Antinociceptive Interaction and Pharmacokinetics of the Combination Treatments of Methyleugenol Plus Diclofenac or Ketorolac
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
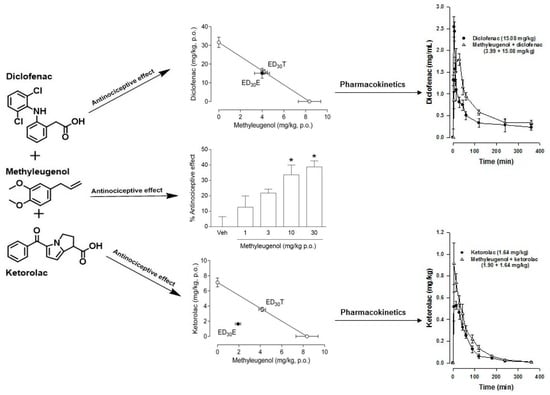
2.1. Antinociceptive Effect of the Individual Drugs
2.2. Antinociceptive Effect of the Drug Combinations
2.3. Effect of Methyleugenol on the Pharmacokinetics of Diclofenac or Ketorolac
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Drugs
4.3. Formalin Test
4.3.1. Data Analysis from the Formalin Test
4.3.2. Isobolographic Analysis
4.4. Evaluation of Pharmacokinetics
4.4.1. Quantifying the Plasma Concentration of Diclofenac and Ketorolac
4.4.2. Non-Compartmental Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, A.C.; Craig, K.D. Updating the definition of pain. Pain 2016, 157, 2420–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickle, A.D.; Shepherd, A.J.; Mohapatra, D.P. Nociceptive TRP Channels: Sensory Detectors and Transducers in Multiple Pain Pathologies. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, J.T.; Seminowicz, D.A. Neuroimaging of pain in animal models: A review of recent literature. Pain Rep. 2019, 4, e732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, C.J. Pain: Moving from symptom control toward mechanism-specific pharmacologic management. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 140, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Vinayak, M. Recent development in antihyperalgesic effect of phytochemicals: Anti-inflammatory and neuro-modulatory actions. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 67, 633–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leith, J.L.; Wilson, A.W.; Donaldson, L.F.; Lumb, B.M. Cyclooxygenase-1-derived prostaglandins in the periaqueductal gray differentially control C-versus A-fiber-evoked spinal nociception. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 11296–11305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhriansyah, M.; Souverein, P.C.; de Boer, A.; Klungel, O.H. Gastrointestinal toxicity among patients taking selective COX-2 inhibitors or conventional NSAIDs, alone or combined with proton pump inhibitors: A case-control study. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug. Saf. 2017, 26, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crofford, L.J. Use of NSAIDs in treating patients with arthritis. Arthritis. Res. Ther. 2013, 15, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosser, T.; Ricciotti, E.; FitzGerald, G.A. The Cardiovascular Pharmacology of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2017, 38, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostom, A.; Muir, K.; Dubé, C.; Jolicoeur, E.; Boucher, M.; Joyce, J.; Tugwell, P.; Wells, G. Gastrointestinal Safety of Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitors: A Cochrane Collaboration Systematic Review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 5, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffa, R.B.; Pergolizzi, J.V., Jr.; Tallarida, R.J. The determination and application of fixed-dose analgesic combinations for treating multimodal pain. J. Pain 2010, 11, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Chen, F.; Ling, X.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Tang, Q.; Tan, X. Inhibitory effect of methyleugenol on IgE-mediated allergic inflammation in RBL-2H3 cells. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 463530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramèr, M.R.; Moore, R.A.; Reynolds, D.J.; McQuay, H.J. Quantitative estimation of rare adverse events which follow a biological progression: A new model applied to chronic NSAID use. Pain 2000, 85, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrot, M. Tests and models of nociception and pain in rodents. Neuroscience 2012, 211, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.W.; Yaksh, T.L. Tissue injury models of persistent nociception. In Pain Research Methods and Protocols Rats; Luo, Z.D., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 25–26. [Google Scholar]
- Yano, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Yuzurihara, M.; Kase, Y.; Takeda, S.; Watanabe, S.; Aburada, M.; Miyamoto, K.I. Antinociceptive effect of methyleugenol on formalin-induced hyperalgesia in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 553, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, M.I. Blockade of the antinociception induced by diclofenac, but not of indomethacin, by sulfonylureas and biguanides. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2011, 99, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Silverio, J.; Sánchez-Mendoza, M.E.; Arrieta-Valencia, J.; Rocha-González, H.I.; Flores-Murrieta, F.J. Tizanidine Increases Antinociceptive Effect and Prevents Gastric Damage Induced by Ketorolac in the Rat. Drug Dev. Res. 2013, 74, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, M.I.; Granados-Soto, V.; Castañeda-Hernández, G. The NO-cGMP-K+ channel pathway participates in the antinociceptive effect of diclofenac, but not of indomethacin. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2003, 76, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, R.Y.; Ding, Y.; Gan, Y.H. Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs Attenuate Hyperalgesia and Block Upregulation of Trigeminal Ganglionic Sodium Channel 1.7 after Induction of Temporomandibular Joint Inflammation in Rats. Chin. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 19, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.J.; Tabakoff, B.; Levinson, S.R.; Heinbockel, T. Inhibition of Nav1.7 channels by methyl eugenol as a mechanism underlying its antinociceptive and anesthetic actions. Acta. Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Antonio, L.; Sánchez-Mendoza, M.E.; López-Lorenzo, Y.; Rocha-González, H.I.; Robles-Sánchez, A.; Arrieta, J. Pharmacokinetics Effect of Diclofenac or Ketorolac-methyl Eugenol and Their Implication in the Gastroprotection. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 16, 375–381. [Google Scholar]
- Committee on Herbal Medicinal Products (HMPC). Public Statement on the Use of Herbal Medicinal Products Containing Methyleugenol. 2005. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/public-statement-use-herbal-medicinal-products-containing-methyleugenol_en.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- Adeyeye, C.M.; Li, P.K. Diclofenac Sodium. In Analytical Profiles of Drug Substances; Florey, K., Ed.; Academic Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 123–144. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Ma, H.; Cen, N.; Zhou, A.; Tao, H. A pharmacokinetic study of diclofenac sodium in rats. Biomed. Rep. 2017, 7, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris-Ribera, J.E.; Torres-Molina, F.; Garcia-Carbonell, M.C.; Aristorena, J.C.; Pla-Delfina, J.M. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of diclofenac in the rat. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1991, 19, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudie, D.M.; Amidon, G.L.; Amidon, G.E. Physiological parameters for oral delivery and in vitro testing. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 1388–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM-062-ZOO-1999. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/203498/NOM-062-ZOO-1999_220801.pdf (accessed on 12 October 2020).
