules, 25(17), 3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173905