- Zimmermann, M. Ethical guidelines for investigation of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain 1983, 16, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Trujano, M.E.; Peña, E.I.; Martínez, A.L.; Moreno, J.; Guevara-Fefer, P.; Déciga-Campos, M.; López-Muñoz, F.J. Evaluation of the antinociceptive effect of Rosmarinus officinalis L. using three different experimental models in rodents. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 111, 476–482. [Google Scholar]
- Tallarida, R.J. Calculations for combination drug analysis. In Drug Synergism and Dose-Effect Data Analysis; Chapman and Hall/CRC: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 57–71. [Google Scholar]
- Tallarida, R.J. The interaction index: A measure of drug synergism. Pain 2002, 98, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Drug | ED30 ± SEM (mg/kg) | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Methyleugenol | 8.4 ± 1.0 | 0.983 |
| Diclofenac | 31.6 ± 2.8 | 0.997 |
| Ketorolac | 7.1 ± 0.6 | 0.992 |
| Dose Ratio | Theoretical ED30 ± SEM (CI at 90%) | Experimental ED30 ± SEM (CI at 90%) | γ ± SEM (CI at 90%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| methyleugenol + diclofenac 1:1 | 20.0 ± 1.5 (16.2 − 24.5) | 19.1 ± 3.3 (9.0 − 40.5) | 0.96 ± 0.18 (0.63 − 1.46) |
| methyleugenol + ketorolac 1:1 | 7.7 ± 0.6 (6.3 − 9.6) | 3.6 ± 0.5 * (2.0 − 6.2) | 0.46 ± 0.07 (0.33 − 0.65) |
| Parameter | Diclofenac | Methyleugenol + Diclofenac |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax (µg/mL) | 2.80 ± 0.09 | 1.83 ± 0.18 * |
| t½ (min) | 126.71 ± 22.25 | 103.87 ± 12.11 |
| Tmax (min) | 6.00 ± 0.55 | 10.83 ± 2.00 |
| AUC0→t (µg × min/mL) | 149.02 ± 30.83 | 158.76 ± 19.83 |
| AUC0→∞ (µg × min/mL) | 191.63 ± 49.50 | 189.05 ± 27.39 |
| Parameter | Ketorolac | Methyleugenol + Ketorolac |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax (µg/mL) | 0.66 ± 0.06 | 0.97 ± 0.16 |
| t½ (min) | 39.45 ± 5.45 | 44.82 ± 5.79 |
| Tmax (min) | 13.33 ± 5.27 | 10.00 ± 2.33 |
| AUC0→t (µg × min/mL) | 39.77 ± 4.01 | 53.13 ± 6.99 |
| AUC0→∞ (µg × min/mL) | 41.29 ± 4.51 | 56.34 ± 7.09 |
Sample Availability: Not available. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rocha-González, H.I.; Sánchez-Mendoza, M.E.; Cruz-Antonio, L.; Flores-Murrieta, F.J.; Cornelio-Huerta, X.I.; Arrieta, J. Antinociceptive Interaction and Pharmacokinetics of the Combination Treatments of Methyleugenol Plus Diclofenac or Ketorolac. Molecules 2020, 25, 5106. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215106
Rocha-González HI, Sánchez-Mendoza ME, Cruz-Antonio L, Flores-Murrieta FJ, Cornelio-Huerta XI, Arrieta J. Antinociceptive Interaction and Pharmacokinetics of the Combination Treatments of Methyleugenol Plus Diclofenac or Ketorolac. Molecules. 2020; 25(21):5106. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215106
Chicago/Turabian StyleRocha-González, Héctor Isaac, María Elena Sánchez-Mendoza, Leticia Cruz-Antonio, Francisco Javier Flores-Murrieta, Xochilt Itzel Cornelio-Huerta, and Jesús Arrieta. 2020. "Antinociceptive Interaction and Pharmacokinetics of the Combination Treatments of Methyleugenol Plus Diclofenac or Ketorolac" Molecules 25, no. 21: 5106. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215106
APA StyleRocha-González, H. I., Sánchez-Mendoza, M. E., Cruz-Antonio, L., Flores-Murrieta, F. J., Cornelio-Huerta, X. I., & Arrieta, J. (2020). Antinociceptive Interaction and Pharmacokinetics of the Combination Treatments of Methyleugenol Plus Diclofenac or Ketorolac. Molecules, 25(21), 5106. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215106